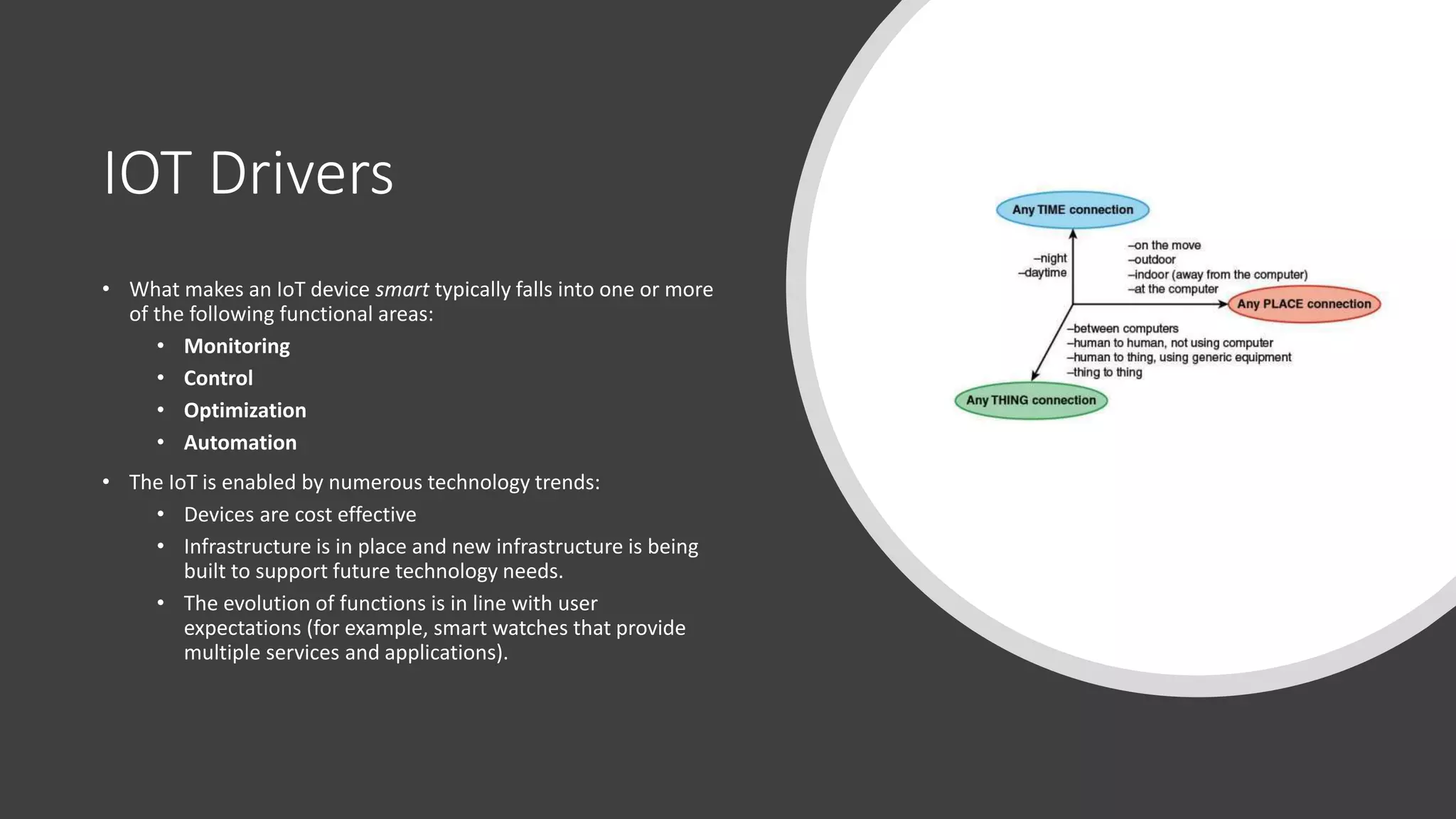
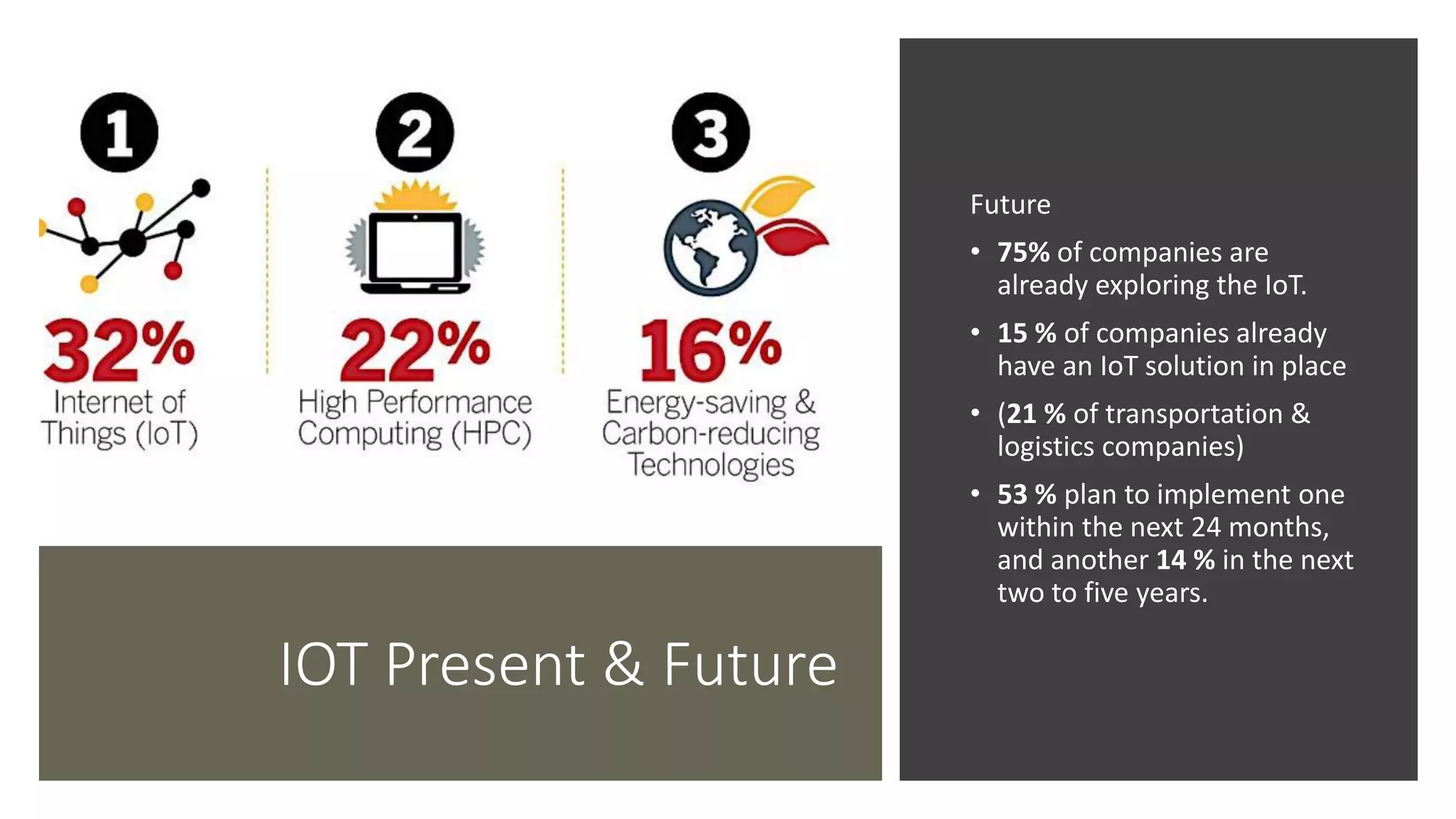
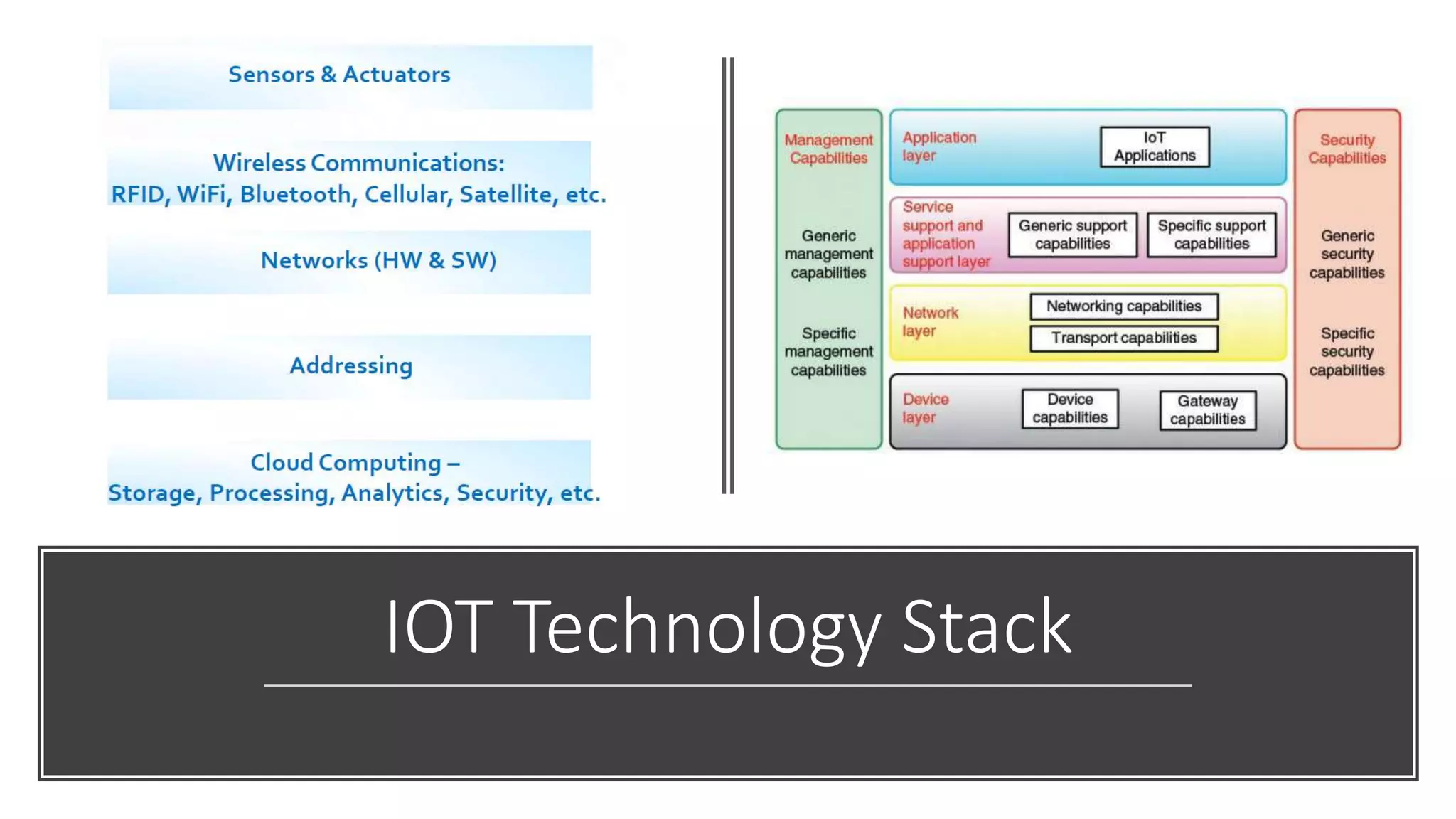
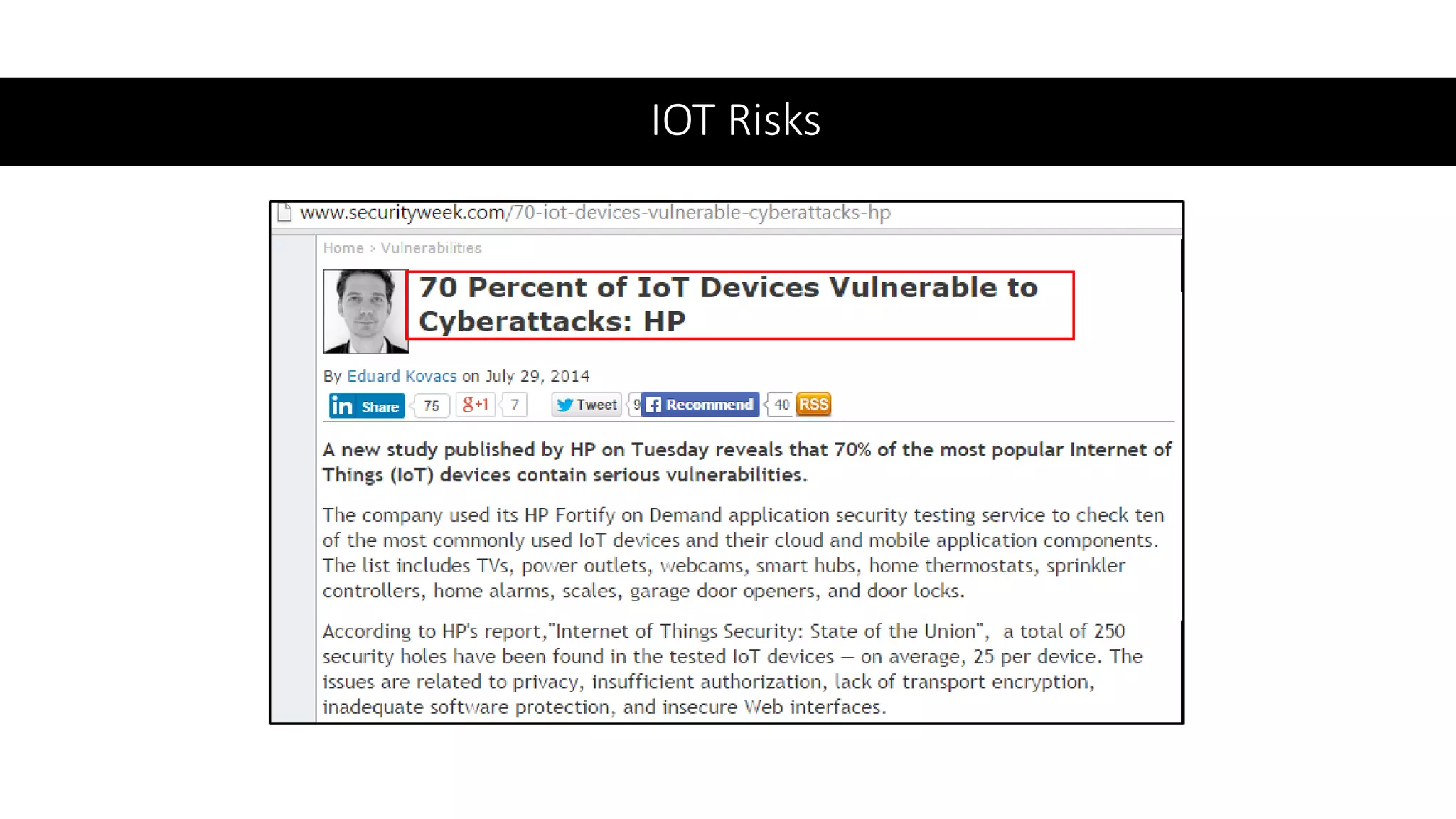
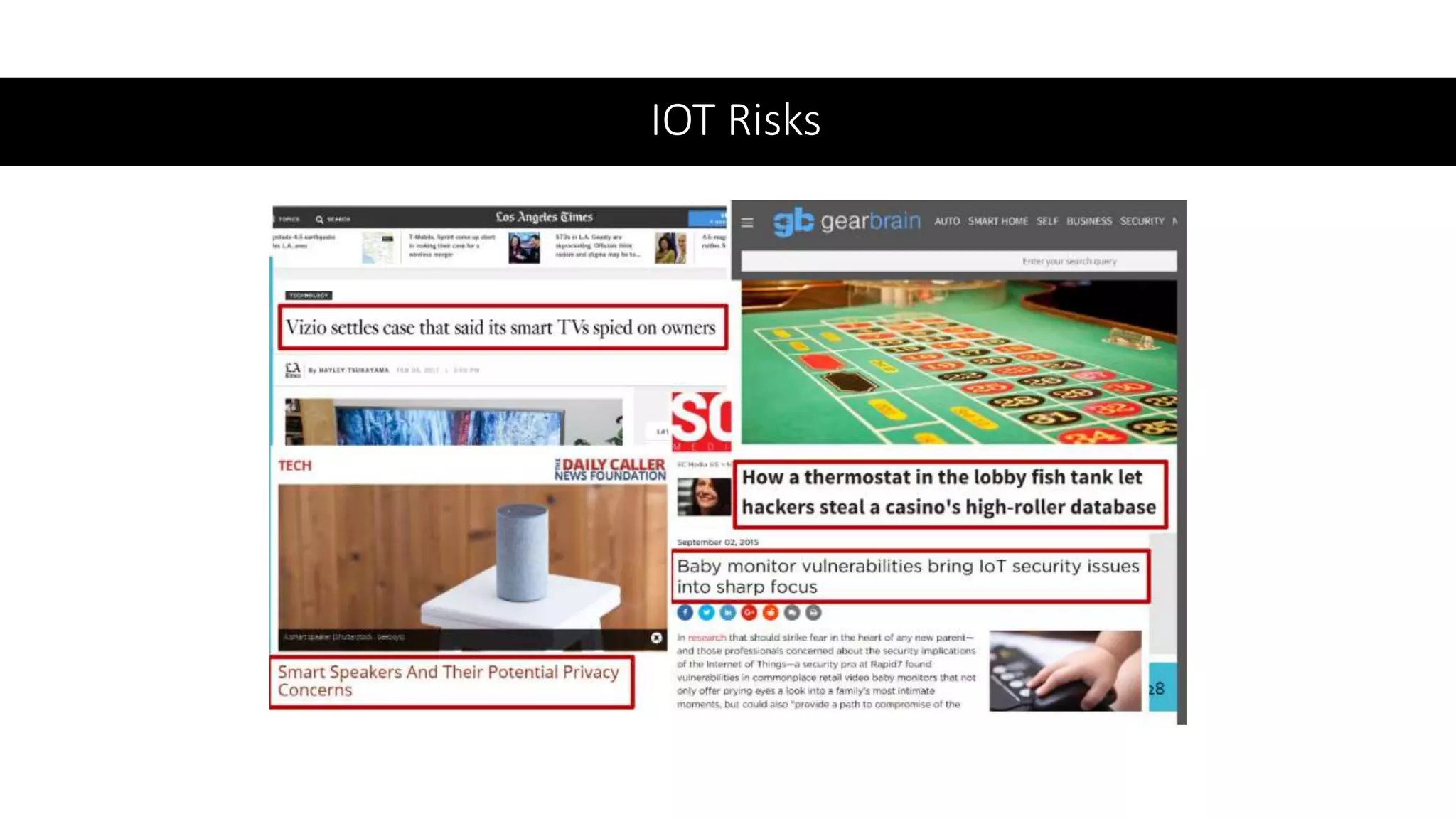
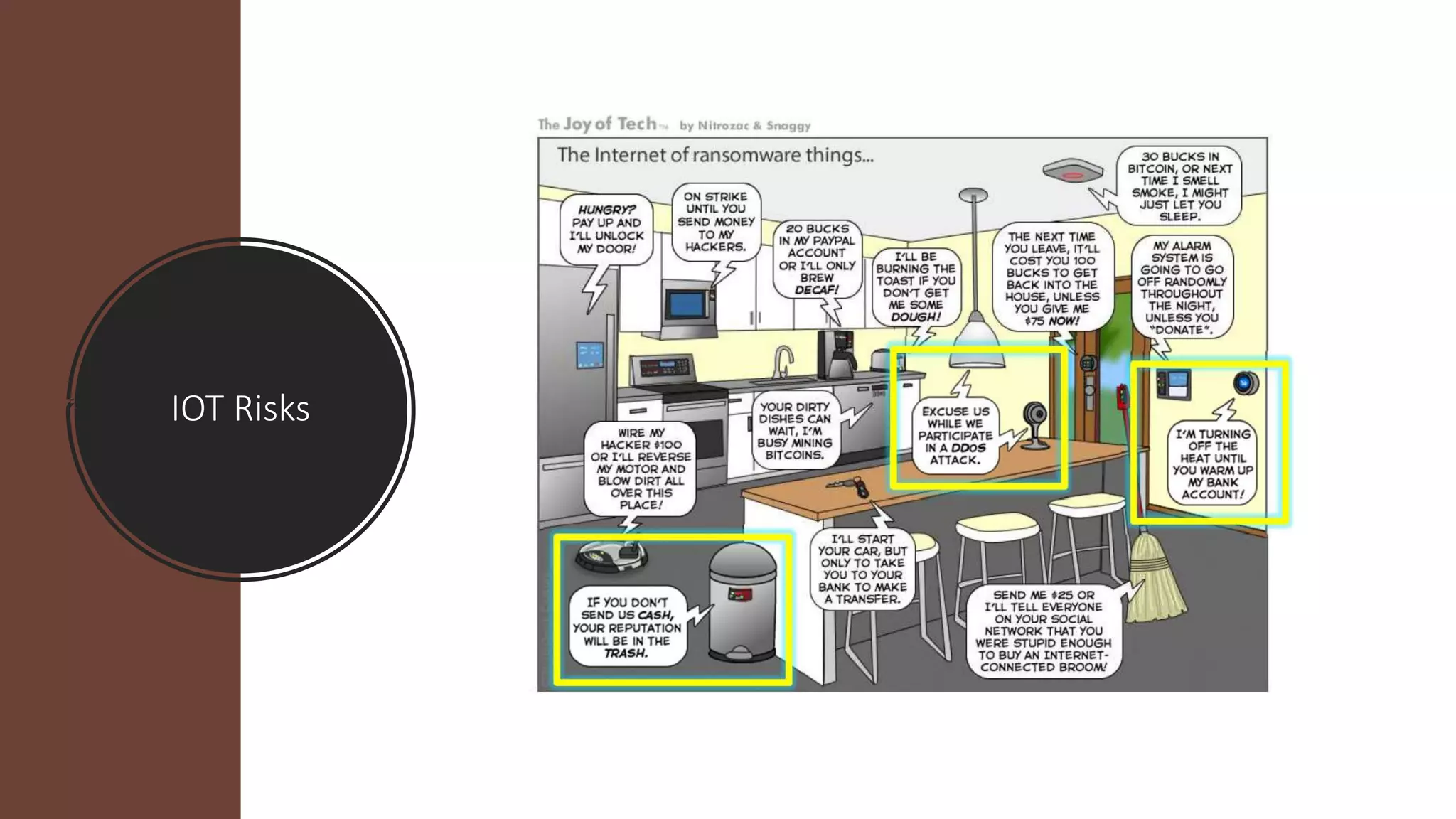
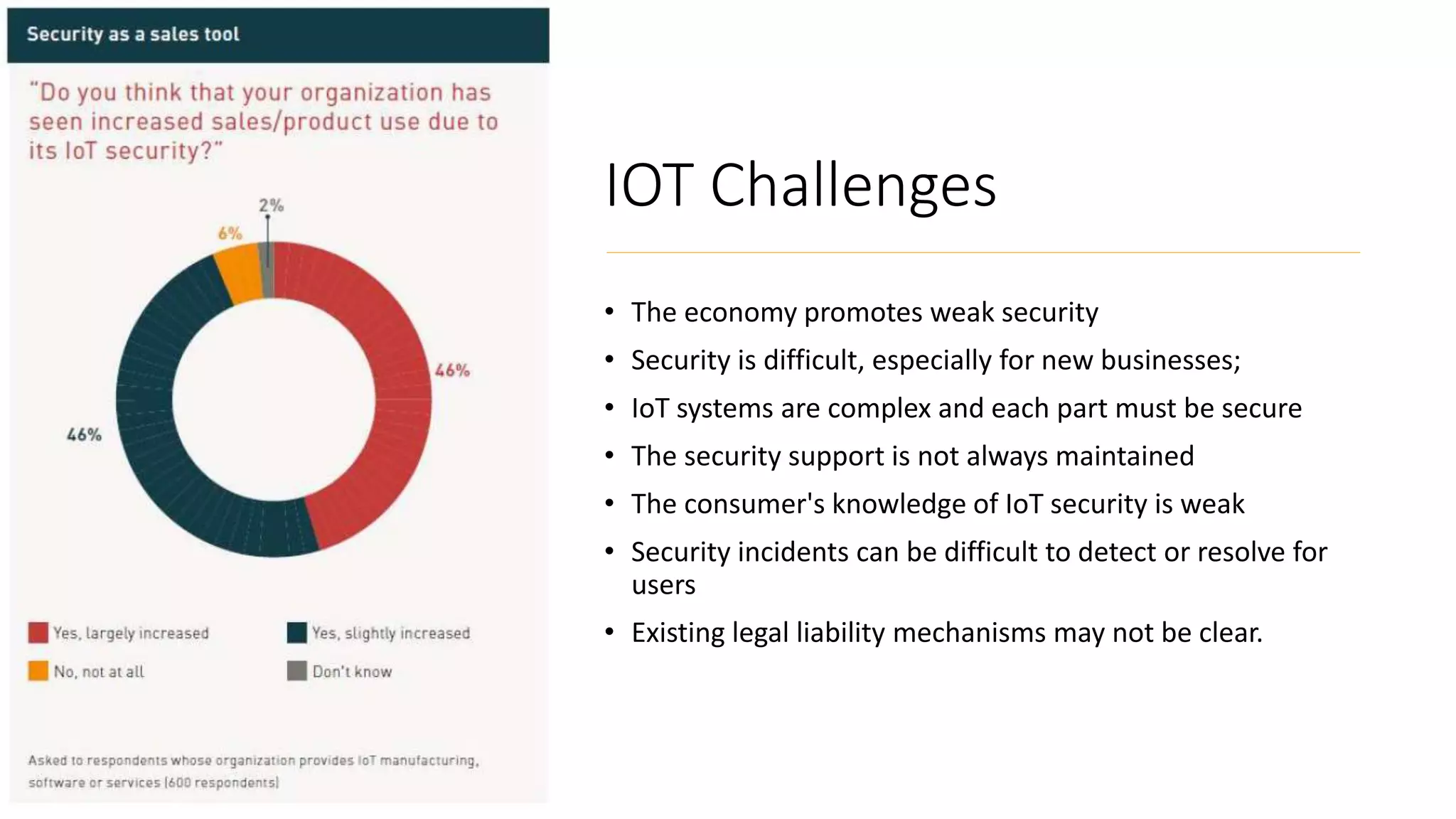
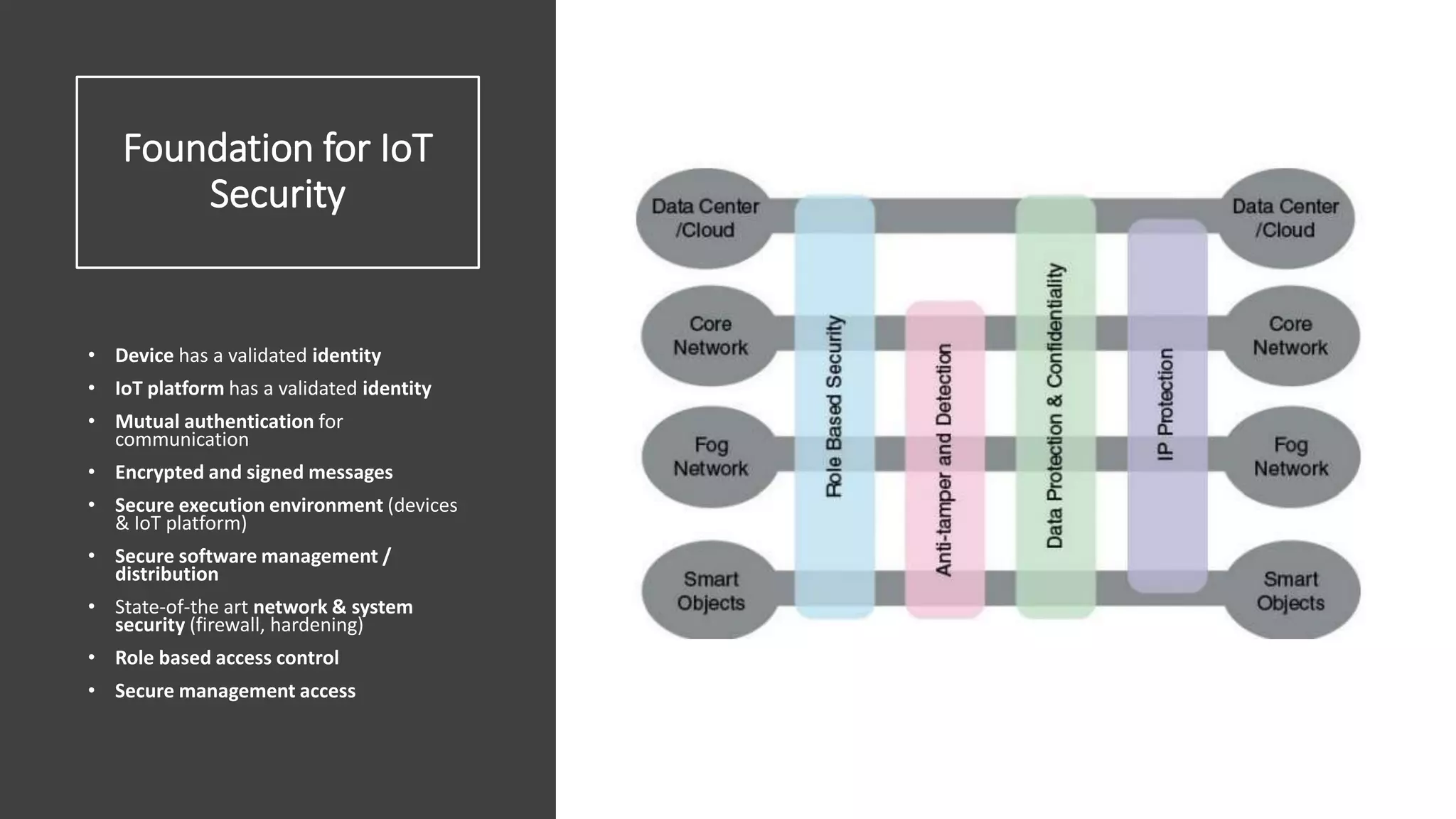
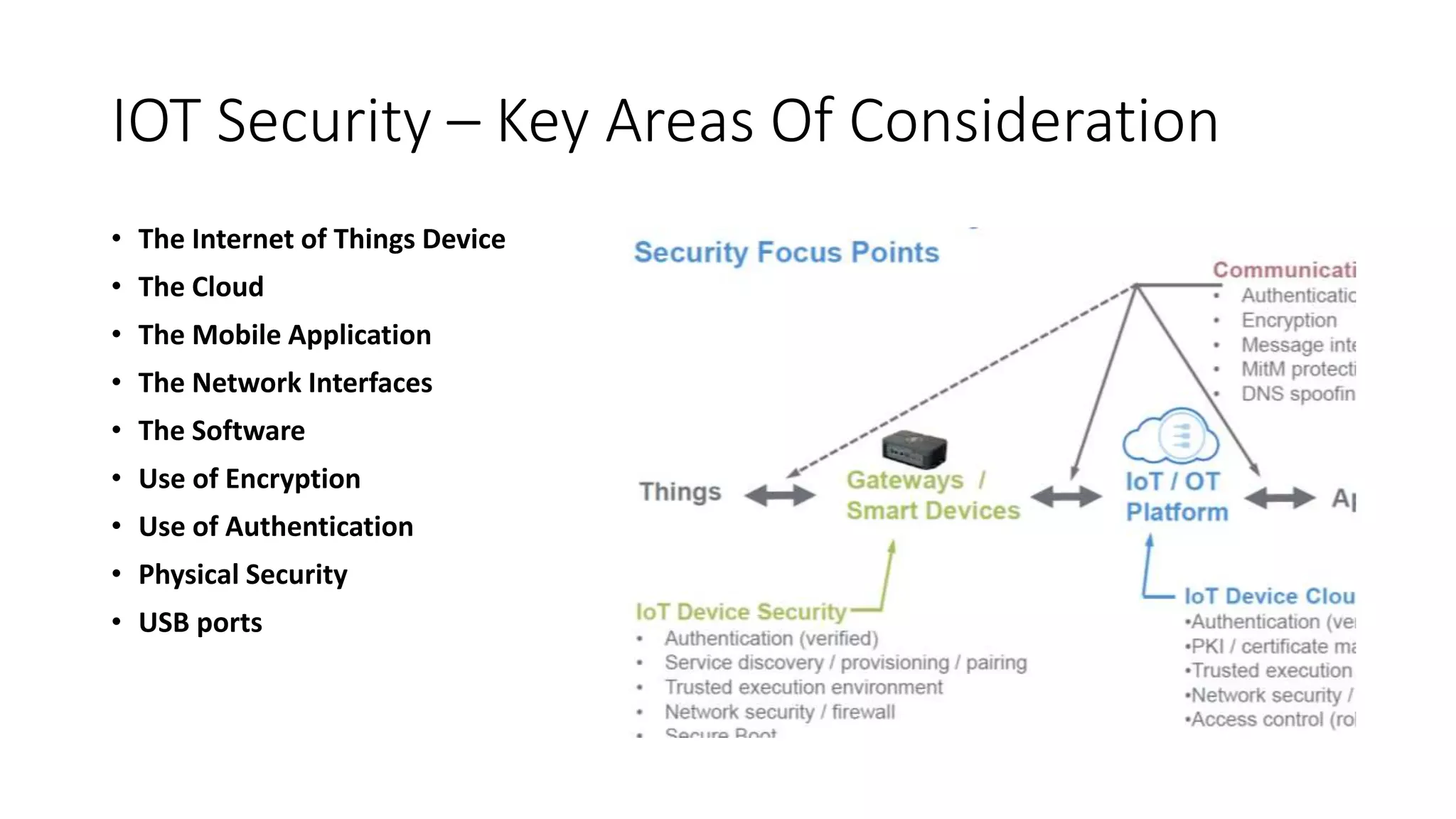
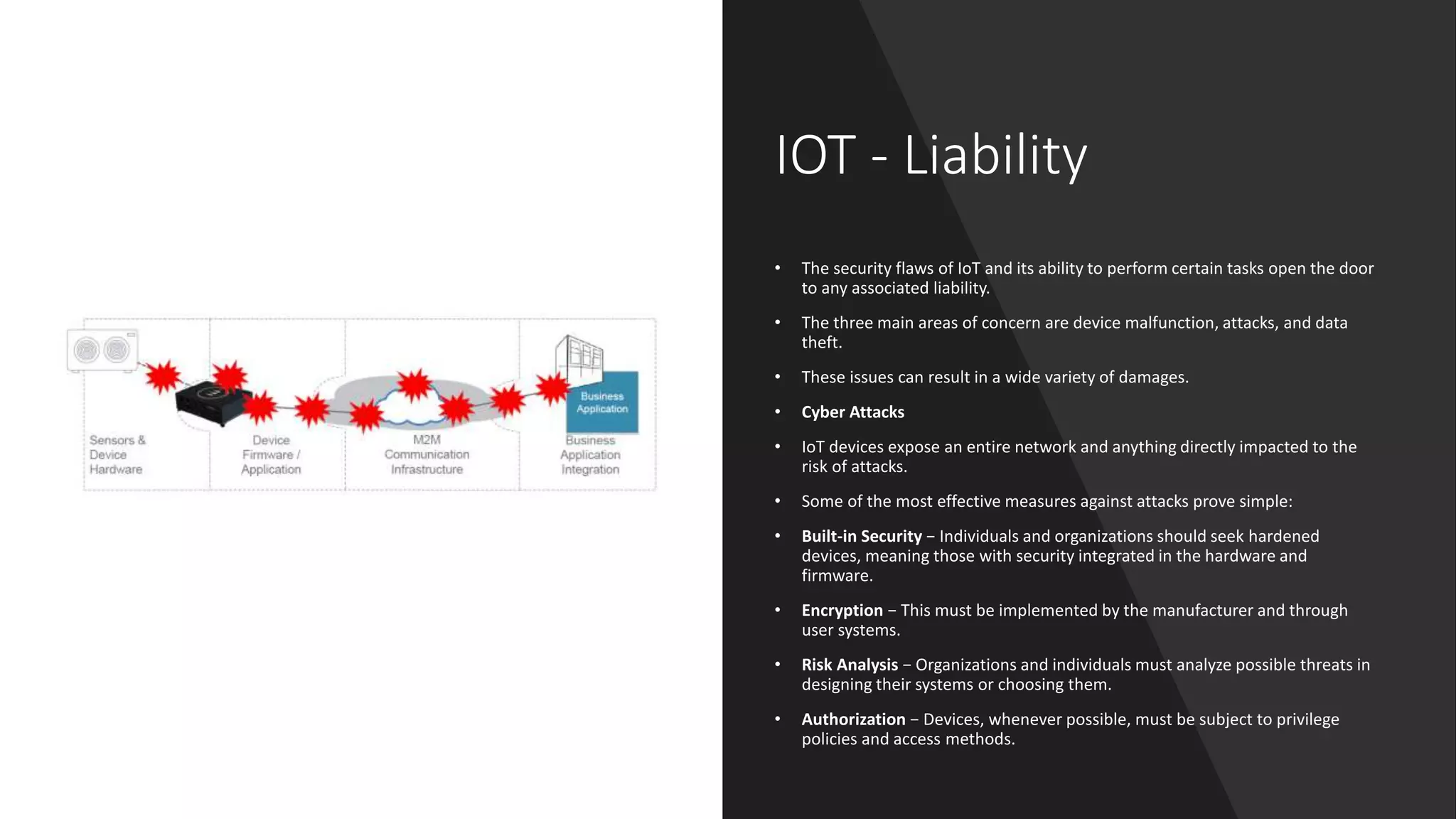
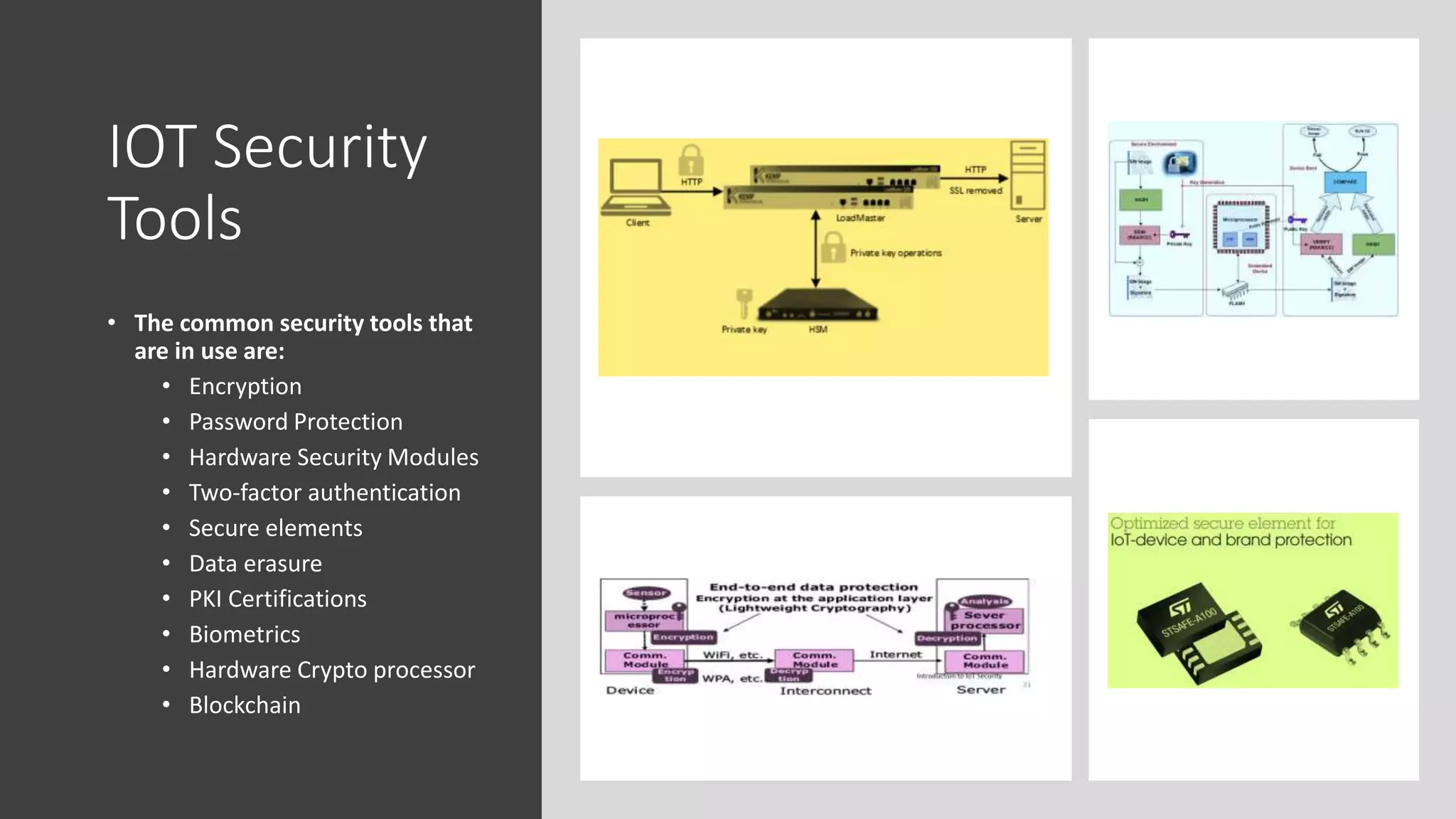
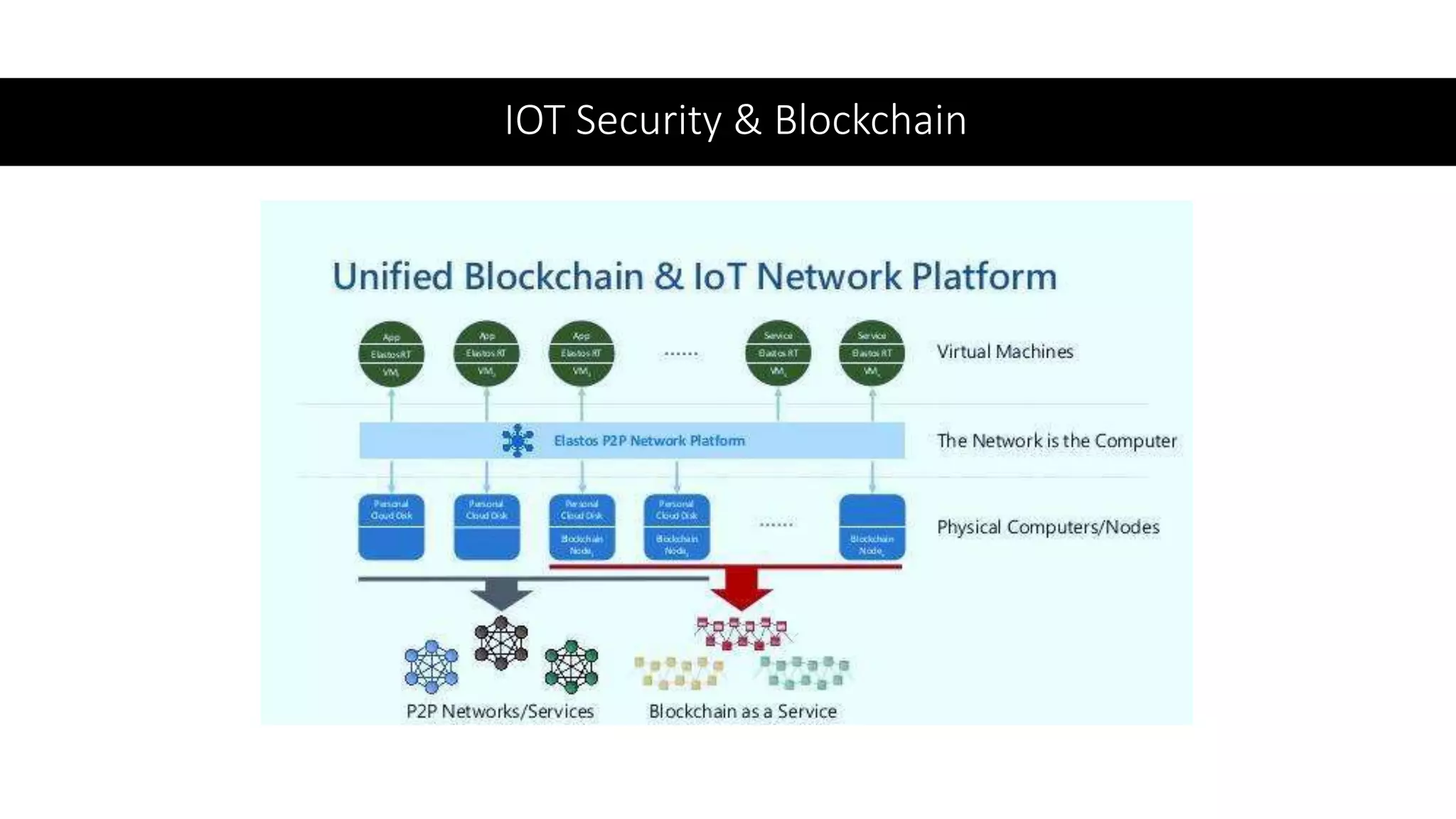
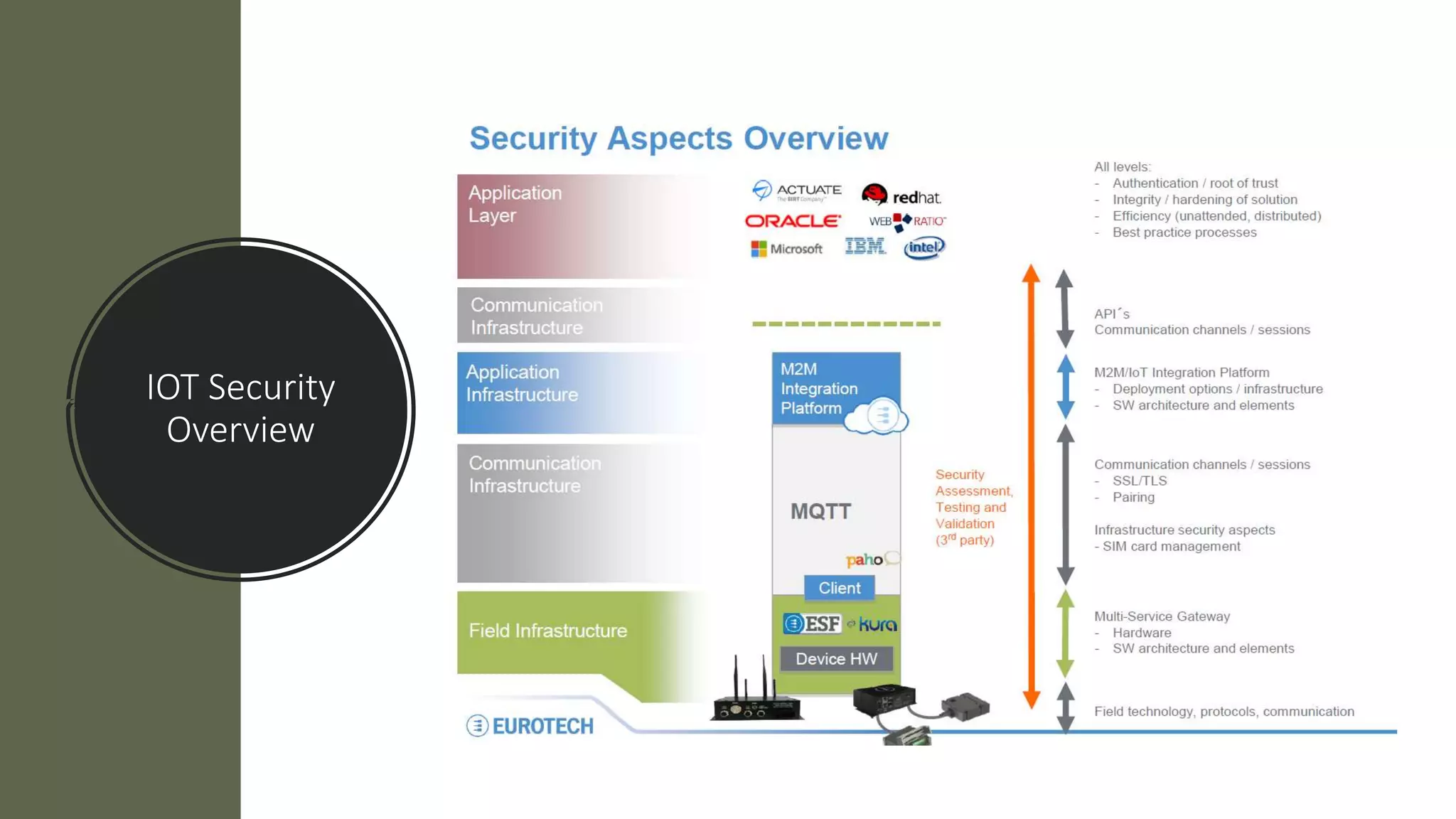
This document provides an overview of IoT security. It begins with defining IoT and describing how physical objects are connected to the internet. It then discusses current IoT usage and forecasts significant future growth. The document outlines several IoT security risks and vulnerabilities, such as insecure interfaces, lack of encryption, and poor physical security. It recommends best practices for IoT security including implementing device and user authentication, access controls, encryption, and regular software updates. Overall the document introduces the topic of IoT security and some foundational aspects to address related risks.