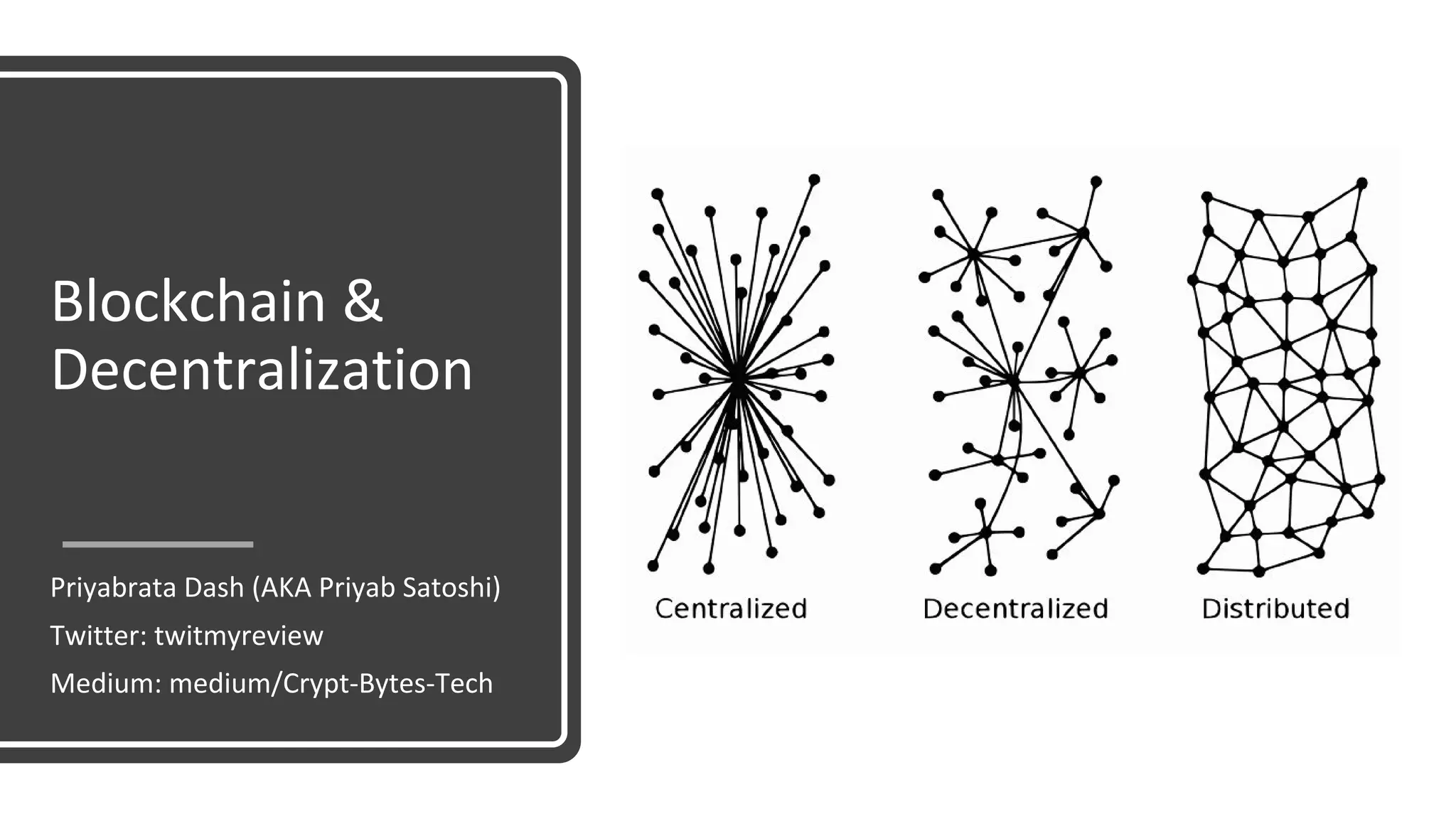
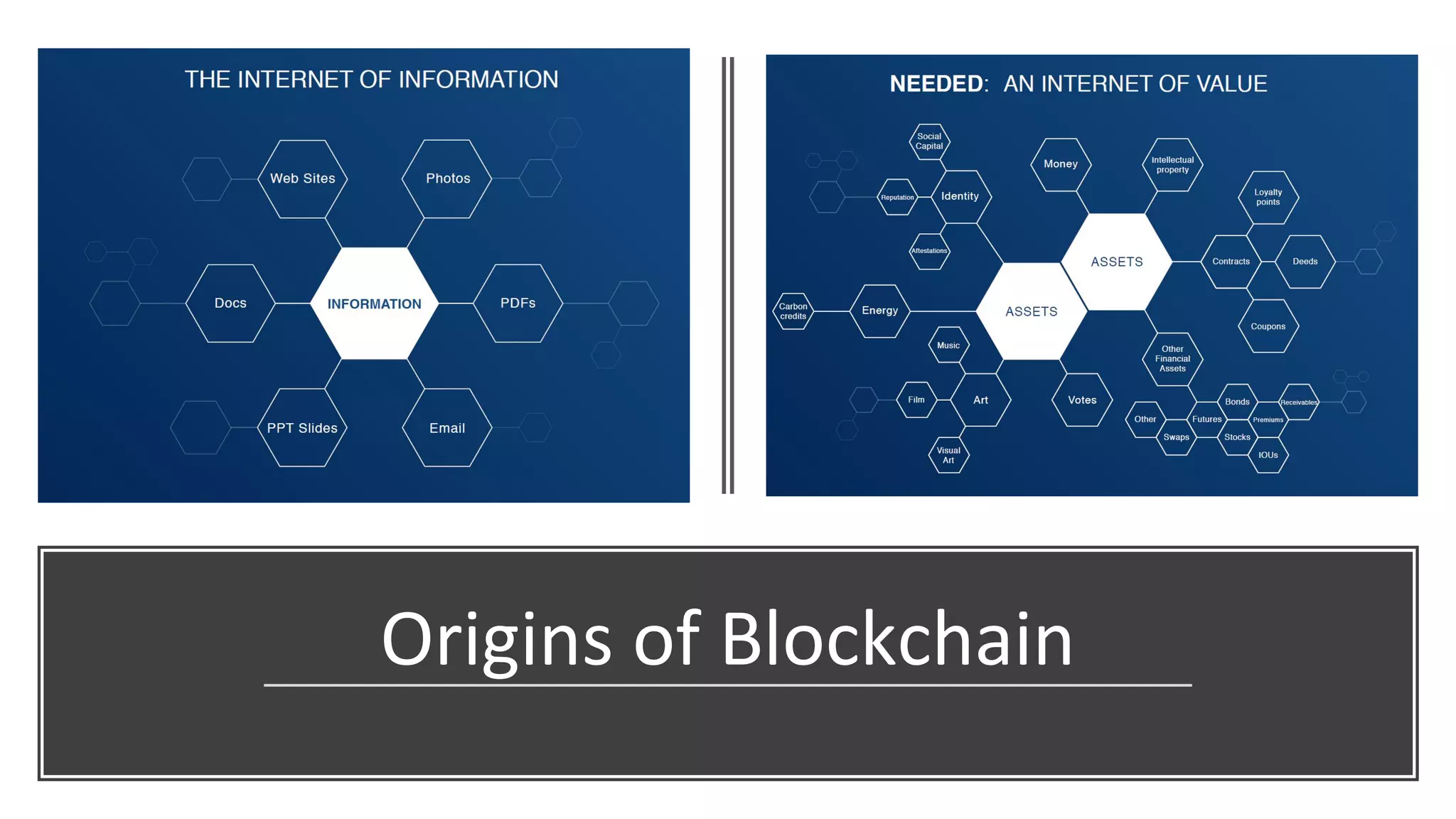
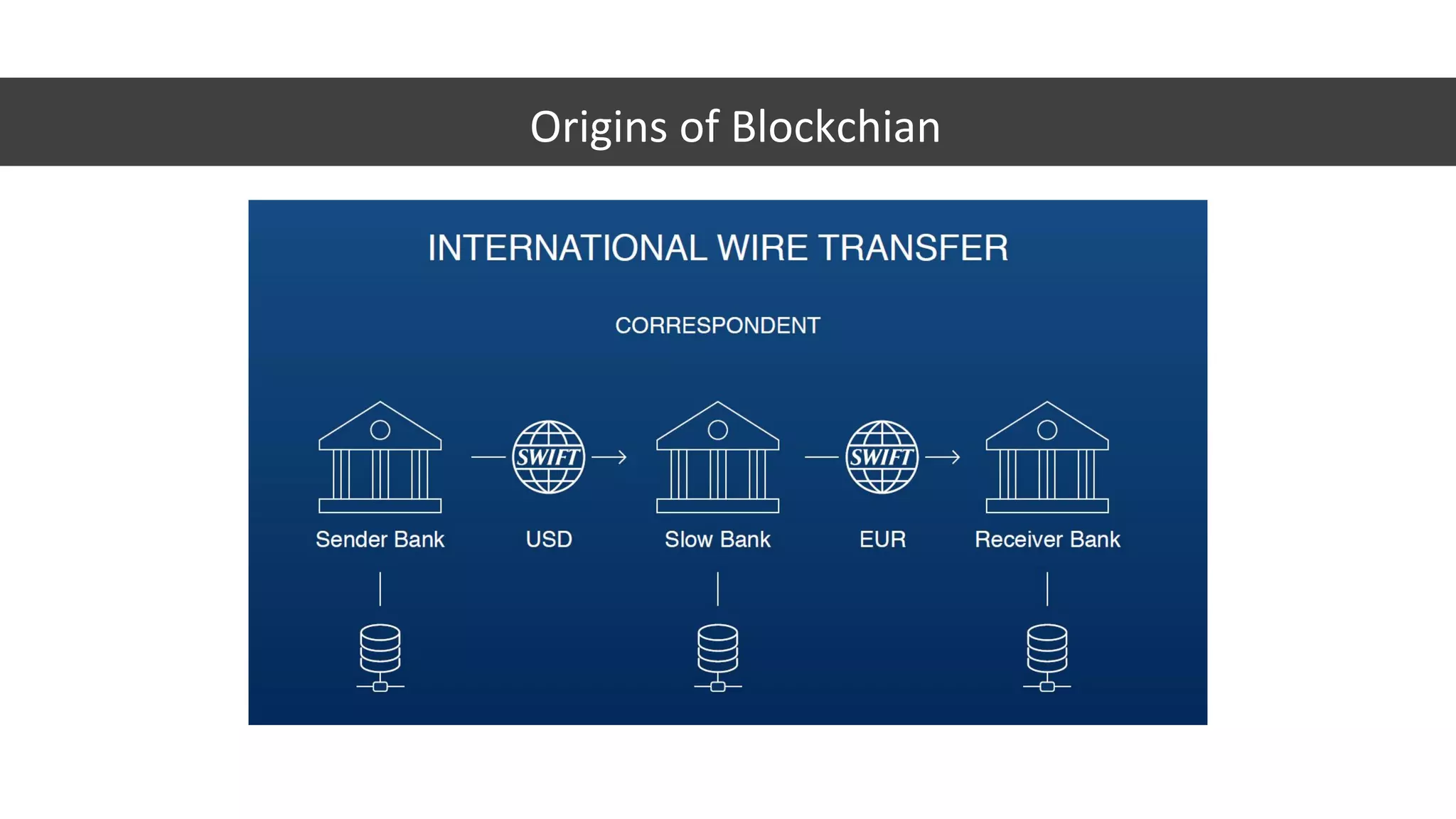
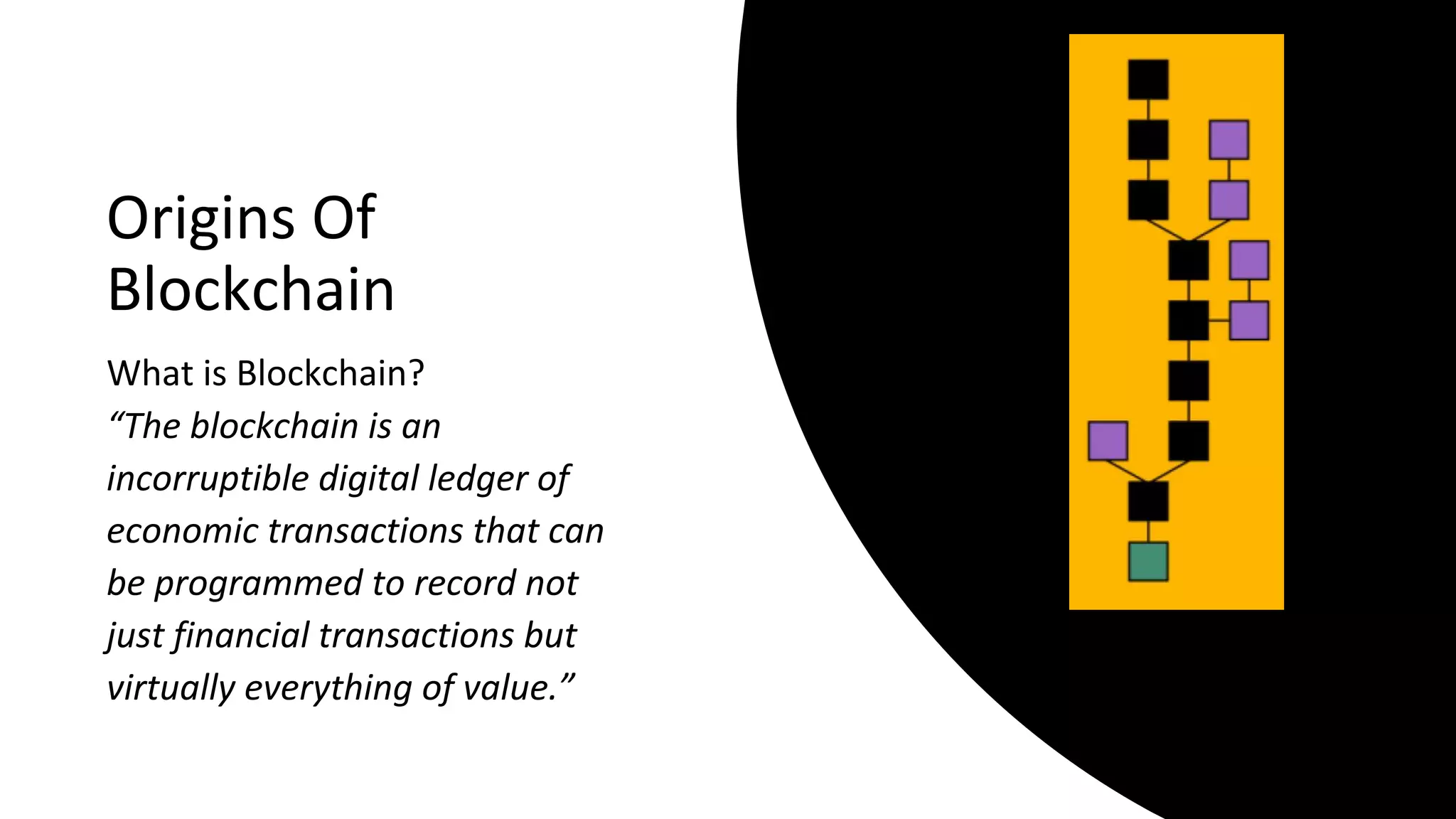
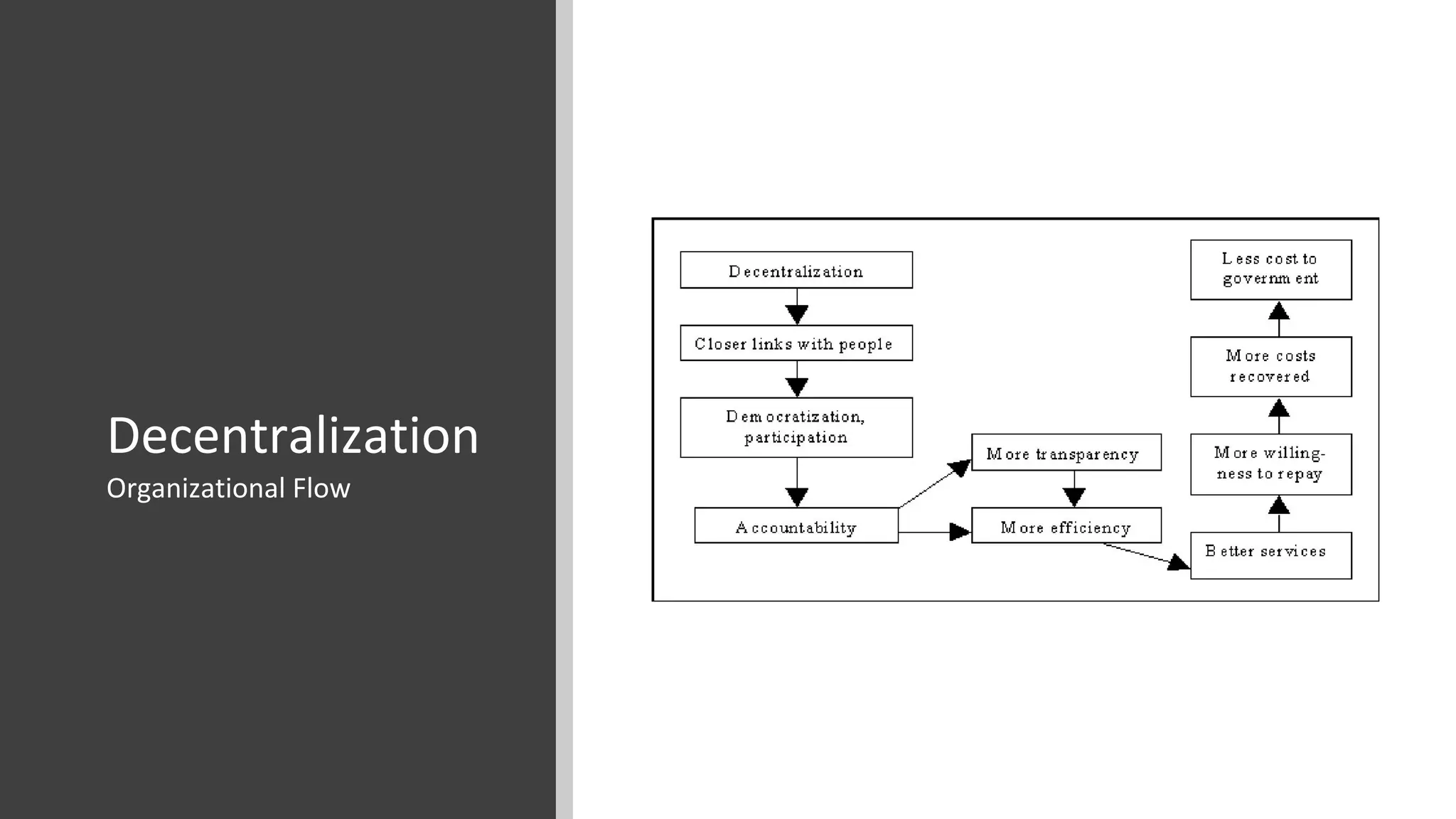
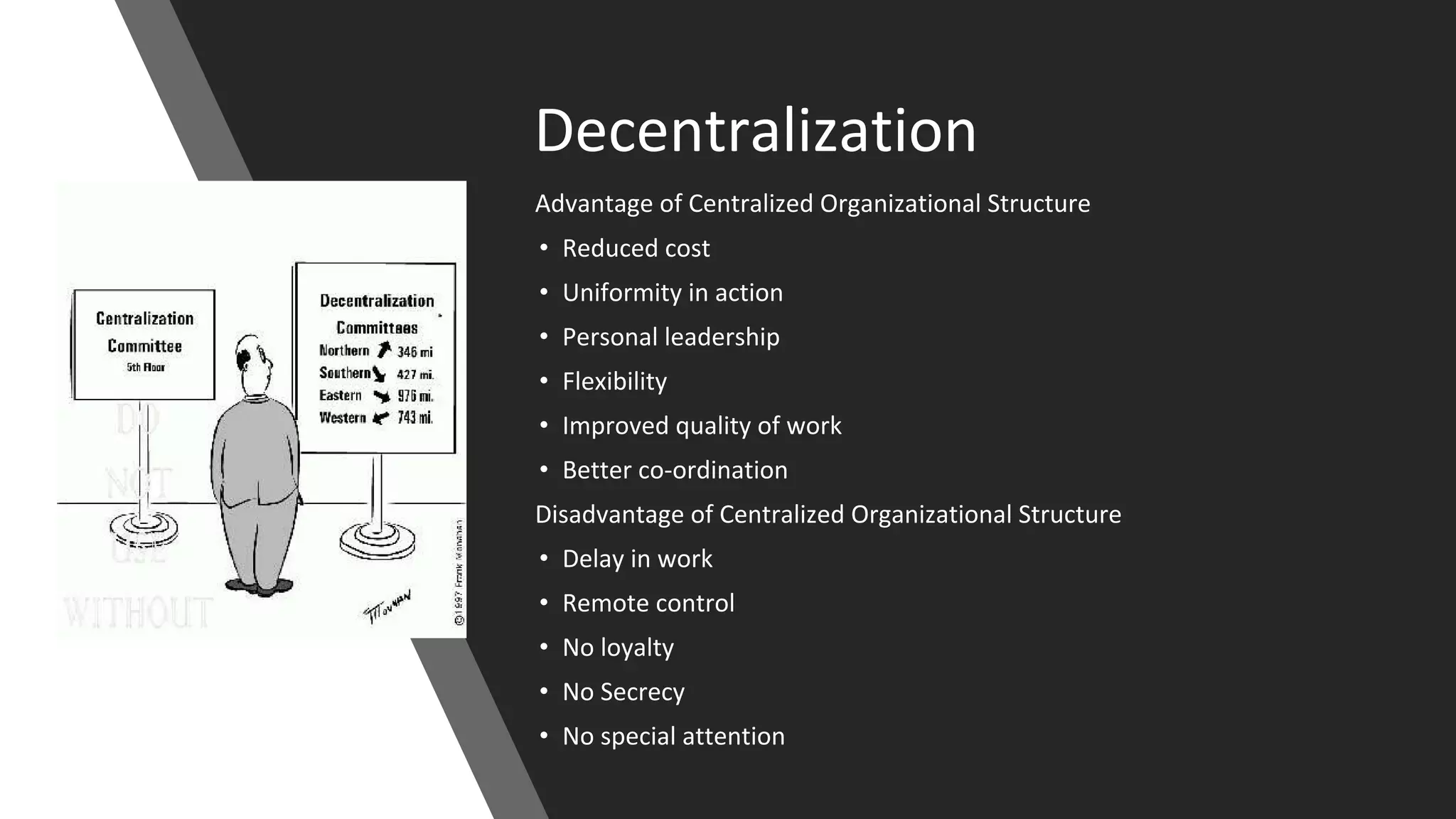
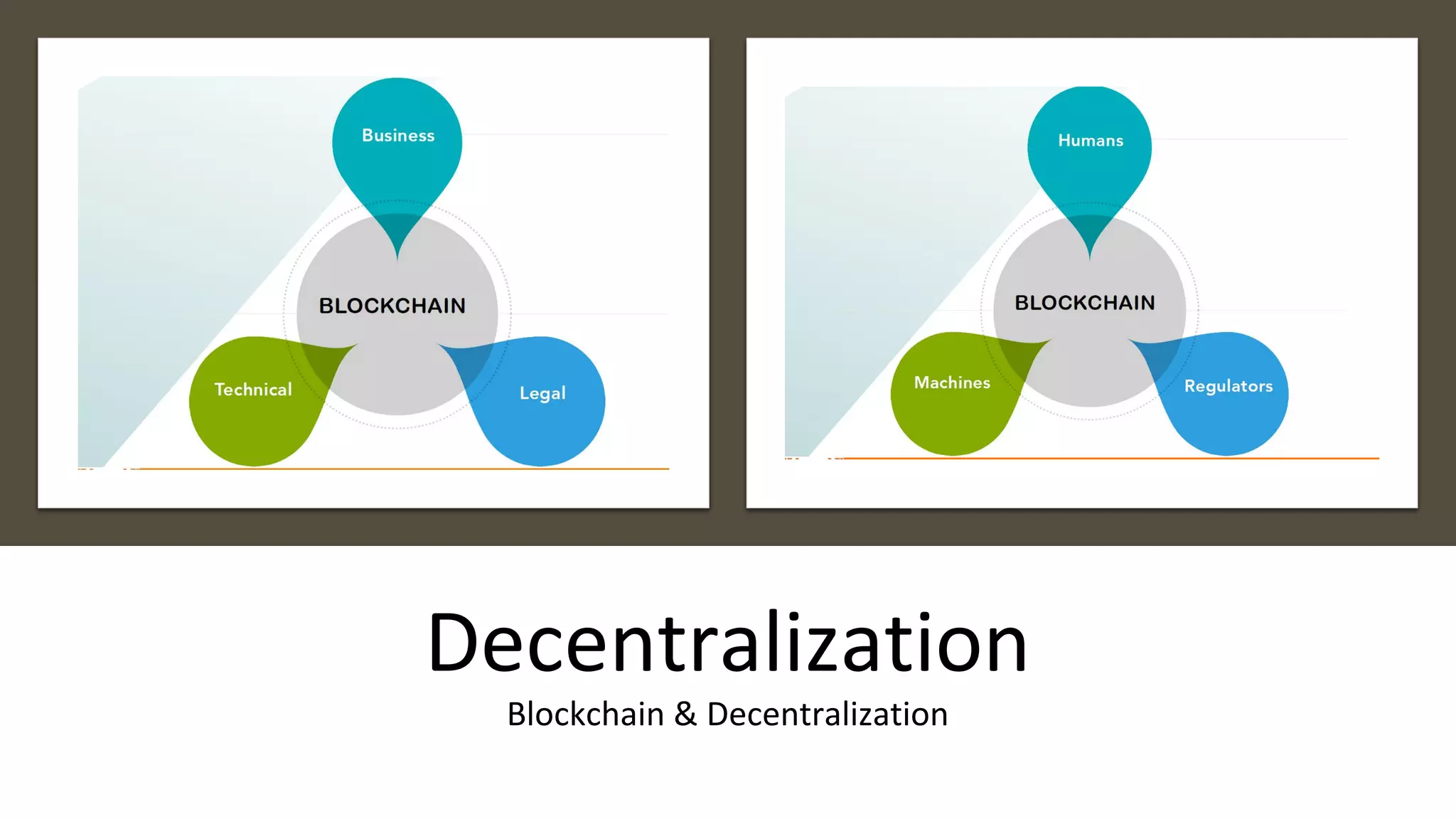
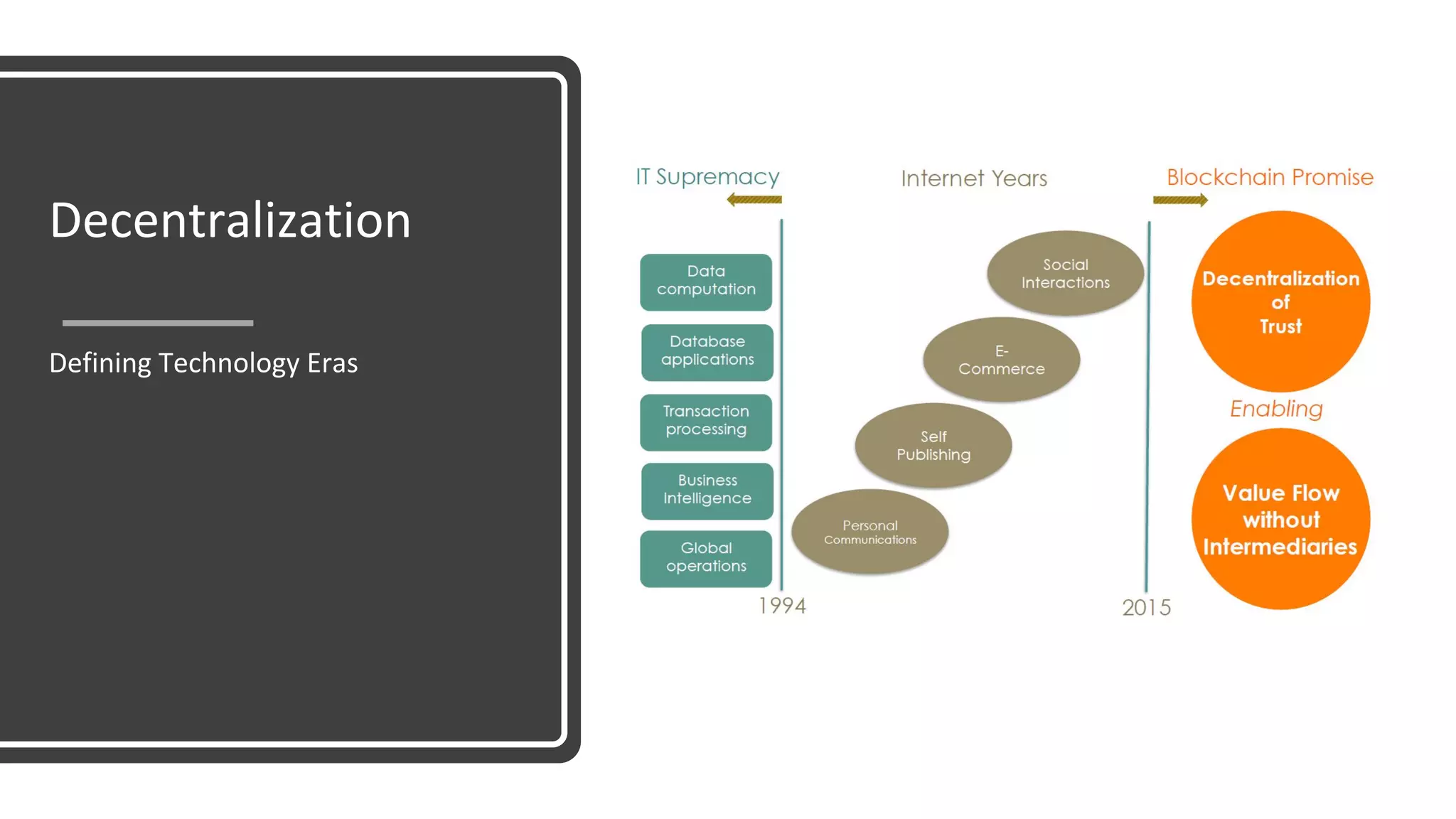
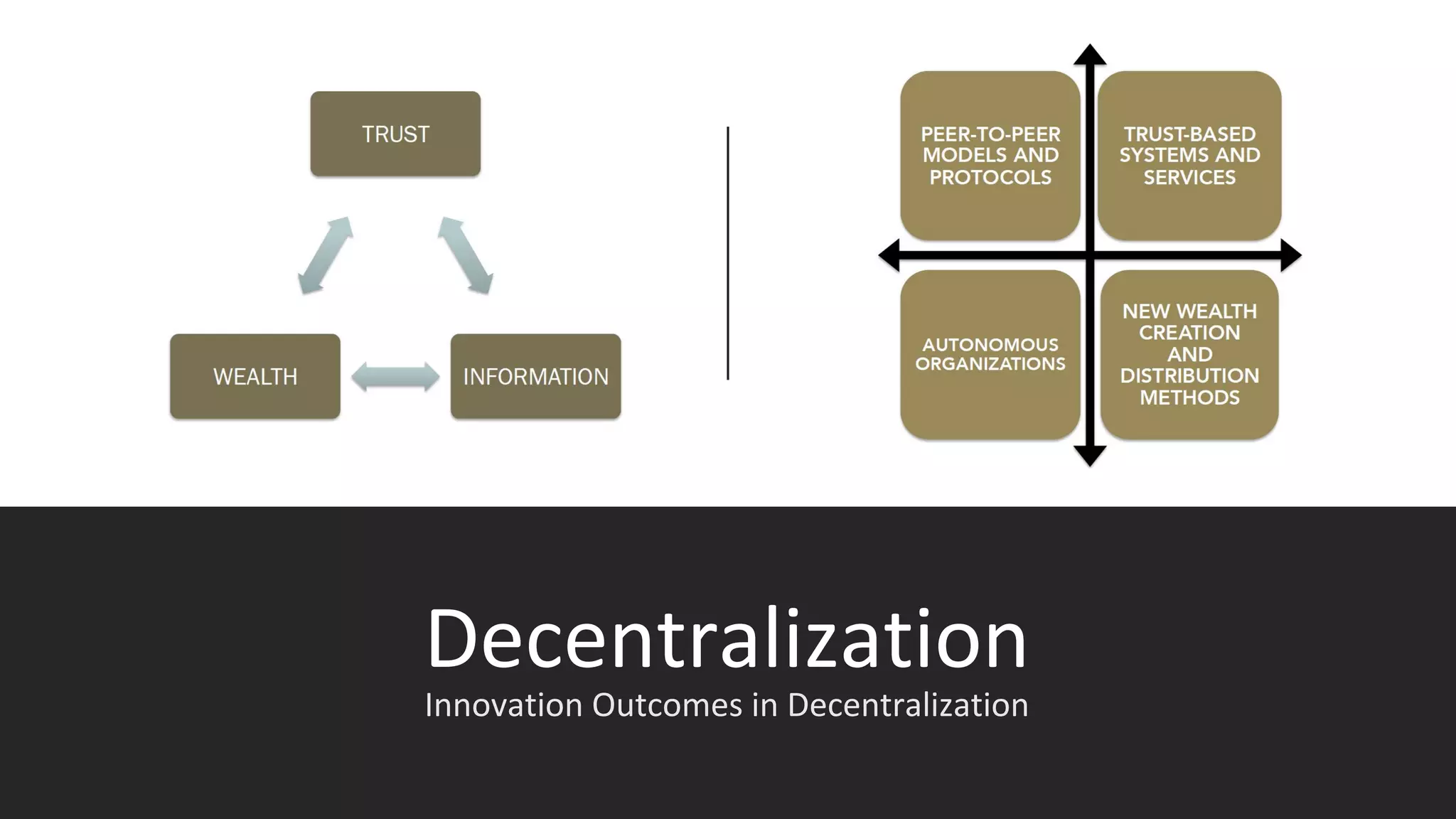
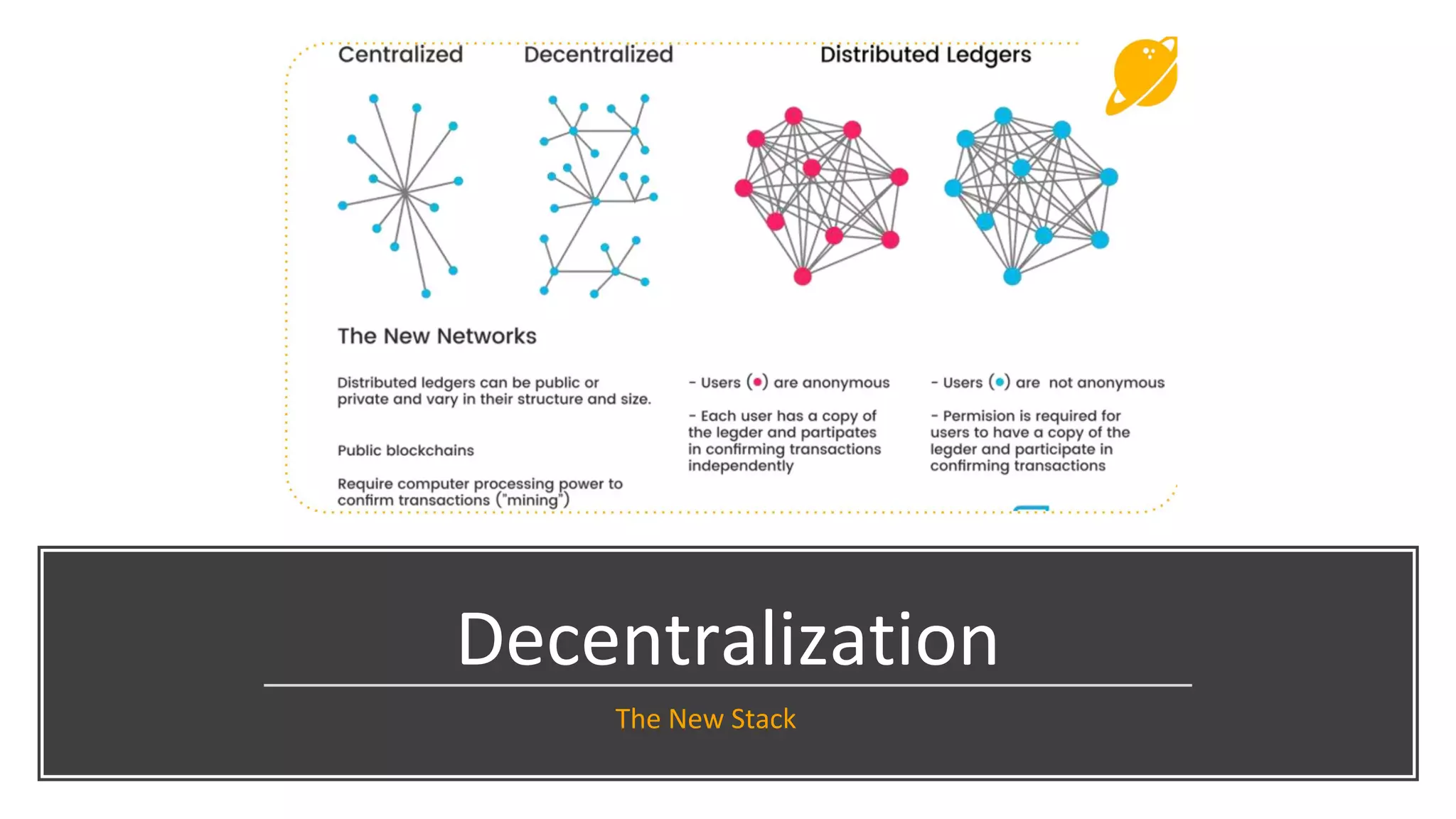
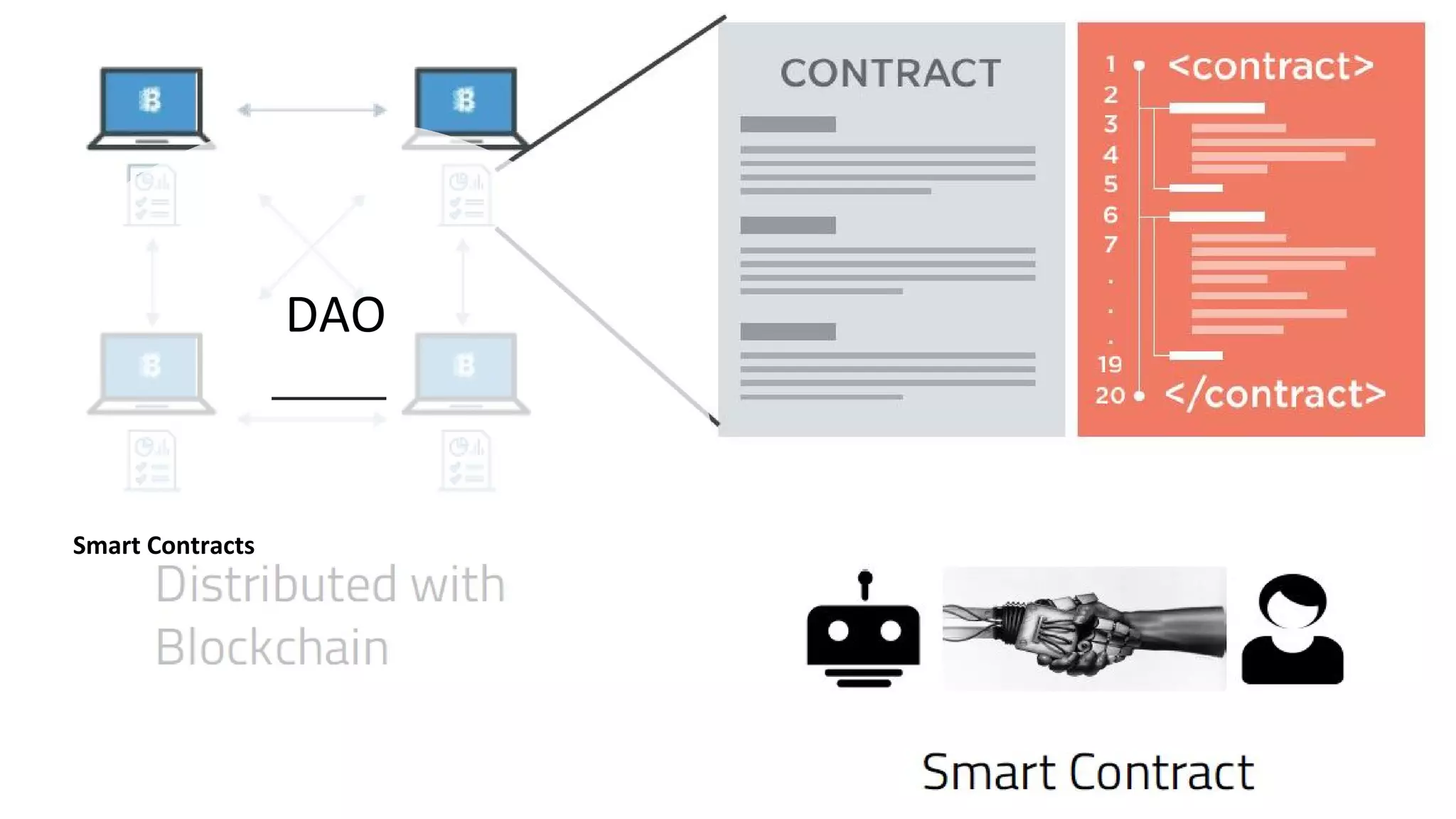
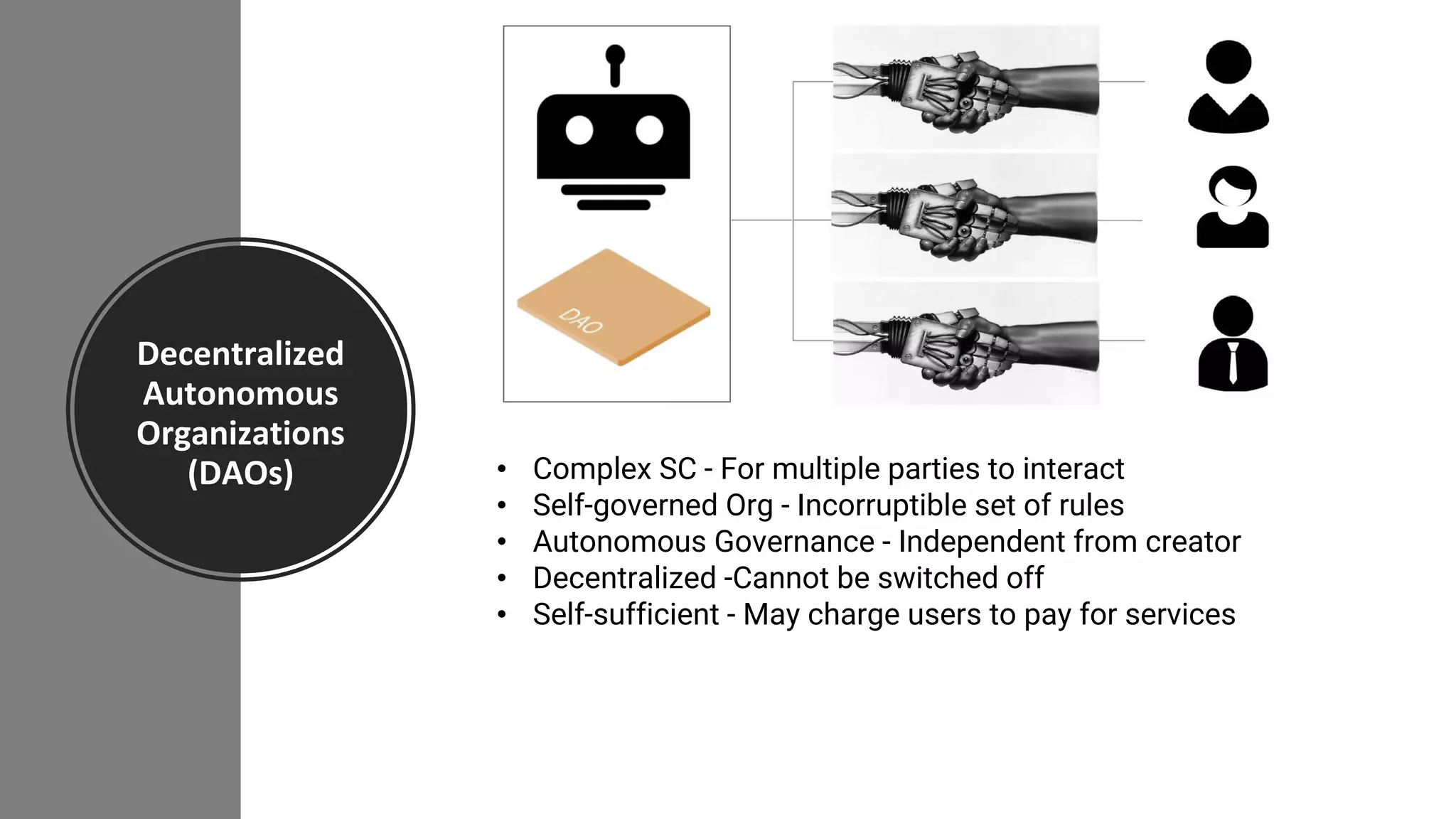
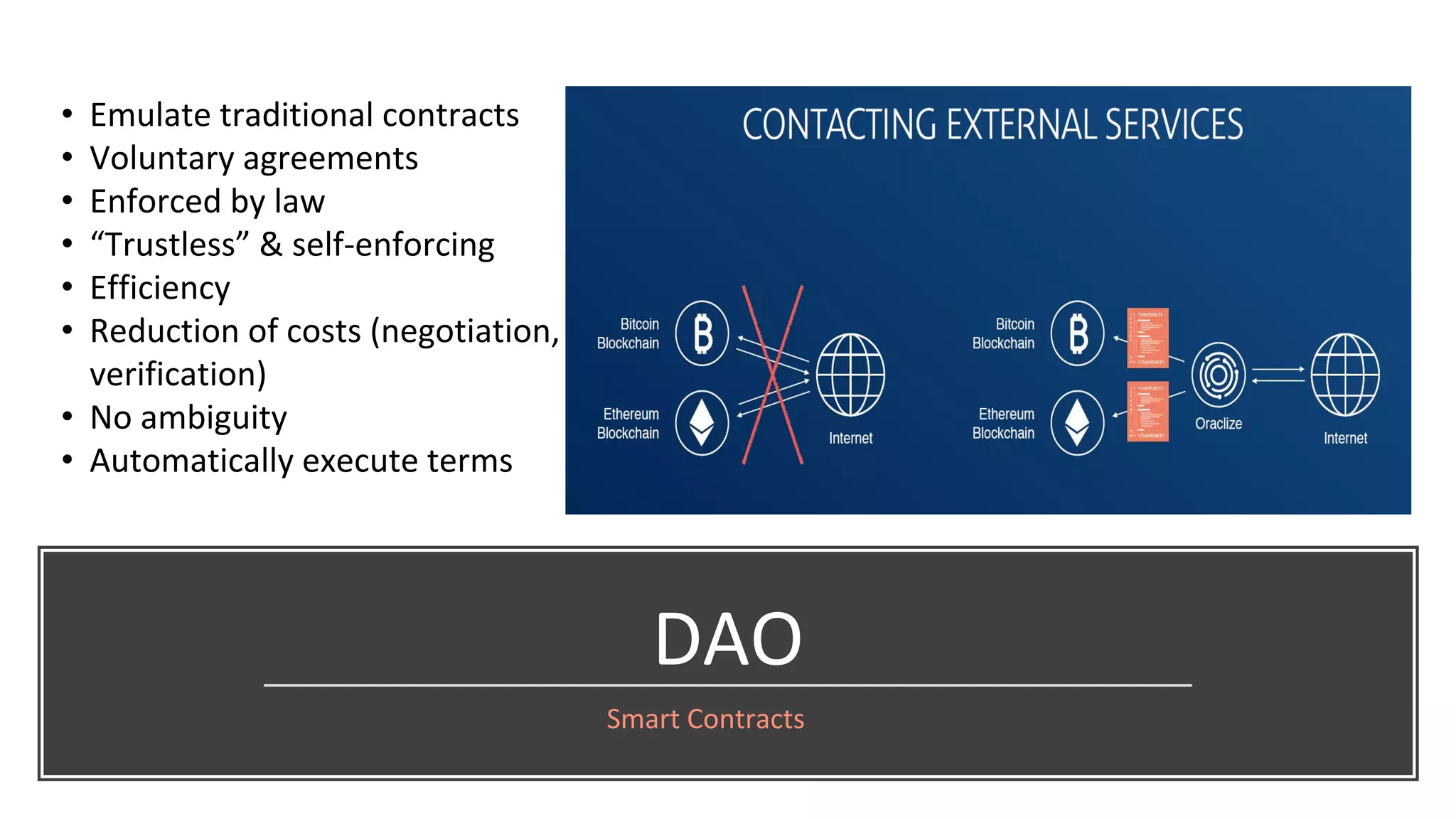
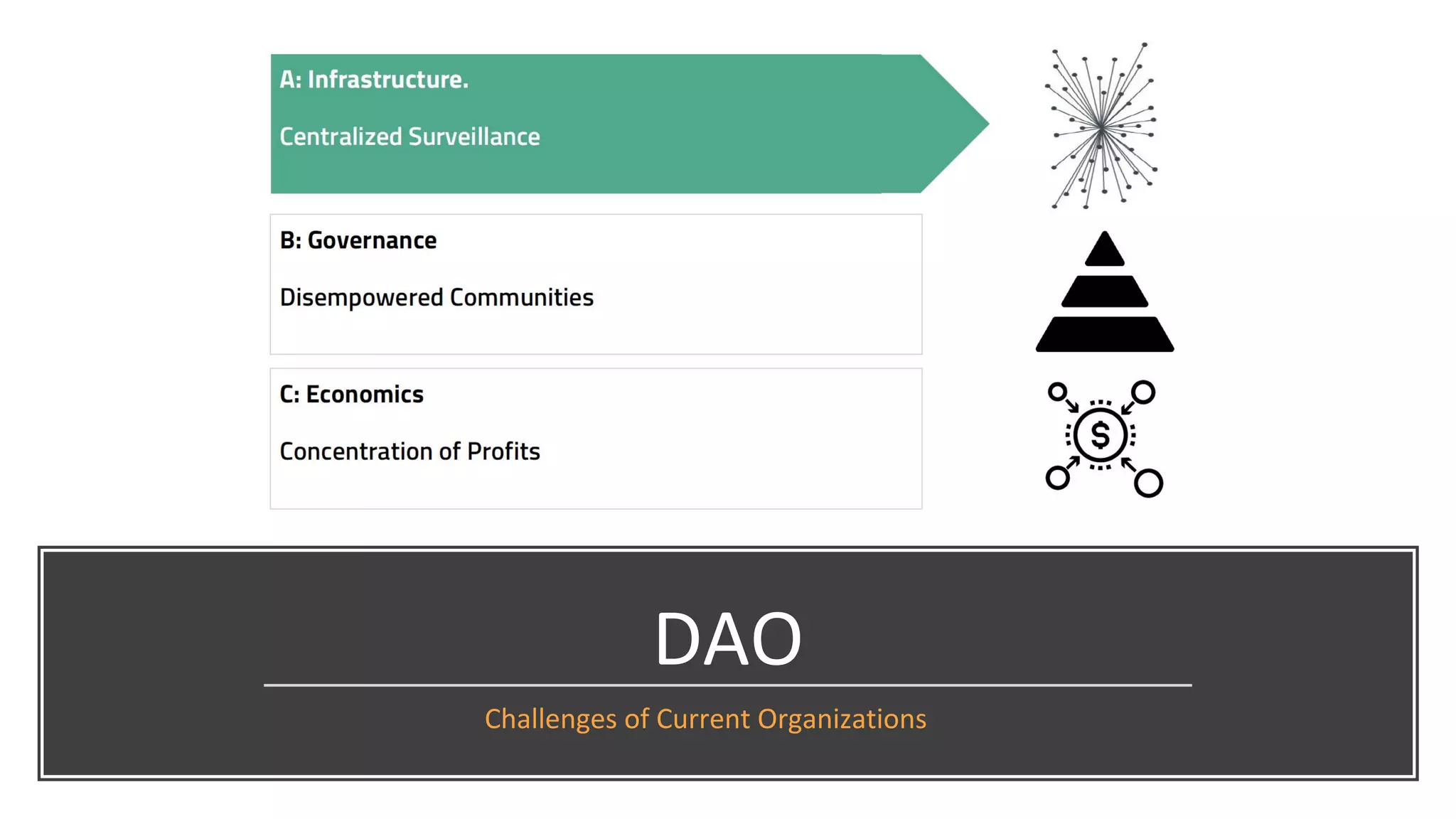
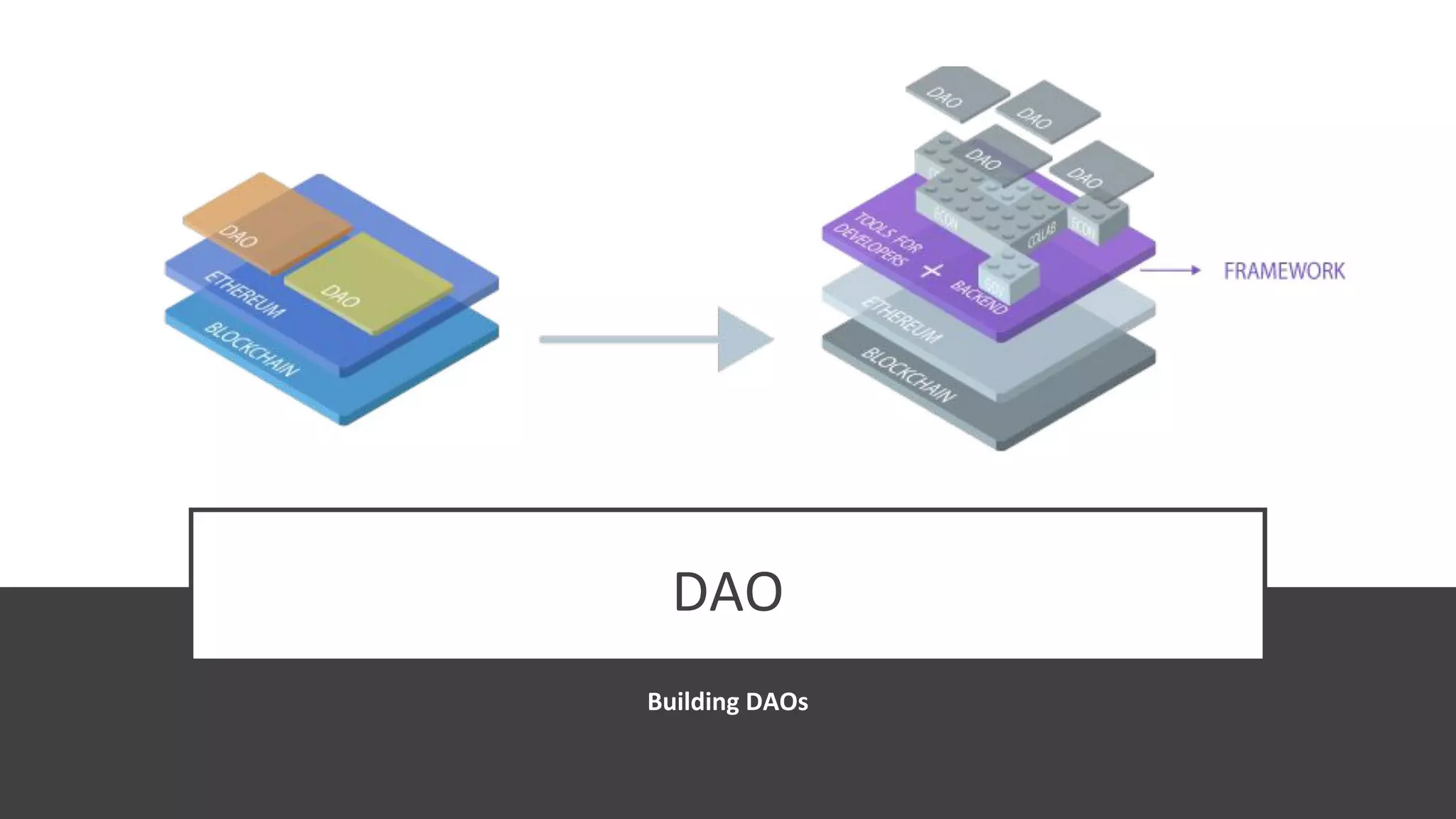
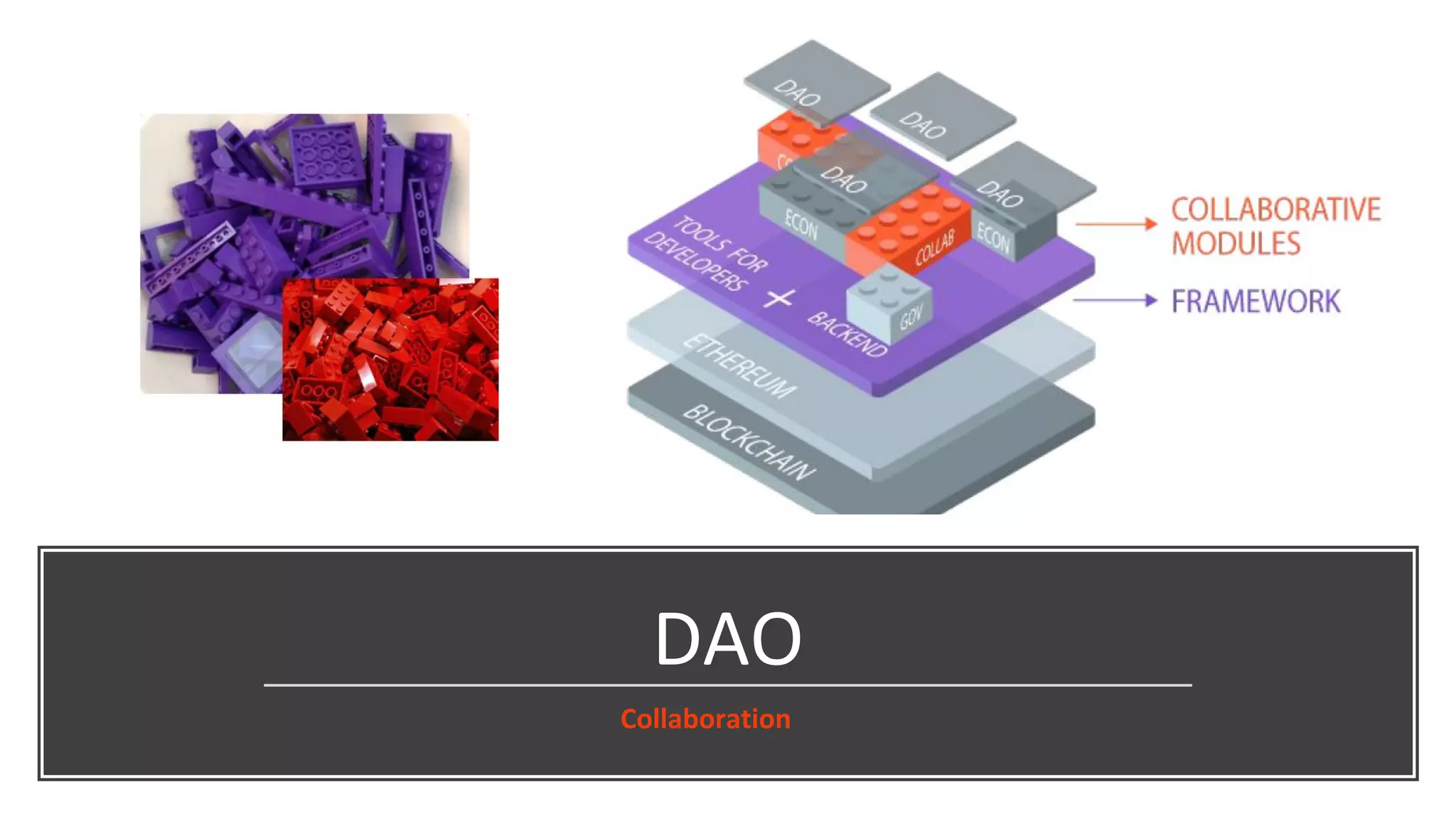
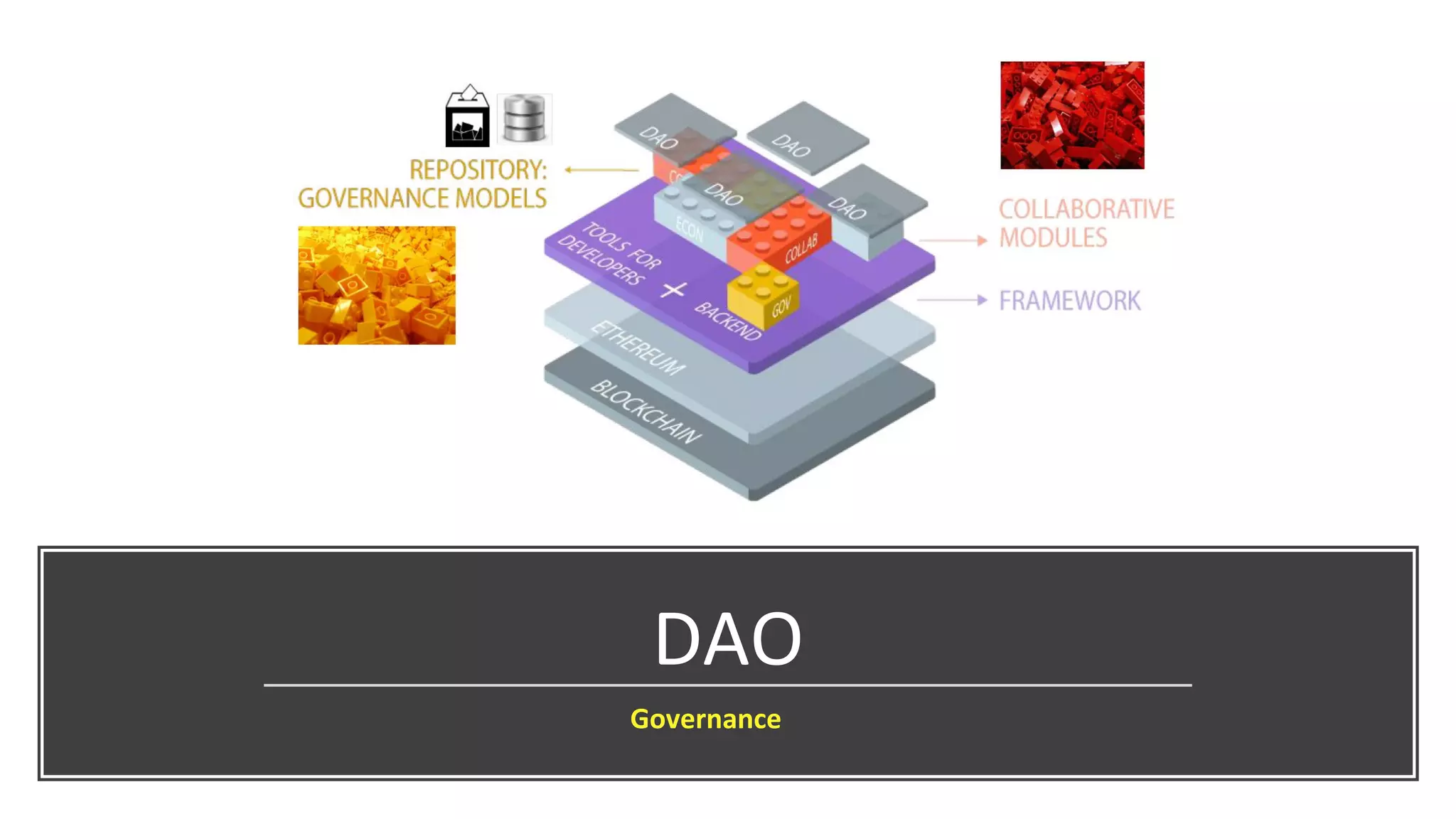
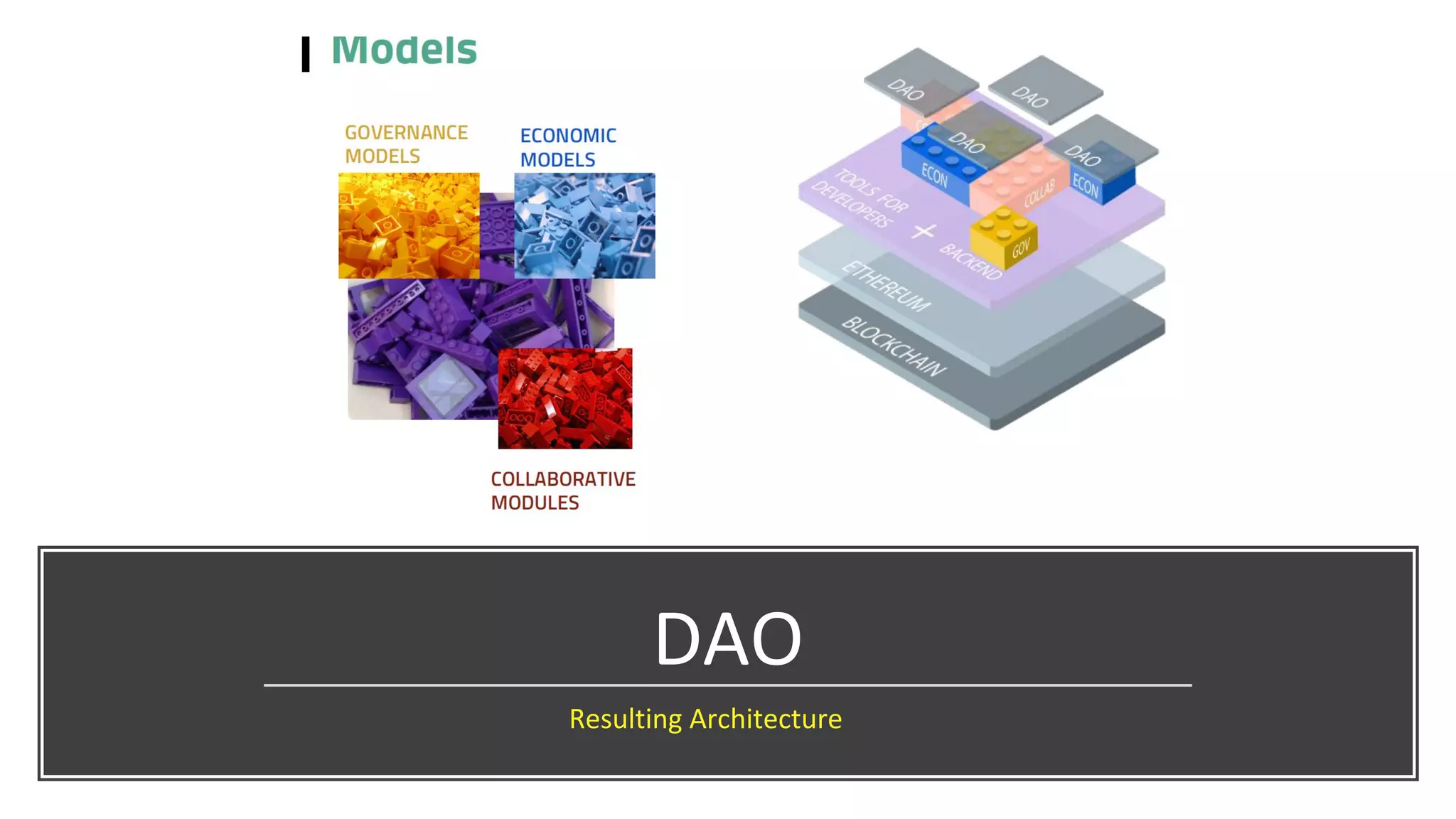
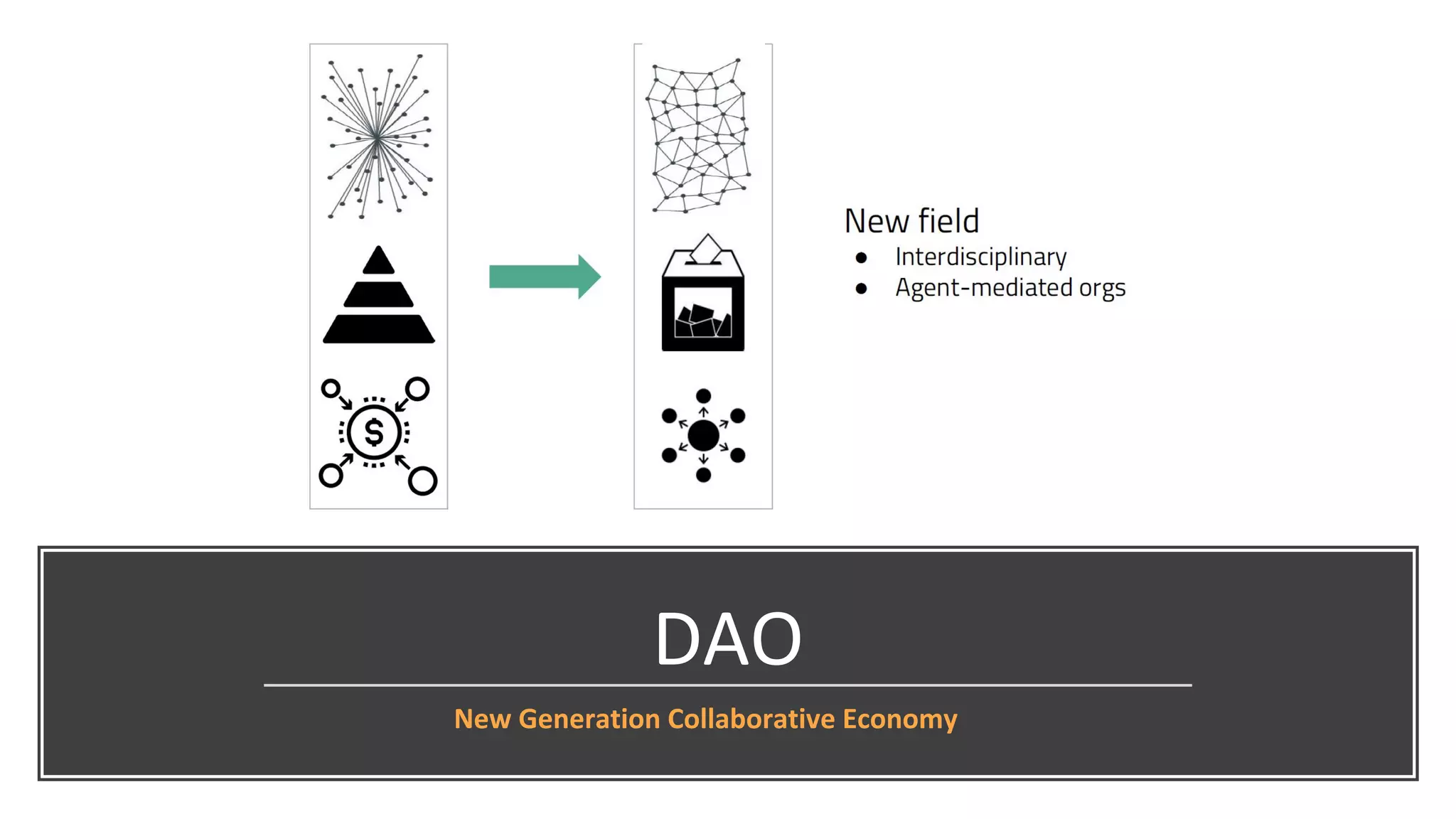
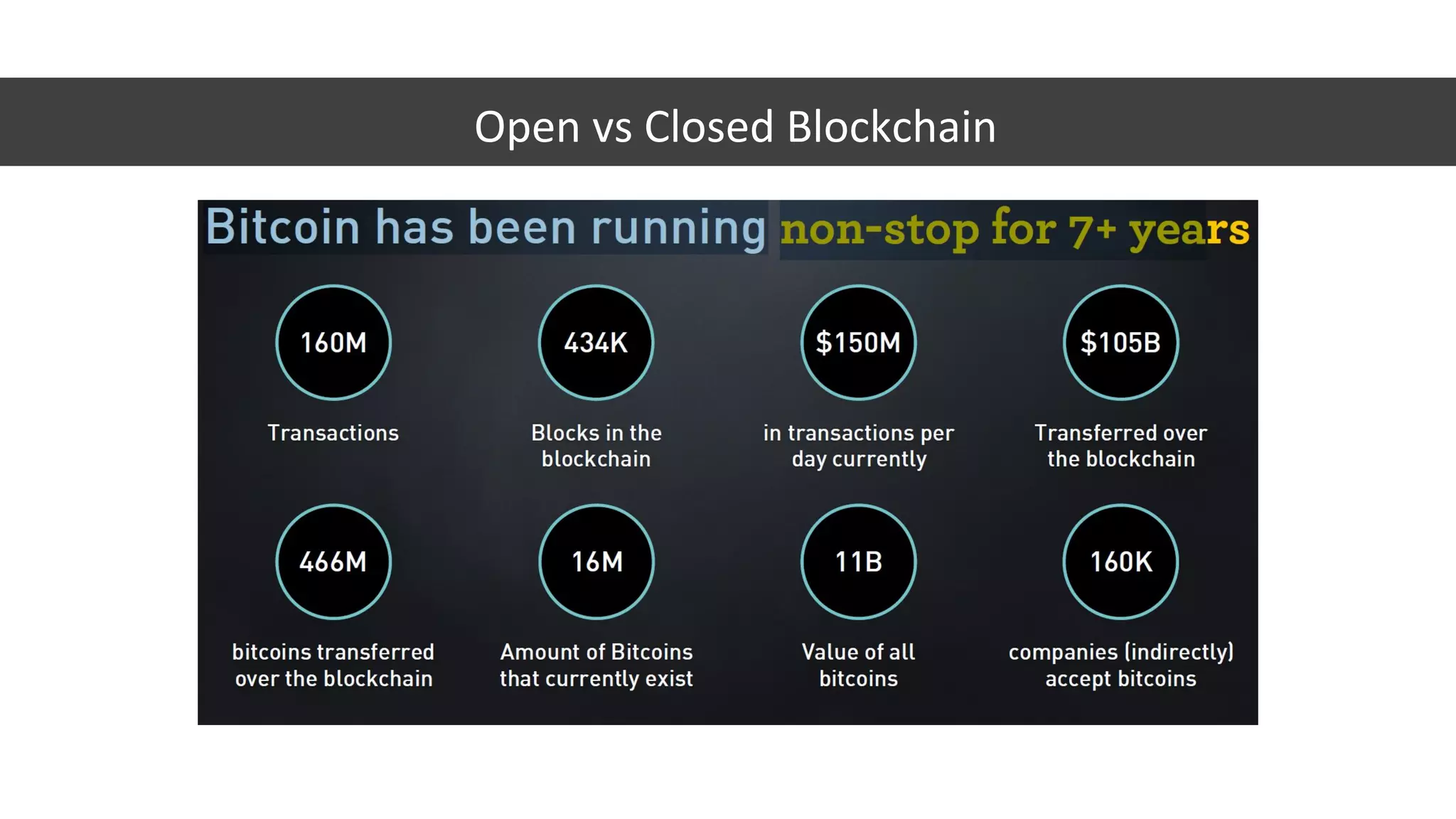
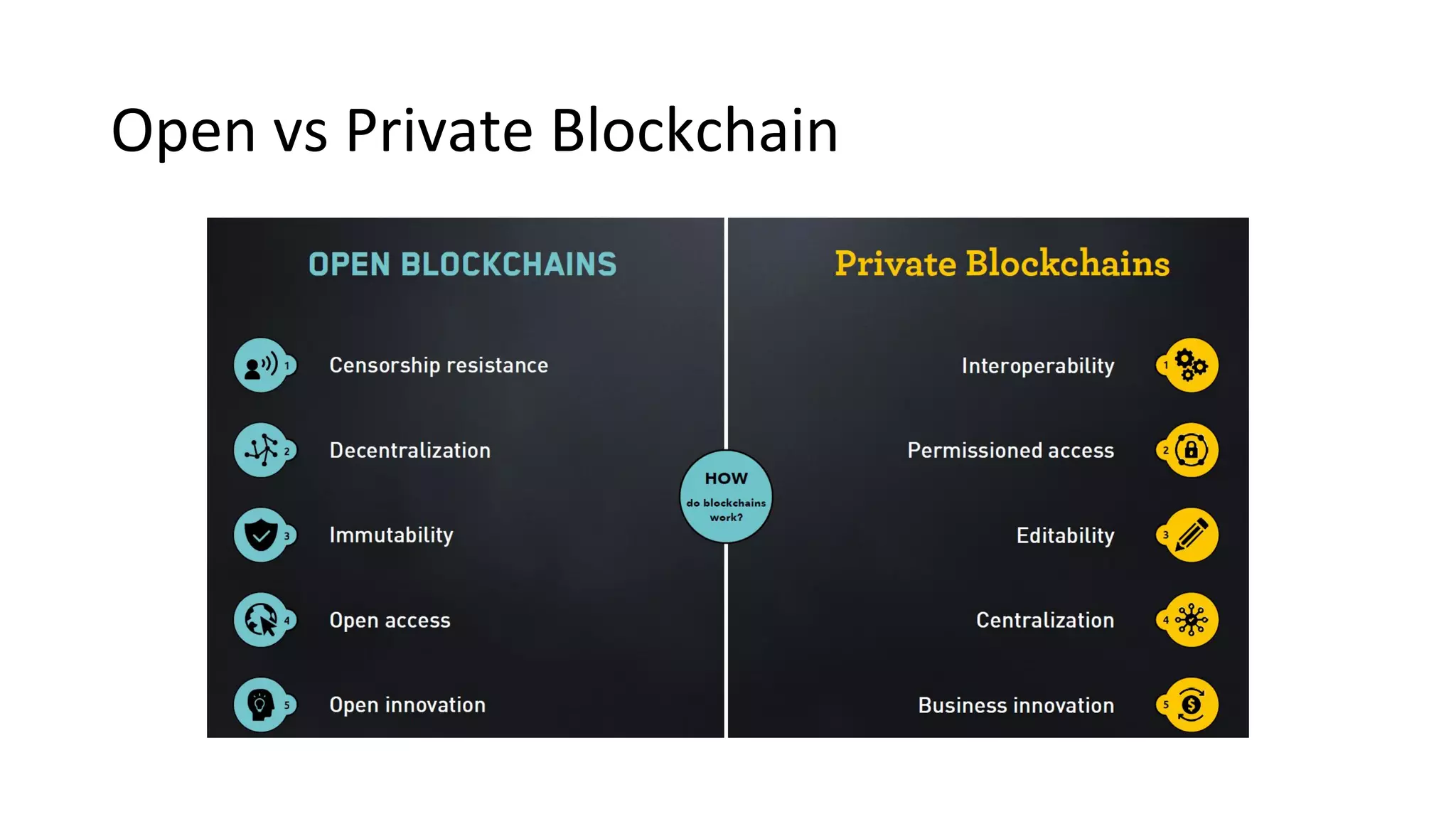
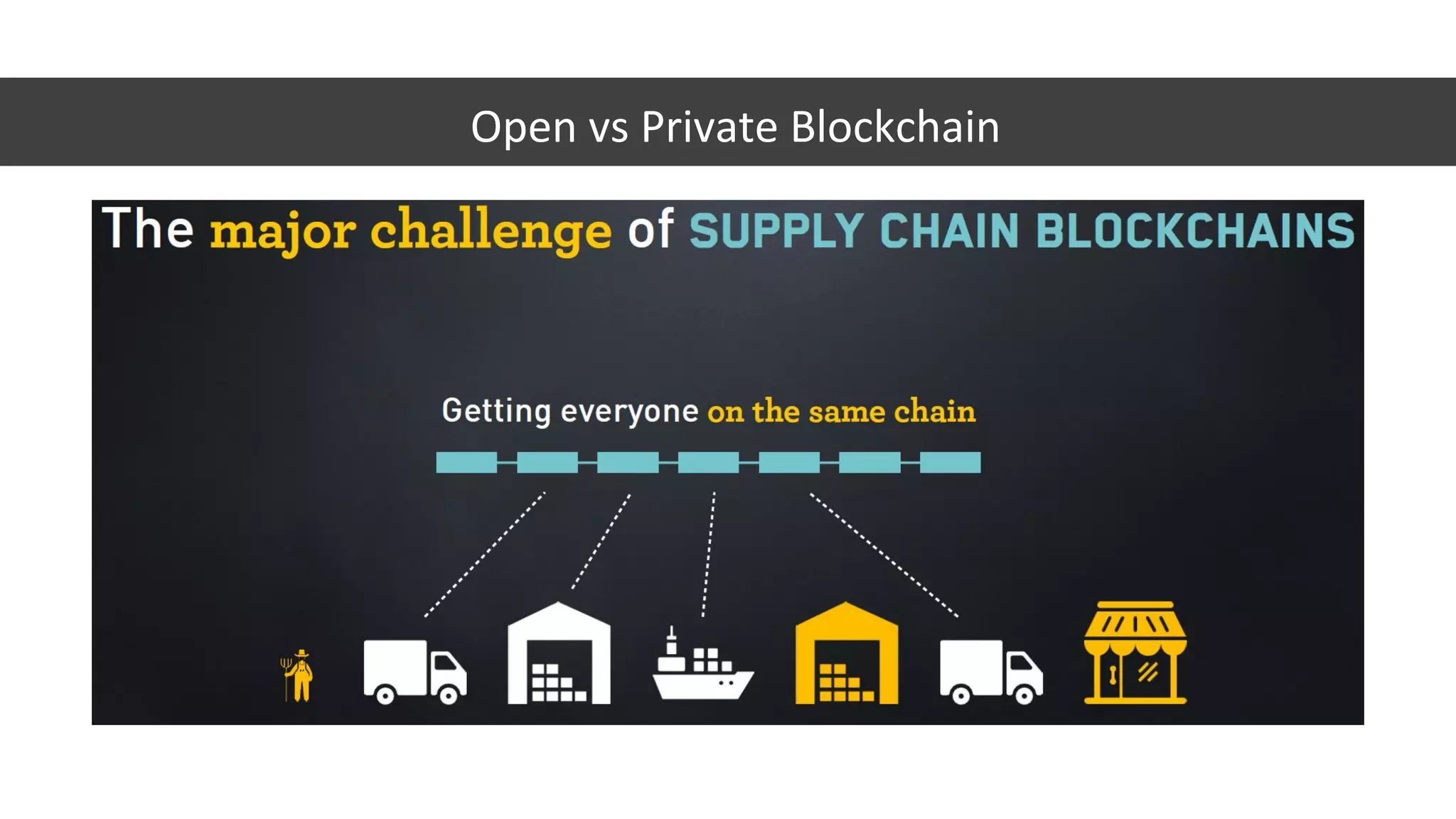
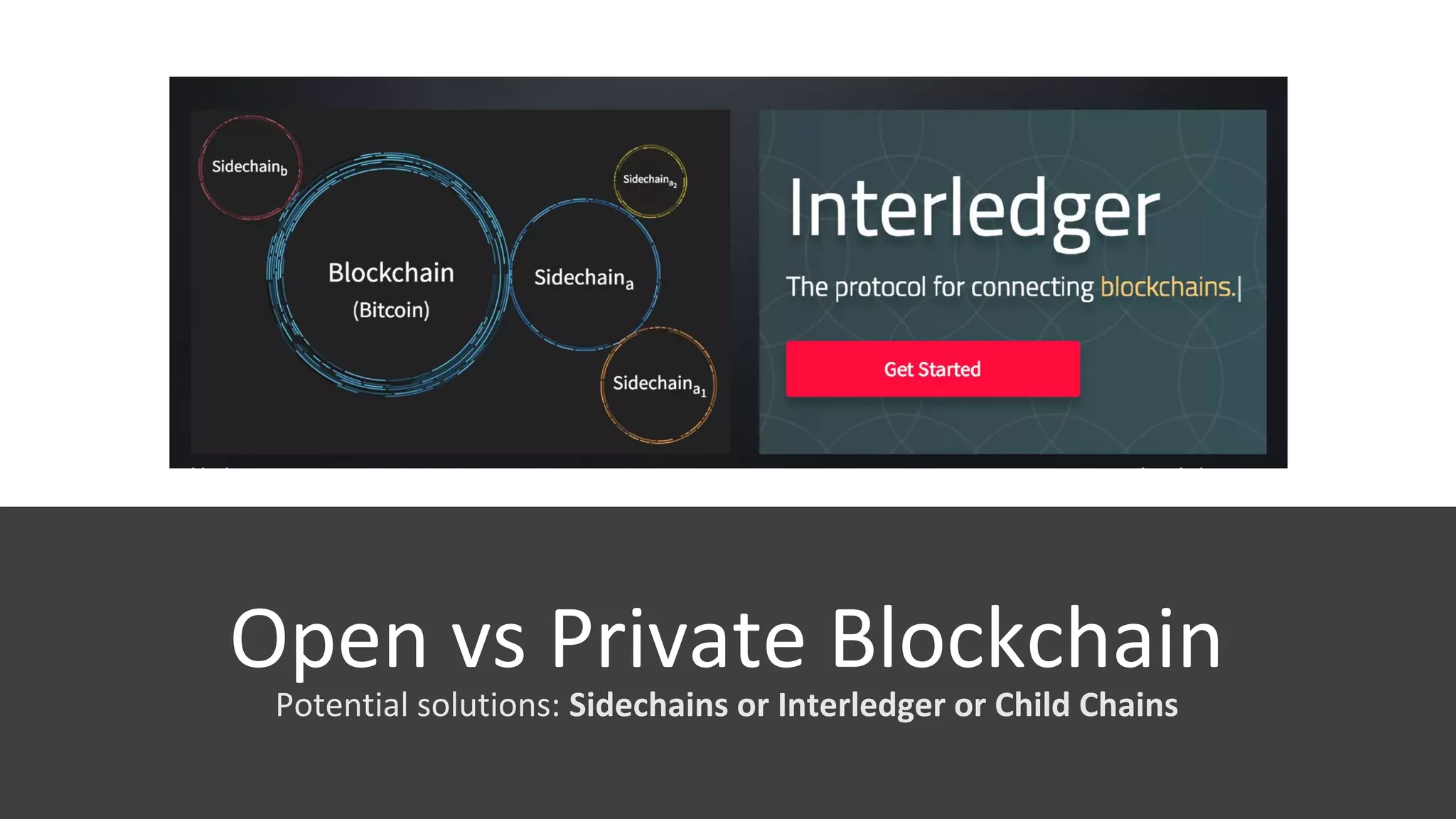
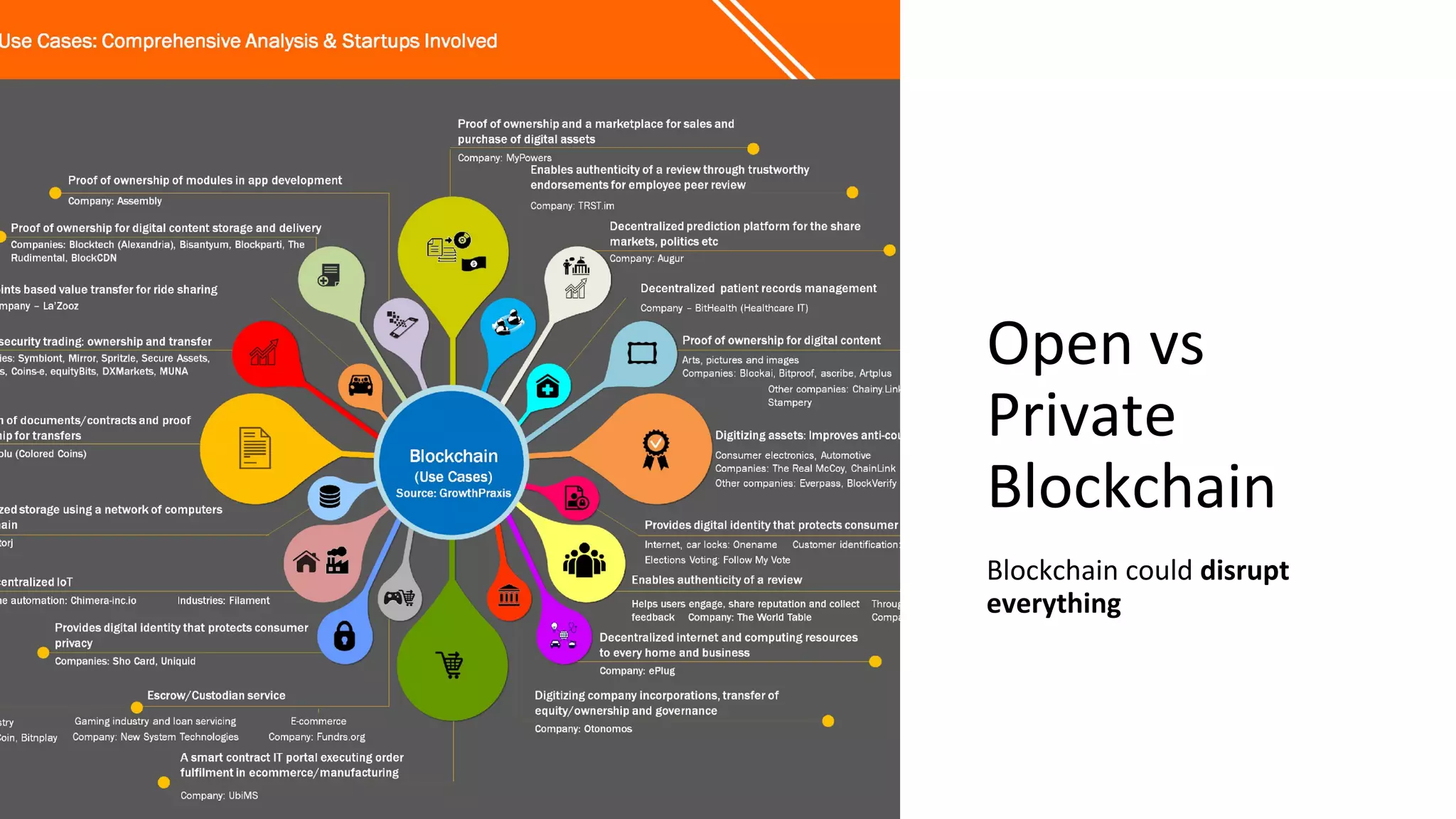
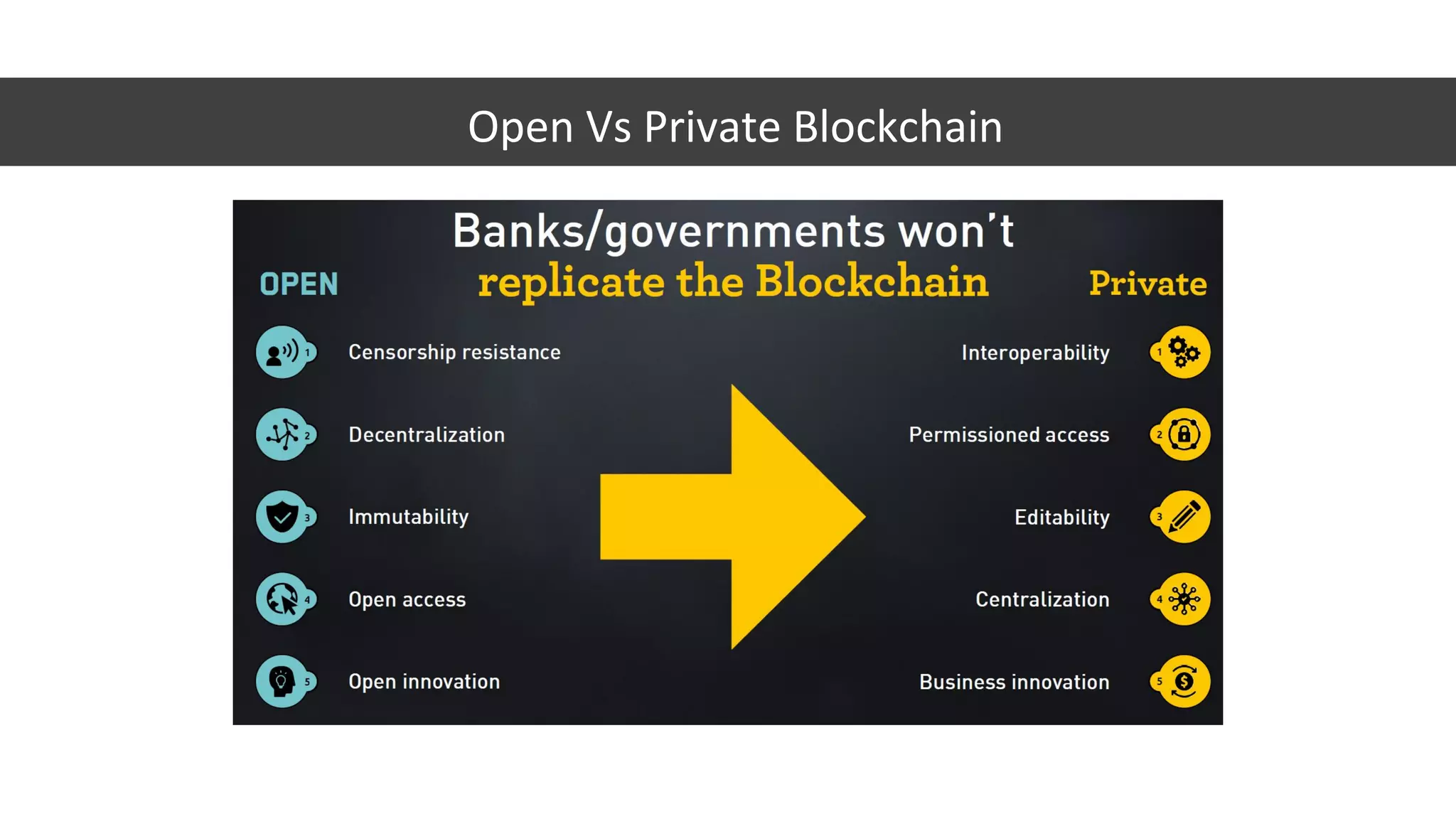
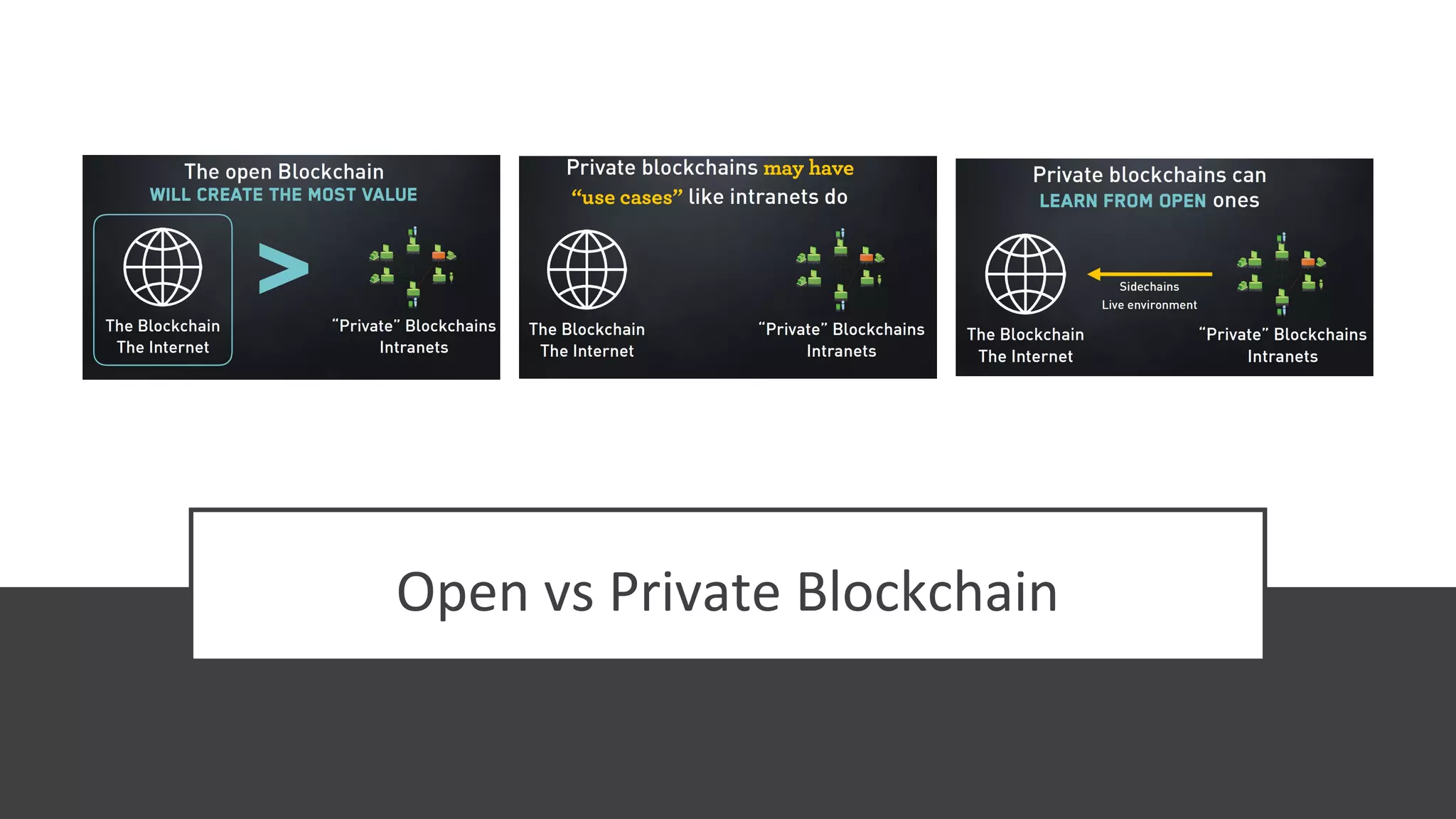
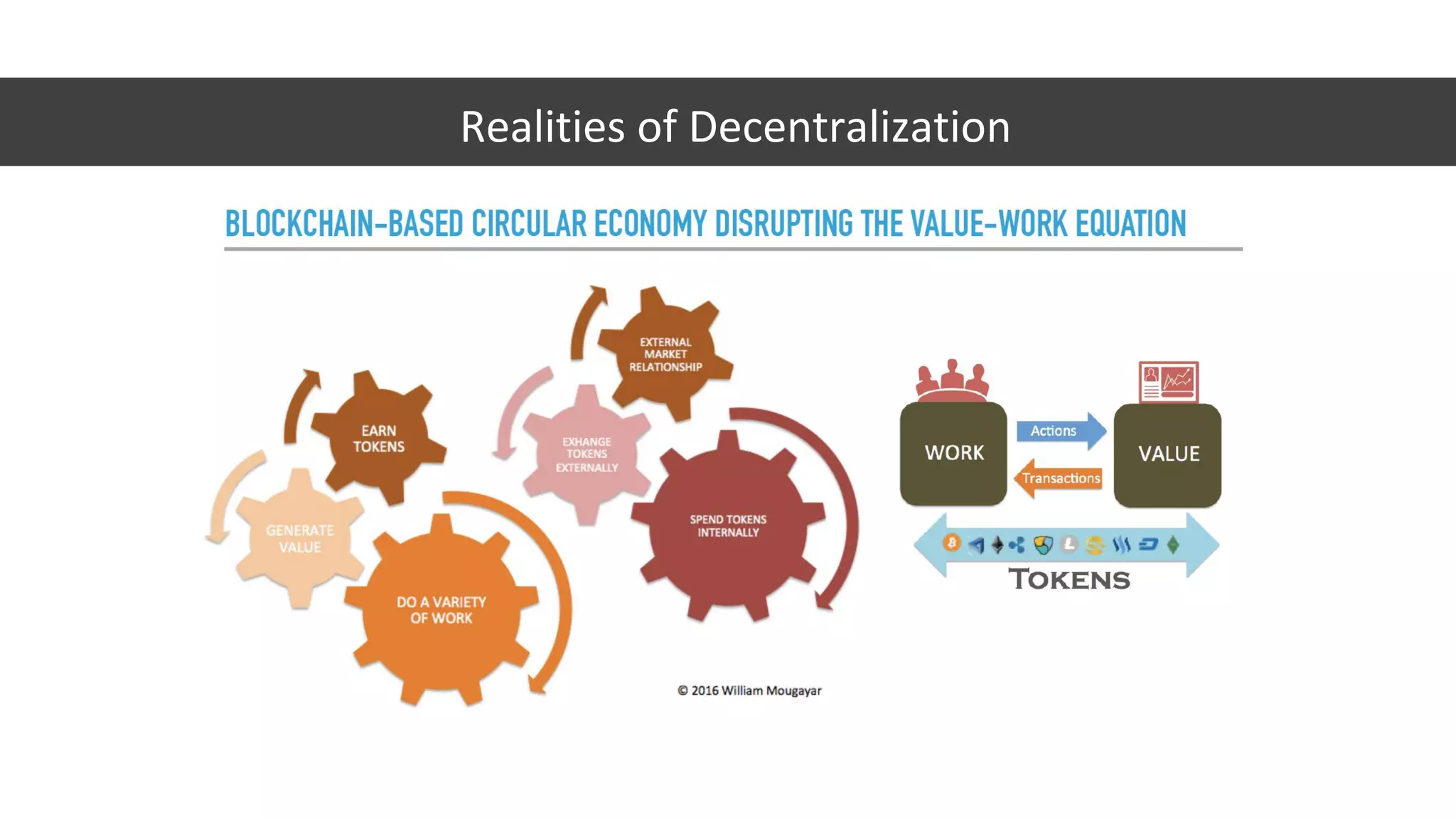
The document discusses the origins and fundamentals of blockchain technology, explaining its decentralized nature and the significance of cryptographic security. It highlights the differences between centralized and decentralized organizational structures and explores concepts like decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and smart contracts. Additionally, it addresses the realities and challenges of adopting blockchain technology, emphasizing the importance of understanding the economic models and governance surrounding tokens.