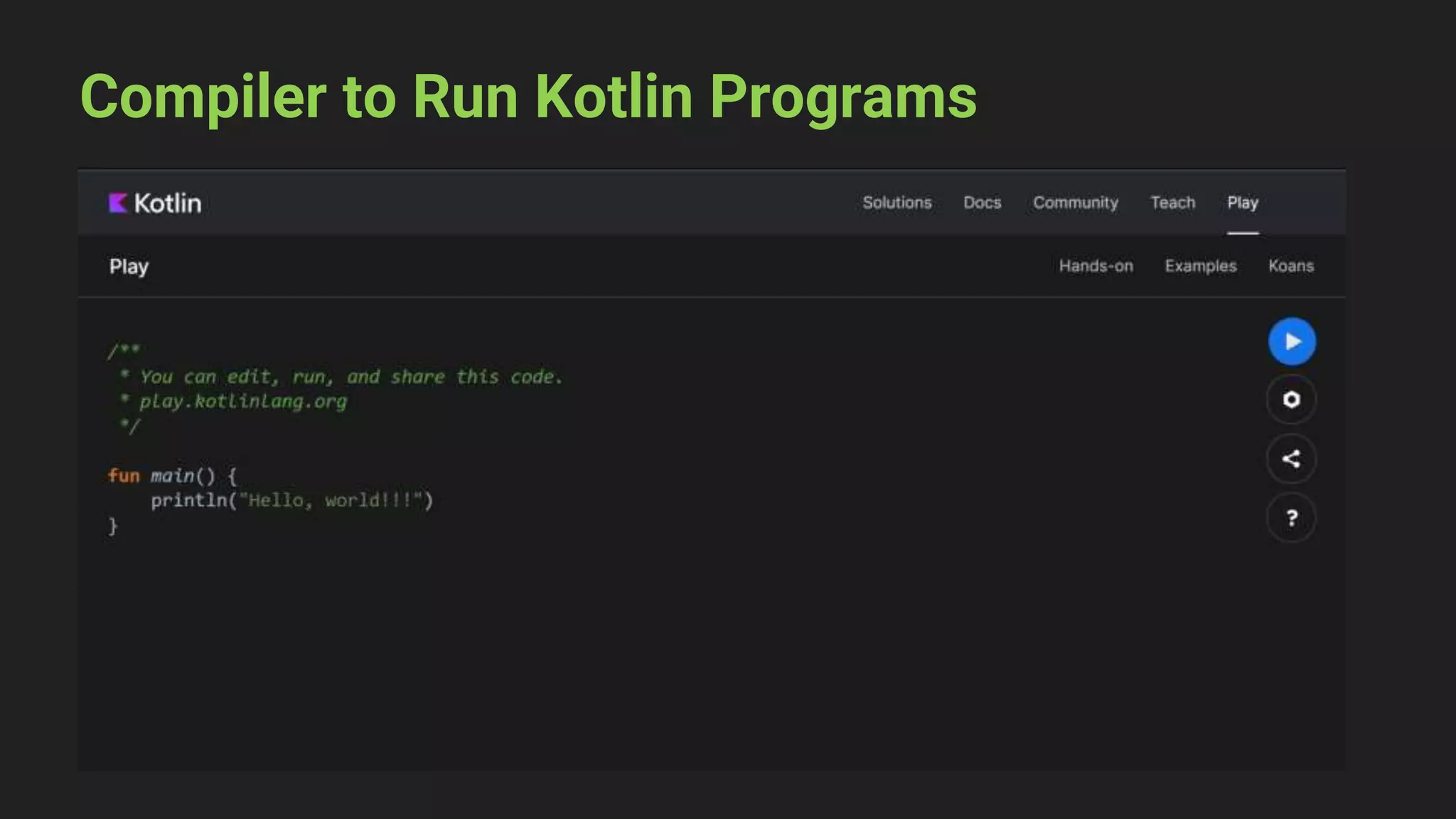
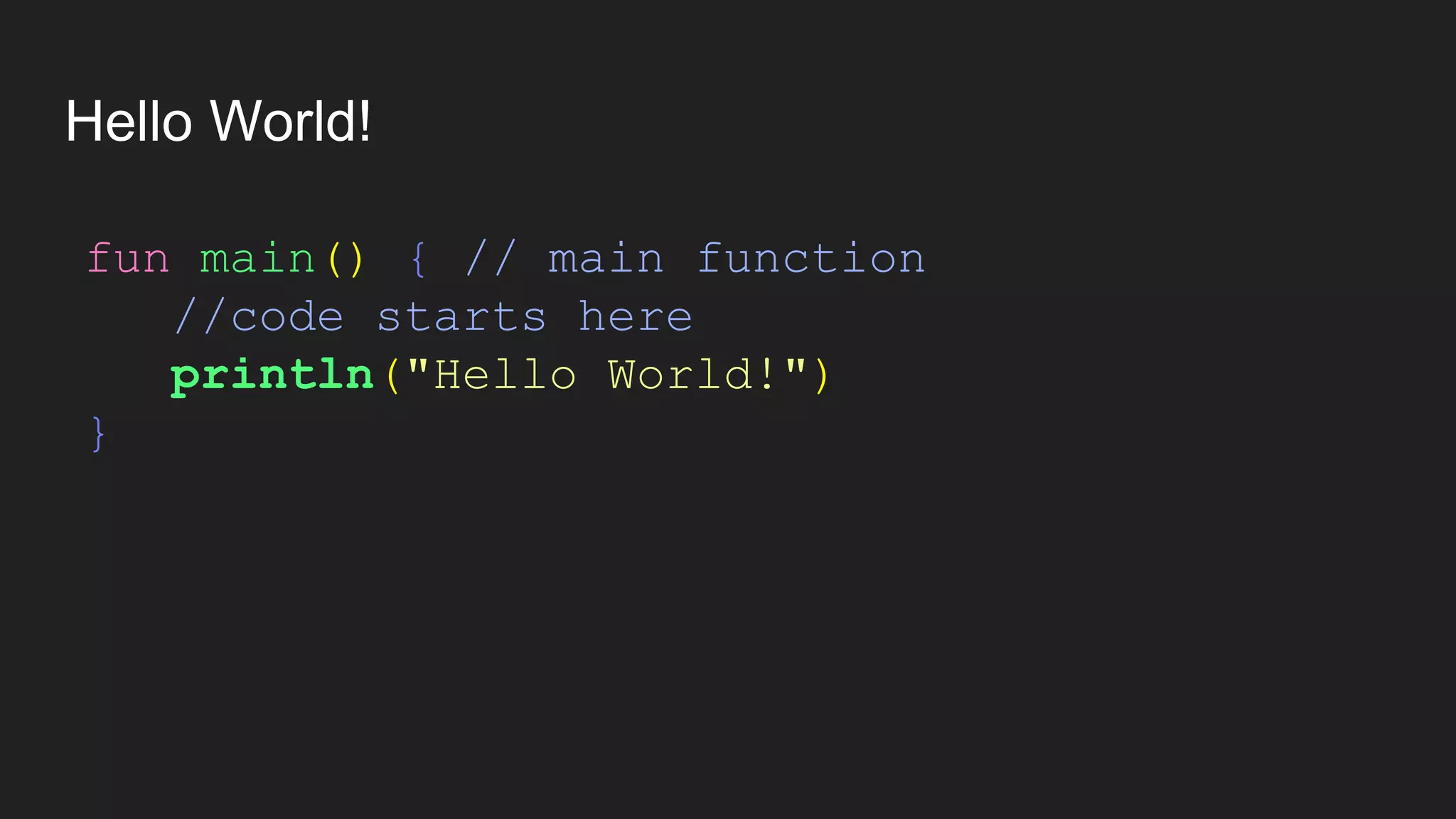
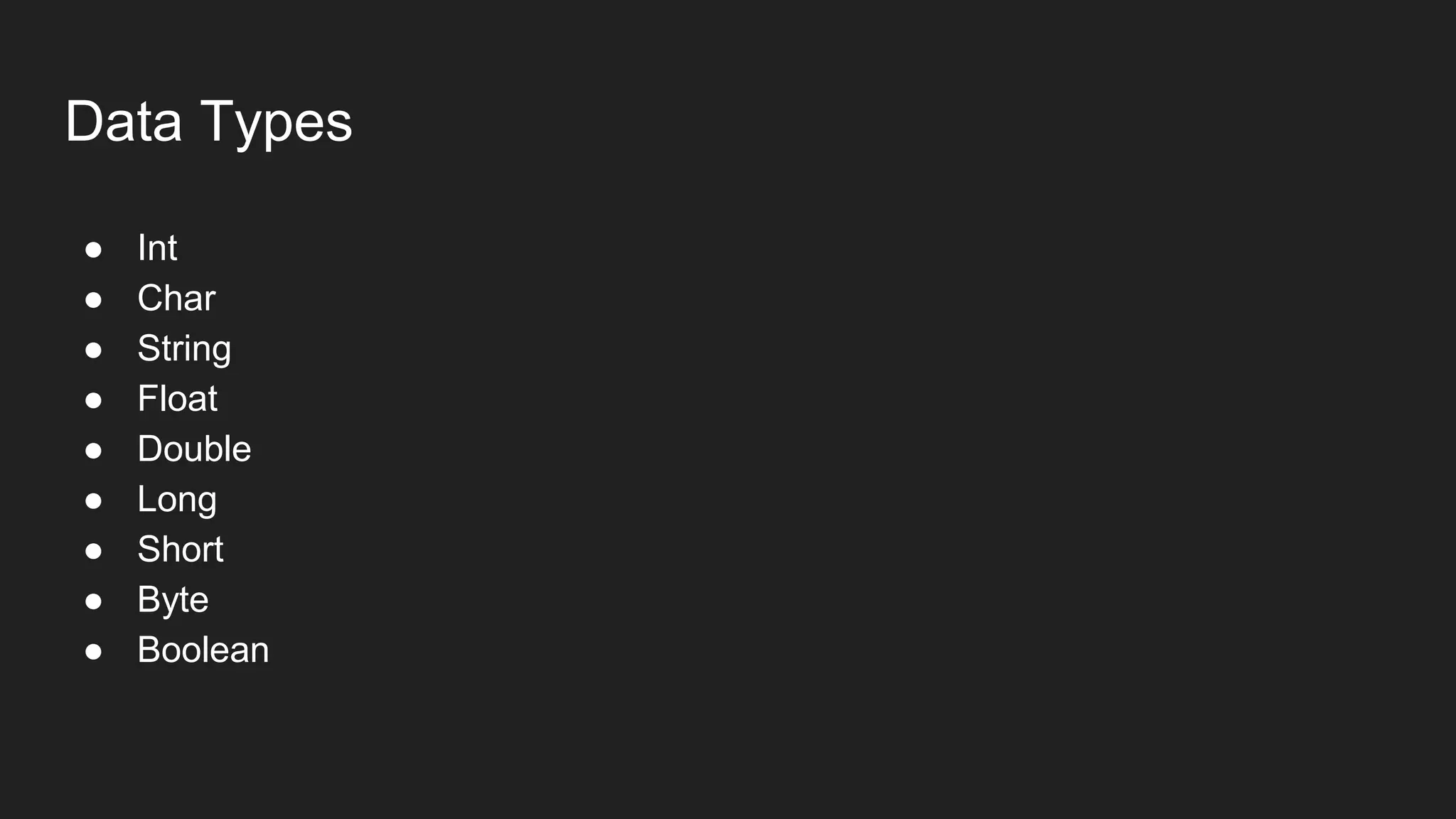
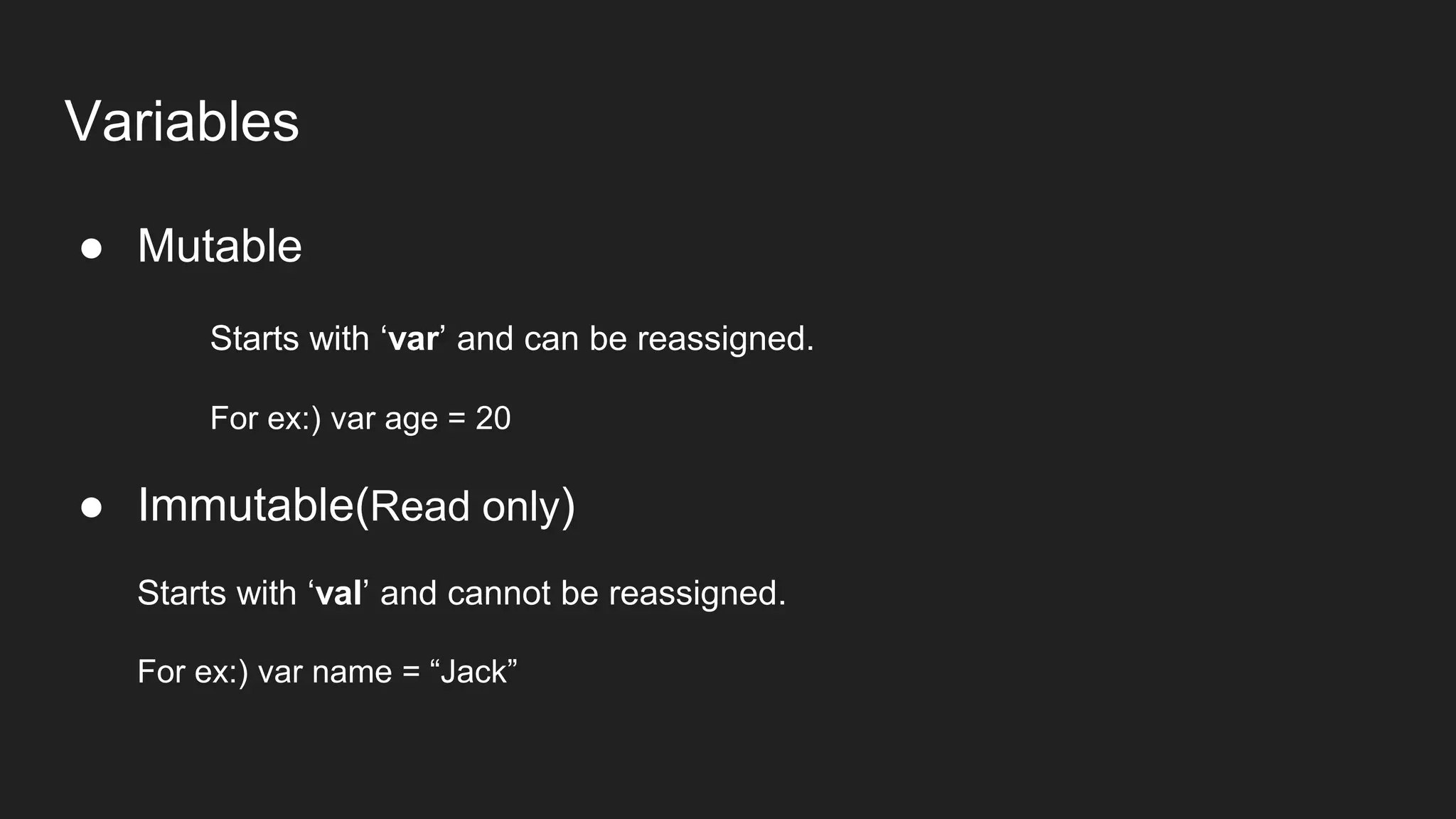
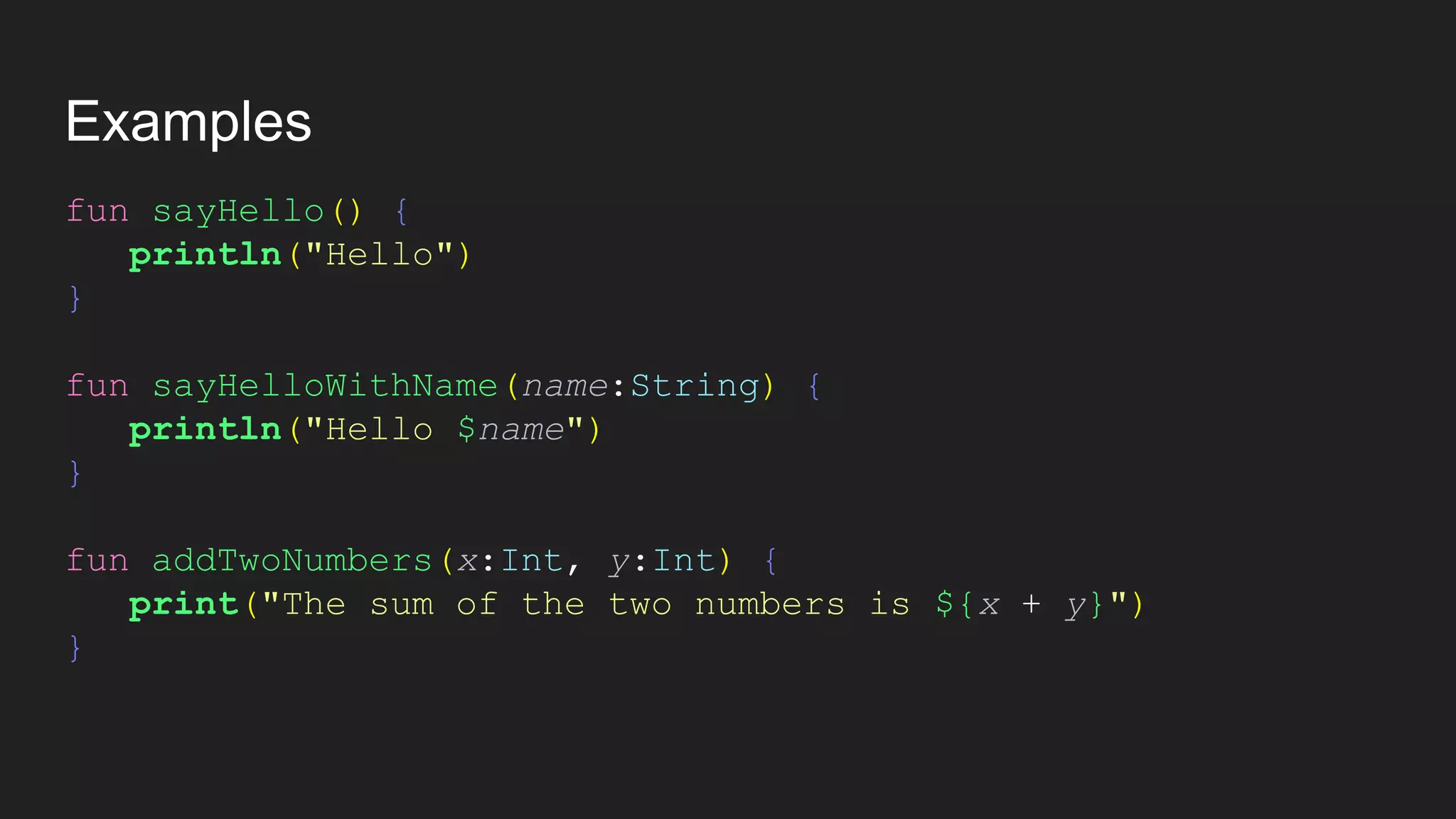
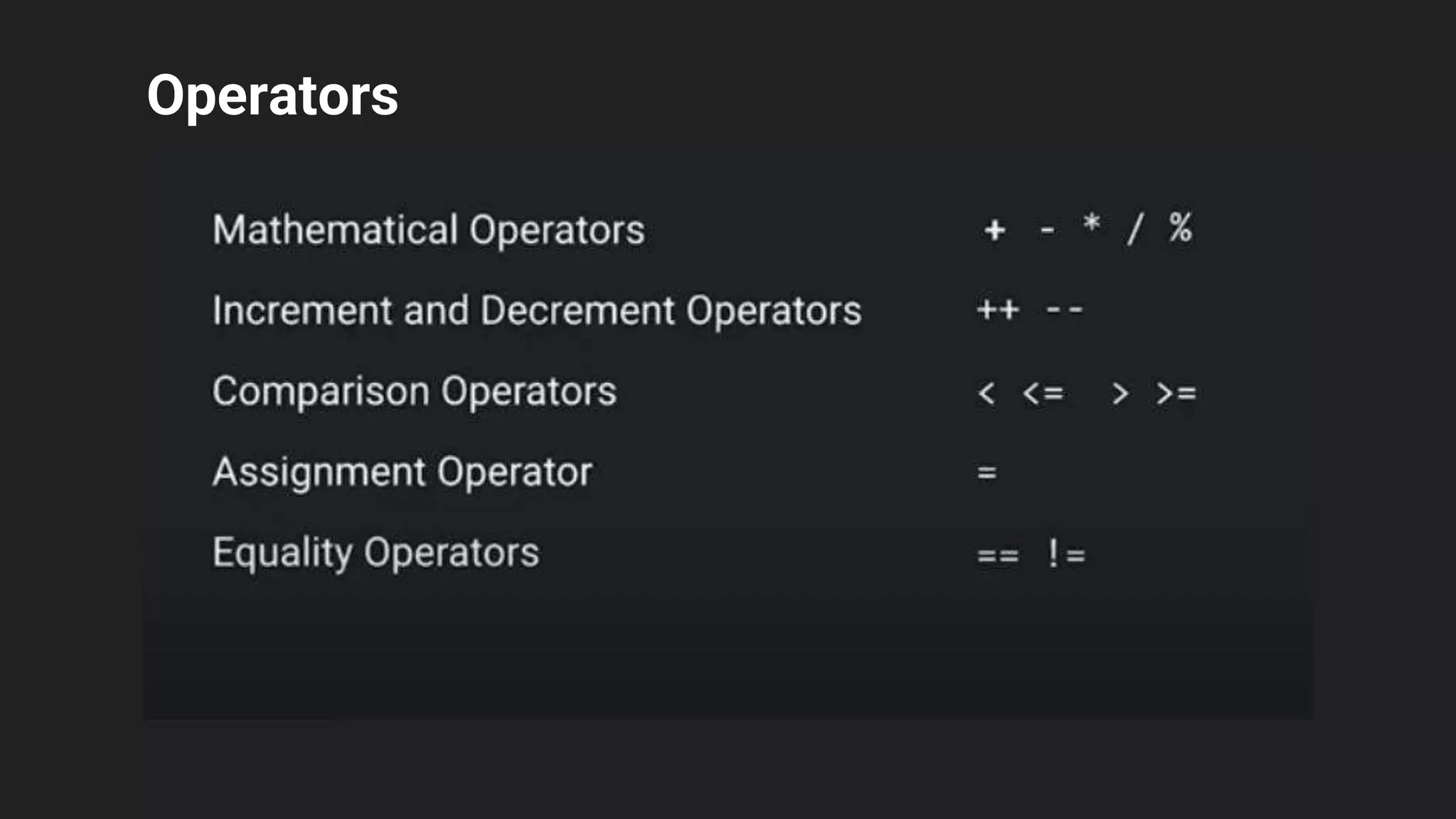
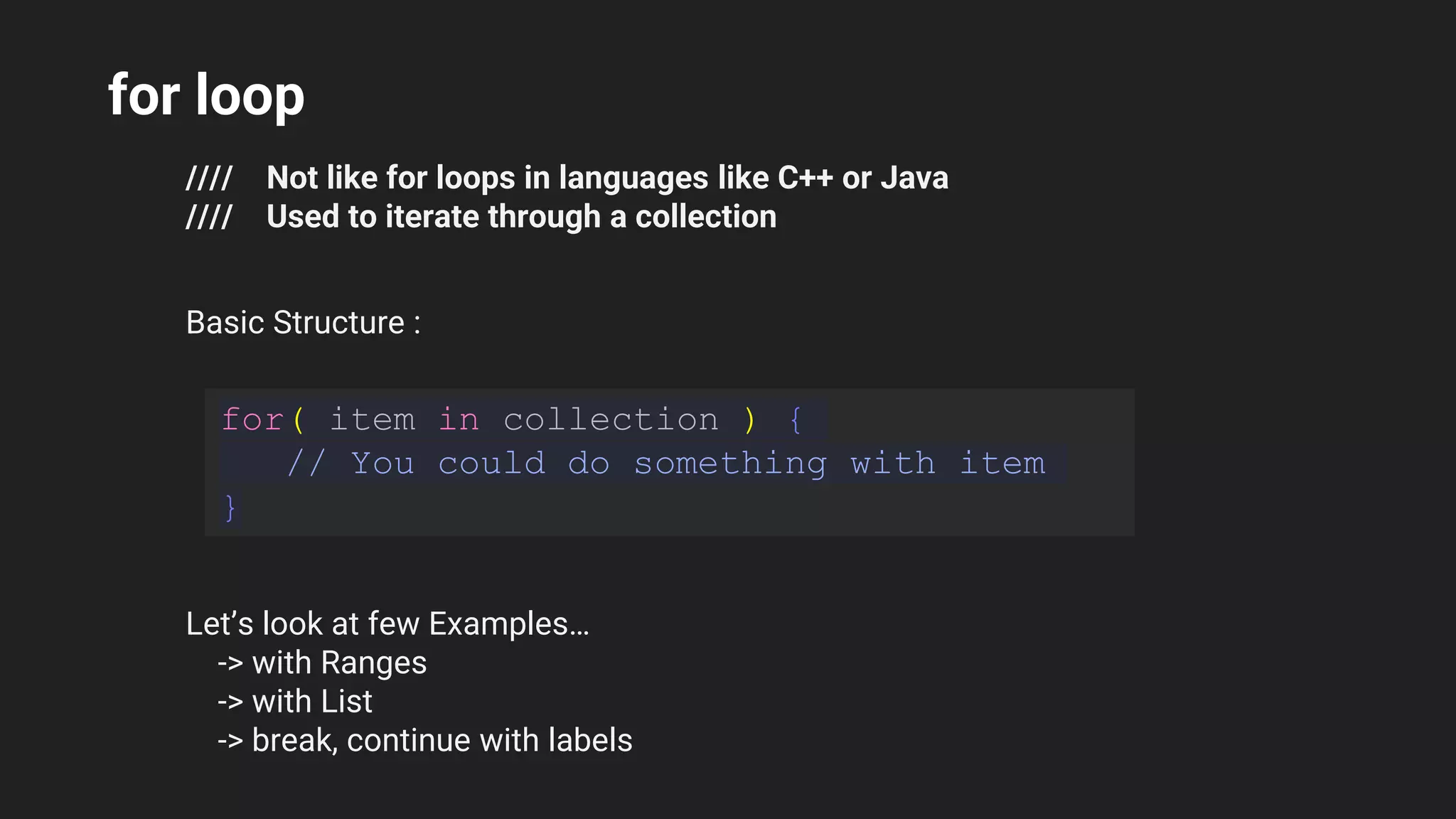
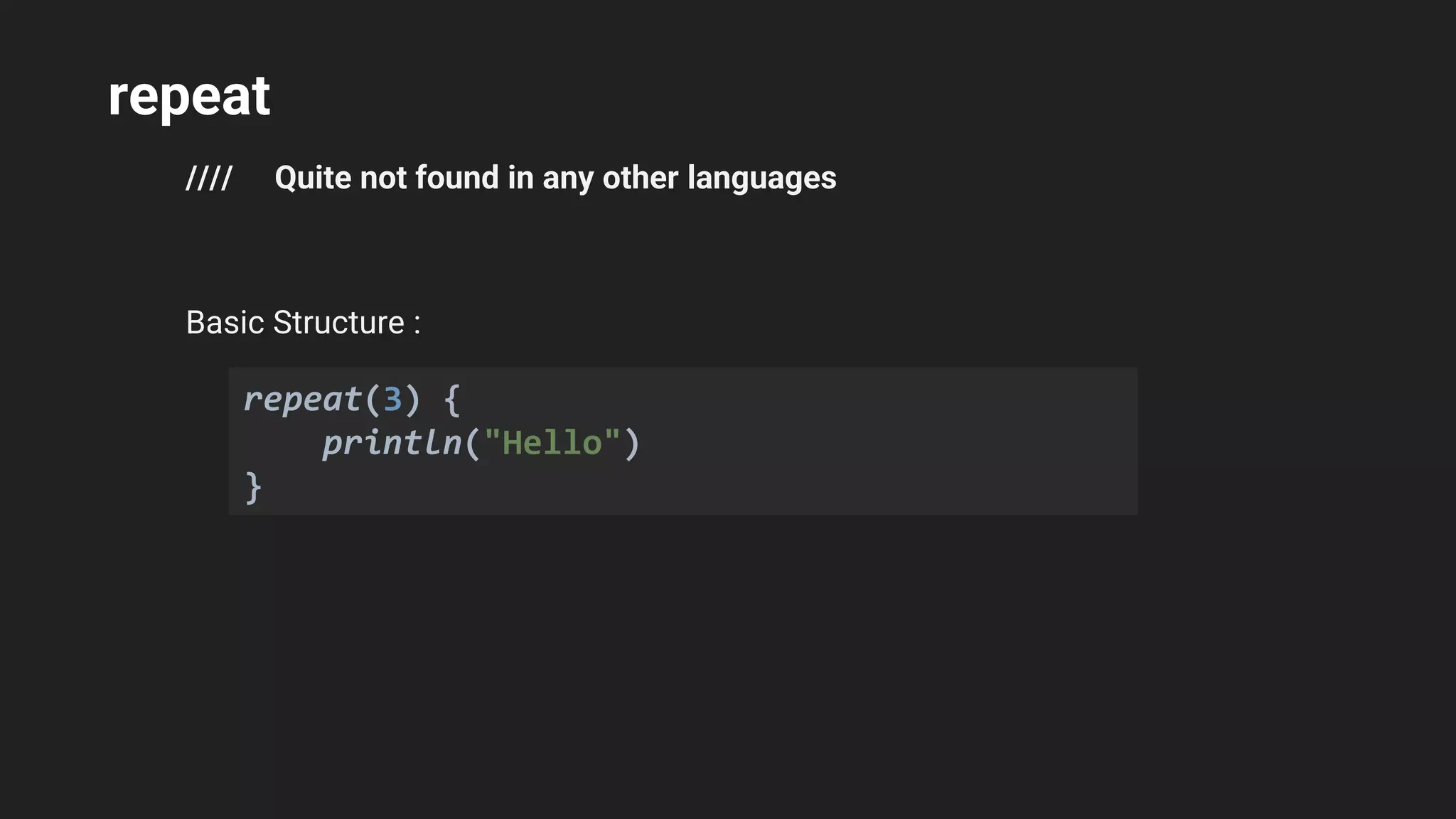
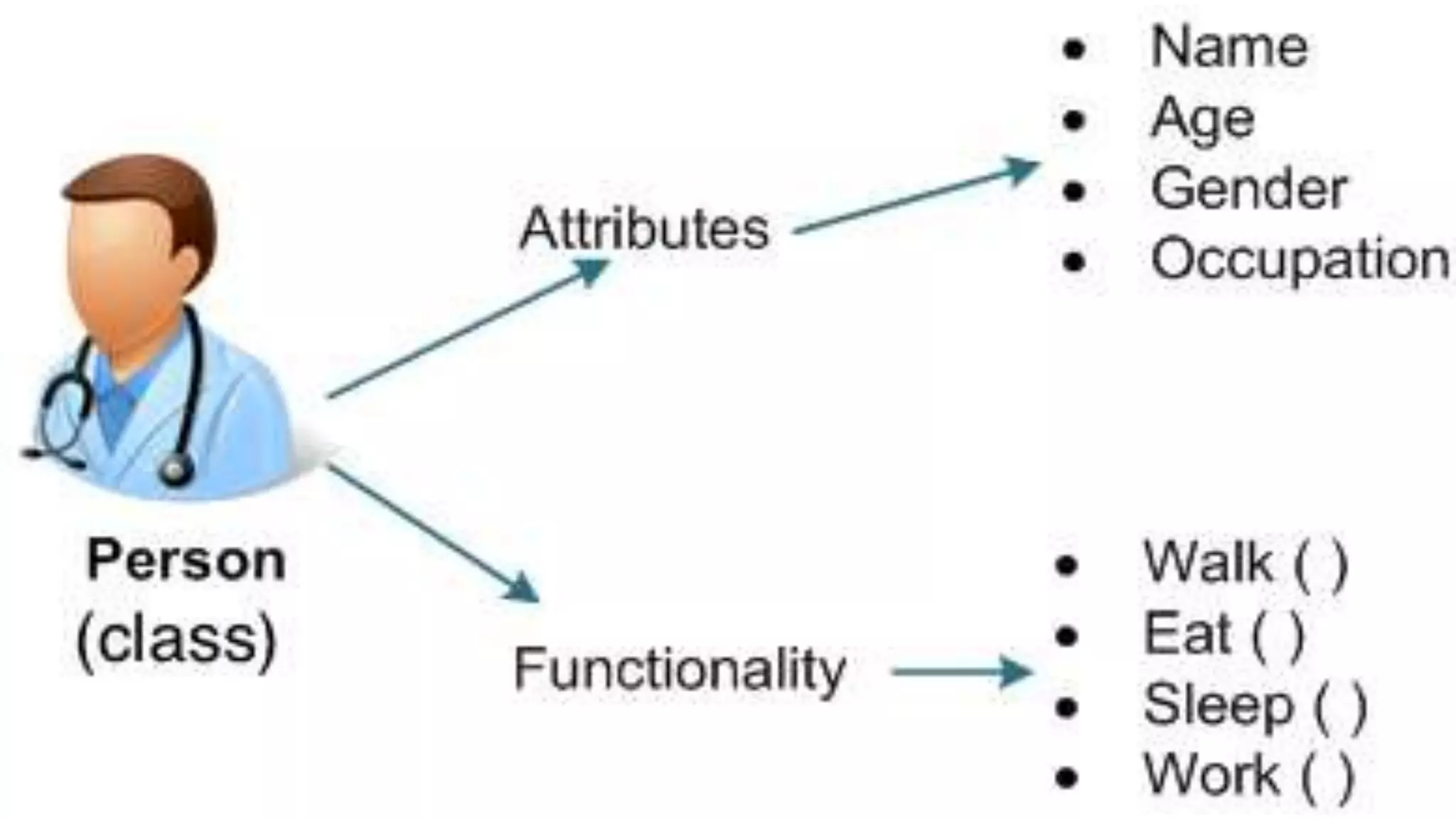
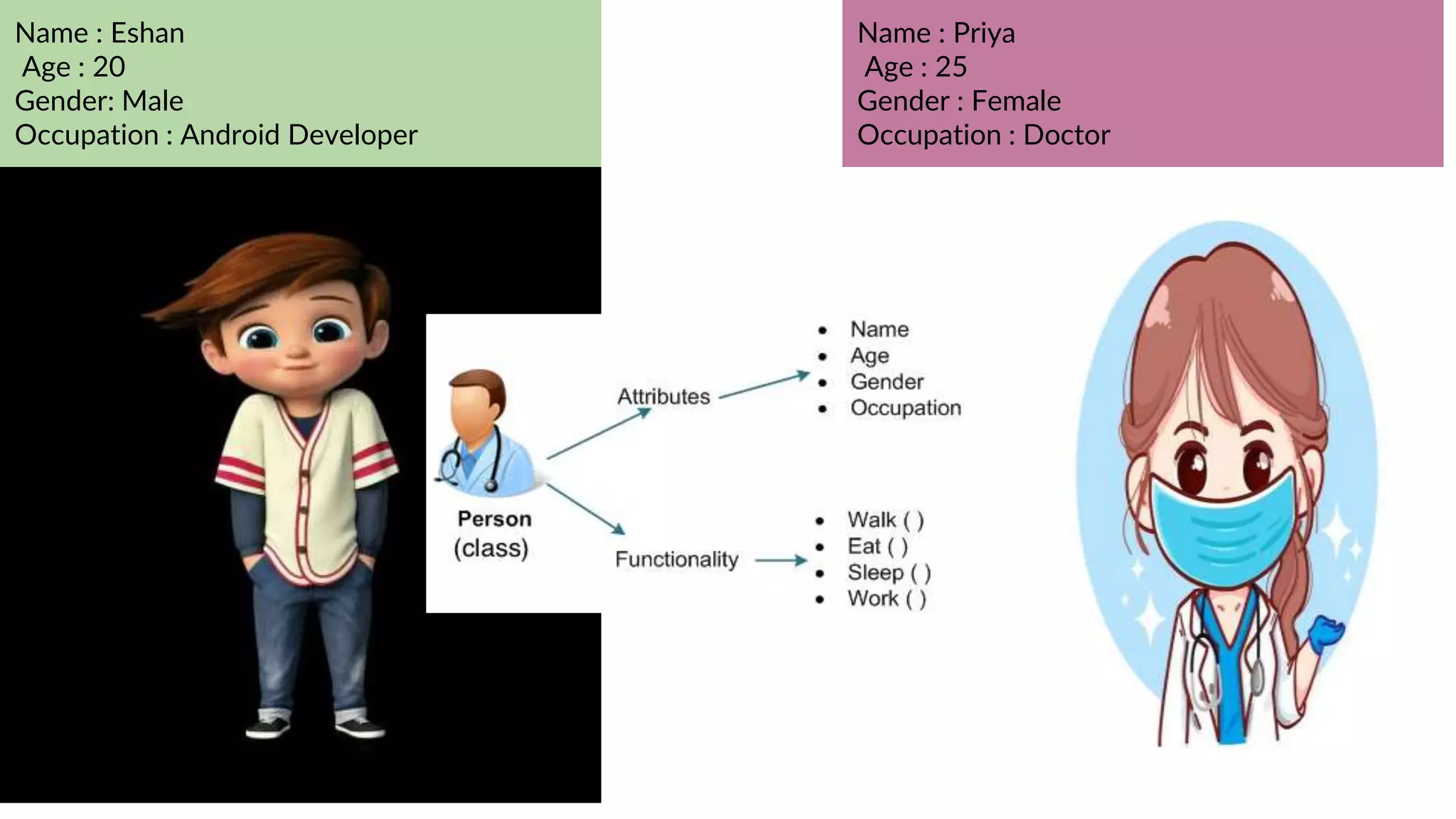
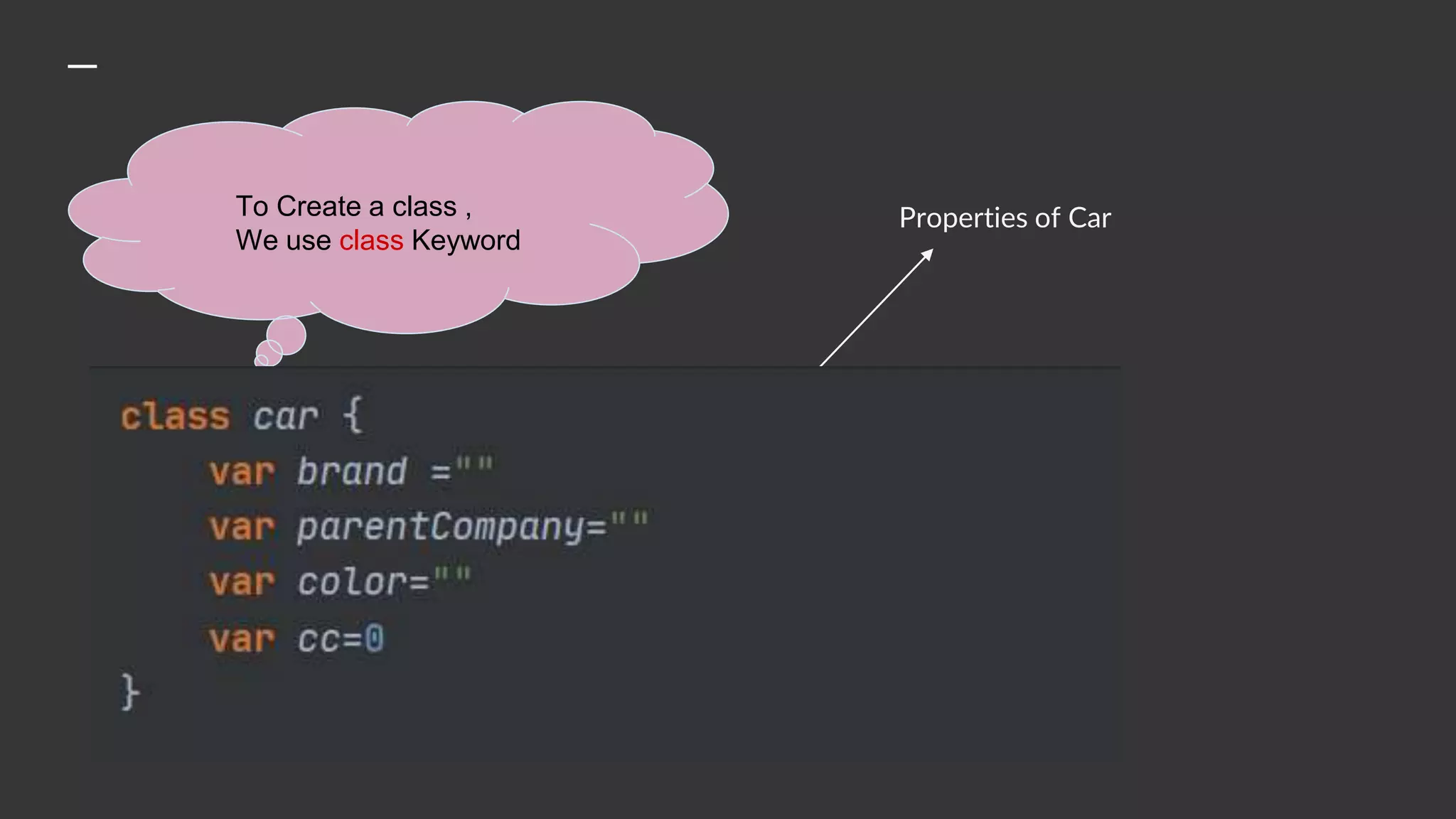
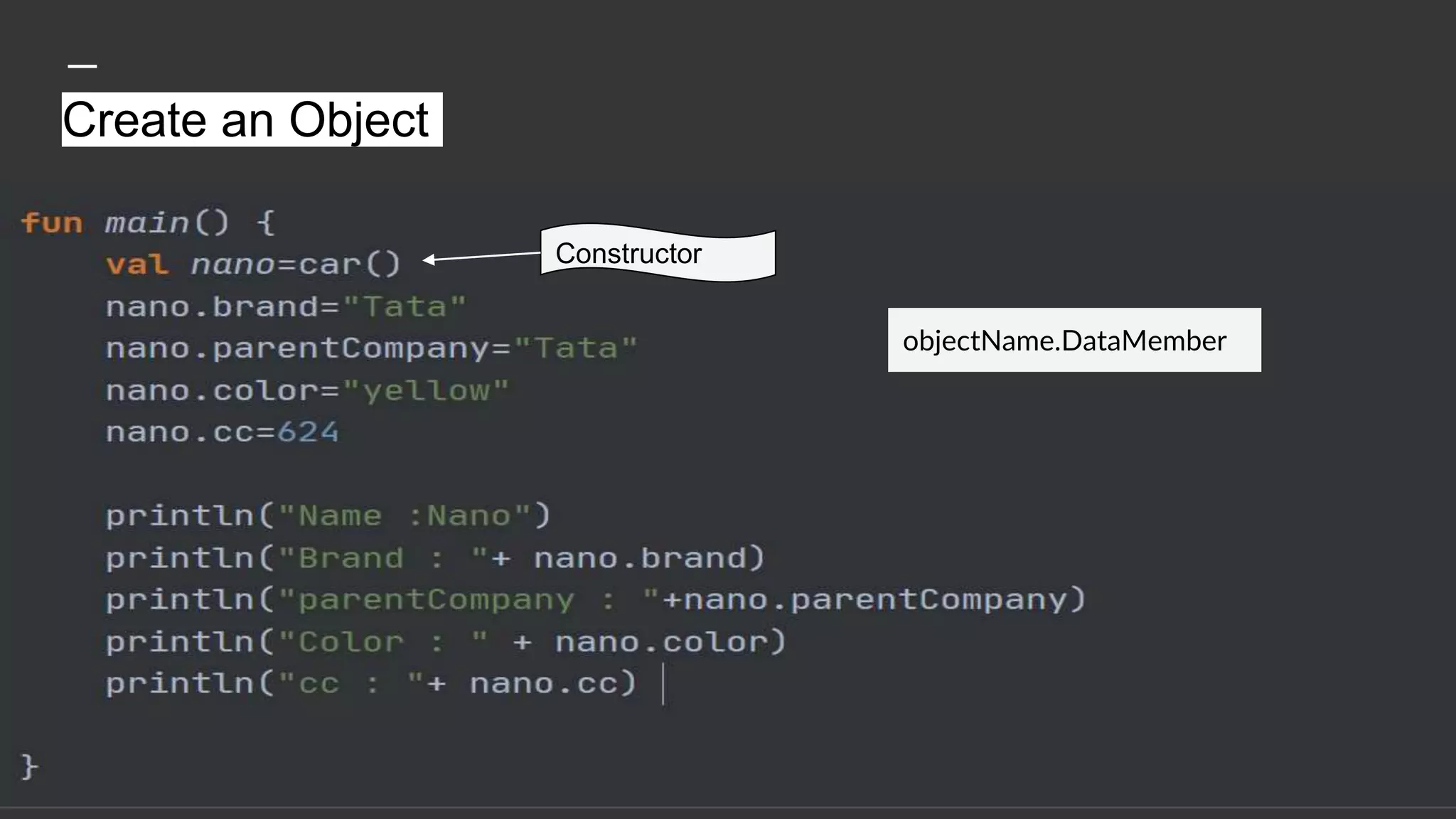
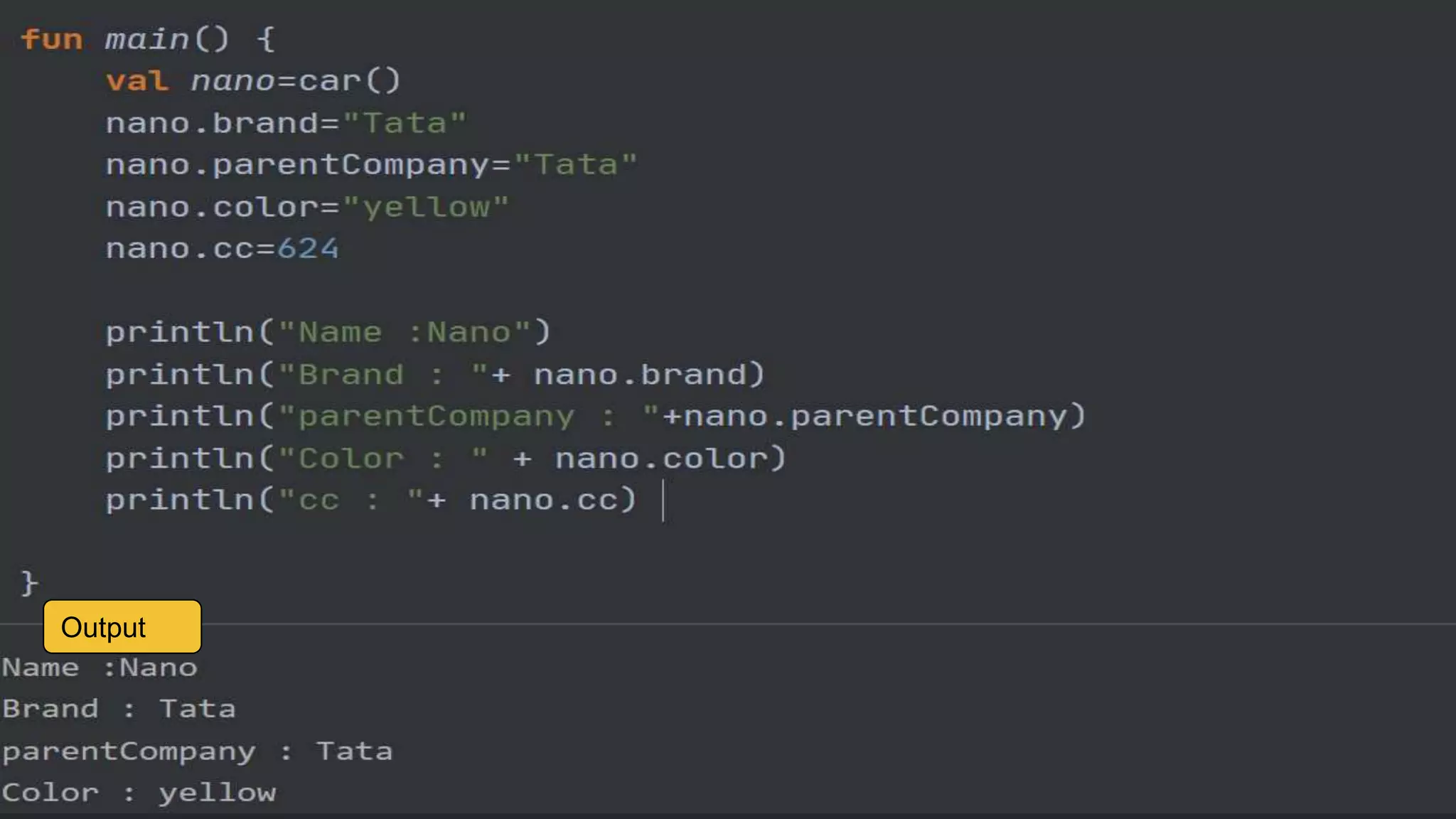
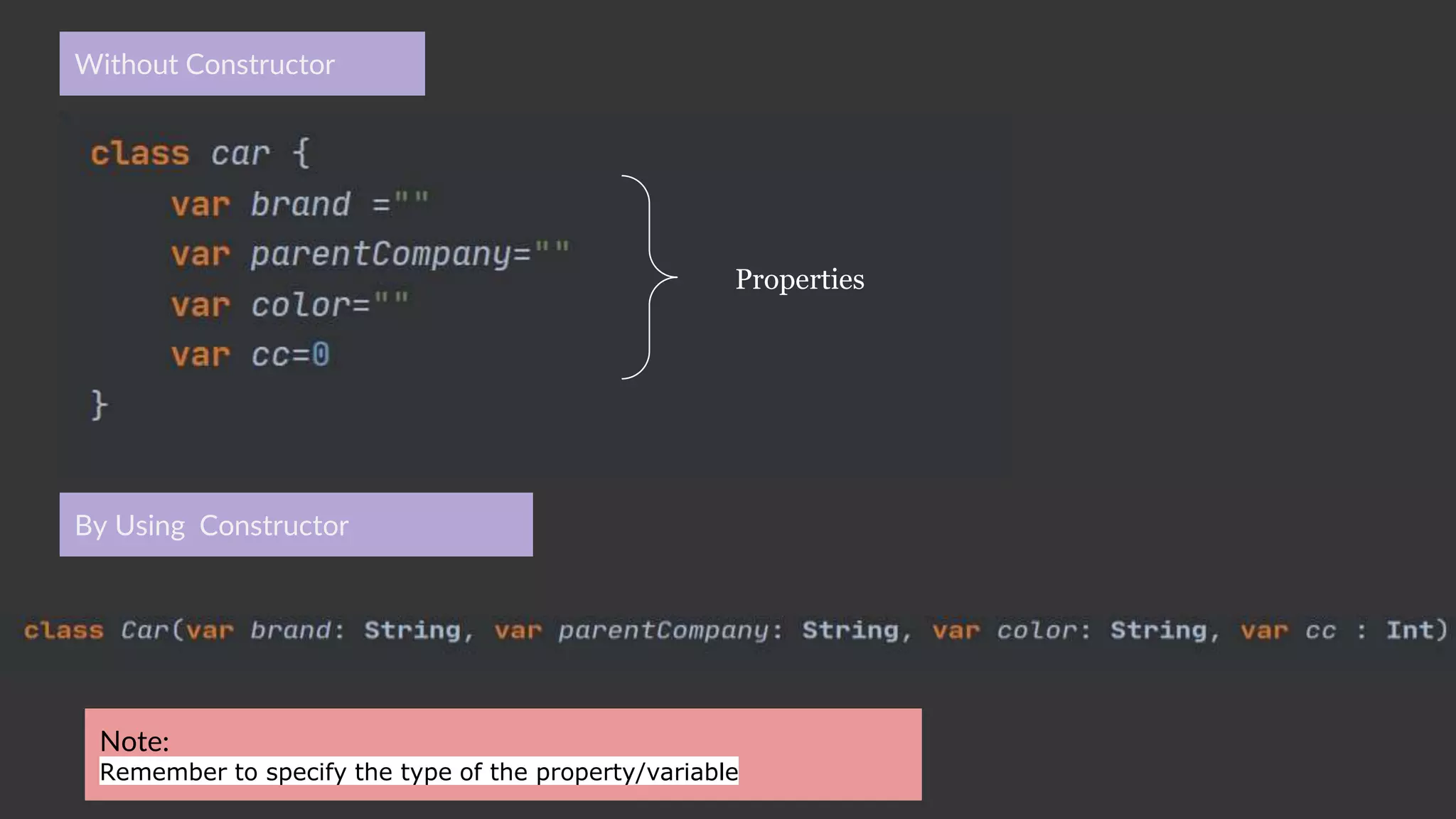
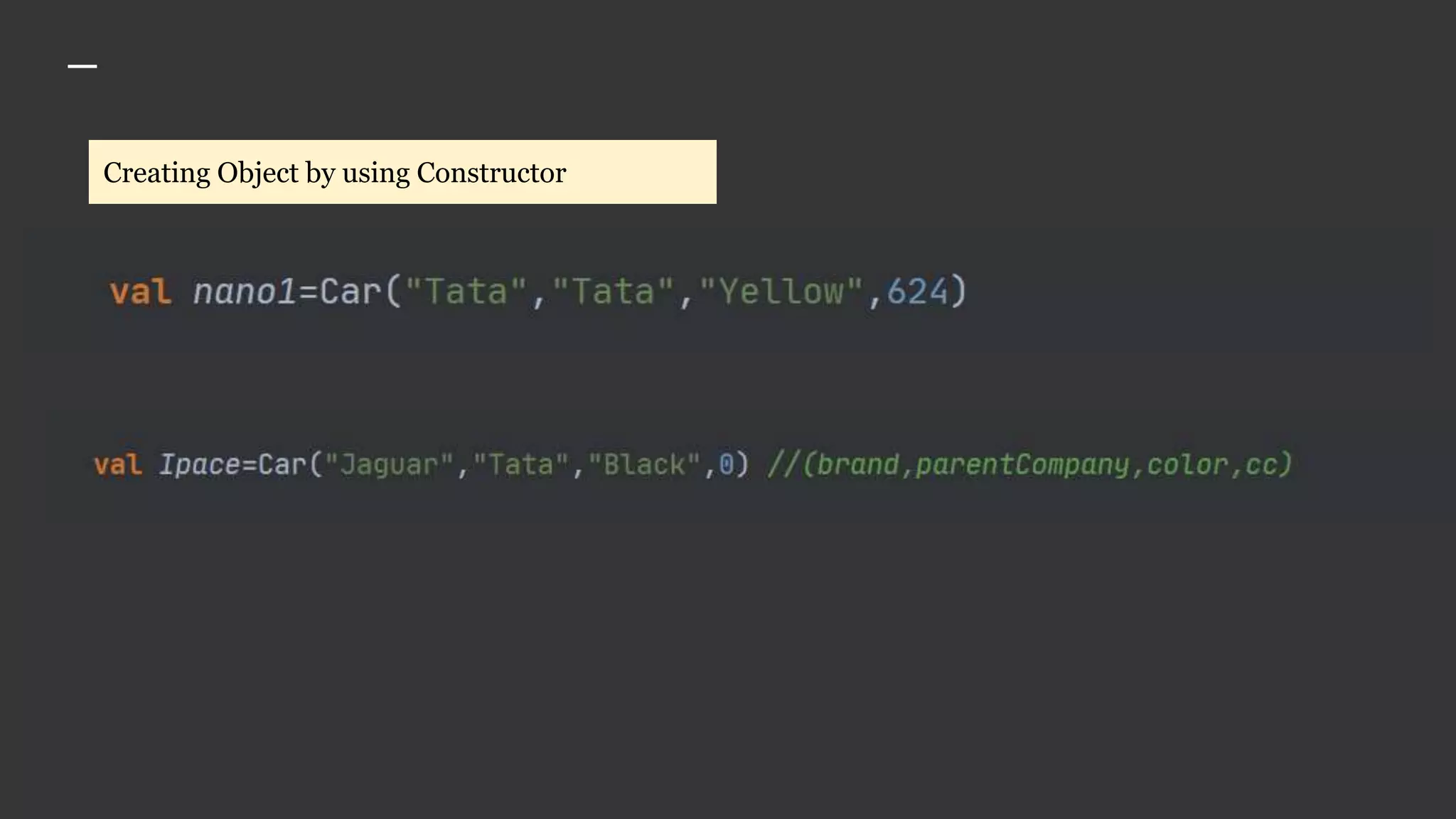
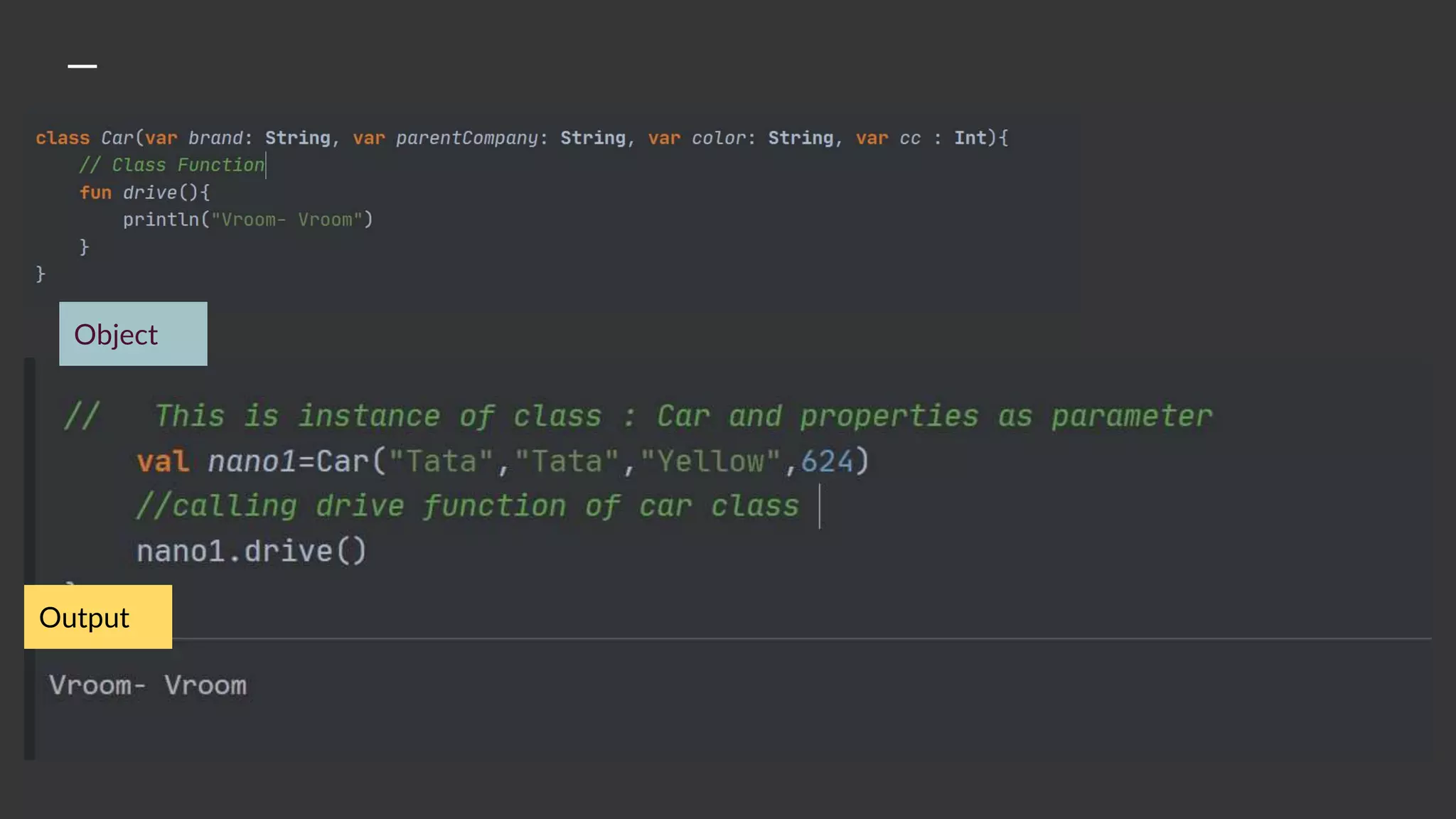
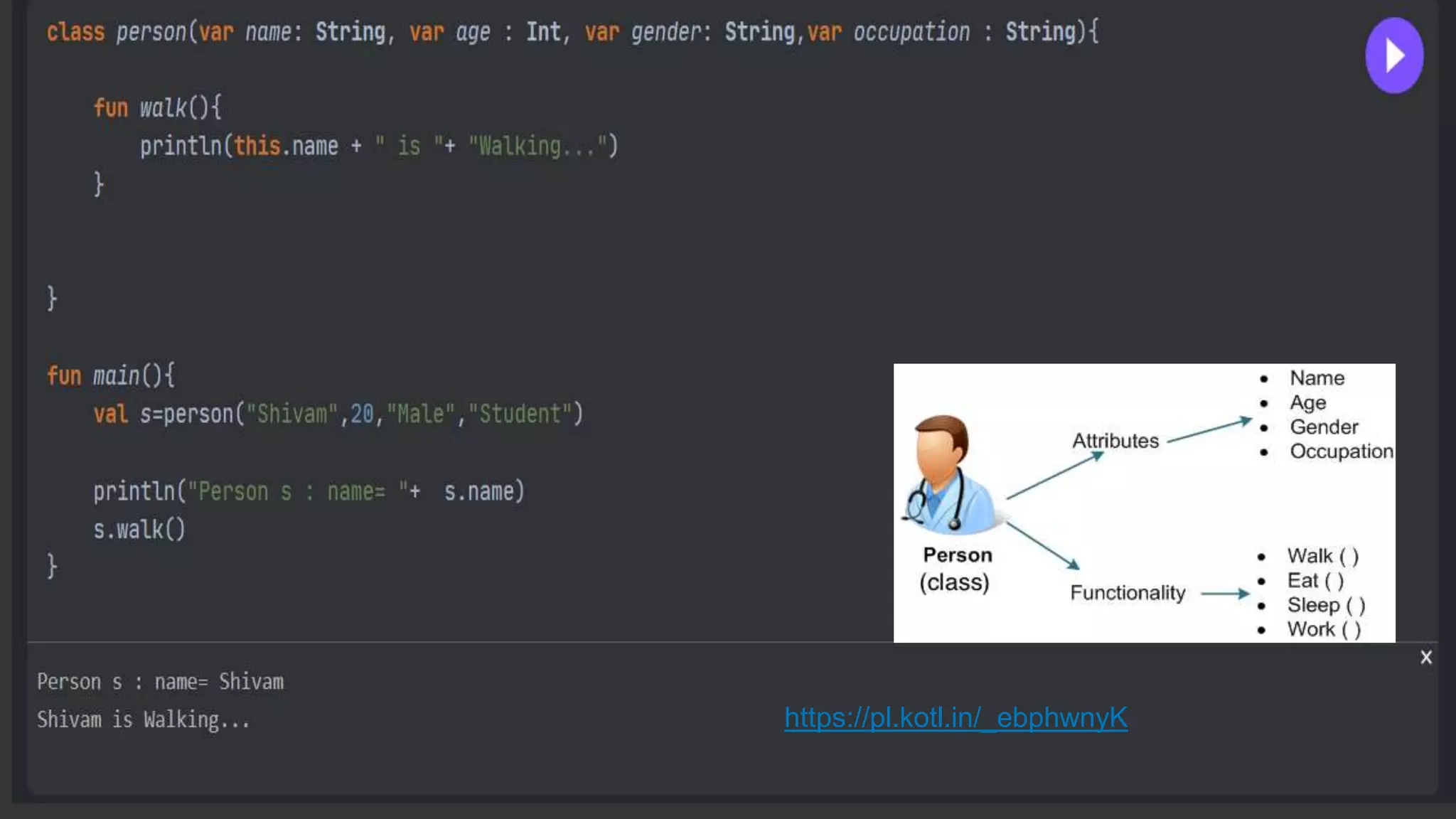
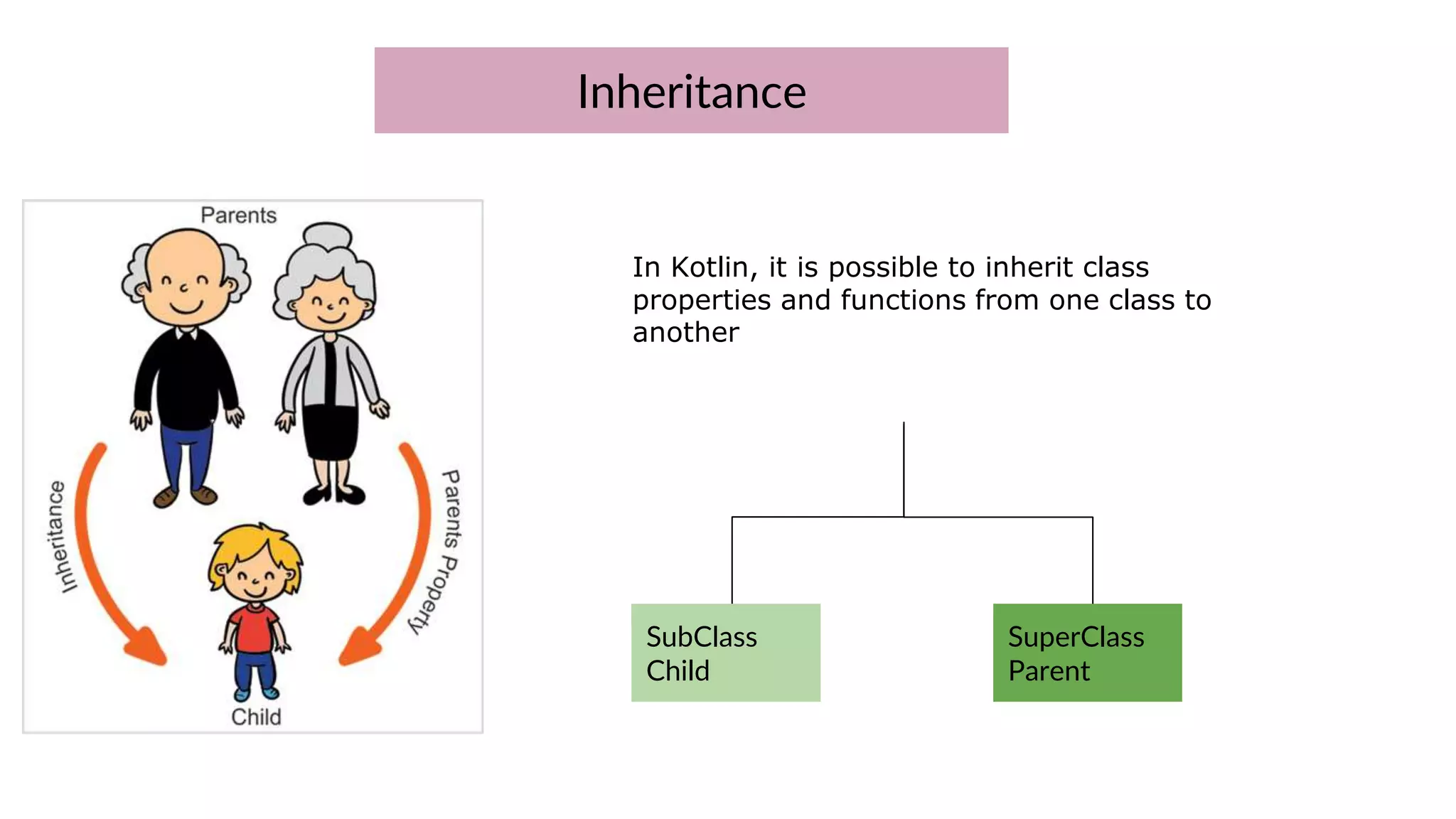
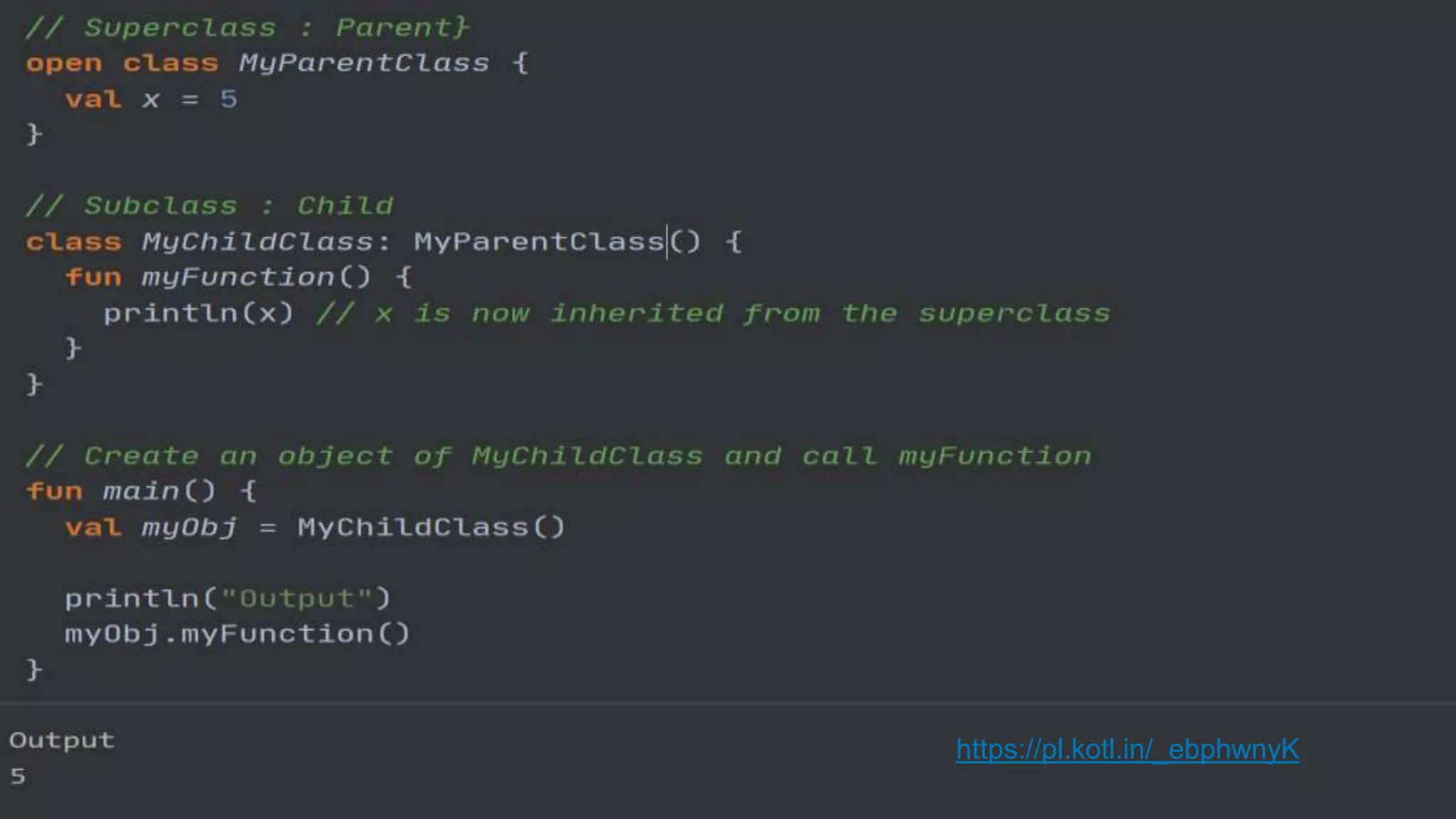
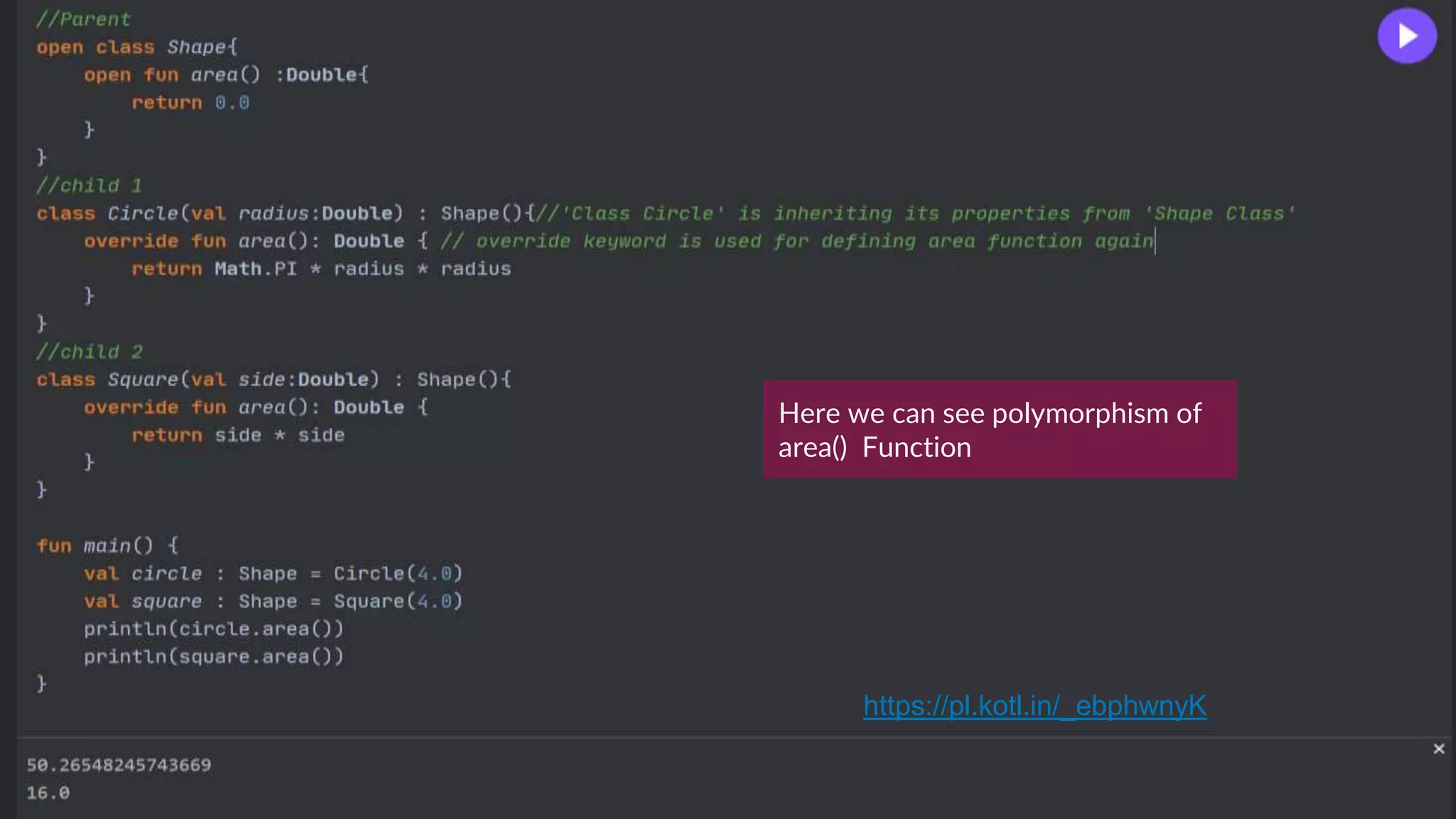
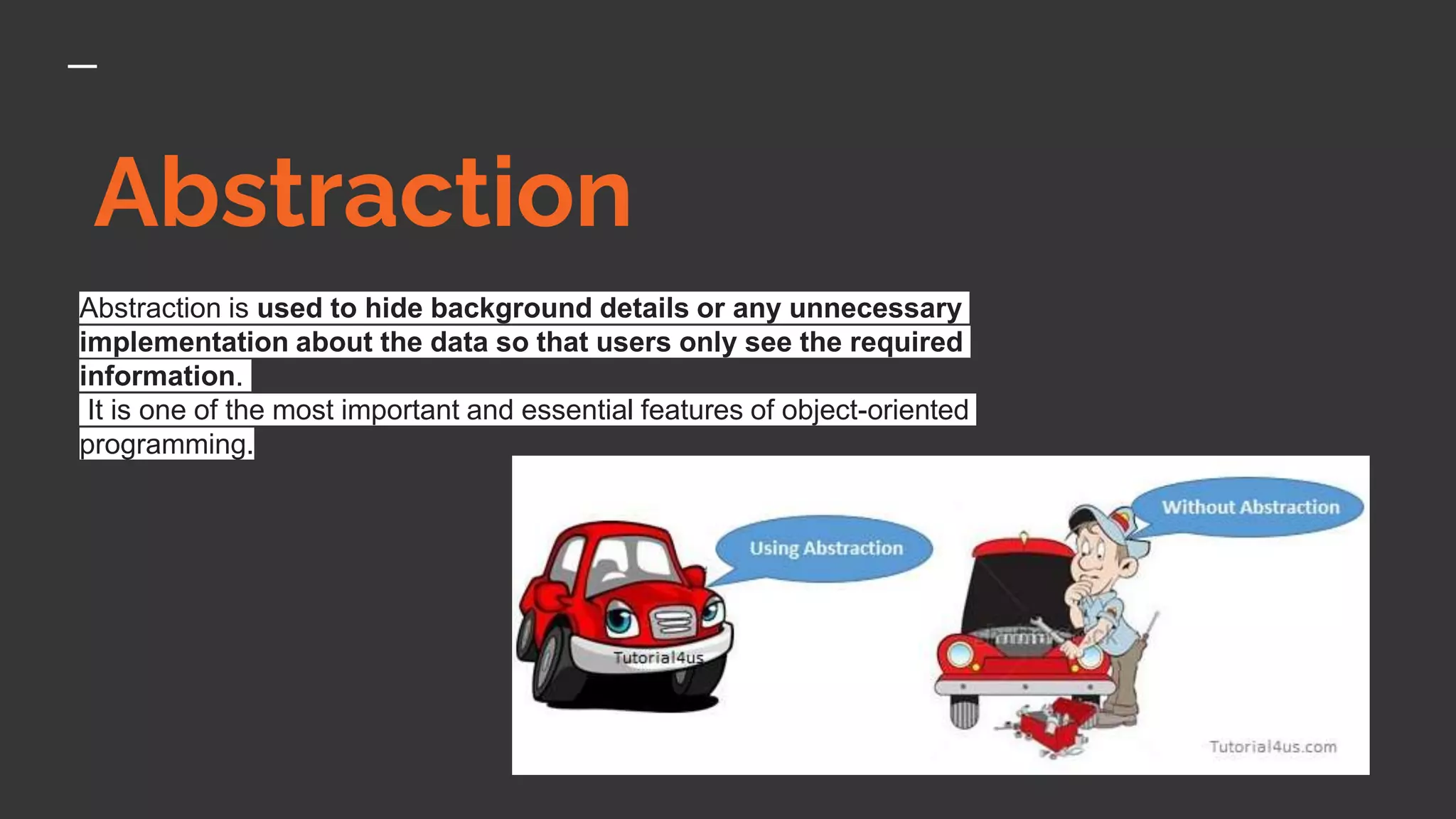
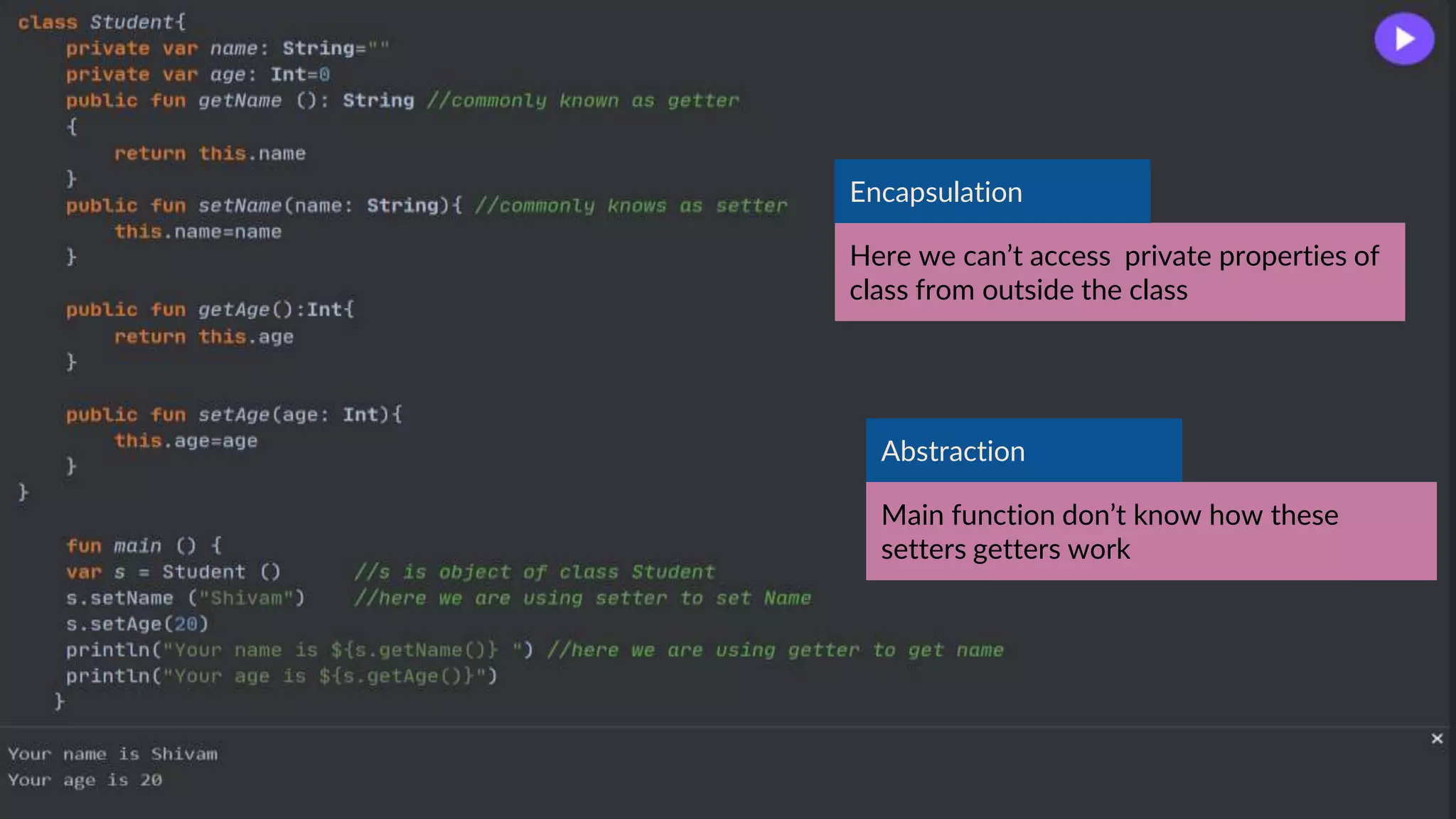
The document provides an introduction to Kotlin, covering the basic syntax for running Kotlin programs, data types, variable declaration, functions, conditionals, loops, classes, and the principles of object-oriented programming such as inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It includes examples and explanations of various coding structures and concepts like ranges, for loops, while loops, and class constructors. Additionally, it emphasizes Kotlin's unique features and offers practical coding scenarios throughout.