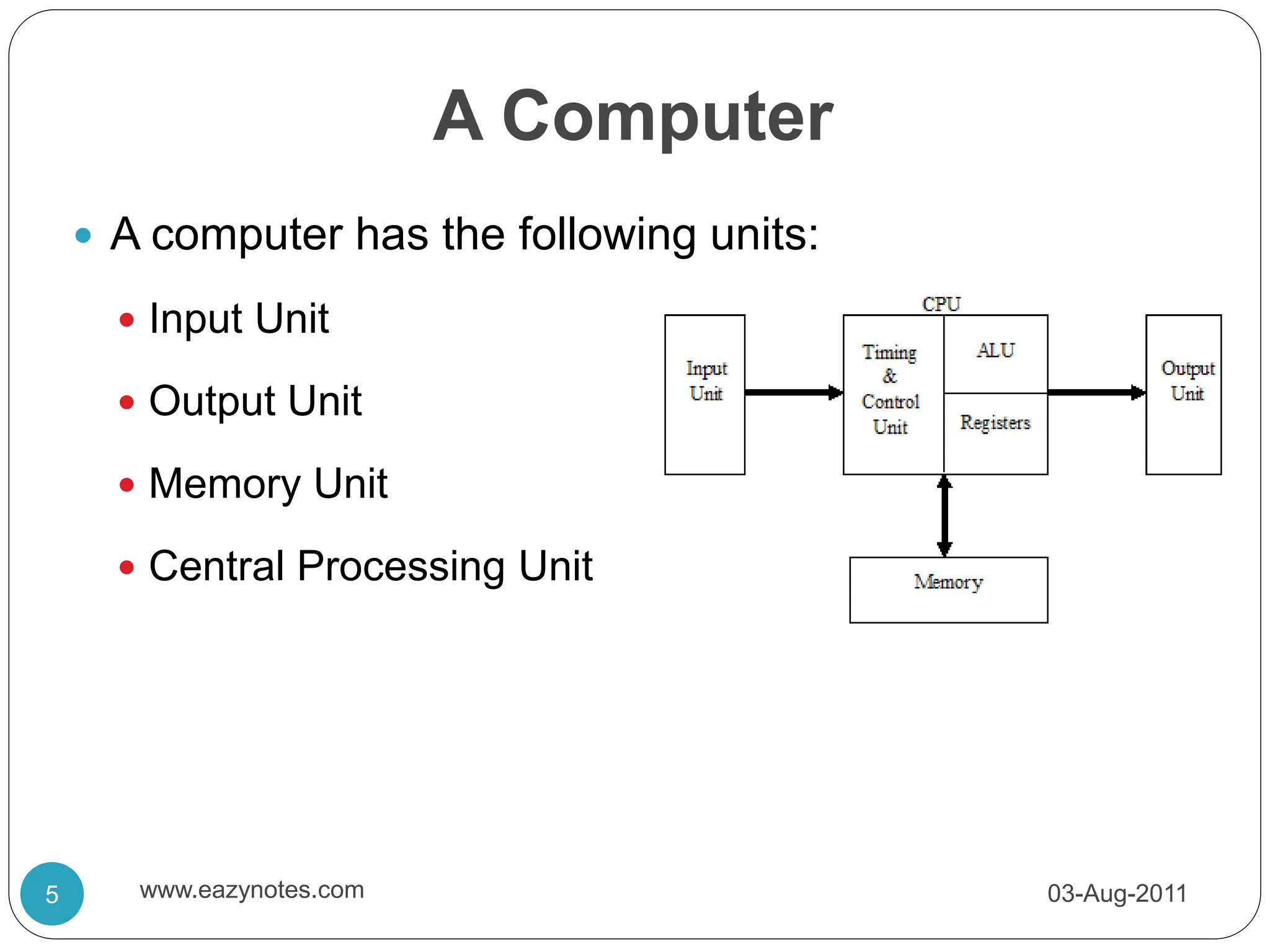
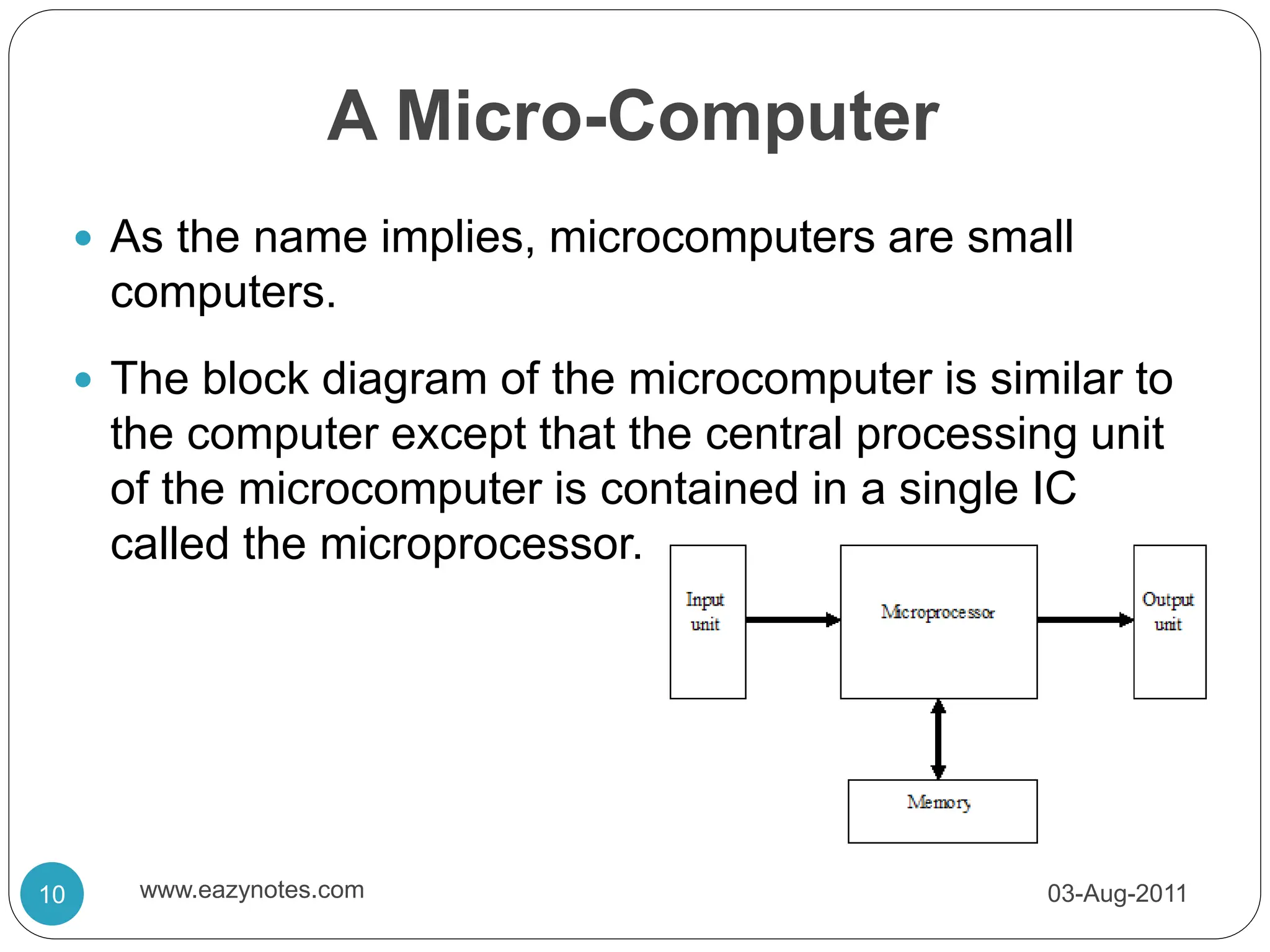
The microprocessor is a central processing unit contained on a single chip. It acts as the central component of a microcomputer. As technology has advanced, microprocessors have become faster, smaller, and able to perform more work per clock cycle. A microprocessor is fabricated on a very small chip and is capable of performing arithmetic and logic operations and communicating with external devices.