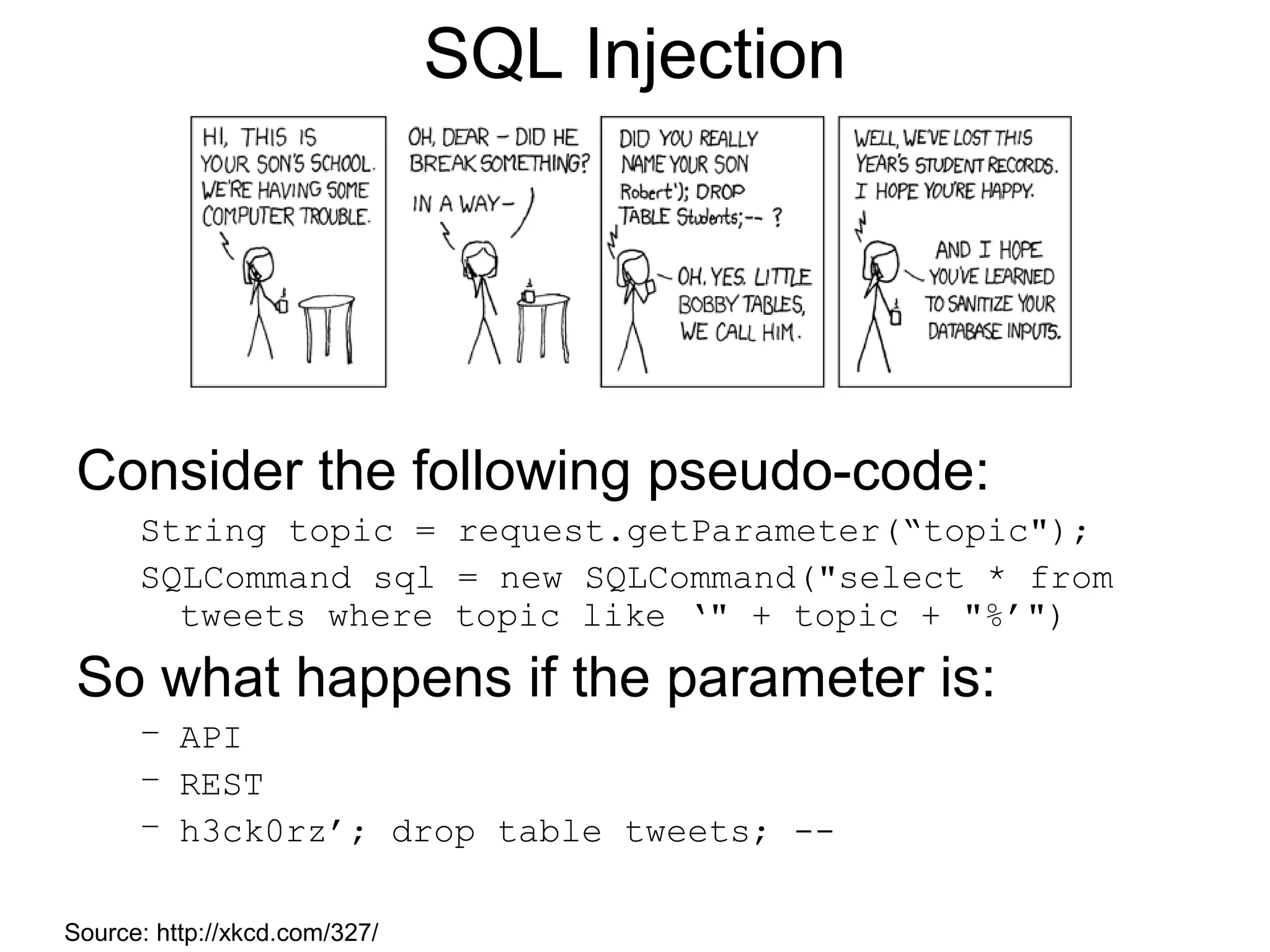
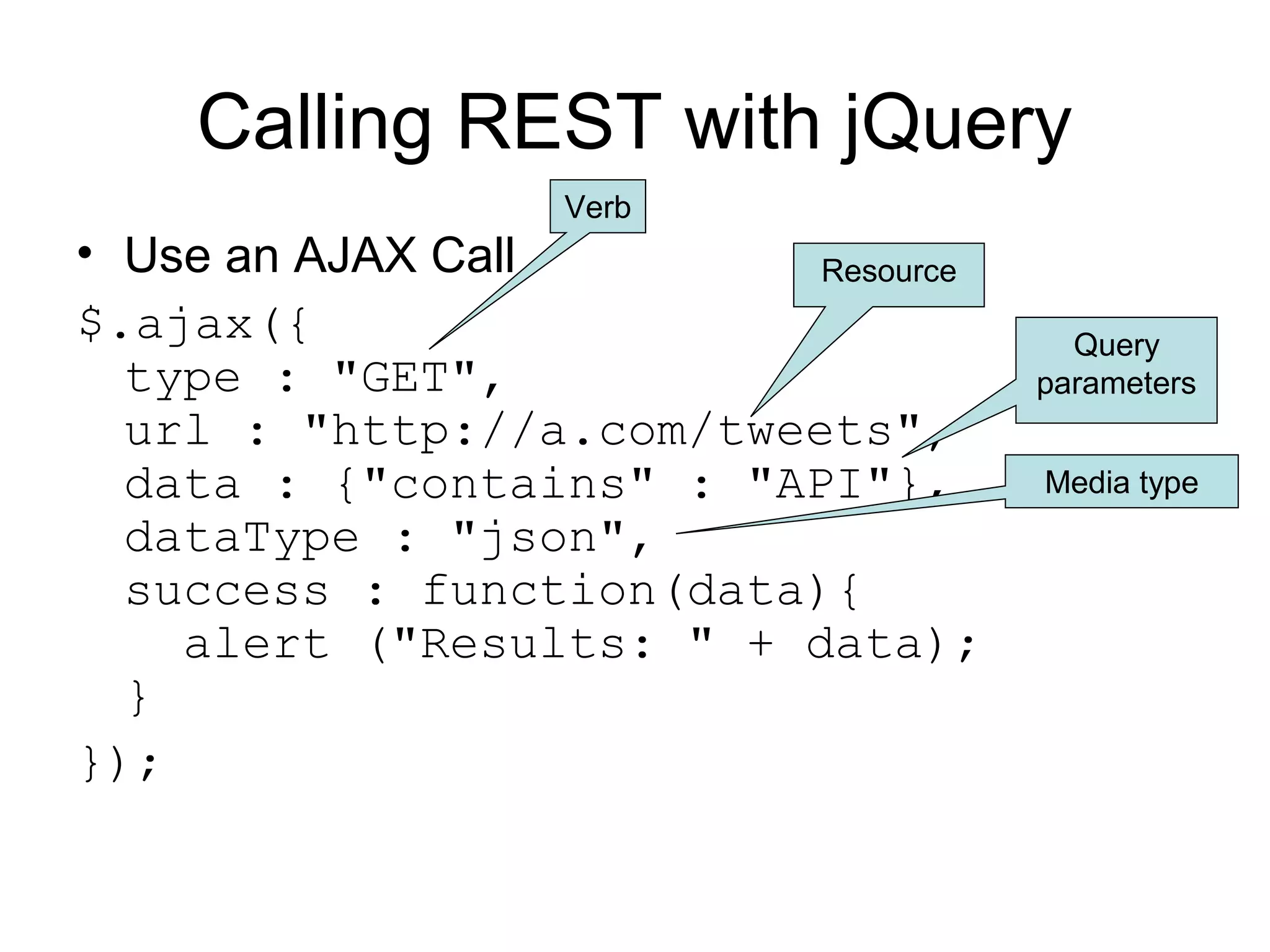
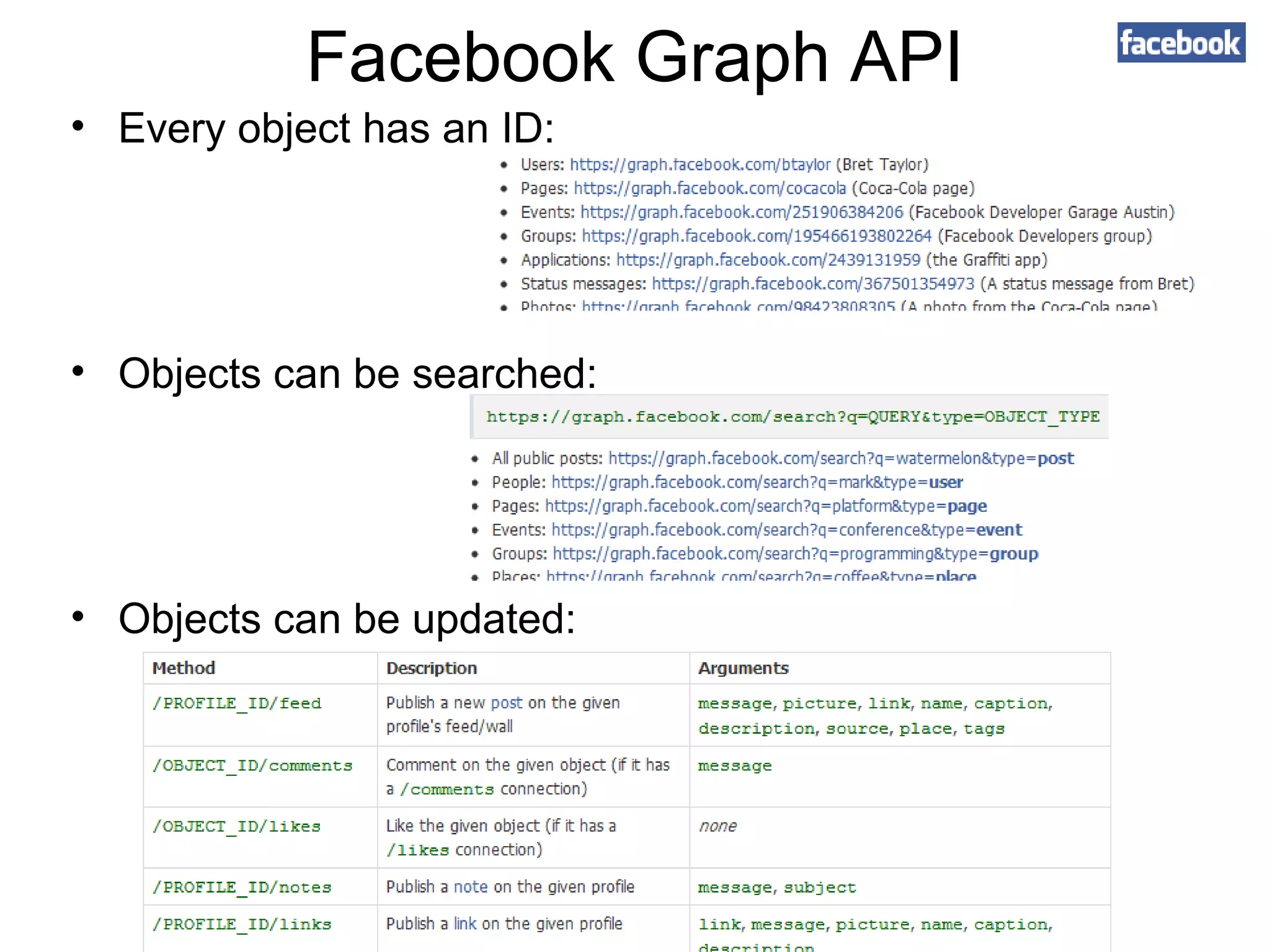
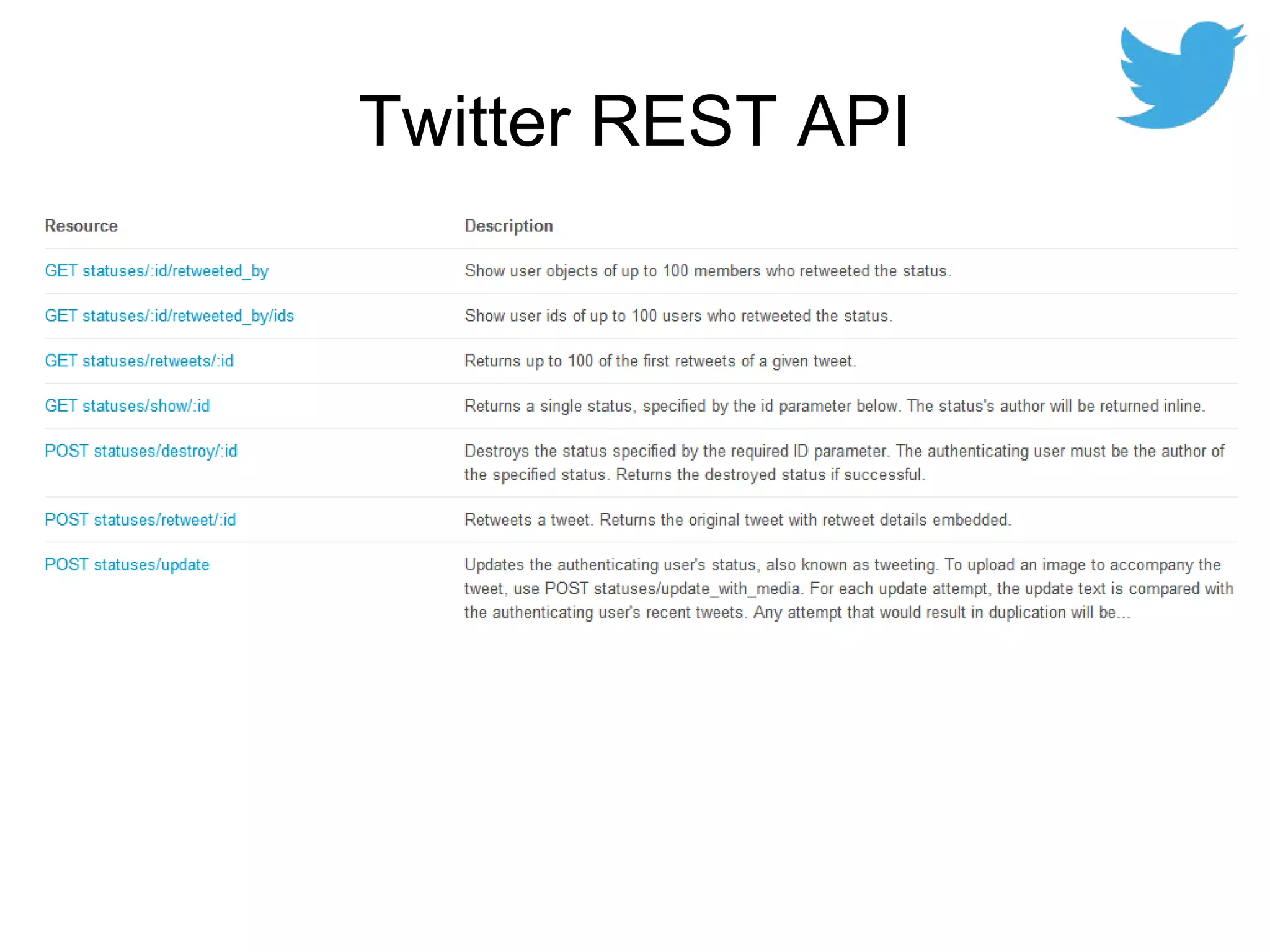
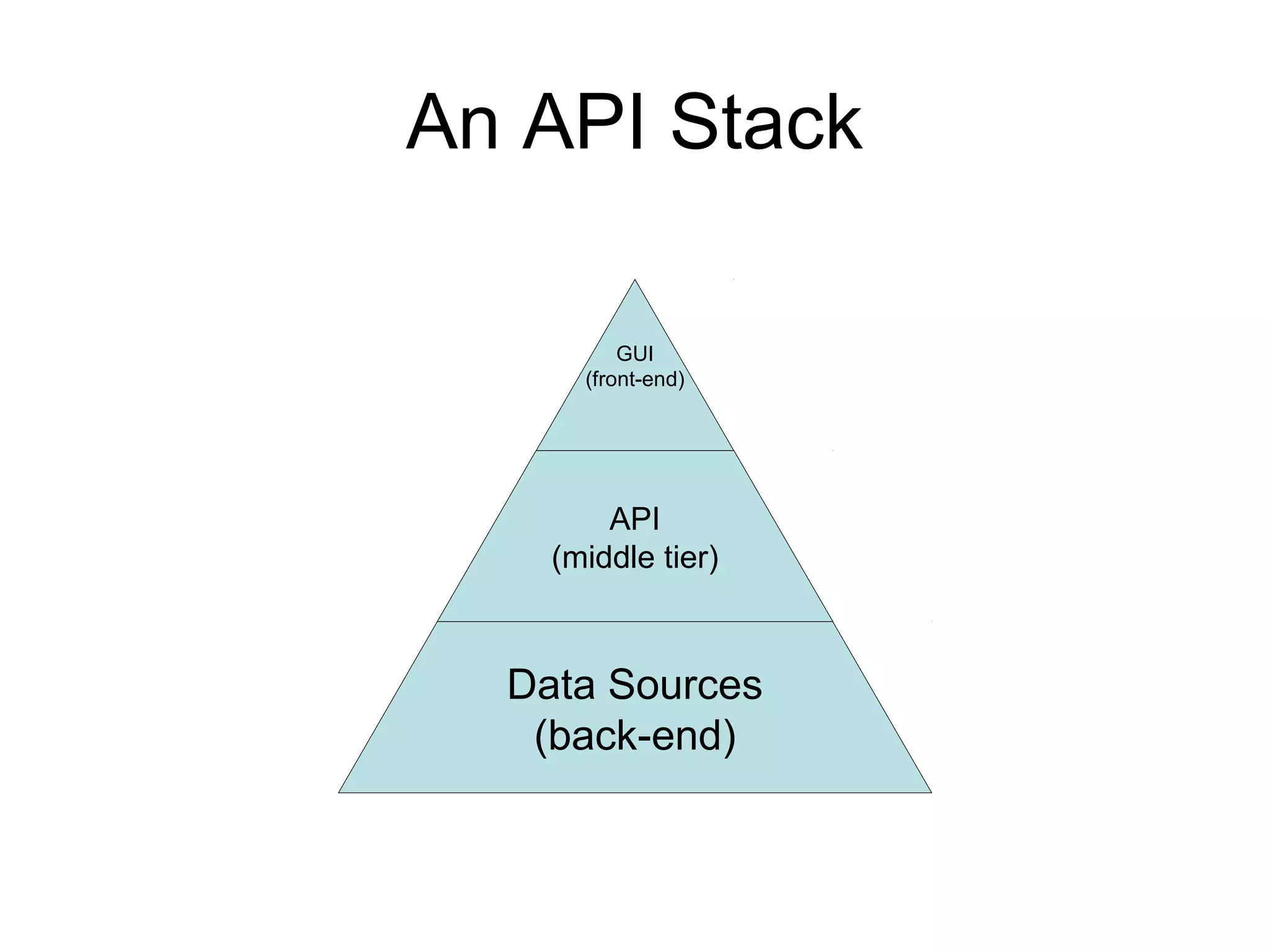
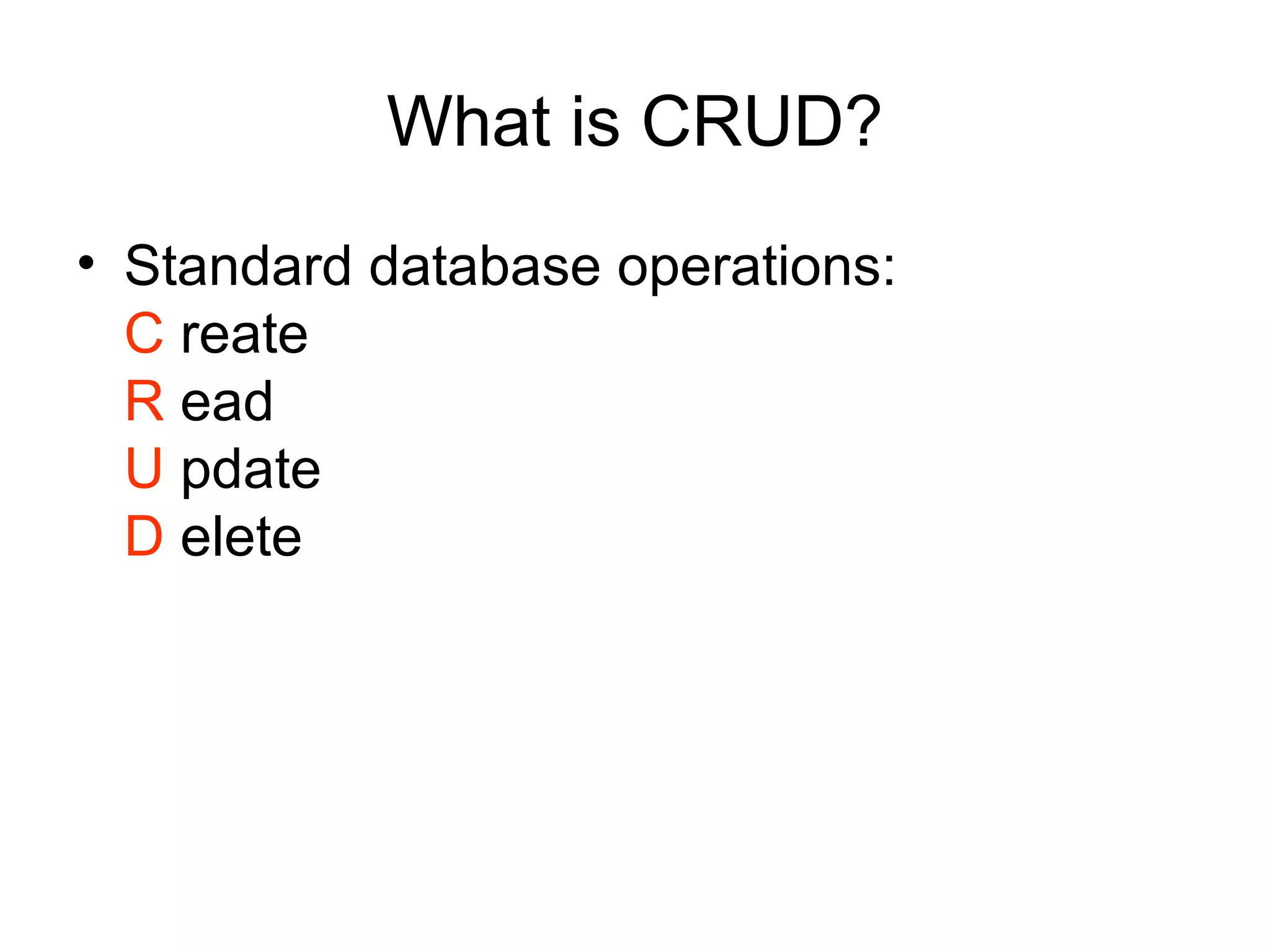
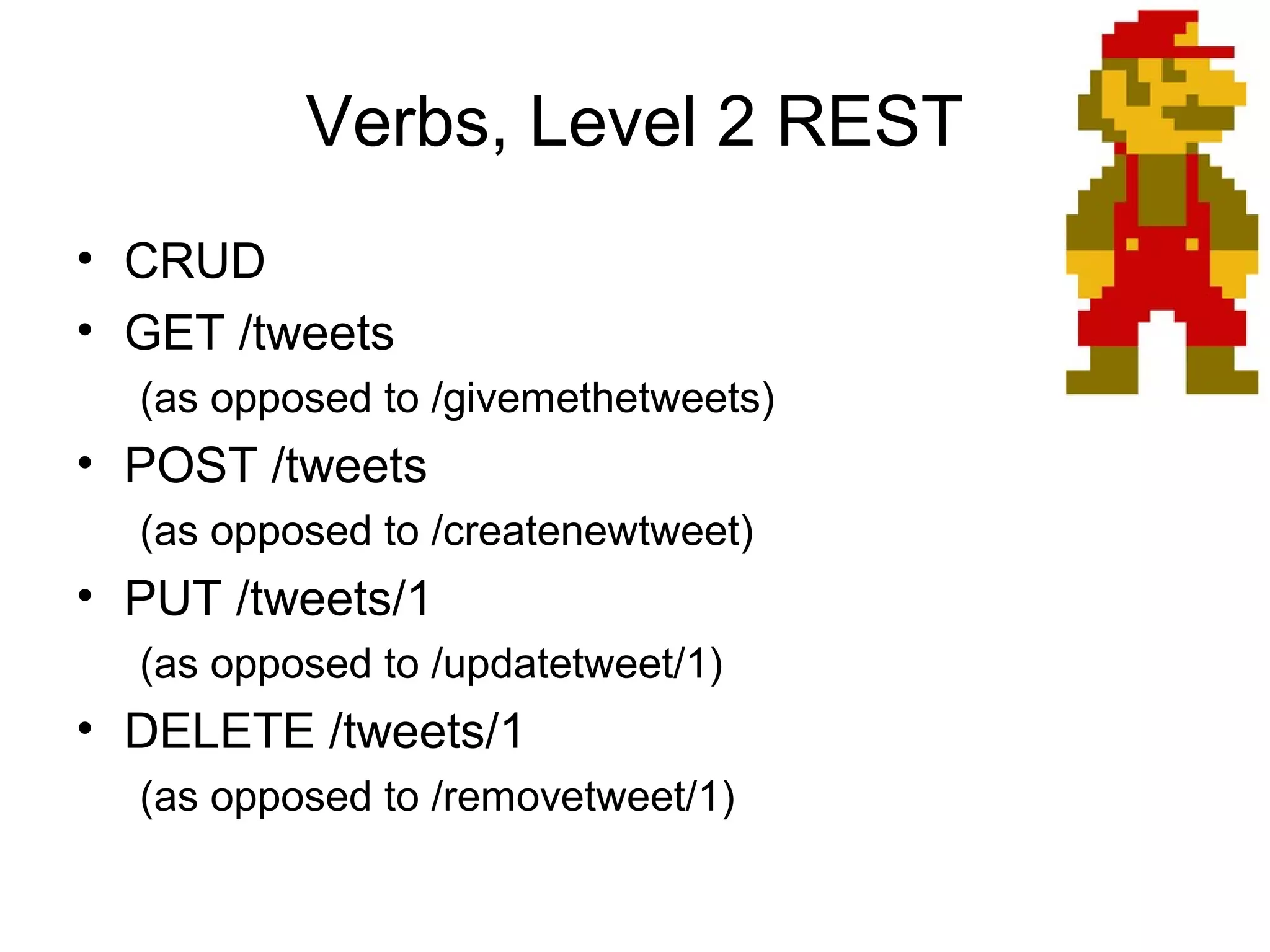
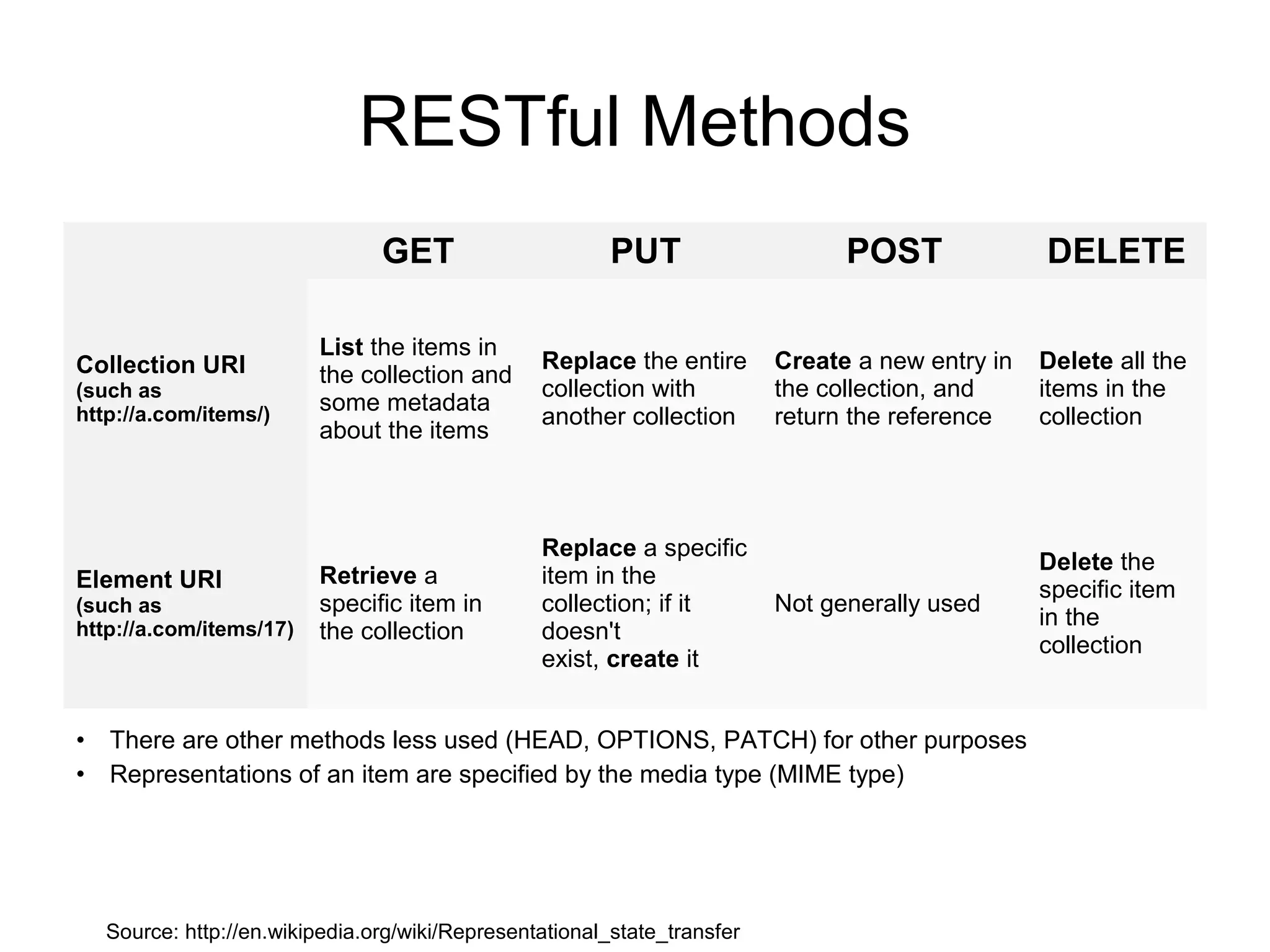
The document provides an introduction to web APIs and REST. It defines APIs as methods to access data and workflows from an application without using the application itself. It describes REST as an architectural style for APIs that uses a client-server model with stateless operations and a uniform interface. The document outlines best practices for REST APIs, including using HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT and DELETE to perform CRUD operations on resources identified by URIs. It also discusses authentication, authorization, security concerns and gives examples of popular REST APIs from Facebook, Twitter and other services.














![HATEOAS, Level 3 REST
• Hypermedia as the engine of
application state
"ids" : [
12345678,
87654321,
11223344
]
"links": [
{
"rel": "UserInfo",
"href": "https://.../user/12345678"
},
{
"rel": "Tweets",
"href": "https://.../tweet/87654321"
},
{
"rel": "Messages",
"href": "https://.../msgs/11223344"
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontothewebapiweb-140222034402-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-the-Web-API-22-2048.jpg)
![Data Formats (XML and JSON)
XML (135 characters):
<tweets>
<tweet type="text" id="1">
<text>REST is great!</text>
</tweet>
<tweet type="text" id="2">
<text>APIs forever!</text>
</tweet>
</tweets>
JSON (109 characters):
{
"tweets": [
{"type": "text", "id": "1",
"text": "REST is great!"},
{"type": "text", "id": "2",
"text": "APIs forever!"}
]
}
XML can be validated (XML Schema), stylized (XSL), traversed
(XPath), queried (XQuery), transformed (XSLT), and
namespaced
JSON is easier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontothewebapiweb-140222034402-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-the-Web-API-23-2048.jpg)