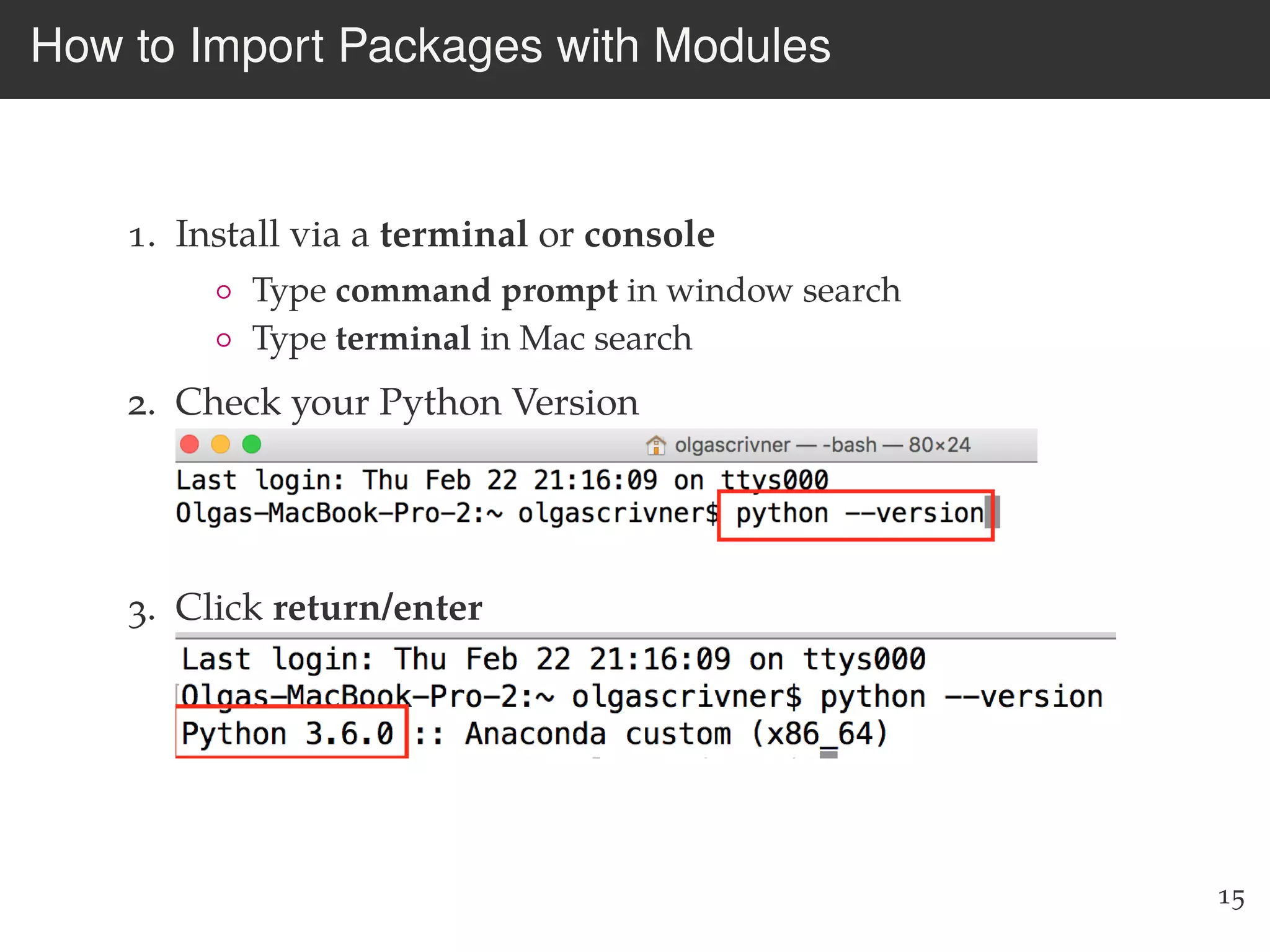
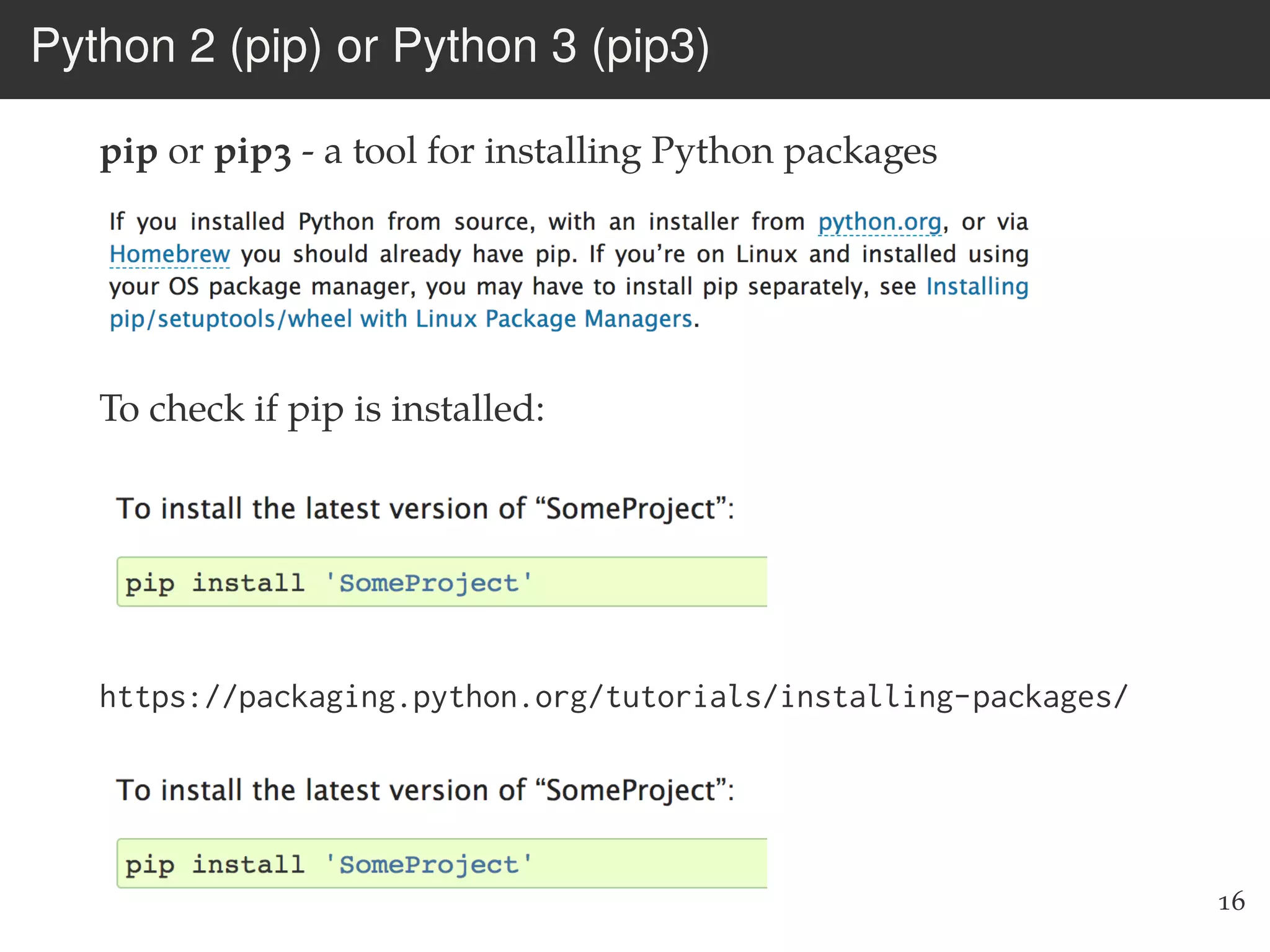
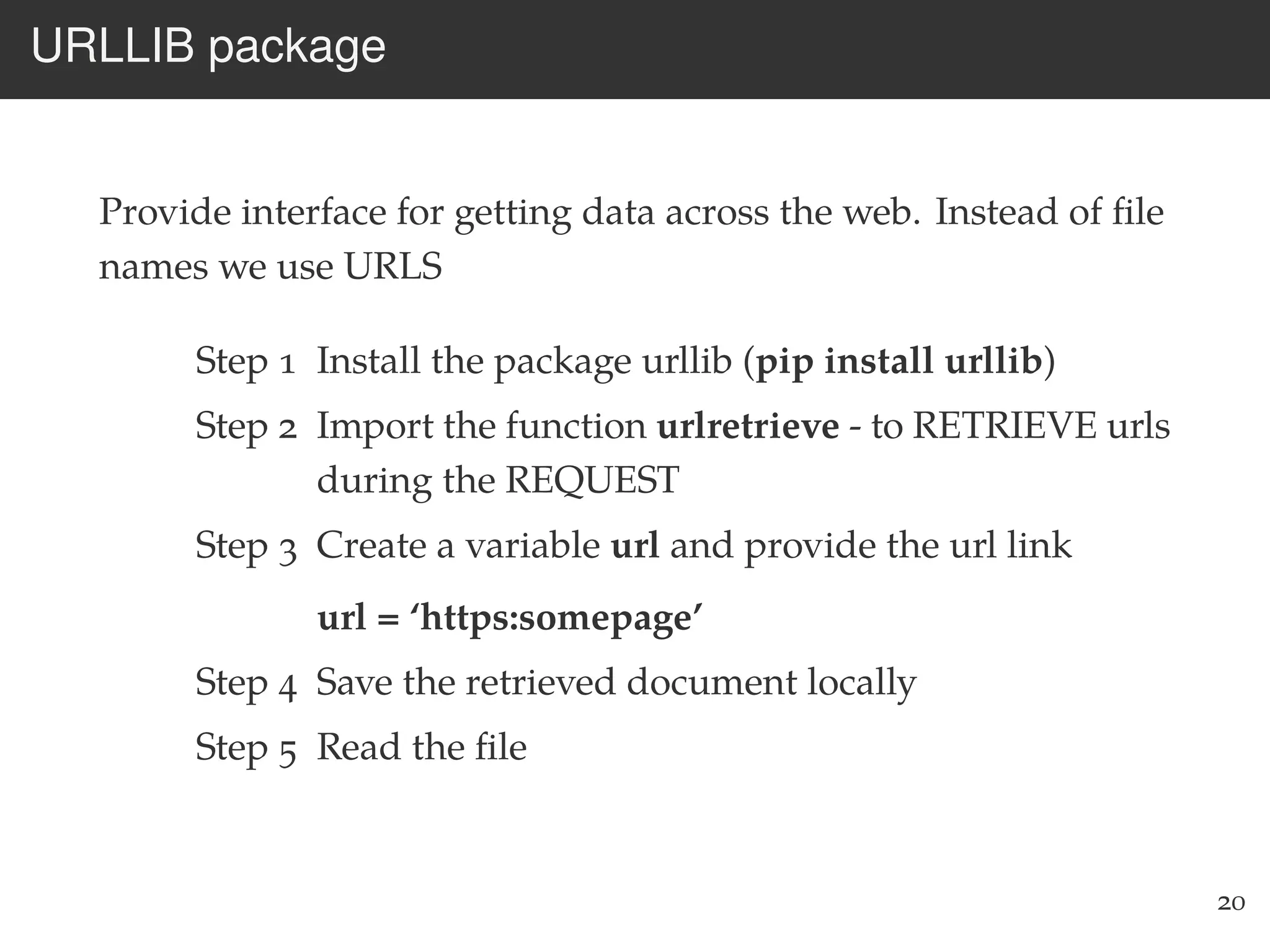
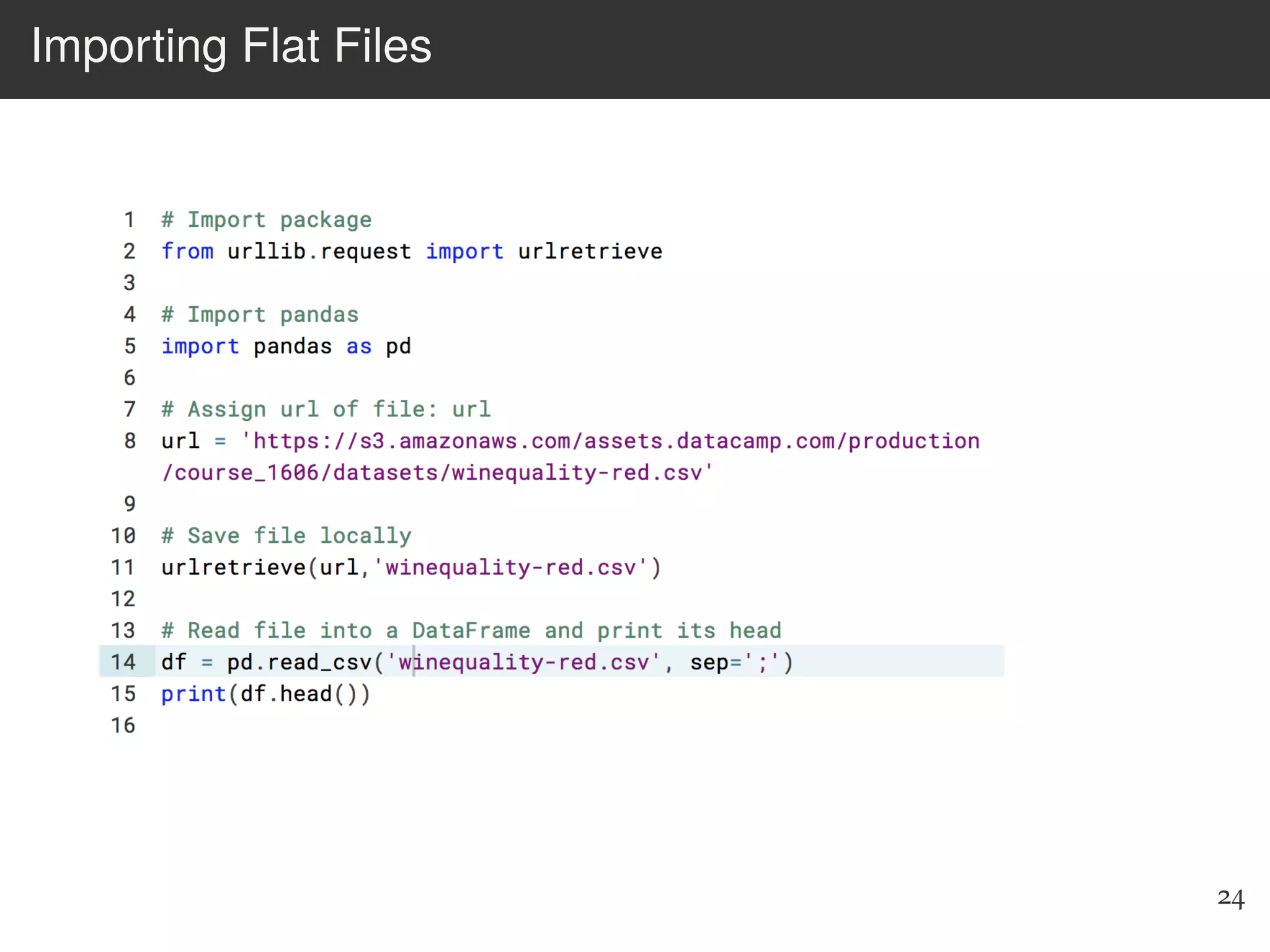
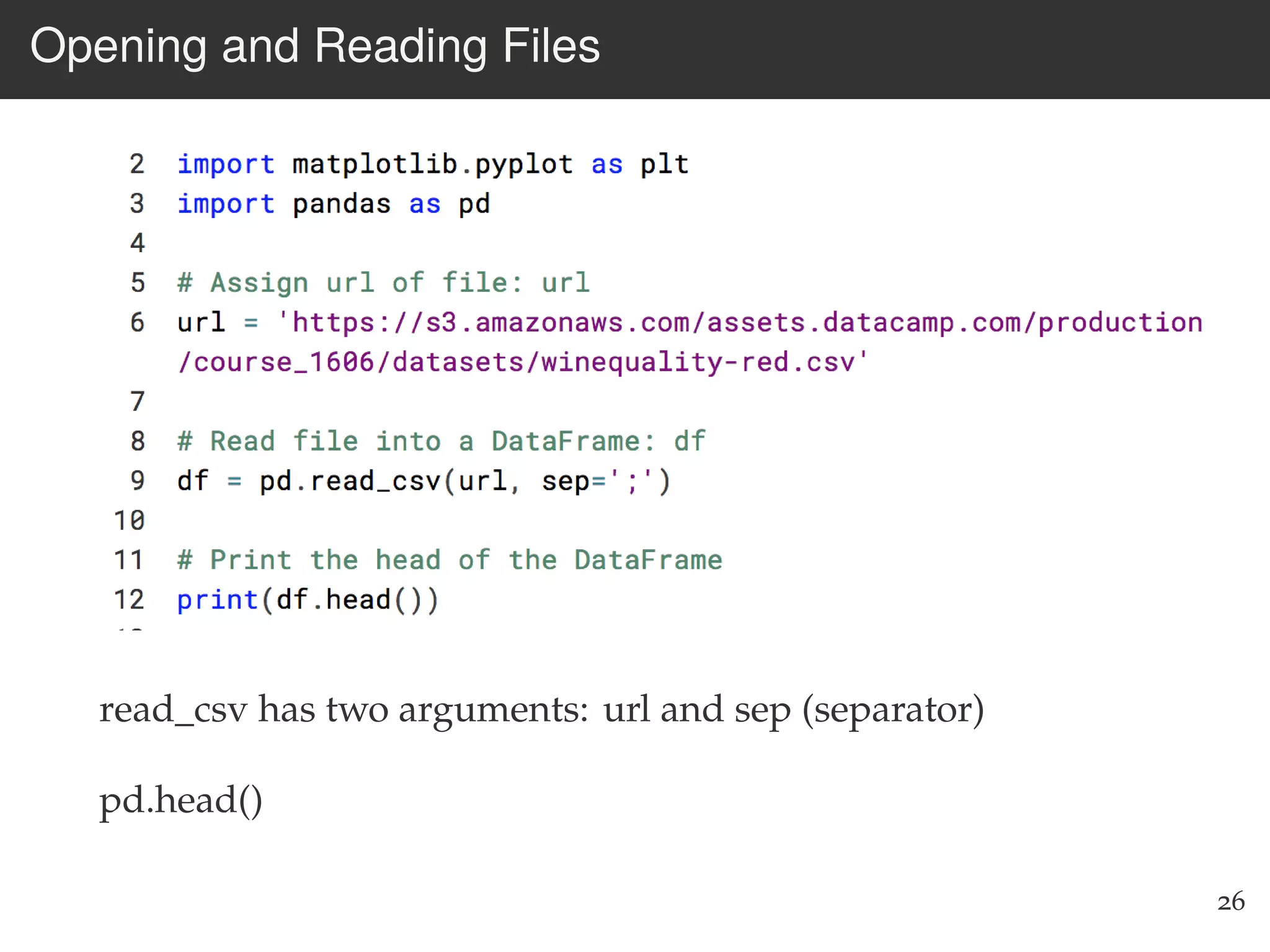
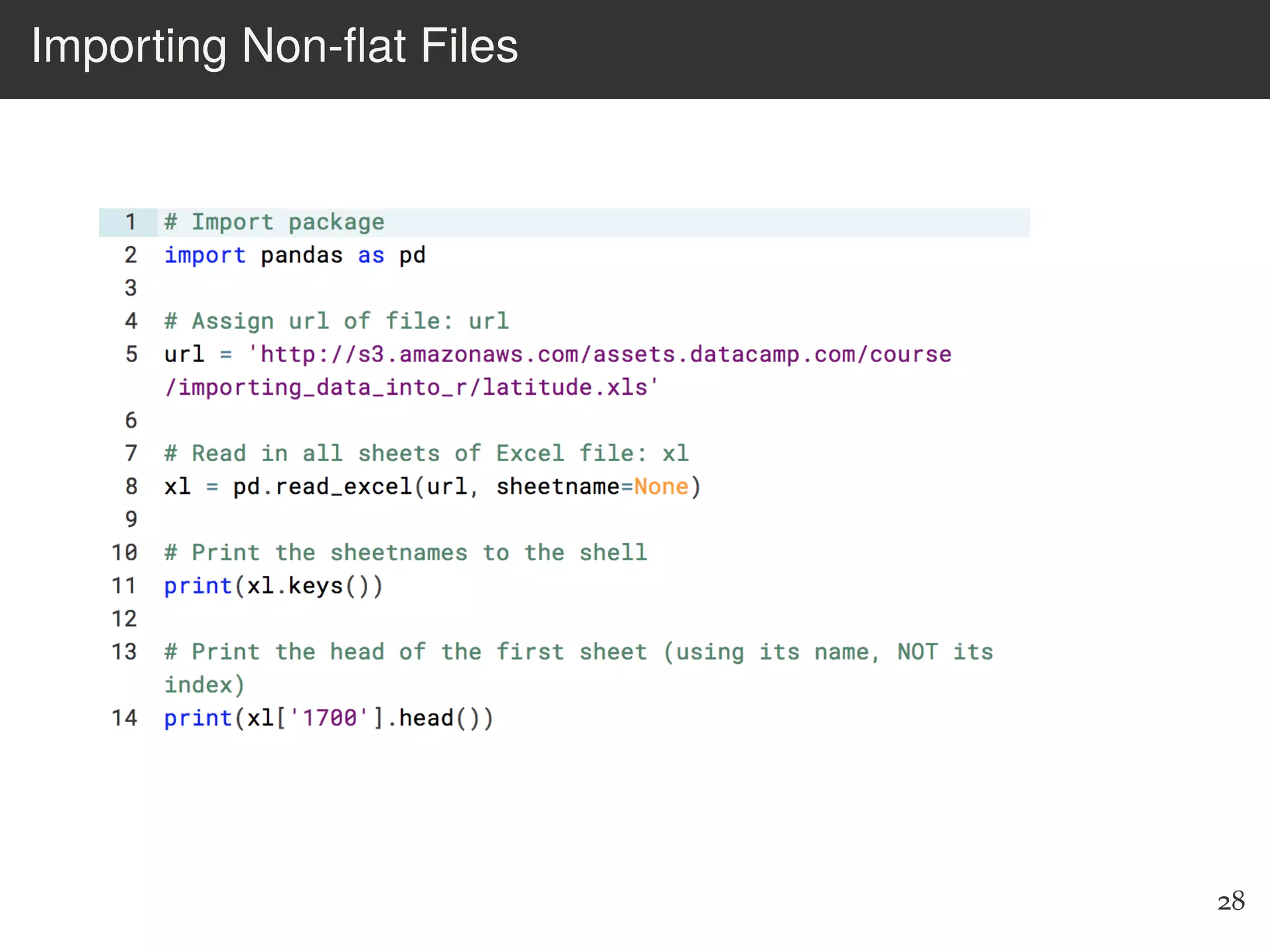
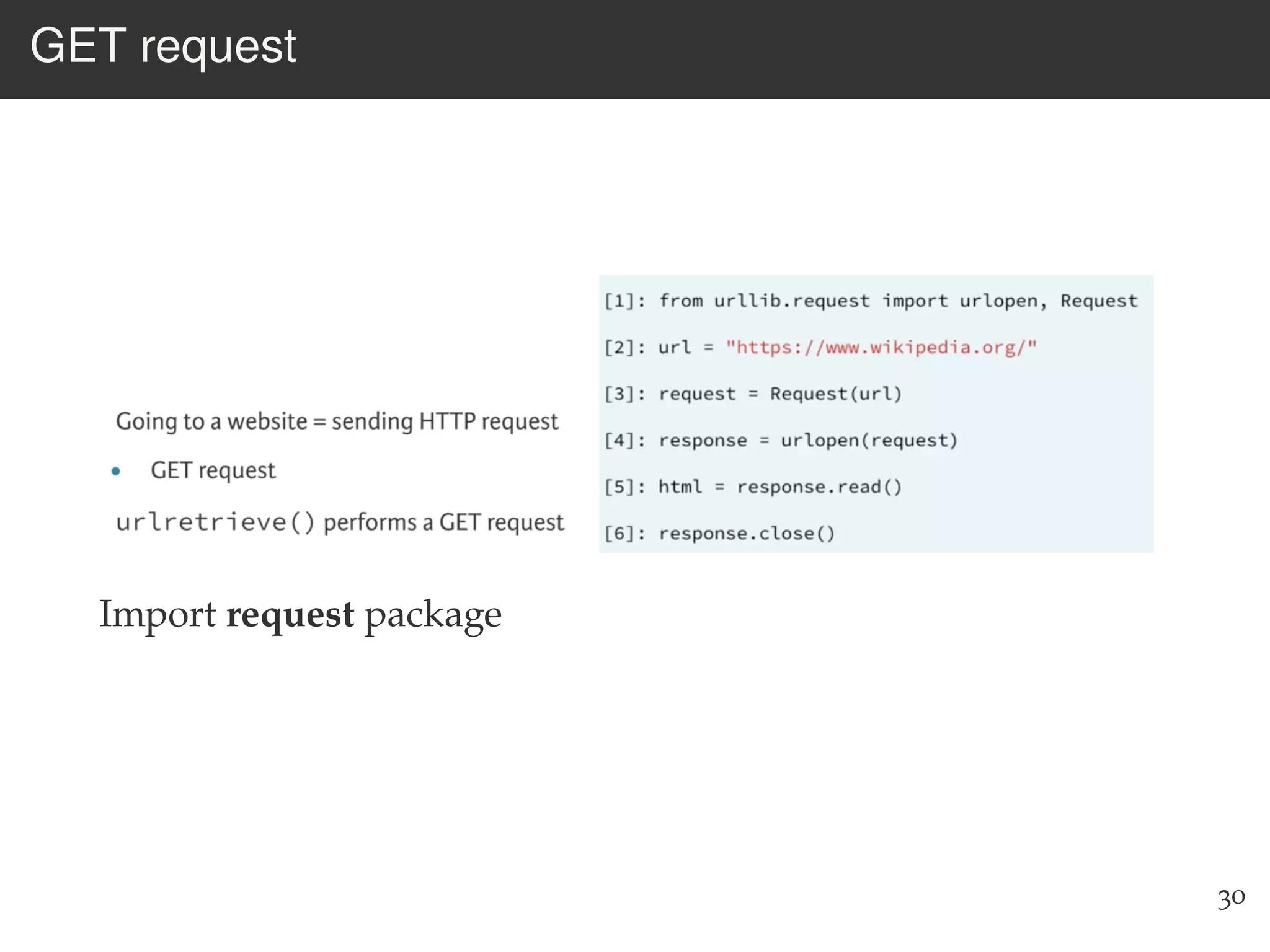
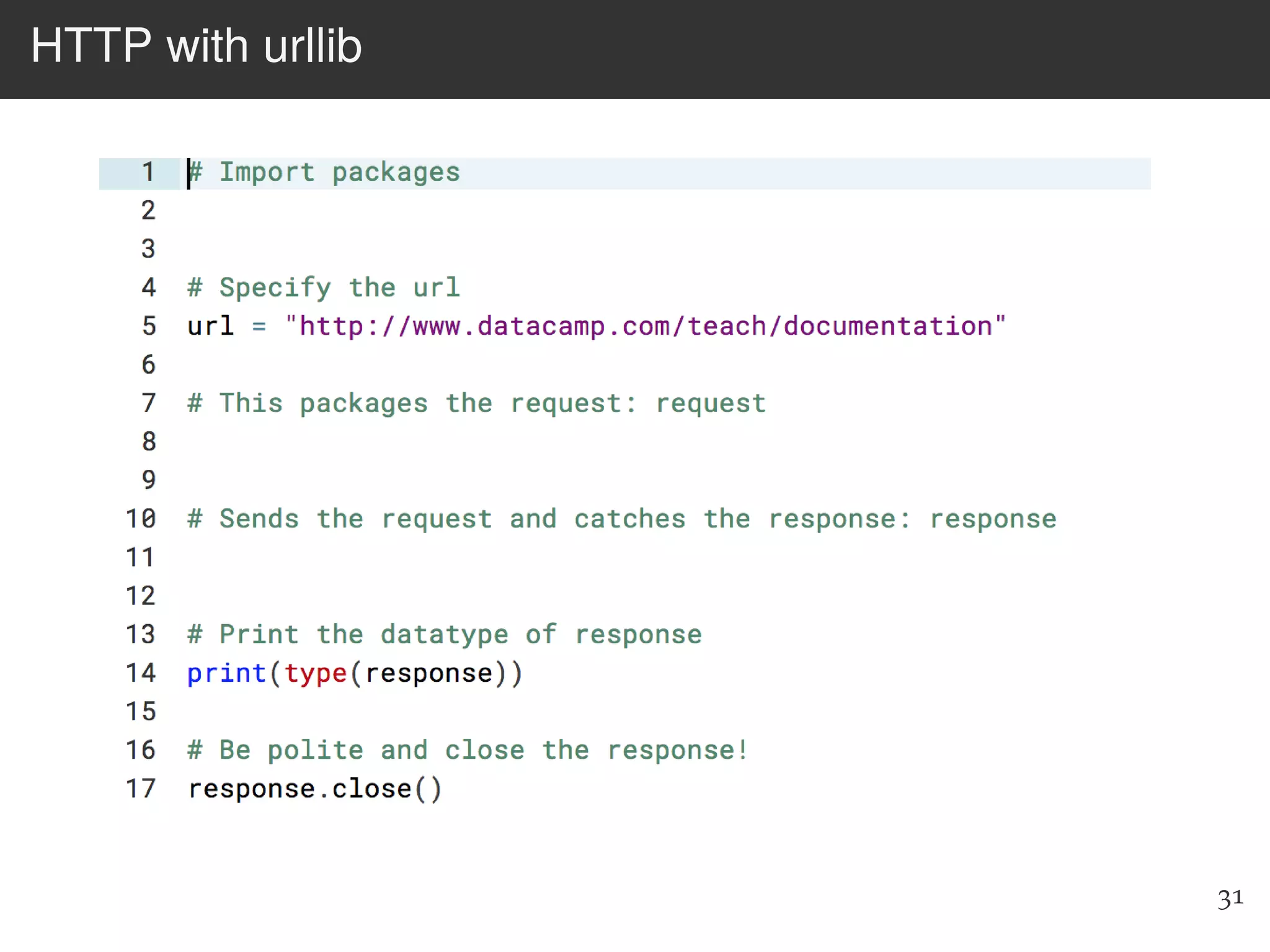
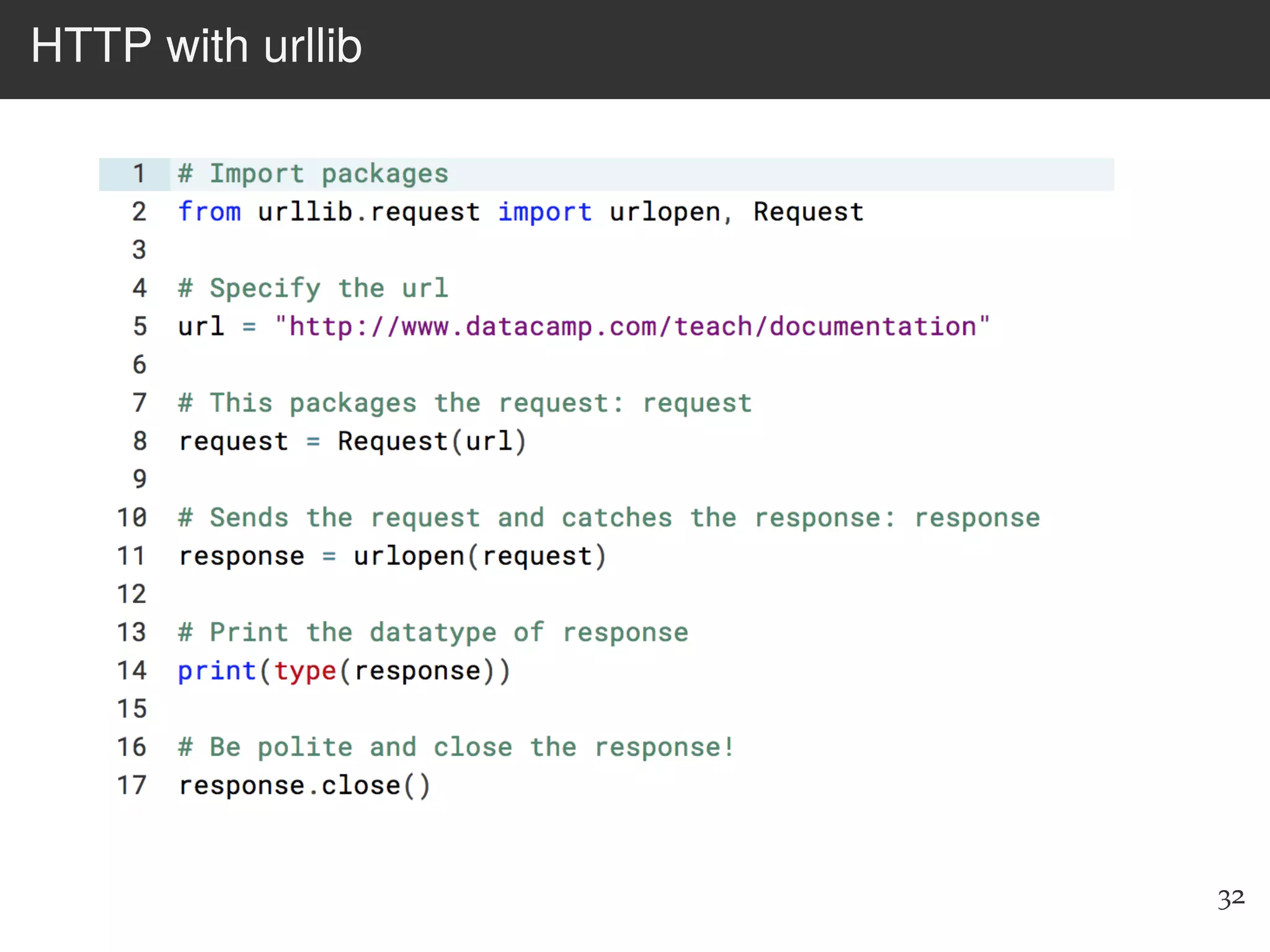
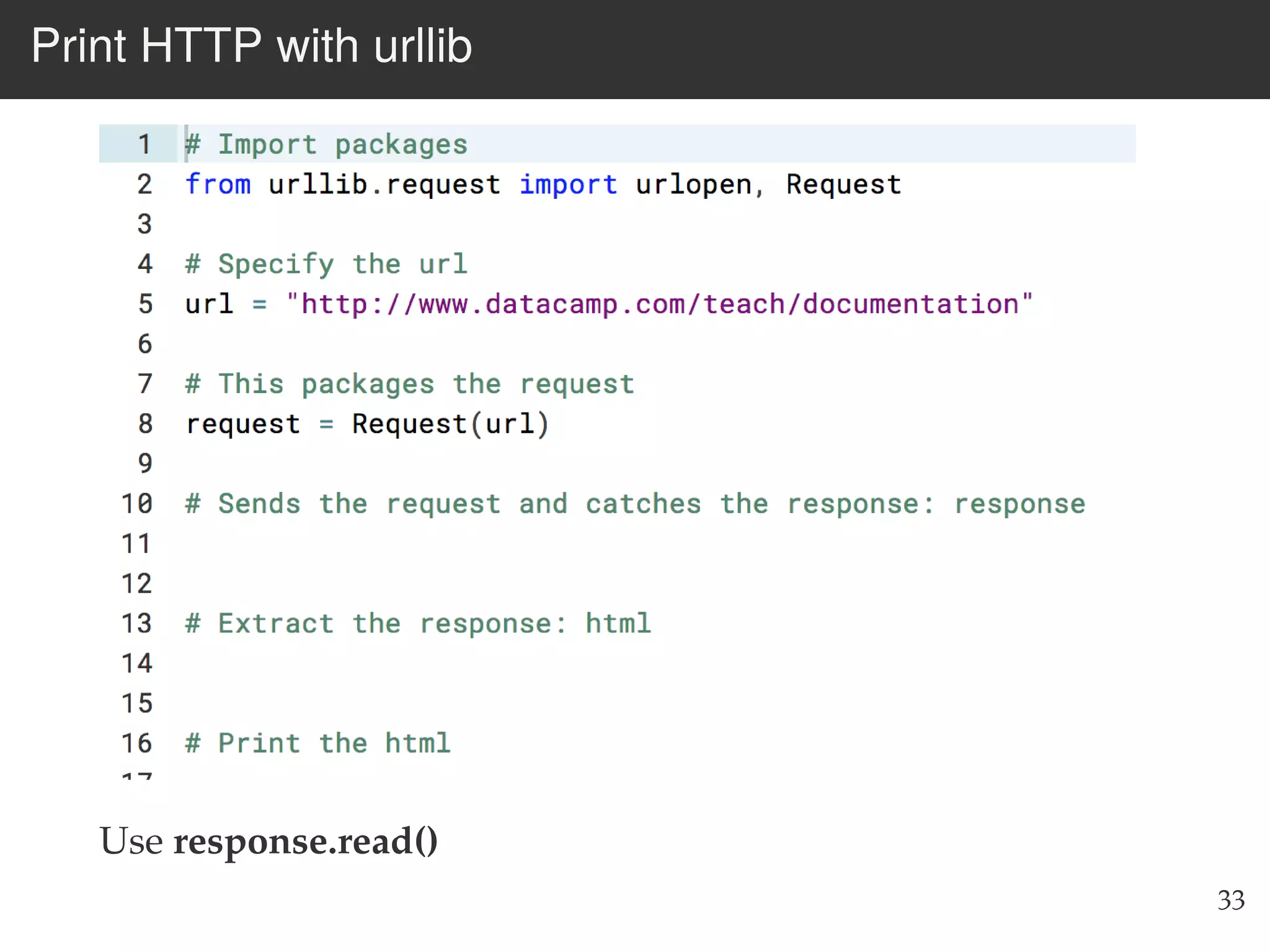
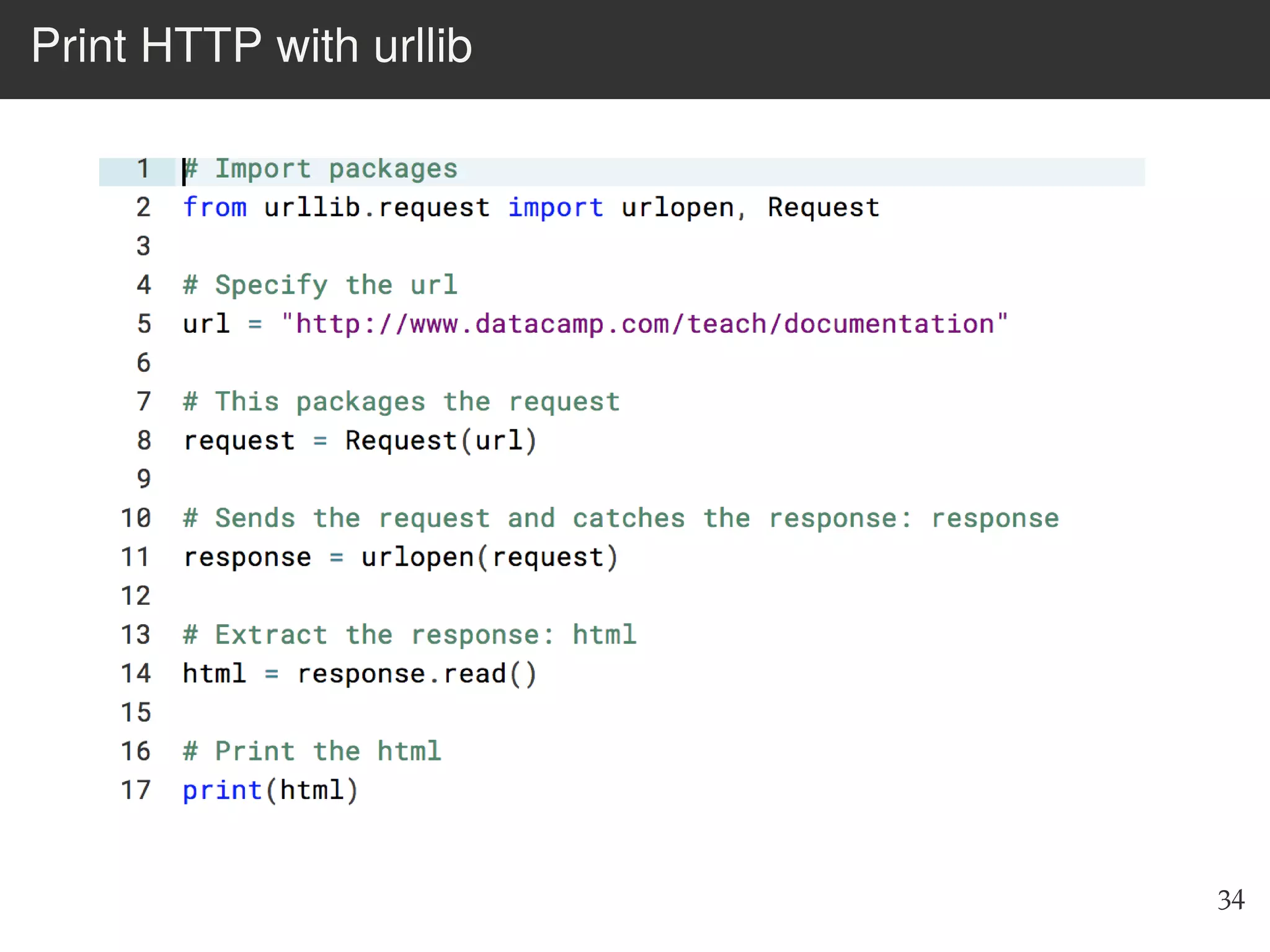
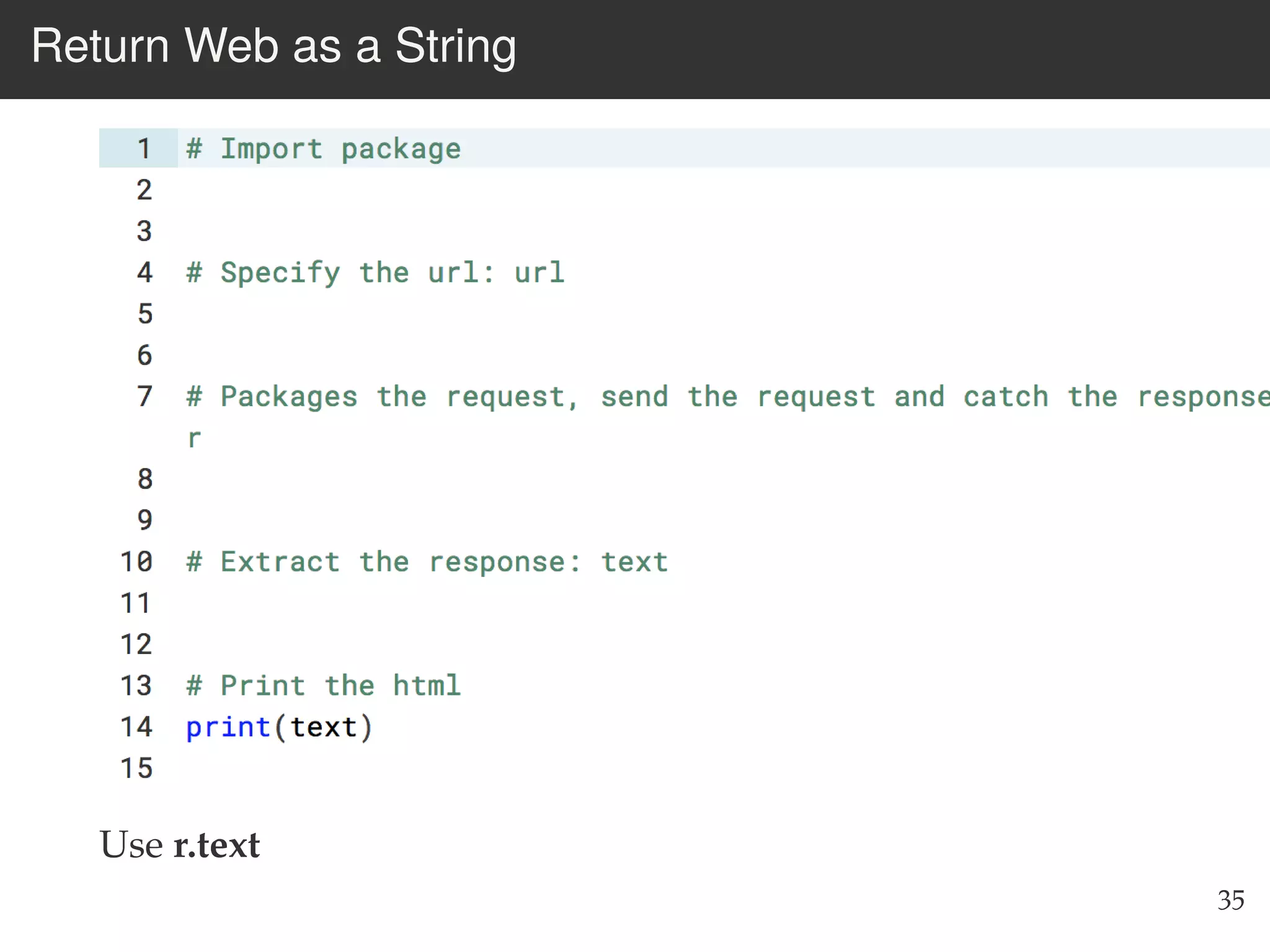
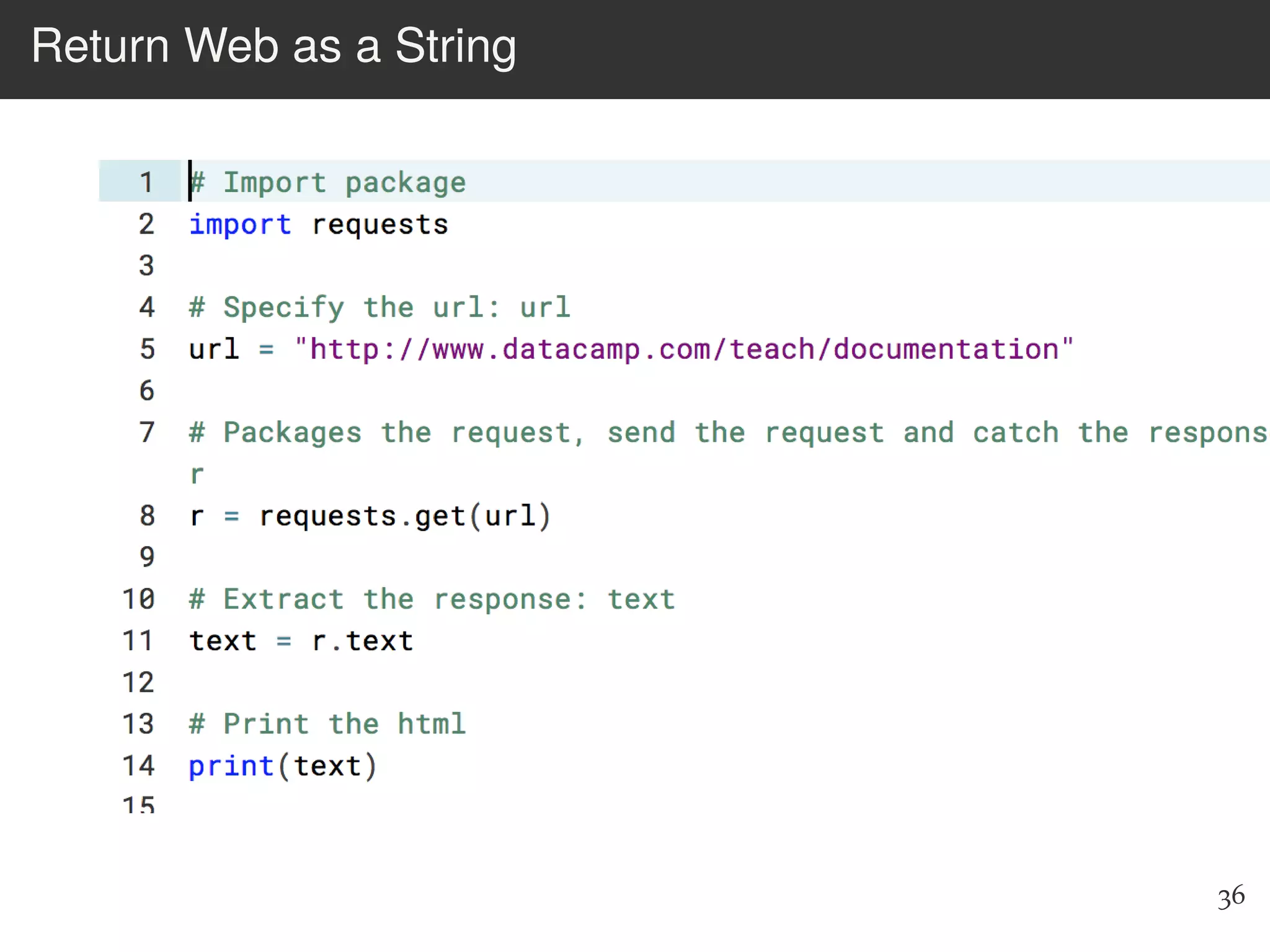
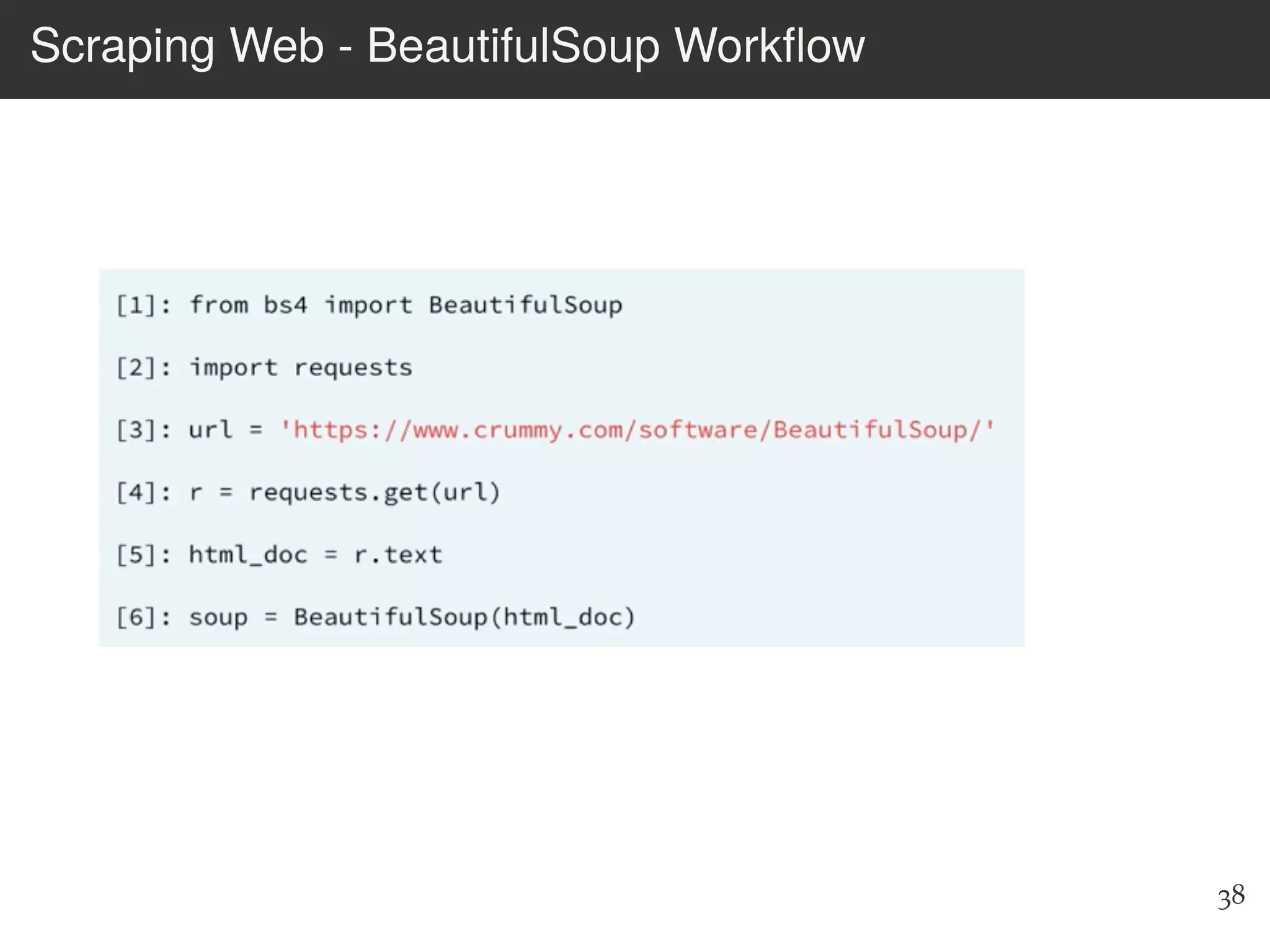
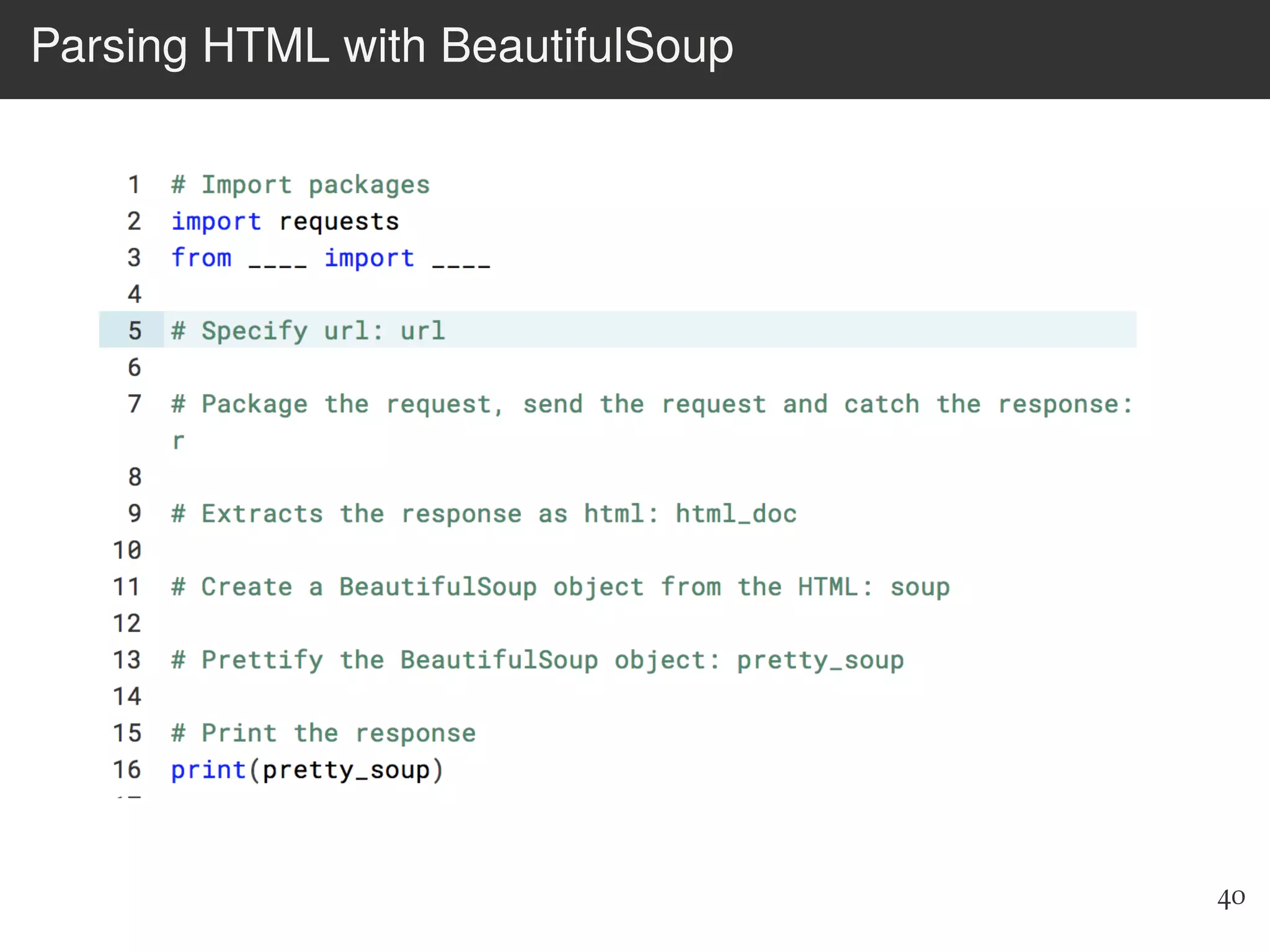
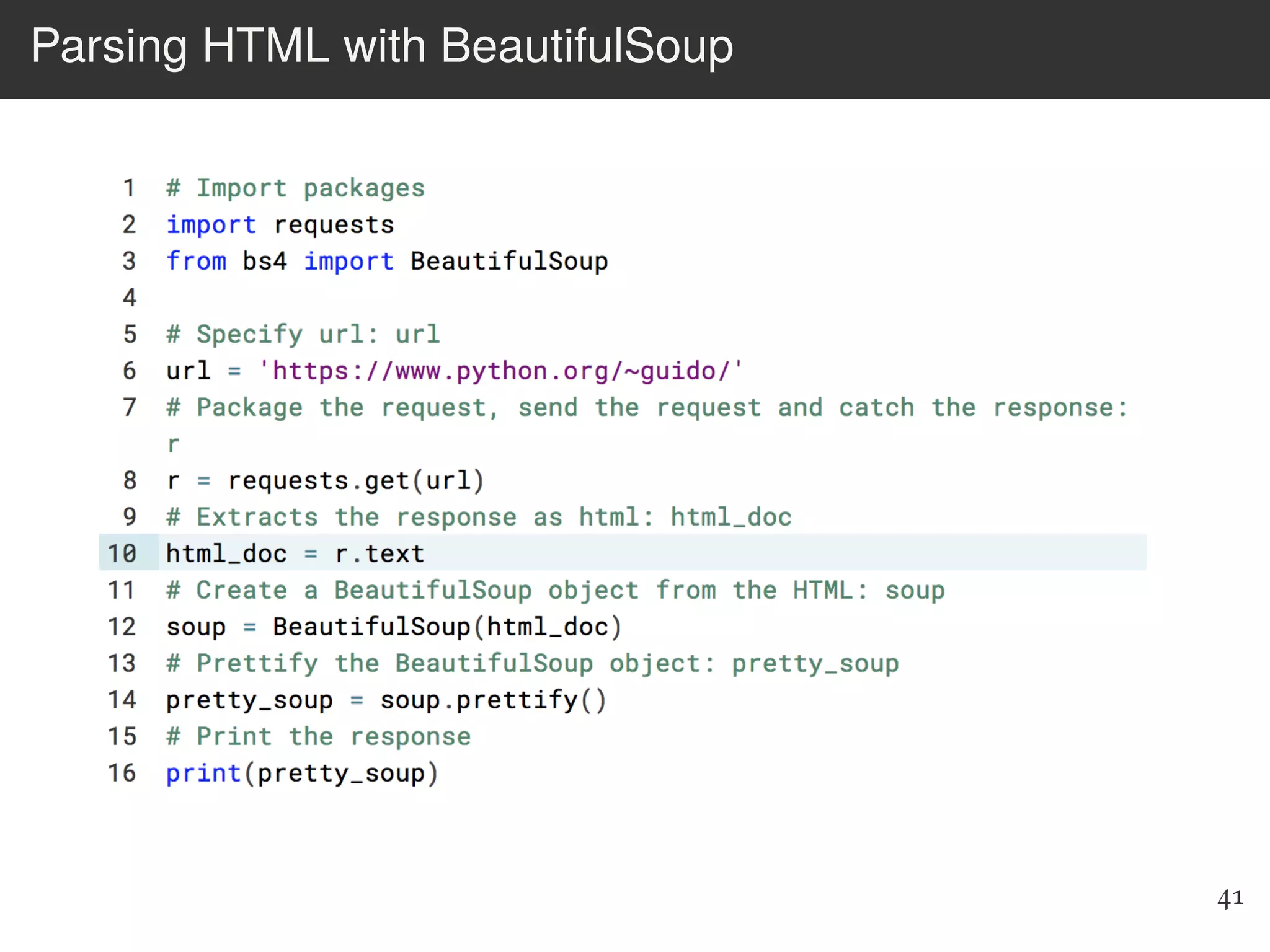
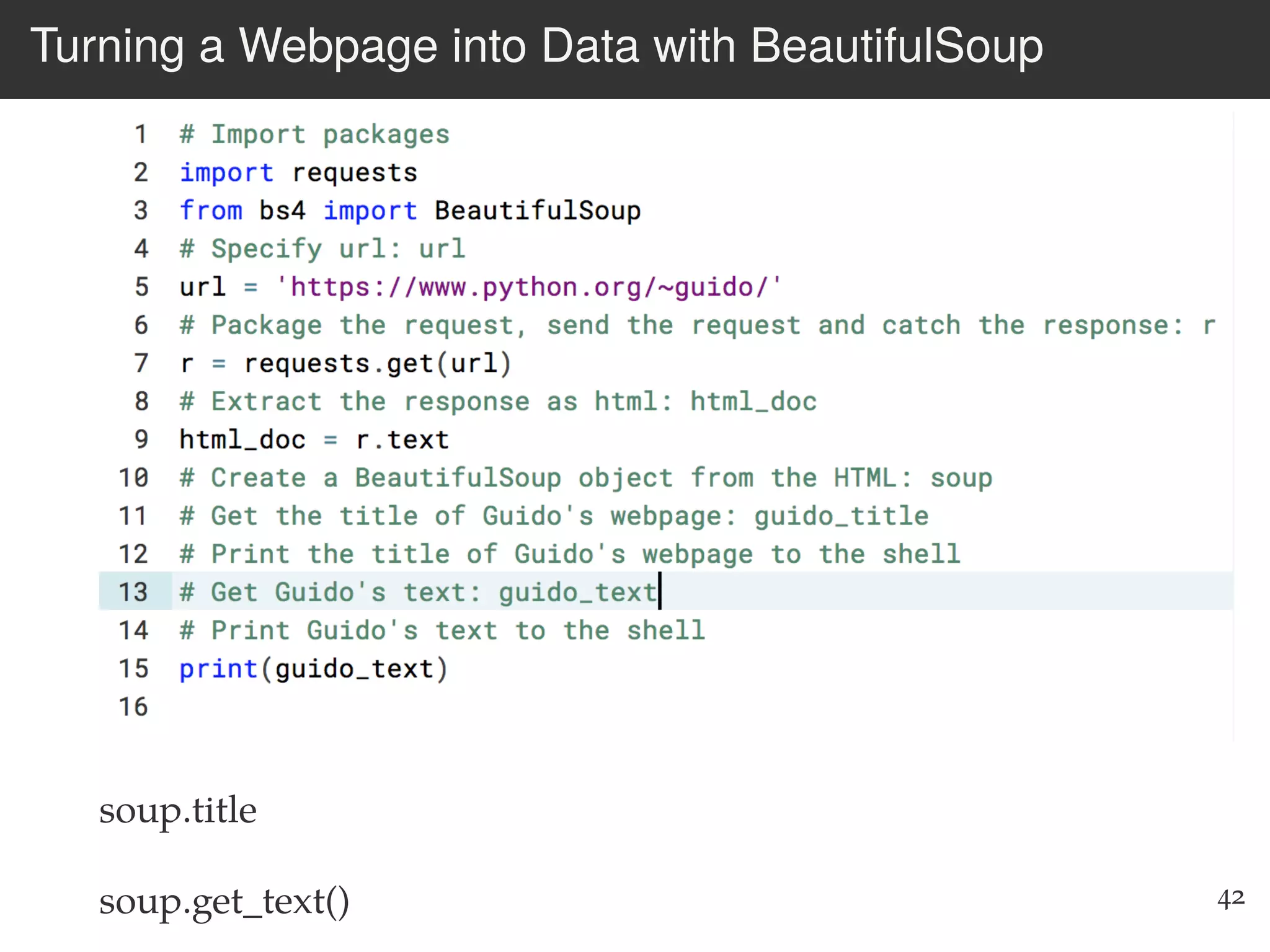
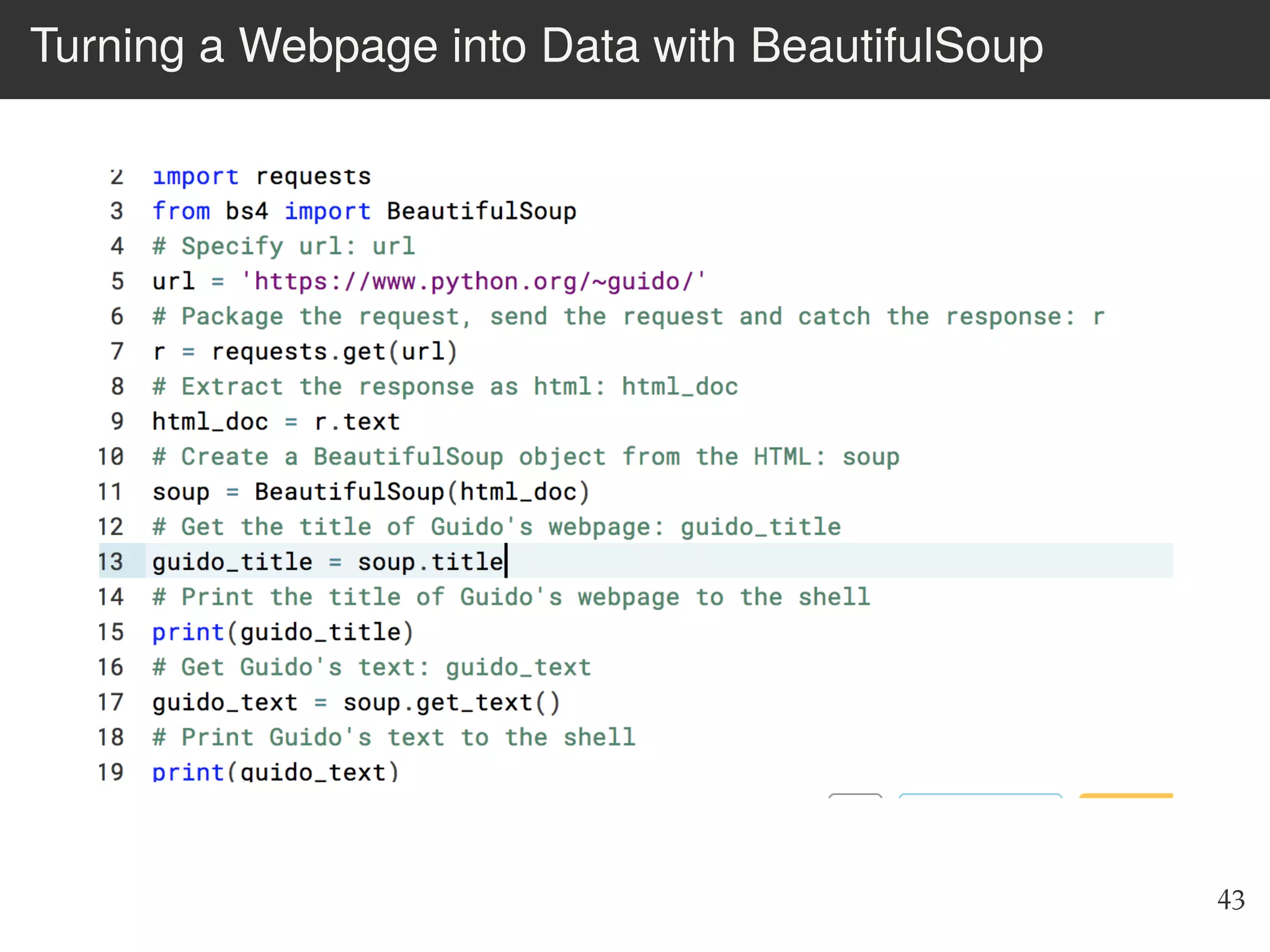
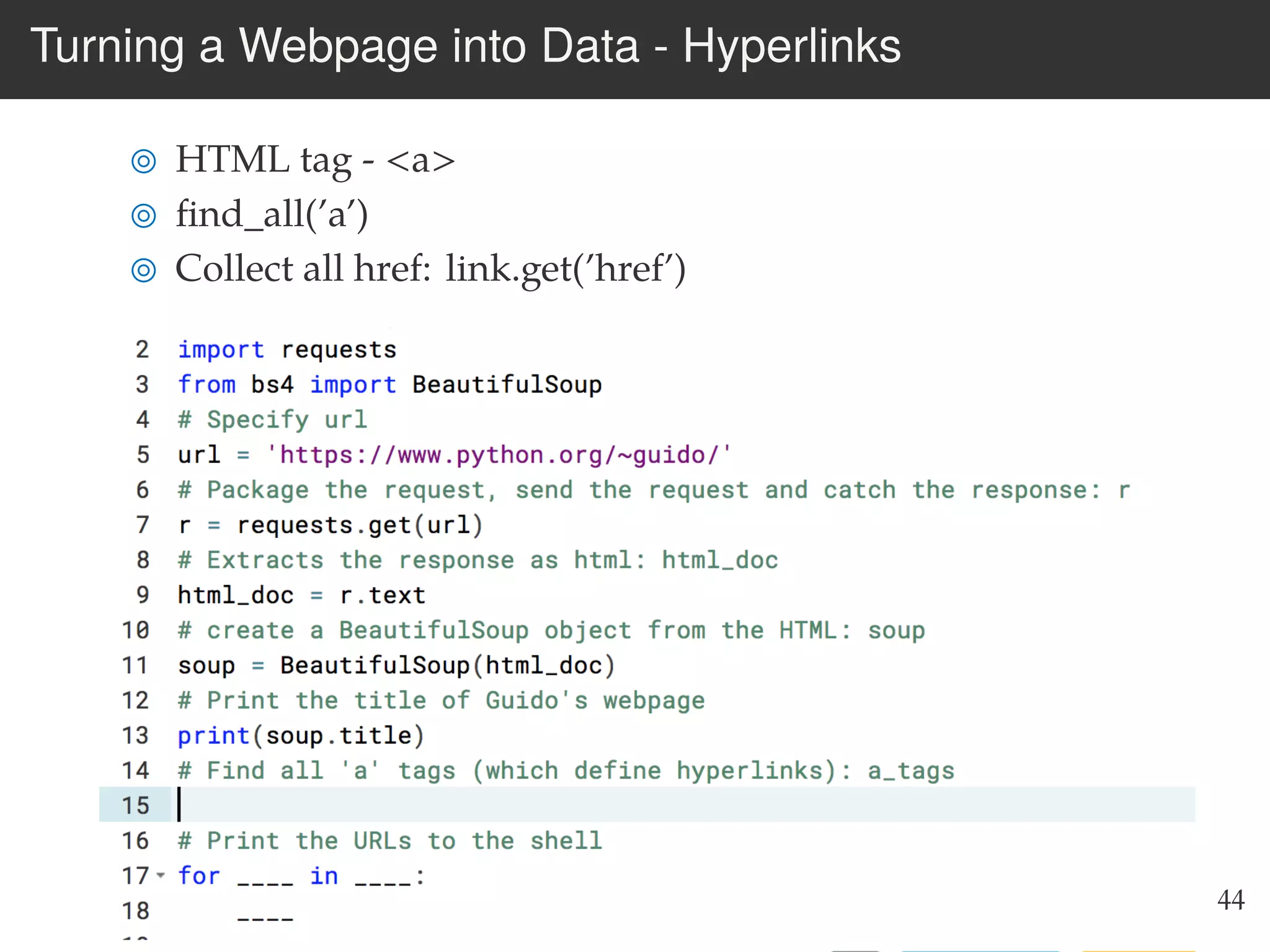
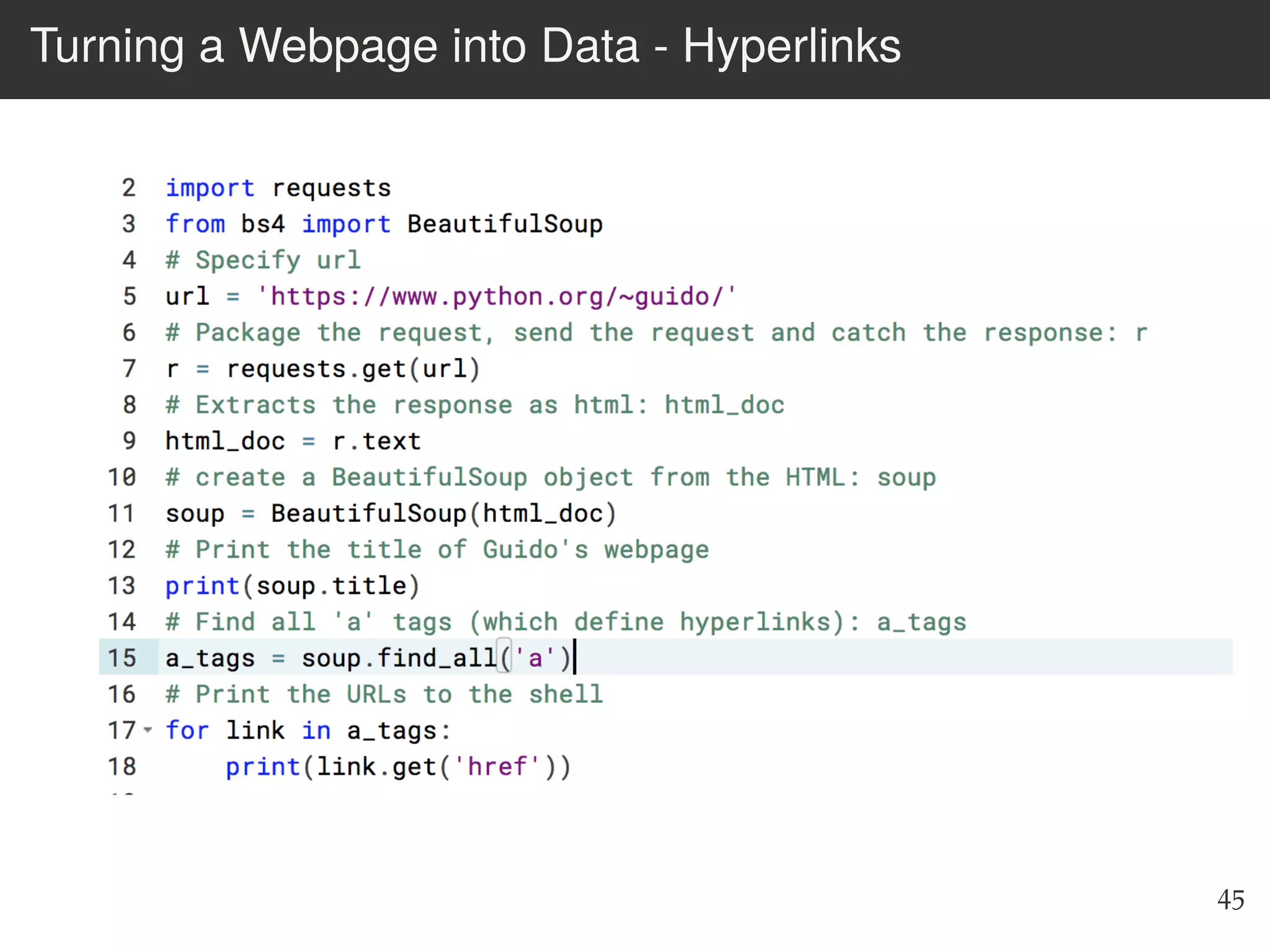
The document is an introduction to web scraping using Python, focusing on essential topics such as importing files, using libraries like Beautiful Soup, and understanding web requests. It outlines the workflow for web scraping, including how to retrieve data from URLs and process HTML responses. Additionally, it provides practical steps for installation, importing modules, and performing specific functions in Python related to web scraping.