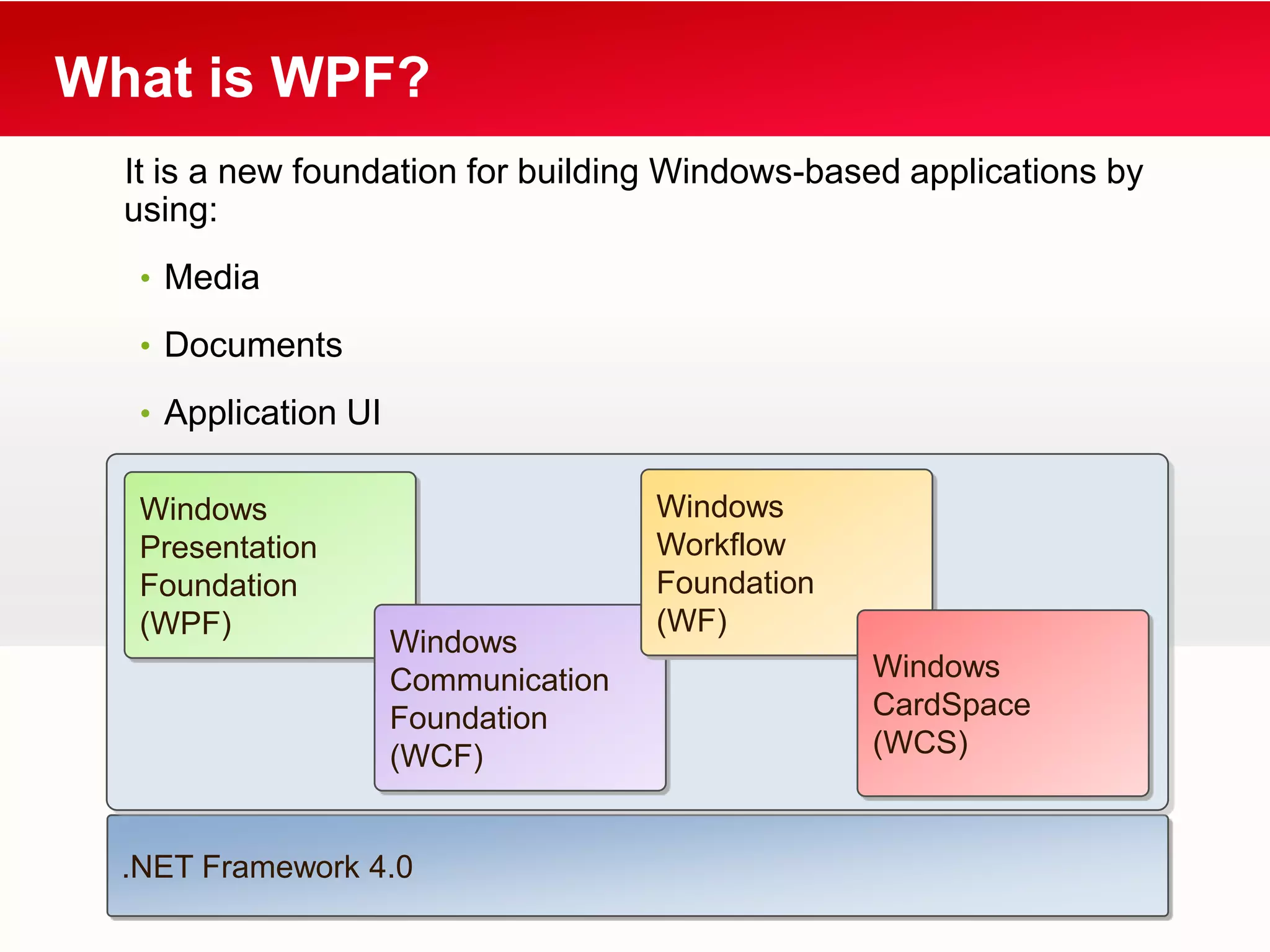
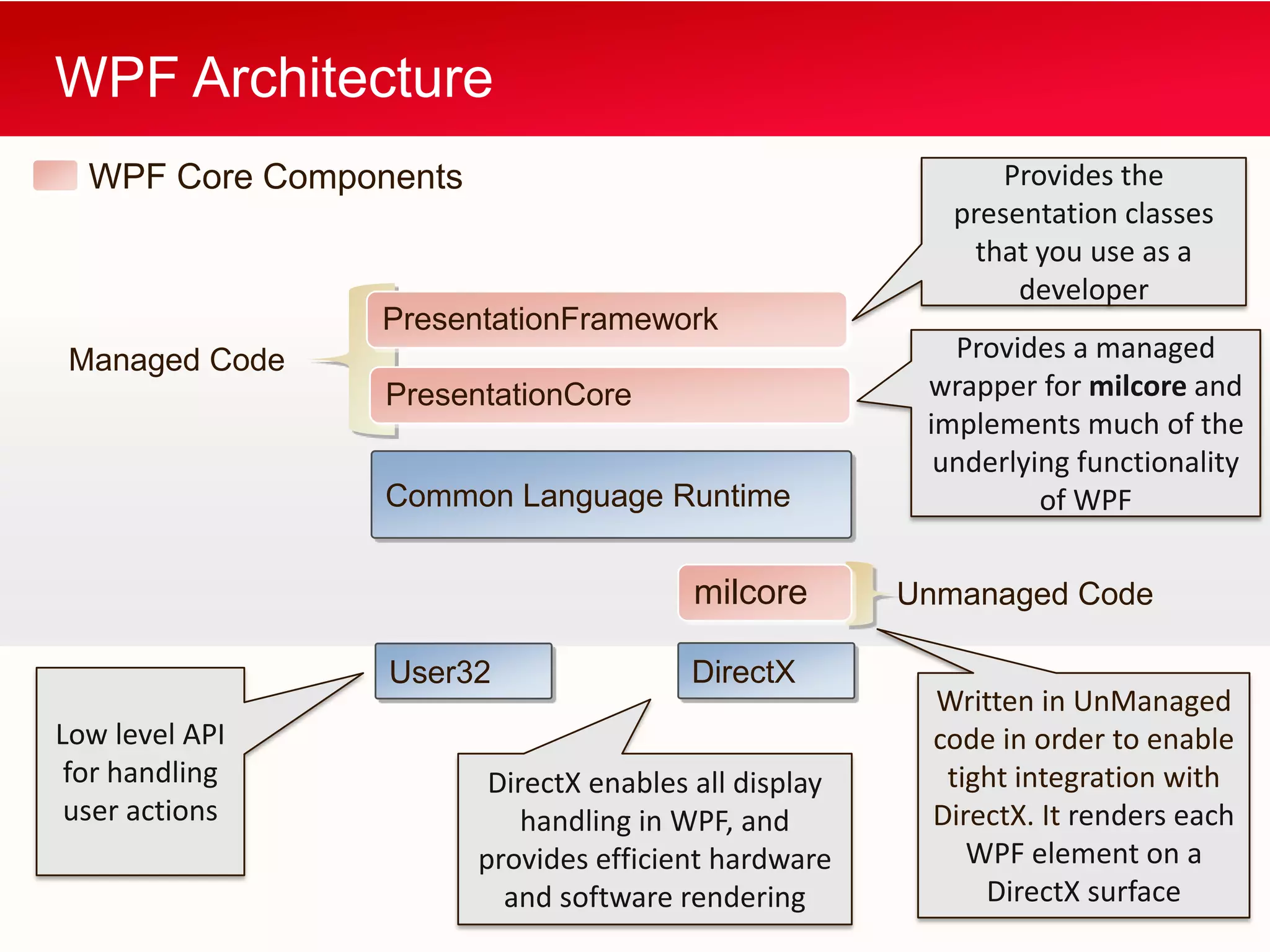
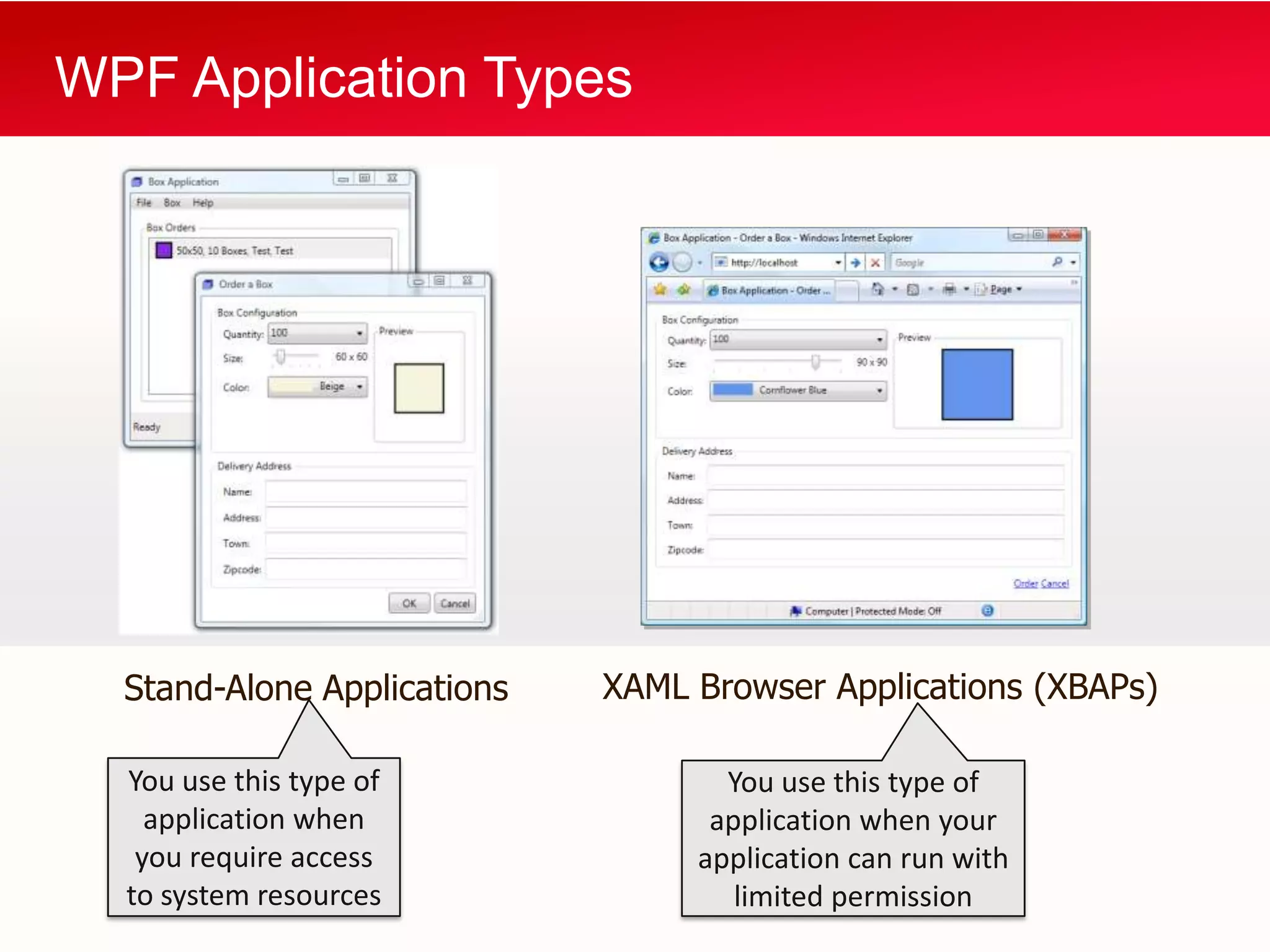
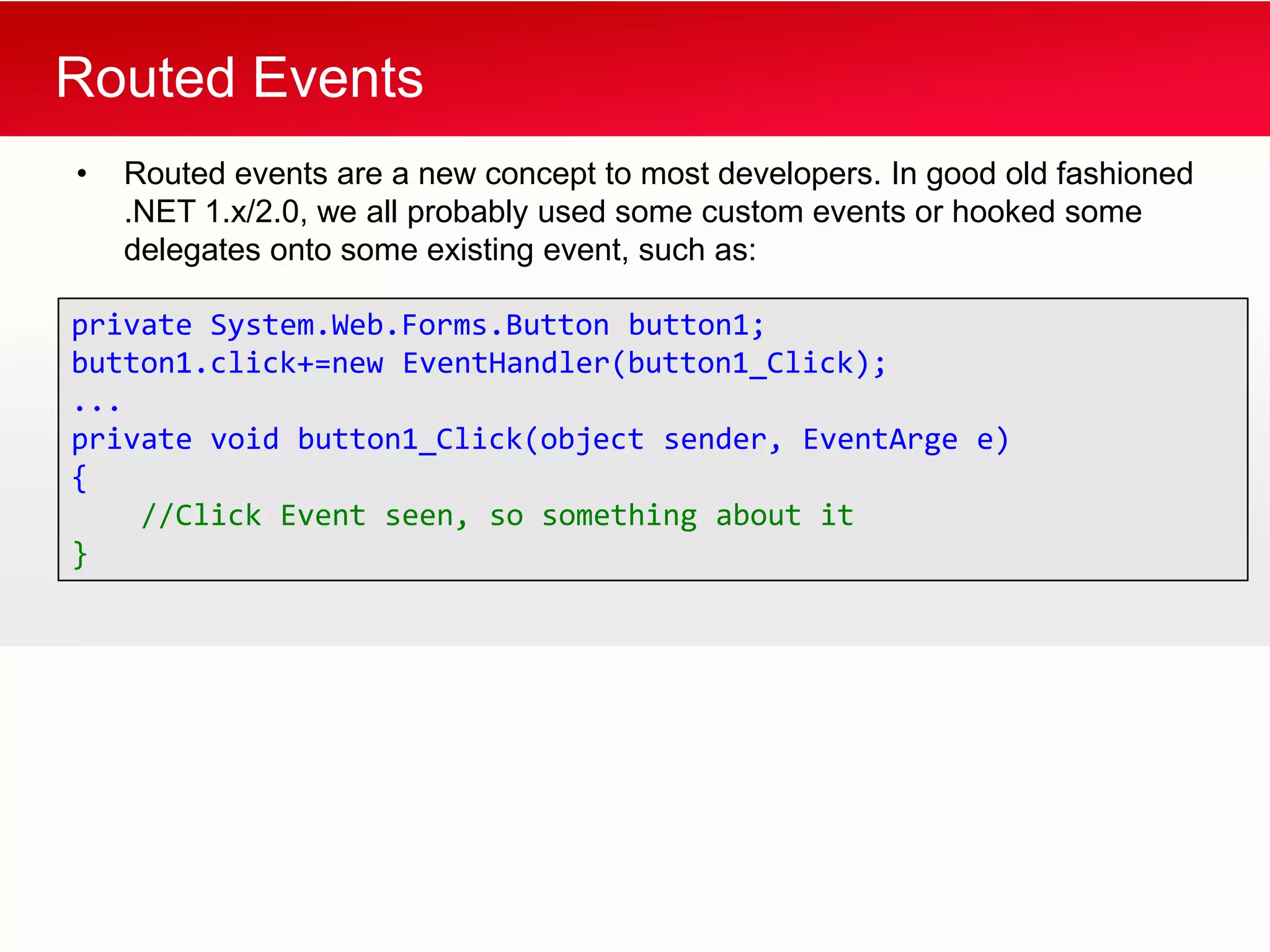
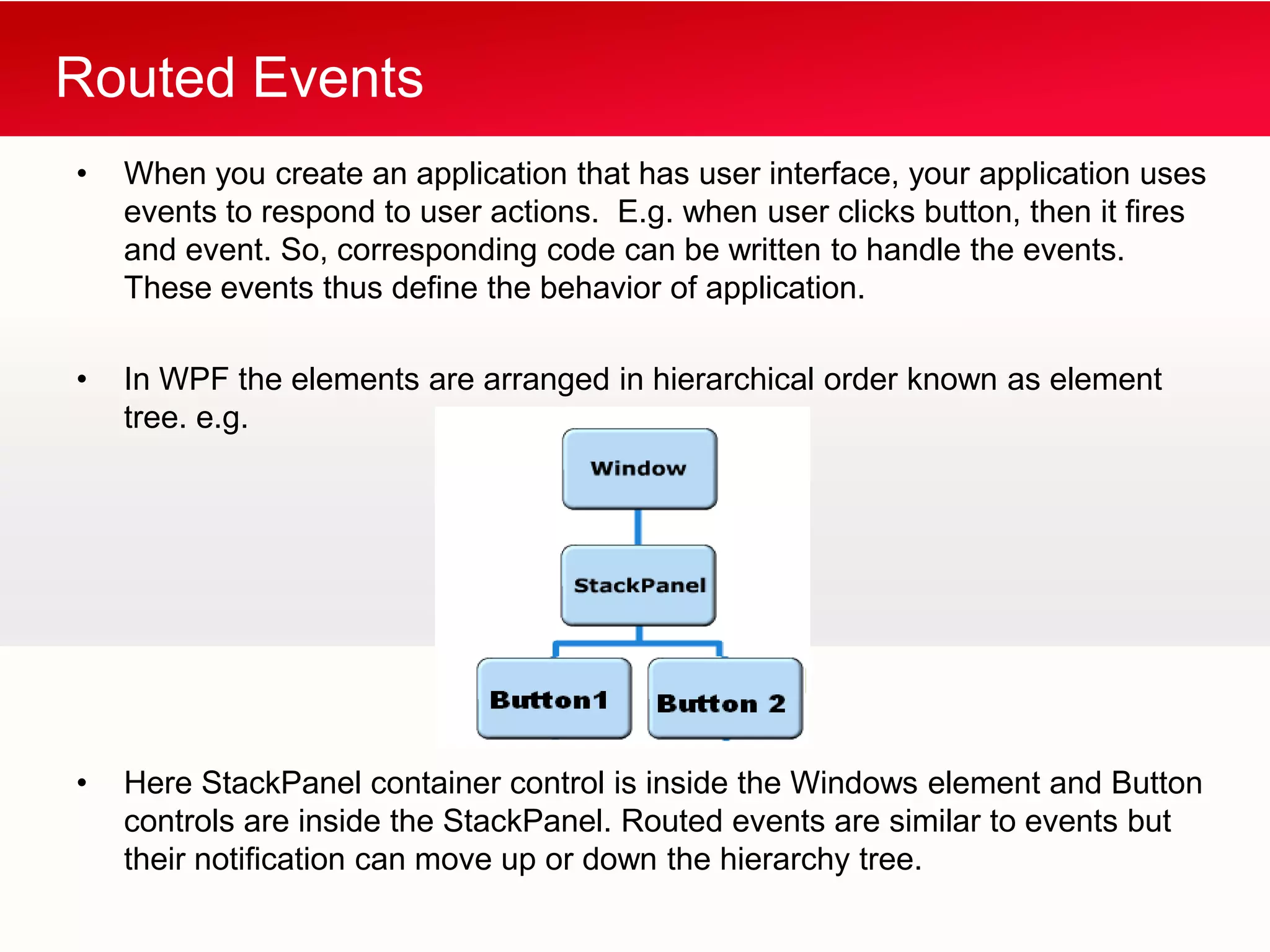
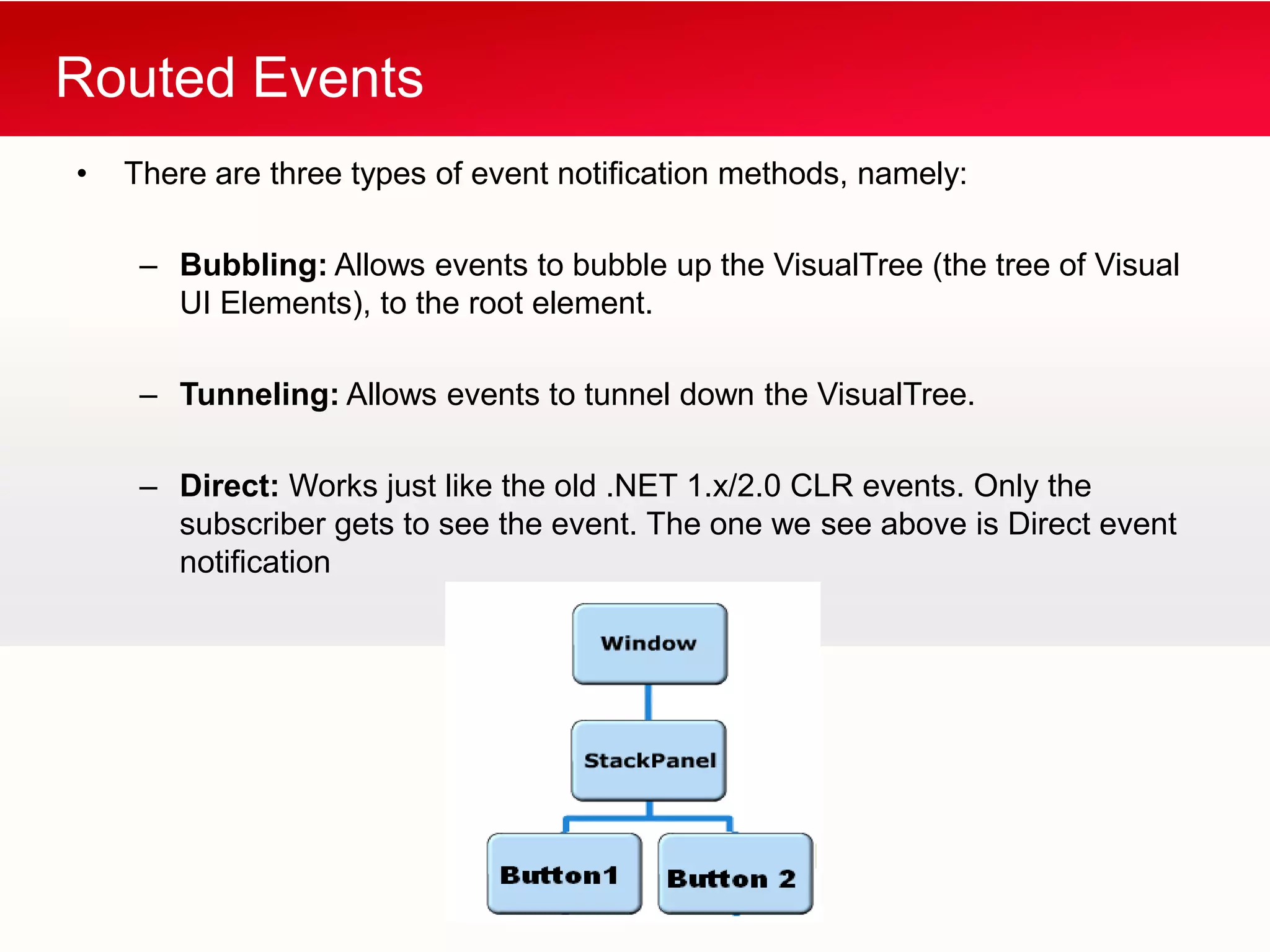
WPF allows building Windows applications using media, documents, and user interfaces. It includes a XAML markup language and supports C# code behind. WPF has a core that provides presentation classes and renders elements using DirectX. It supports different application types like standalone apps and browser apps. Routed events in WPF follow a bubbling or tunneling model to propagate from child elements up or down the visual tree.