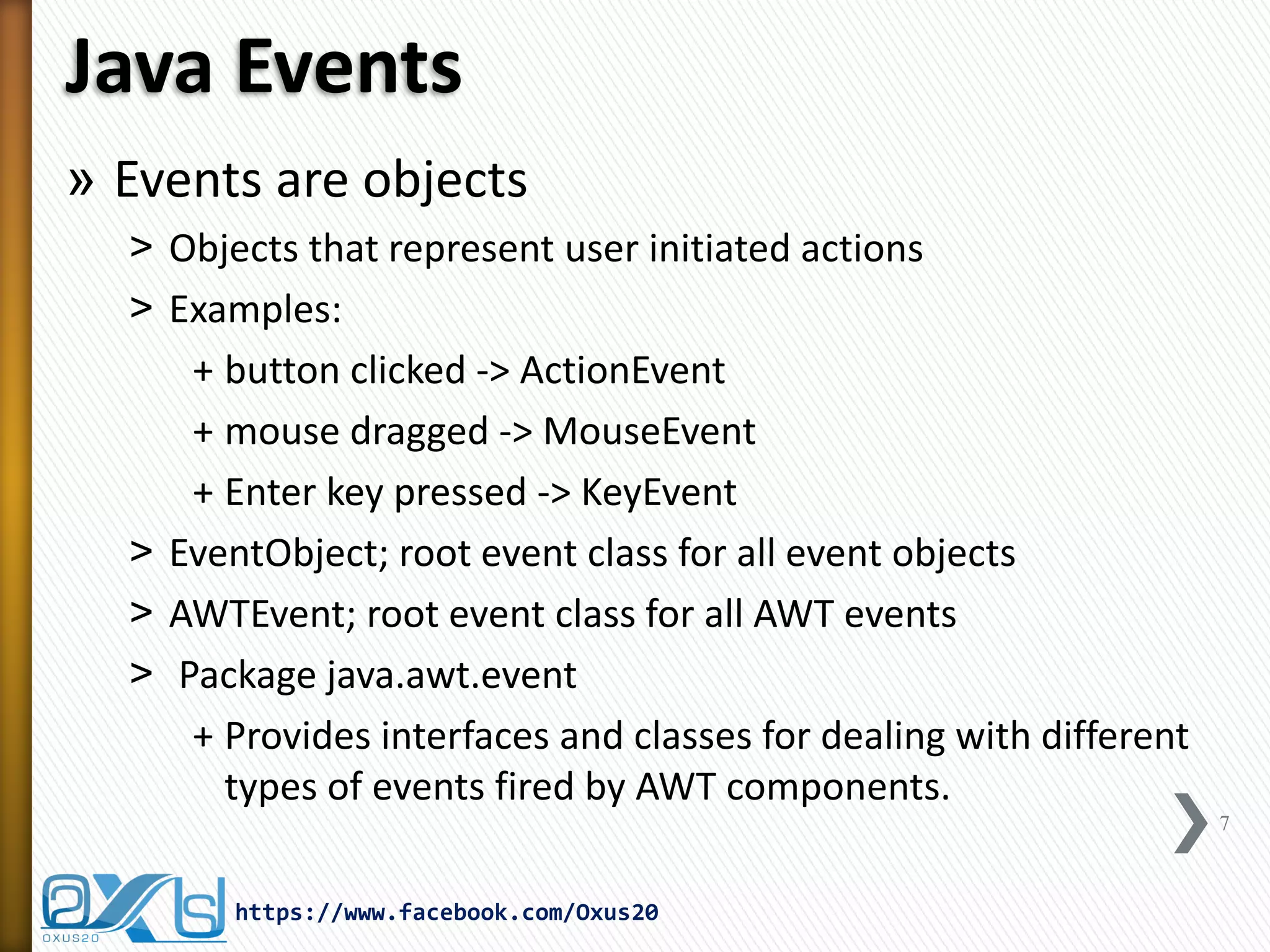
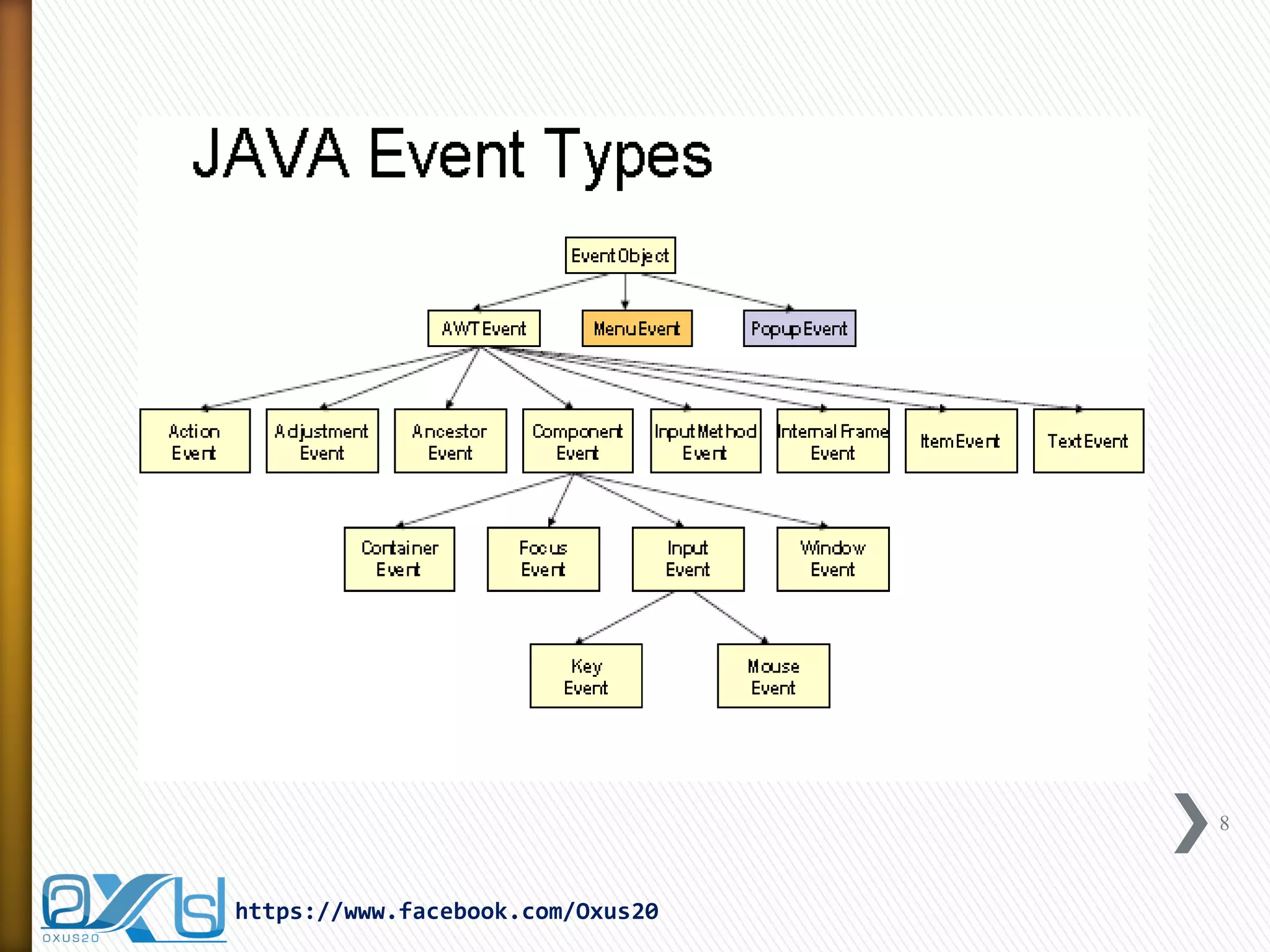
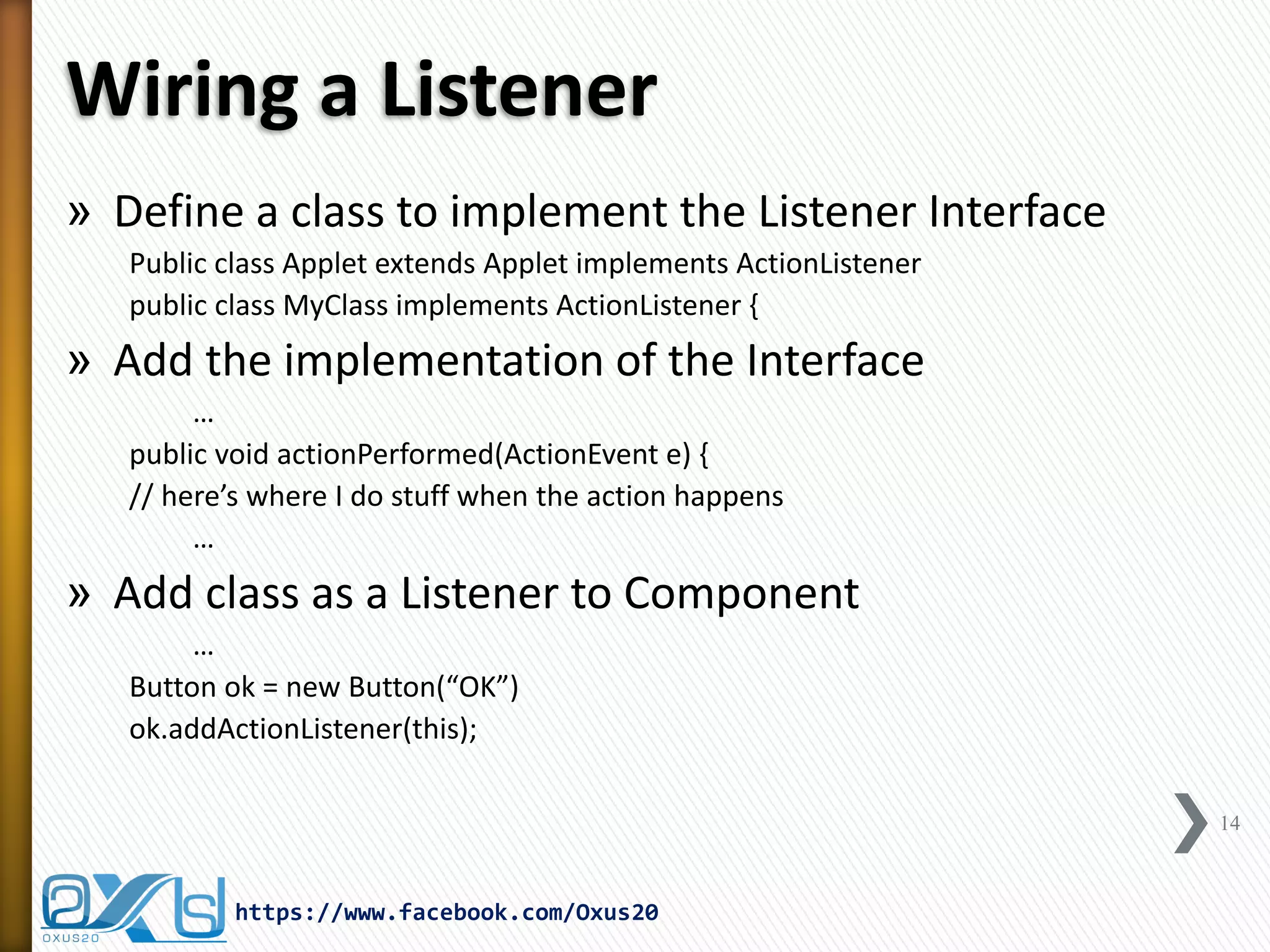
The document discusses GUI event handling in Java. It explains that window-based Java programs are event-driven, meaning they wait for and respond to user-initiated events like button clicks or key presses. When an event occurs, an event object is passed to a listener object that handles the event. Listeners implement interfaces that correspond to different event types, like ActionListener for button clicks. The delegation event model in Java handles event passing from components to listeners.














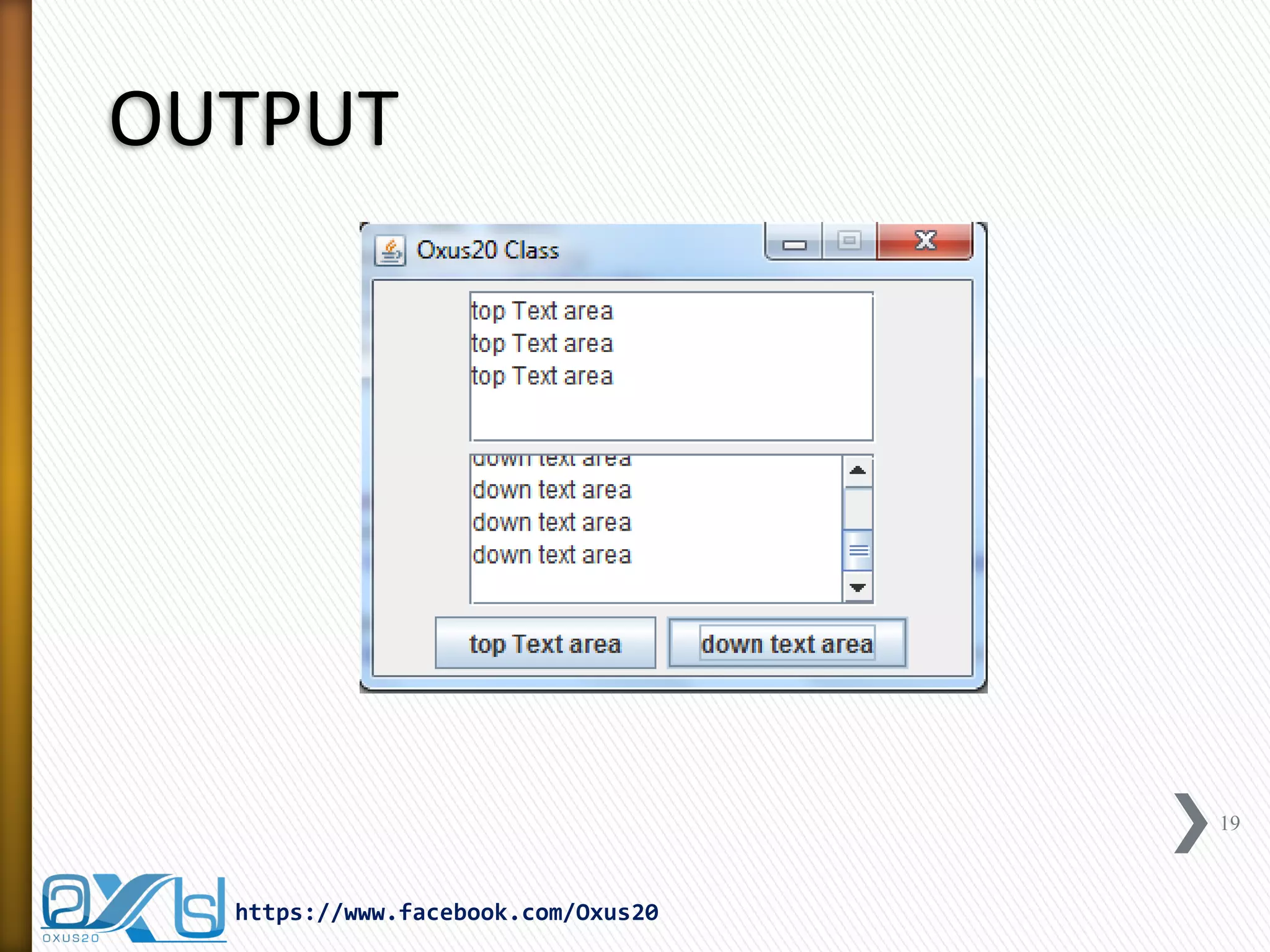
![ActionListener Example(cont.)
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource() == button1) {
topTextArea.append(e.getActionCommand() + newline);
}
if (e.getSource() == button2) {
bottomTextArea.append(e.getActionCommand() + newline);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ActionListenerTest();
}
}
18
https://www.facebook.com/Oxus20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaguipartiii-140225085452-phpapp01/75/JAVA-GUI-PART-III-18-2048.jpg)