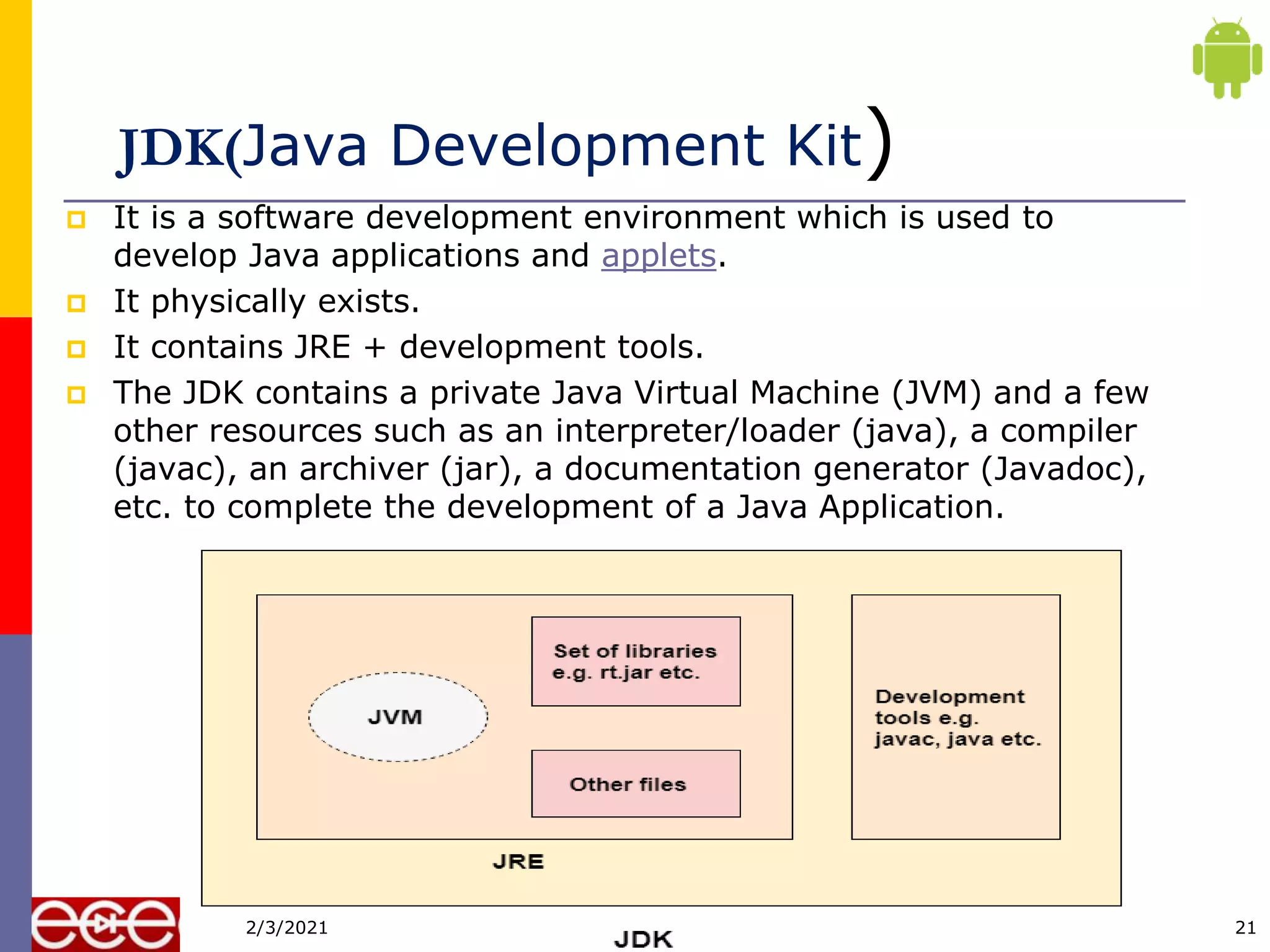
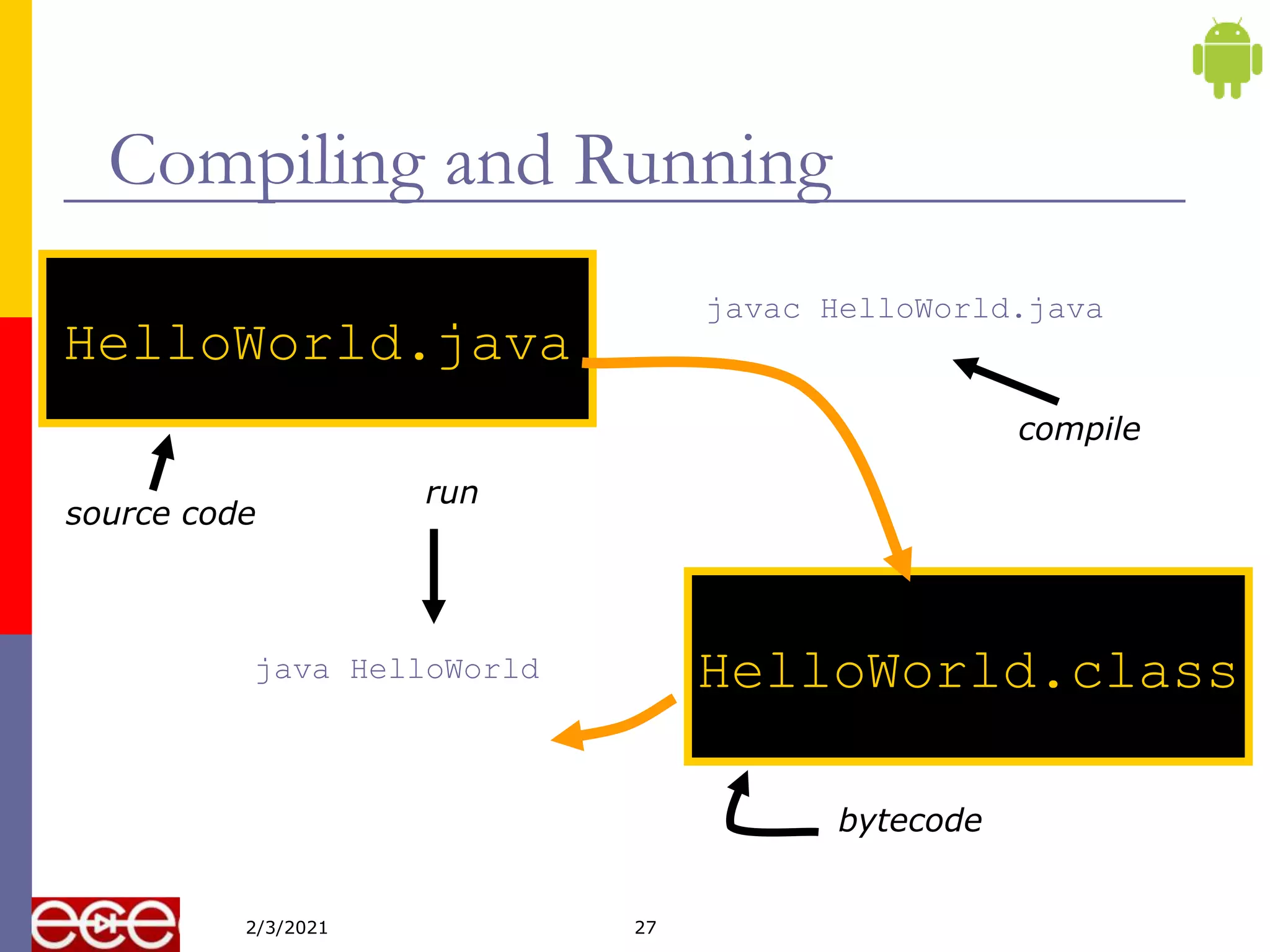
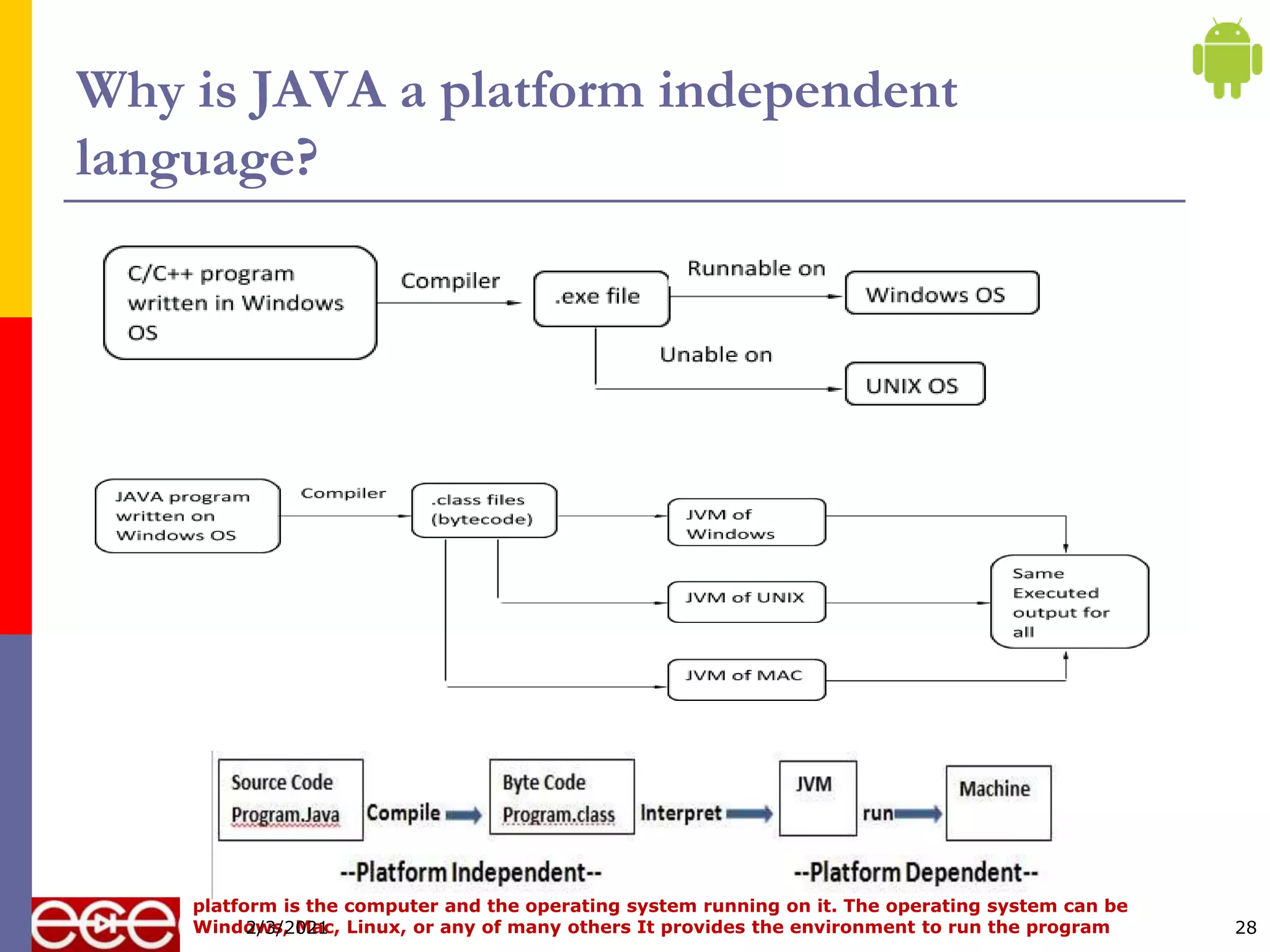
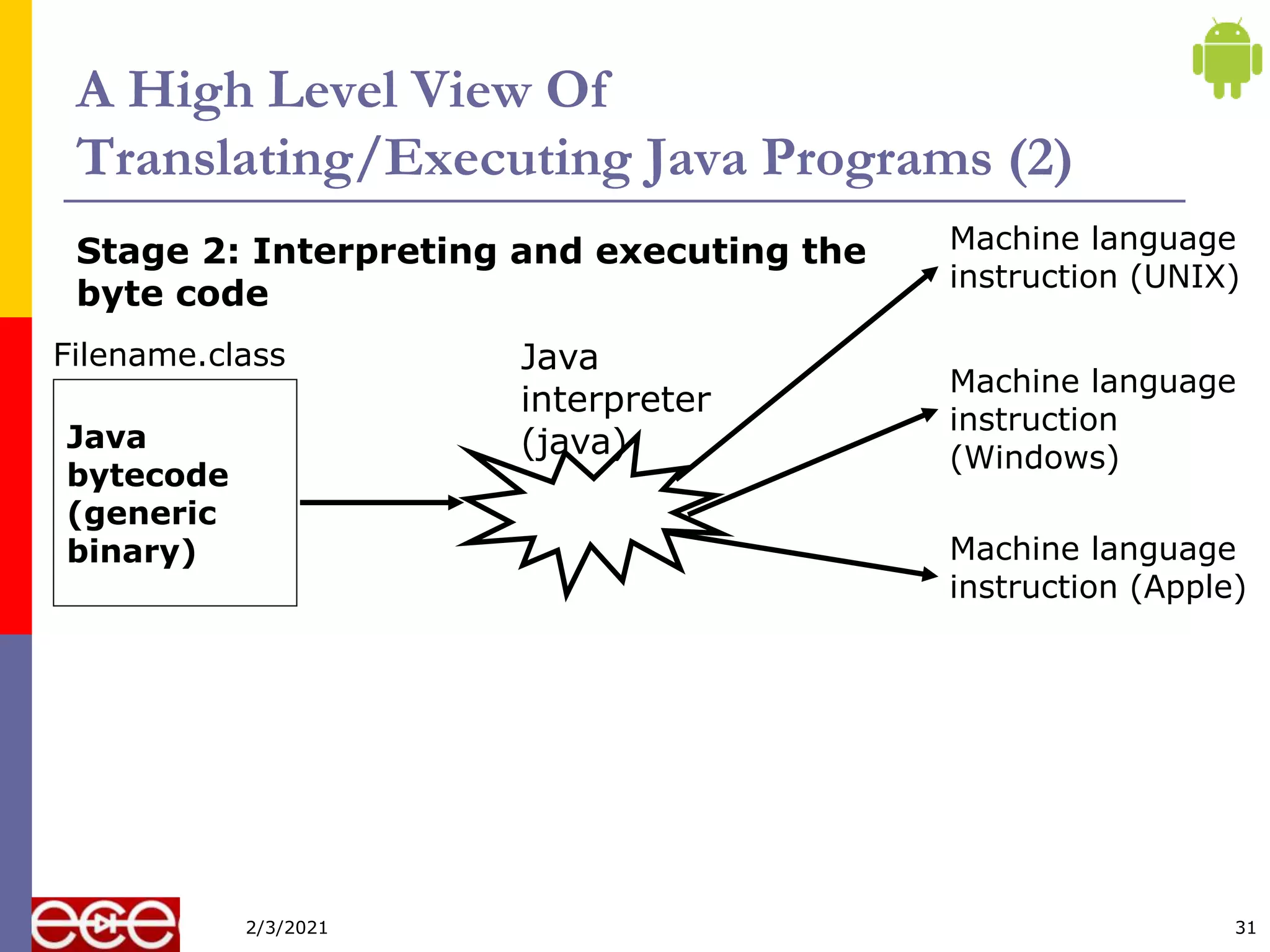
Java is an object-oriented programming language that is platform independent. It was created in 1995 by Sun Microsystems with James Gosling as the lead developer. Java programs are first compiled into bytecode, which can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM) regardless of computer hardware or operating system. This allows Java programs to run on any platform that supports Java without being recompiled.





















![26
First Program
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
2/3/2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaintroduction-210203064244/75/Java-Programming-introduction-26-2048.jpg)


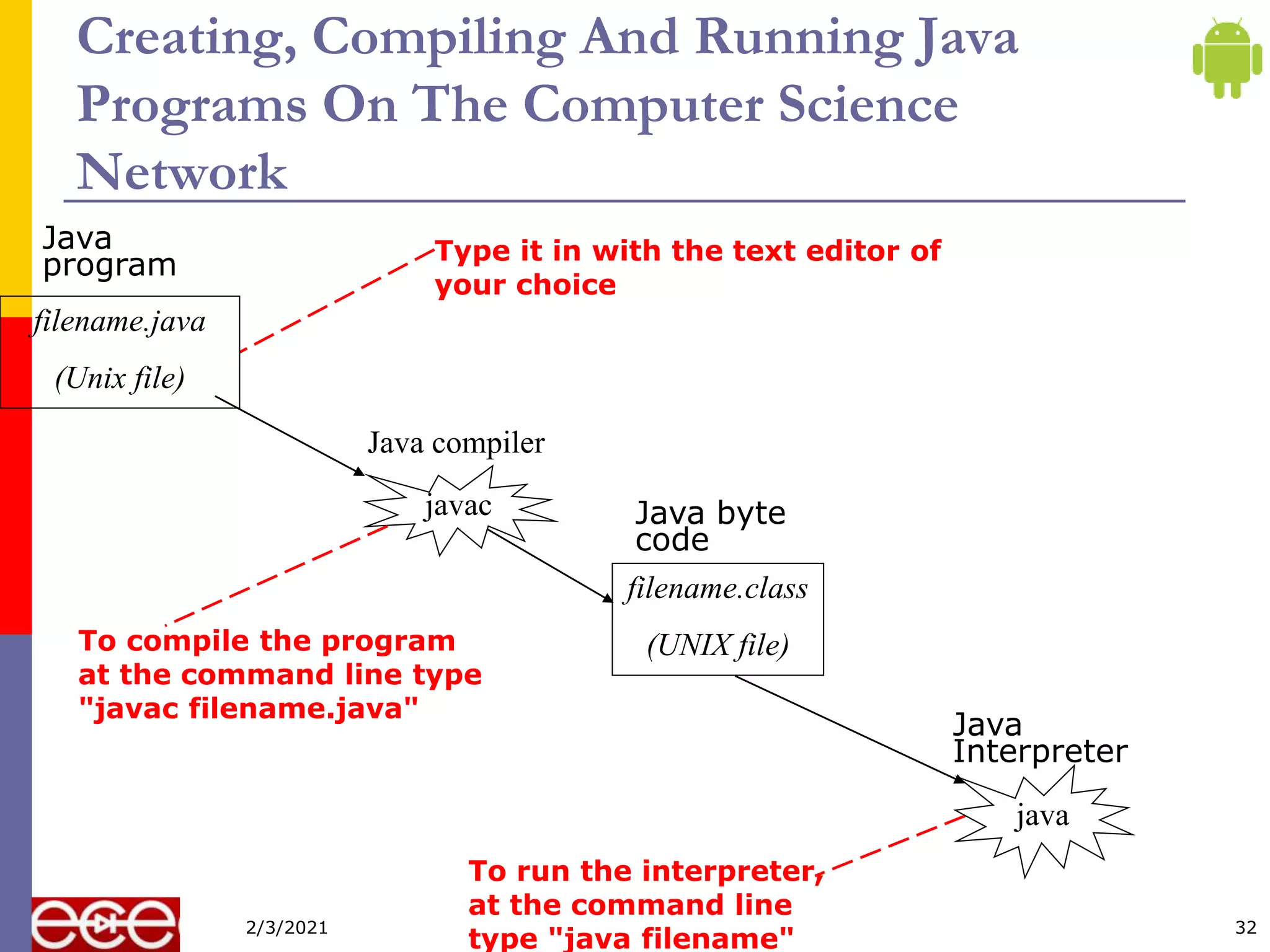
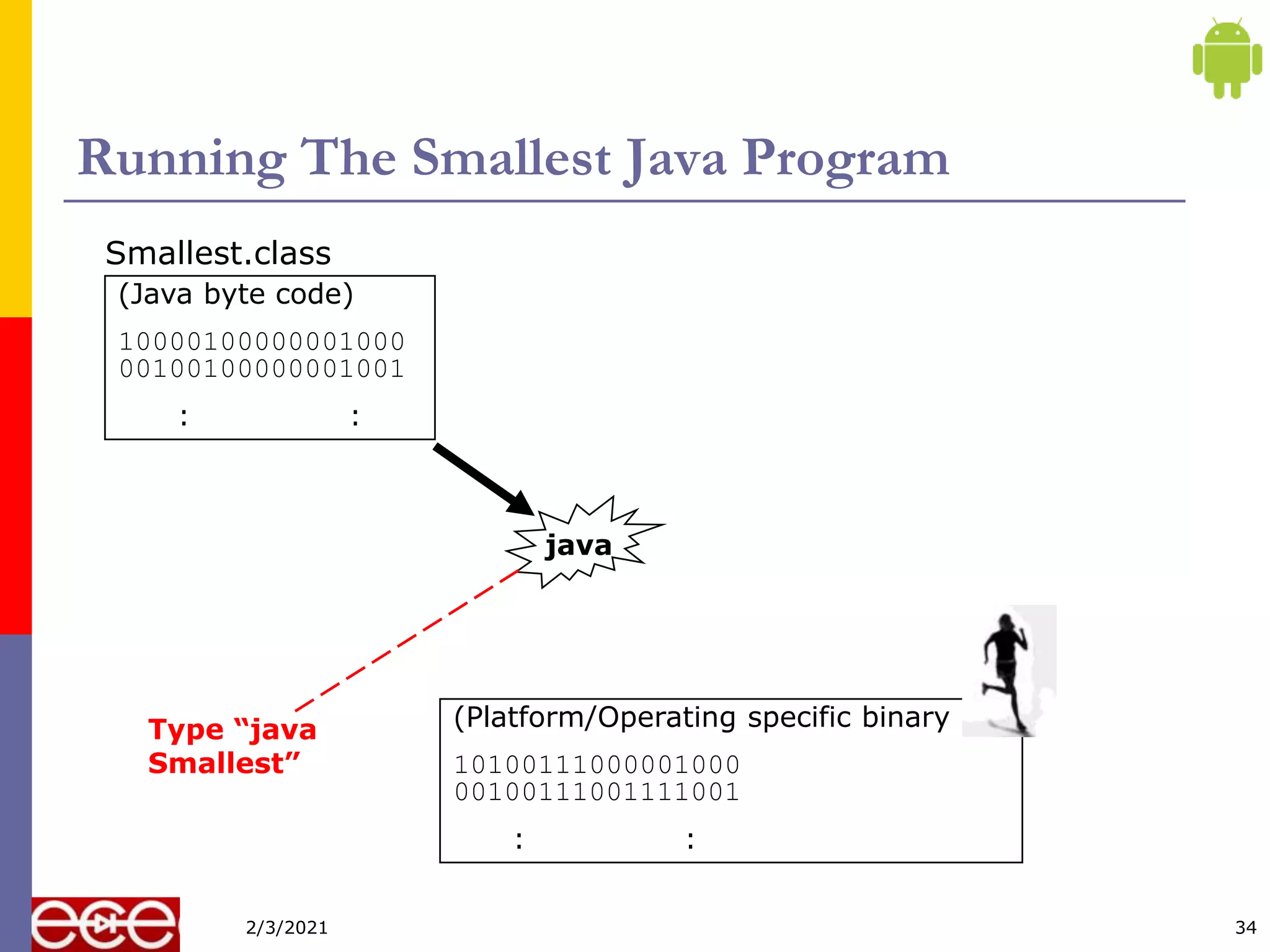
![Compiling The Smallest Java Program
public class Smallest
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
}
}
Smallest.java
javac
(Java byte code)
10000100000001000
00100100000001001
: :
Smallest.class
Type “javac
Smallest.java”
33
2/3/2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaintroduction-210203064244/75/Java-Programming-introduction-33-2048.jpg)