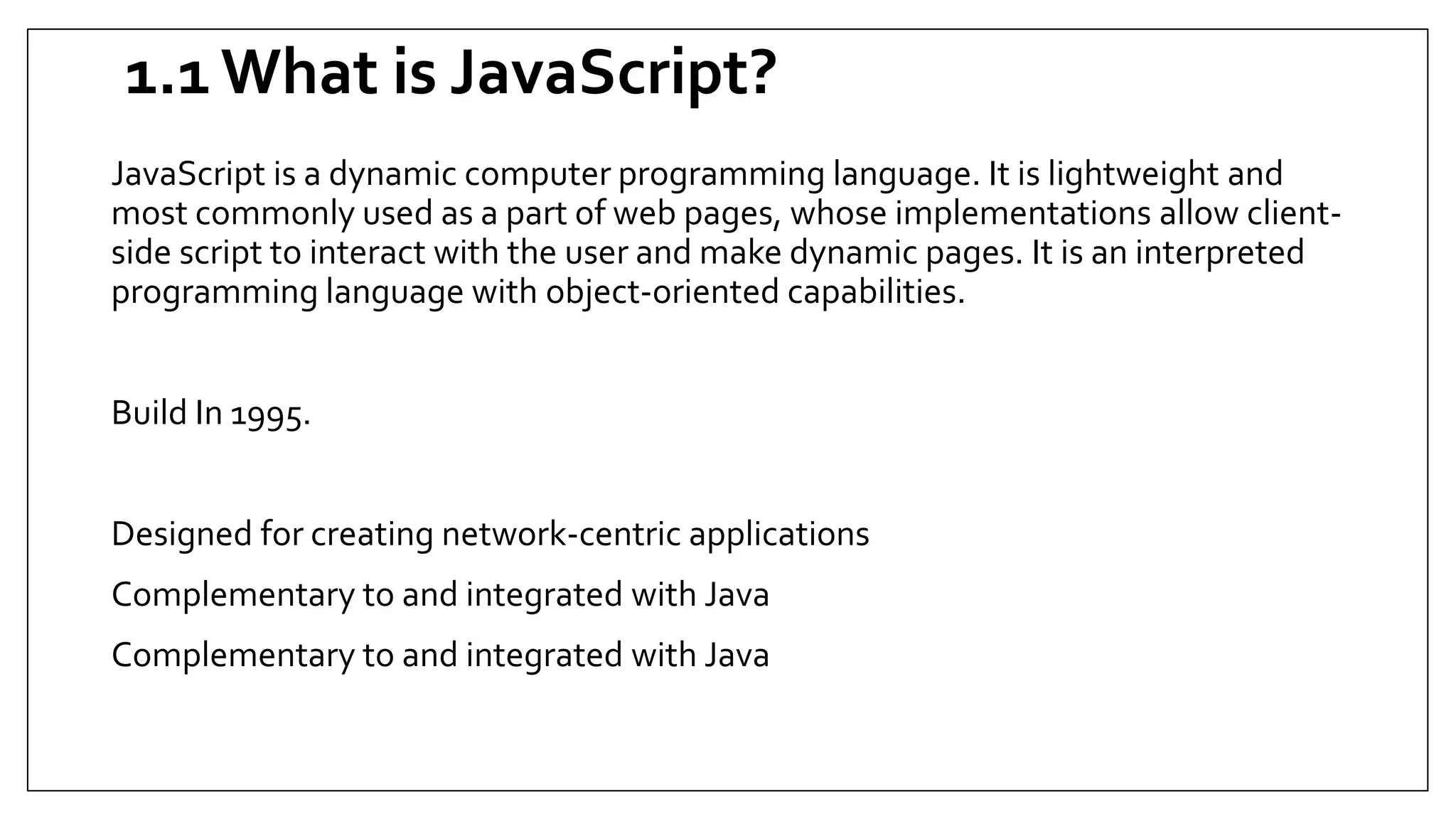
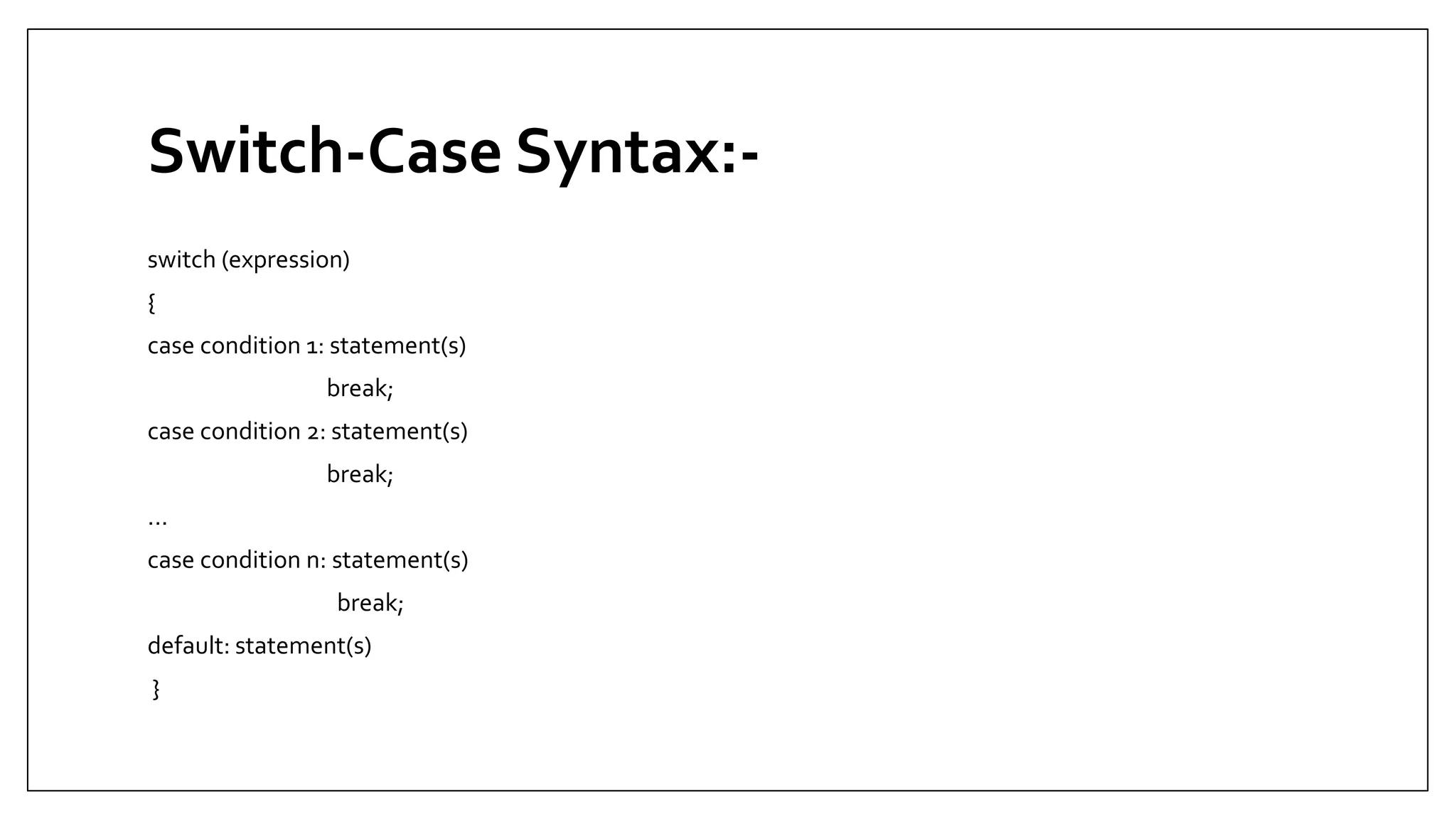
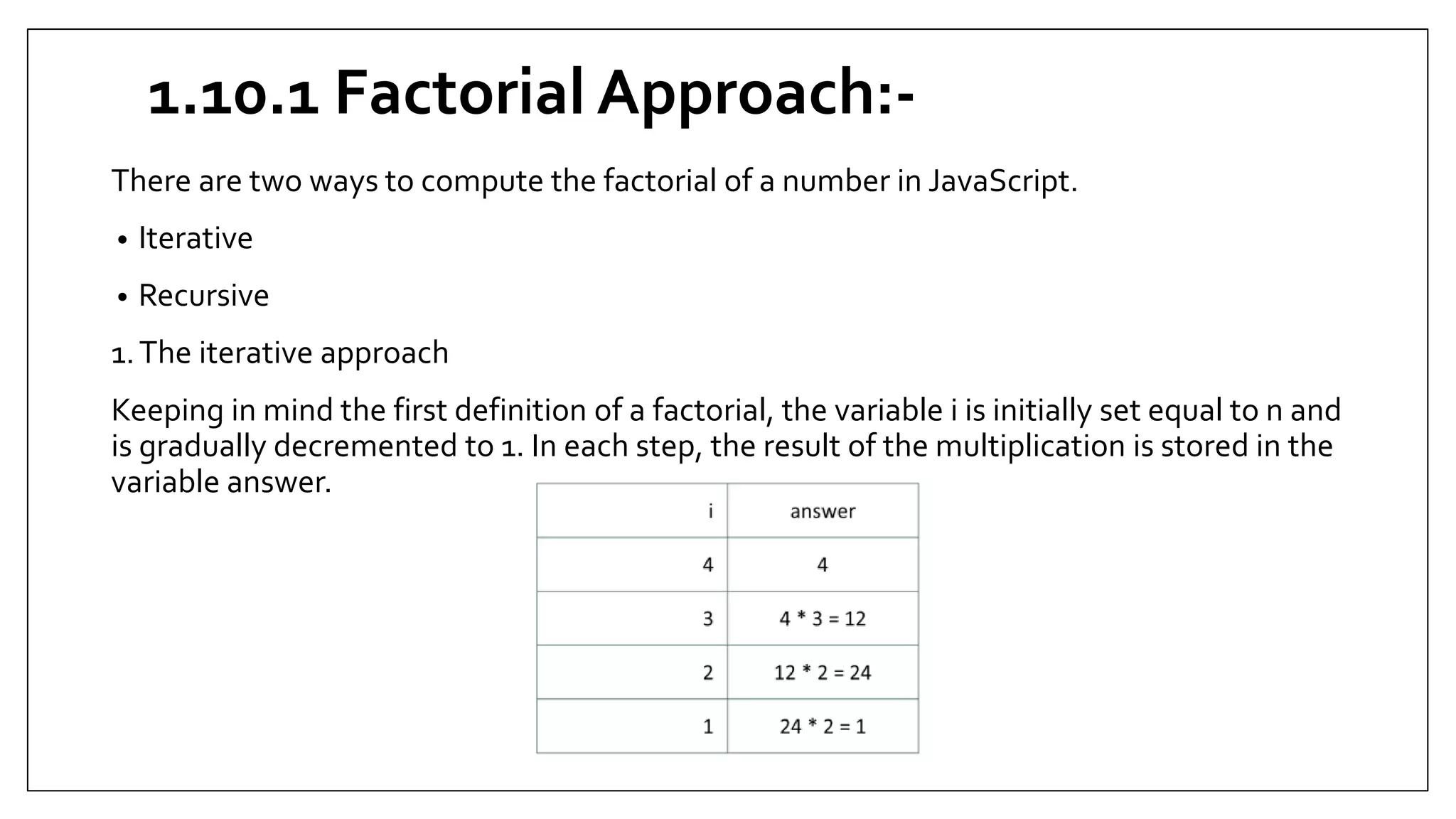
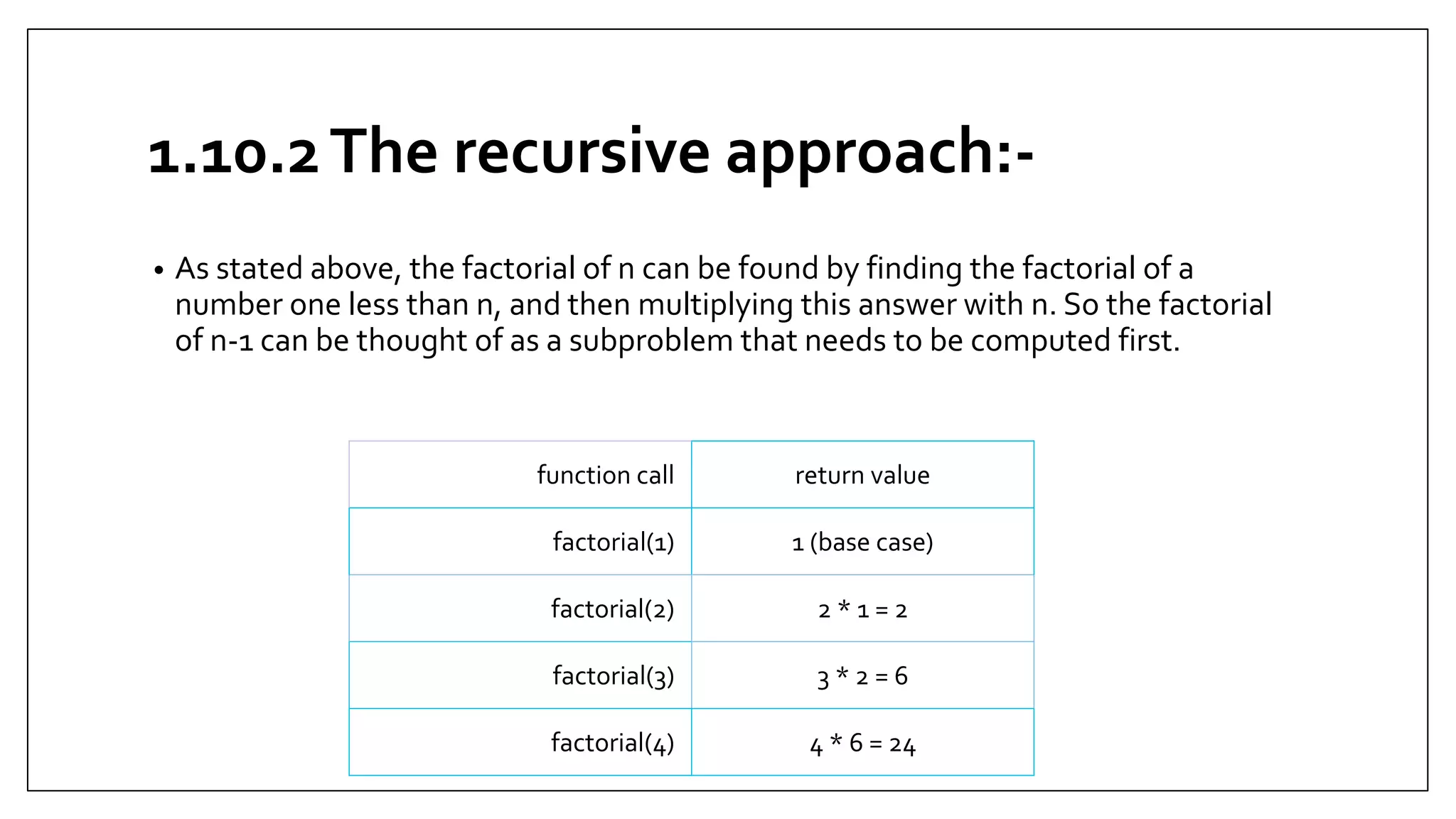
This document provides an overview of basic JavaScript concepts including variables, functions, conditional statements, loops and recursion. It includes code examples and assignments for each concept. The assignments demonstrate core JavaScript syntax and increase in complexity, covering if/else statements, switch cases, while/do-while/for loops, and recursive functions for calculating factorials and Fibonacci series. Later assignments involve more complex tasks like printing multiple patterns and combining different statements. The document serves as a learning guide for JavaScript fundamentals.



































![Assignment no:-15
• Fibonacci series:-
<script>
function fibonancci(n)
{
const arr = [1]
let current = 1;
let previous = 0;
if(n <= 1)
{
return arr
}
while(n>0)
{
current += previous
previous = current - previous
arr.push(current)
n-=1
}
return arr
}
console.log(fibonancci(10));
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasic-auroskills2-220124052804/75/Java-script-basic-auroskills-2-40-2048.jpg)
