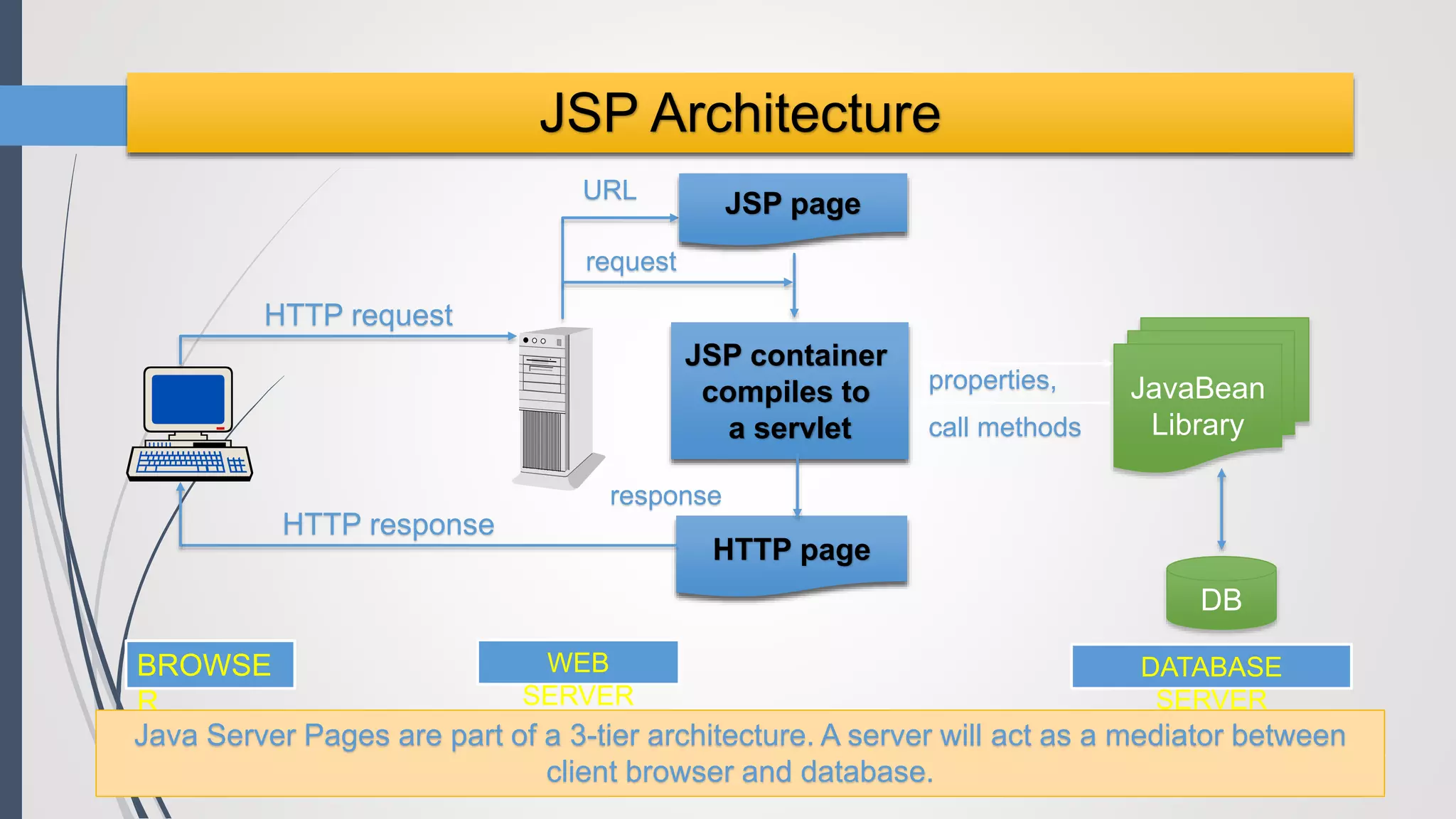
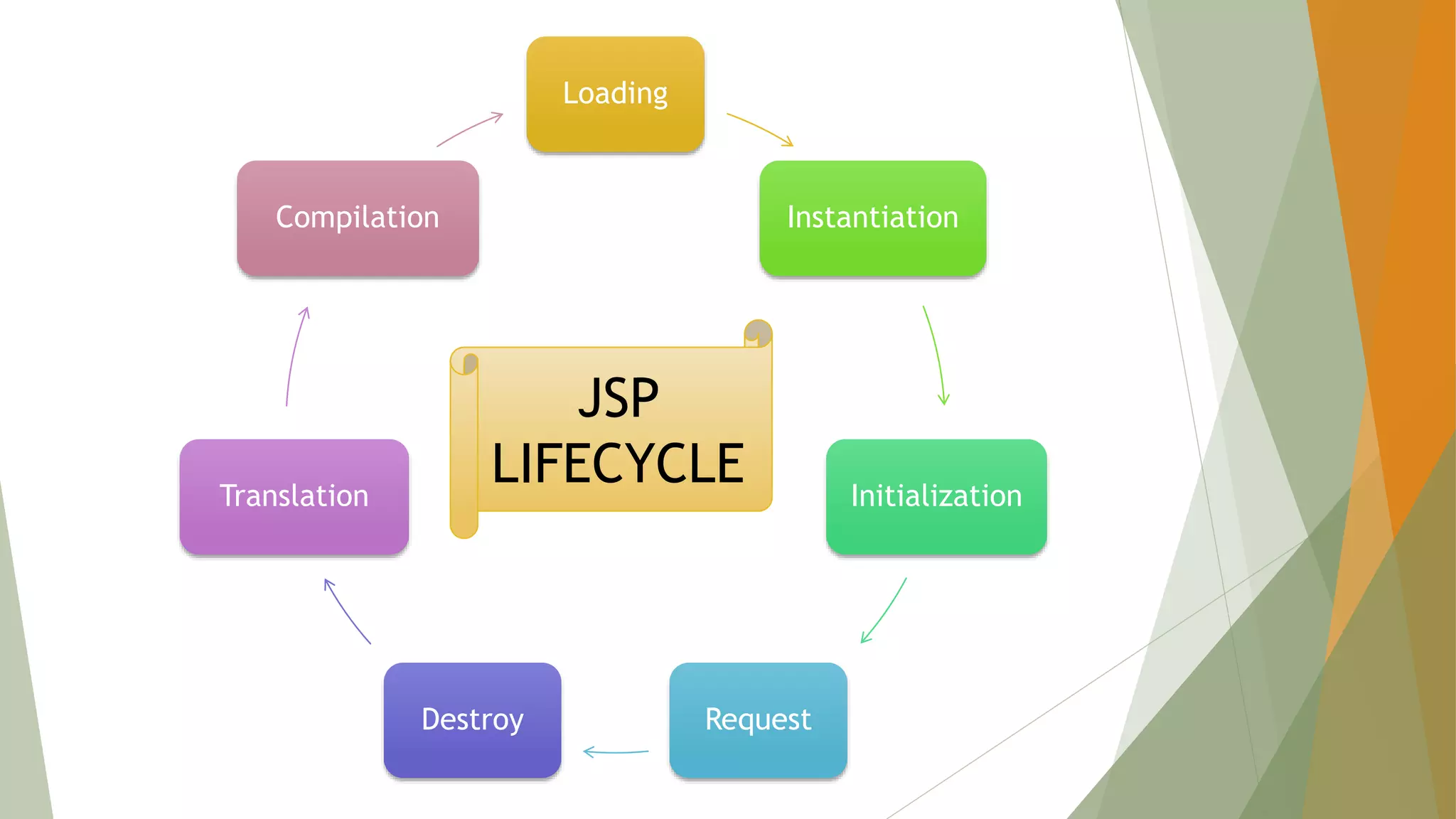
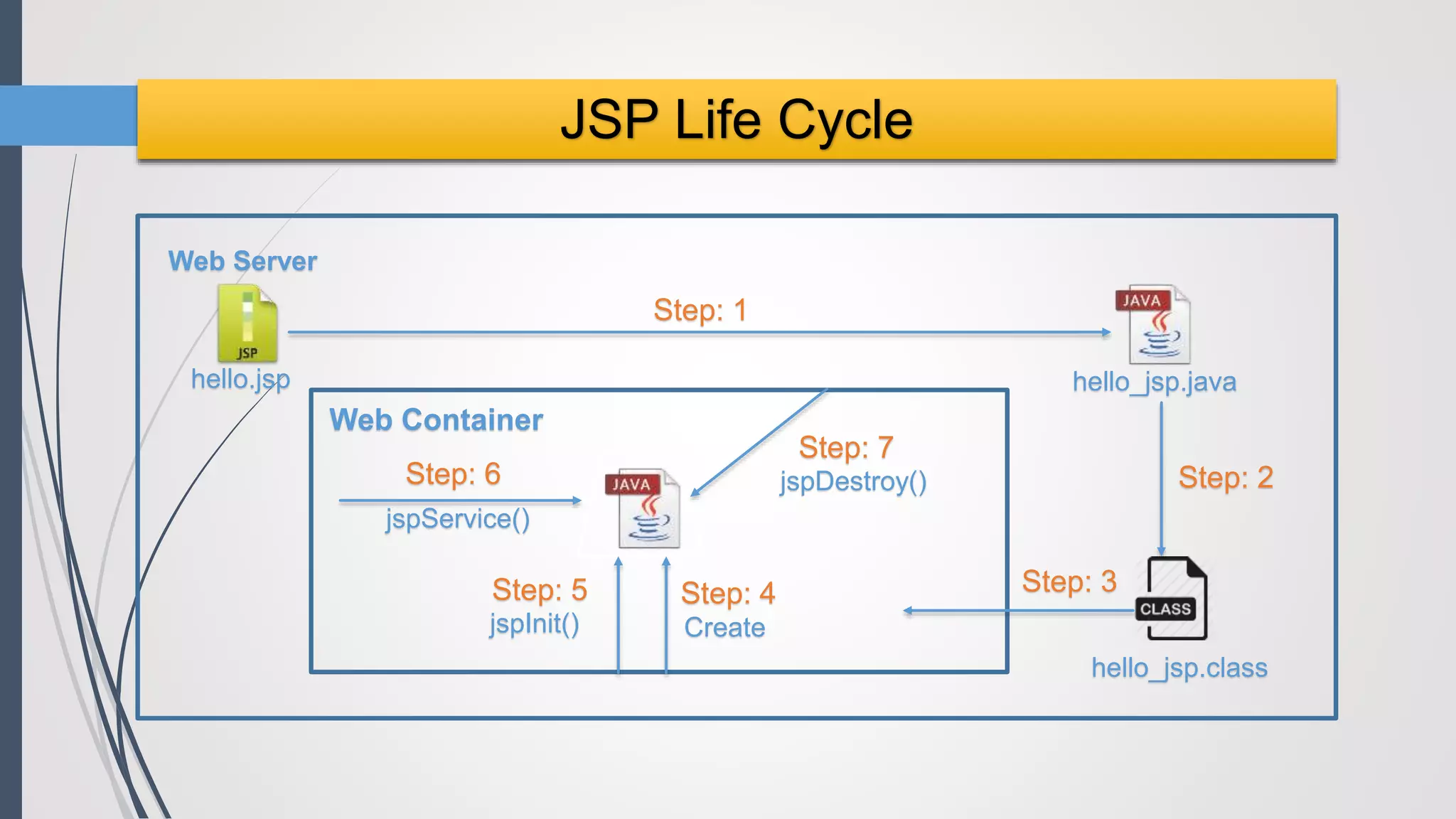
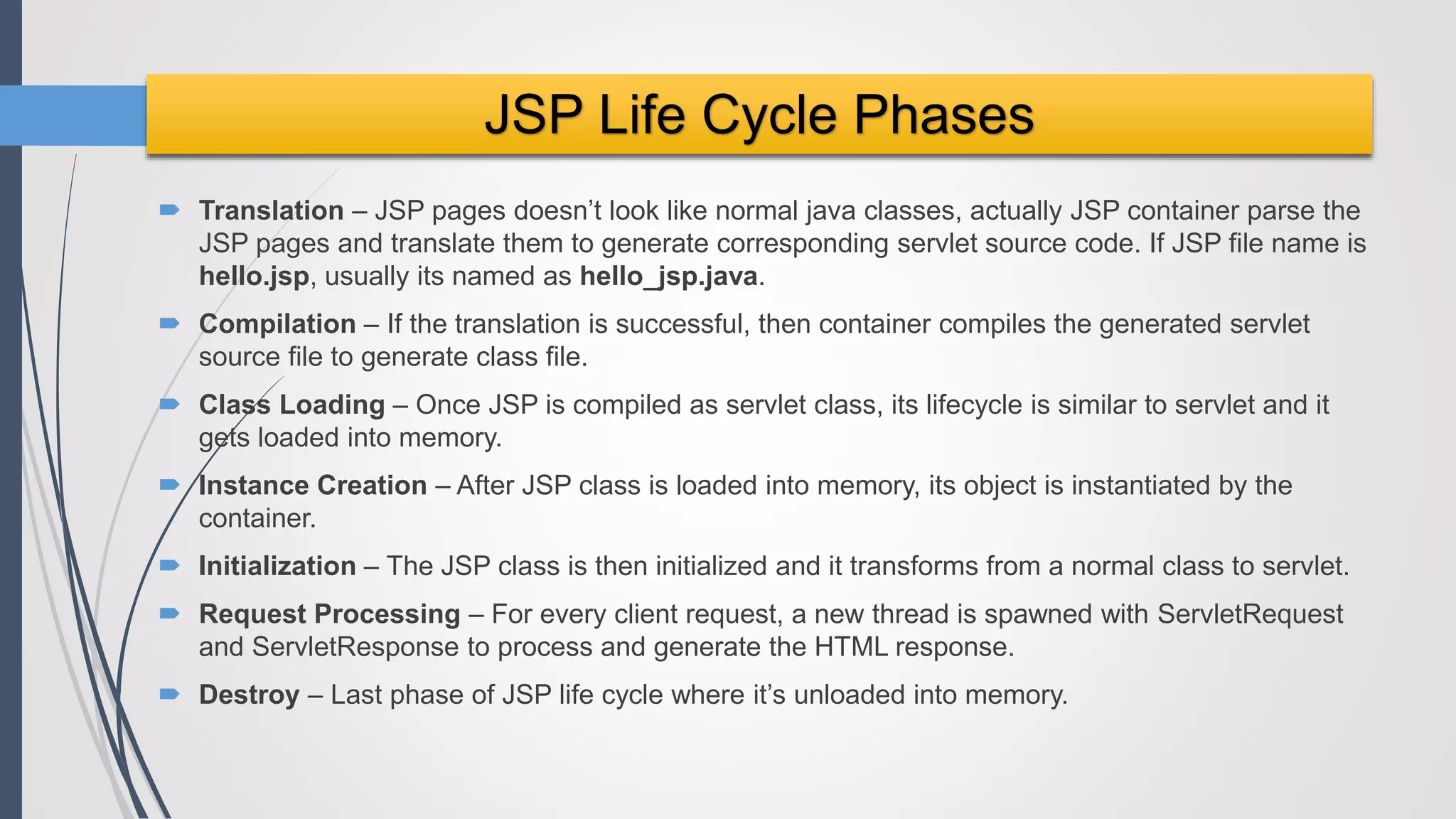
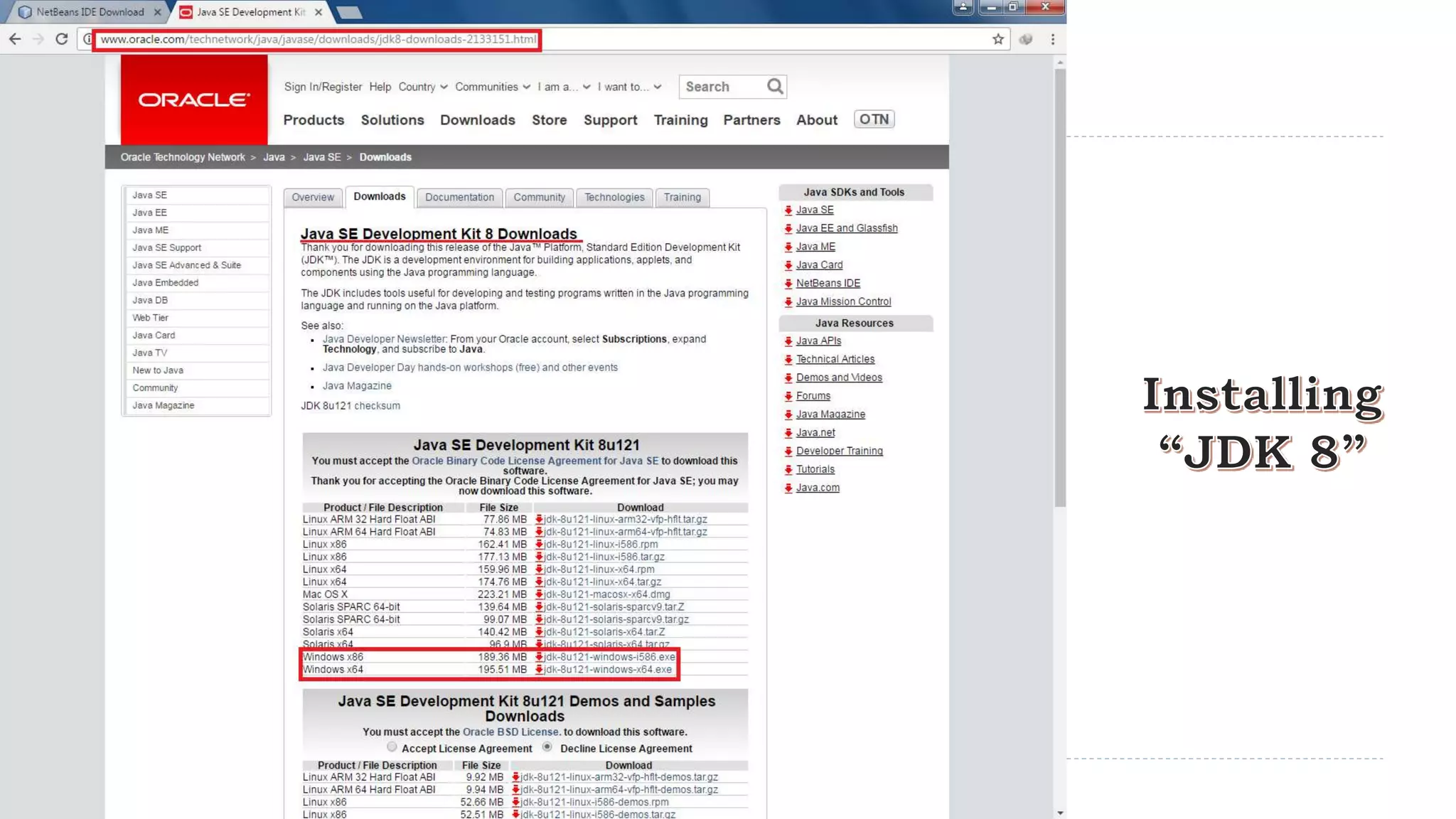
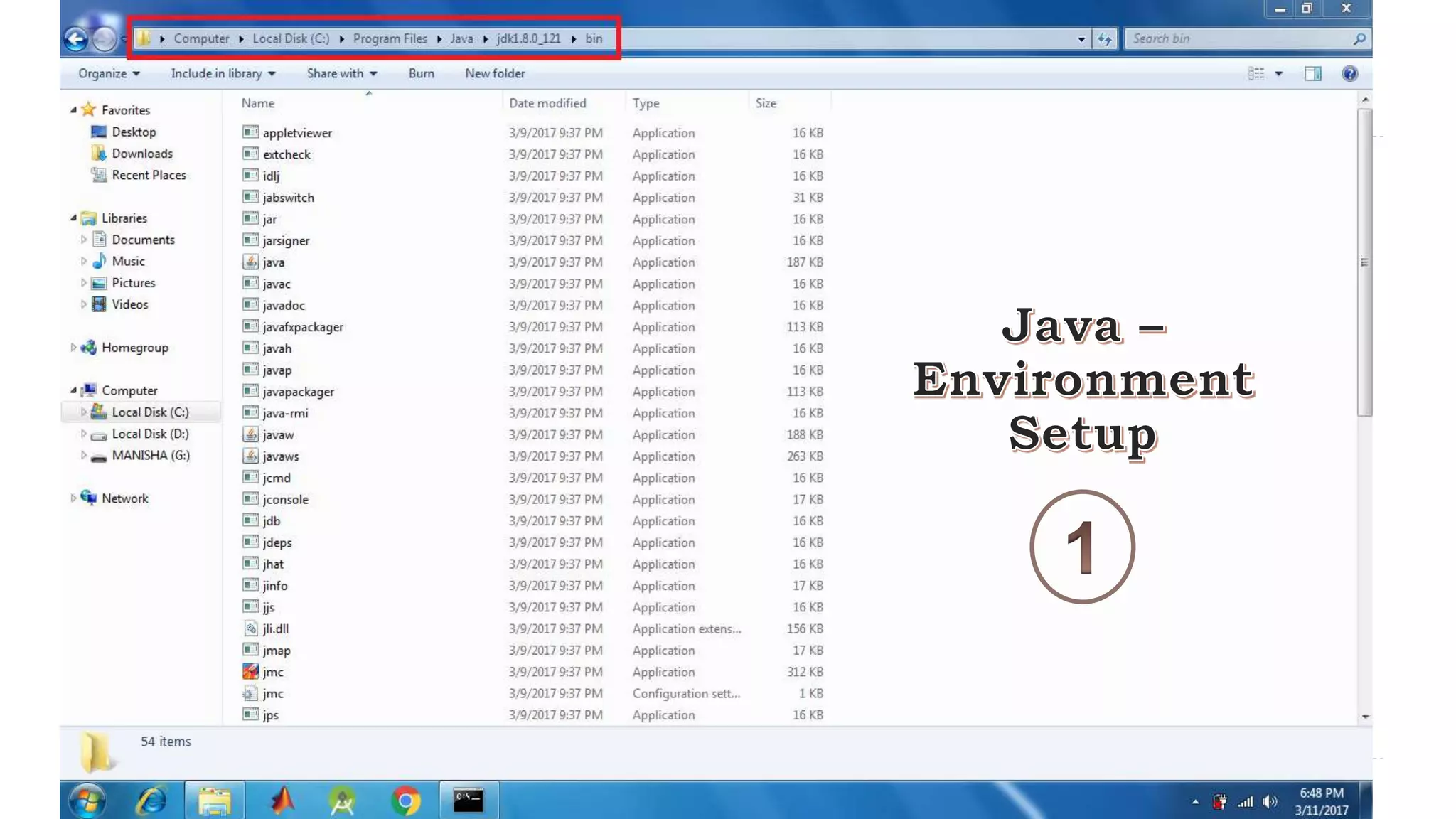
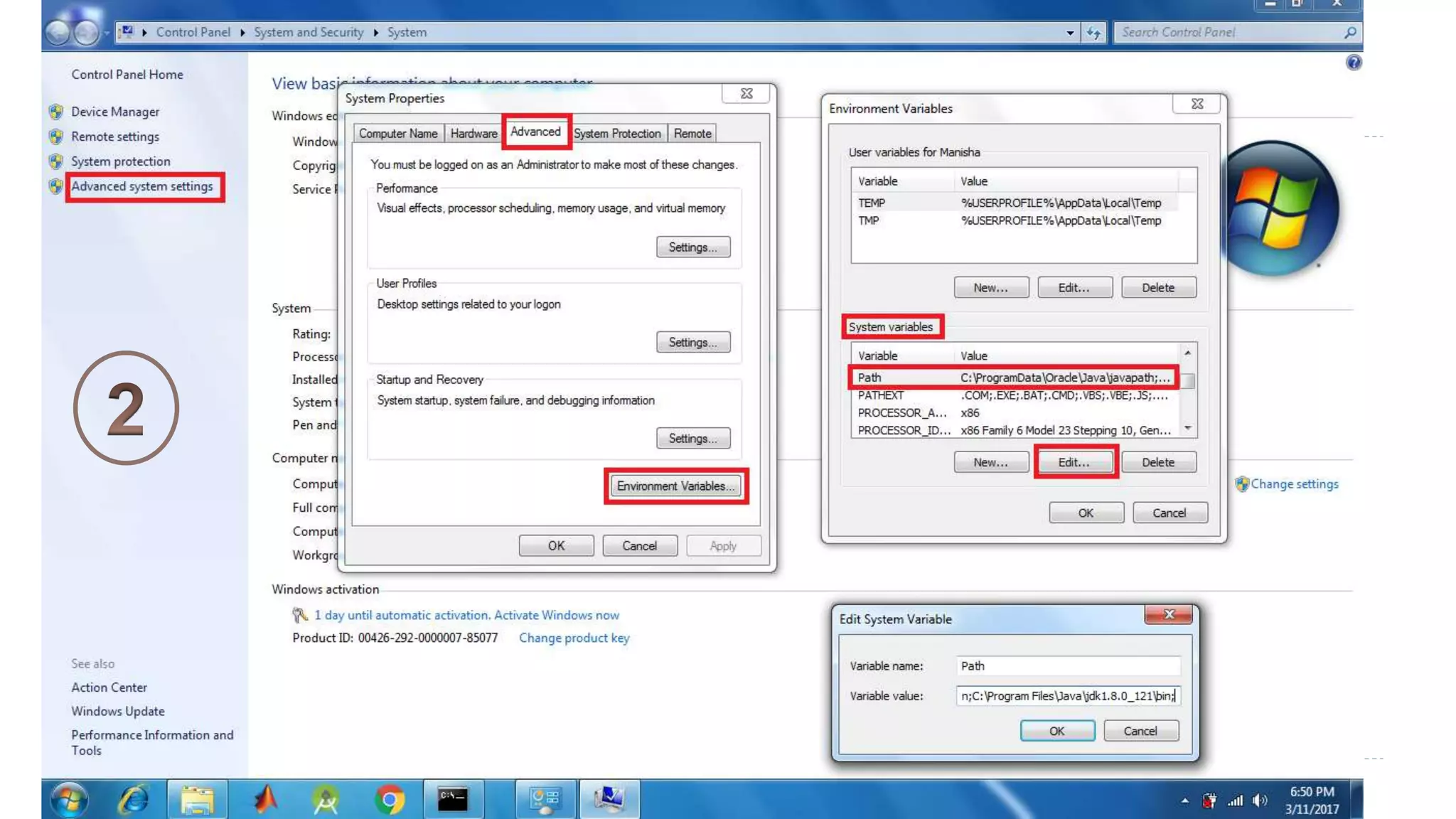
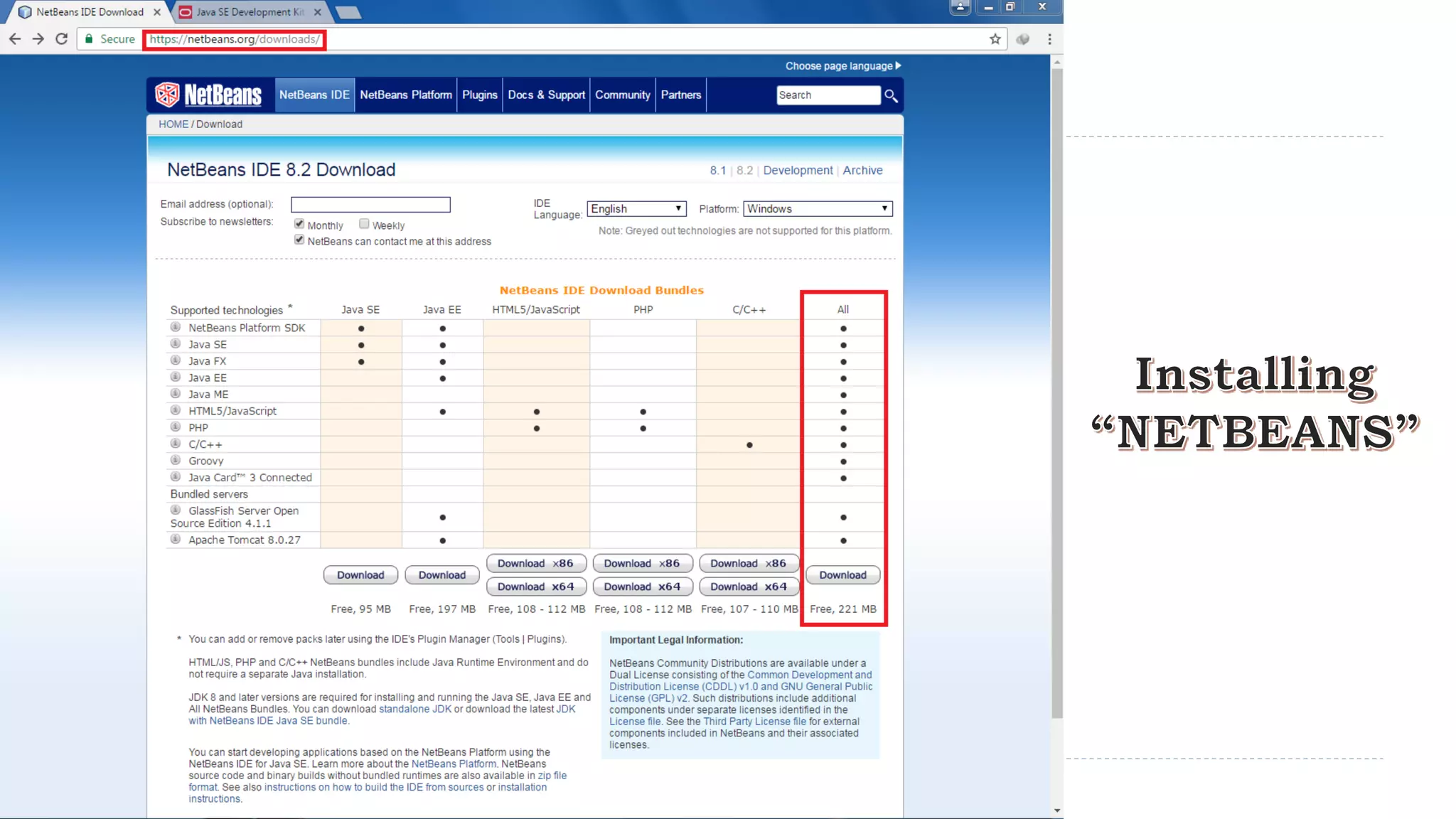
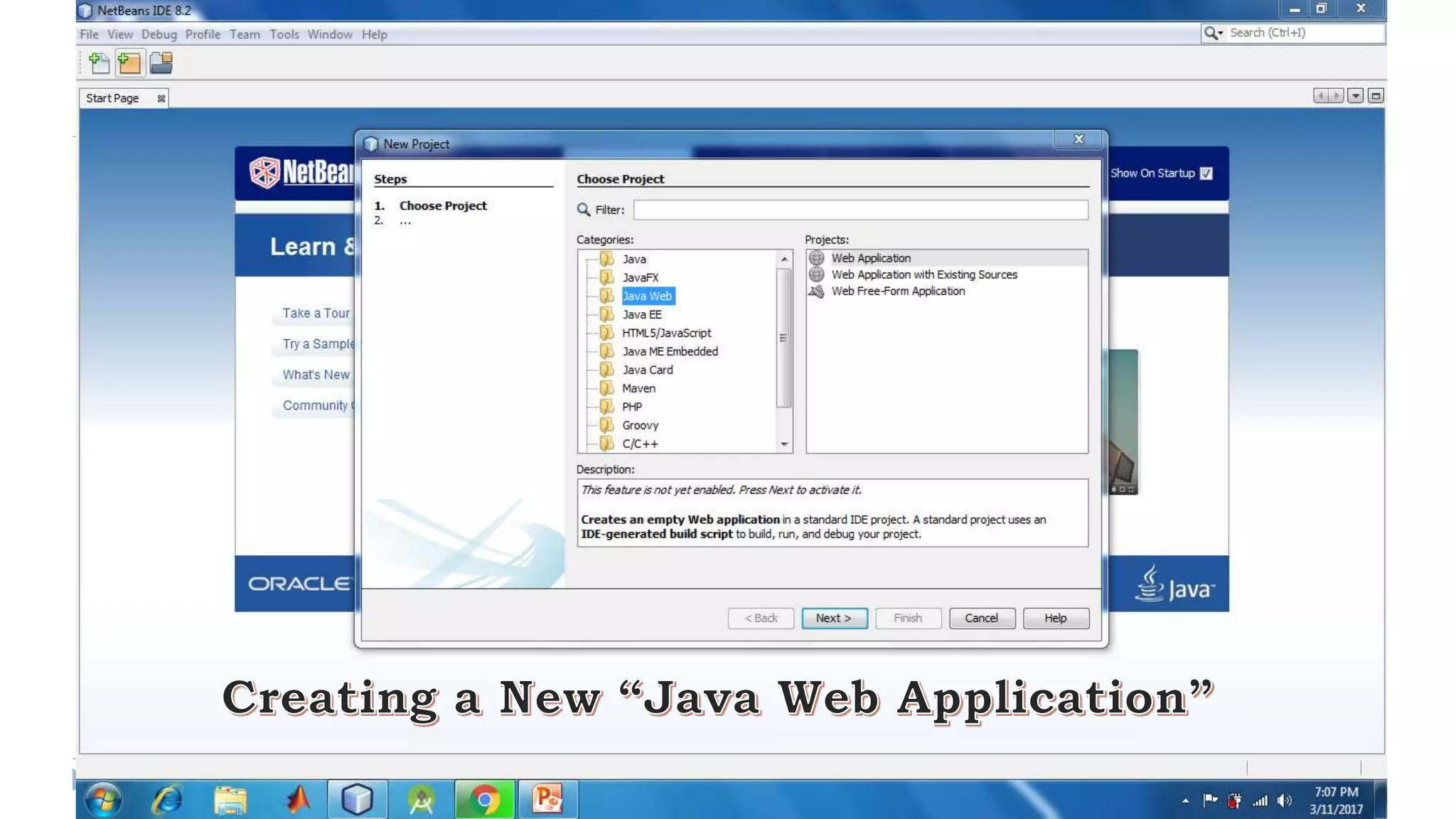
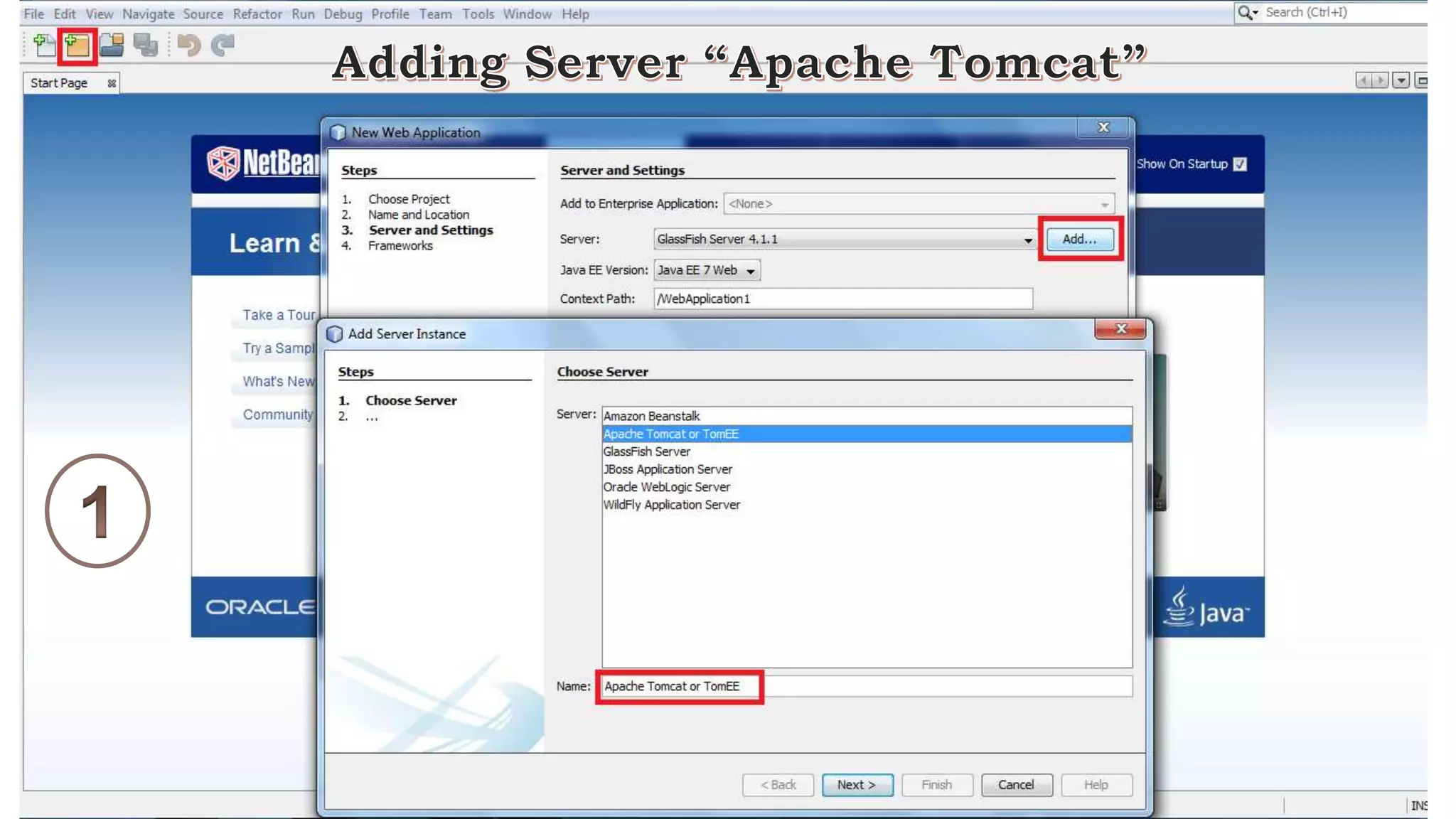
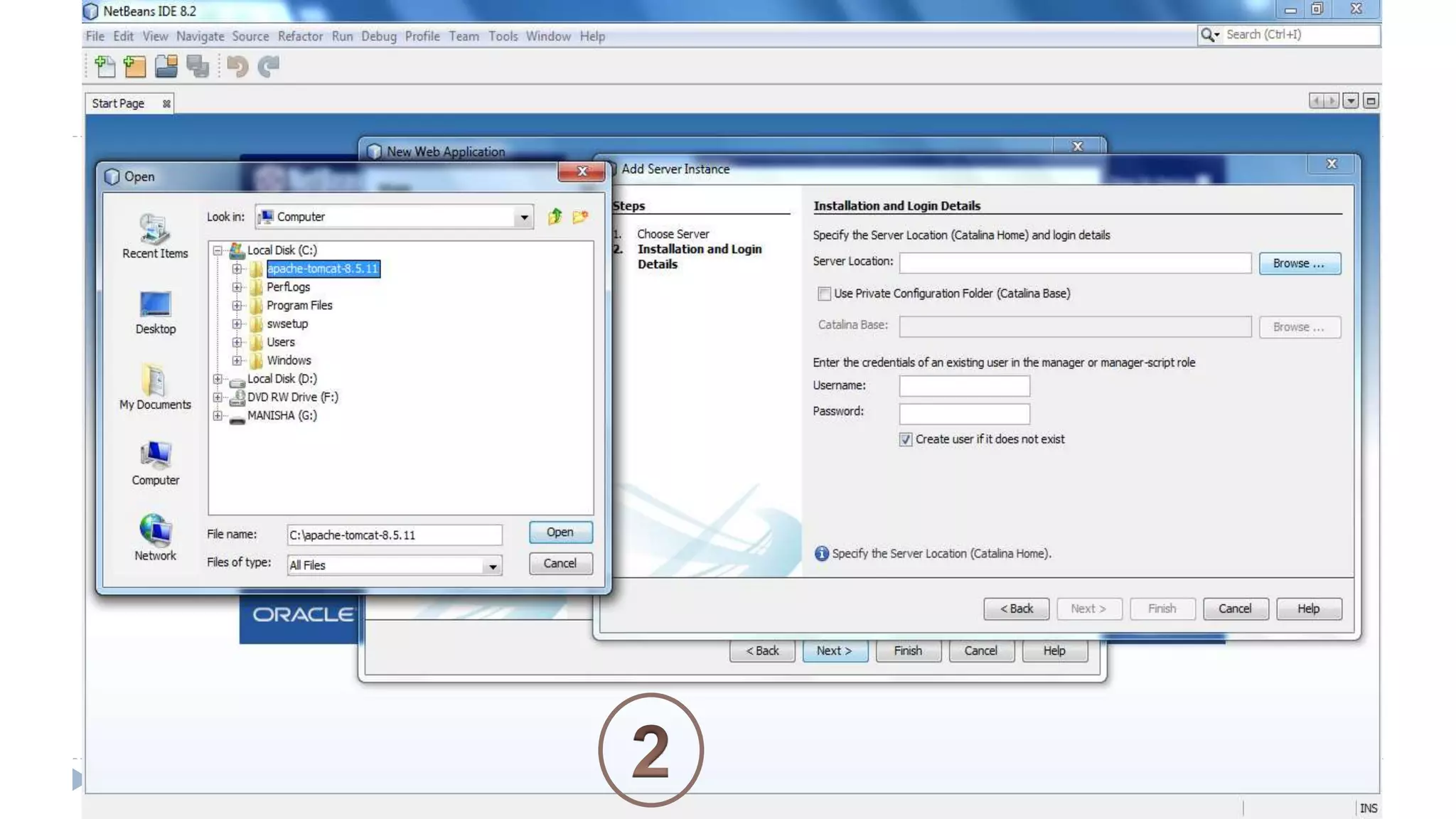
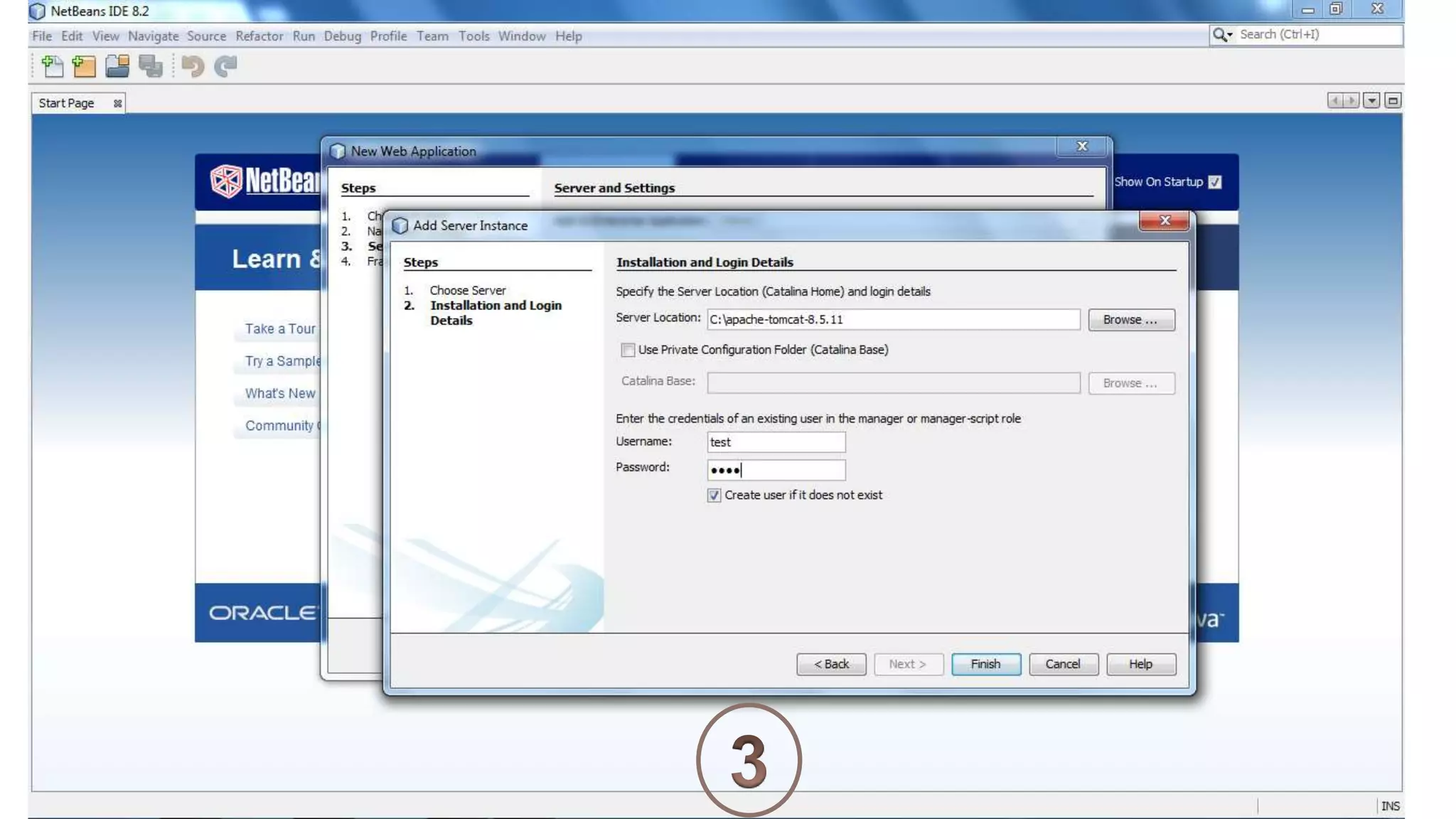
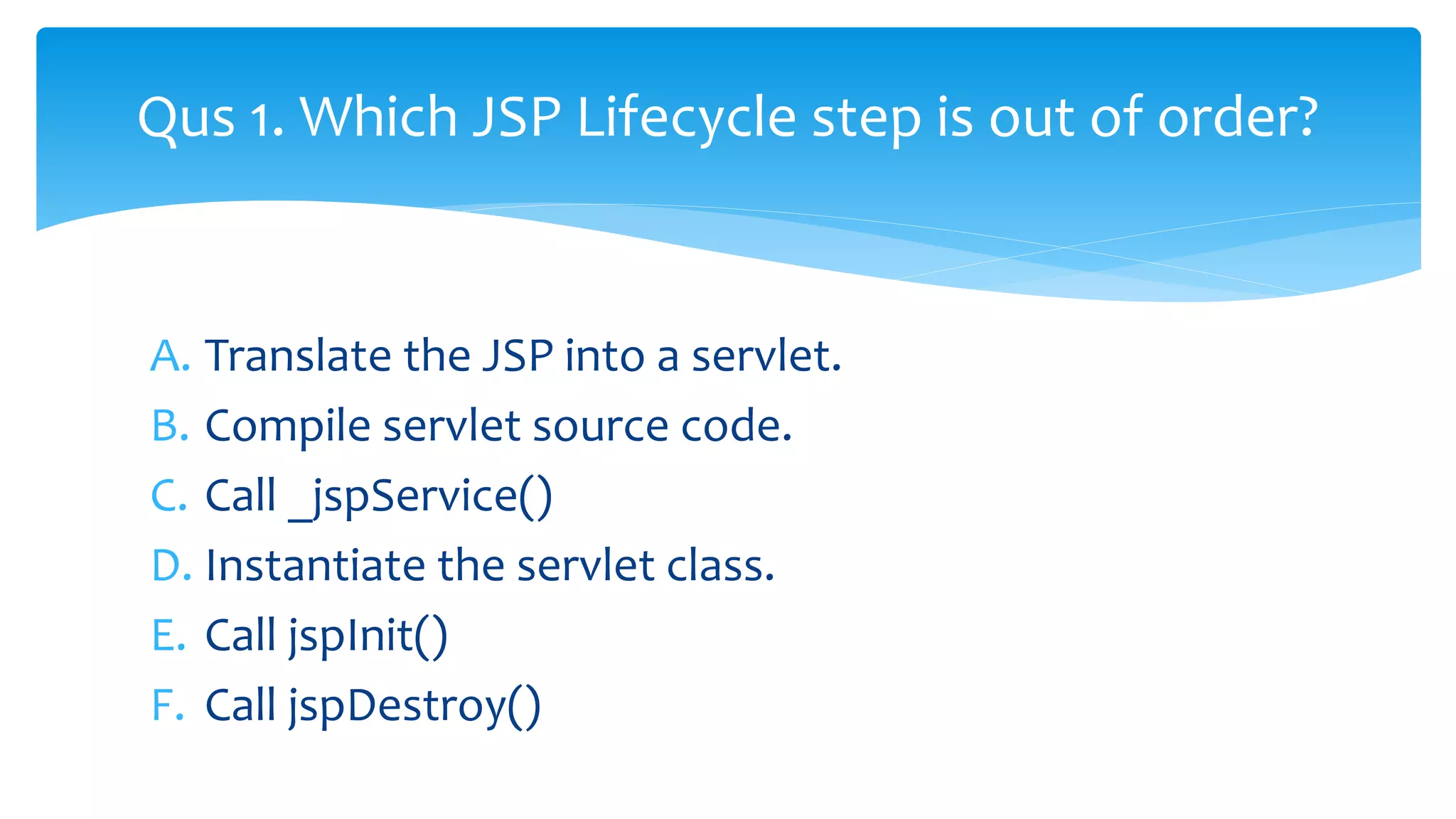
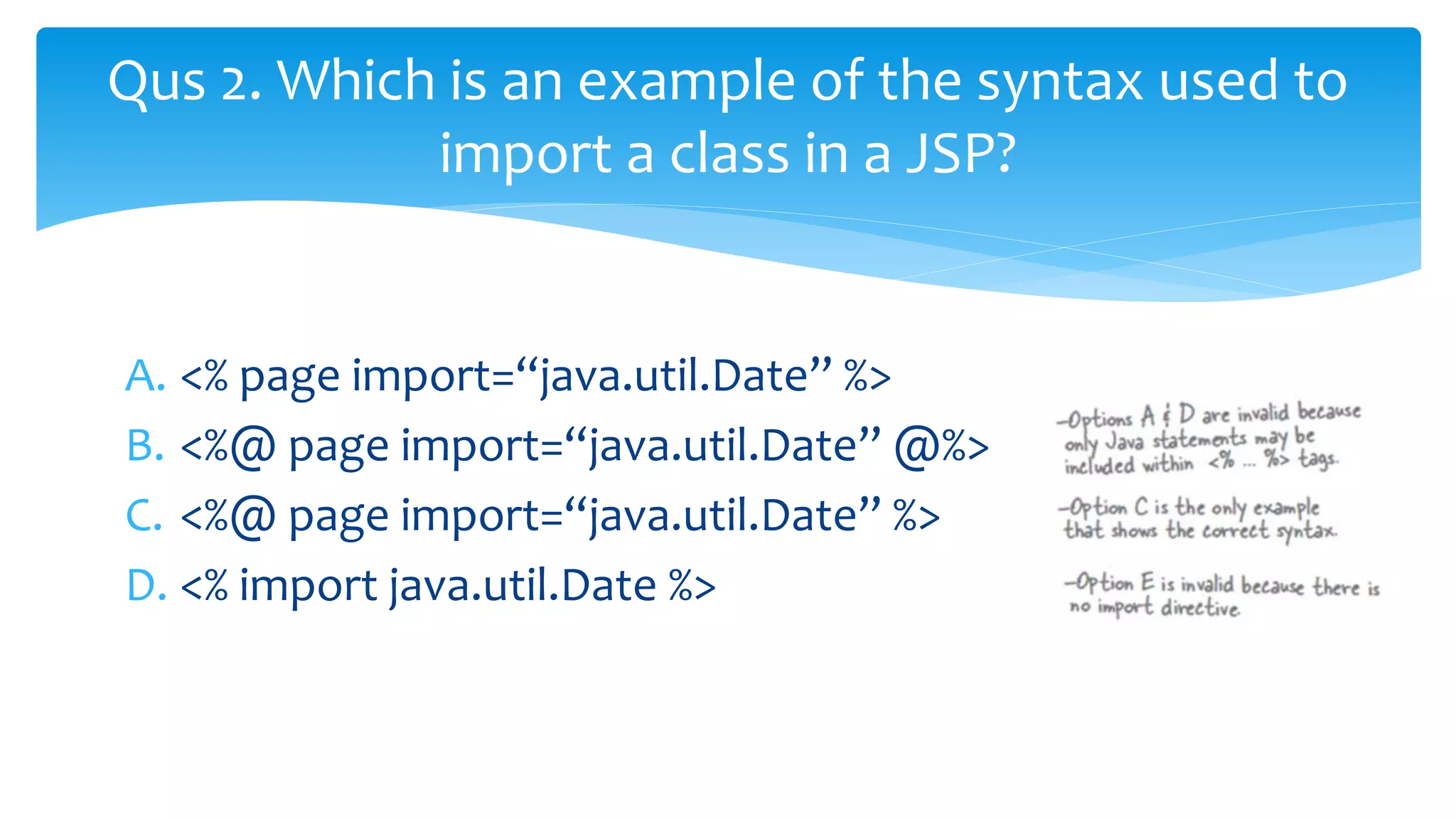
Java Server Pages (JSP) allow Java code to be embedded within HTML pages to create dynamic web content. JSP pages are translated into servlets by the web server. This involves compiling the JSP page into a Java servlet class that generates the HTML response. The servlet handles each request by executing the jspService() method and produces dynamic content which is returned to the client browser.