This document discusses new features in Java 8 including lambda expressions, default methods, streams, optionals, and date/time API improvements. It provides examples of using lambda expressions and streams to more concisely represent and process collections of data in a functional way. The document also discusses optionals as a way to safely handle potential null values without exceptions.




![Groovy Closure
def myConst = 5
def incByConst = { num -> num + myConst }
println incByConst(10) //==>15
myConst = 20
println incByConst(10) //==>30
def result=[]
(1..10).collect(result,{a->a*a})
result==[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-150724022512-lva1-app6891/75/Java8-and-Functional-Programming-5-2048.jpg)










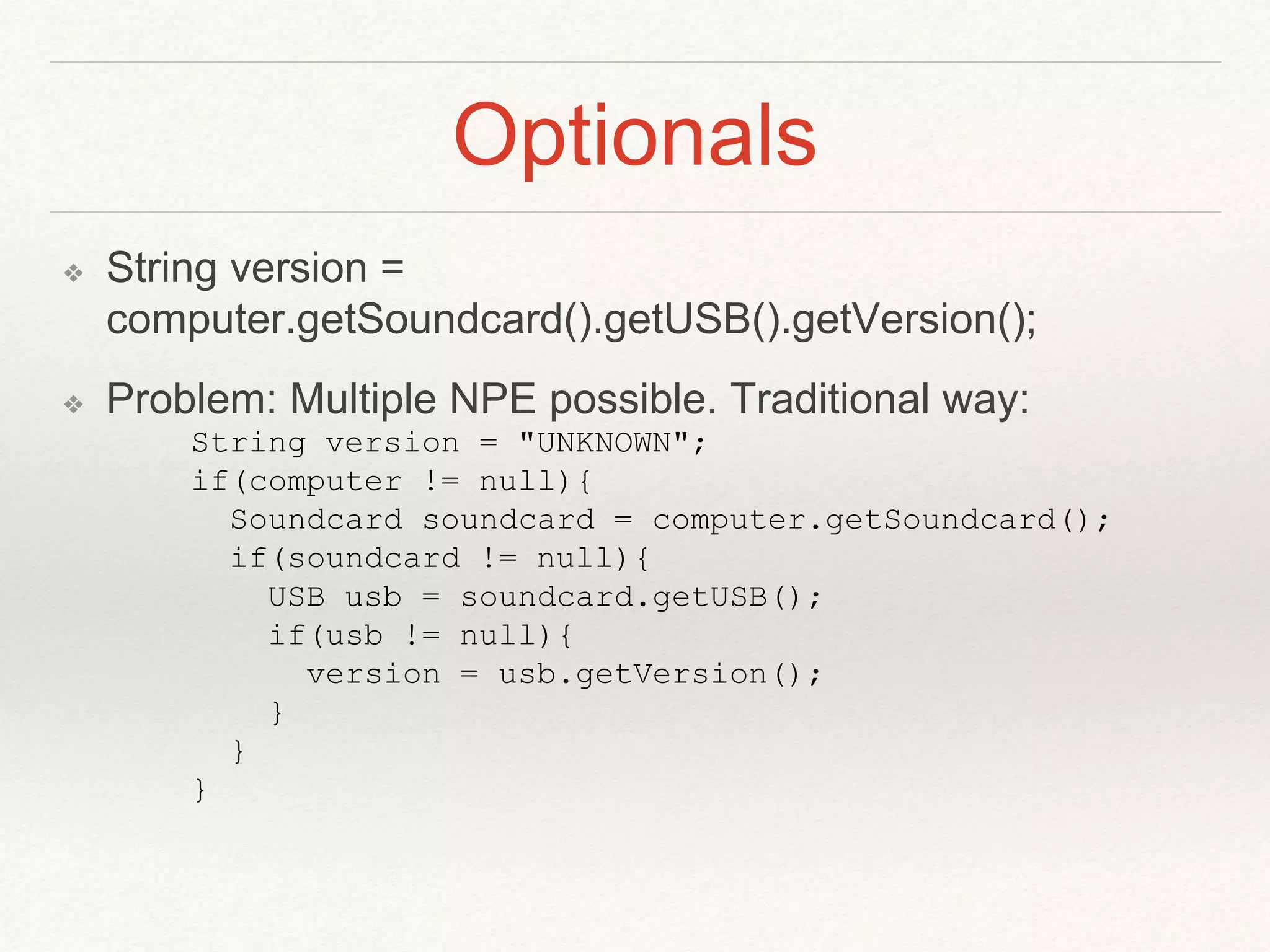



![Optionals
❖ how to model “absence of a value”
❖ Scala introduced Option[T]
❖ Java 8 call it Optional[T]
❖ Optional<String> version =
optcomputer.map(Computer::getSoundcard).map(Sound
Card::getUSB).map(USB::getVersion)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-150724022512-lva1-app6891/75/Java8-and-Functional-Programming-20-2048.jpg)
