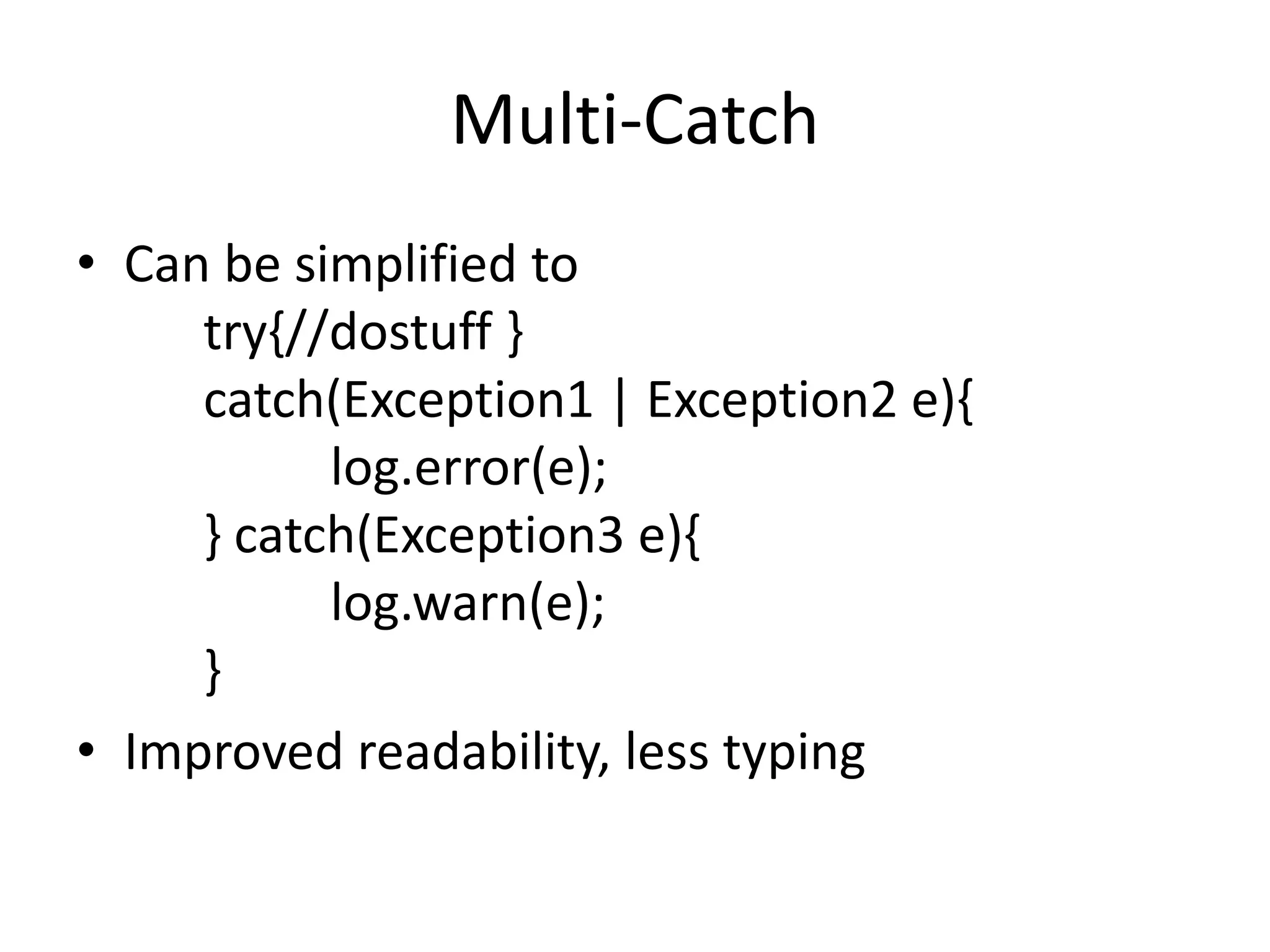
The document summarizes key points from the JavaOne 2011 conference. It discusses new features in Java SE 7 like underscores in numbers, strings in switch statements, and try-with-resources. It also covers upcoming features for Java 8/9 like modularity, closures, and Nashorn JavaScript support. The document notes enhancements to Java EE 7 including elasticity and multi-tenancy. It provides a demo of these features in Glassfish 4.