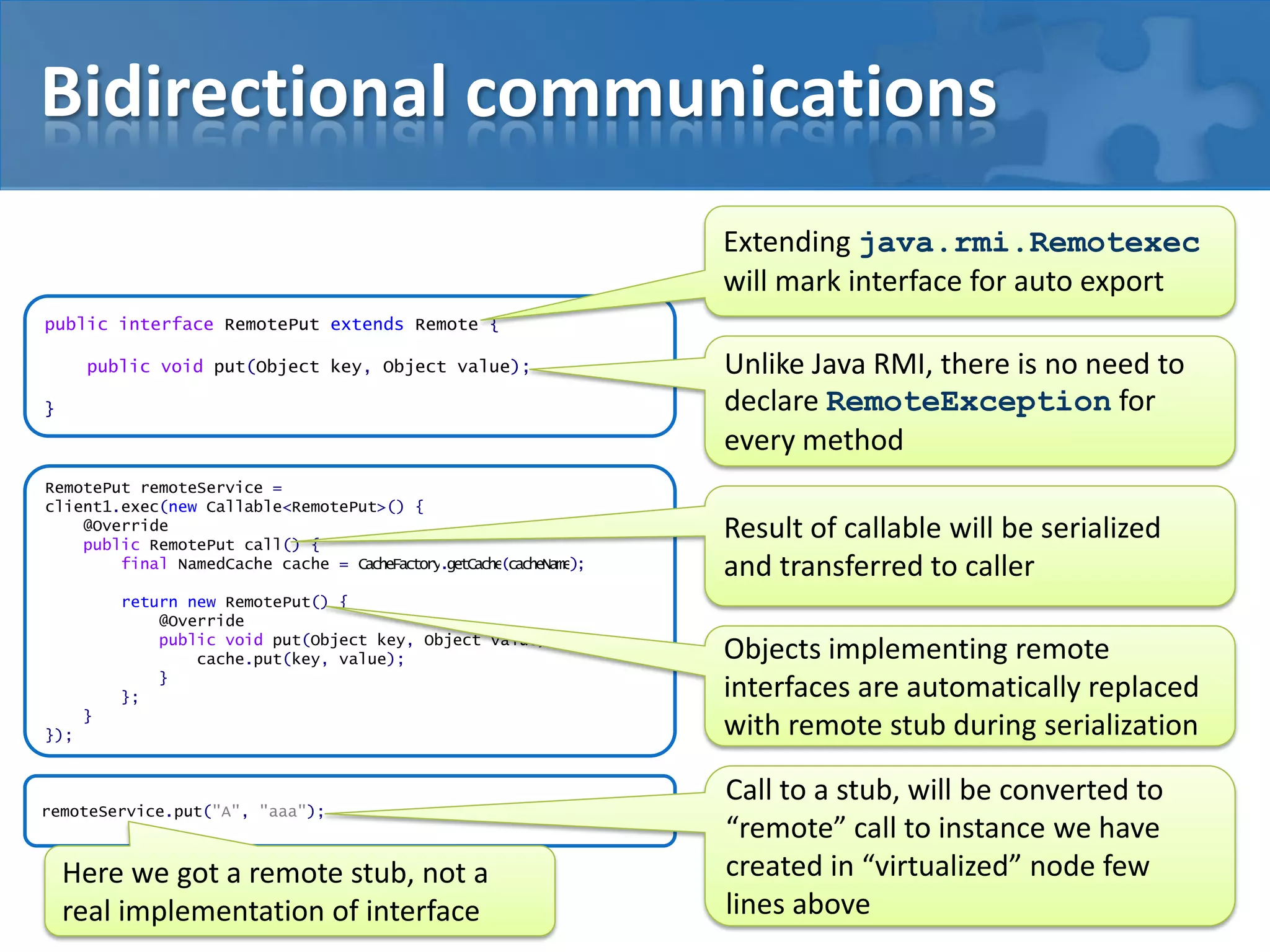
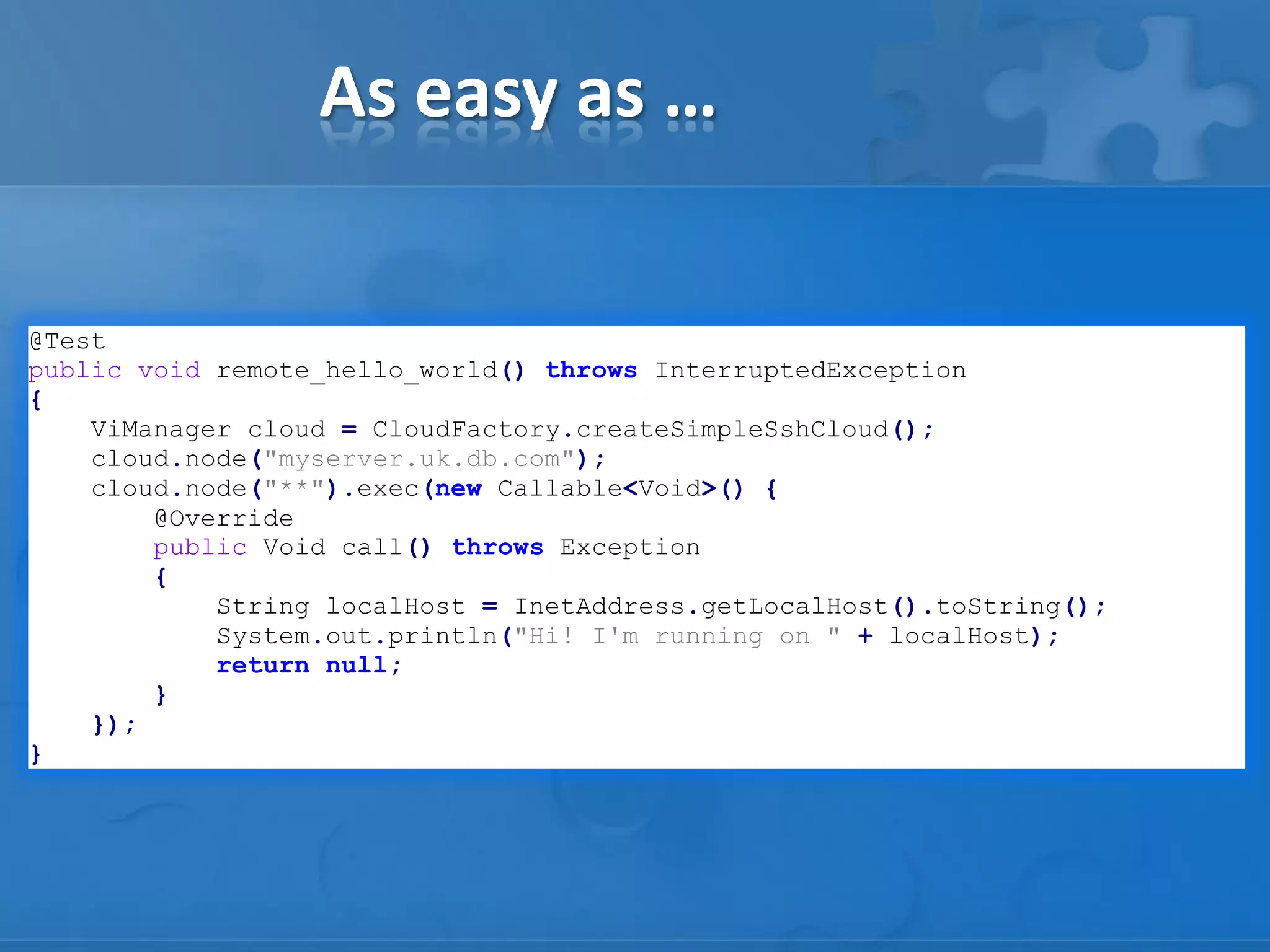
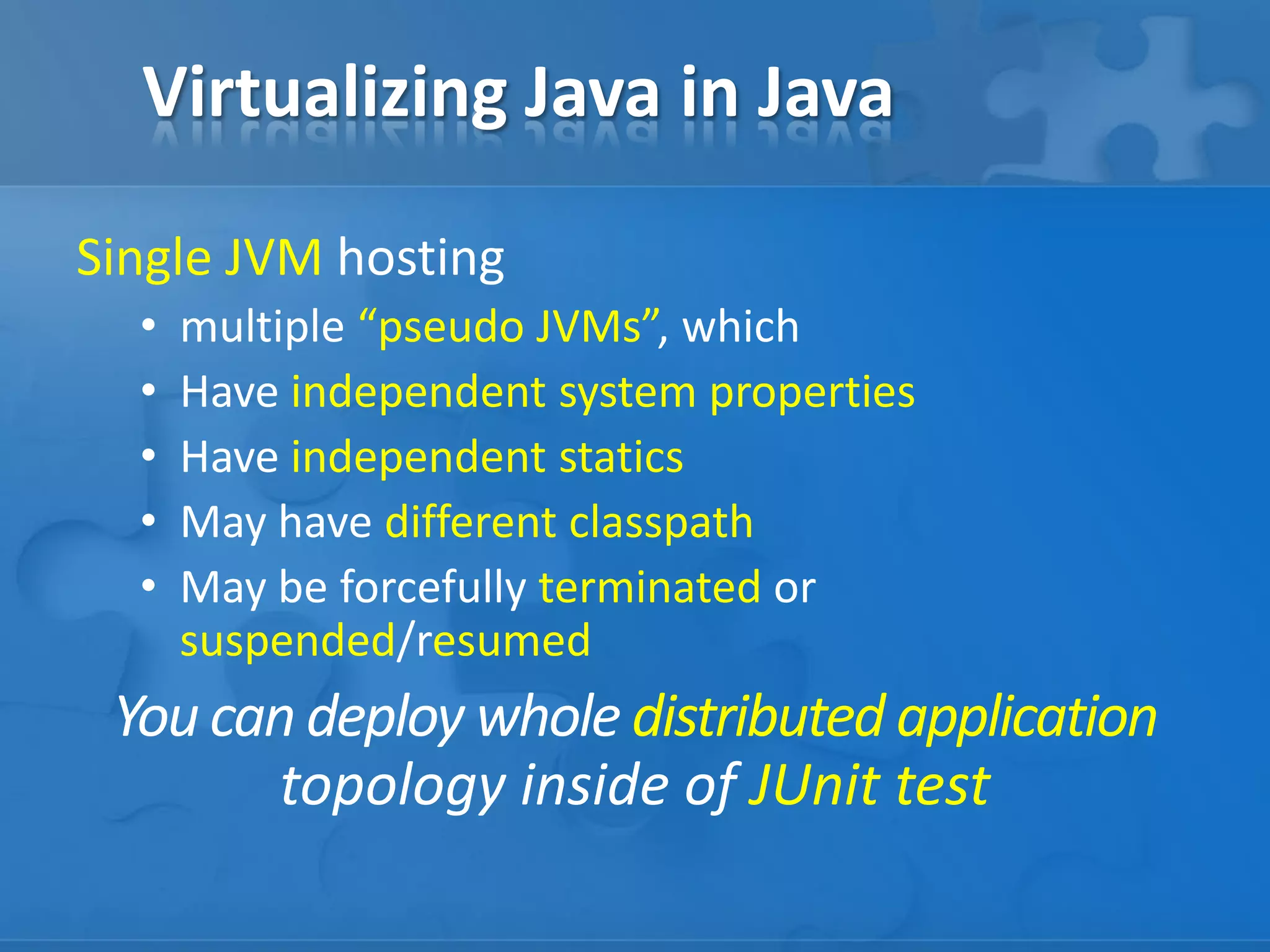
This document describes how to virtualize Java applications in Java by hosting multiple "pseudo JVMs" within a single JVM. This allows deploying distributed applications for testing purposes. Key points covered include:
- Using custom classloaders and system properties to isolate "pseudo JVMs" and simulate distributed environments.
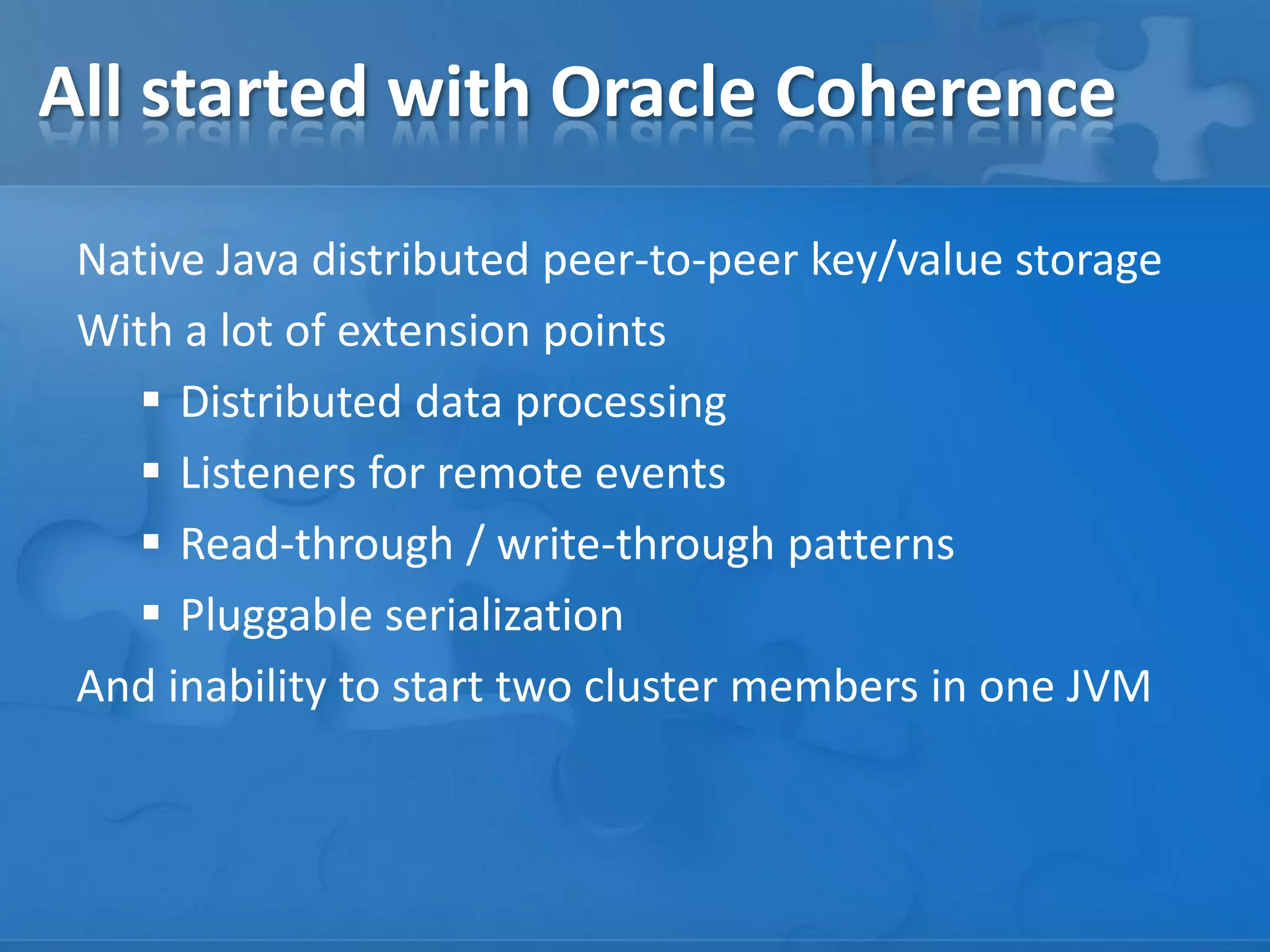
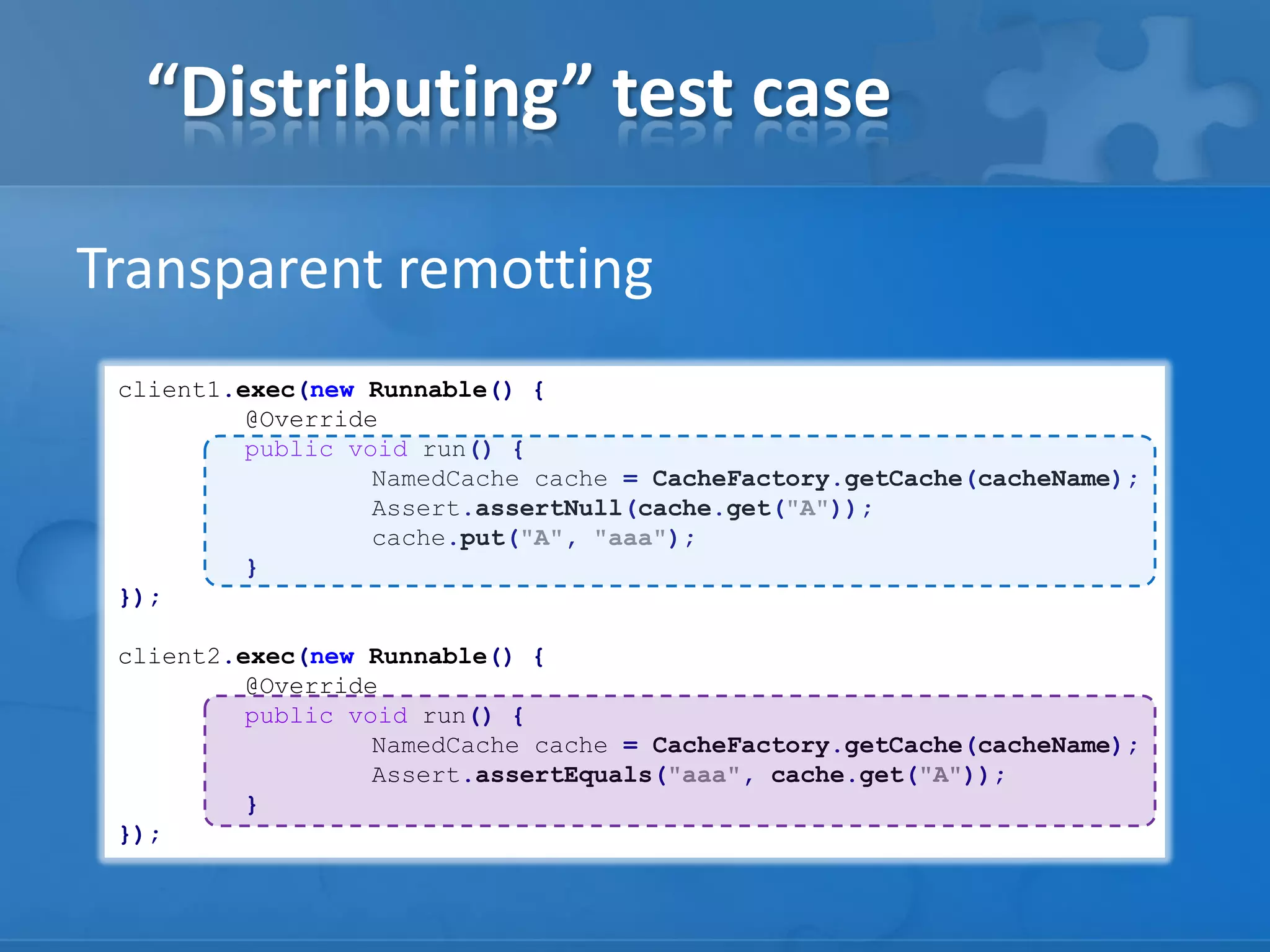
- Frameworks like GridKit that enable starting whole application topologies within JUnit tests for behaviors testing.
- Techniques for testing features like serialization, data routing, and cross-version compatibility.
- Later extensions to deploy virtual nodes across real servers using SSH for performance and deployment testing of distributed systems.







![Backward compatibility testing
Master JVM, client regression test pack
[trunk version]
Case
Client
[version X]
Server
[trunk version]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualizingjavainjava-131215015058-phpapp01/75/Virtualizing-Java-in-Java-jug-ru-11-2048.jpg)
![Cross version tests
Master JVM, client regression test pack
[trunk version]
Case
Client
[version X]
Client
[version Y]
Server
[version Z]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualizingjavainjava-131215015058-phpapp01/75/Virtualizing-Java-in-Java-jug-ru-12-2048.jpg)