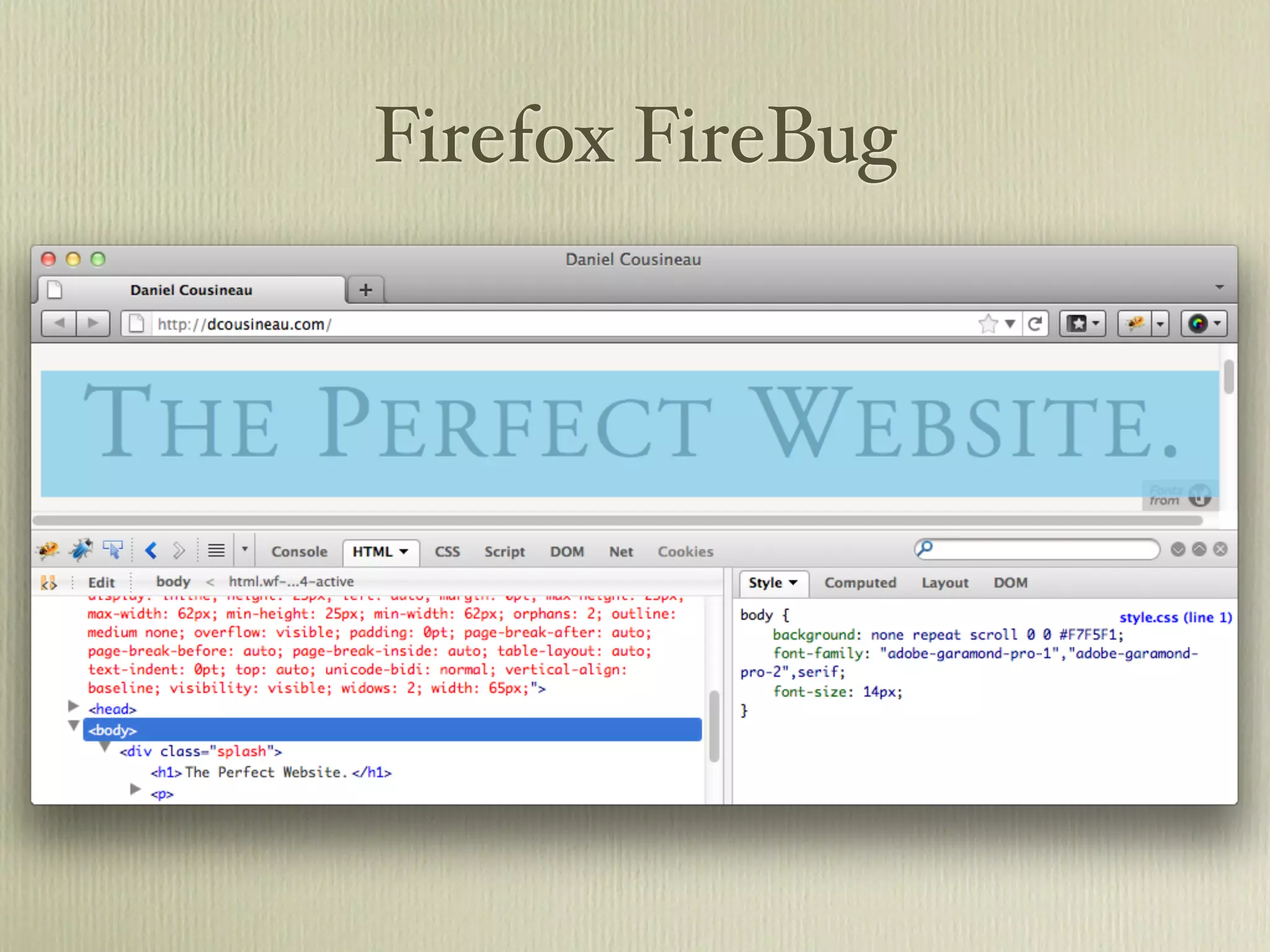
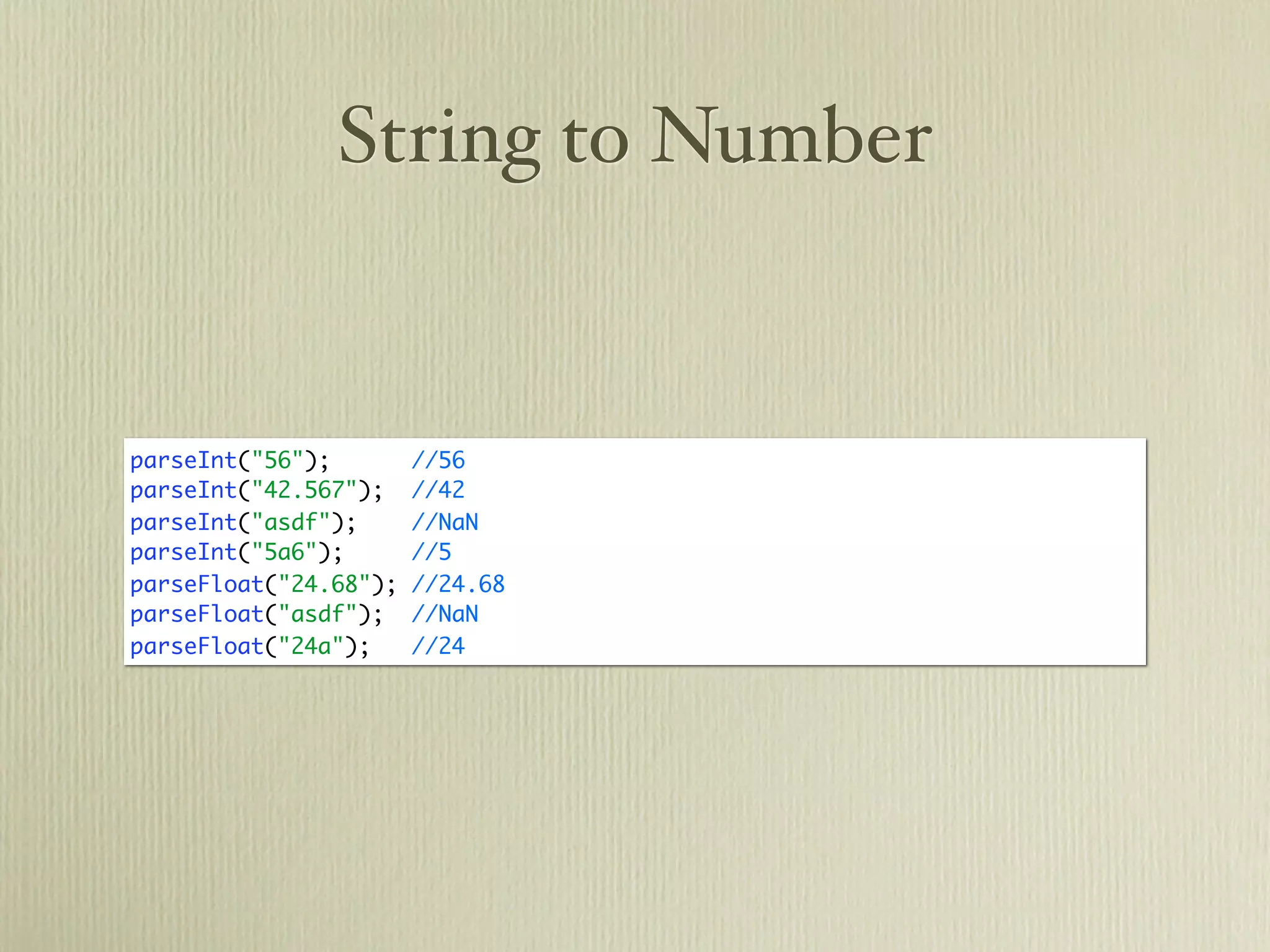
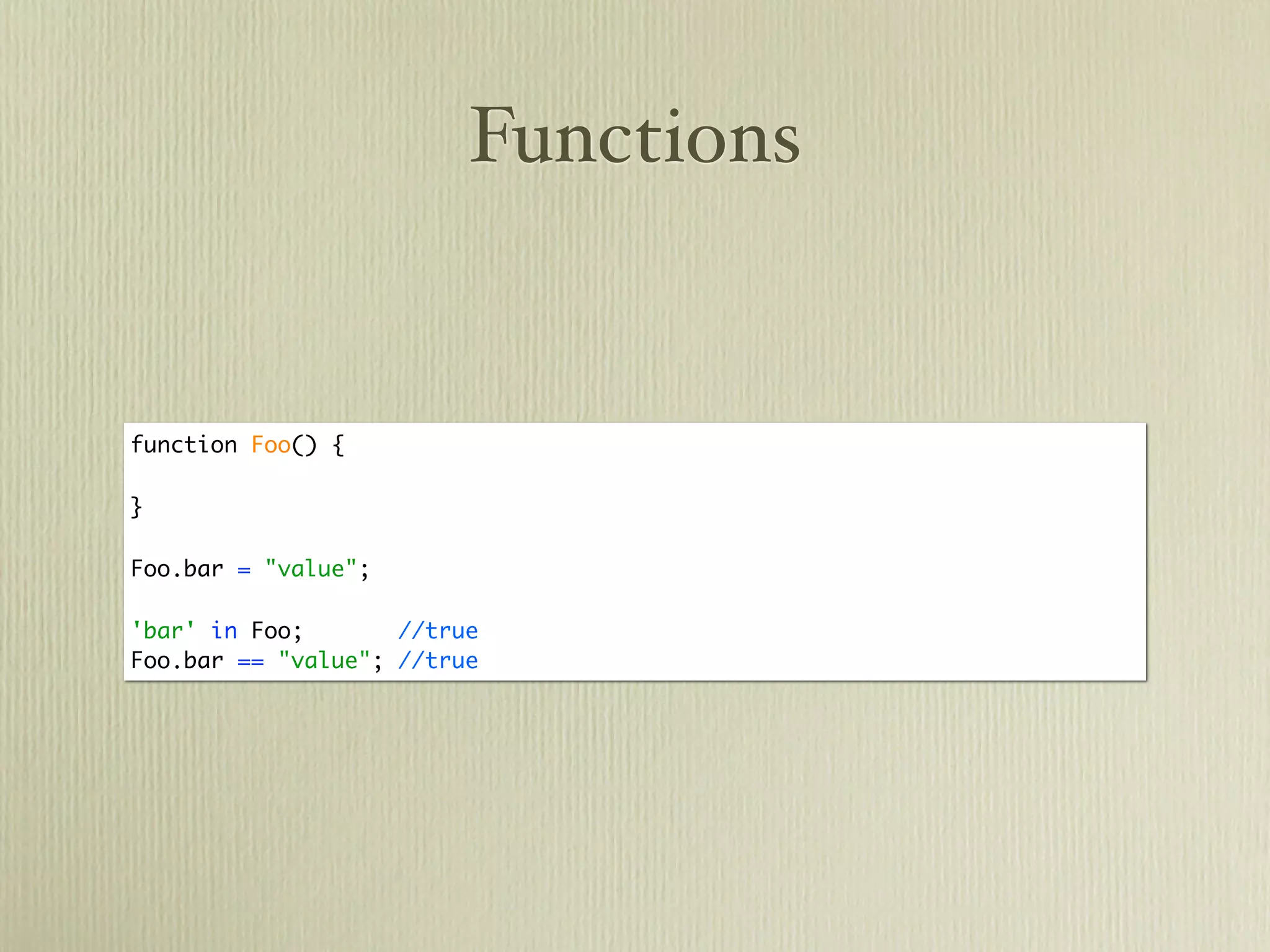
The document provides a comprehensive overview of JavaScript, covering its history, data types, object-oriented programming concepts, functions, and asynchronous behavior. It introduces fundamental elements such as strings, arrays, functions, and their manipulations, along with practical examples and statements. Additionally, it touches on JSON, jQuery, and AJAX as essential tools for web development.






![Strings
"Foo" + "Bar"; //"FooBar"
var str = "Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet";
str.toLowerCase(); //"lorem ipsum dolor sit amet"
str.toUpperCase(); //"LOREM IPSUM DOLOR SIT AMET"
str.split(" "); //["Lorem", "Ispum", "Dolor", "Sit", "Amet"]
str.substring(6,9); //"Ips"
new String("Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet") == str; //true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-8-2048.jpg)
![Objects
• “Dictionary” / “Associative Array”
• Key: Value or 'Key': Value
• Without ': A-Z0-9 only
• Does not keep intrinsic ordering
• Accessed keys using . (dot) or [] notation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-10-2048.jpg)
![Objects
var object = {
foo: 'value',
'complex key': 0,
bar: {
nested: true
}
};
object.foo; //'value'
object.['complex key']; //0
object.bar.nested; //true
object.bar['nested']; //true
object['bar'].nested; //true
object['bar']['nested']; //true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-11-2048.jpg)

![in
var test = {
foo: 'value',
bar: 'value',
baz: 'value'
}
for (var key in test) {
console.log(key + ": " + test[key]);
}
//PRINTS:
//foo: value
//bar: value
//baz: value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-13-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
• Special object
• Numerical keys only
• Keeps intrinsic ordering
• Short ([]) and Long (new Array()) syntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-14-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
var arrayShort = [
'one',
'two'
];
arrayShort[2] = 'three';
var arrayLong = new Array();
arrayLong[0] = 'one';
arrayLong[1] = 'two';
arrayLong[2] = 'three';
//arrayShort: ["one", "two", "three"]
//arrayLong: ["one", "two", "three"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-15-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
var arr = [1,2,3,4,6];
arr.indexOf(2); //1
arr.join(':'); //"1:2:3:4:6"
arr.pop(); //6
//[1,2,3,4]
arr.push(7); //5
//[1,2,3,4,7]
arr.reverse(); //[7,4,3,2,1]
arr.shift(); //1
//[2,3,4,7]
arr.unshift(8); //5
//[8,2,3,4,7]
arr.slice(1); //[2,3,4,7]
arr.slice(1,3); //[2,3]
arr.slice(-3); //[3,4,7]
arr.slice(-3,-1); //[3,4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-16-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
var arr1 = [1,2,3];
var arr2 = [3,4,5];
arr1.concat(arr2); //[1,2,3,3,4,5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-17-2048.jpg)




![arguments
function sum() {
var x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; ++i) {
x += arguments[i];
}
return x;
}
sum(1, 2, 3); //6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-23-2048.jpg)

![typeof
typeof true; //"boolean"
typeof 12; //"number"
typeof "string"; //"string"
typeof []; //"object"
typeof {}; //"object"
typeof NaN; //"number"
typeof null; //"object"
typeof undefined; //"undefined"
function Foo() {}
typeof Foo; //"function"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-25-2048.jpg)














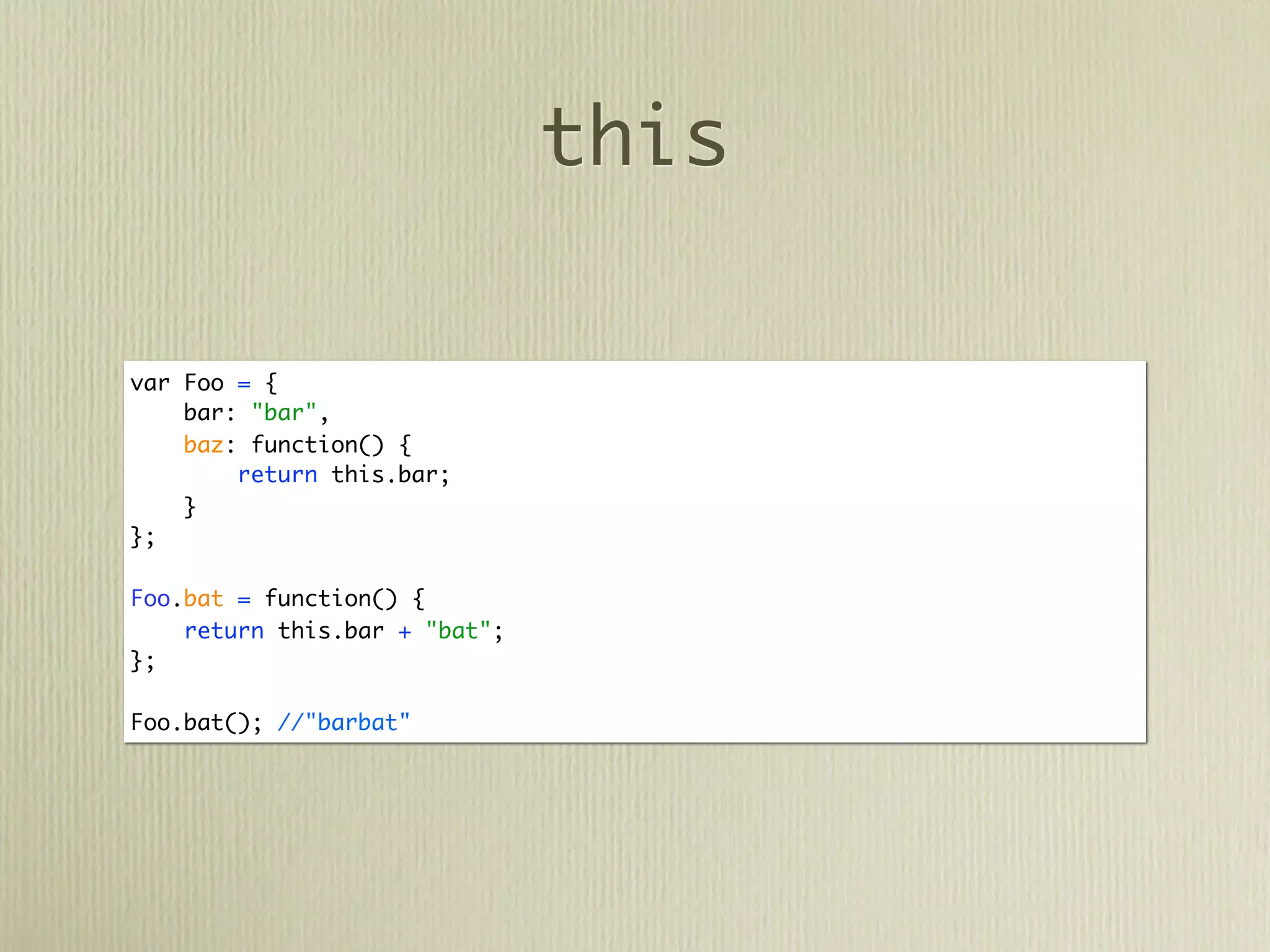

![call & apply
var Foo = {
bar: "bar",
baz = function(param1, param2) {
return this.bar + param1 + param2;
}
};
var Foo2 = {
bar: "123"
};
Foo.baz("baz", "bat"); //"barbazbat"
Foo.baz.apply(Foo2, "baz", "bat"); //"123bazbat"
Foo.baz.call(Foo2, ["baz", "bat"]); //"123bazbat"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-42-2048.jpg)












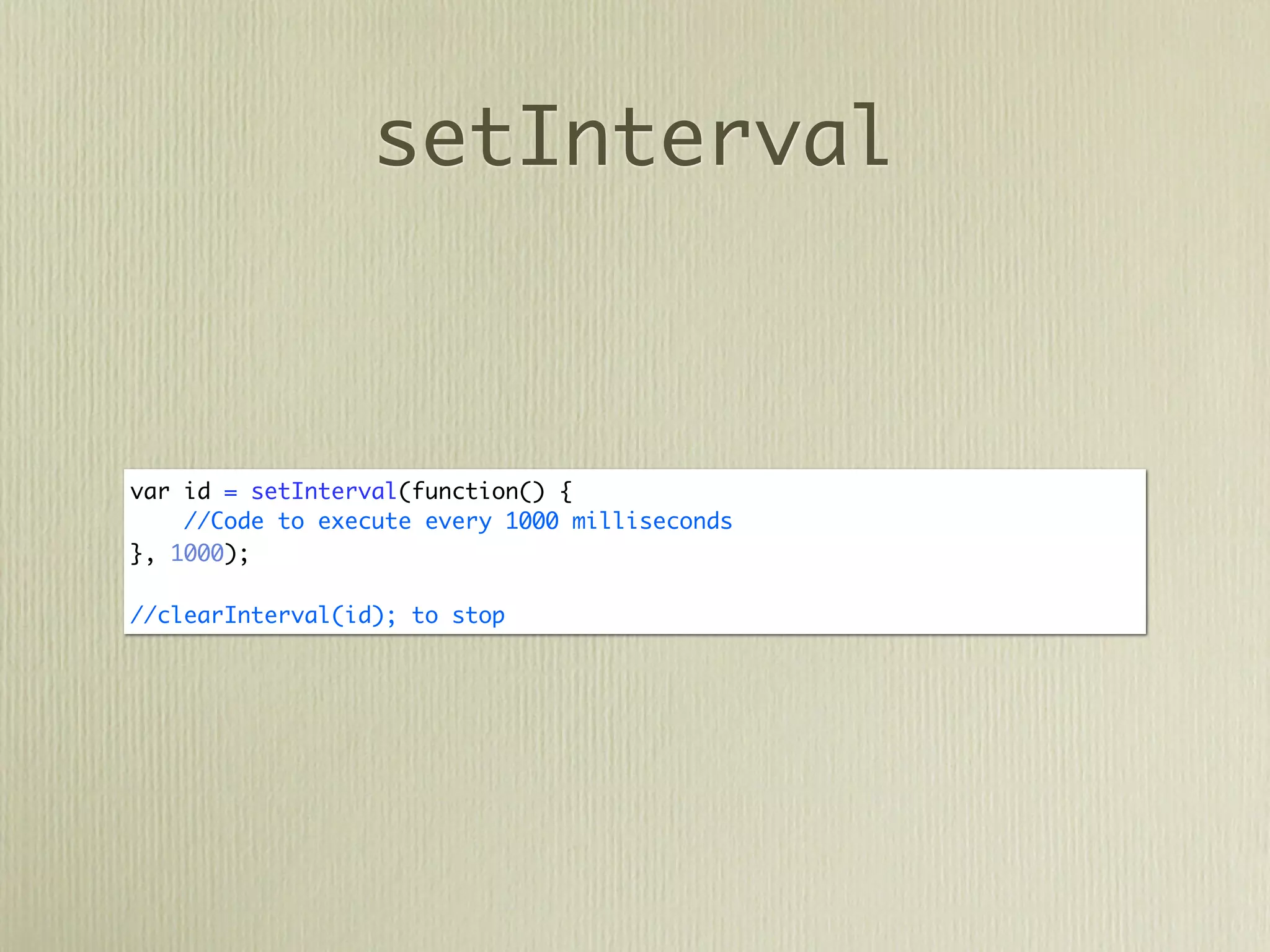
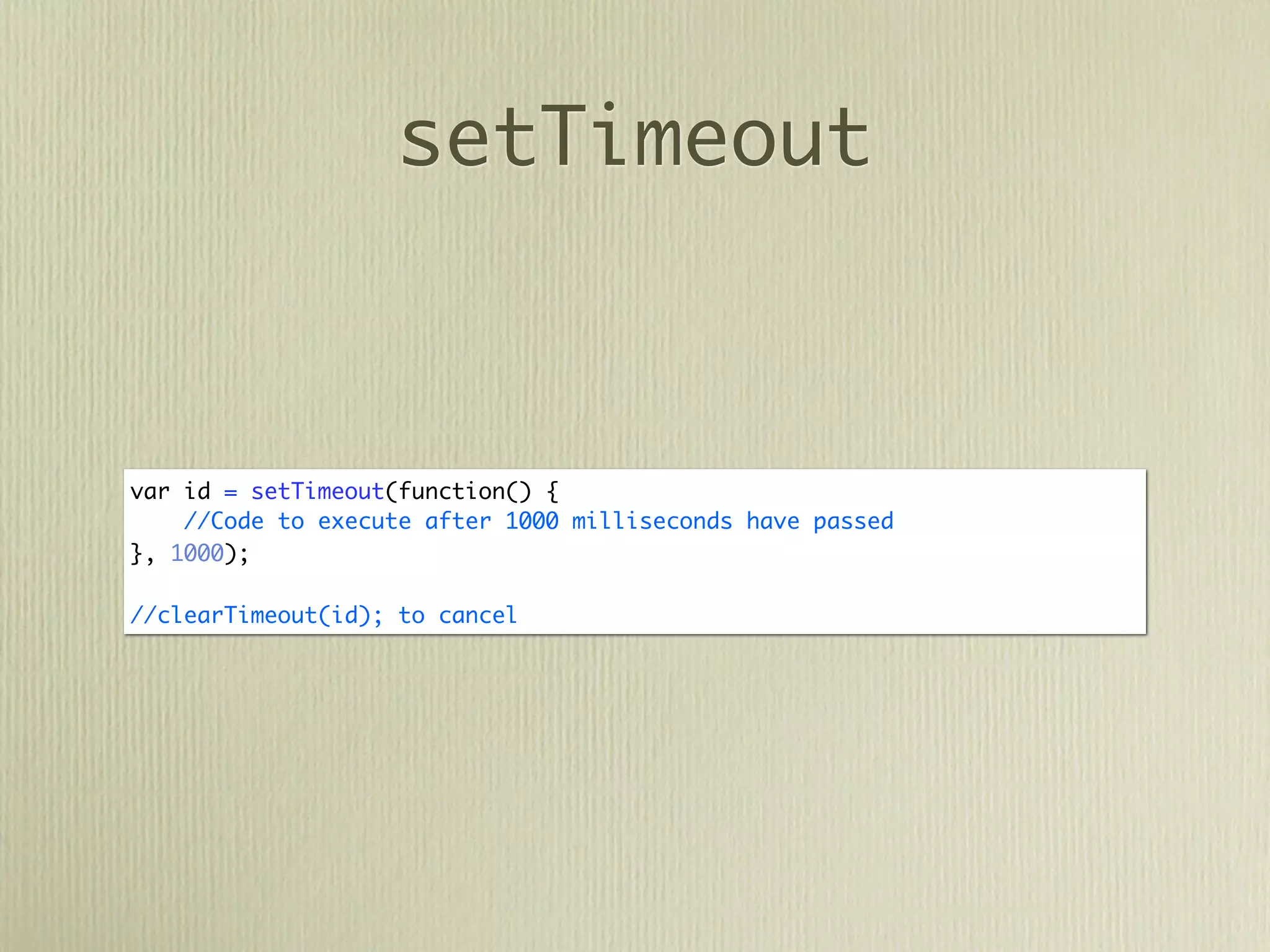
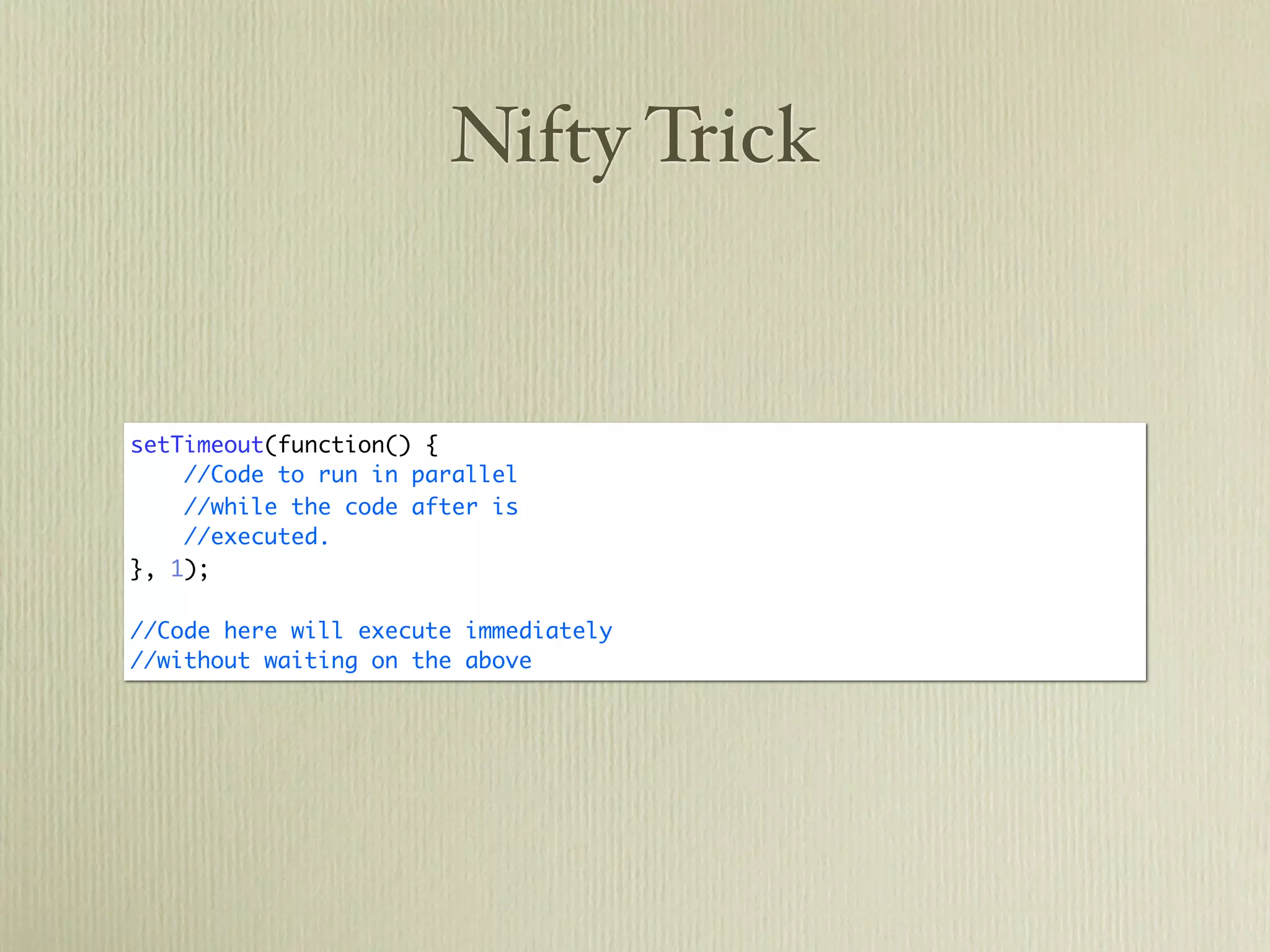


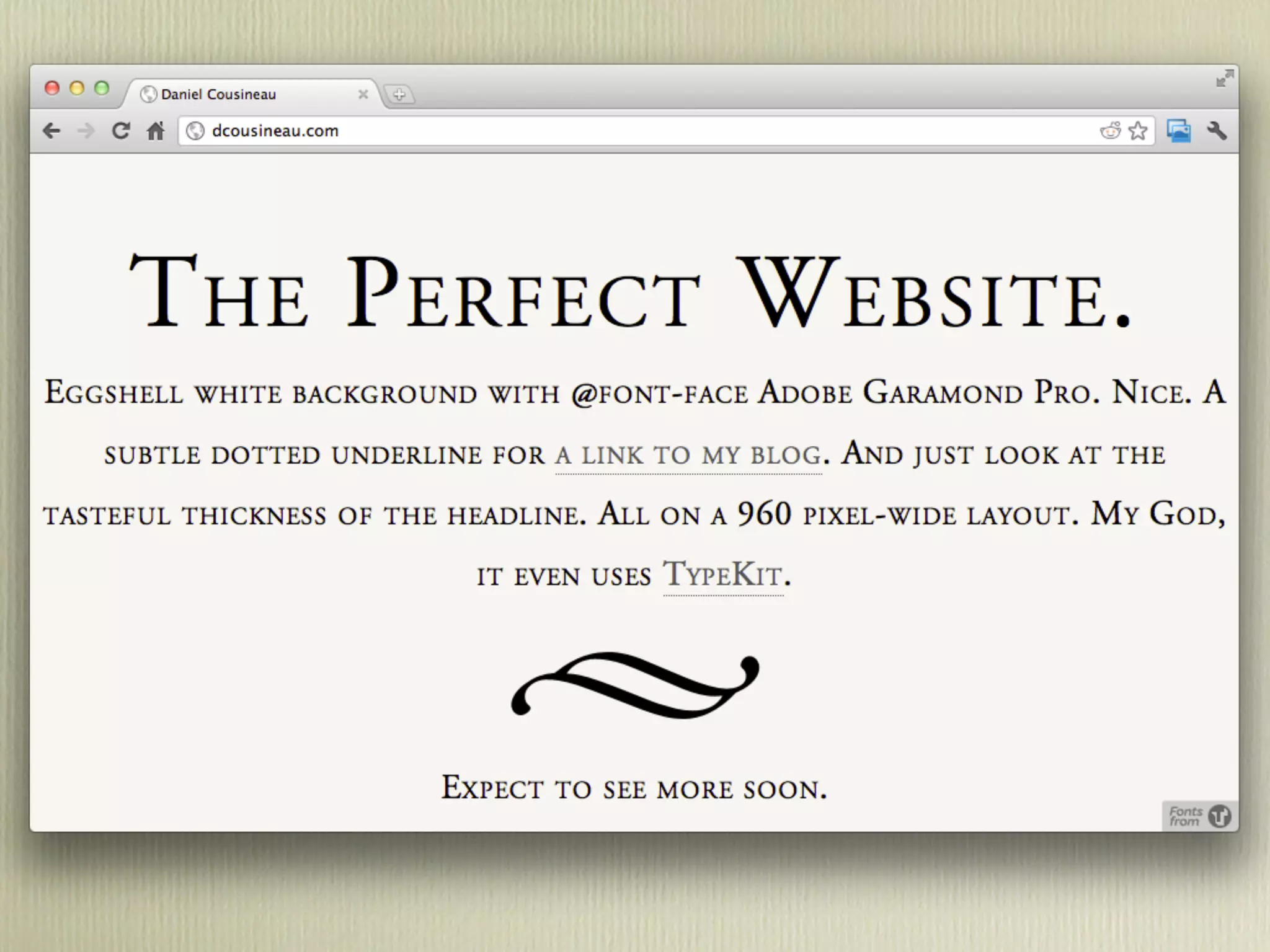
![DOM
var paragraph = document.createElement('p');
var content = document.createTextNode("Lorem Ipsum");
paragraph.appendChild(content);
paragraph.classList.add('my-class');
document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0].appendChild(paragraph);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-61-2048.jpg)



![JSON
{"menu": { <menu id="file" value="File">
"id": "file", <popup>
"value": "File", <menuitem value="New"
"popup": { onclick="CreateNewDoc()" />
"menuitem": [ <menuitem value="Open"
{"value": "New", onclick="OpenDoc()" />
"onclick": "CreateNewDoc()"}, <menuitem value="Close"
{"value": "Open", onclick="CloseDoc()" />
"onclick": "OpenDoc()"}, </popup>
{"value": "Close", </menu>
"onclick": "CloseDoc()"}
]
}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-Primer-66-2048.jpg)