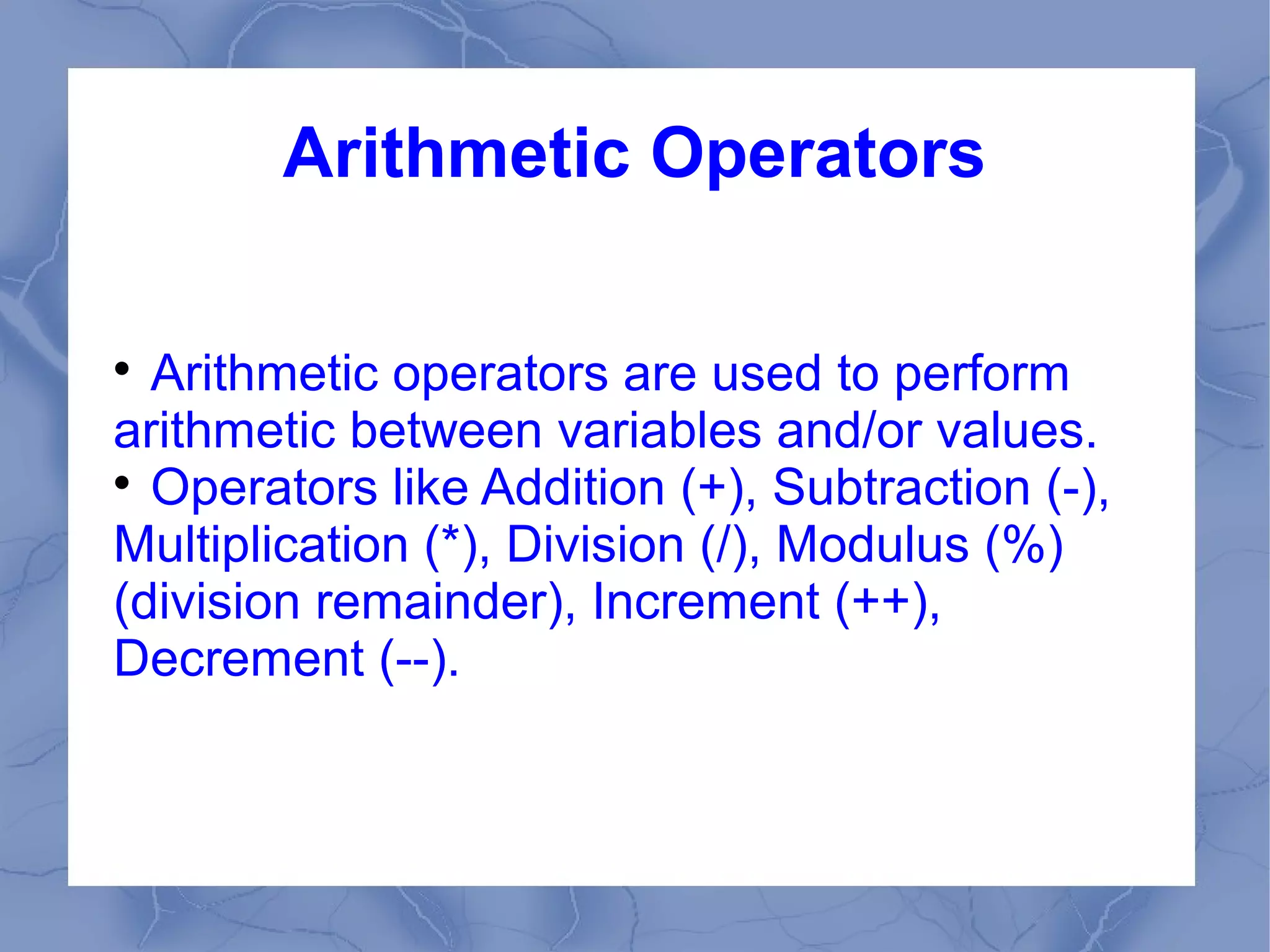
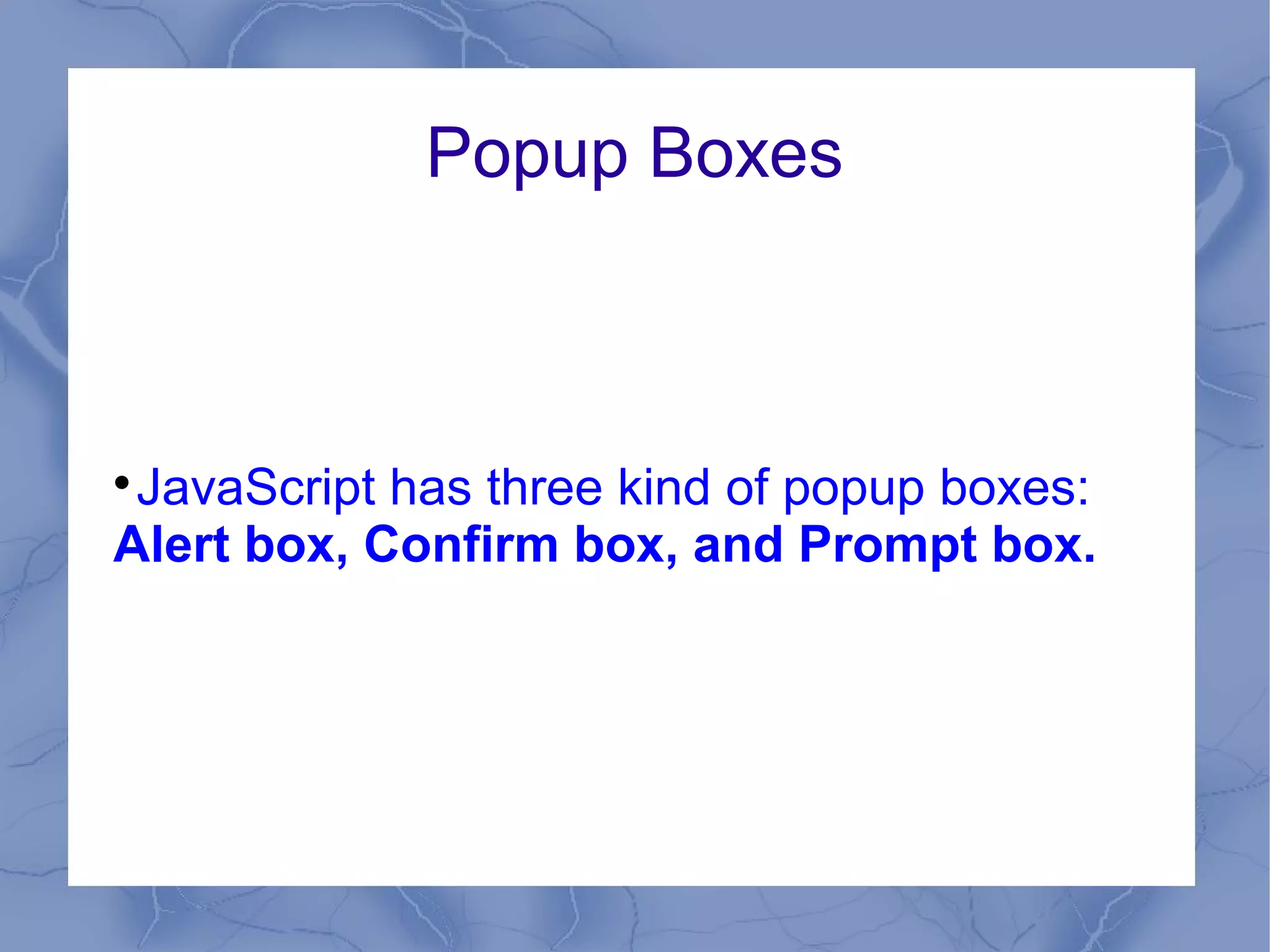
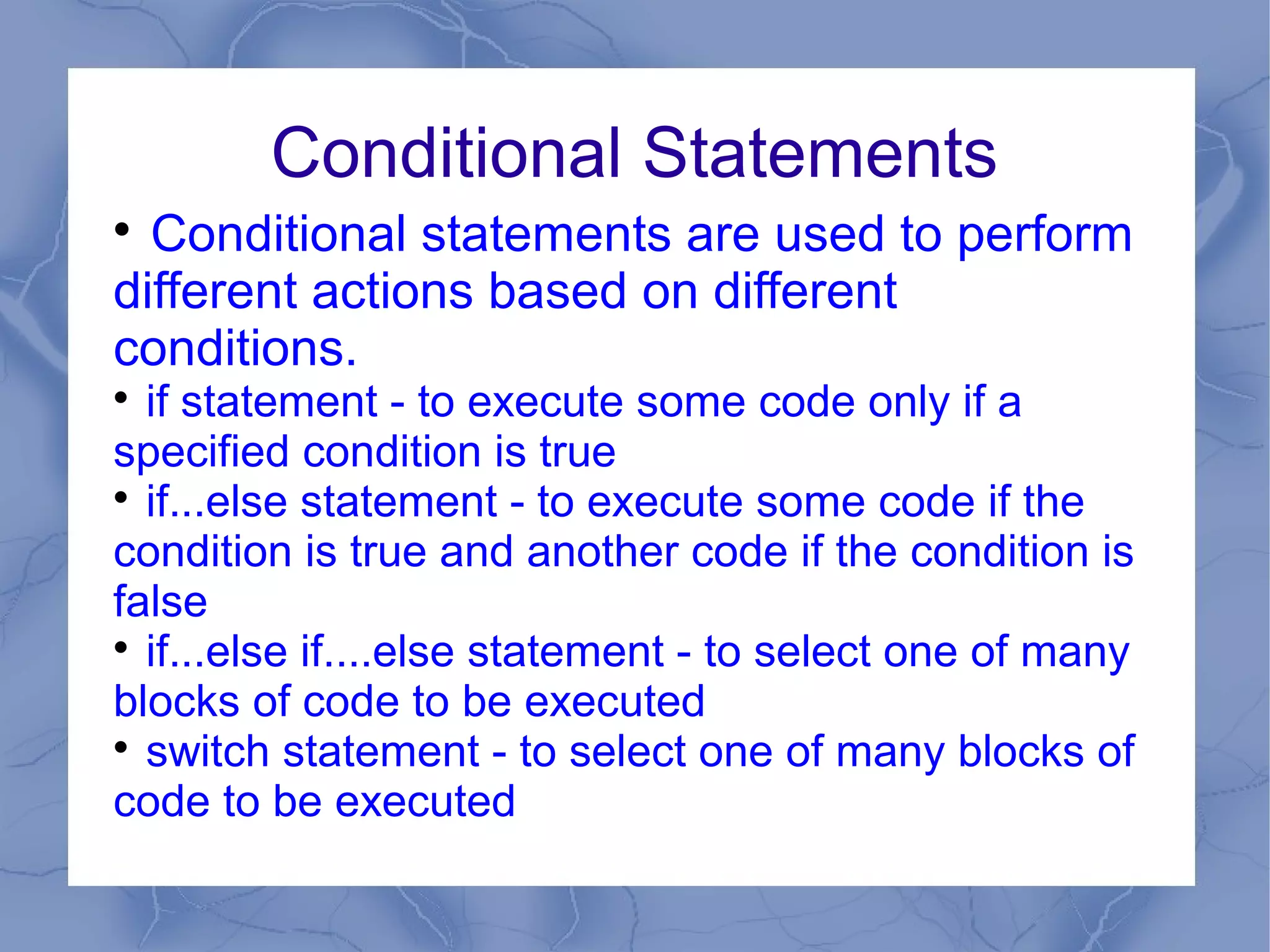
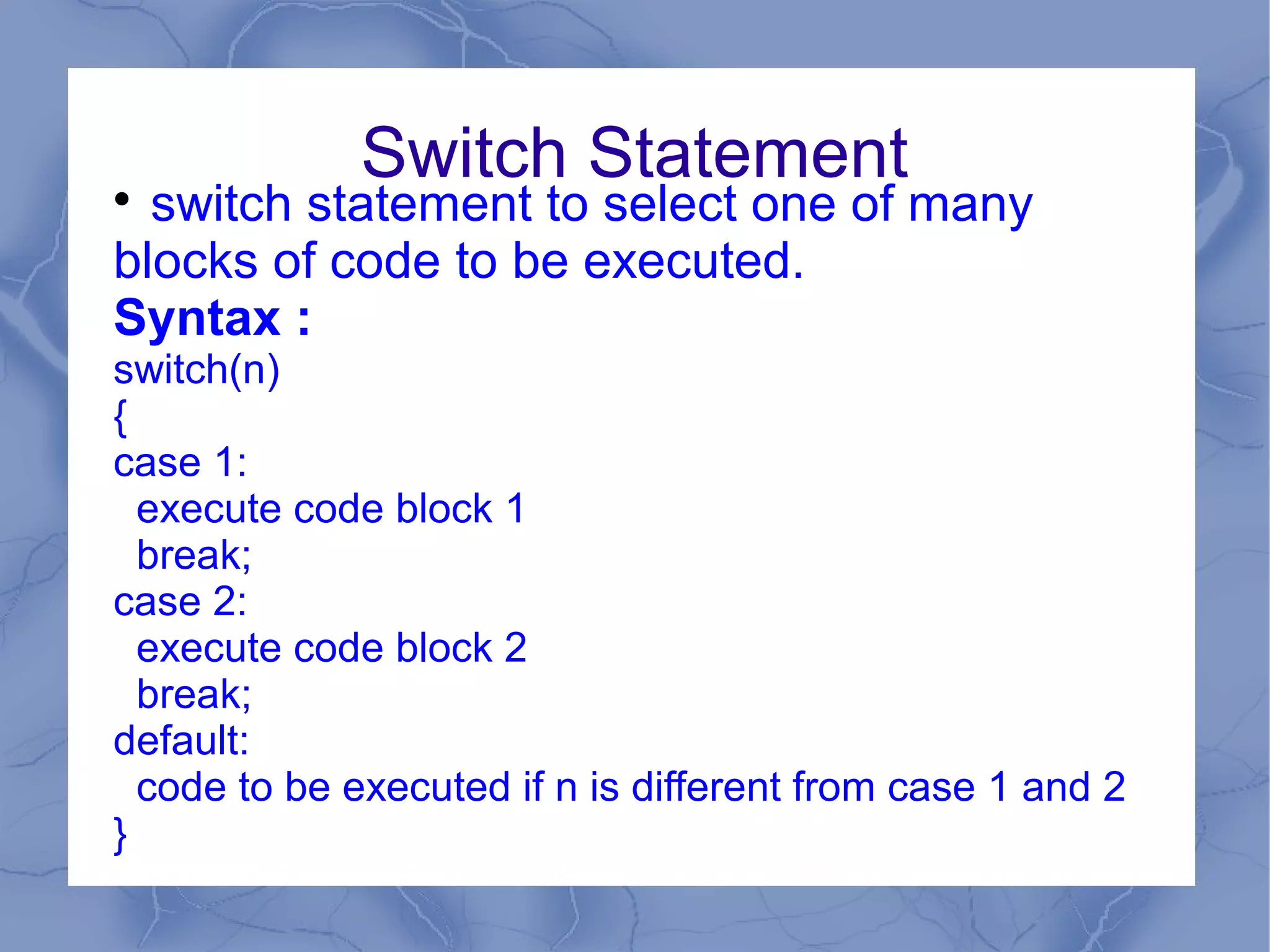
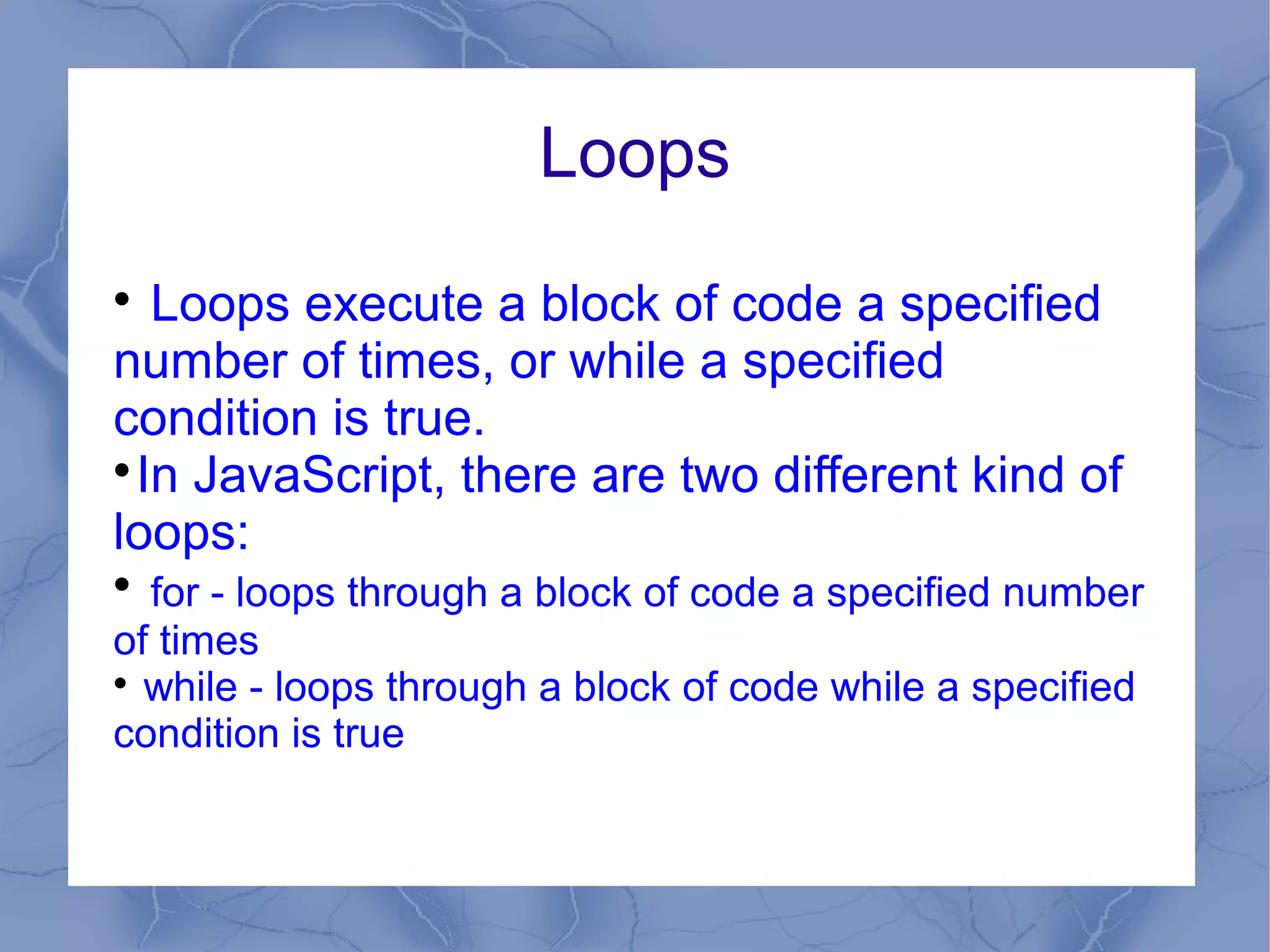
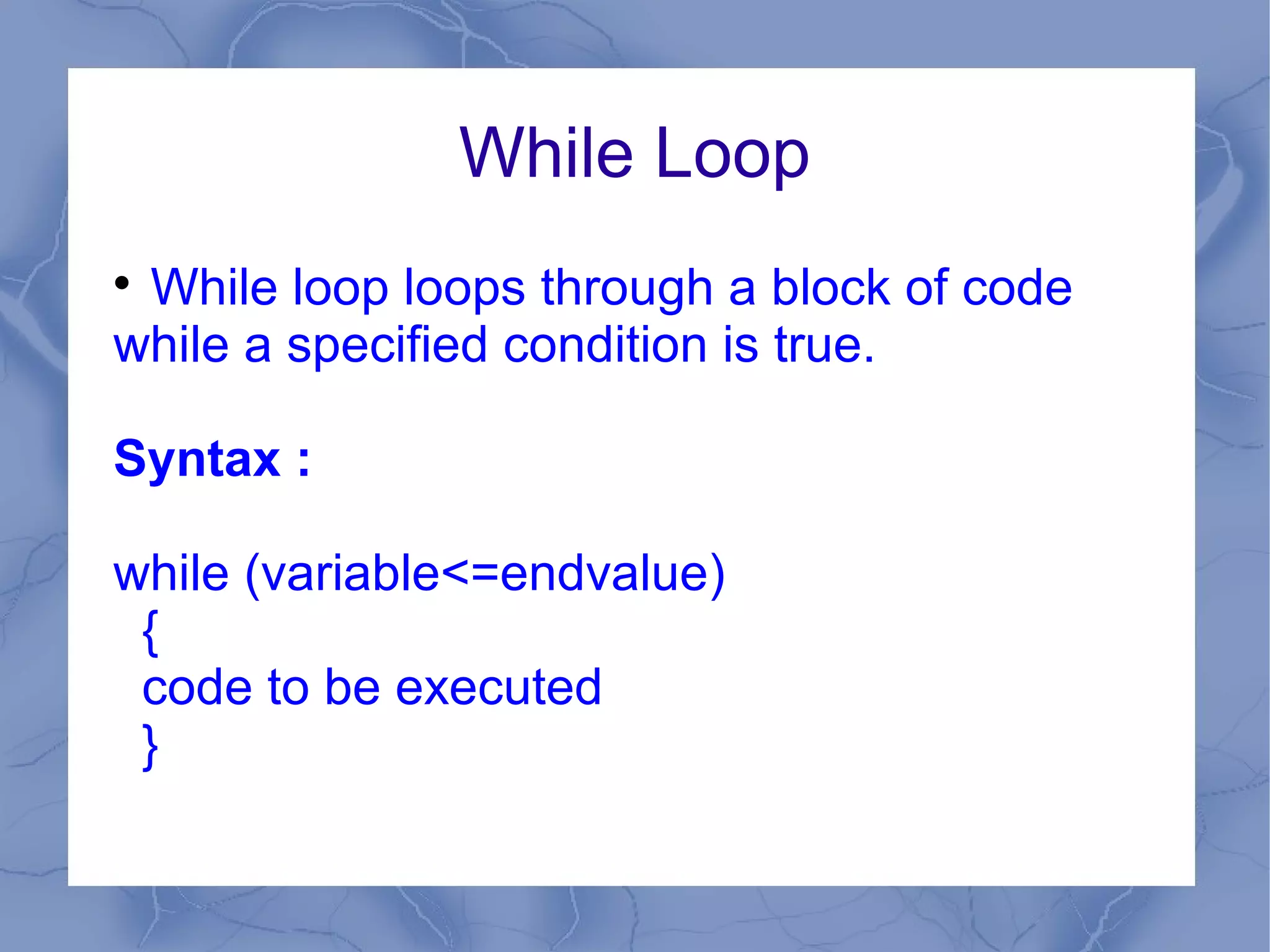
This document provides an overview of JavaScript concepts and features. It introduces JavaScript, its uses, basic syntax like variables, operators, and popup boxes. It also covers conditional statements, loops, functions, arrays, objects like Date and Math objects, regular expressions, and cookies. The document is intended as an introduction to JavaScript for learning its basic concepts.