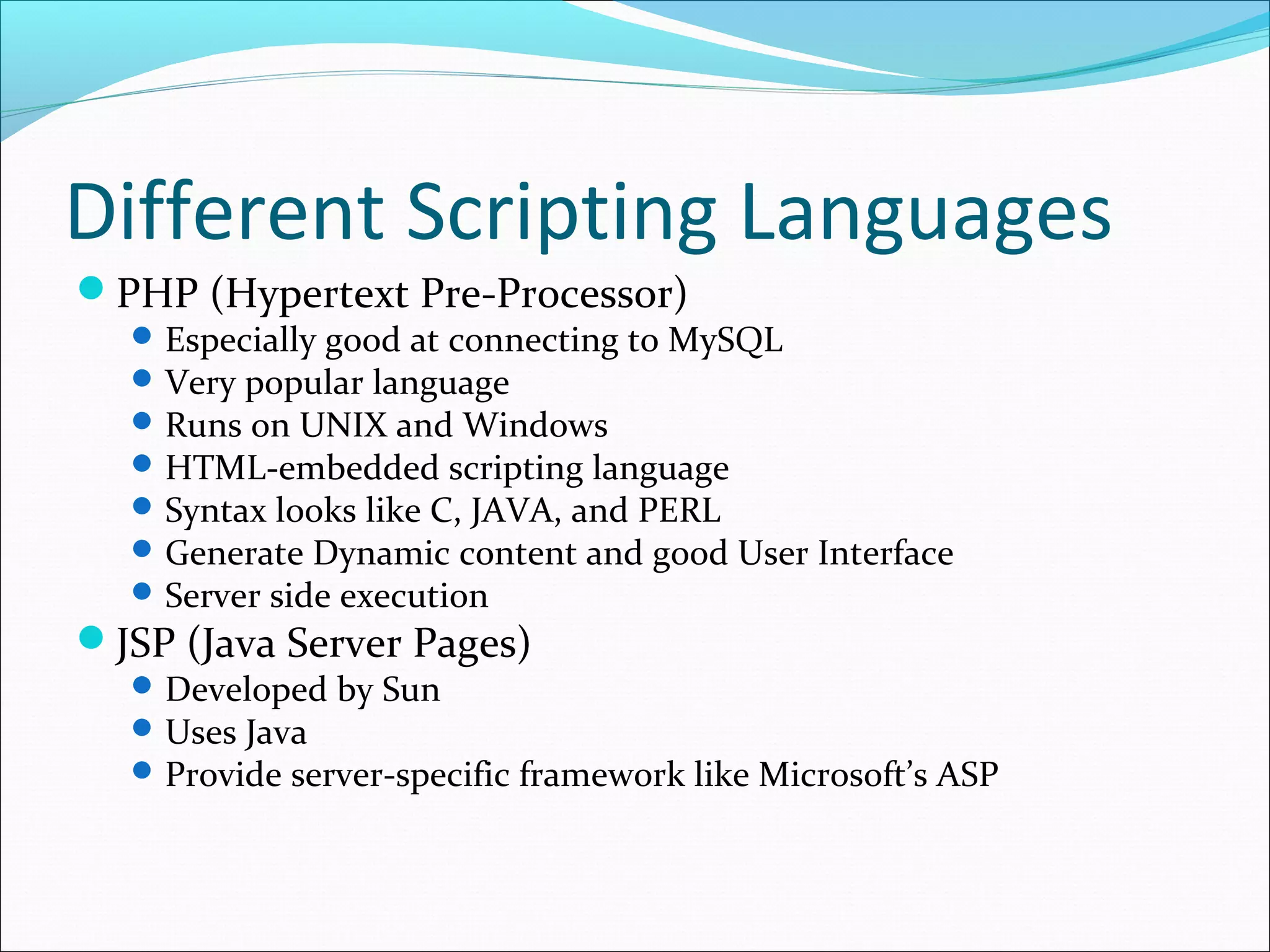
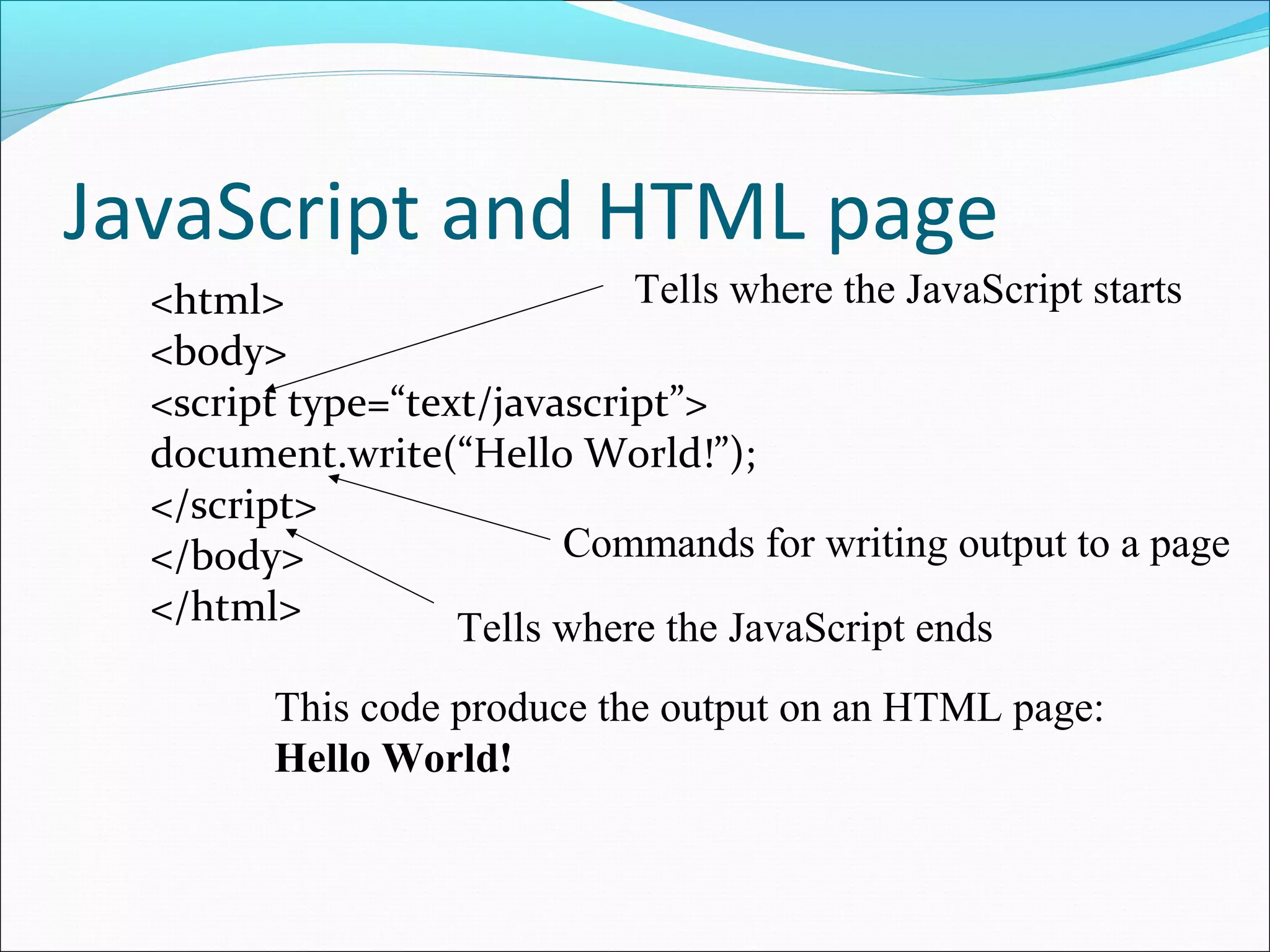
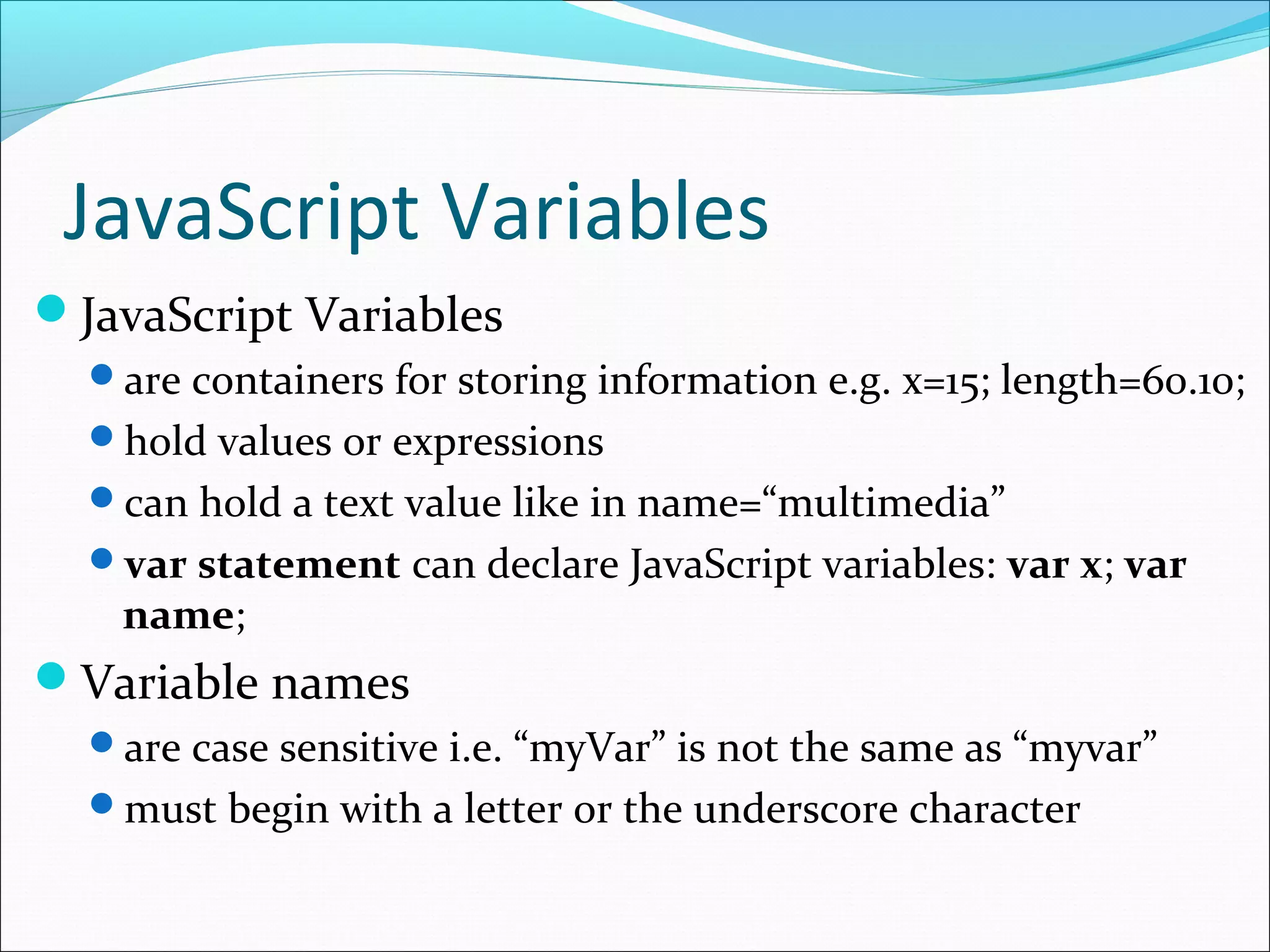
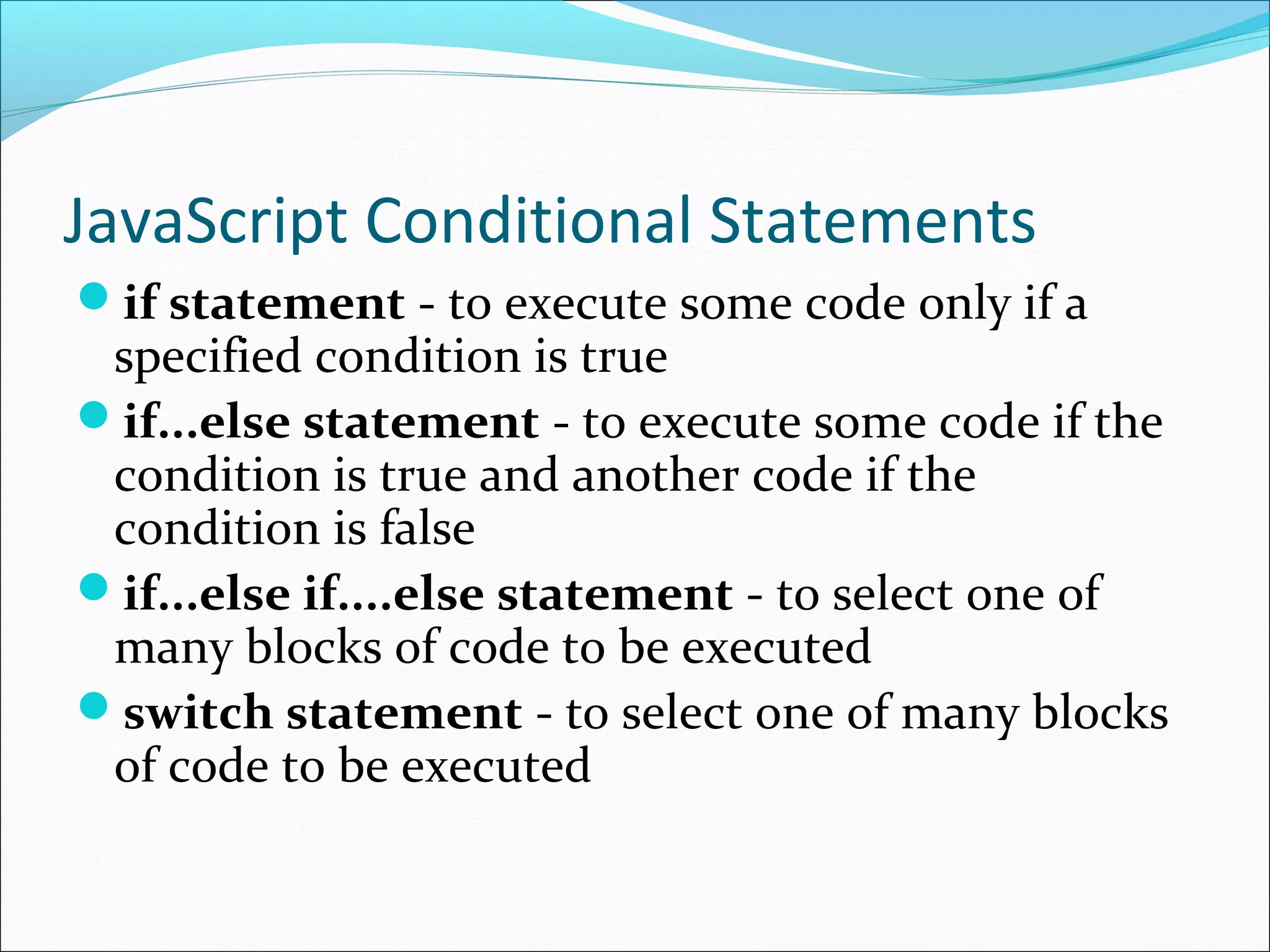
This document provides an overview of scripting languages, including both client-side and server-side languages. It discusses what scripting languages are and how they differ from other programming languages. Several popular scripting languages are described, including JavaScript, PHP, ASP.NET, and more. JavaScript is discussed in more depth as a commonly used client-side language for adding interactivity to web pages. The document also covers JavaScript syntax like variables, operators, and functions, and how JavaScript interacts with web pages using the Document Object Model (DOM).