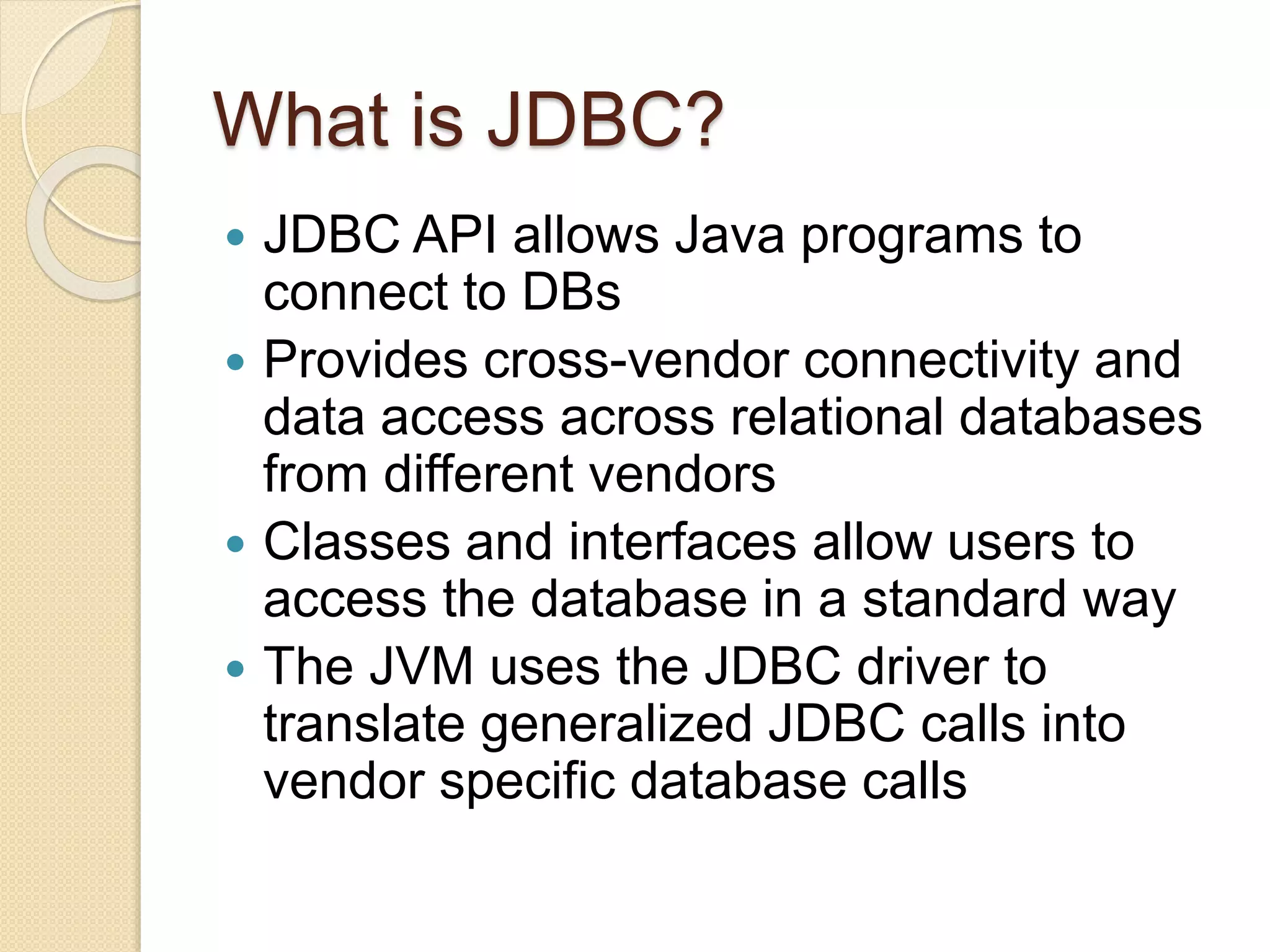
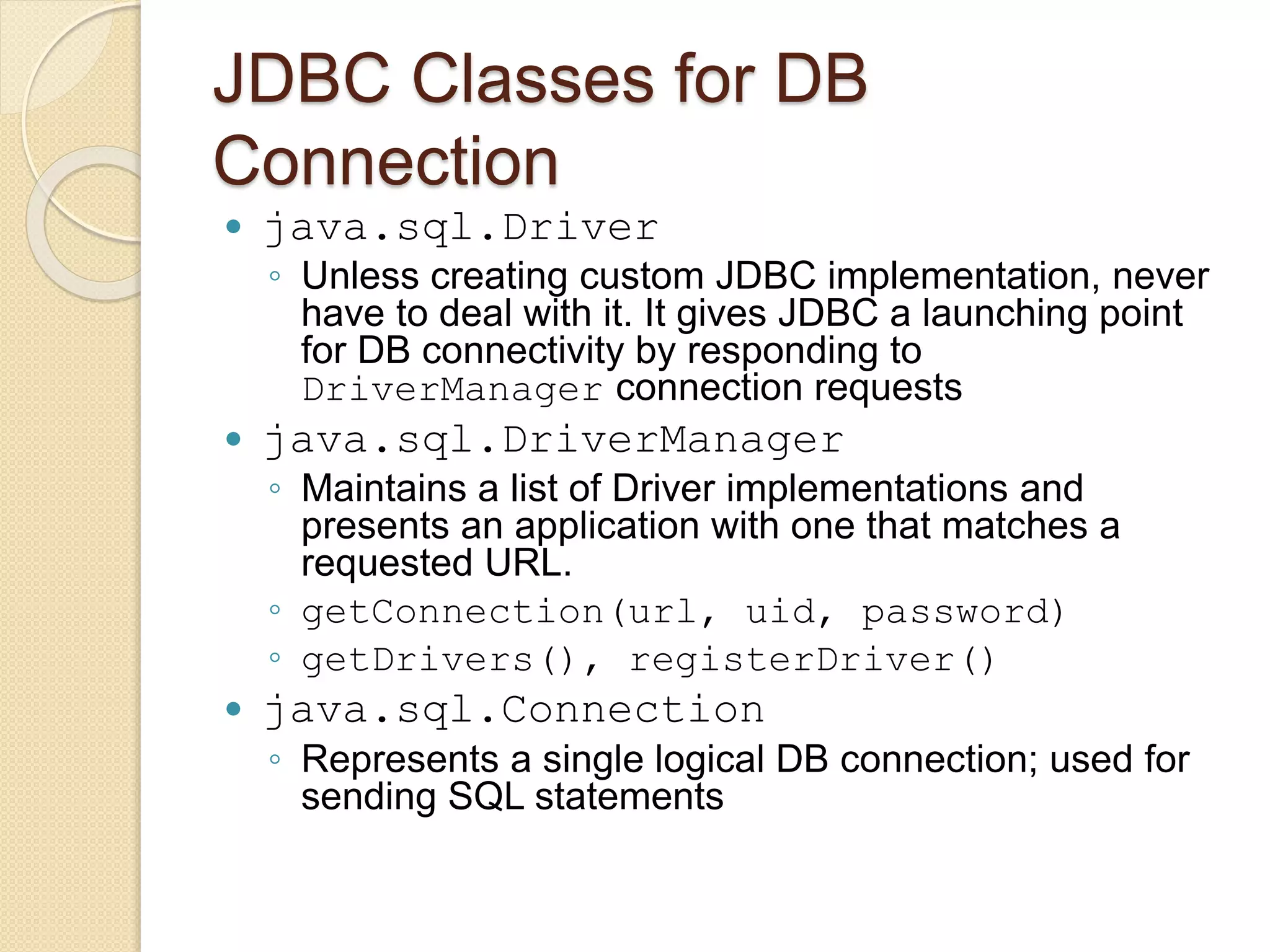
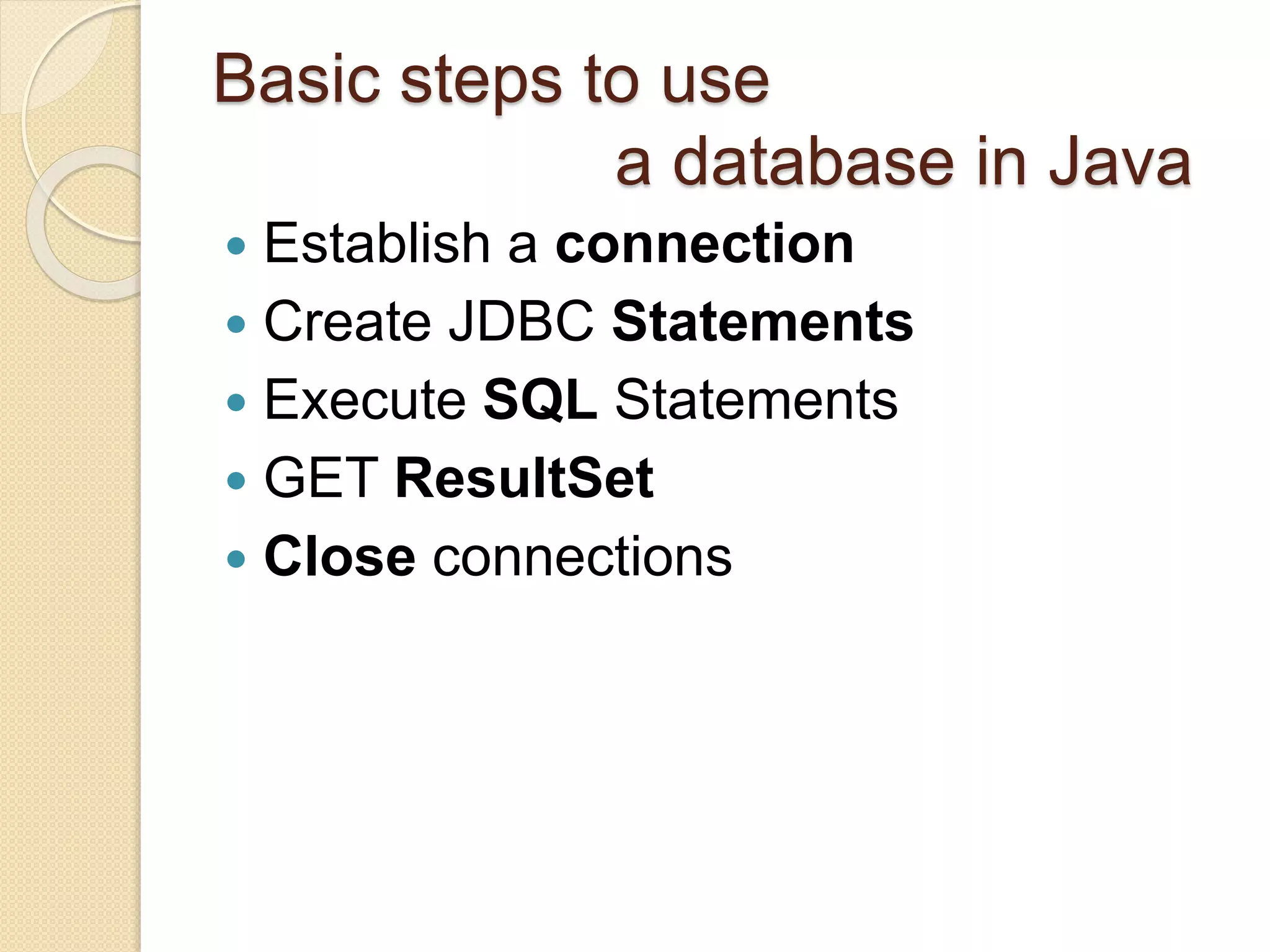
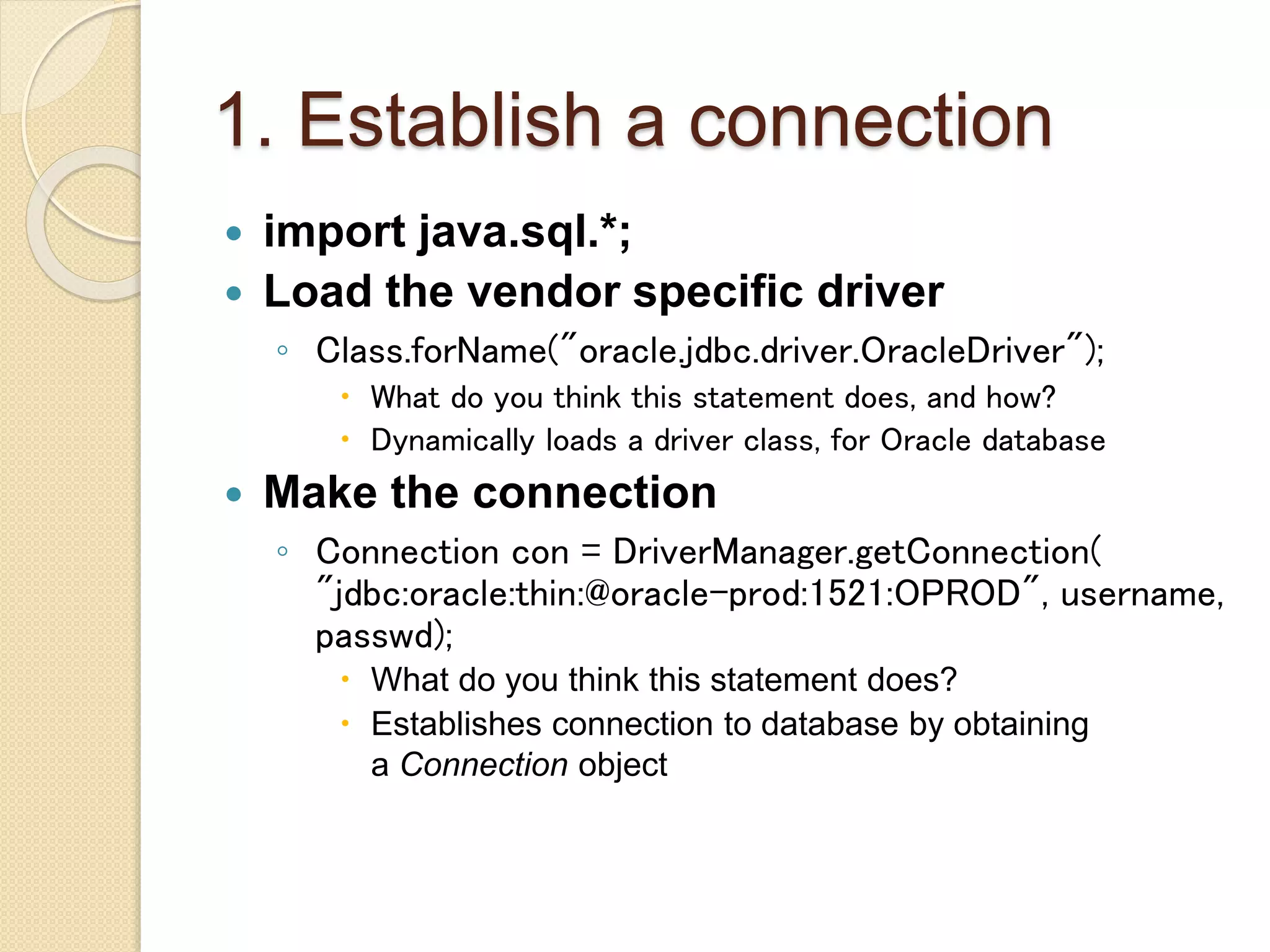
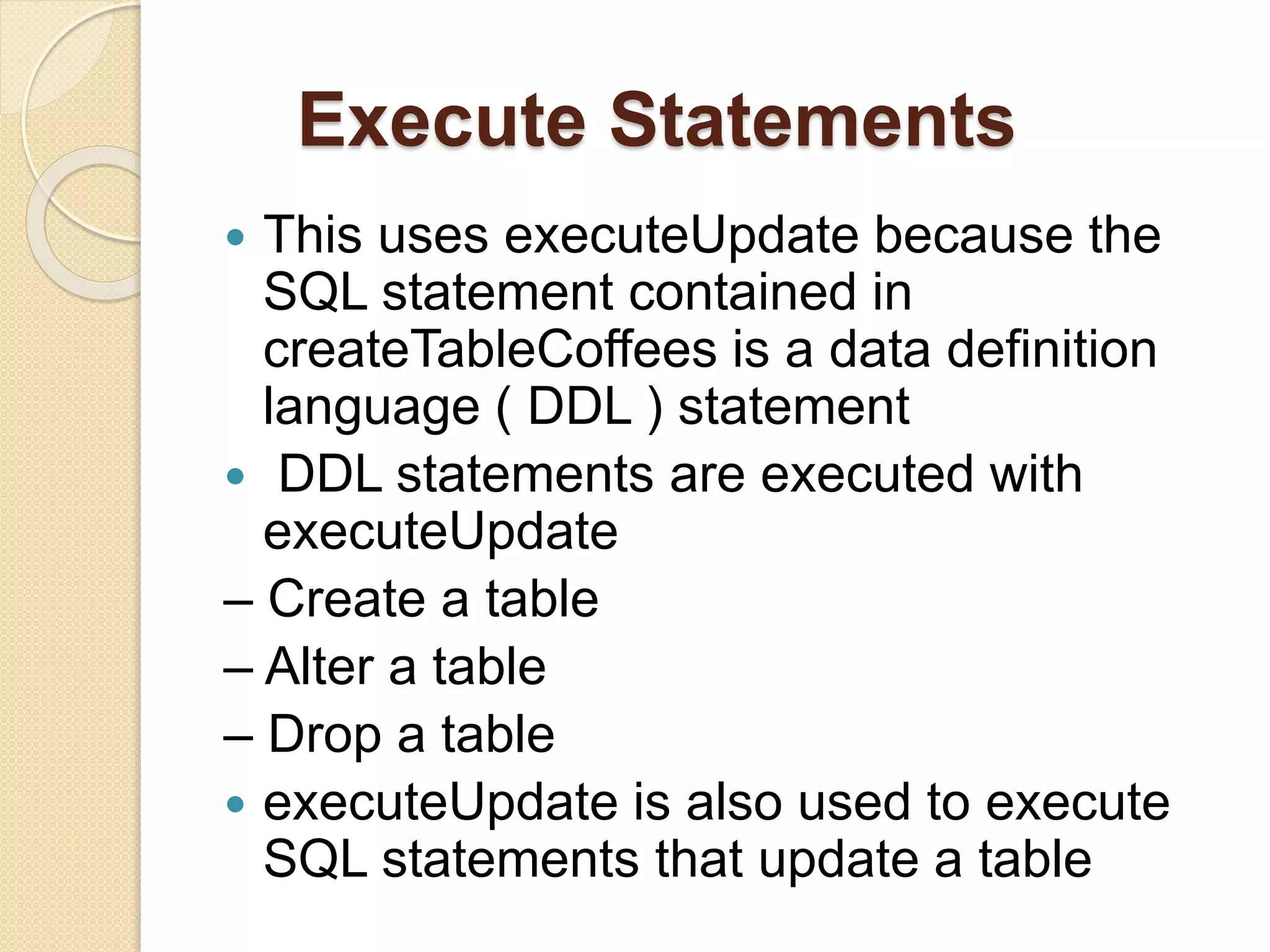
JDBC allows Java programs to connect to databases in a standard way. It provides cross-vendor connectivity and data access across relational databases. The key classes and interfaces in JDBC establish database connections, send SQL statements, and process query results. To use JDBC, a program first loads the appropriate driver, gets a connection, creates statements to execute queries and updates, processes the results, and closes the connection. This allows Java applications to access databases in a uniform manner independent of the underlying database.














![Sample Program
import java.sql.*;
class TestThinApp {
public static void main (String args[])
throws ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
");
// or you can use:
DriverManager.registerDriver(new
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver());
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","scott","ti](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbcwithoracle-151214063641/75/JDBC-ppt-21-2048.jpg)


