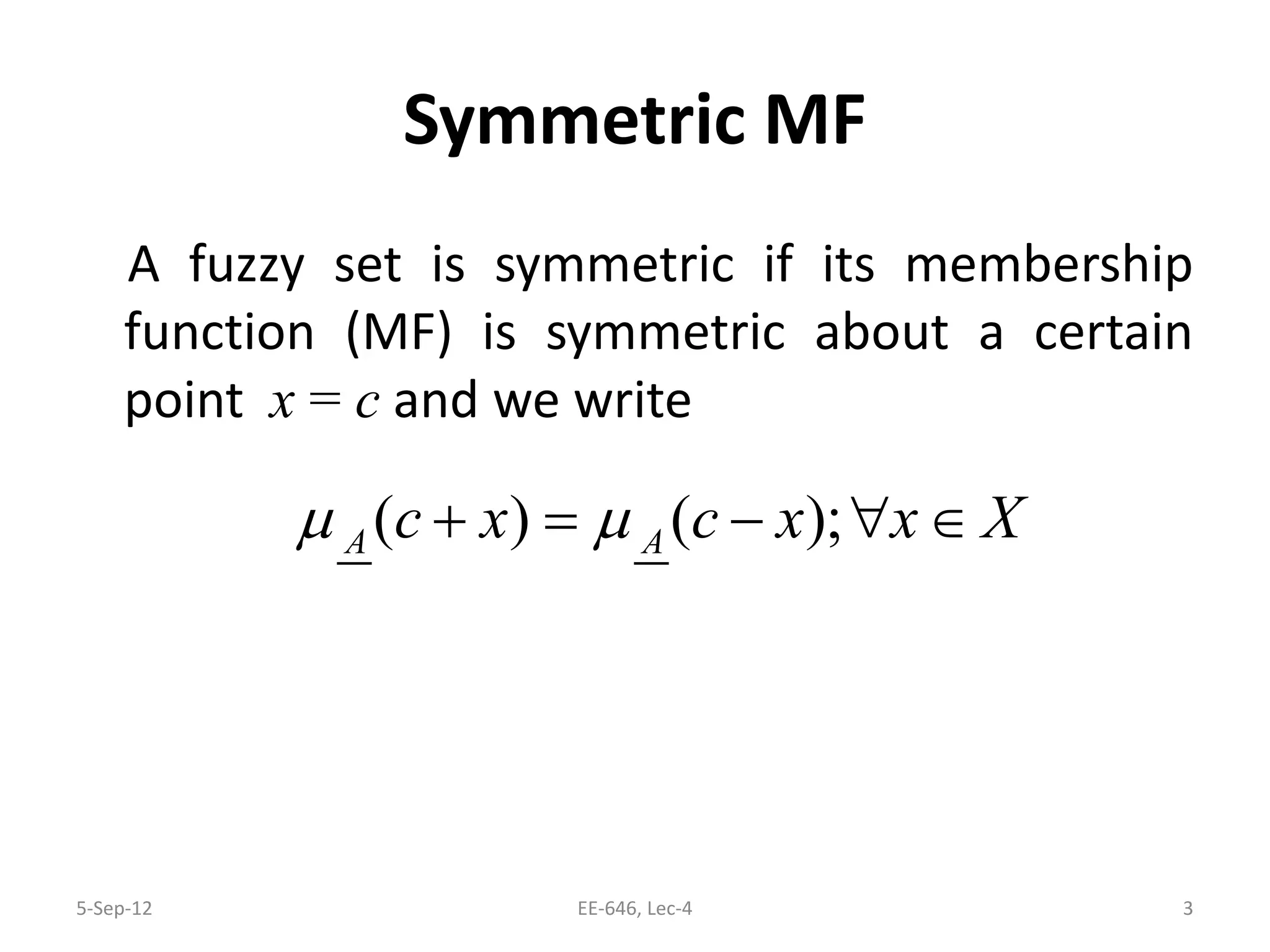
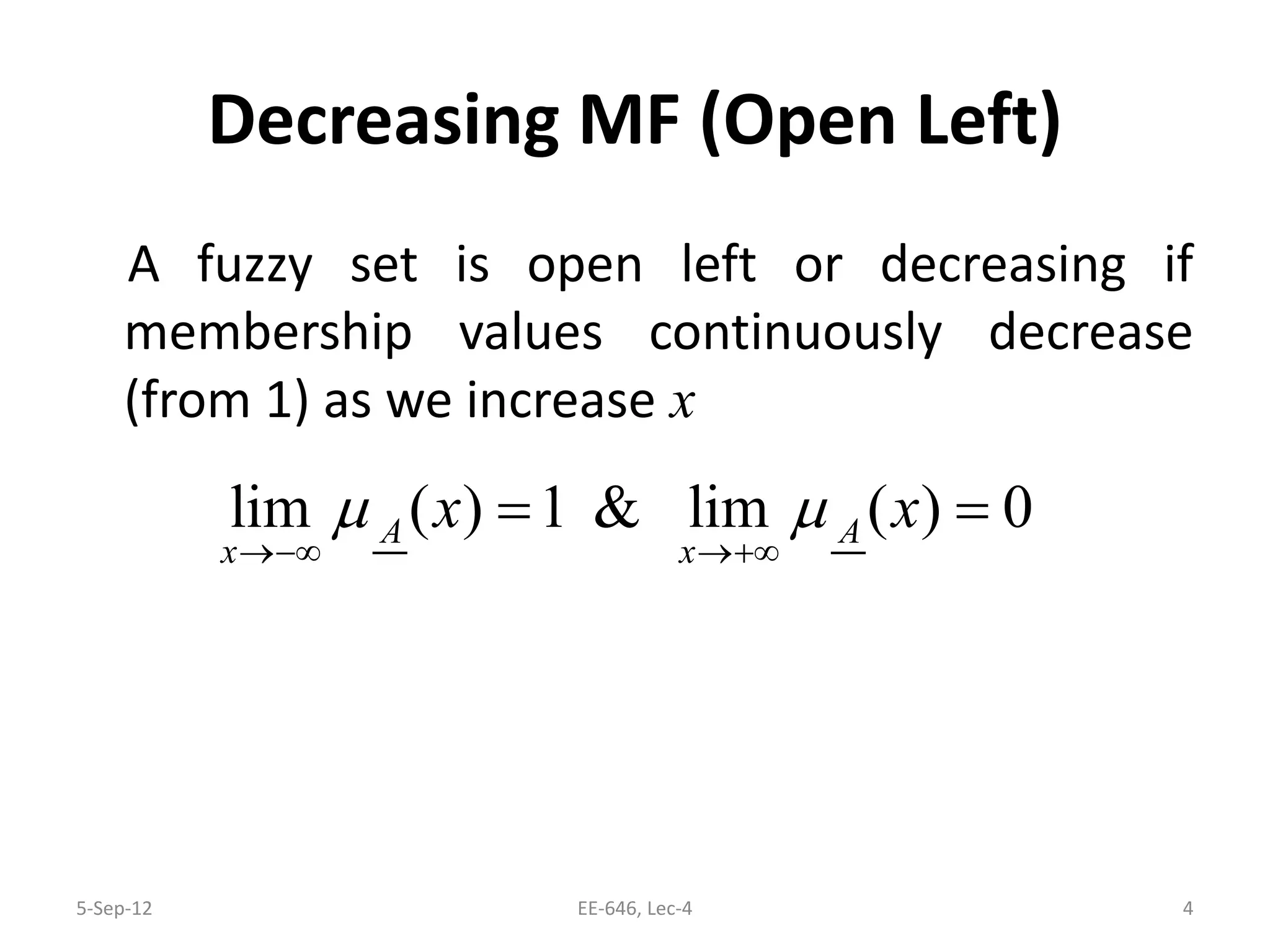
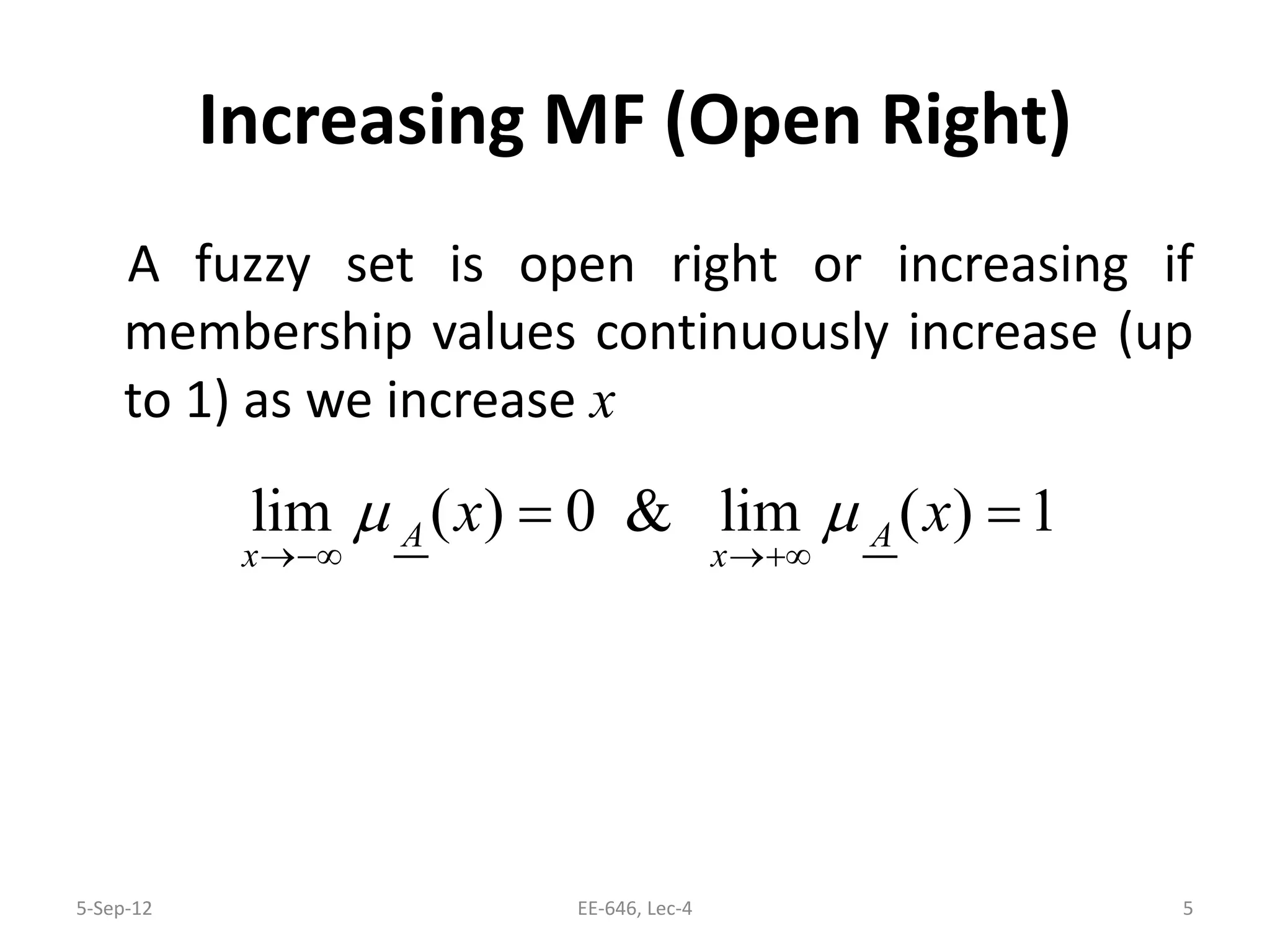
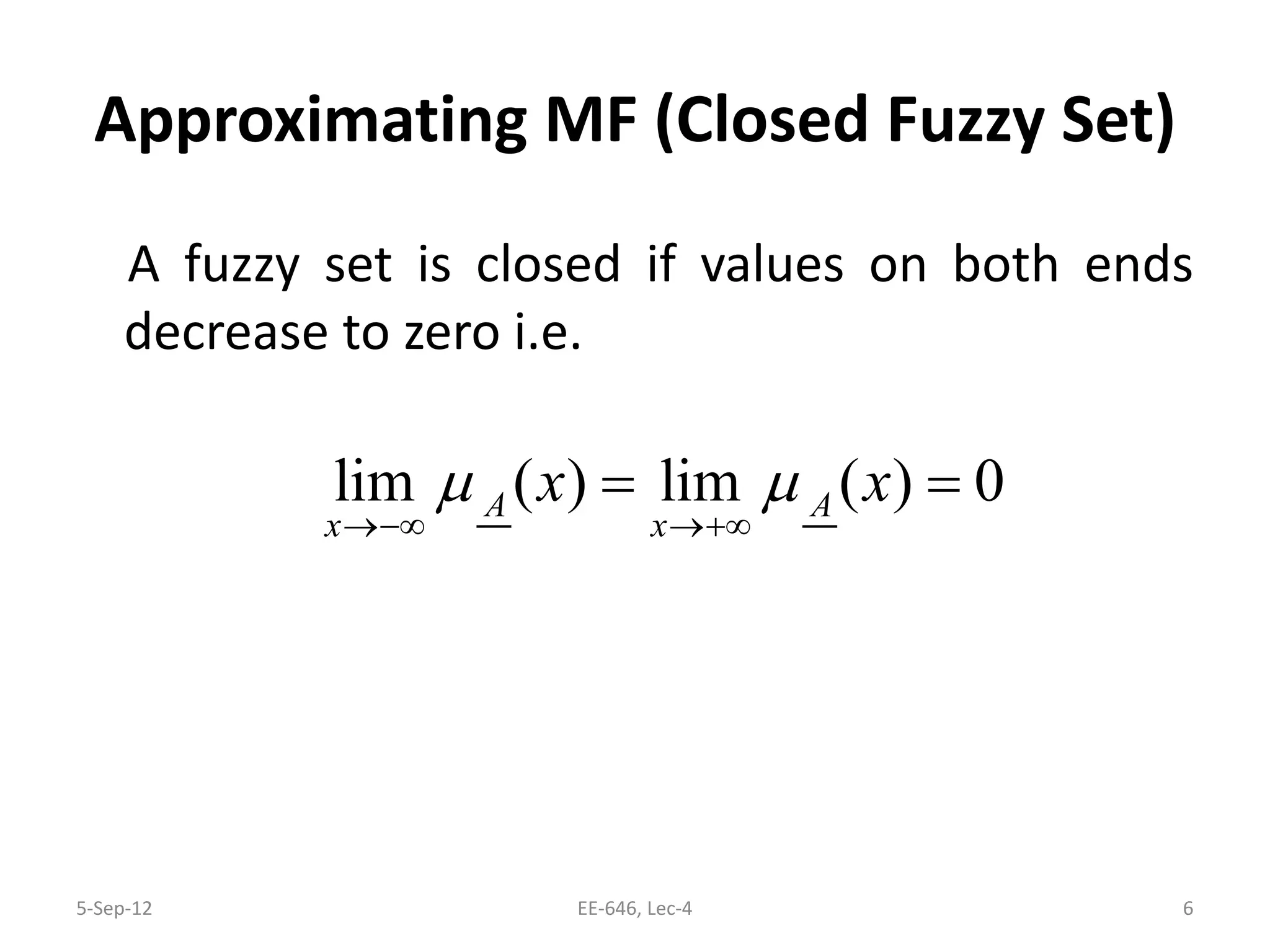
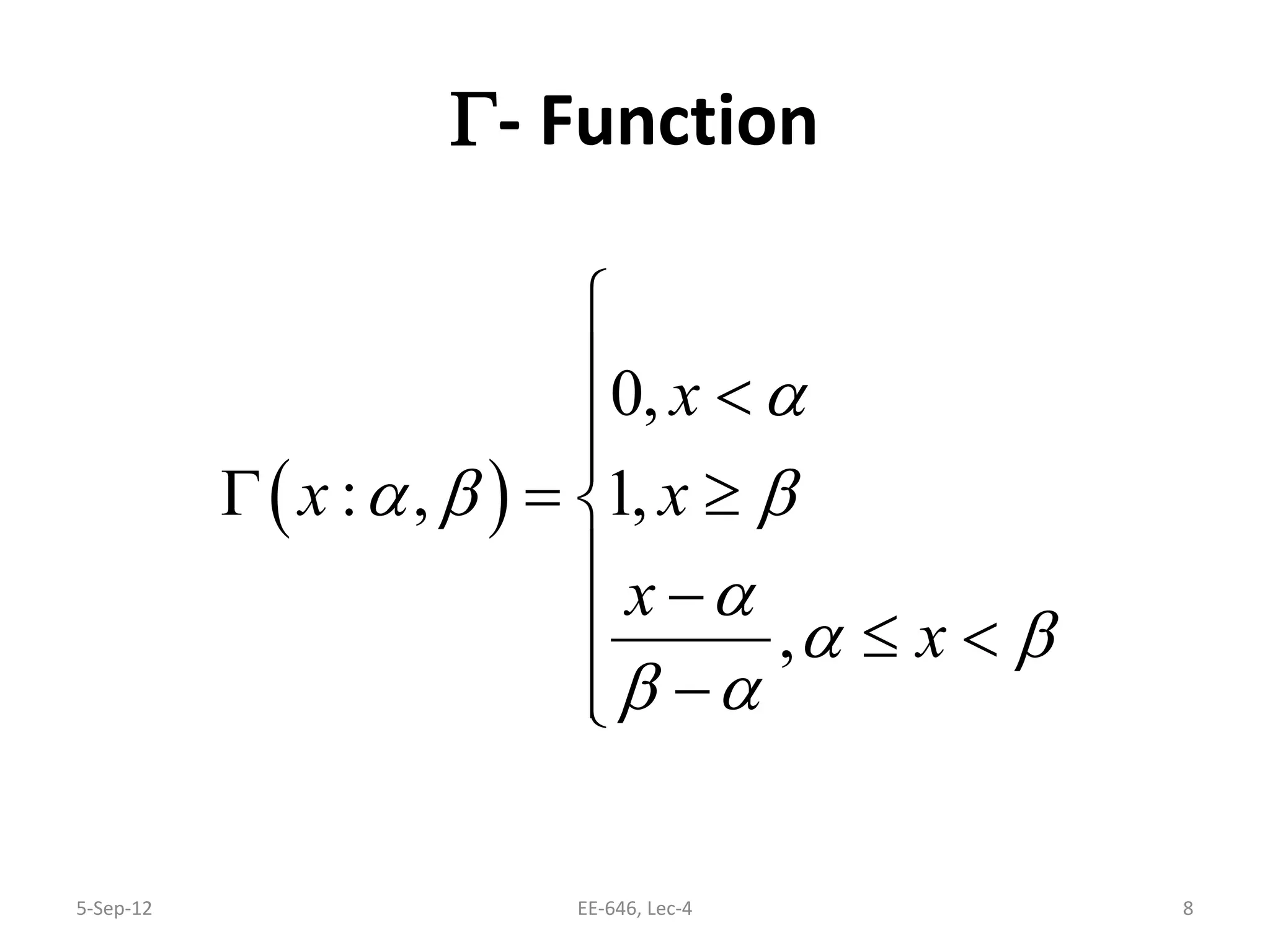
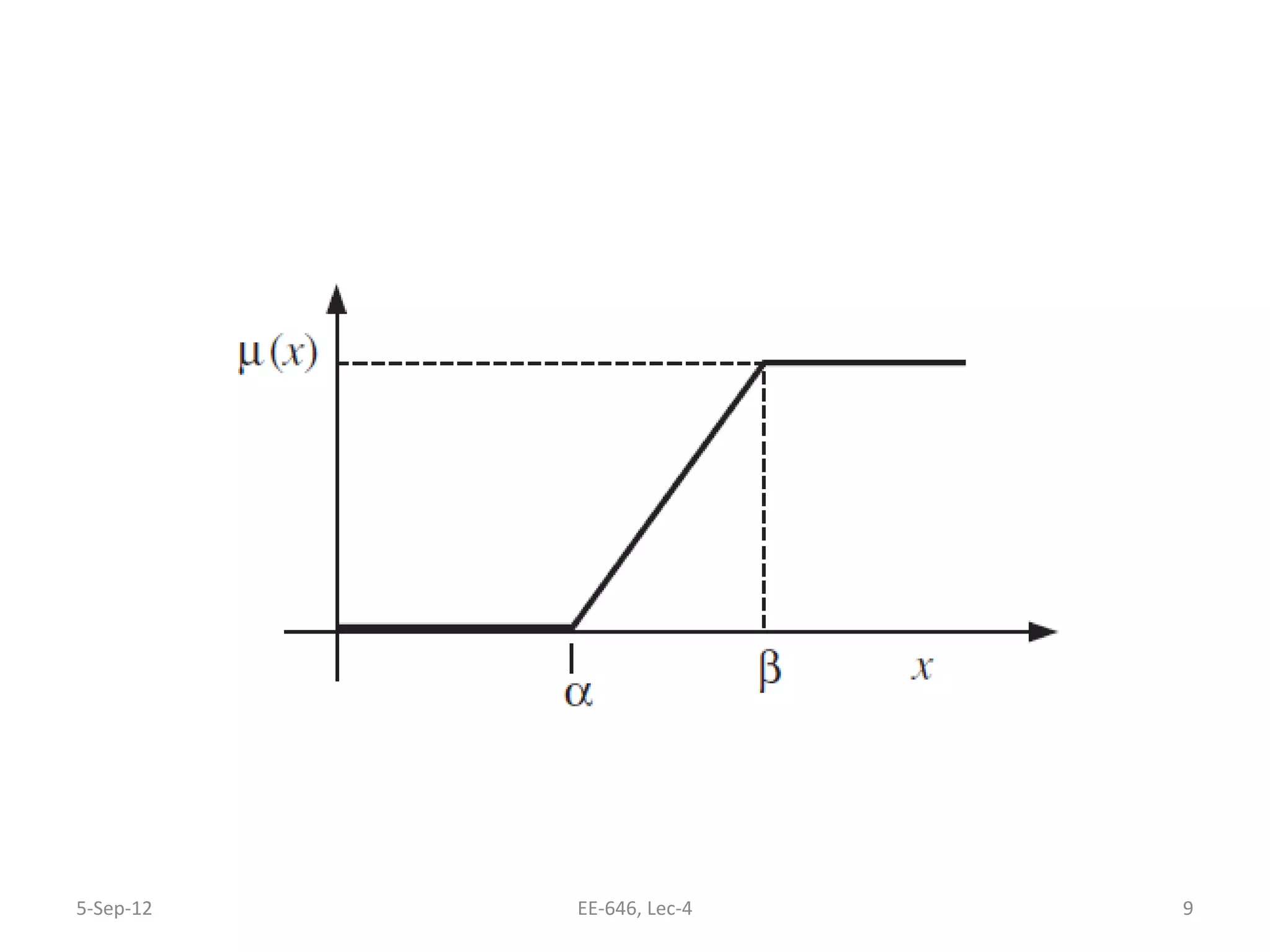
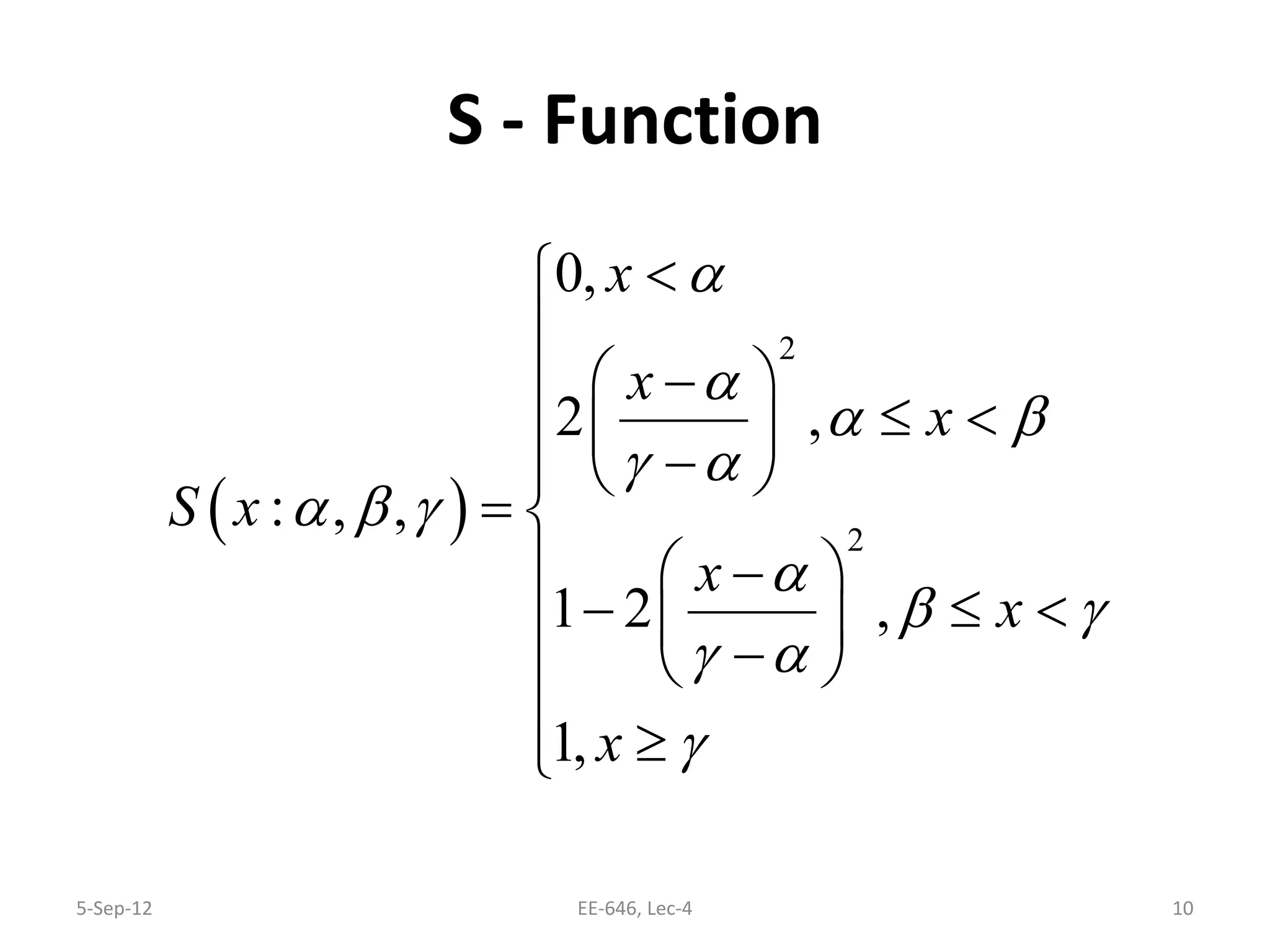
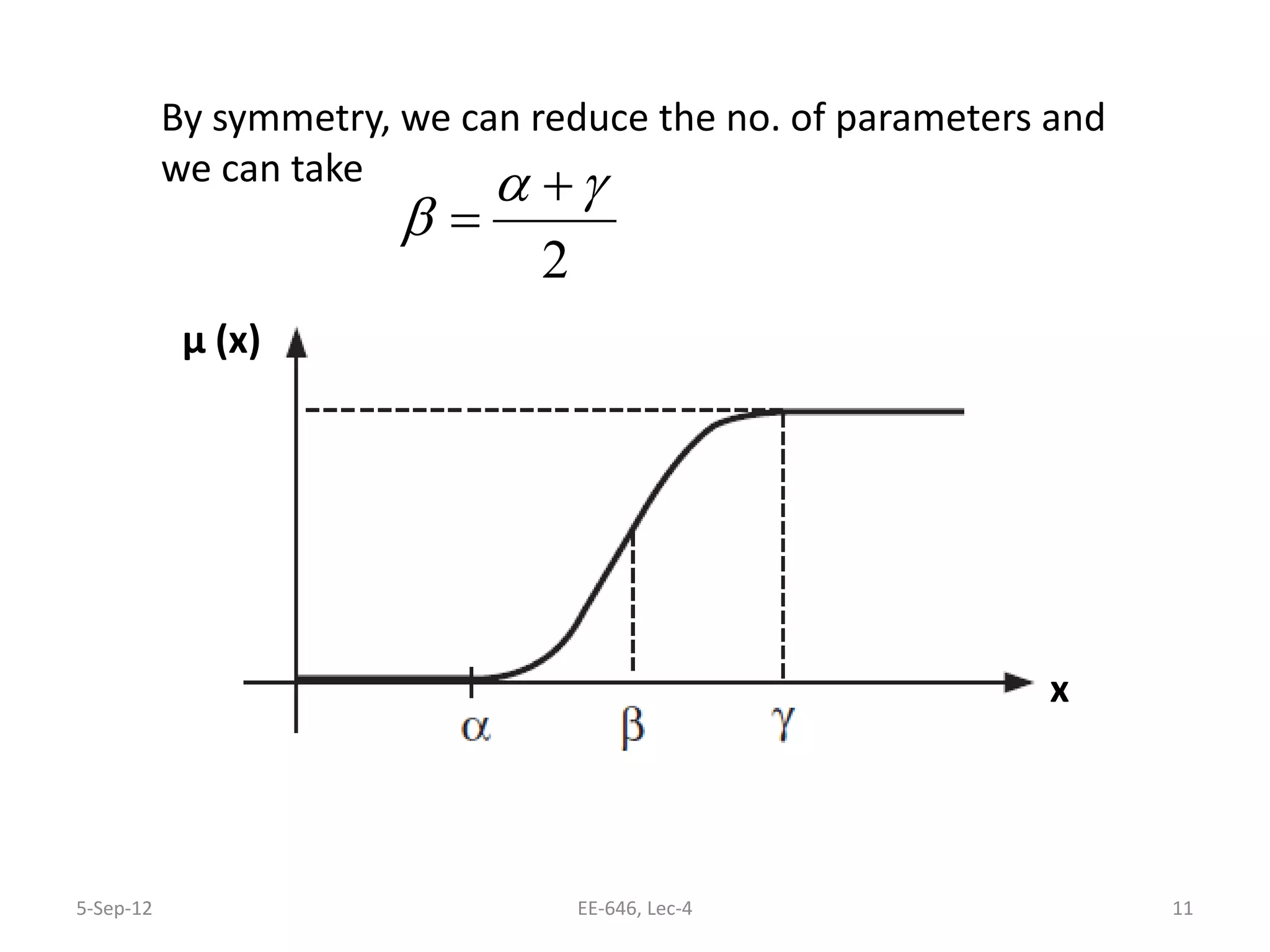
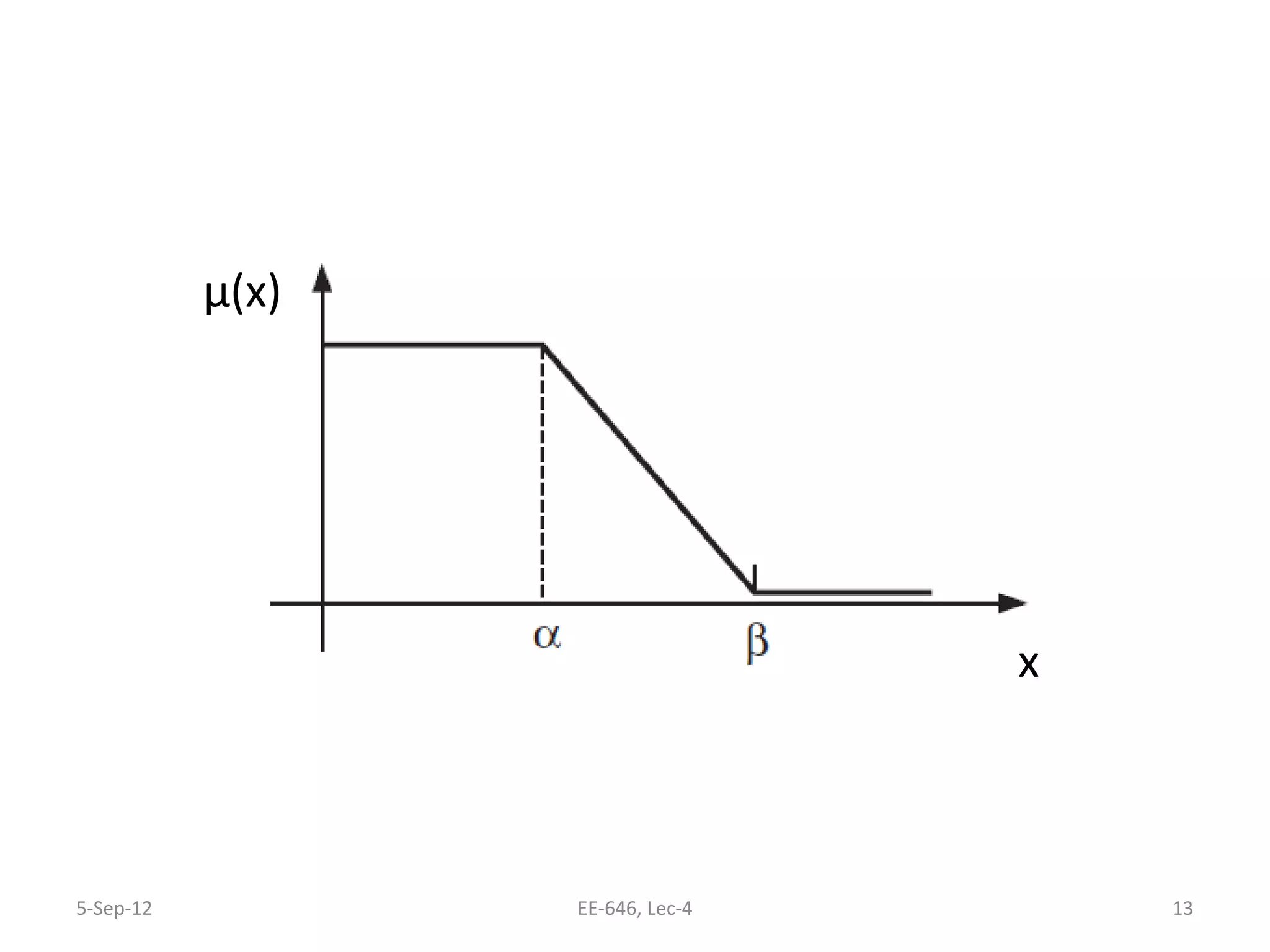
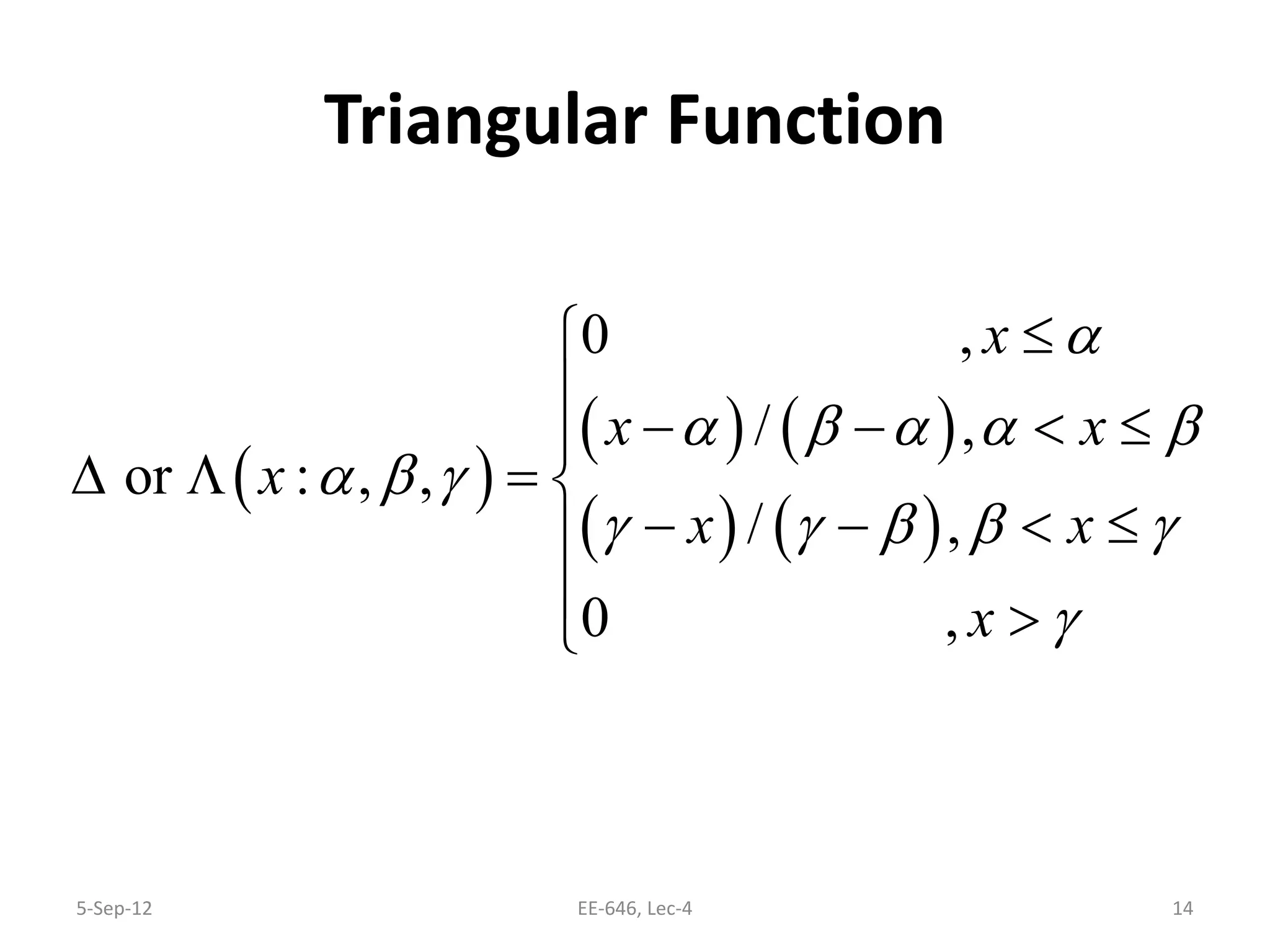
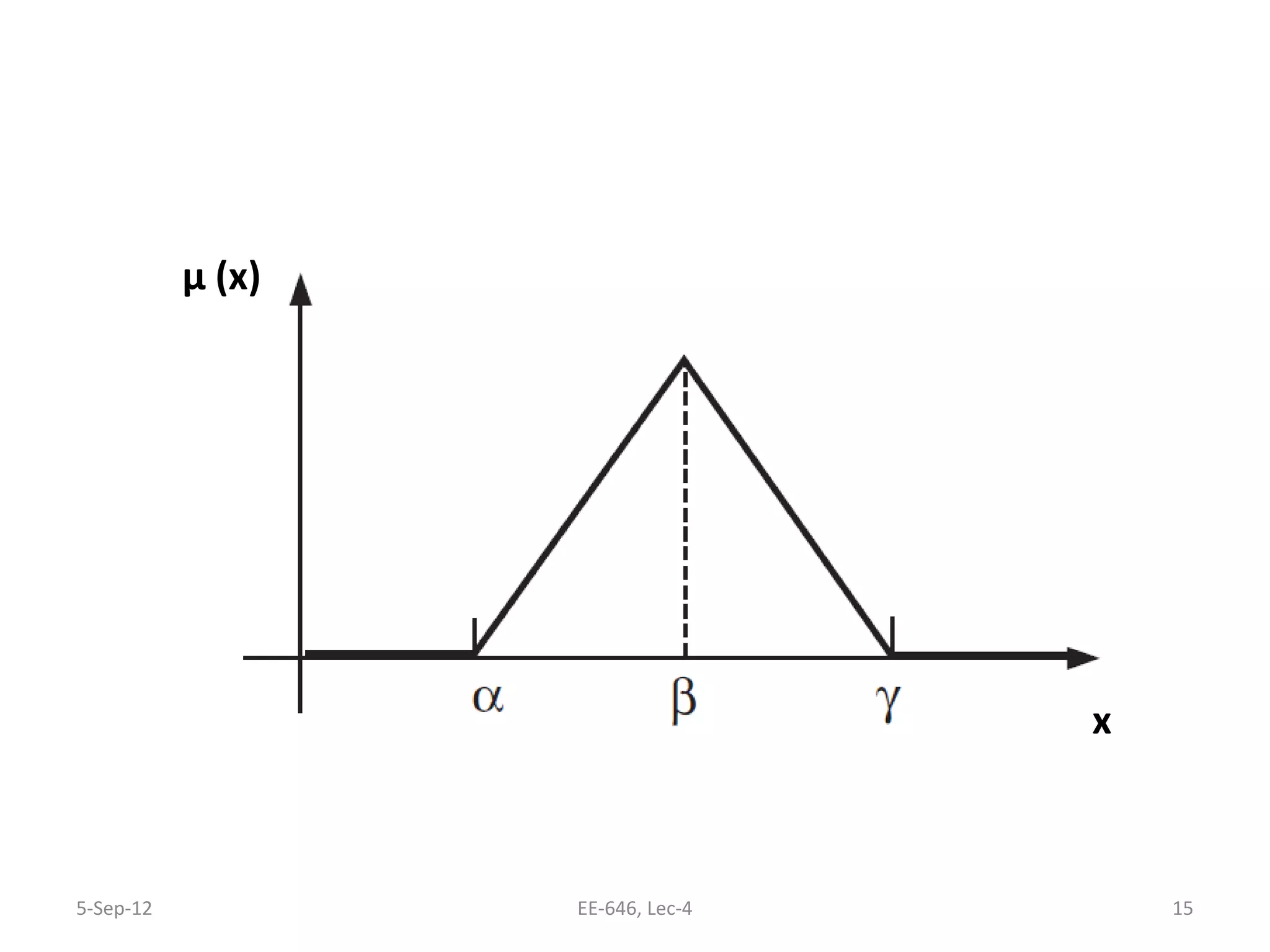
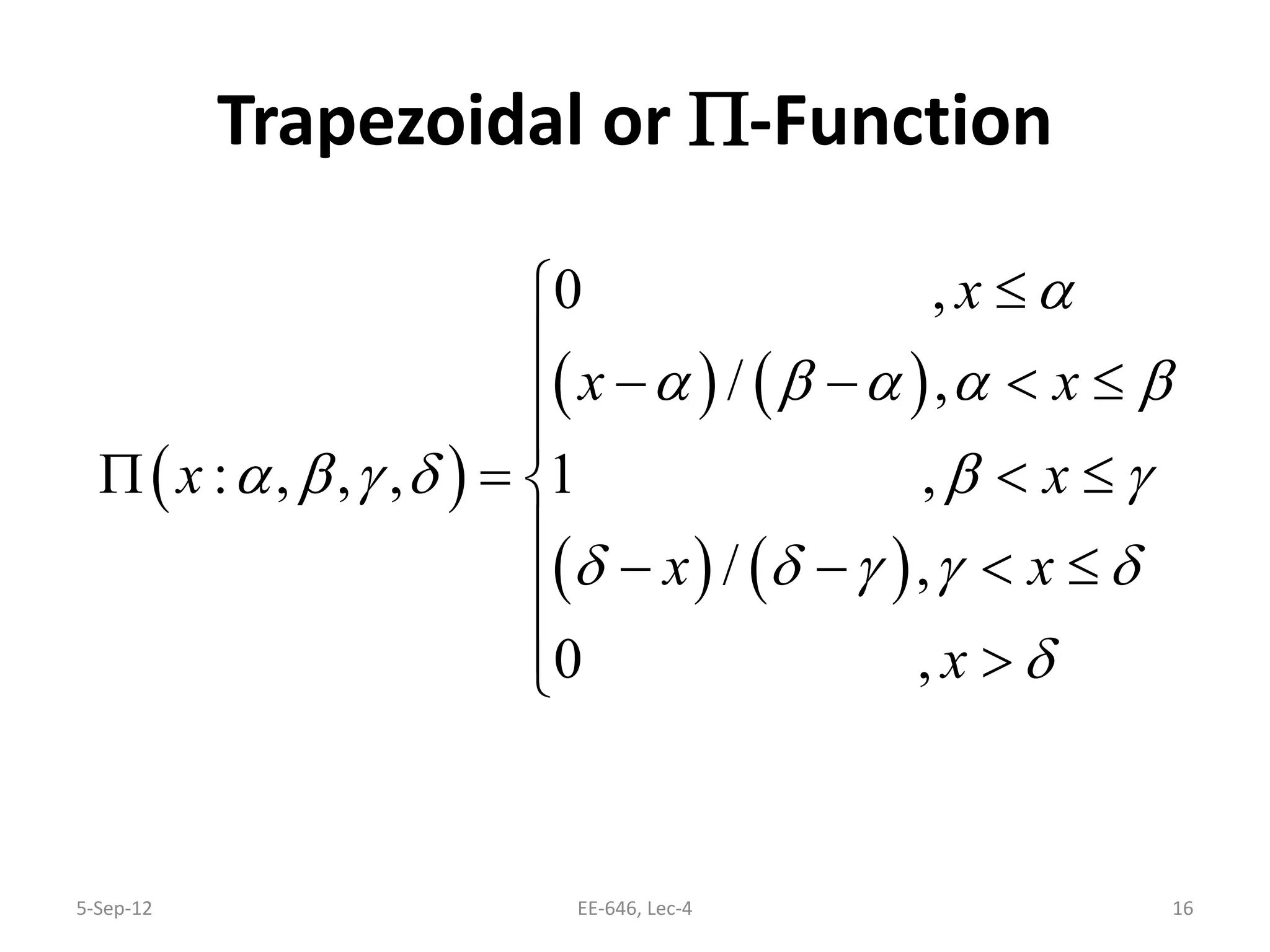
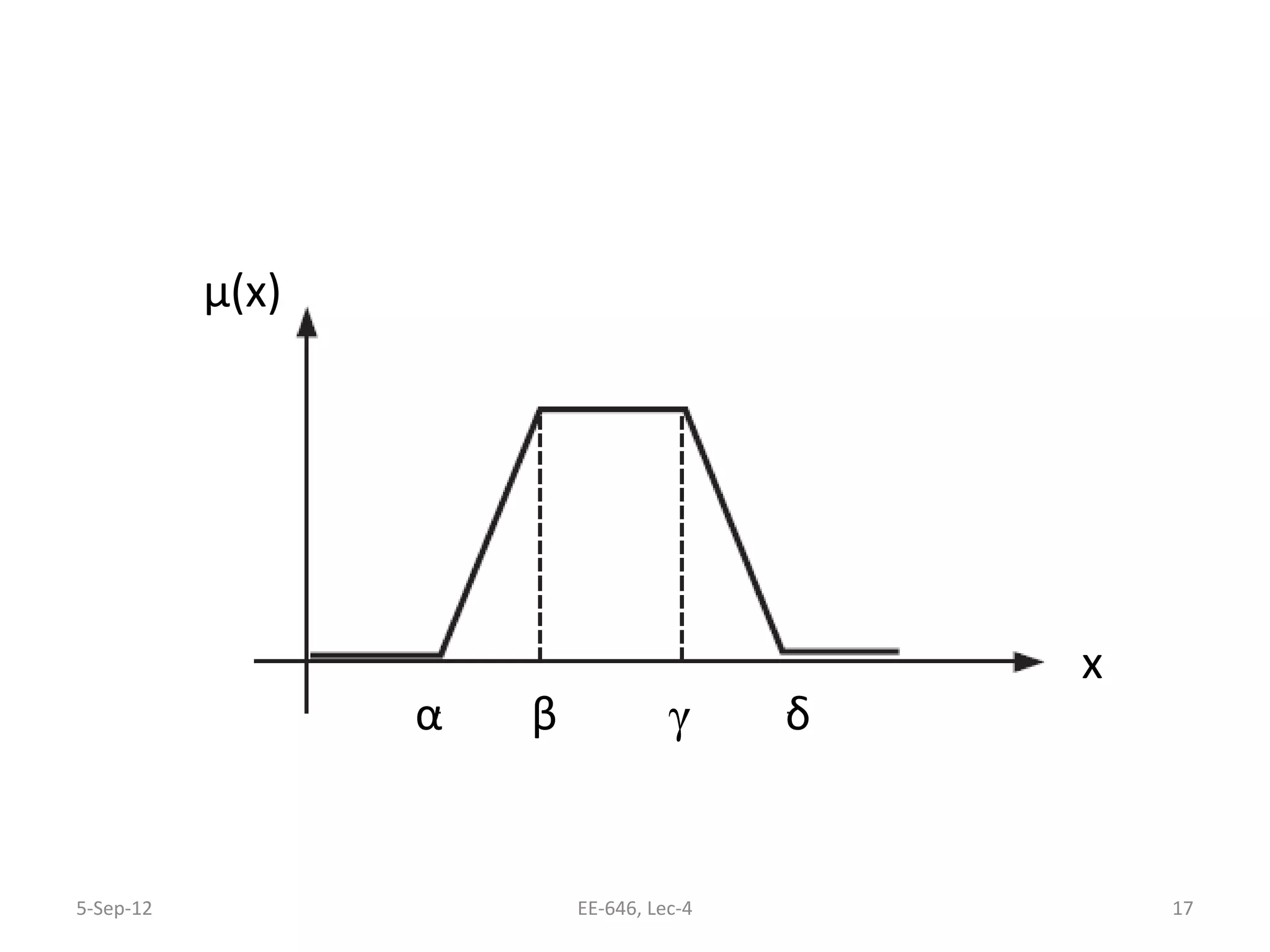
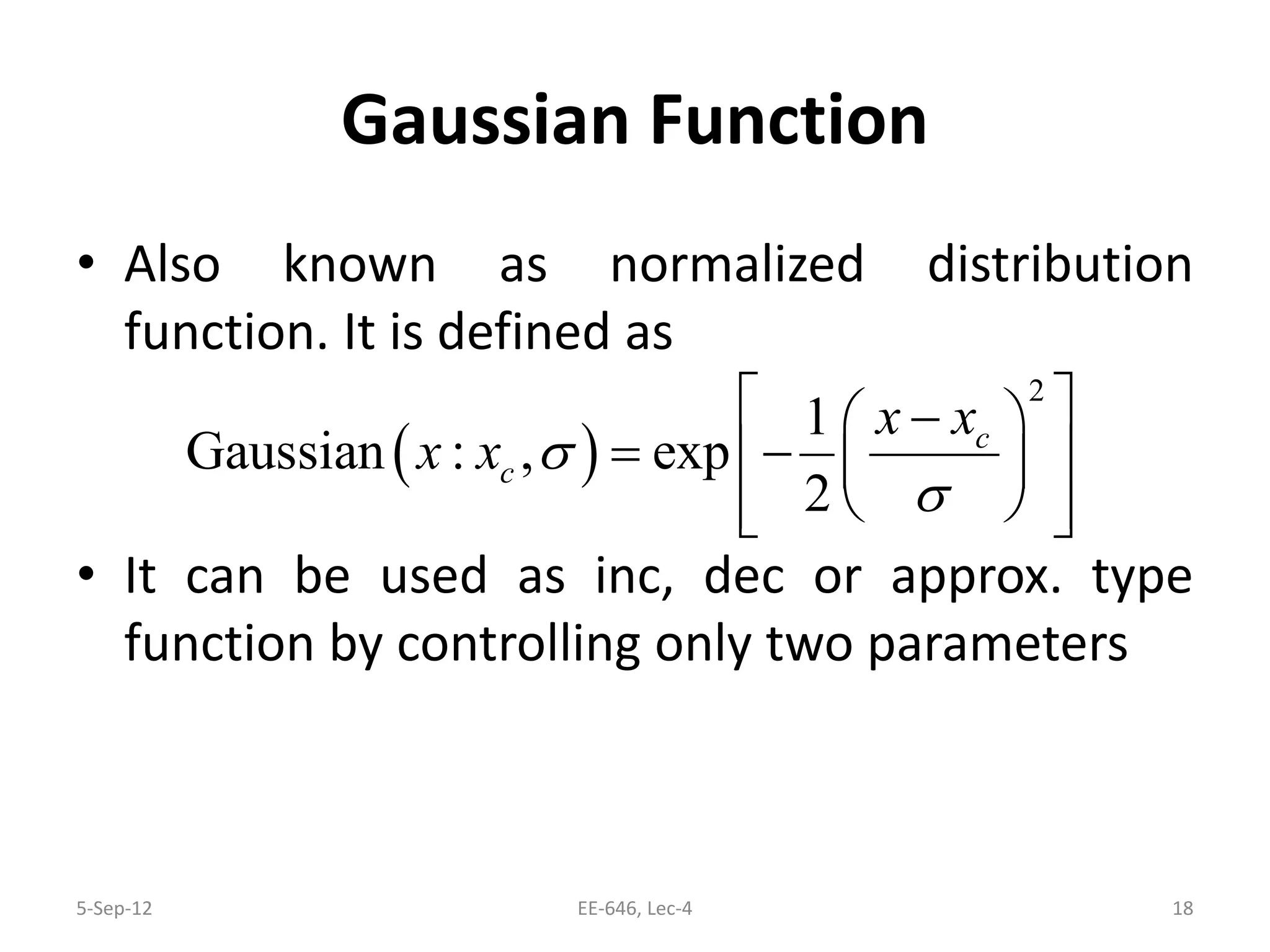
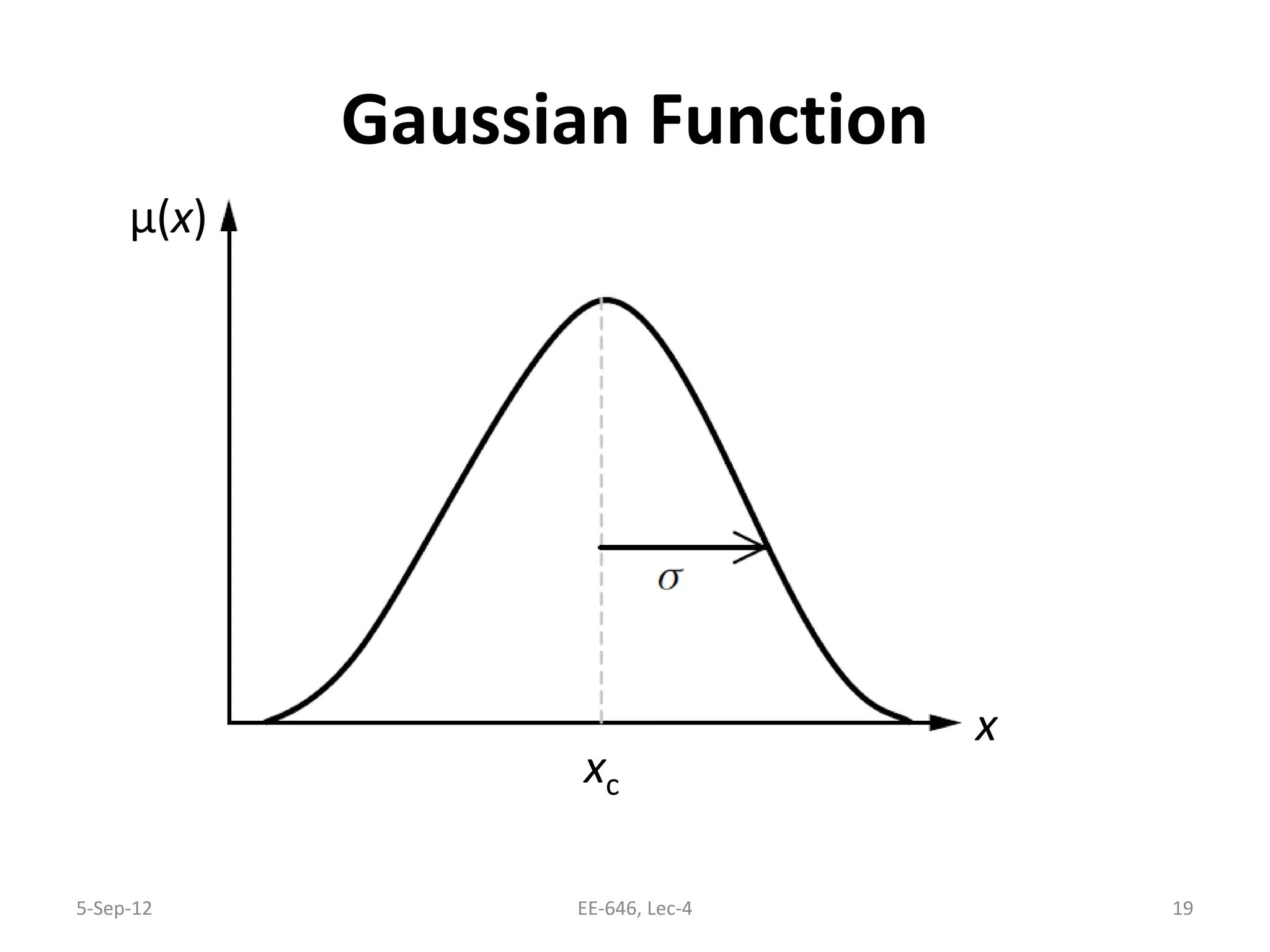
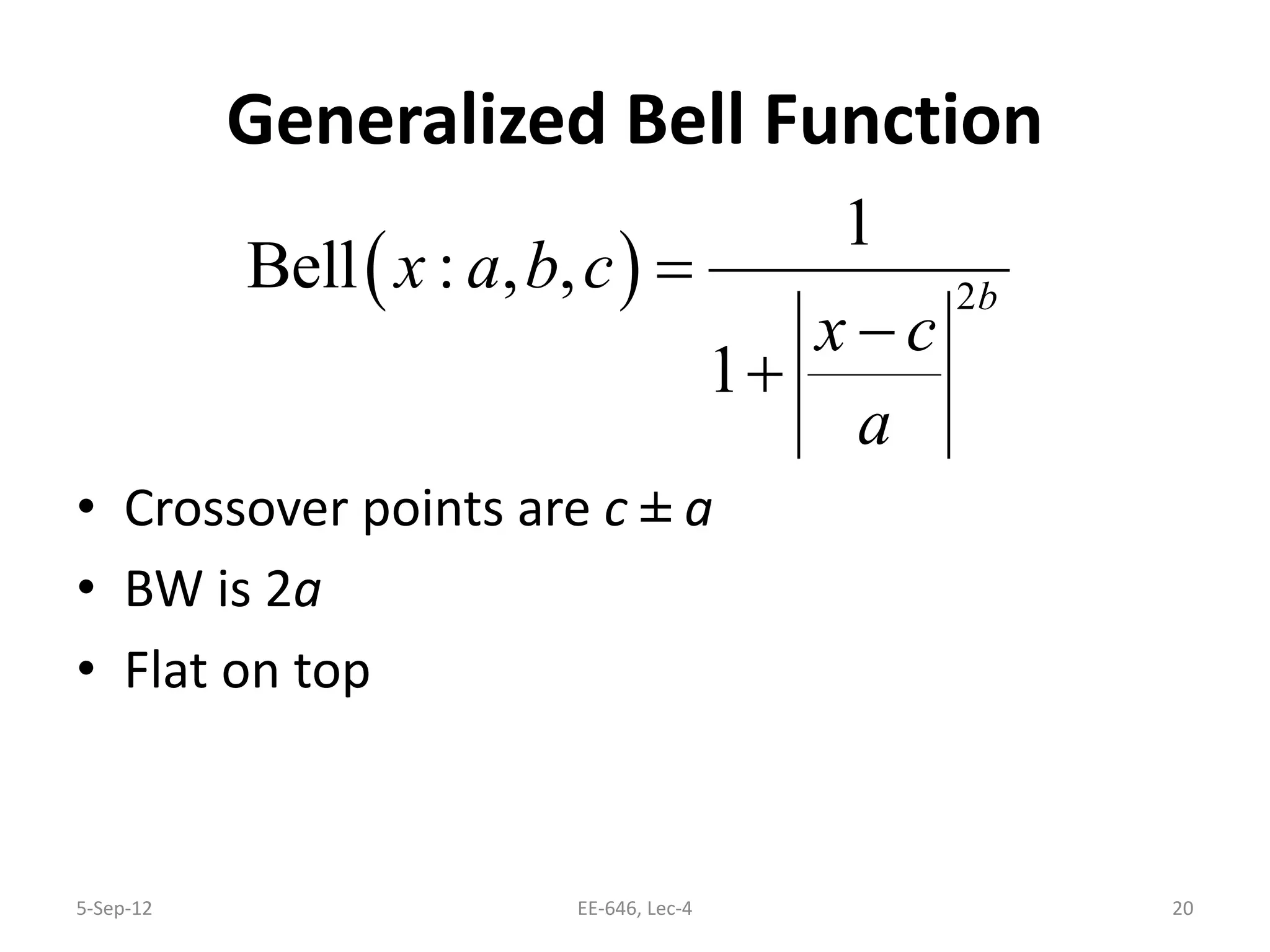
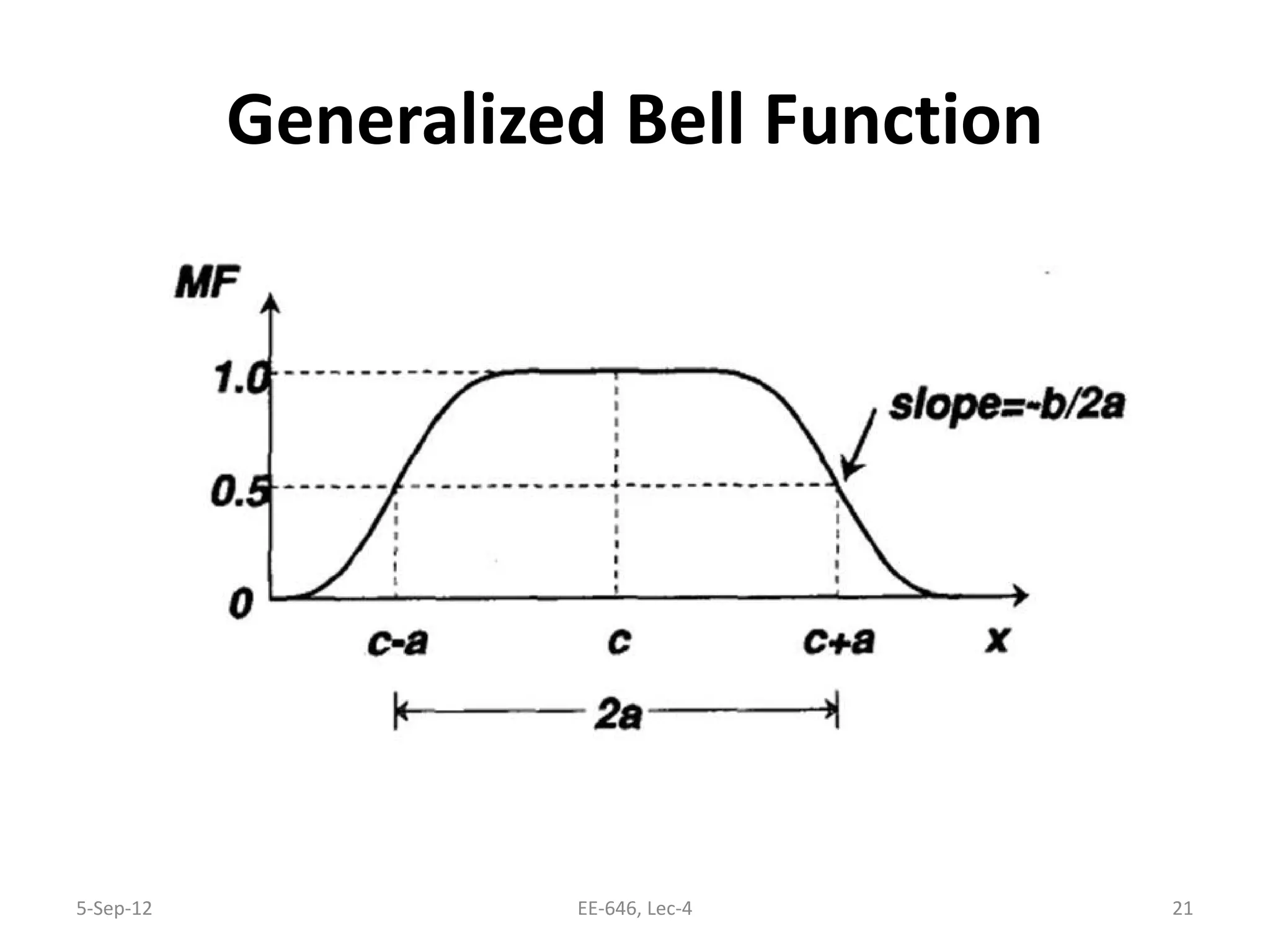
The lecture discusses various types of membership functions in fuzzy sets, including symmetric, decreasing, increasing, and approximating functions. It also details specific functions such as γ-function, s-function, l or z-function, triangular function, trapezoidal function, Gaussian function, and generalized bell function. Additionally, the session concludes with a task to explore MATLAB commands for these functions.