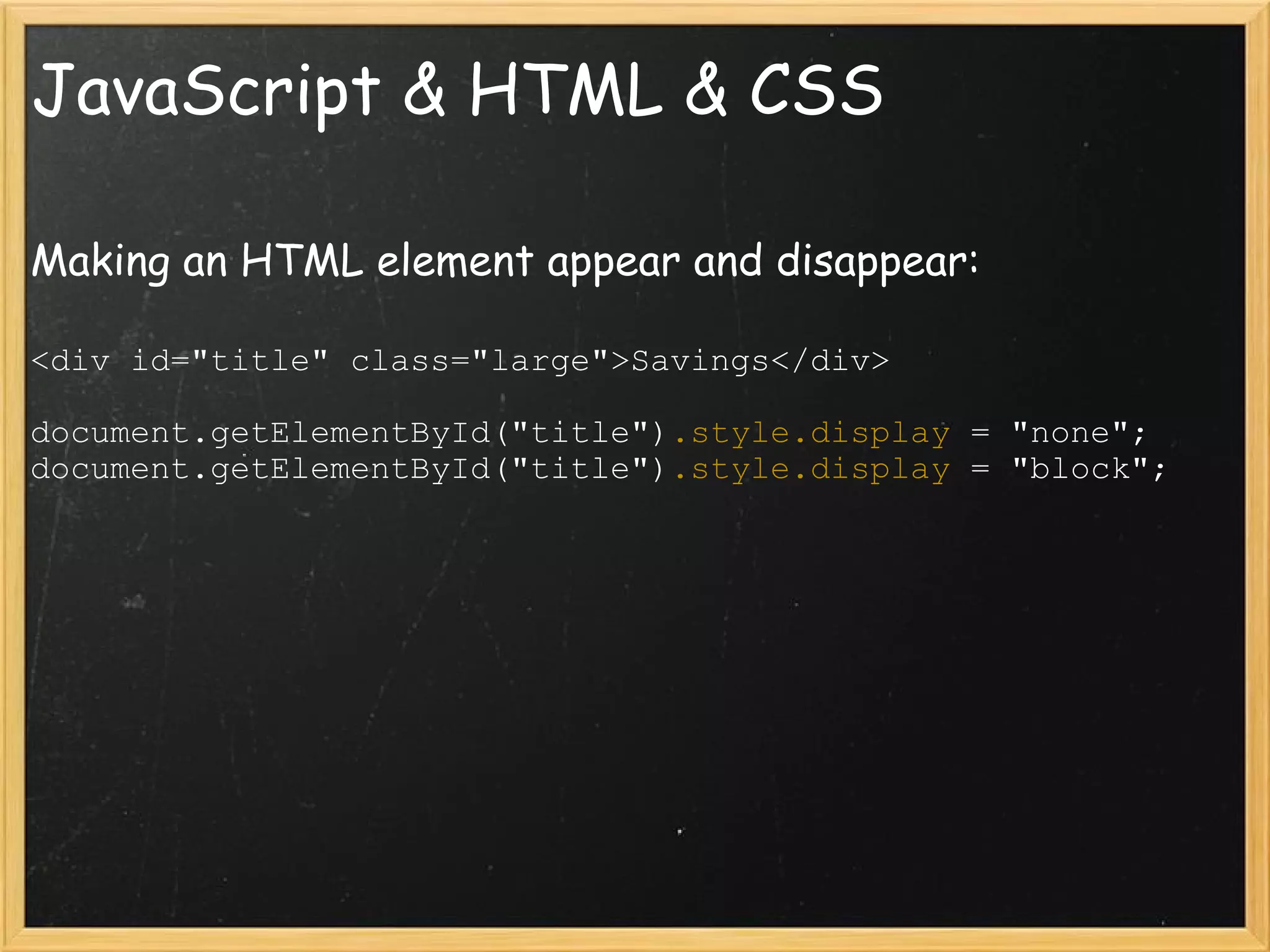
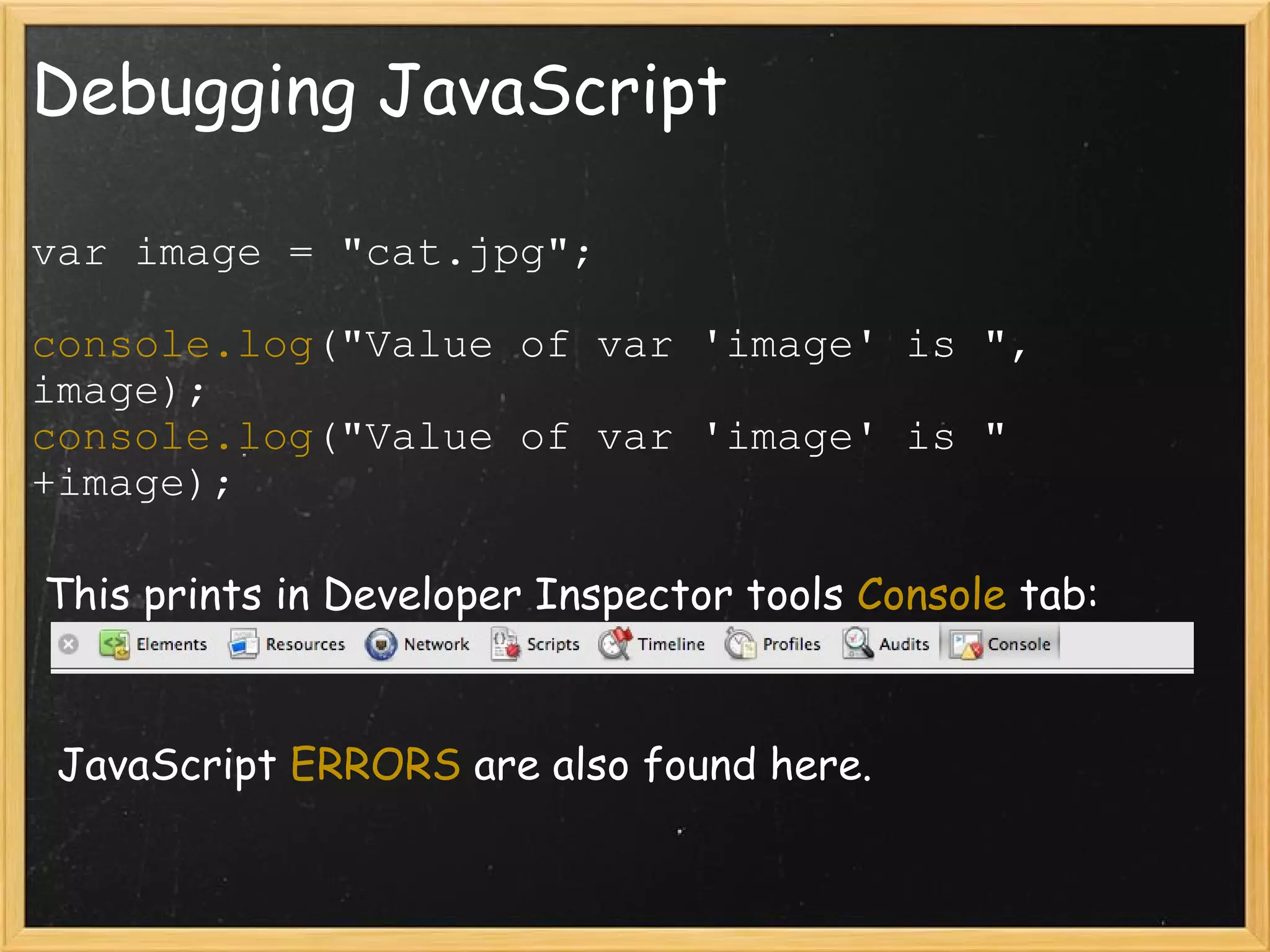
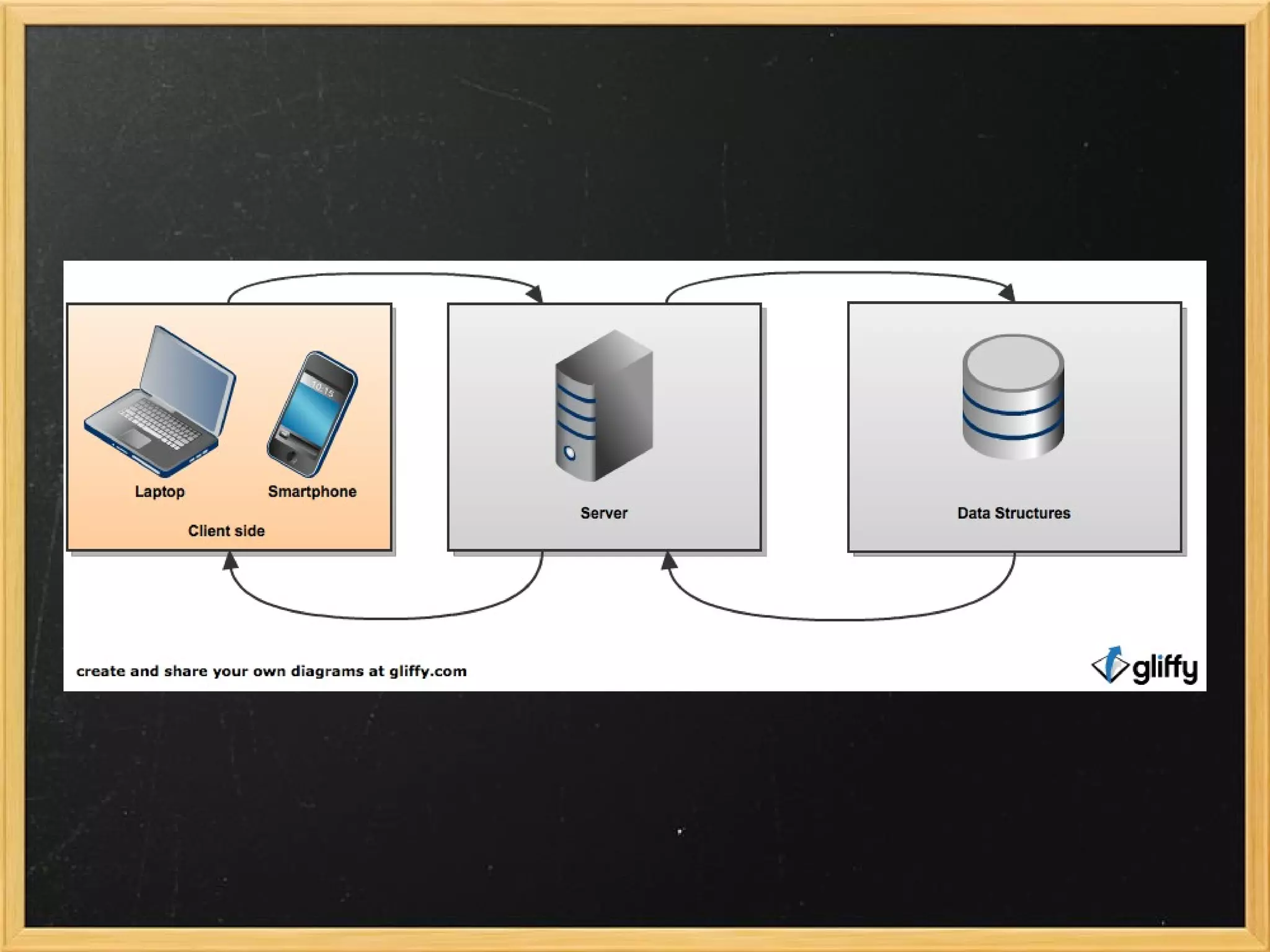
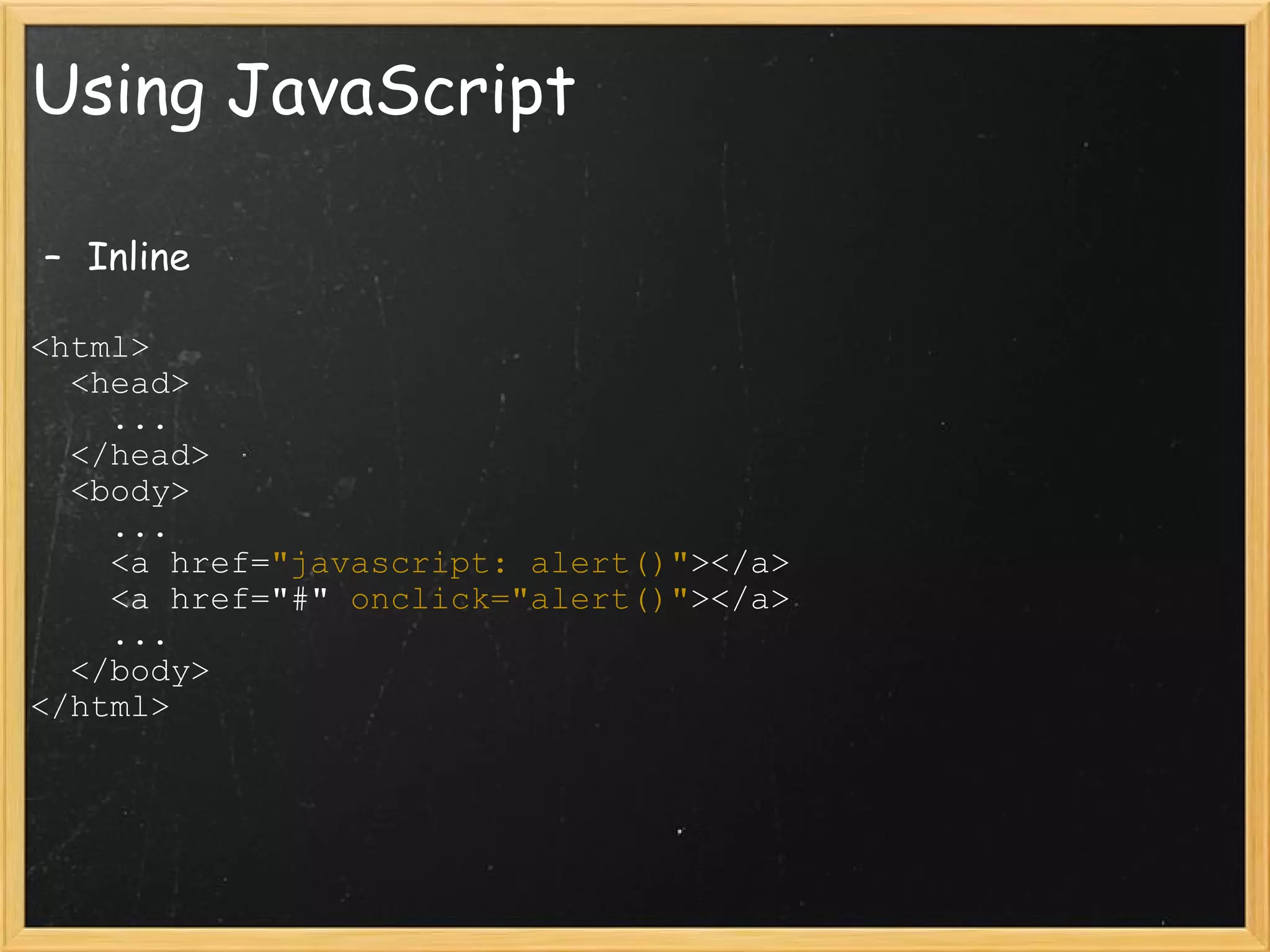
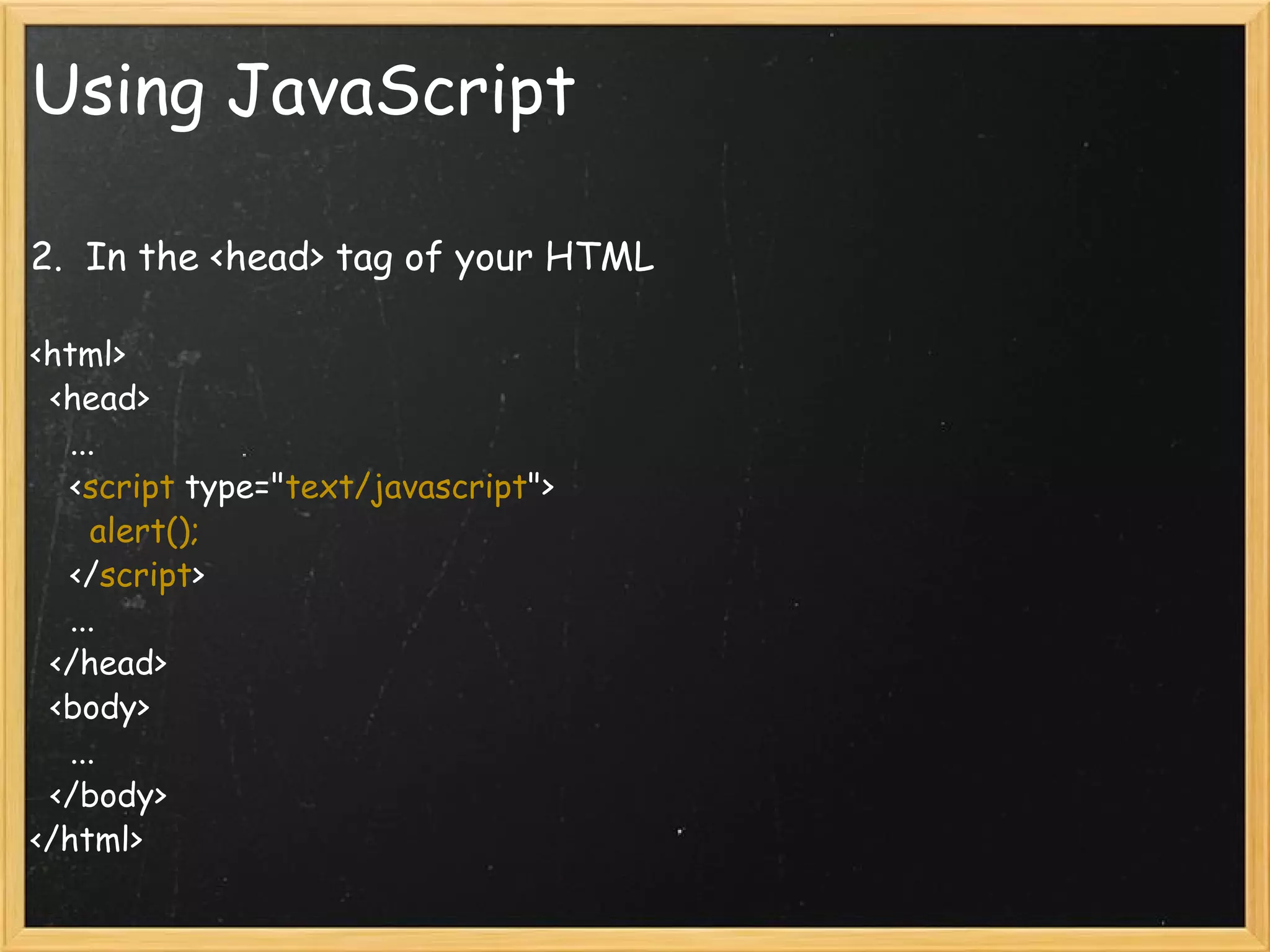
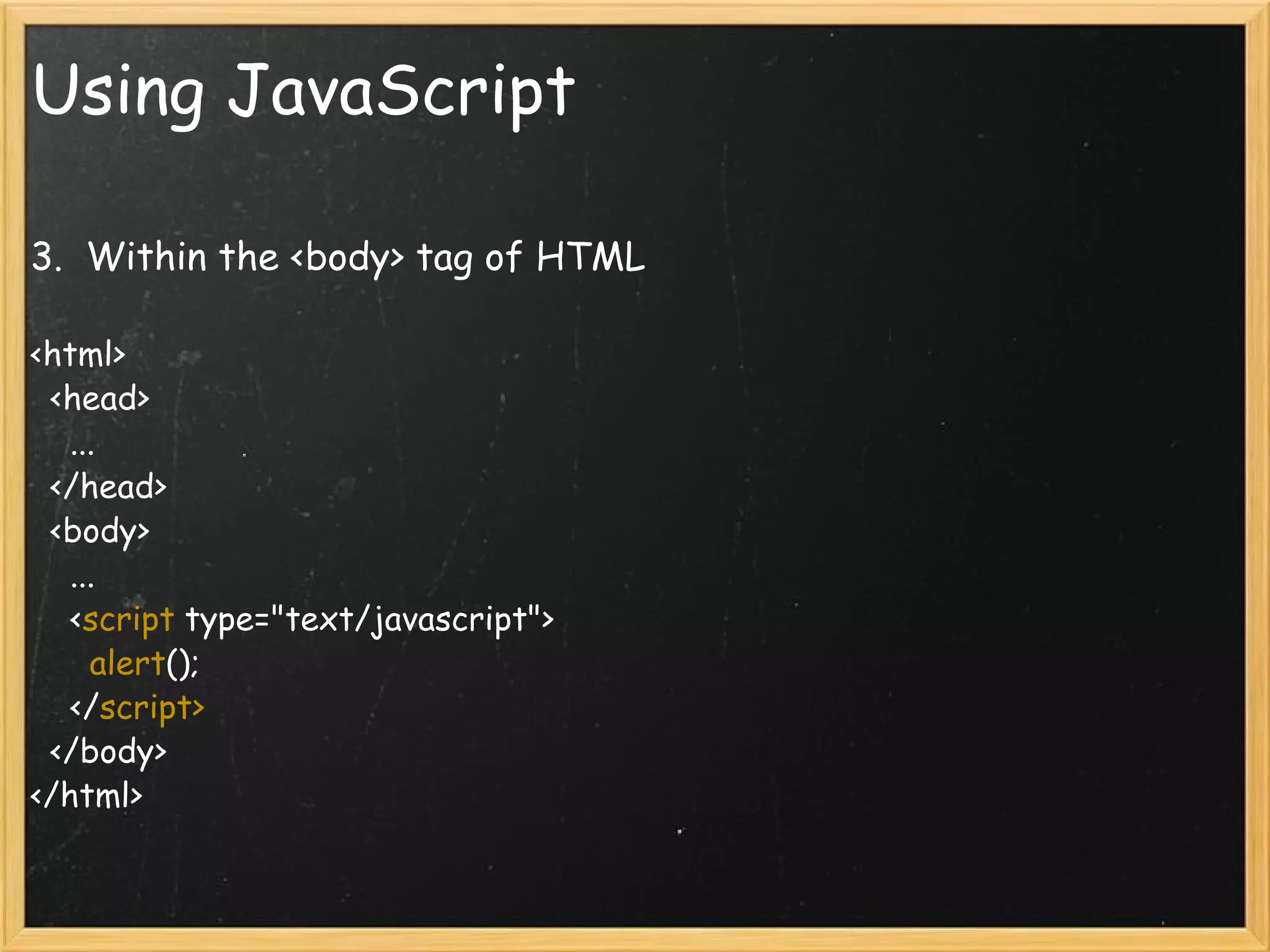
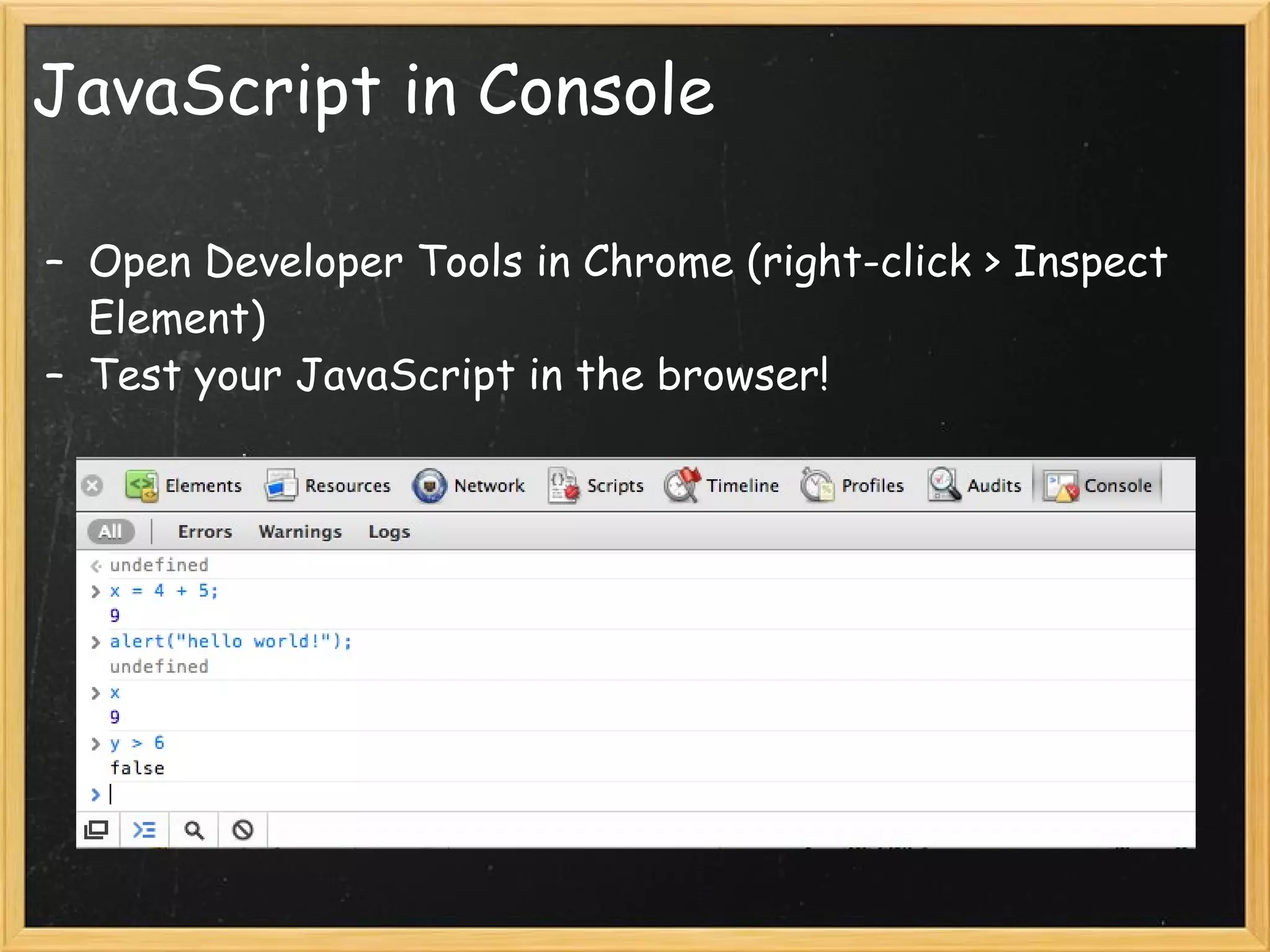
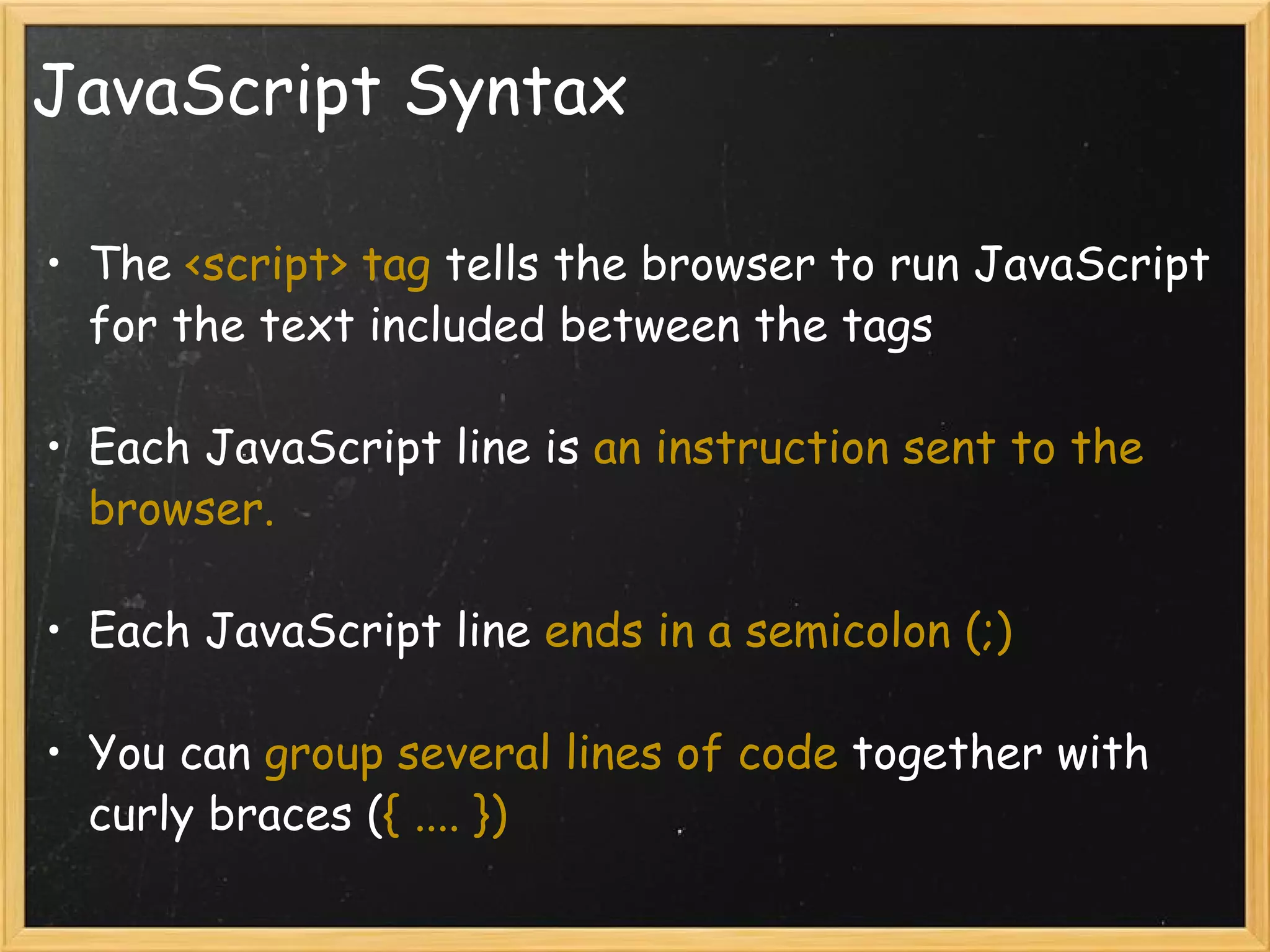
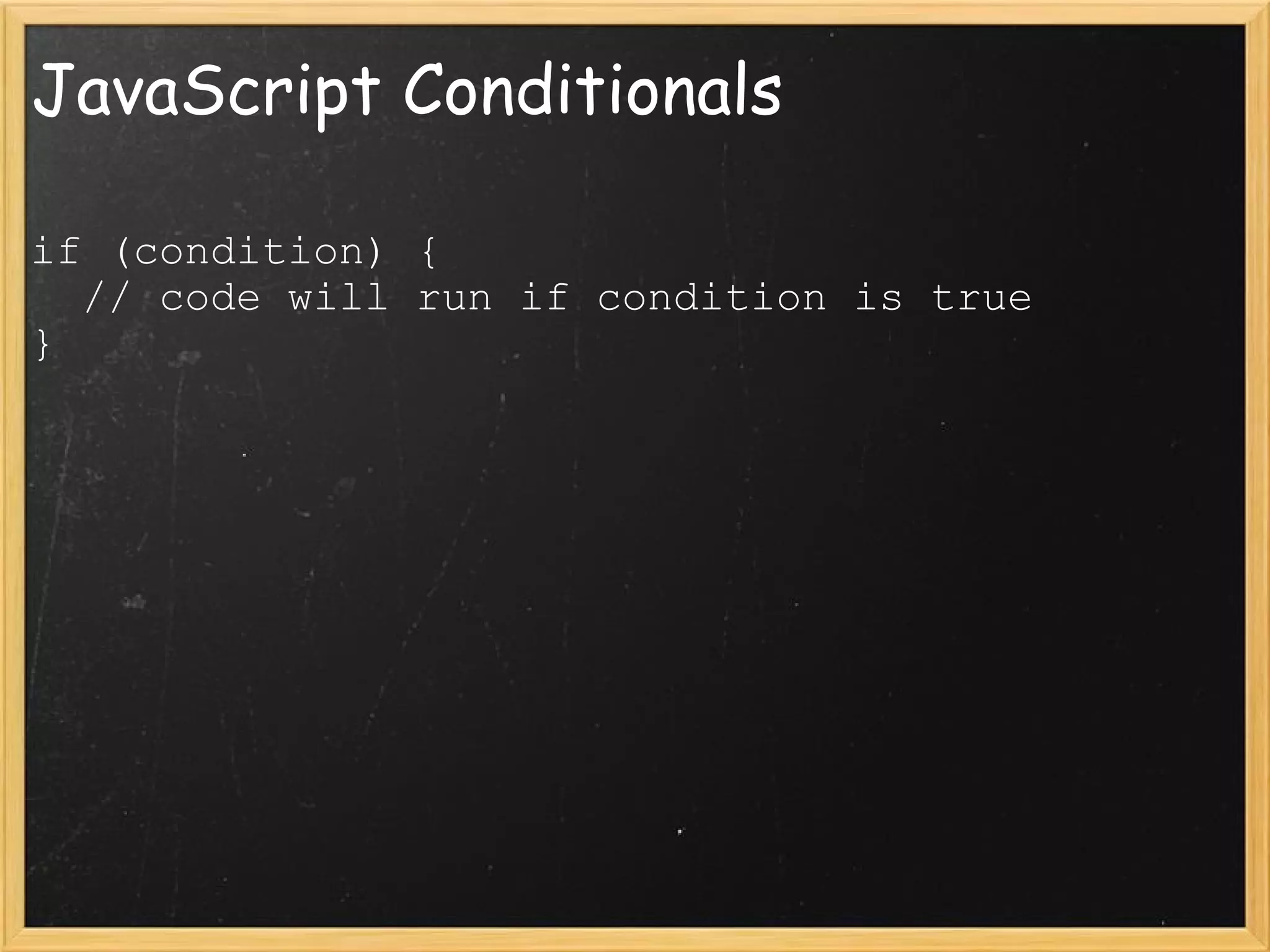
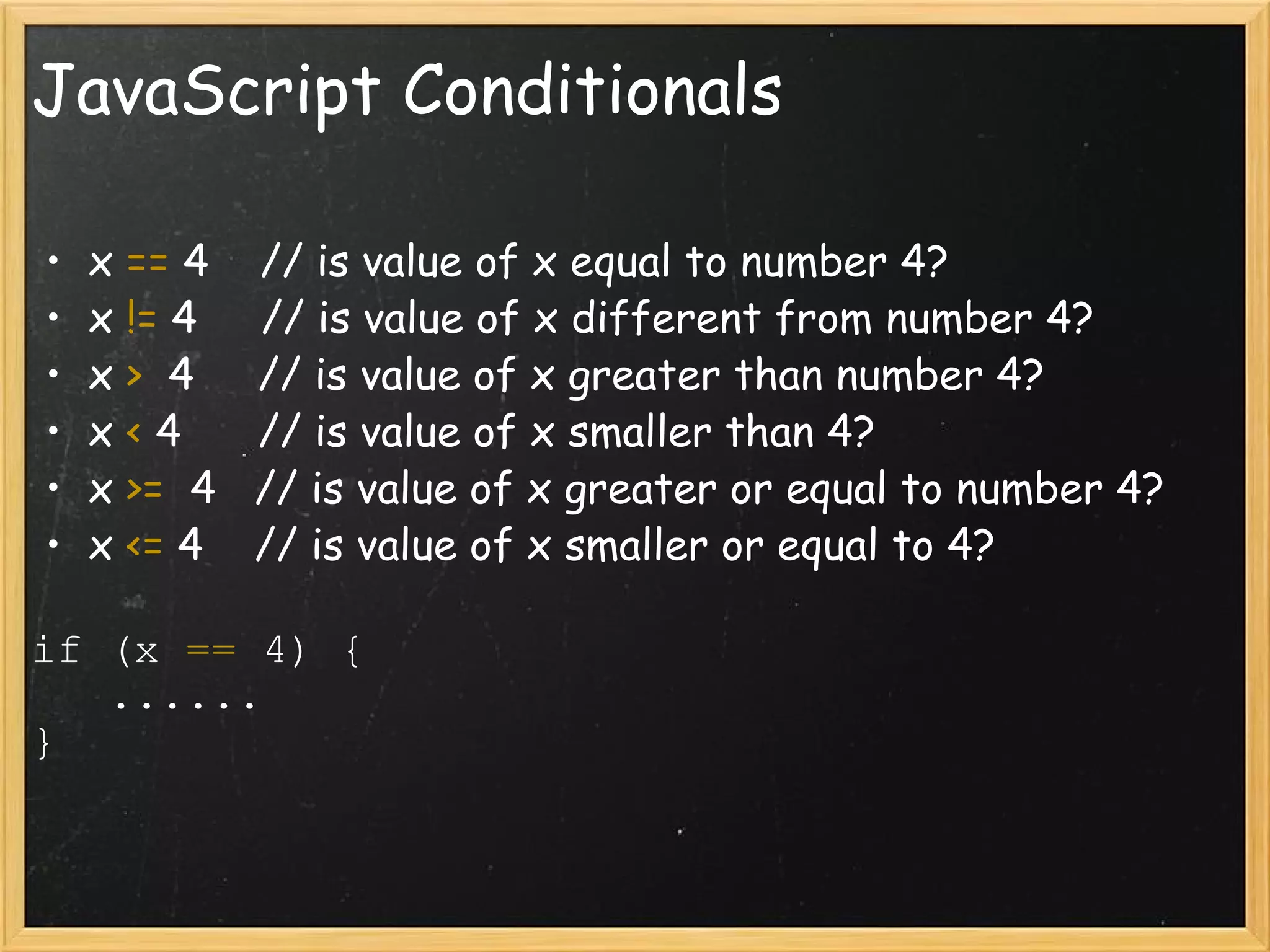
This document provides an introduction to JavaScript, covering syntax, variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, functions, events, and how to manipulate HTML elements with JavaScript. It discusses different ways to include JavaScript in HTML documents, such as inline, internally, and externally. Examples are provided for common JavaScript tasks like alerts, form validation, and dynamic content.










![JavaScript Variable Types Numbers var x = 0; Strings - used for representing text var message = "Please try again." var car = 'Ford' You can use either "" or '' Arrays - a list of values var arr = [3, 4, 5]; var pets = new Array();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5commlabweb-111024124504-phpapp02/75/Lecture-5-Comm-Lab-Web-ITP-19-2048.jpg)

![JavaScript Arrays var pets= new Array() ; pets [0] ="cat"; pets [1] ="dog"; pets [2] ="fish"; var pets= new Array( "cat","dog","fish" ) ; var pets= [ "cat","dog","fish" ] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5commlabweb-111024124504-phpapp02/75/Lecture-5-Comm-Lab-Web-ITP-21-2048.jpg)
![JavaScript Arrays var fave_pet = pets[2] // will get "fish" pets[2] = parrots; // This reassigns the value var pet_count = pets.length; // Returns 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5commlabweb-111024124504-phpapp02/75/Lecture-5-Comm-Lab-Web-ITP-22-2048.jpg)



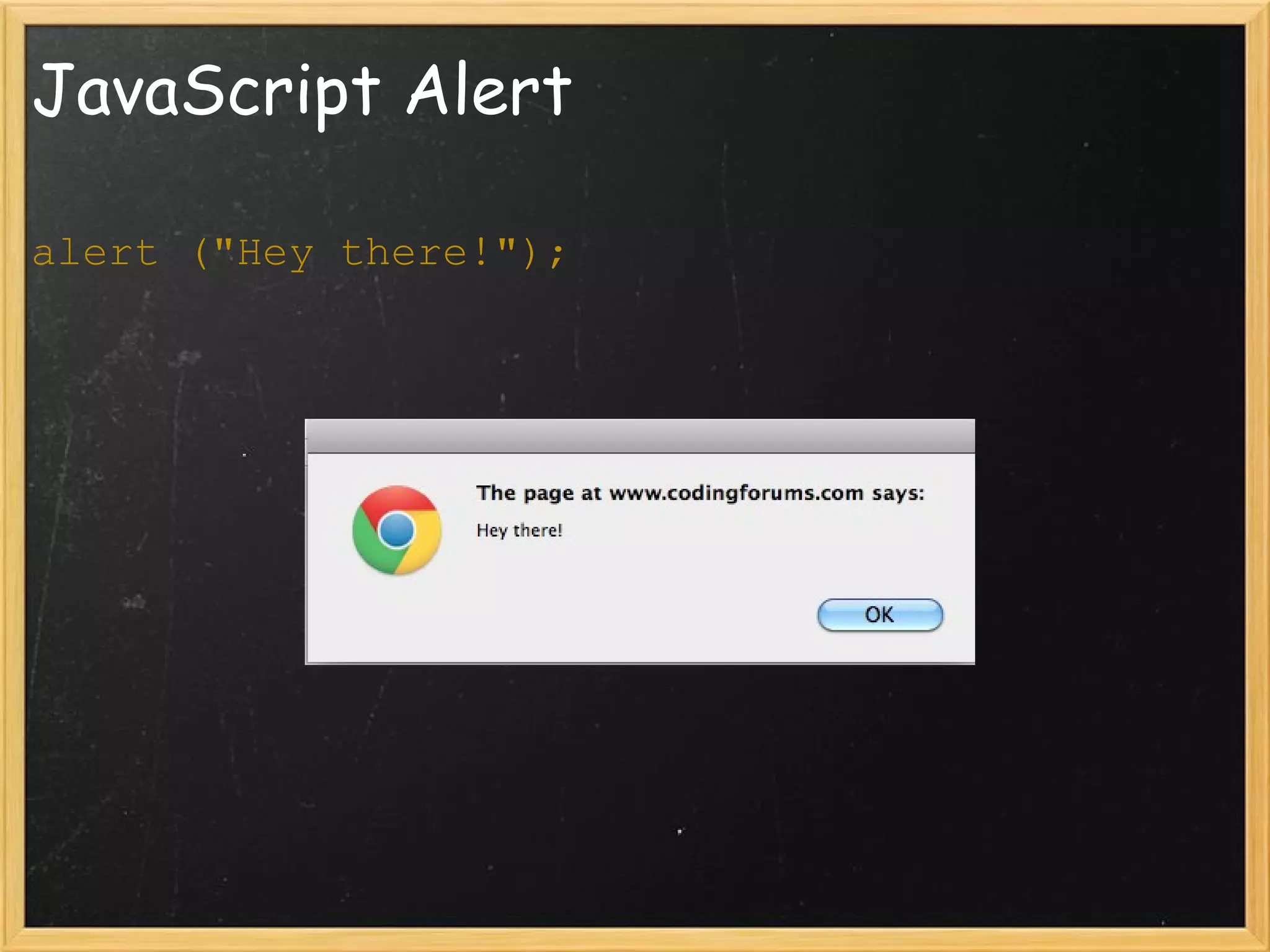




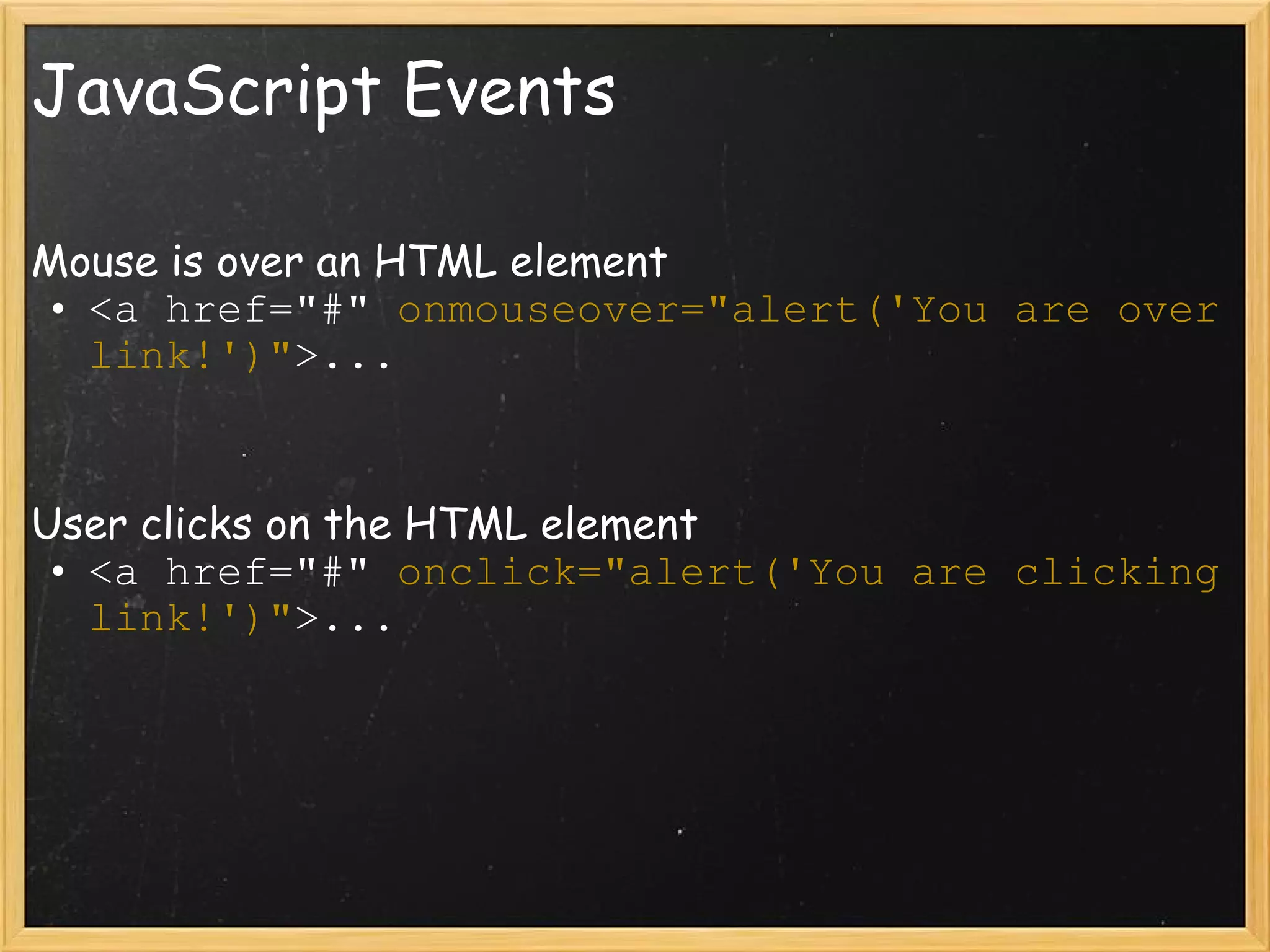
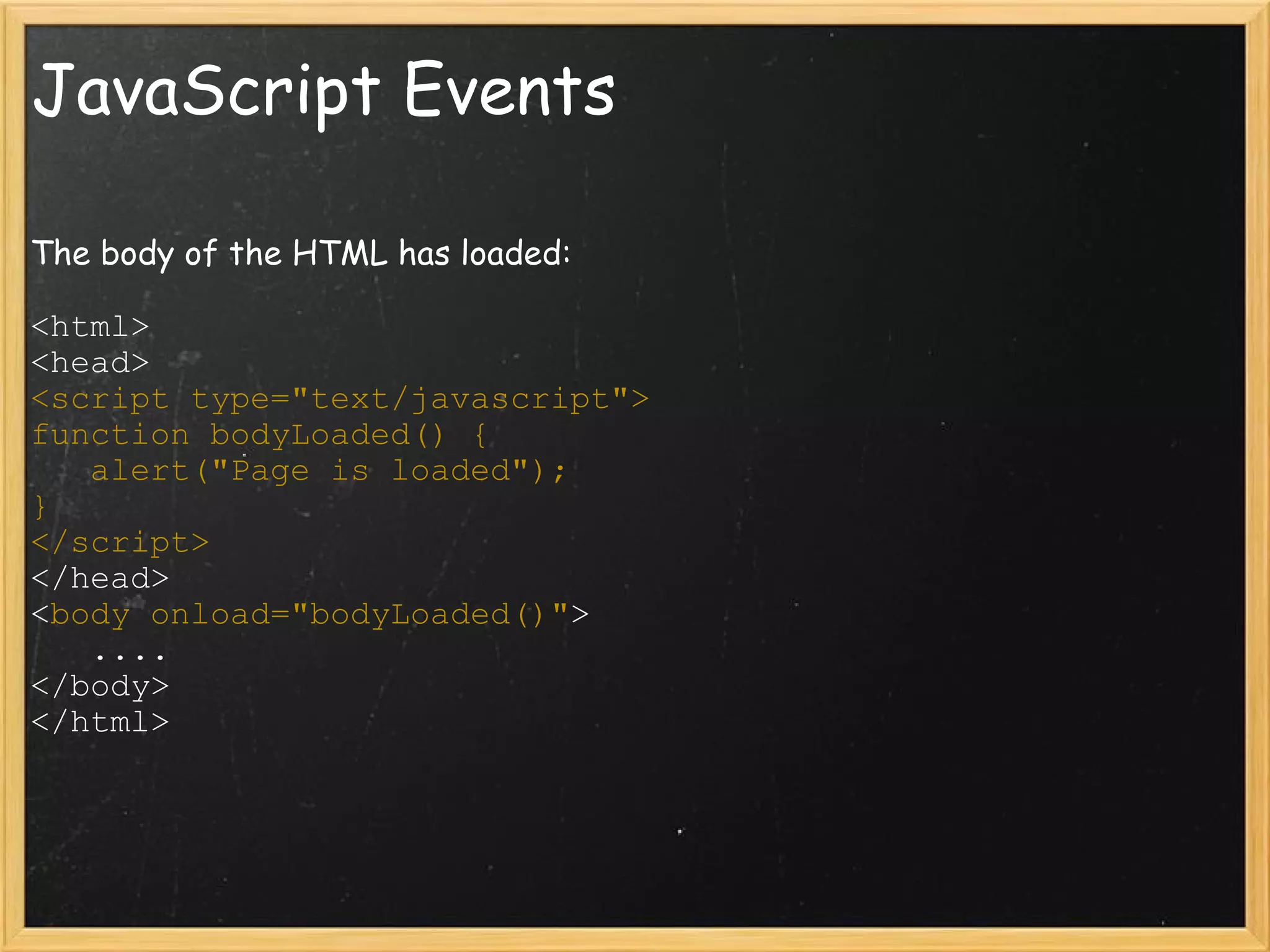






![JavaScript and HTML document .anchors // Array containing all links document. anchors[2] // Third link element on page (<a>) document .forms[0] // Returns the first form HTML element document .forms // Array of all form elements on page document .images.length // How many image tags on page document .images // Array of all image elements on page](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5commlabweb-111024124504-phpapp02/75/Lecture-5-Comm-Lab-Web-ITP-41-2048.jpg)


![JavaScript and HTML Create HTML elements dynamically: var body = document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]; var newdiv = document .createElement('div') ; newdiv .setAttribute ('id',"images"); newdiv .innerHTML = "Images: <img src='plant.jpg' onclick='alert('Plant!')'/>"; body .appendChild(newdiv) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5commlabweb-111024124504-phpapp02/75/Lecture-5-Comm-Lab-Web-ITP-44-2048.jpg)