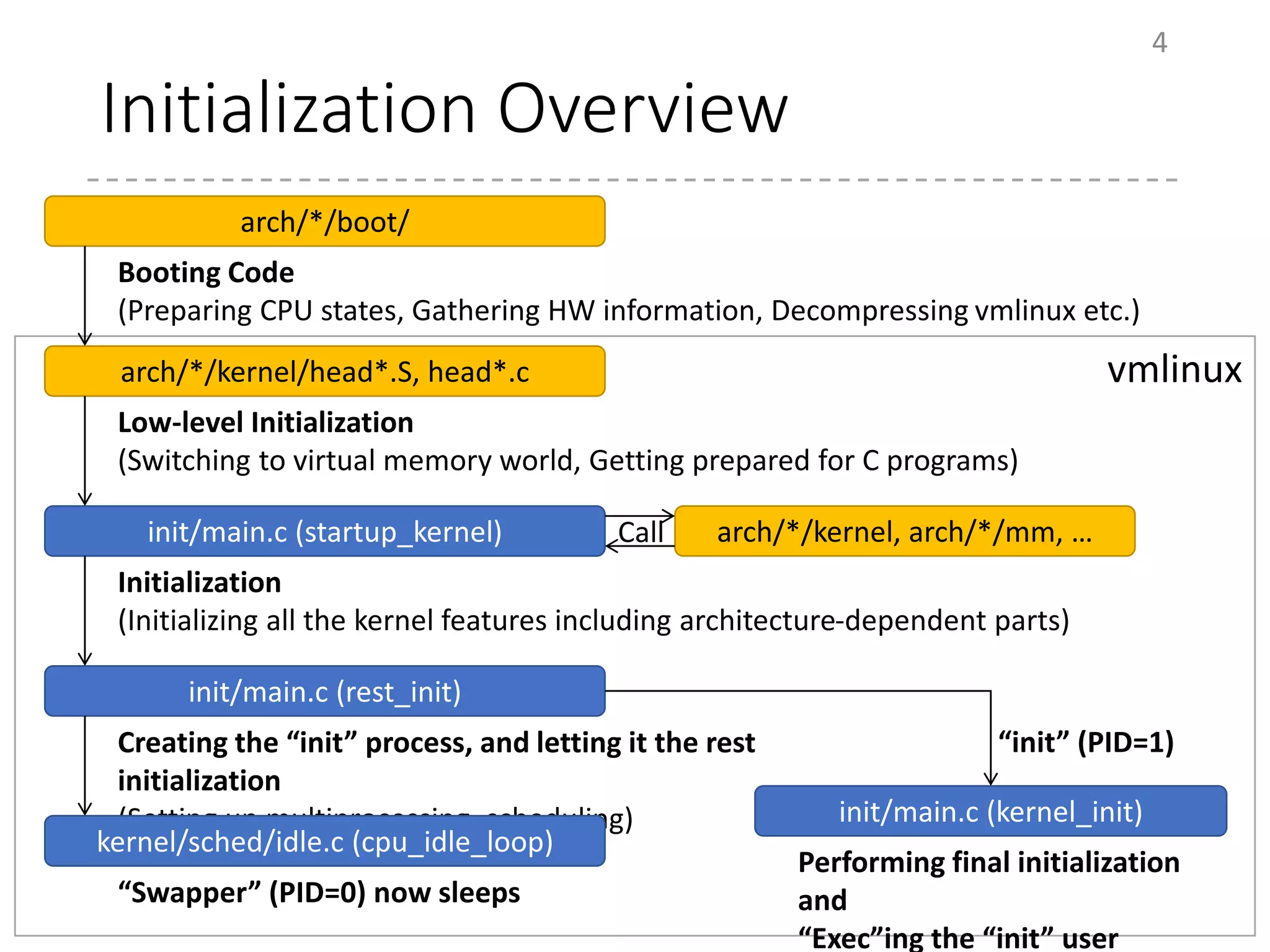
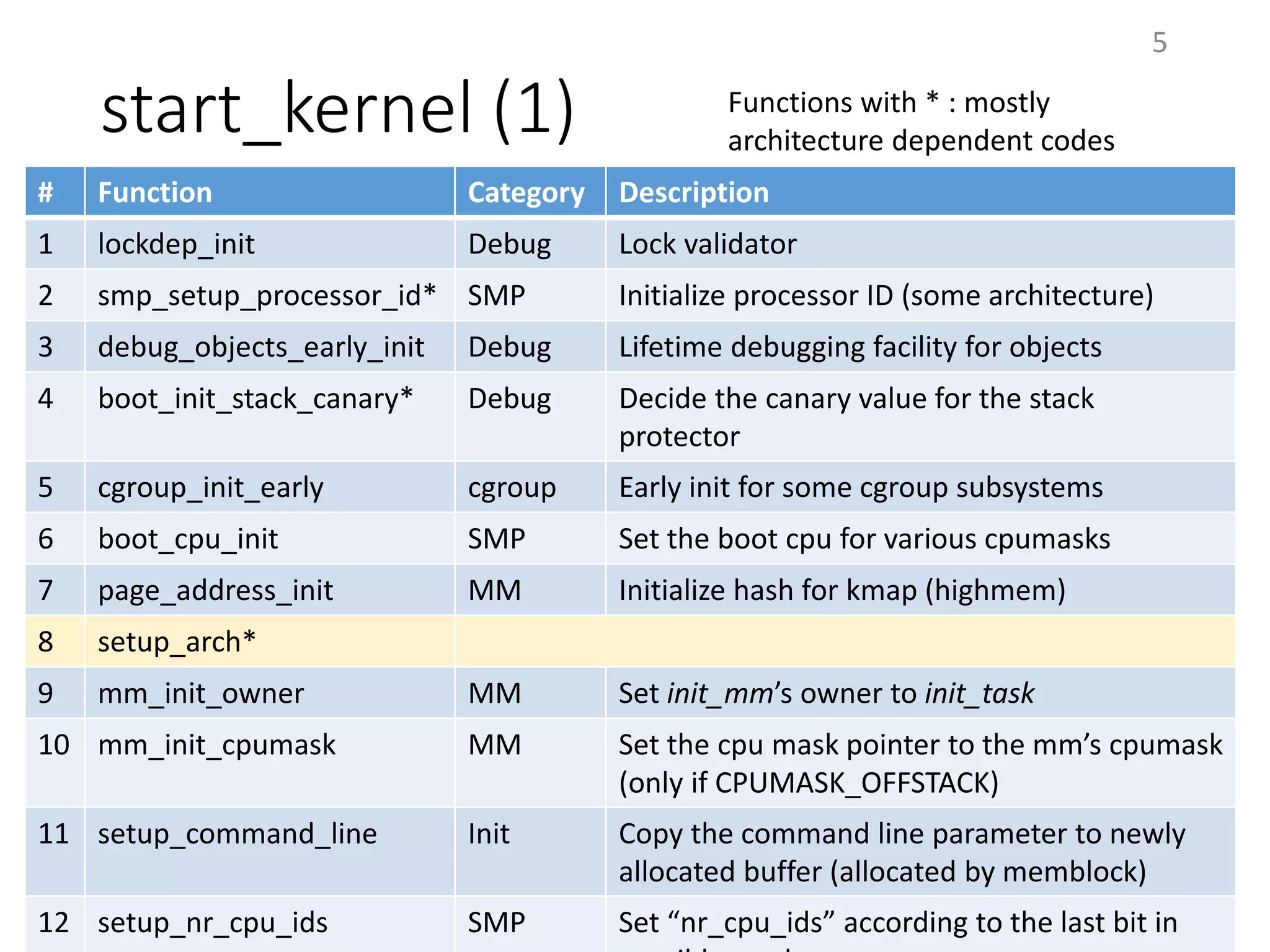
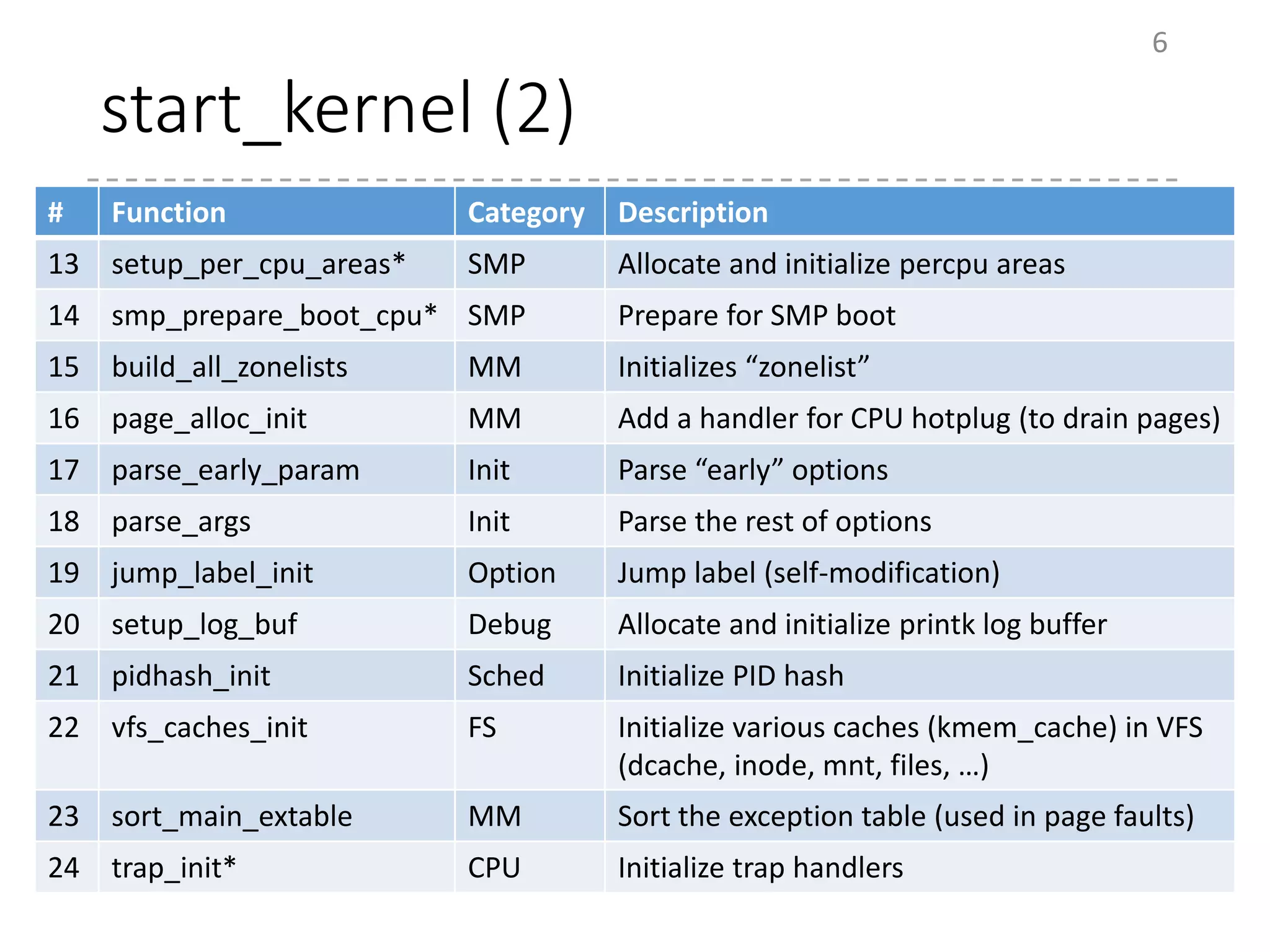
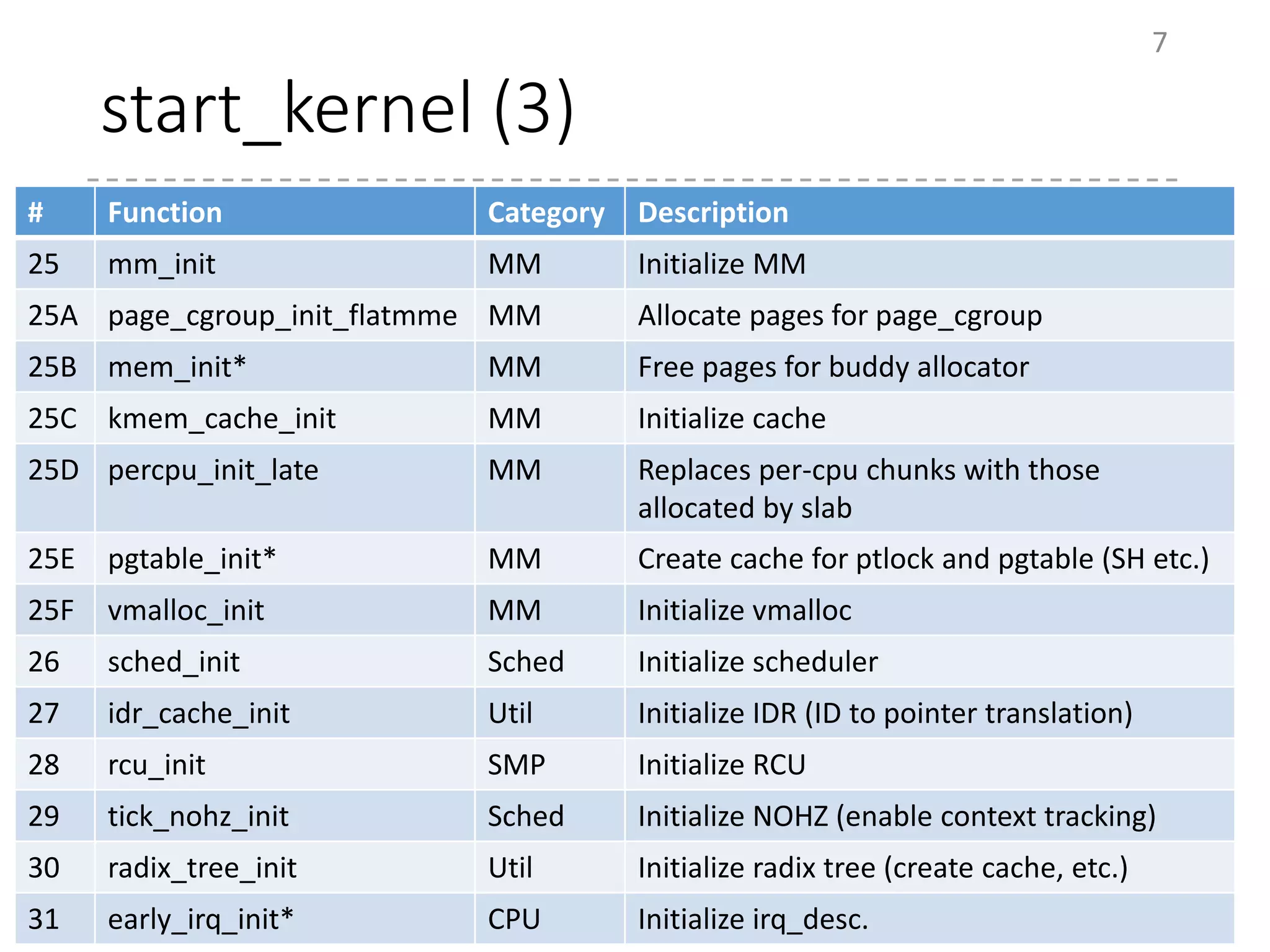
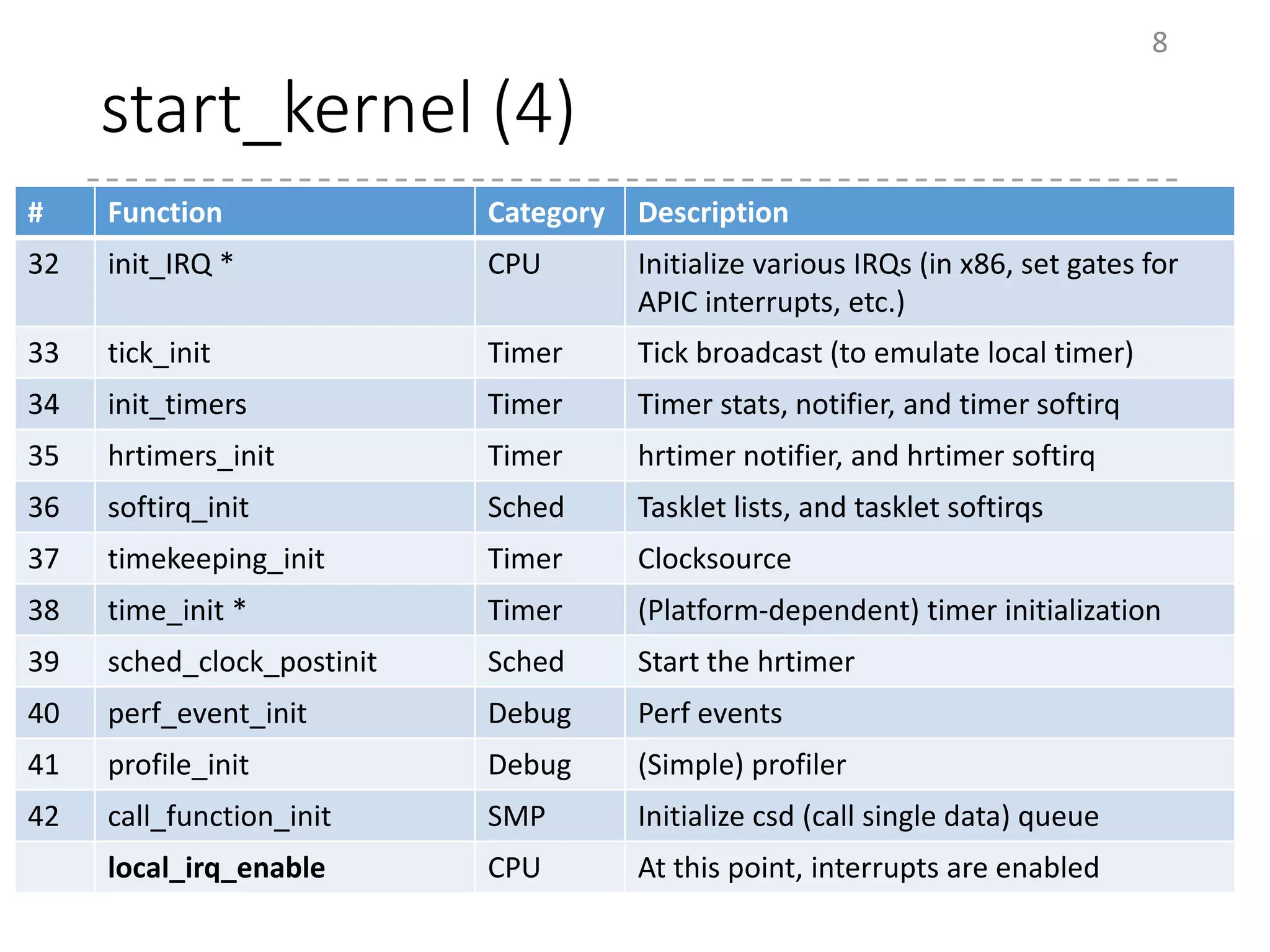
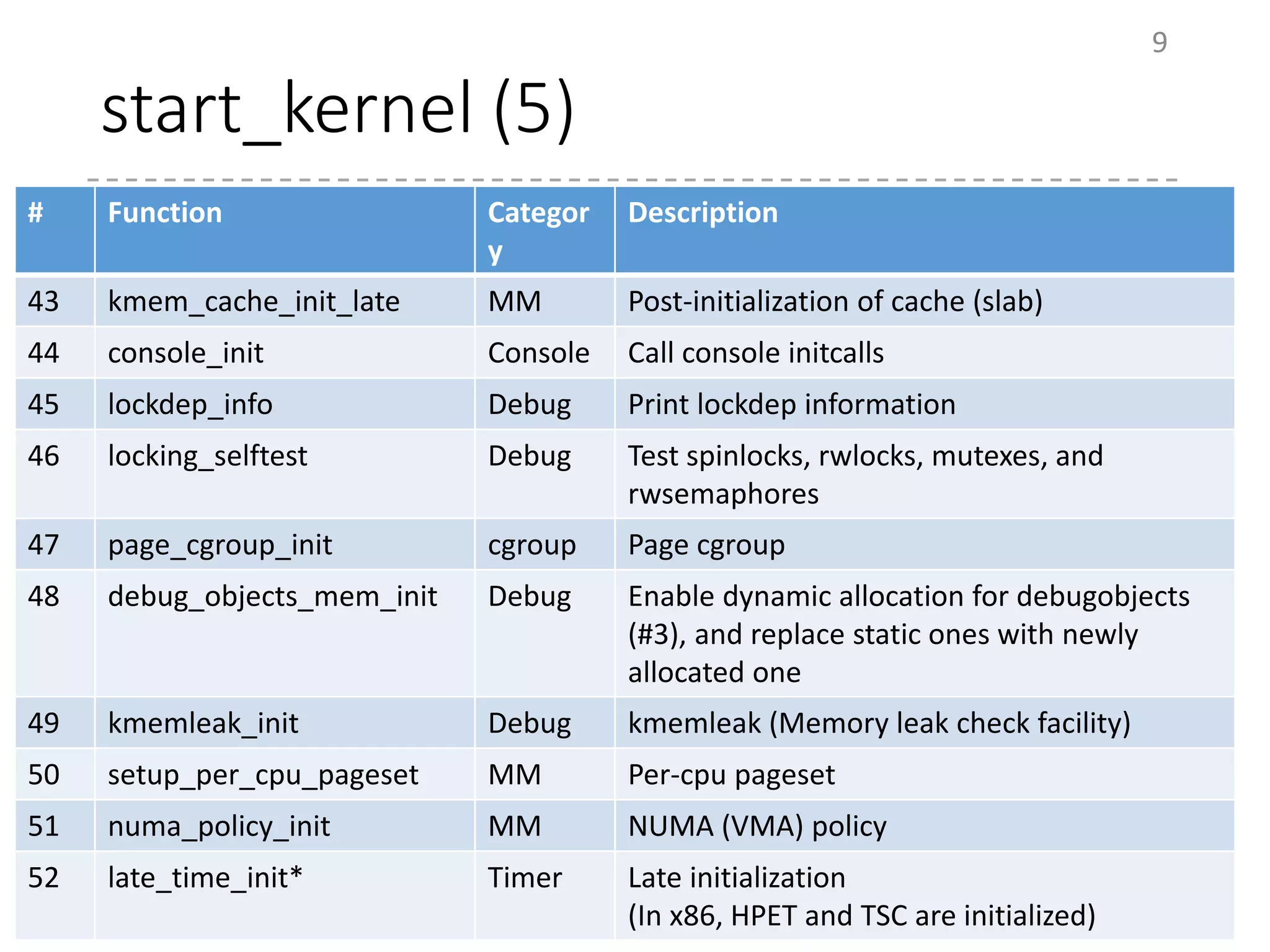
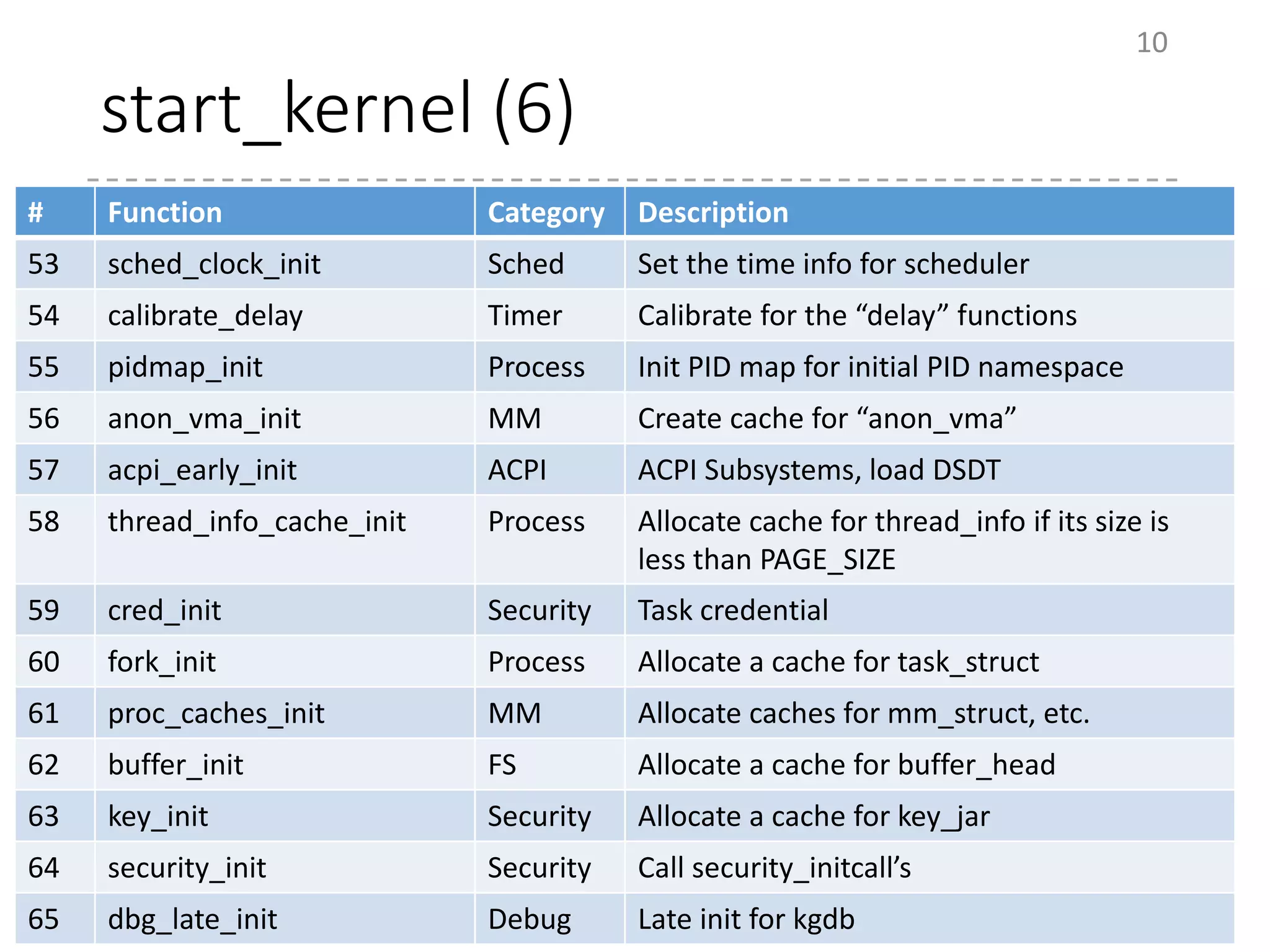
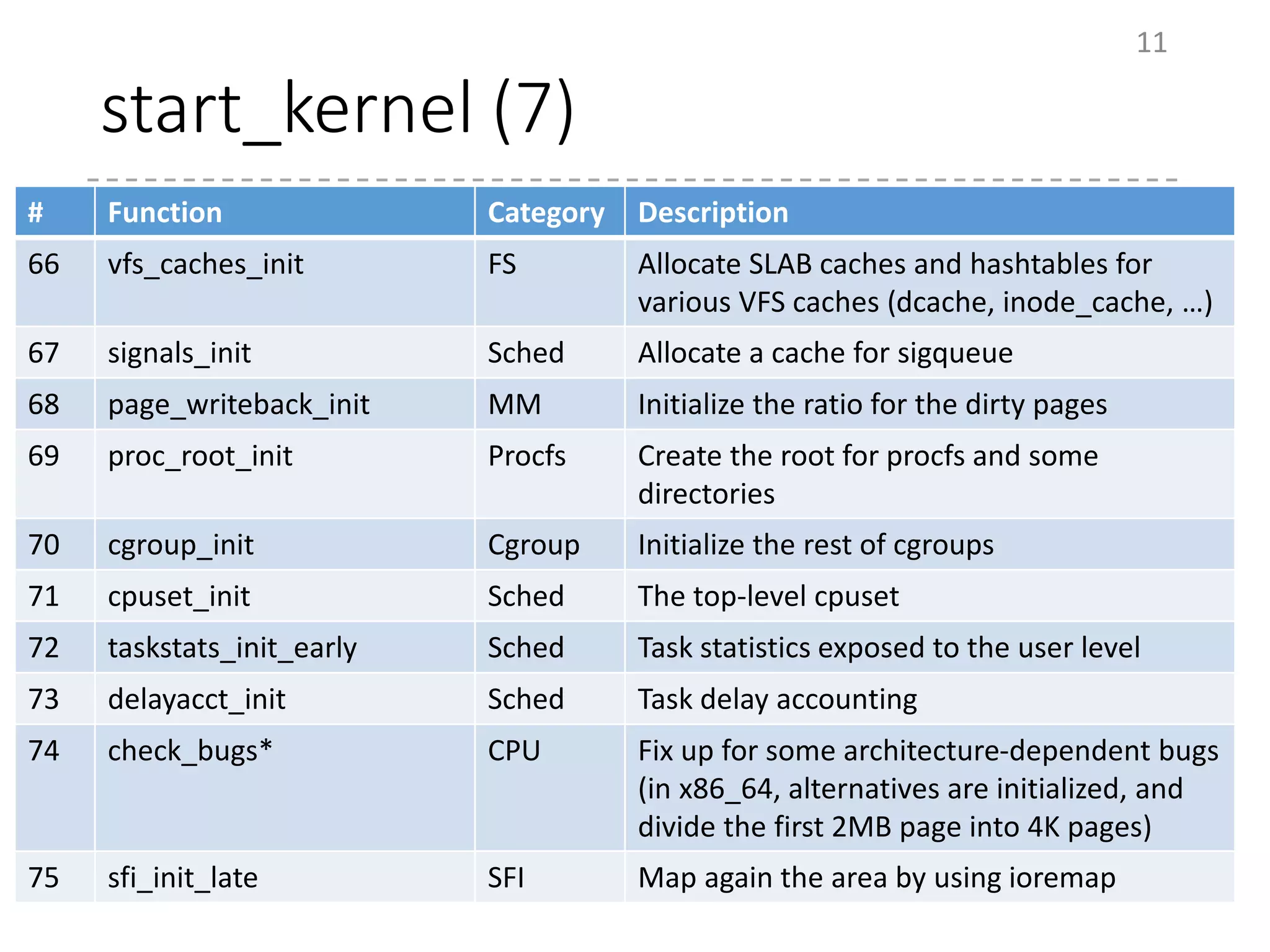
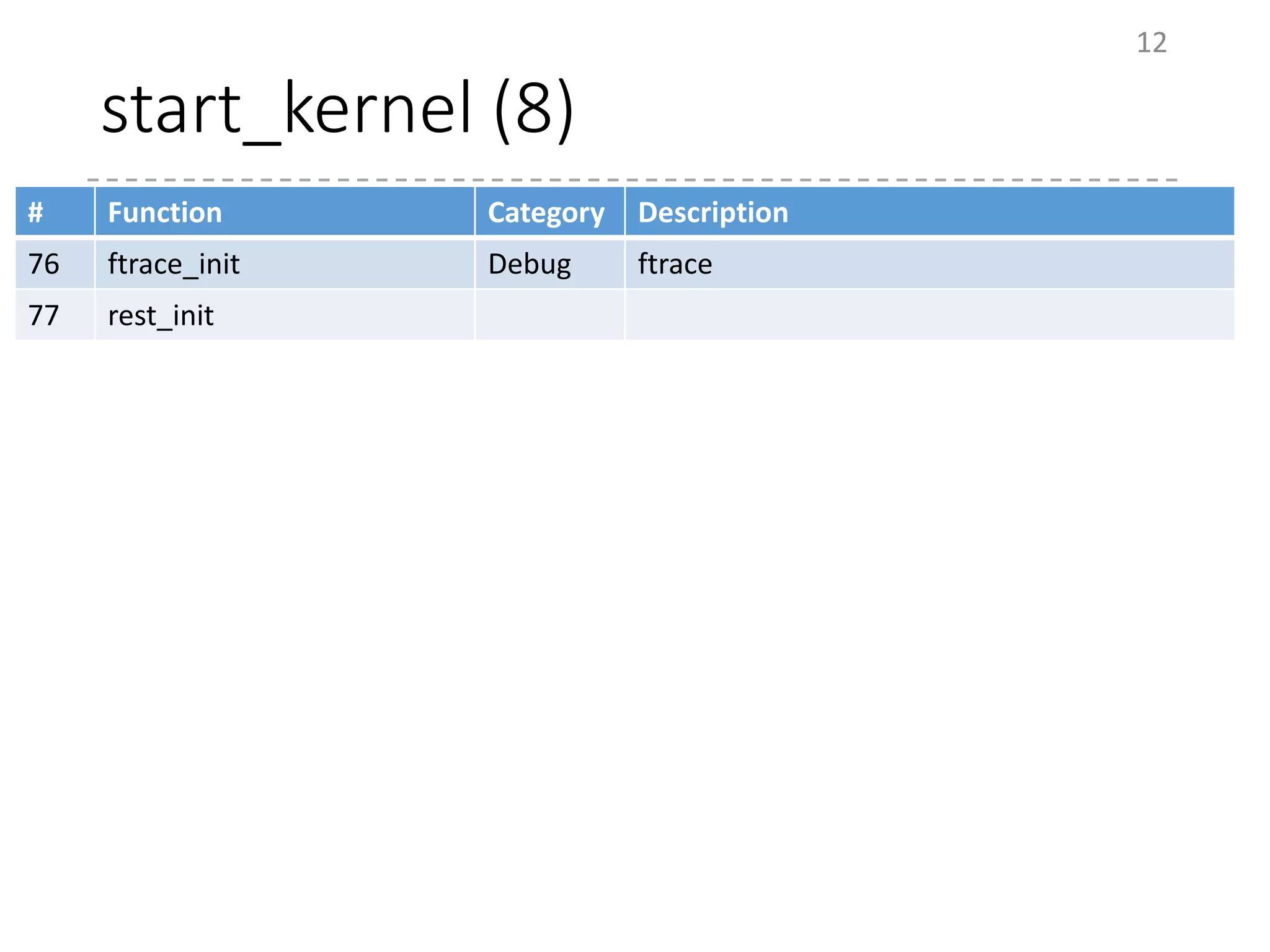
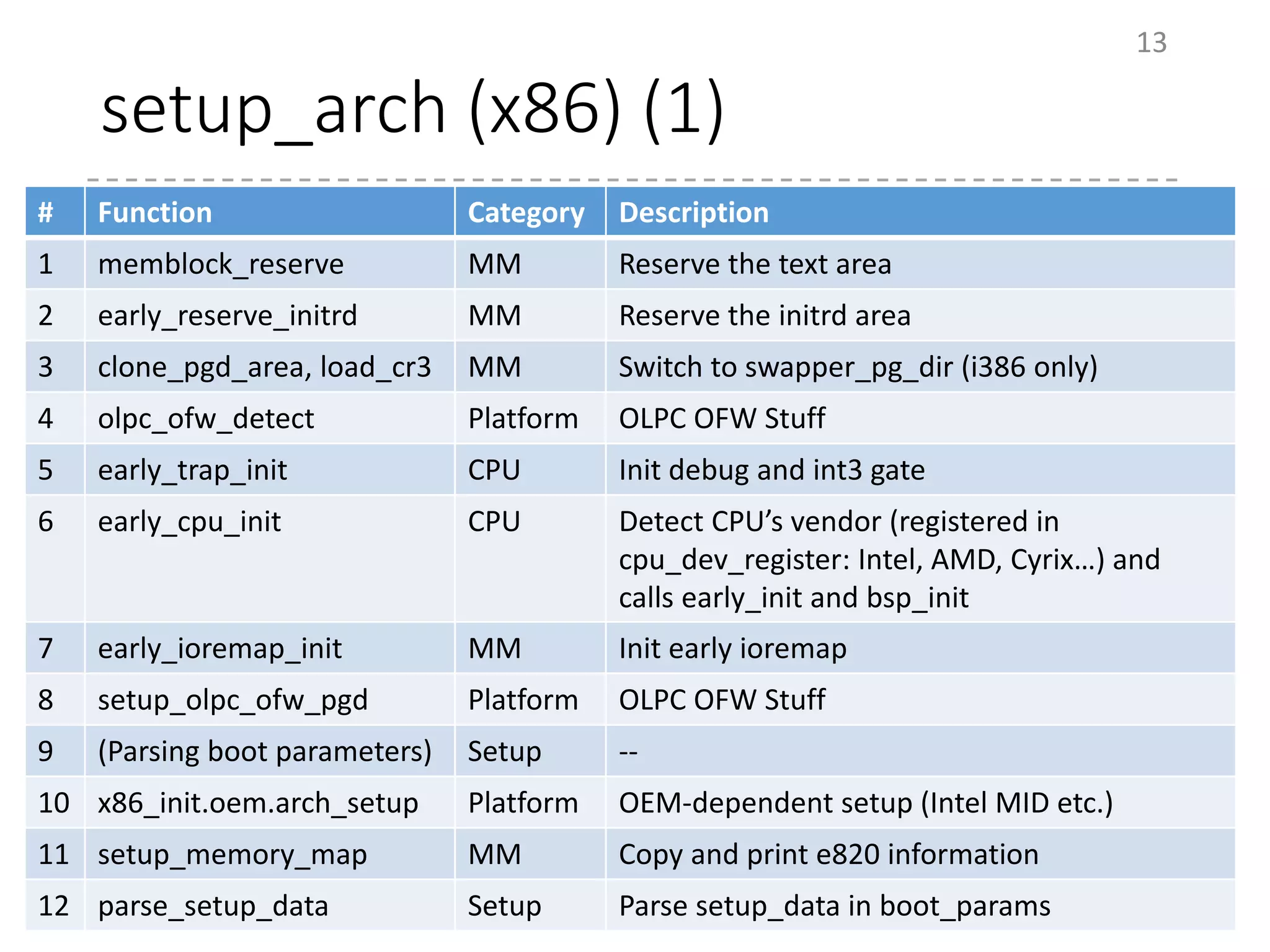
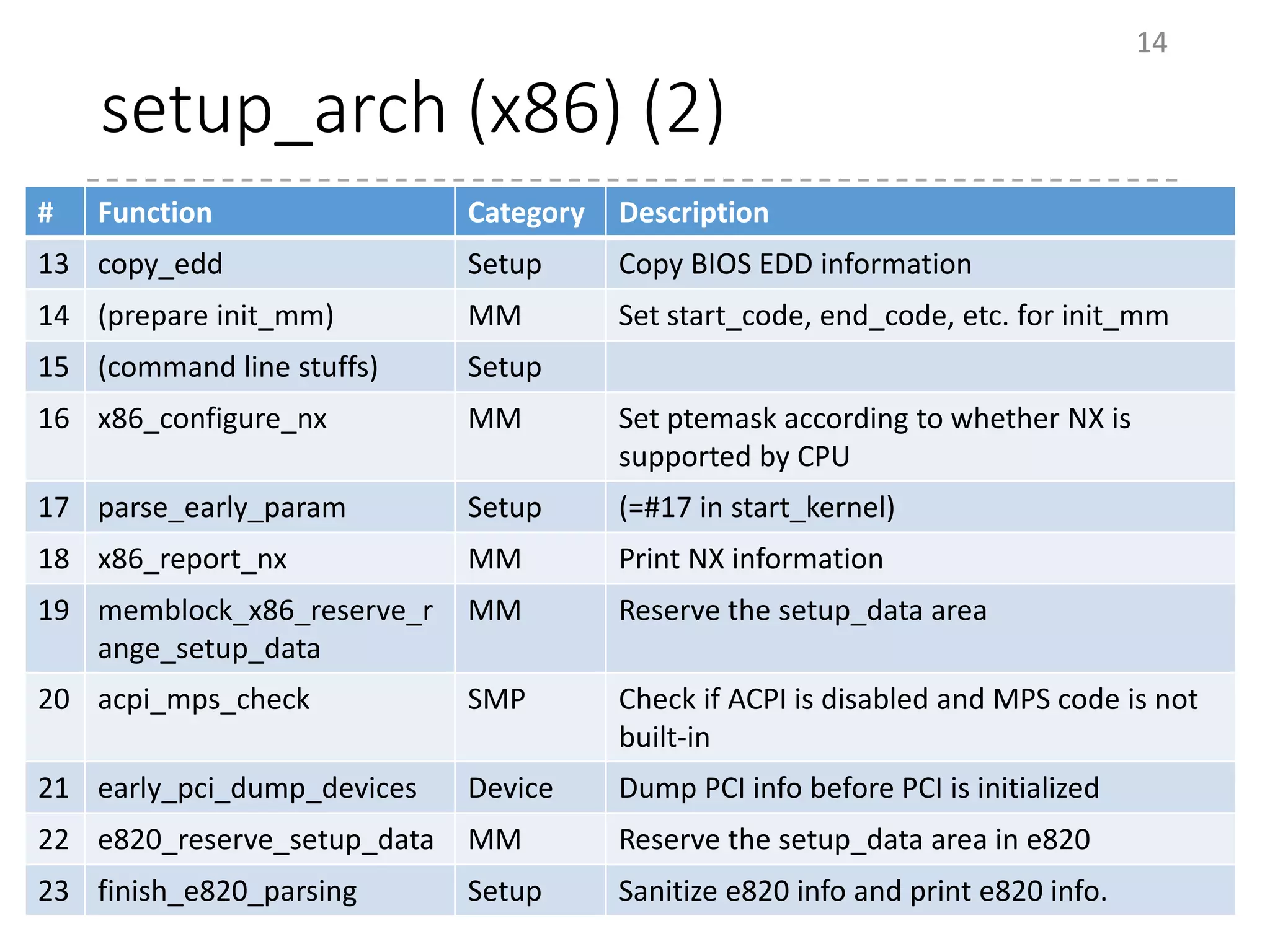
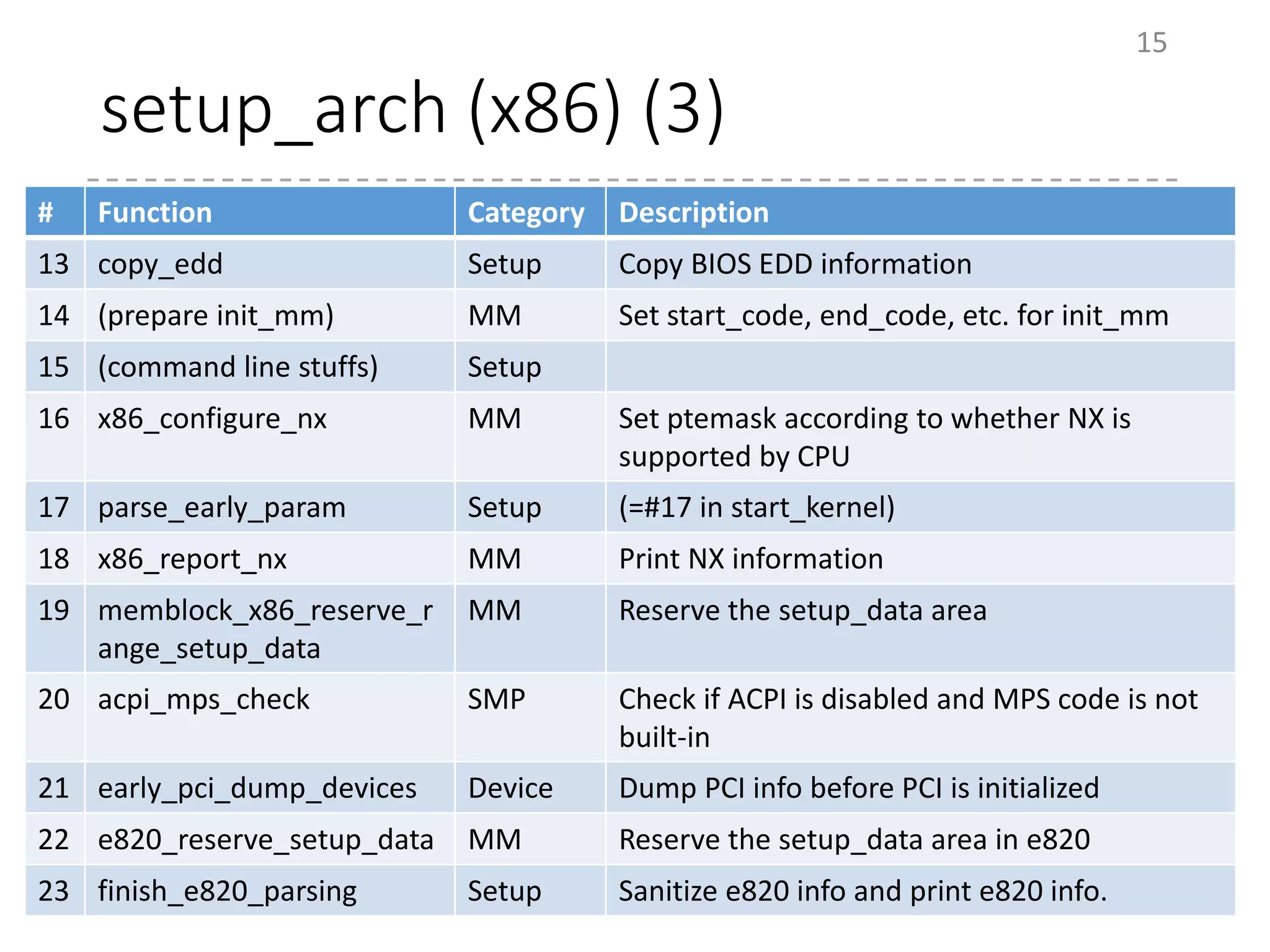
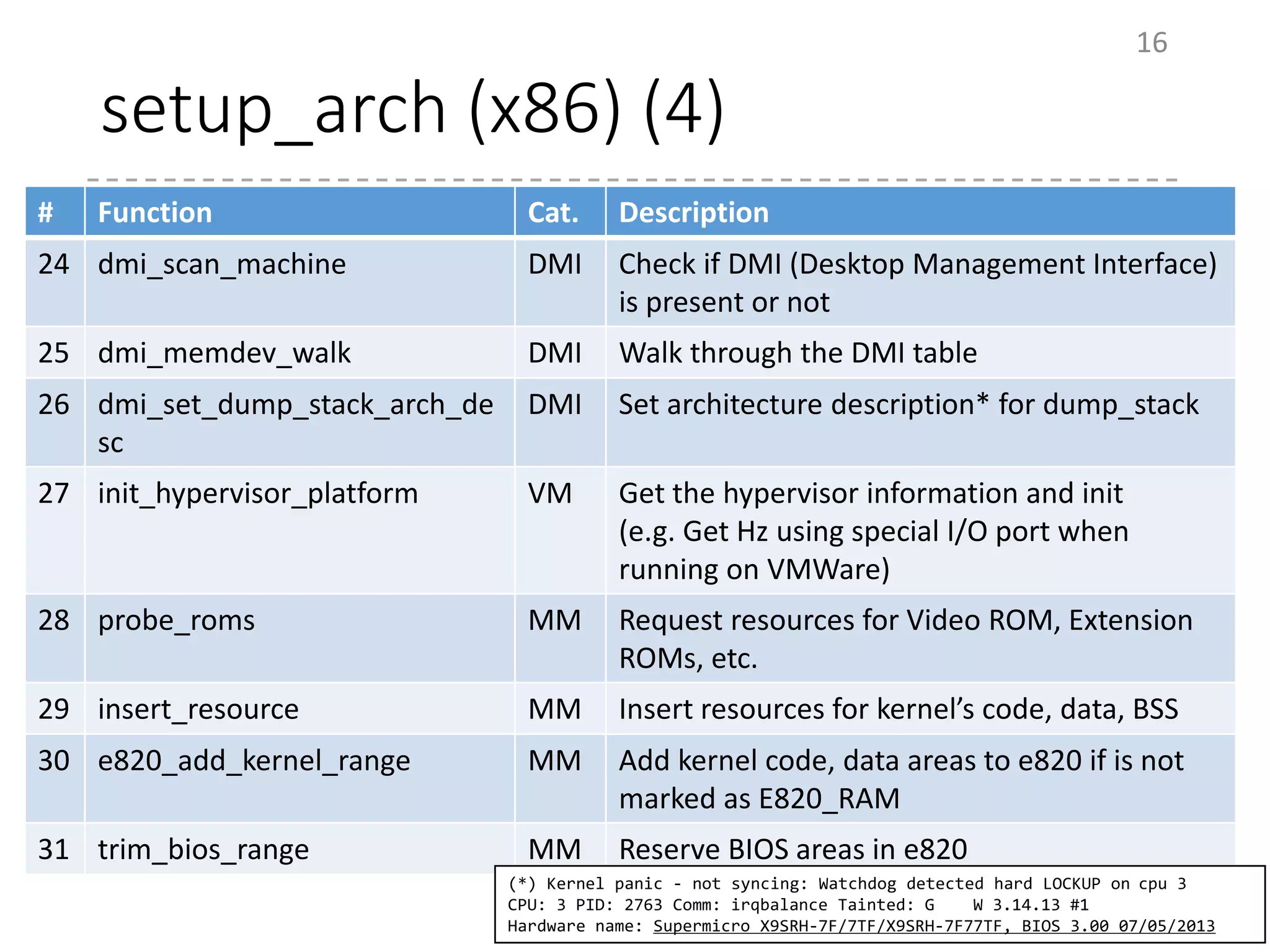
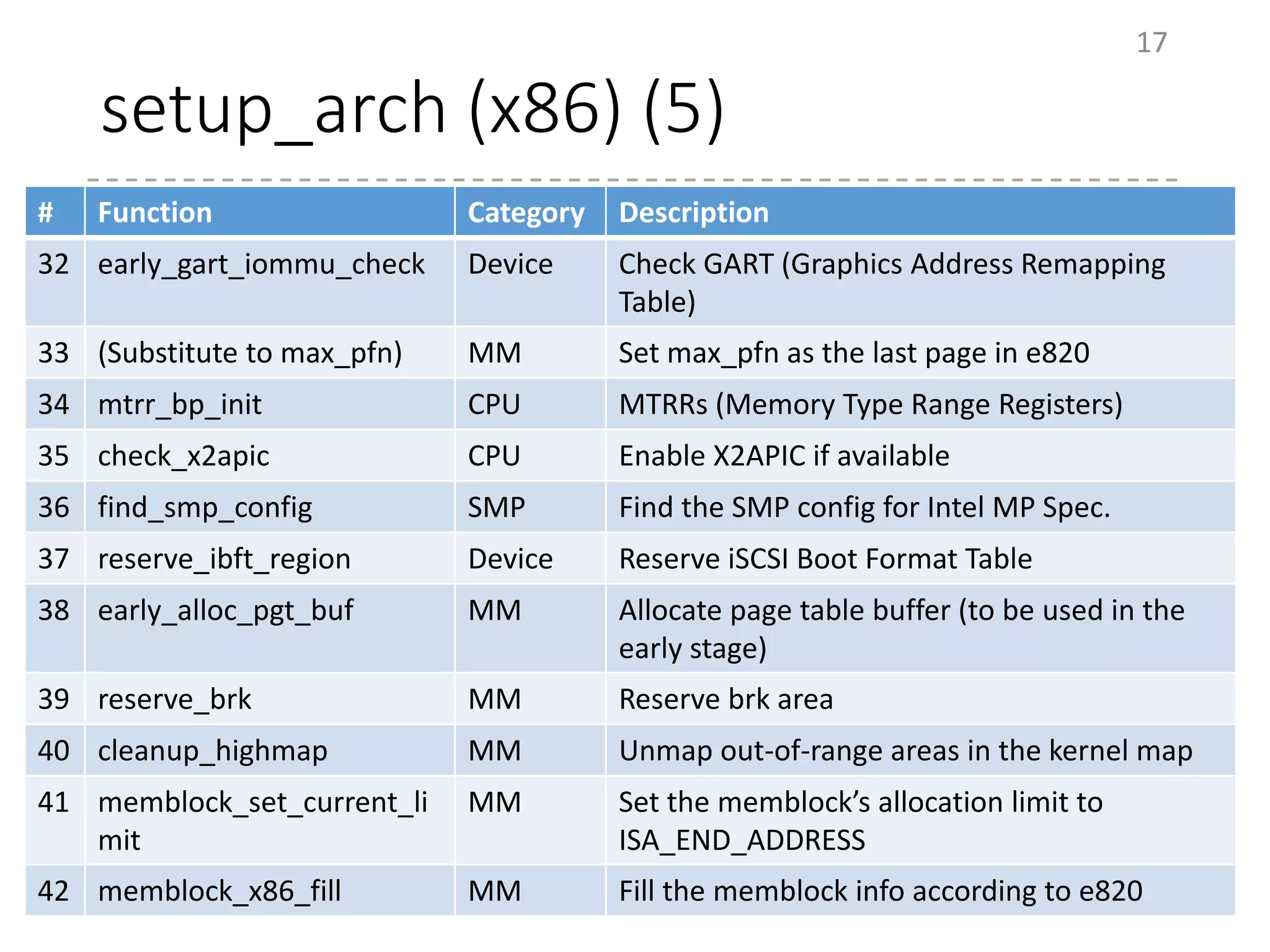
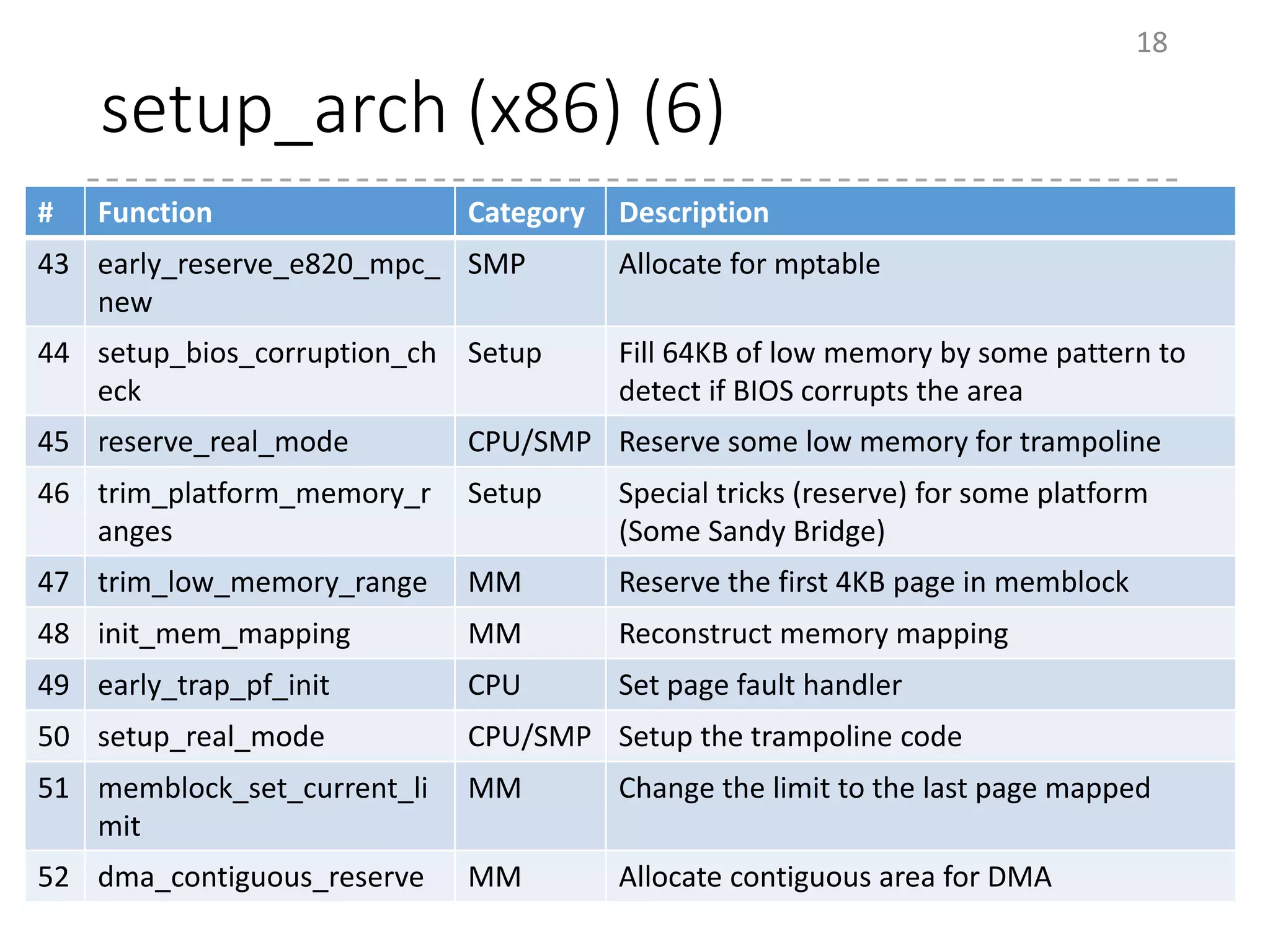
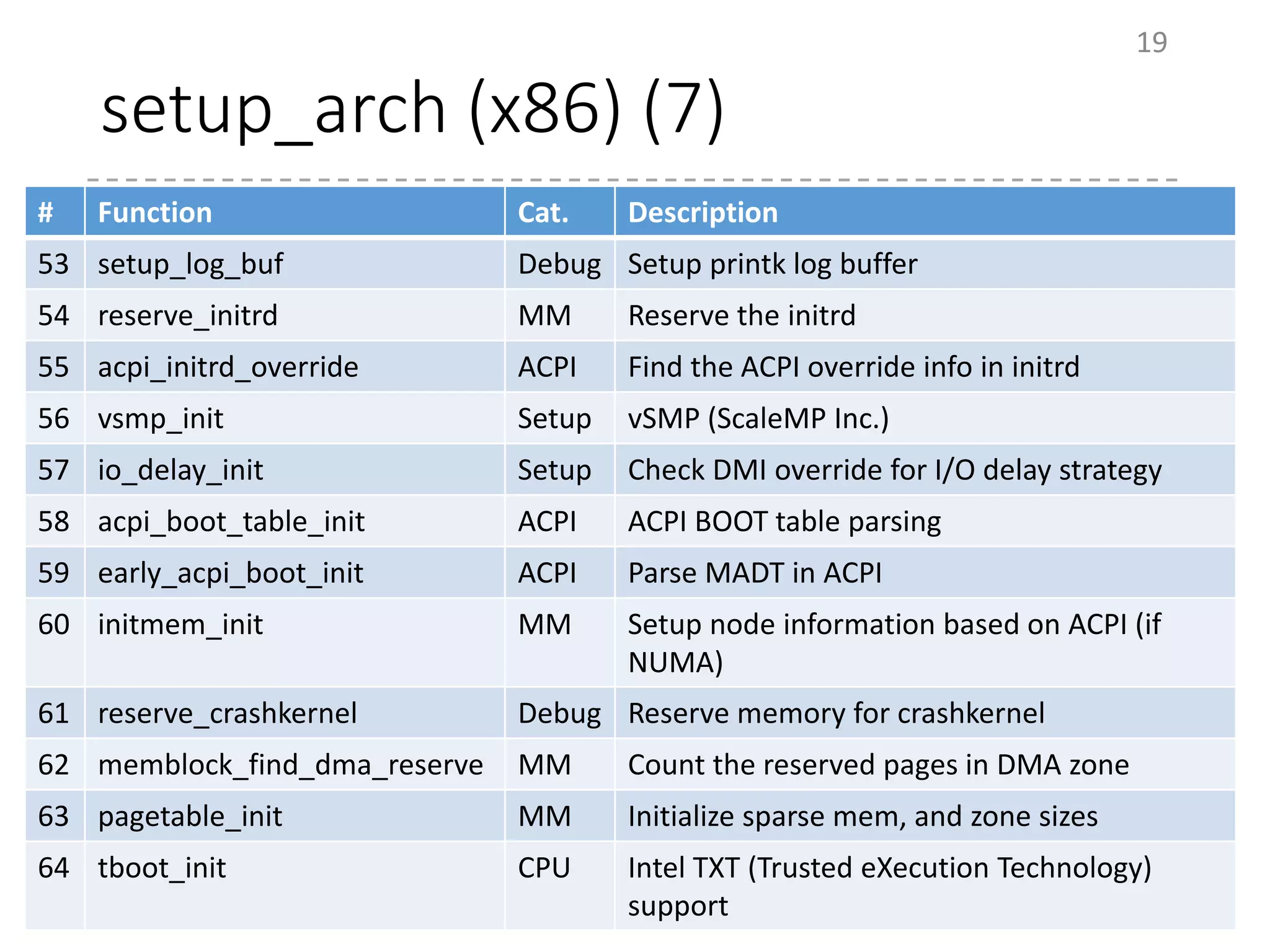
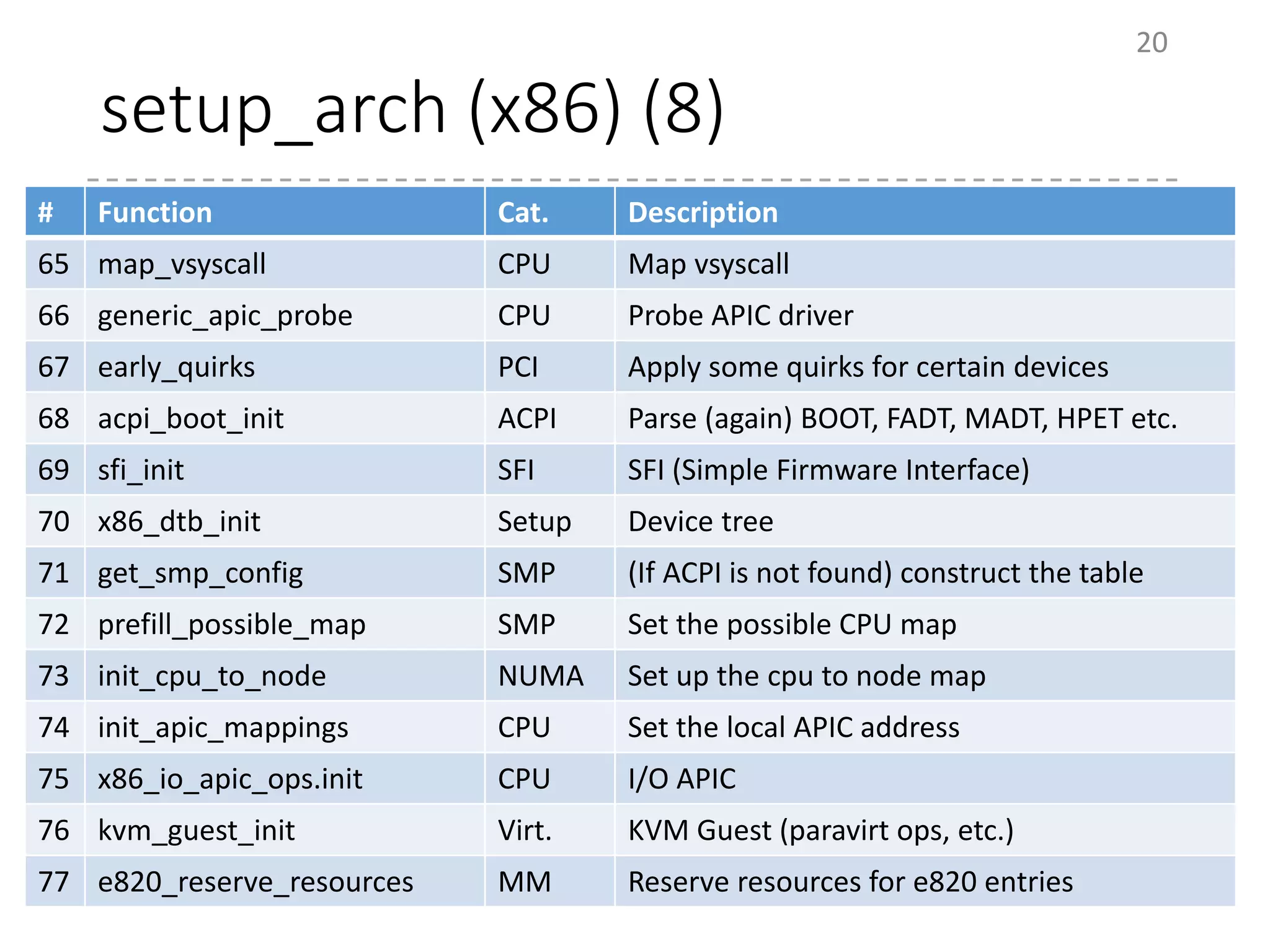
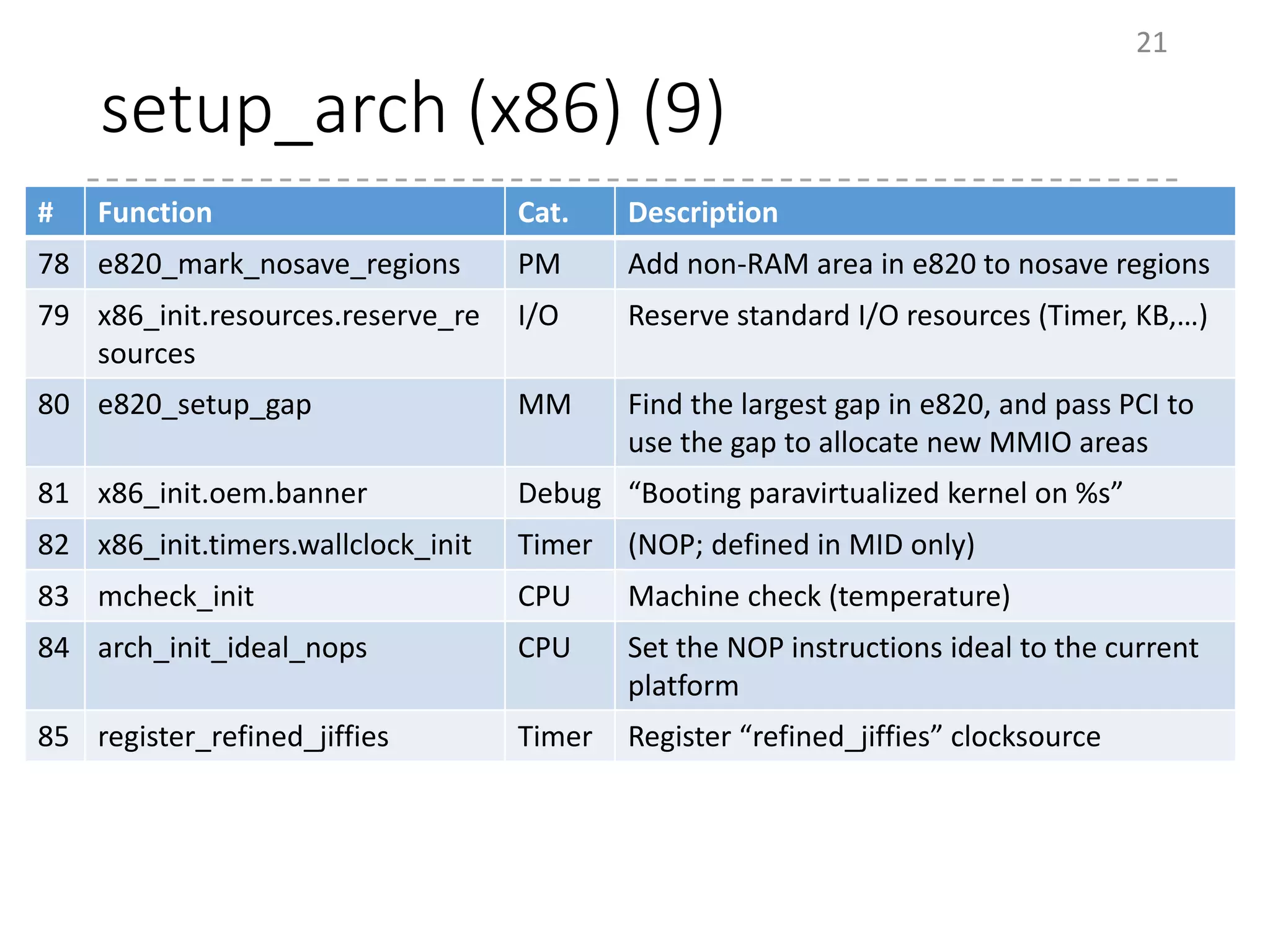
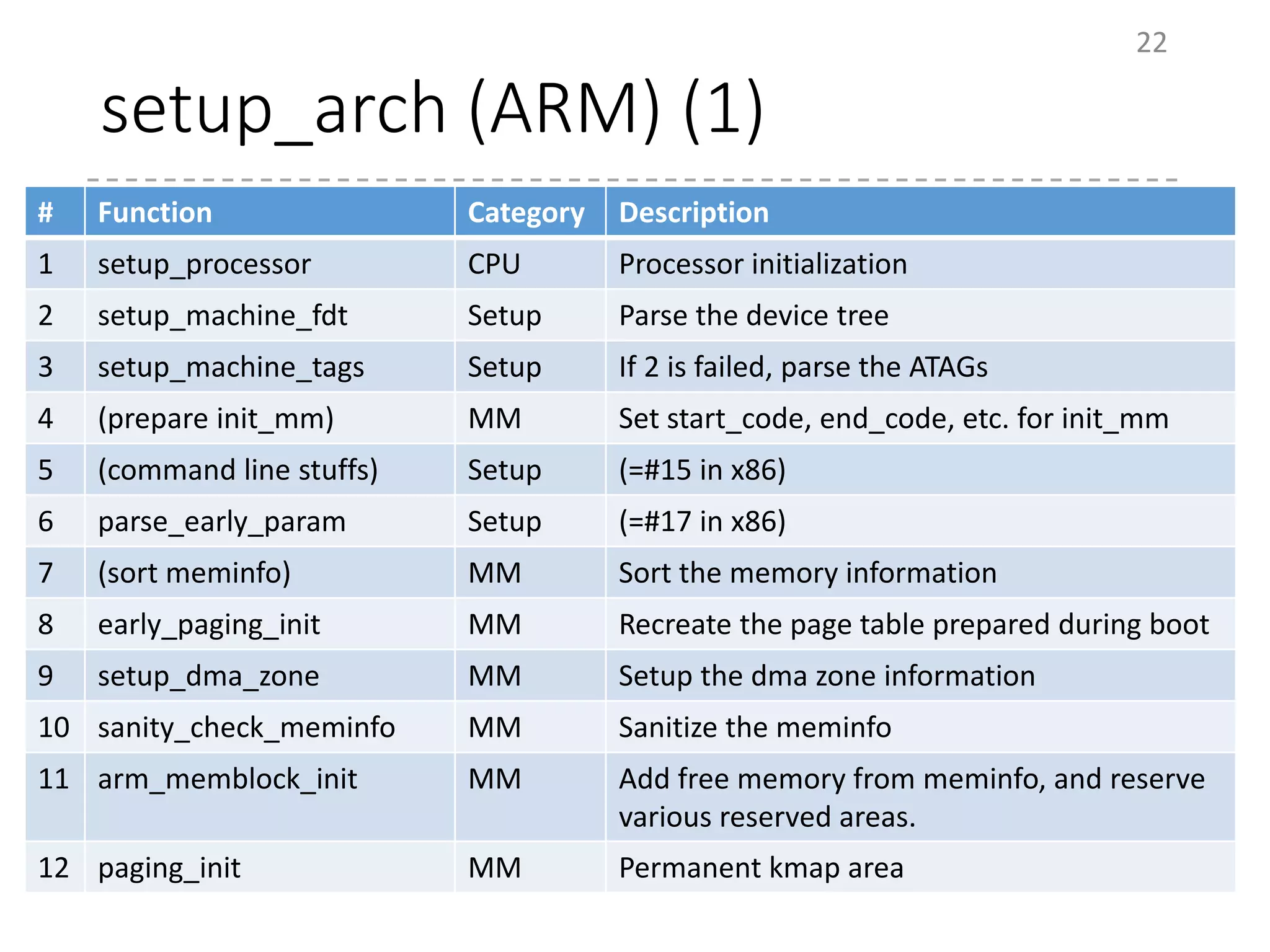
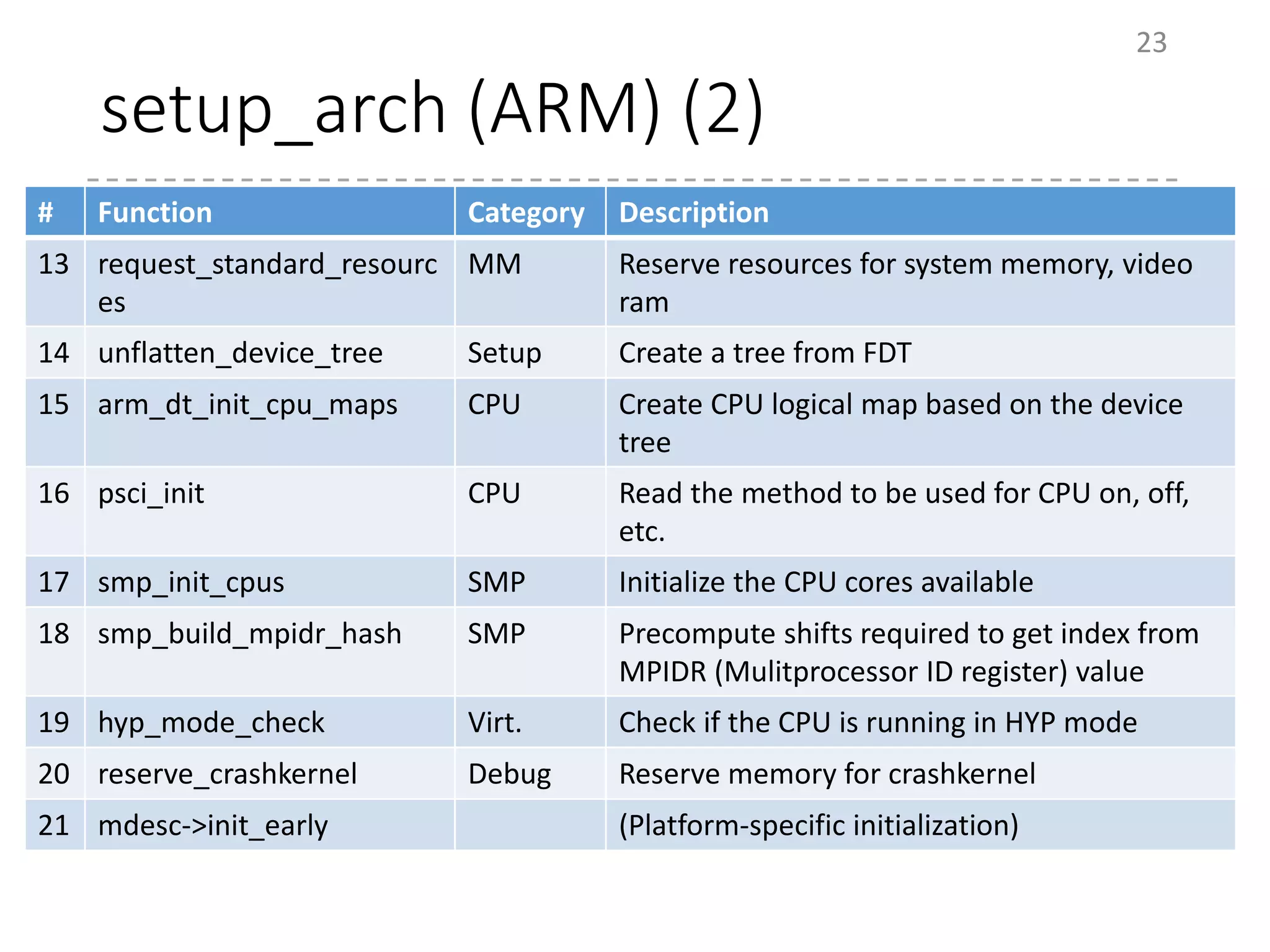
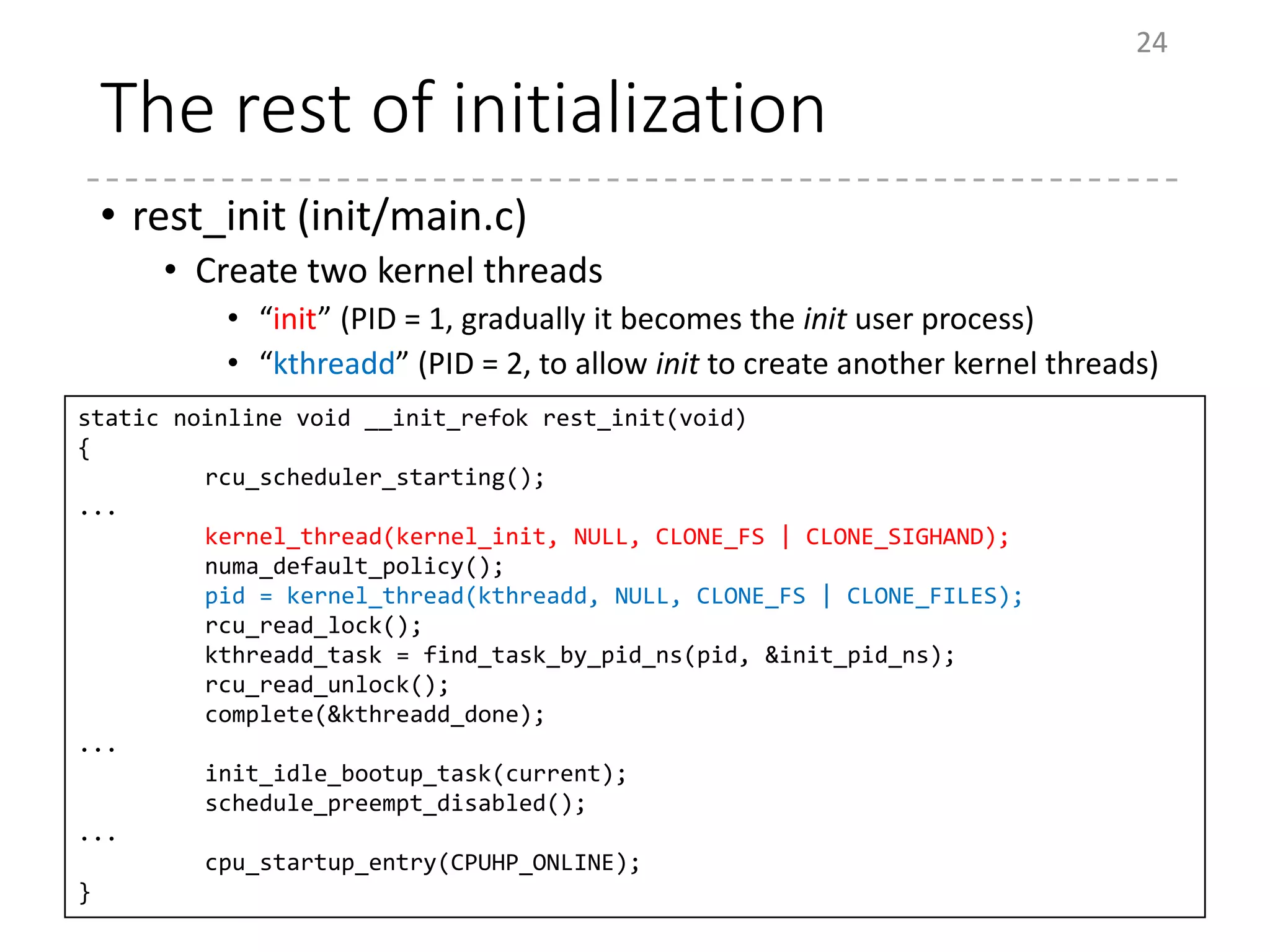
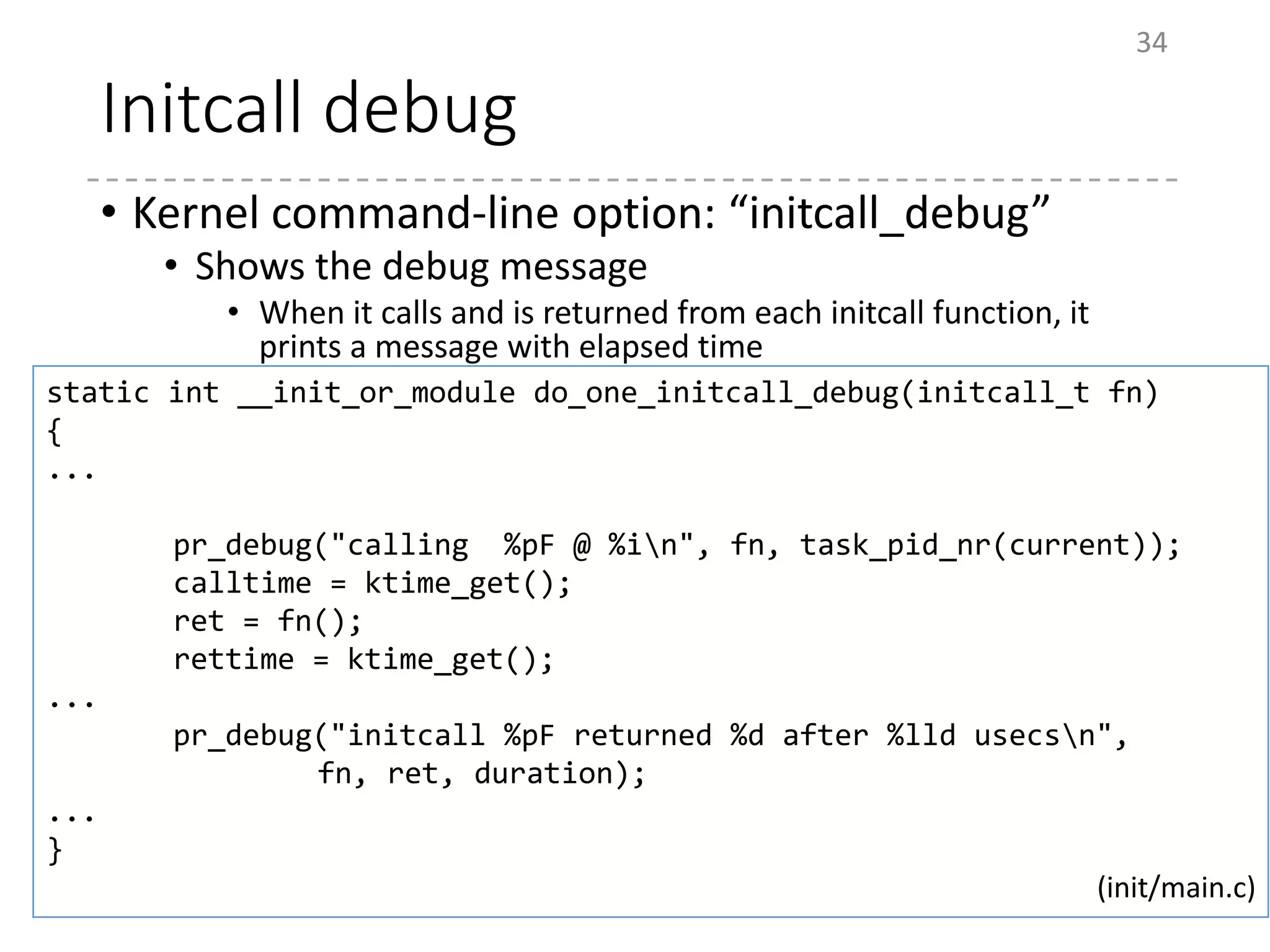
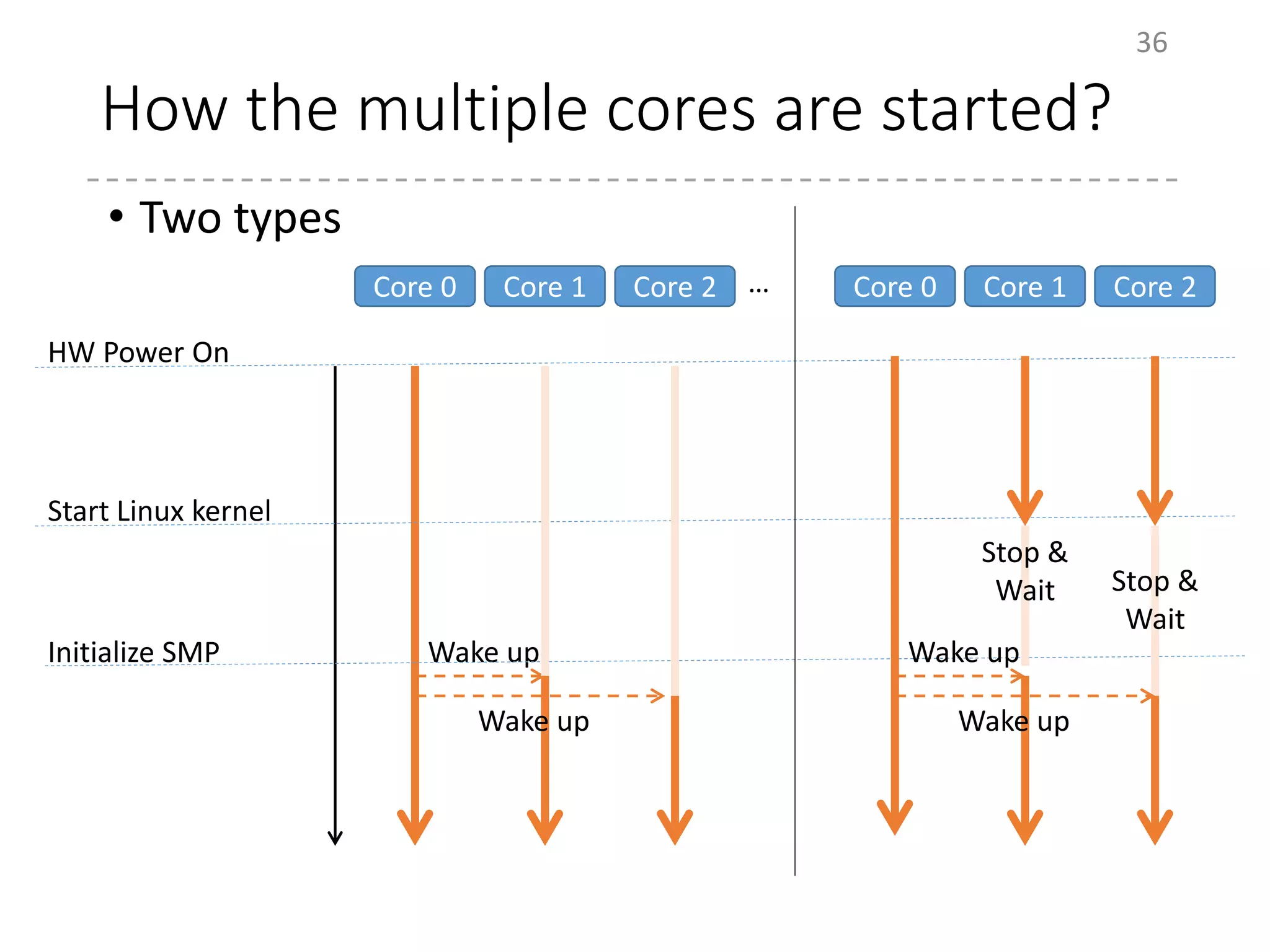
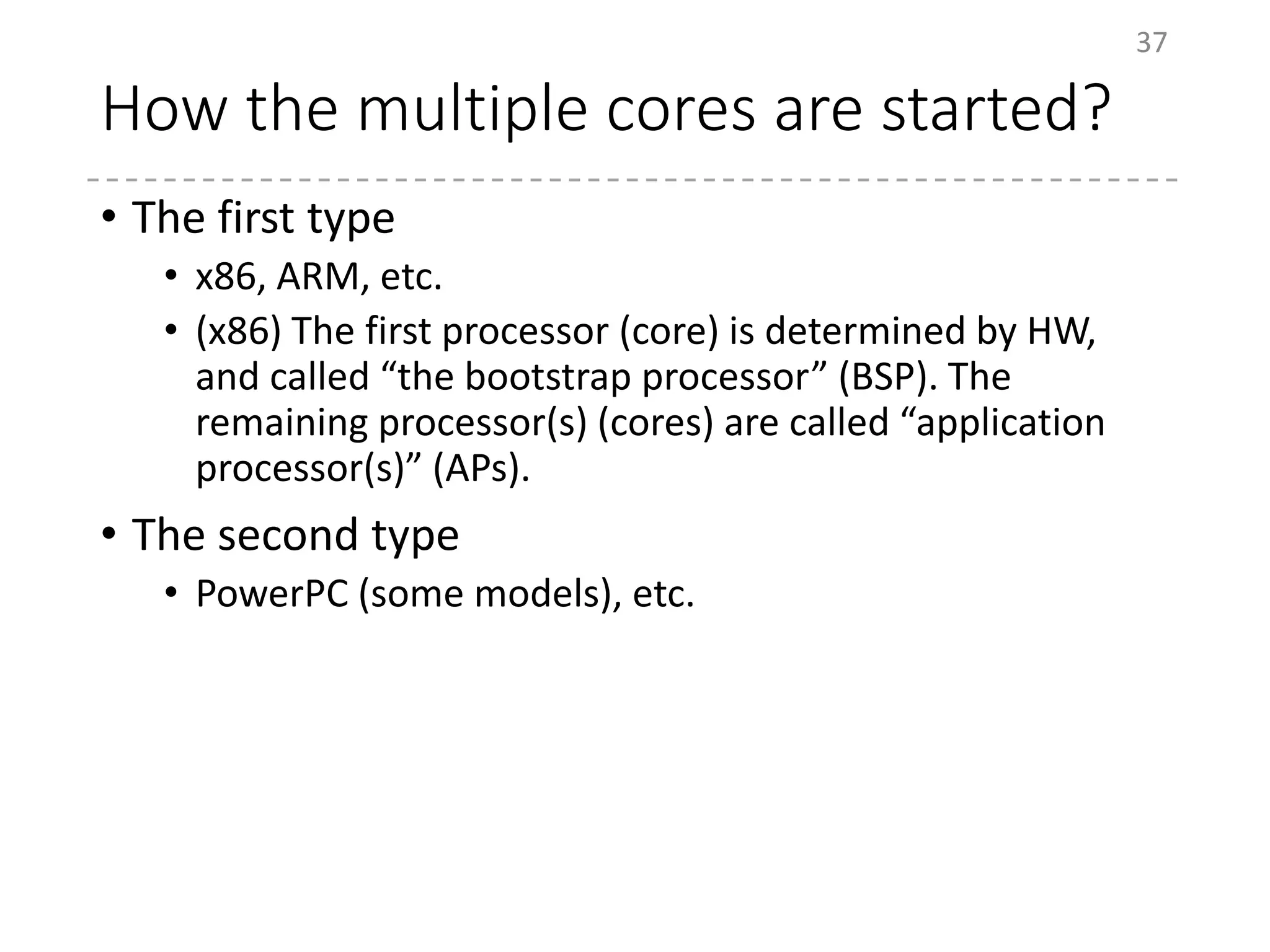
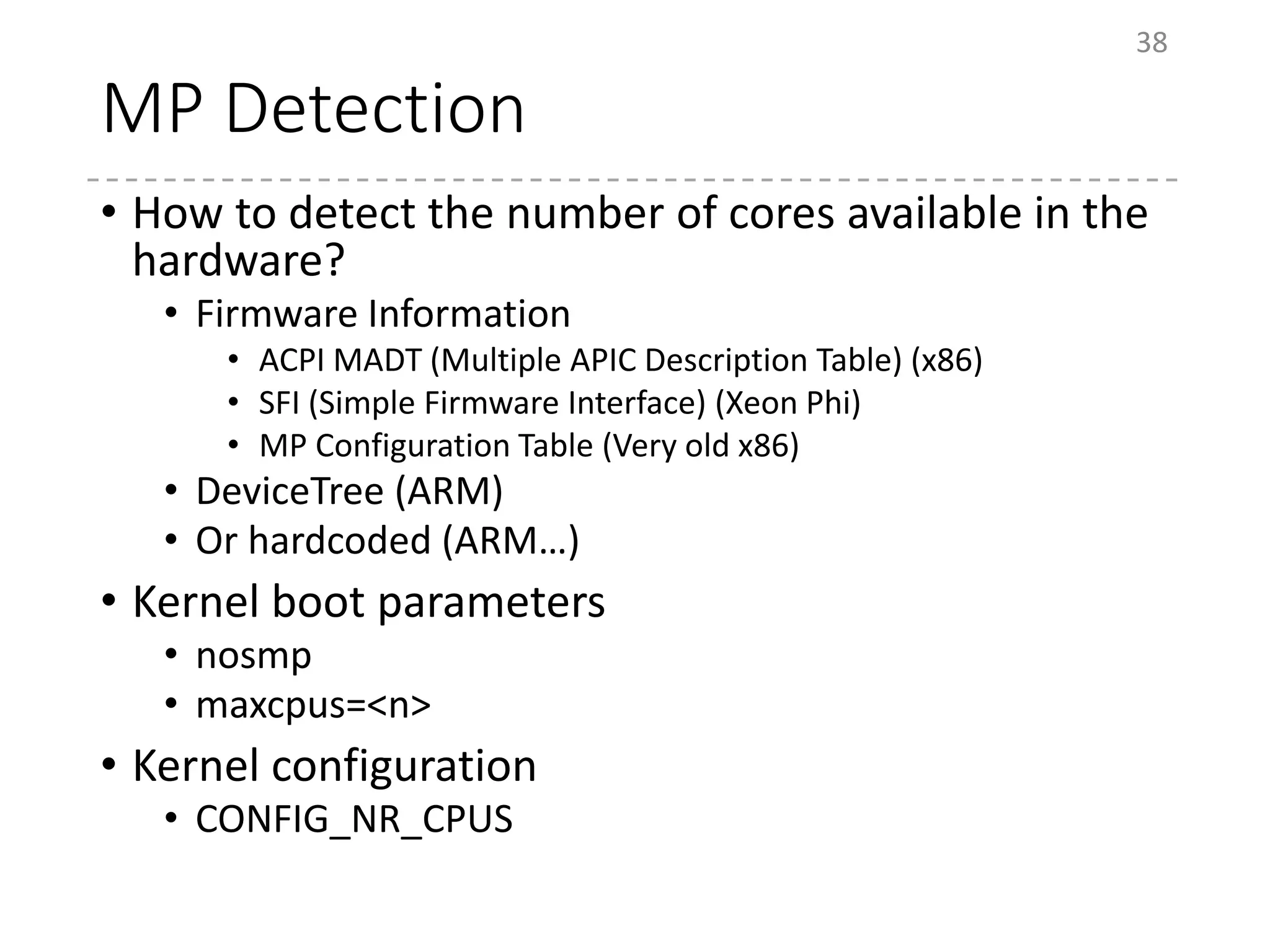
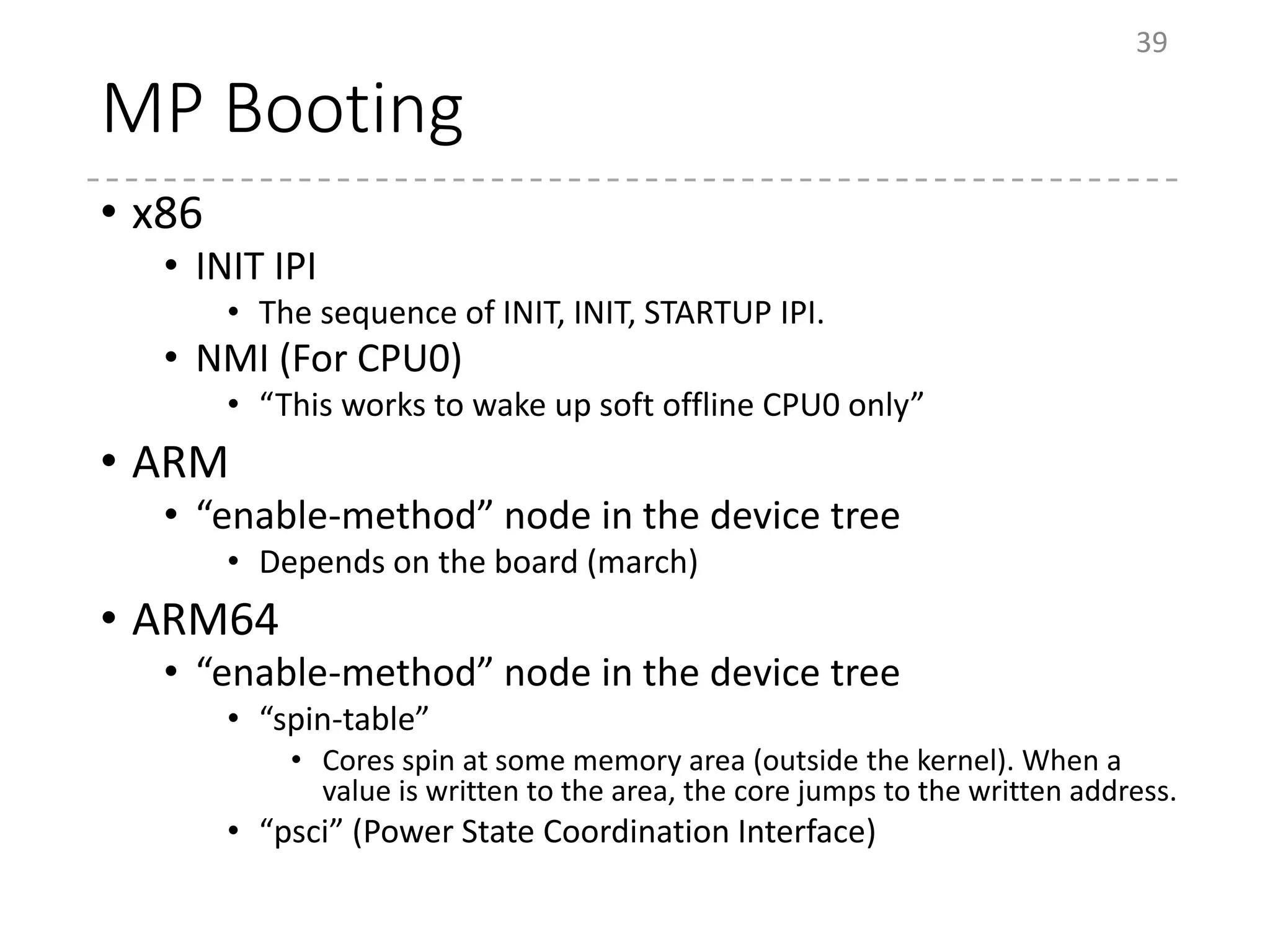
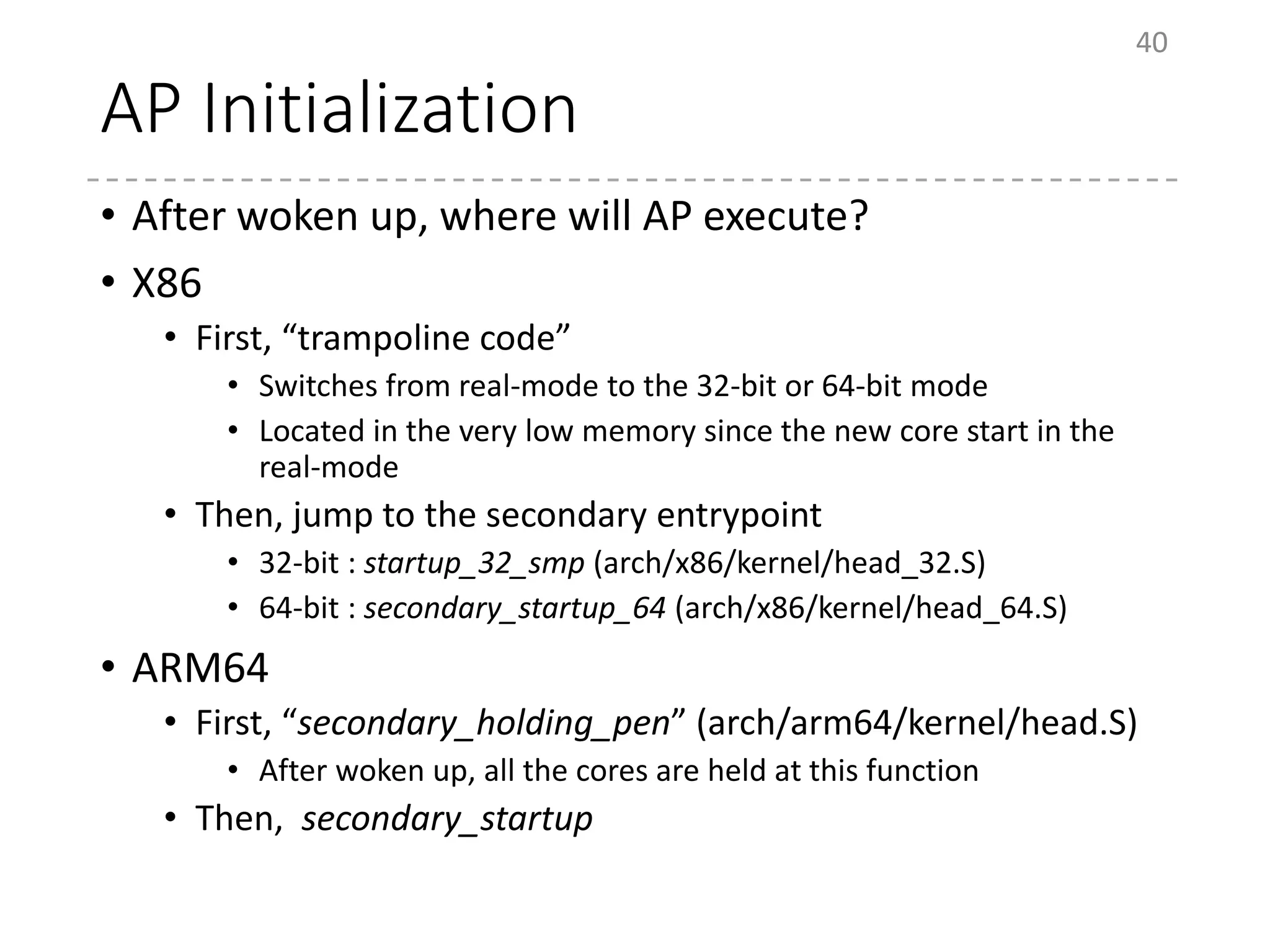
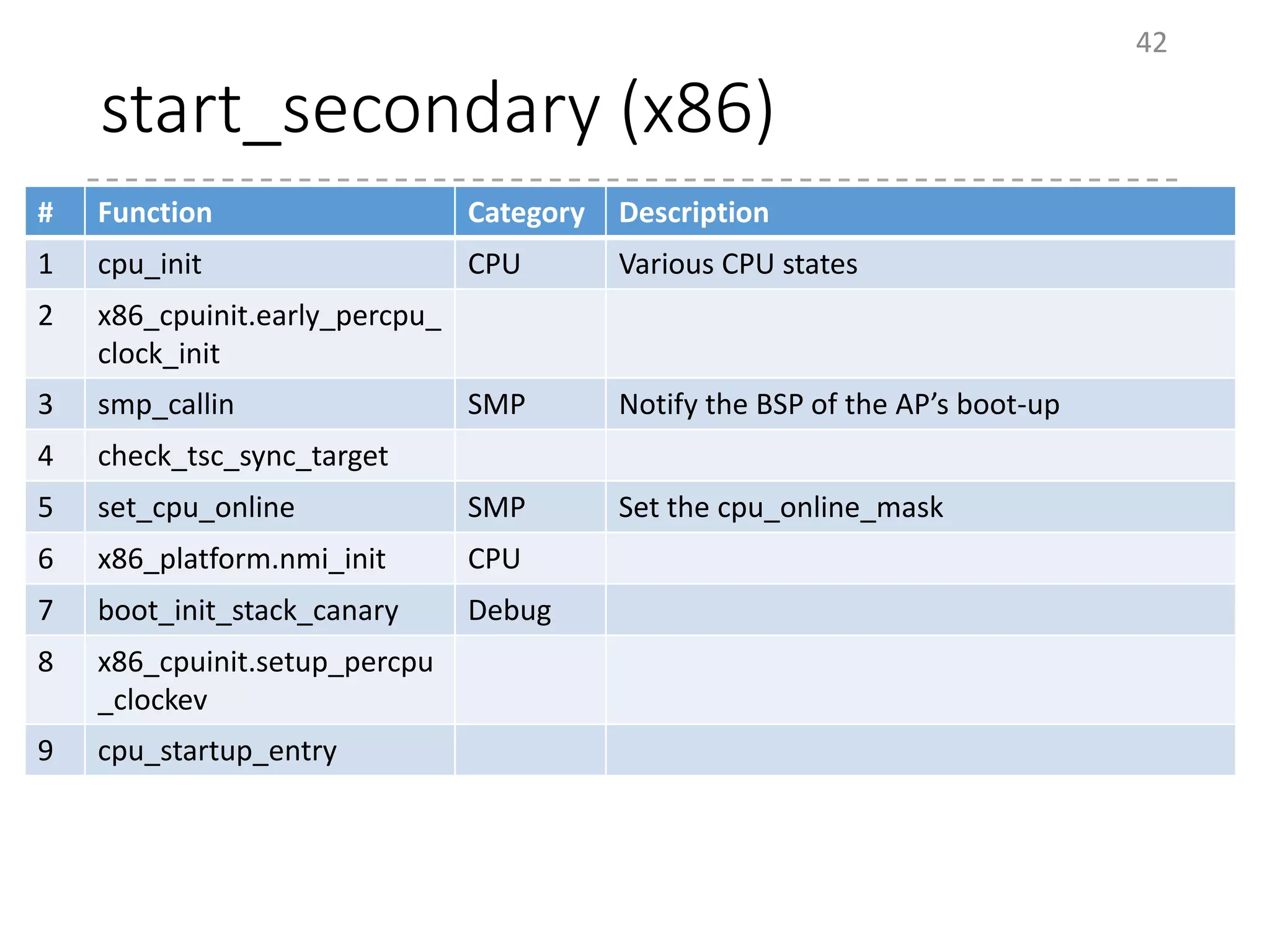
The document provides an overview of the initialization process in the Linux kernel from start_kernel to rest_init. It lists the functions called during this process organized by category including functions for initialization of multiprocessor support (SMP), memory management (MM), scheduling, timers, interrupts, and architecture specific setup. The setup_arch section focuses on x86 architecture specific initialization functions such as reserving memory regions, parsing boot parameters, initializing memory mapping and MTRRs.











![secondary_start_kernel (ARM64)
43
# Function Category Description
1 (Set the current mm to
init_mm)
MM
2 set_my_cpu_offset SMP Set per-cpu offset
3 cpu_set_reserved_ttbr0 CPU Set TTBR0 to the zero page
4 cpu_ops[cpu]-
>cpu_postboot
CPU
5 notify_cpu_starting
6 smp_store_cpu_info
7 set_cpu_online
8 complete Notify the boot CPU of the core’s boot
9 cpu_startup_entry Go to the idle loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlkb20141130-150116201747-conversion-gate02/75/Linux-Initialization-Process-2-43-2048.jpg)
