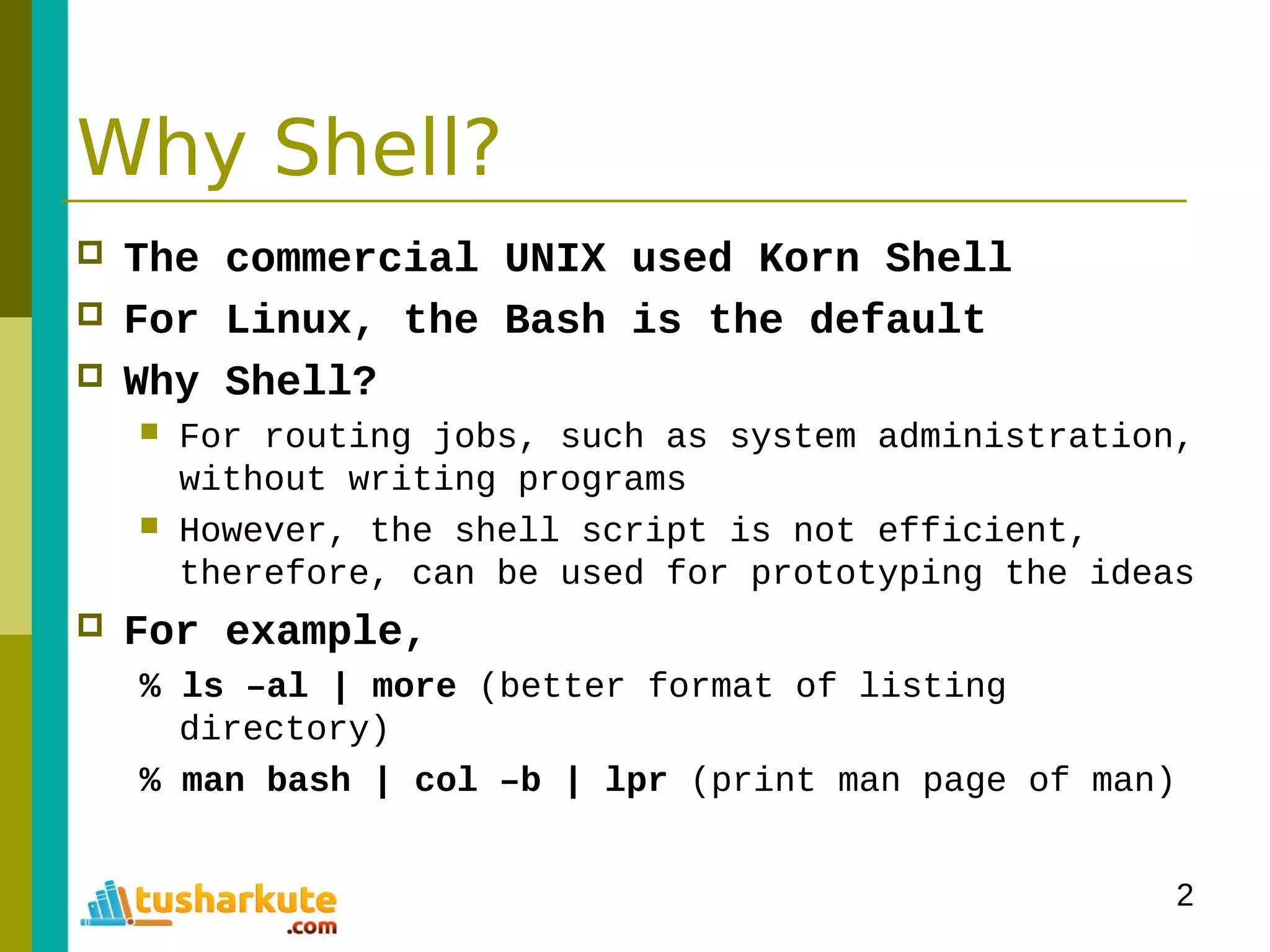
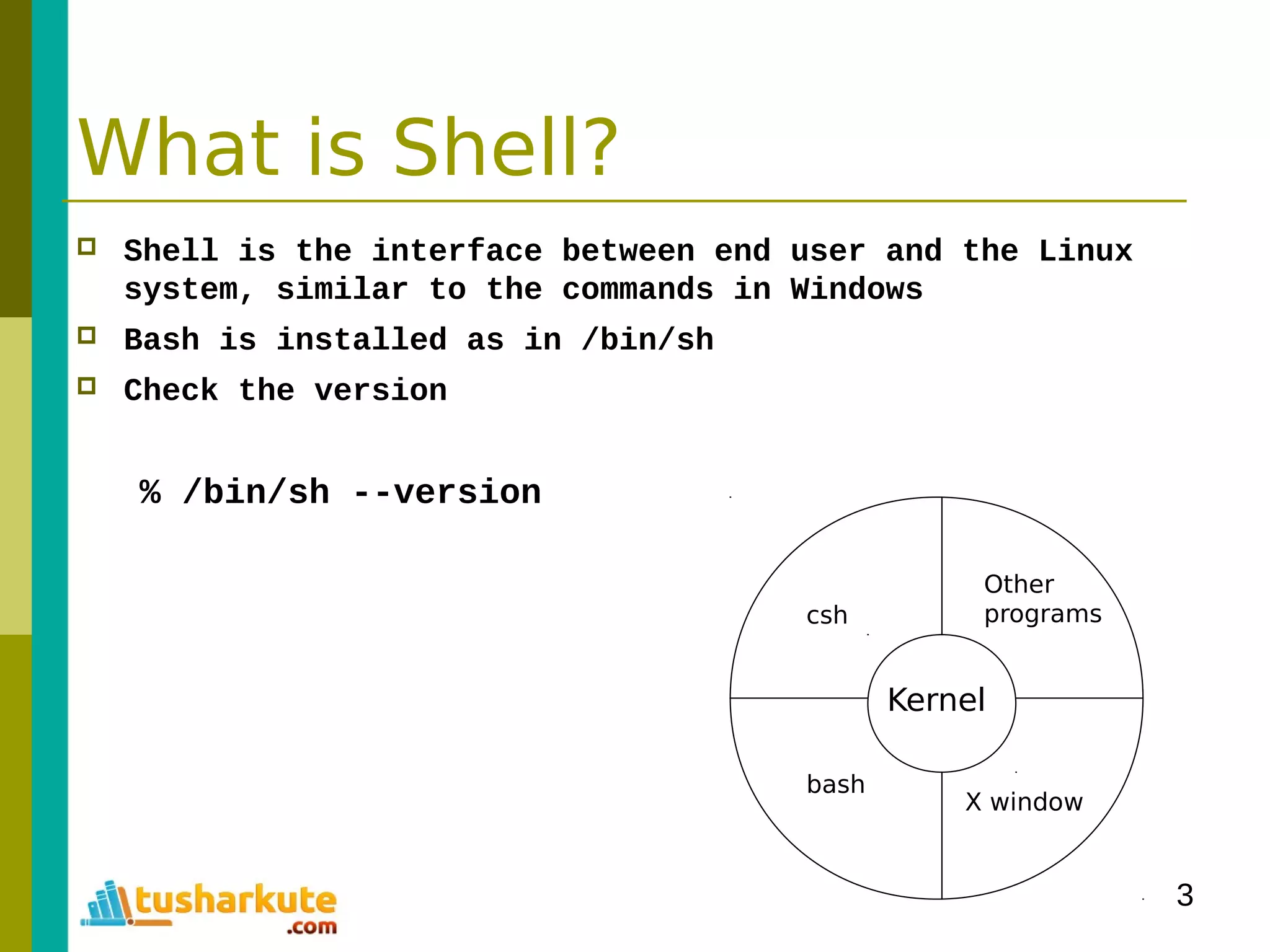
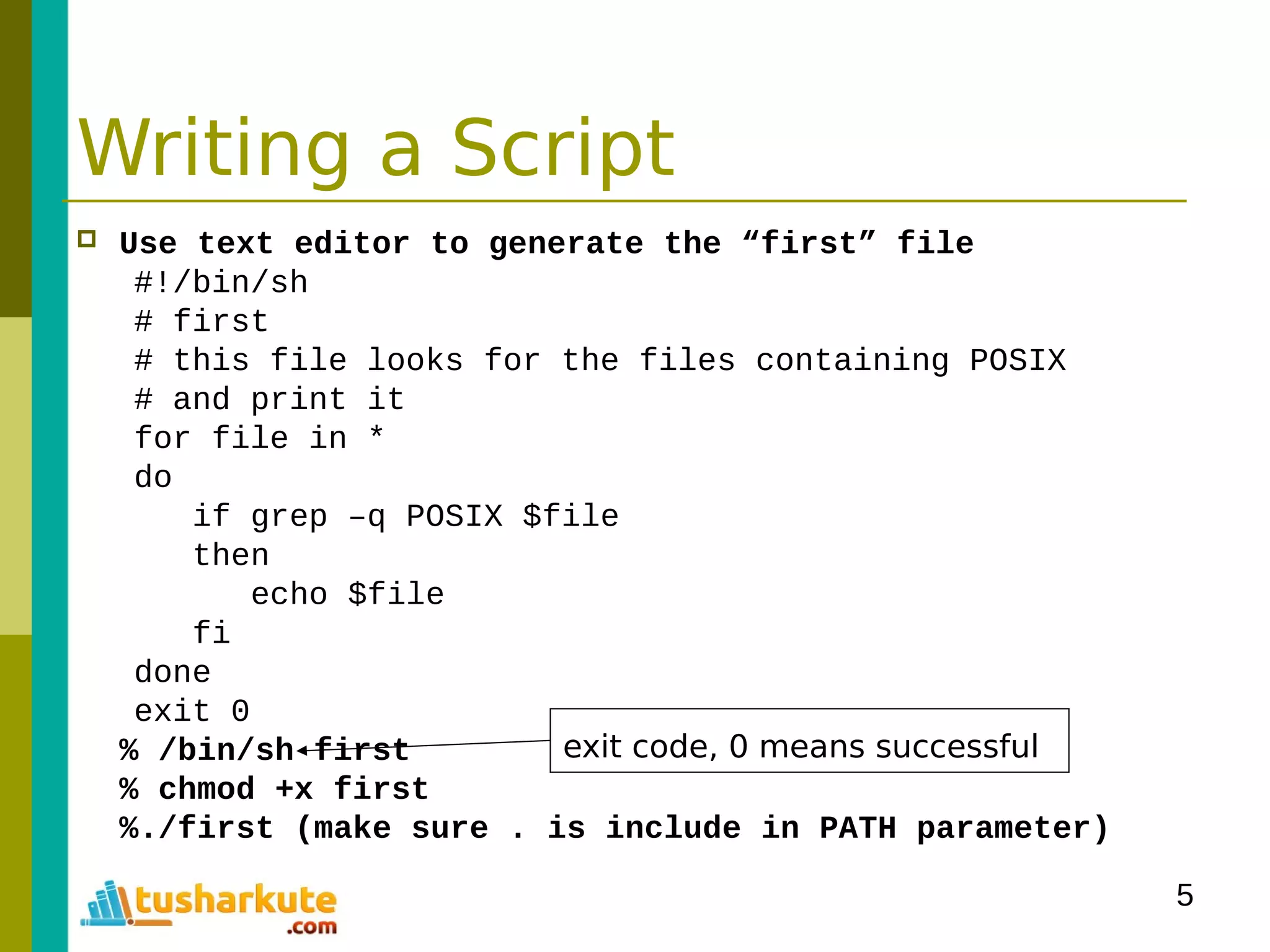
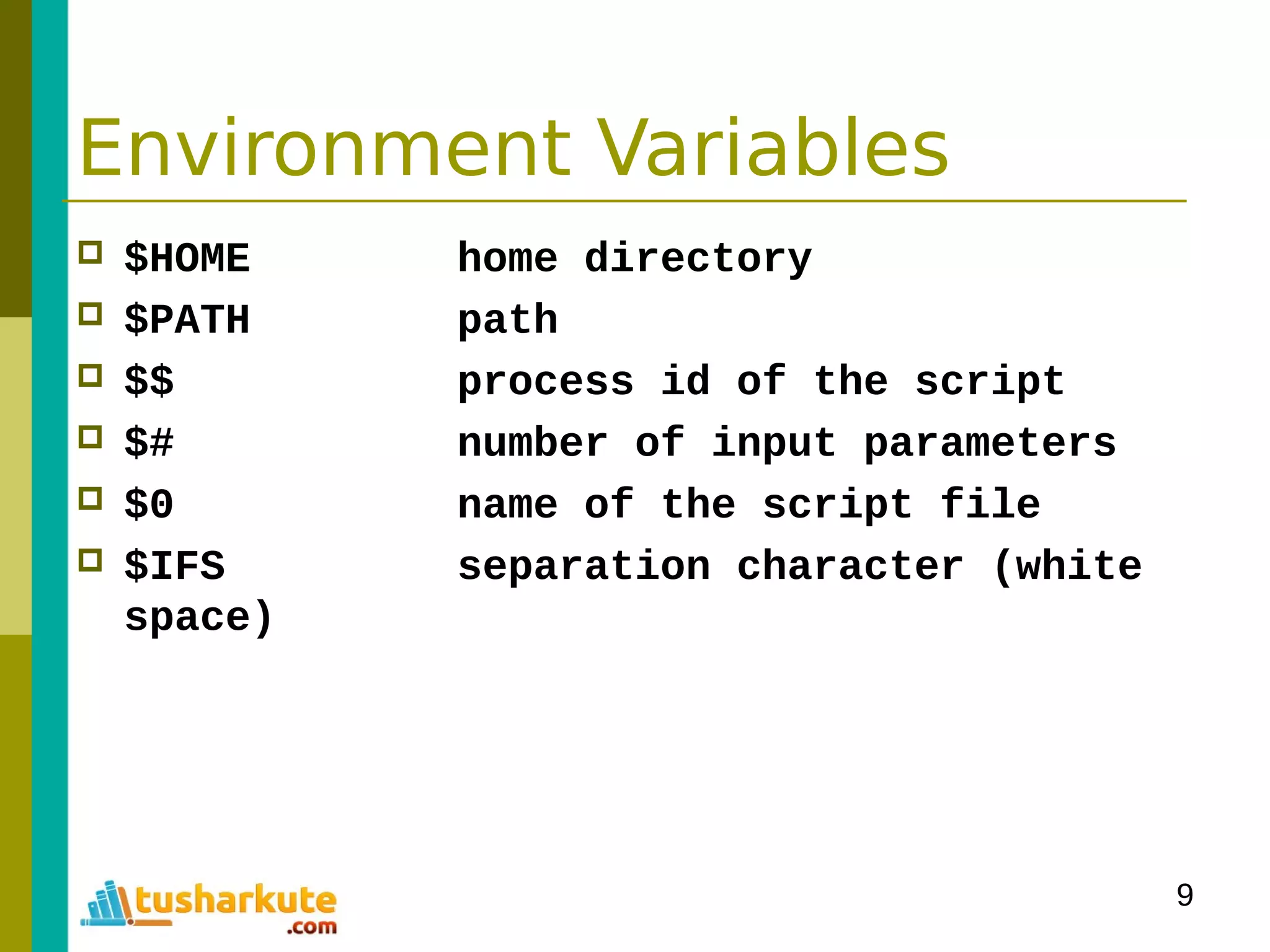
The document is a comprehensive guide on basic shell scripting, covering topics such as the purpose of shell scripts, syntax, variables, control structures, loops, and pattern matching. It includes examples to demonstrate commands and constructs in shell scripting for effective system administration. Additionally, it provides links to further resources like the Bash Beginners Guide.





![10
Condition
test or ‘ [ ‘
if test –f fred.c
then
...
fi
If [ -f
fred.c ]
then
...
fi
if [ -f fred.c ];then
...
fi
expression1 –eq expression2
expression1 –ne expression2
expression1 –gt expression2
expression1 –ge expression2
expression1 -lt expression2
expression1 –le expression2
!expression
-d file if directory
-e file if exist
-f file if file
-g file if set-group-id
-r file if readable
-s file if size >0
-u file if set-user-id
-w file if writable
-x file if executableString1 = string2
String1 != string 2
-n string (if not empty string)
-z string (if empty string)
need space !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-10-2048.jpg)
![11
Control Structure
Syntax
if condition
then
statement
else
statement
fi
#!/bin/sh
echo “Is it morning? Please answer yes or no”
read timeofday
if [ $timeofday = “yes” ]; then
echo “Good morning”
else
echo “Good afternoon”
fi
exit 0
Is it morning? Please answer yes or no
yes
Good morning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-11-2048.jpg)
![12
Condition Structure
#!/bin/sh
echo “Is it morning? Please answer yes or no”
read timeofday
if [ $timeofday = “yes” ]; then
echo “Good morning”
elif [ $timeofday = “no” ]; then
echo “Good afternoon”
else
echo “Sorry, $timeofday not recongnized. Enter yes or no”
exit 1
fi
exit 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-12-2048.jpg)
![13
Condition Structure
#!/bin/sh
echo “Is it morning? Please answer yes or no”
read timeofday
if [ “$timeofday” = “yes” ]; then
echo “Good morning”
elif [ $timeofday = “no” ]; then
echo “Good afternoon”
else
echo “Sorry, $timeofday not recongnized. Enter yes or no”
exit 1
fi
exit 0
If input “enter” still returns Good morning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-13-2048.jpg)
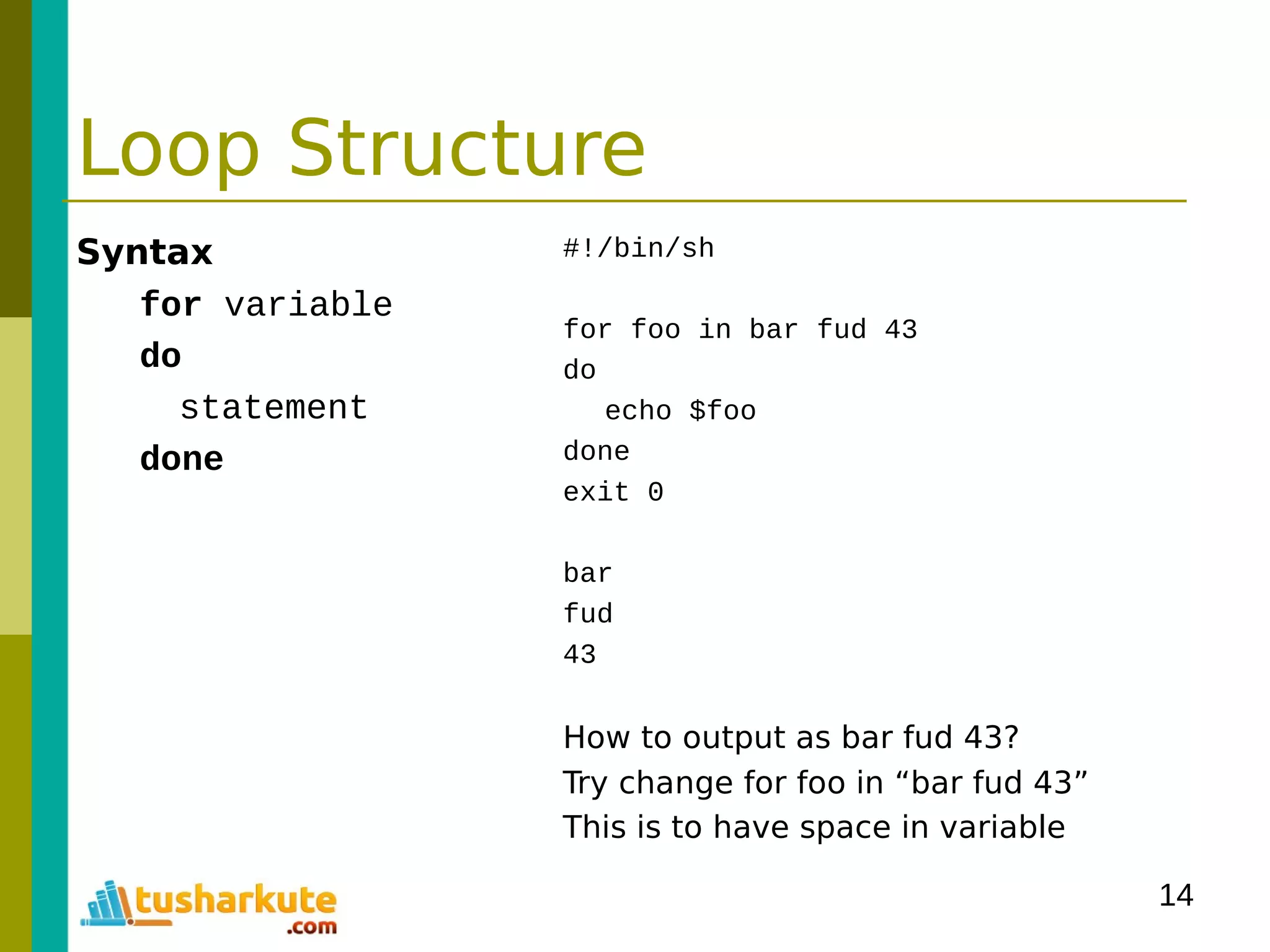
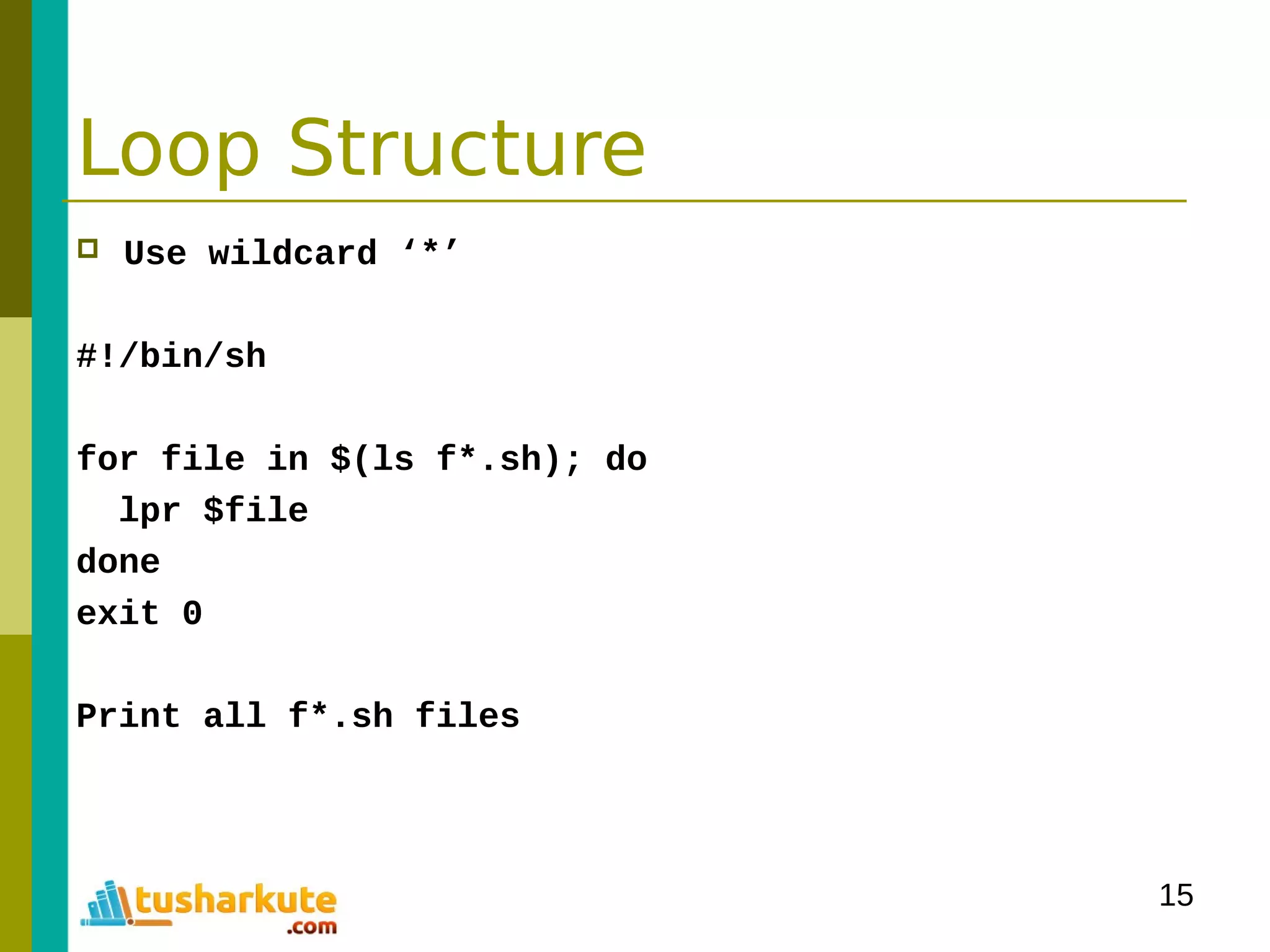
![16
Loop Structure
Syntax
while condition
do
statement
done
#!/bin/sh
for foo in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
do
echo “here we go again”
done
exit 0
#!/bin/sh
foo = 1
while [ “$foo” –le 10 ]
do
echo “here we go again”
foo = $foo(($foo+1))
done
exit 0
Syntax
until condition
do
statement
done
Note: condition is
Reverse to while
How to re-write
previous sample?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-16-2048.jpg)
![17
Case Statement
Syntax
case variable in
pattern [ | pattern ] …) statement;;
pattern [ | pattern ] …) statement;;
…
esac
#!/bin/sh
echo “Is it morning? Please answer yes or no”
read timeofday
case “$timeofday” in
yes) echo “Good Morning”;;
y) echo “Good Morning”;;
no) echo “Good Afternoon”;;
n) echo “Good Afternoon”;;
* ) echo “Sorry, answer not recongnized”;;
esac
exit 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-17-2048.jpg)


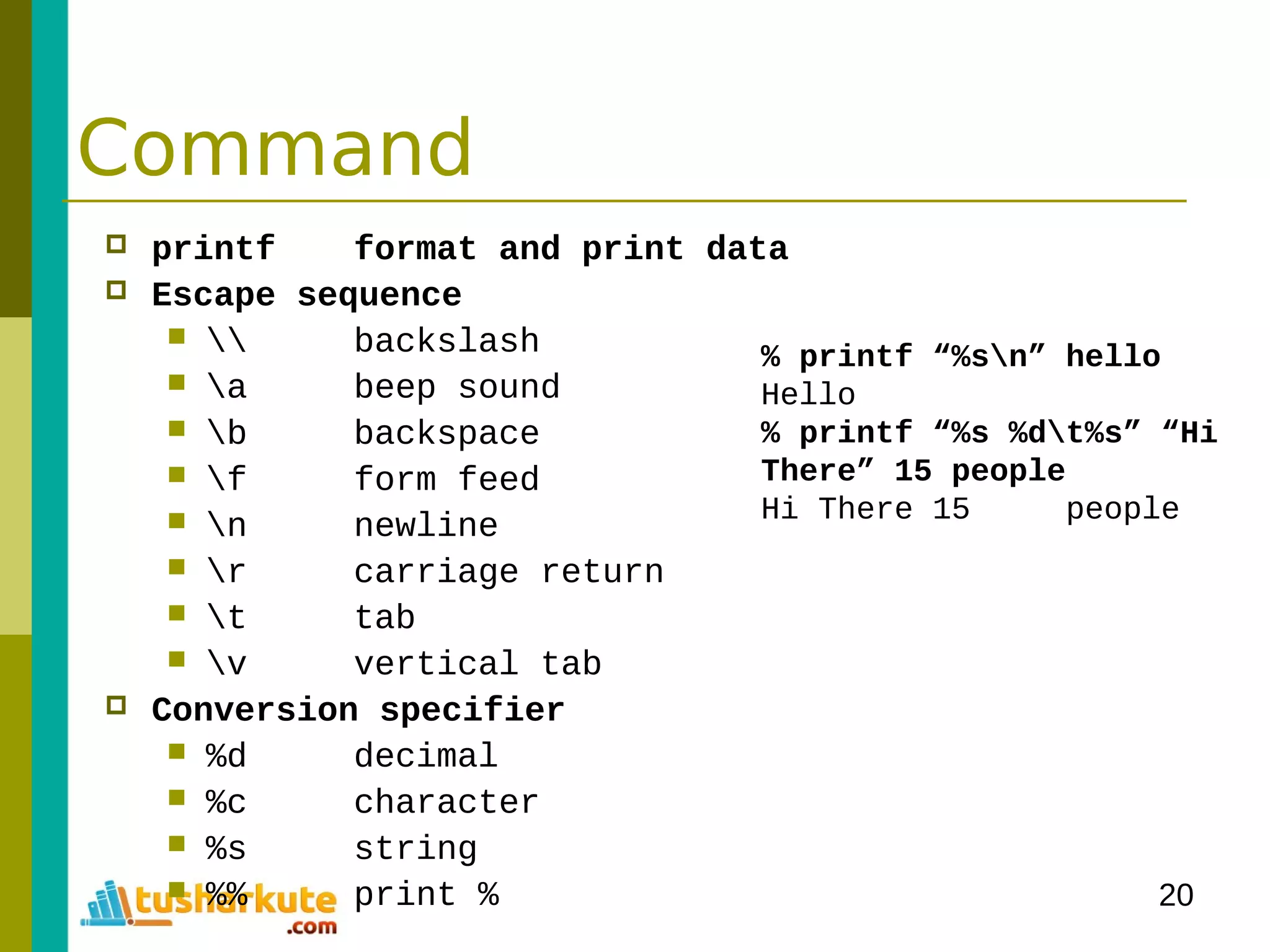
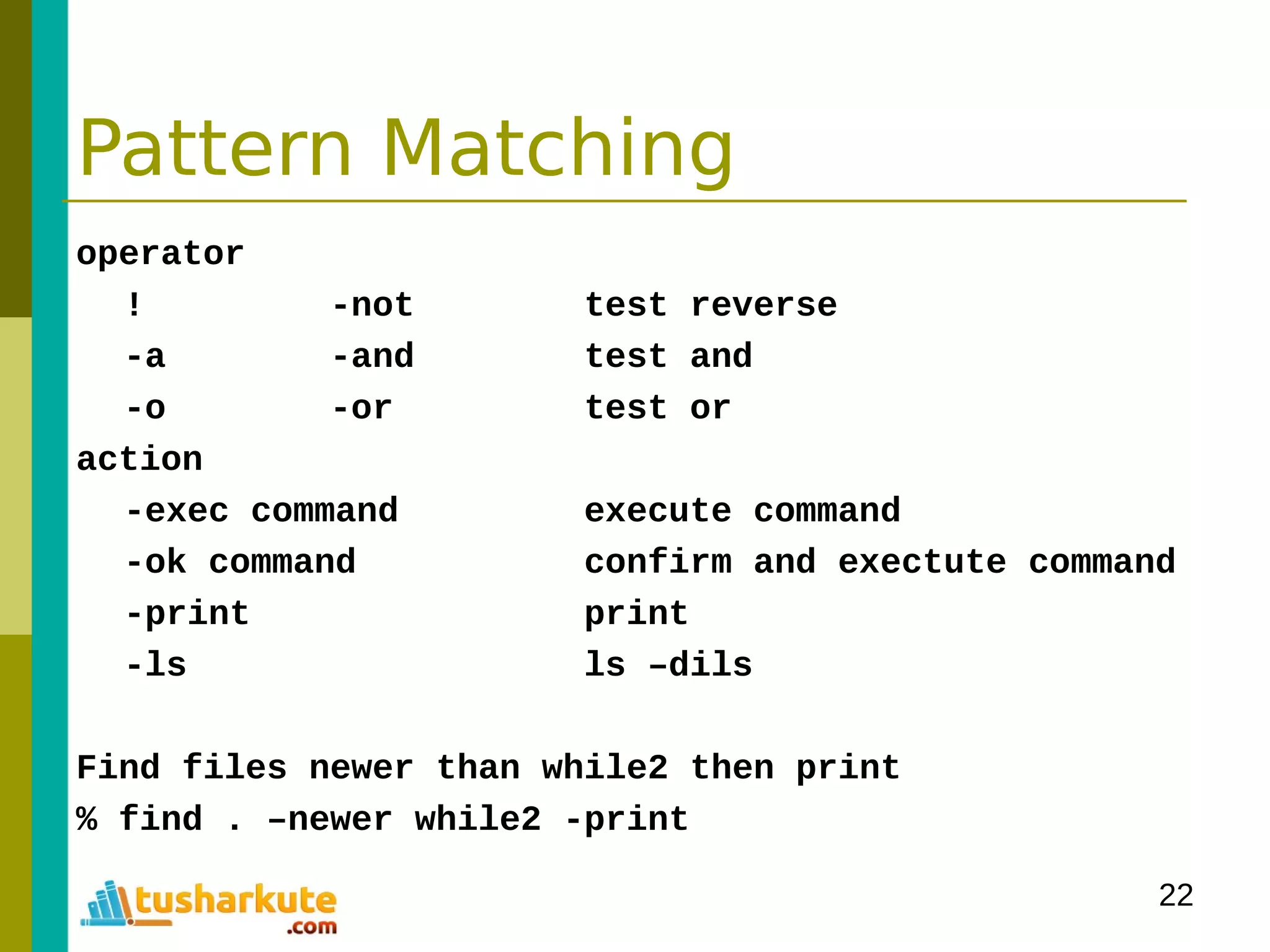
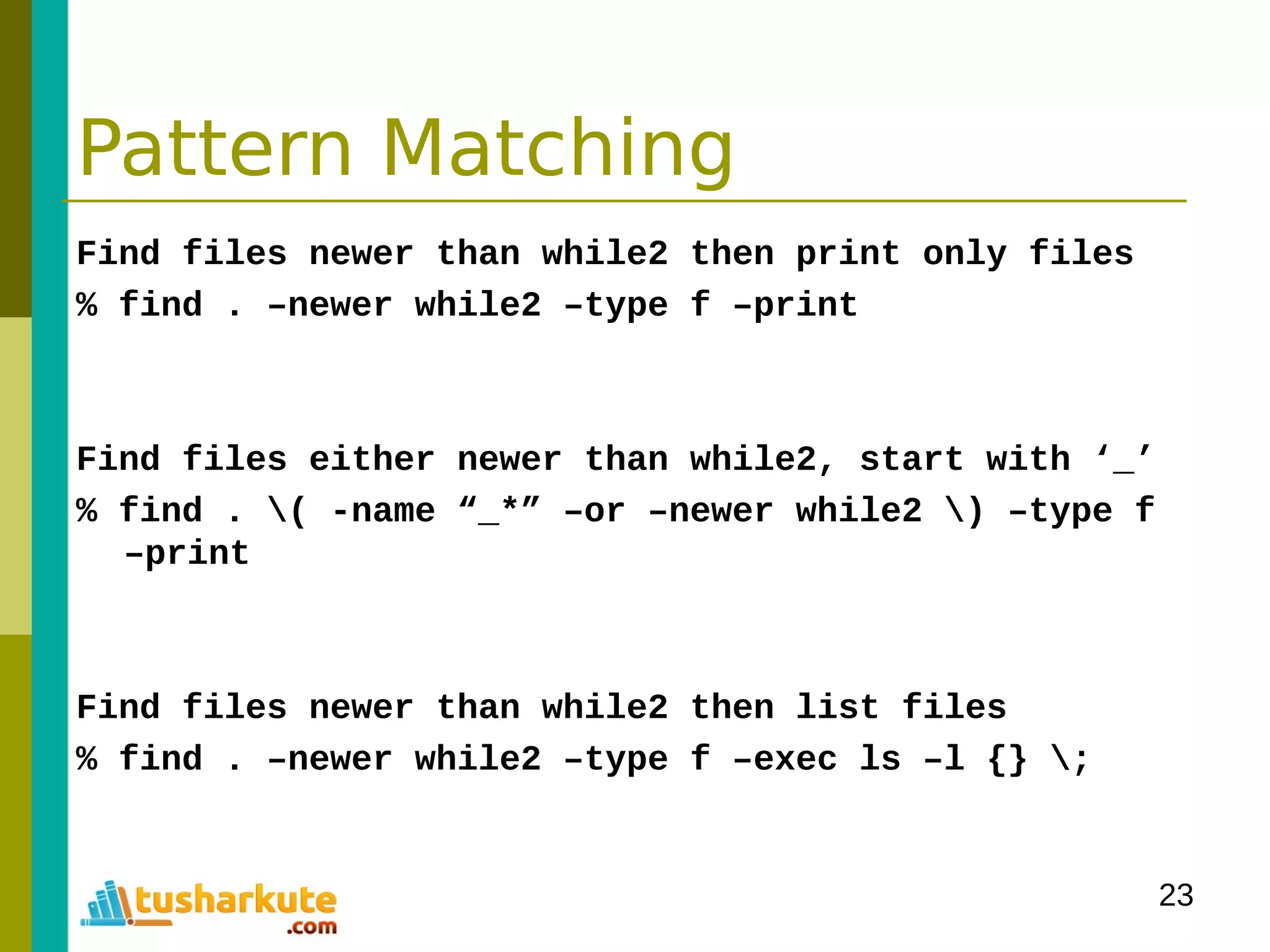
![24
Pattern Matching
grep print lines matching a pattern
(General Regular Expression Parser)
grep [options] PATTERN [FILES]
option
-c print number of output context
-E Interpret PATTERN as an extended regular expression
-h Supress the prefixing of filenames
-i ignore case
-l surpress normal output
-v invert the sense of matching
% grep in words.txt
% grep –c in words.txt words2.txt
% grep –c –v in words.txt words2.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-3programmingonlinux-140329094714-phpapp02/75/Module-03-Programming-on-Linux-24-2048.jpg)
