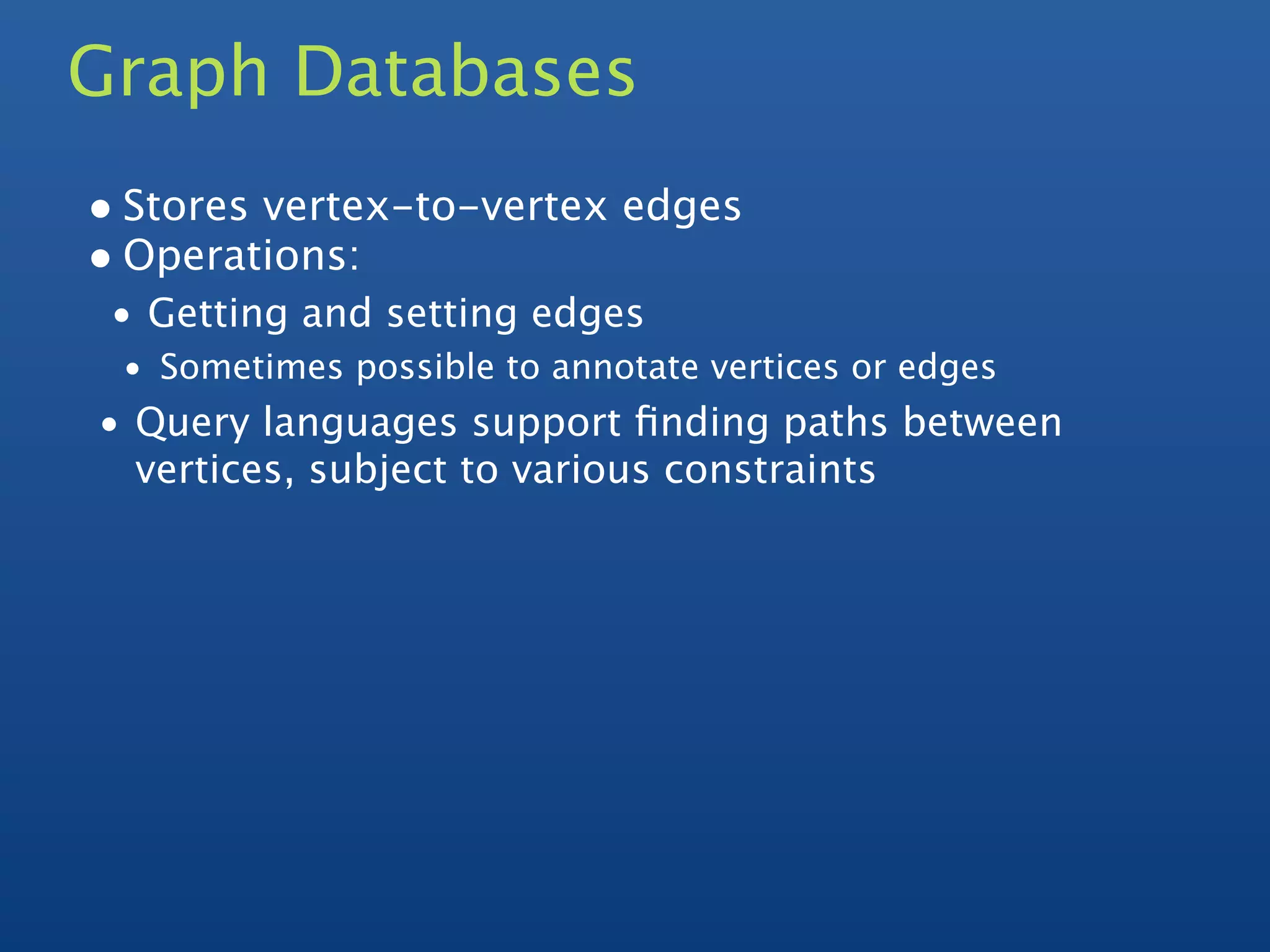
Christian Kvalheim gave an introduction to NoSQL and MongoDB. Some key points:
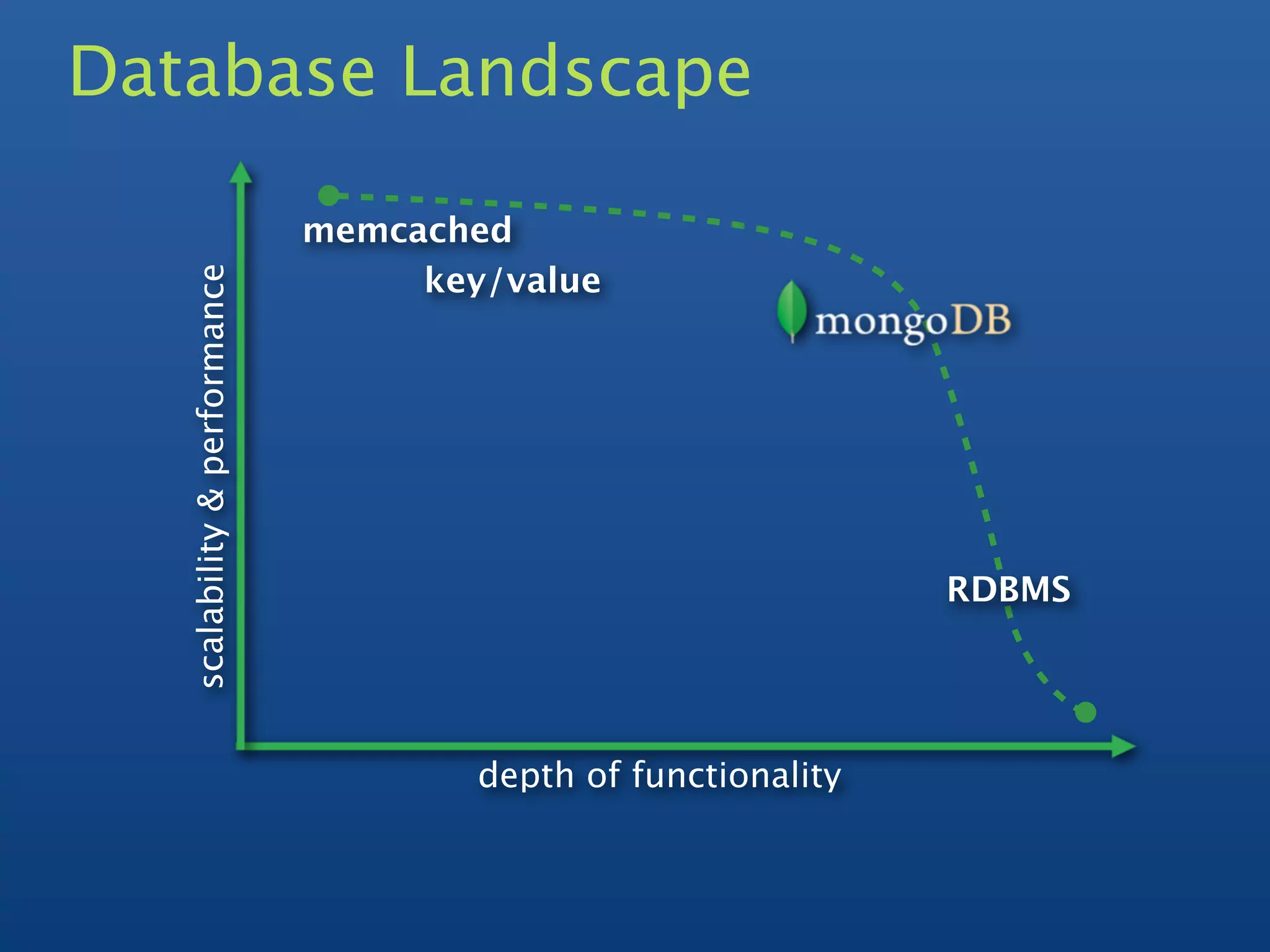
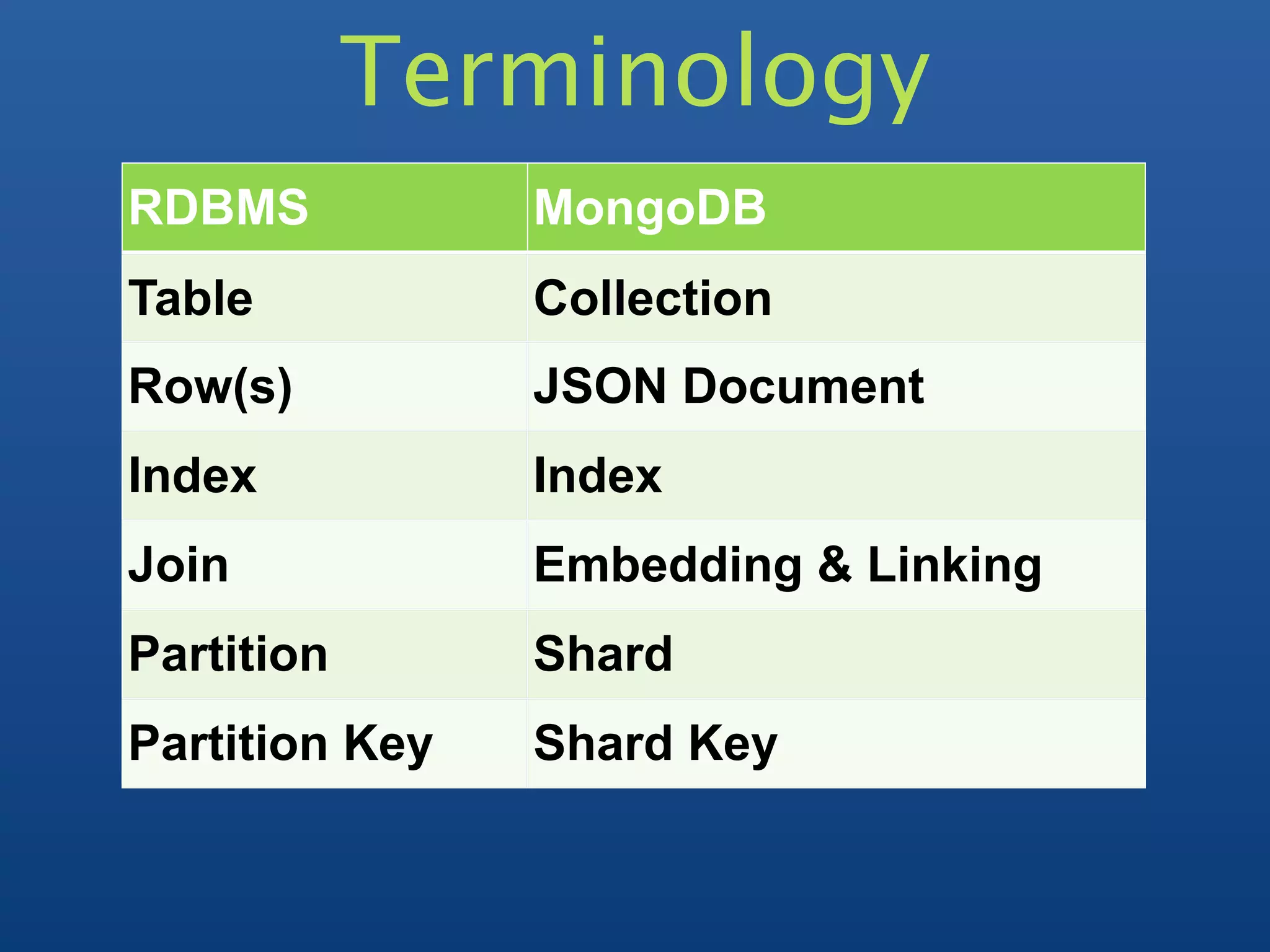
1) MongoDB is a scalable, high-performance, open source NoSQL database that uses a document-oriented model.
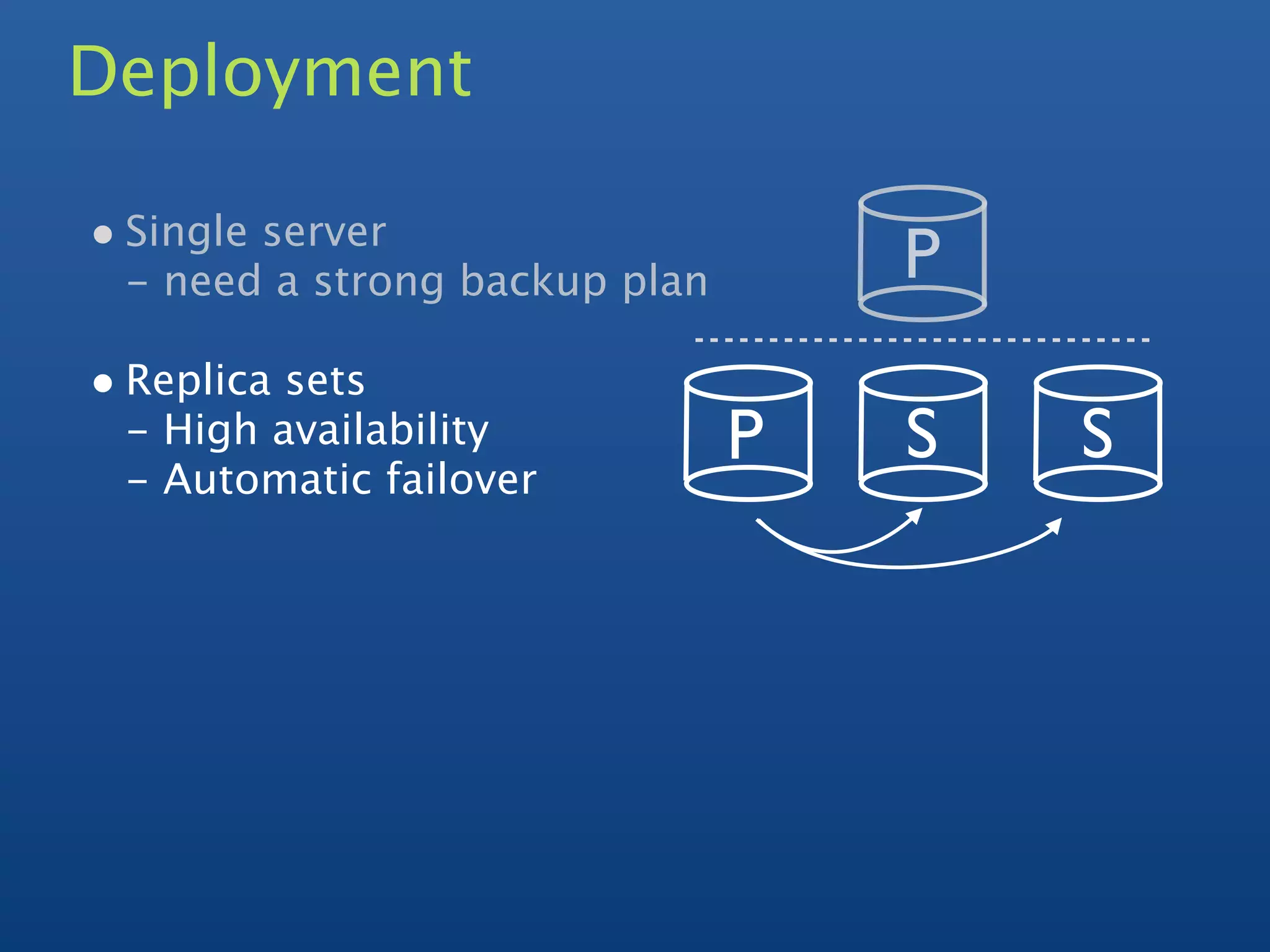
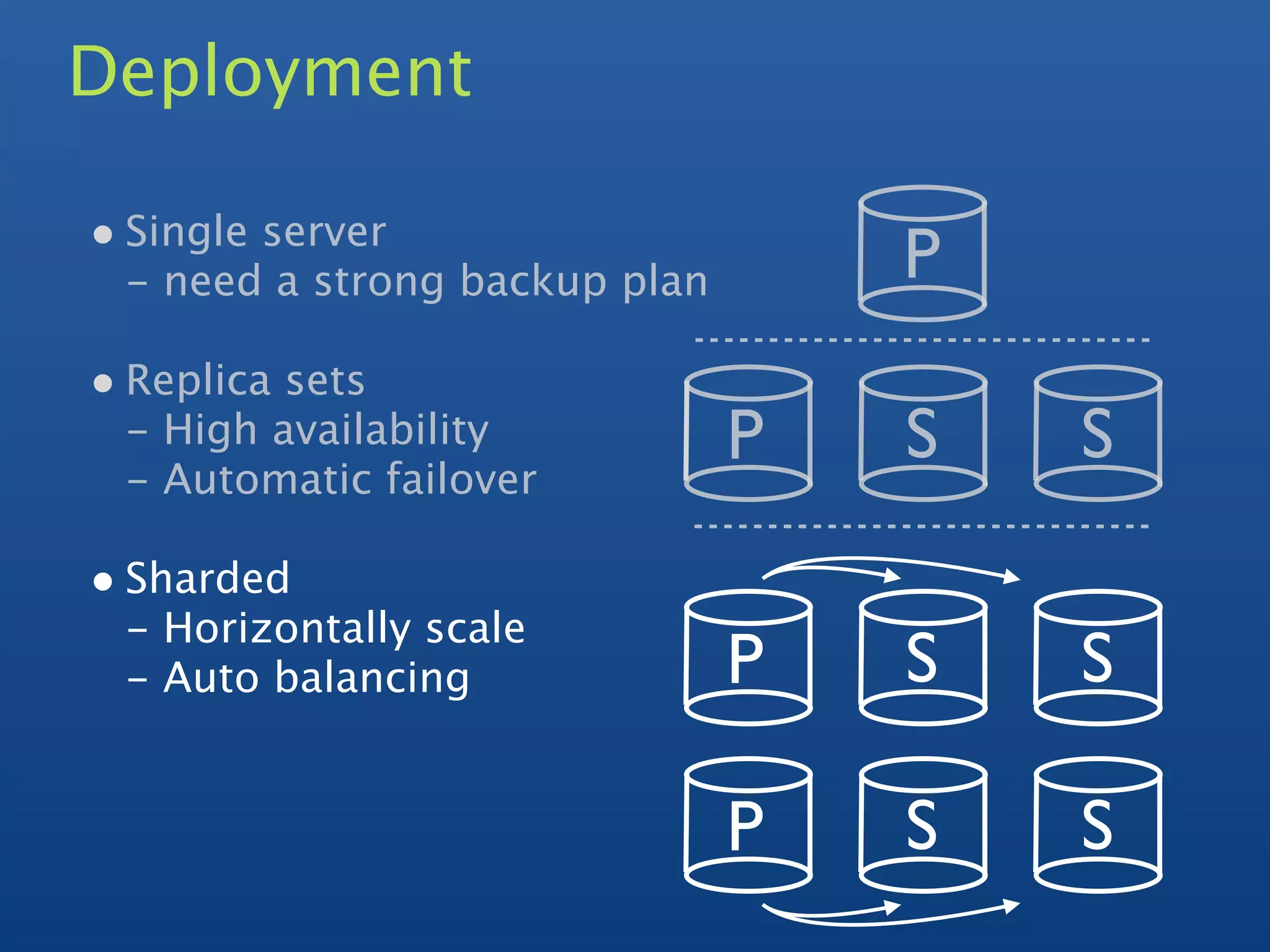
2) It supports indexing, replication, auto-sharding for horizontal scaling, and querying.
3) Documents are stored in JSON-like records which can contain various data types including nested objects and arrays.









![Documents
Blog Post Document
> p = { author: "Chris",
date: new ISODate(),
text: "About MongoDB...",
tags: ["tech", "databases"]}
> db.posts.save(p)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-14-2048.jpg)
![Querying
> db.posts.find()
{ _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"),
author : "Chris",
date : ISODate("2012-02-02T11:52:27.442Z"),
text : "About MongoDB...",
tags : [ "tech", "databases" ] }
Notes:
_id is unique, but can be anything you'd like](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-15-2048.jpg)


![Compound Indexes
Create index on multiple fields in a Document
// 1 means ascending, -1 means descending
> db.posts.ensureIndex({author: 1, ts: -1})
> db.posts.find({author: 'Chris'}).sort({ts: -1})
[{ _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"),
author: "Chris", ...},
{ _id : ObjectId("4f61d325c496820ceba84124"),
author: "Chris", ...}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-18-2048.jpg)

![Examine the query plan
> db.posts.find({"author": 'Ross'}).explain()
{
"cursor" : "BtreeCursor author_1",
"nscanned" : 1,
"nscannedObjects" : 1,
"n" : 1,
"millis" : 0,
"indexBounds" : {
"author" : [
[
"Chris",
"Chris"
]
]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-20-2048.jpg)

![Nested Documents
{ _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"),
author : "Chris",
date : "Thu Feb 02 2012 11:50:01",
text : "About MongoDB...",
tags : [ "tech", "databases" ],
comments : [{
author : "Fred",
date : "Fri Feb 03 2012 13:23:11",
text : "Best Post Ever!"
}],
comment_count : 1
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-22-2048.jpg)
![Nested Documents
{ _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"),
author : "Chris",
date : "Thu Feb 02 2012 11:50:01",
text : "About MongoDB...",
tags : [ "tech", "databases" ],
comments : [{
author : "Fred",
date : "Fri Feb 03 2012 13:23:11",
text : "Best Post Ever!"
}],
comment_count : 1
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-23-2048.jpg)

![Geo
• Geo-spatial queries
• Require a geo index
• Find points near a given point
• Find points within a polygon/sphere
// geospatial index
> db.posts.ensureIndex( "author.location": "2d" )
> db.posts.find( "author.location" :
{ $near : [22, 42] } )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-25-2048.jpg)
![Map Reduce
The caller provides map and reduce functions written
in JavaScript
// Emit each tag
> map = "this['tags'].forEach(
function(item) {emit(item, 1);}
);"
// Calculate totals
> reduce = "function(key, values) {
var total = 0;
var valuesSize = values.length;
for (var i=0; i < valuesSize; i++) {
total += parseInt(values[i], 10);
}
return total;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-26-2048.jpg)
![Map Reduce
// run the map reduce
> db.posts.mapReduce(map, reduce, {"out": { inline : 1}});
{
"results" : [
{"_id" : "databases", "value" : 1},
{"_id" : "tech", "value" : 1 }
],
"timeMillis" : 1,
"counts" : {
"input" : 1,
"emit" : 2,
"reduce" : 0,
"output" : 2
},
"ok" : 1,
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-27-2048.jpg)
![Aggregation - coming in 2.2
// Count tags
> agg = db.posts.aggregate(
{$unwind: "$tags"},
{$group : {_id : "$tags",
count : {$sum: 1}}}
)
> agg.result
[{"_id": "databases", "count": 1},
{"_id": "tech", "count": 1}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-28-2048.jpg)
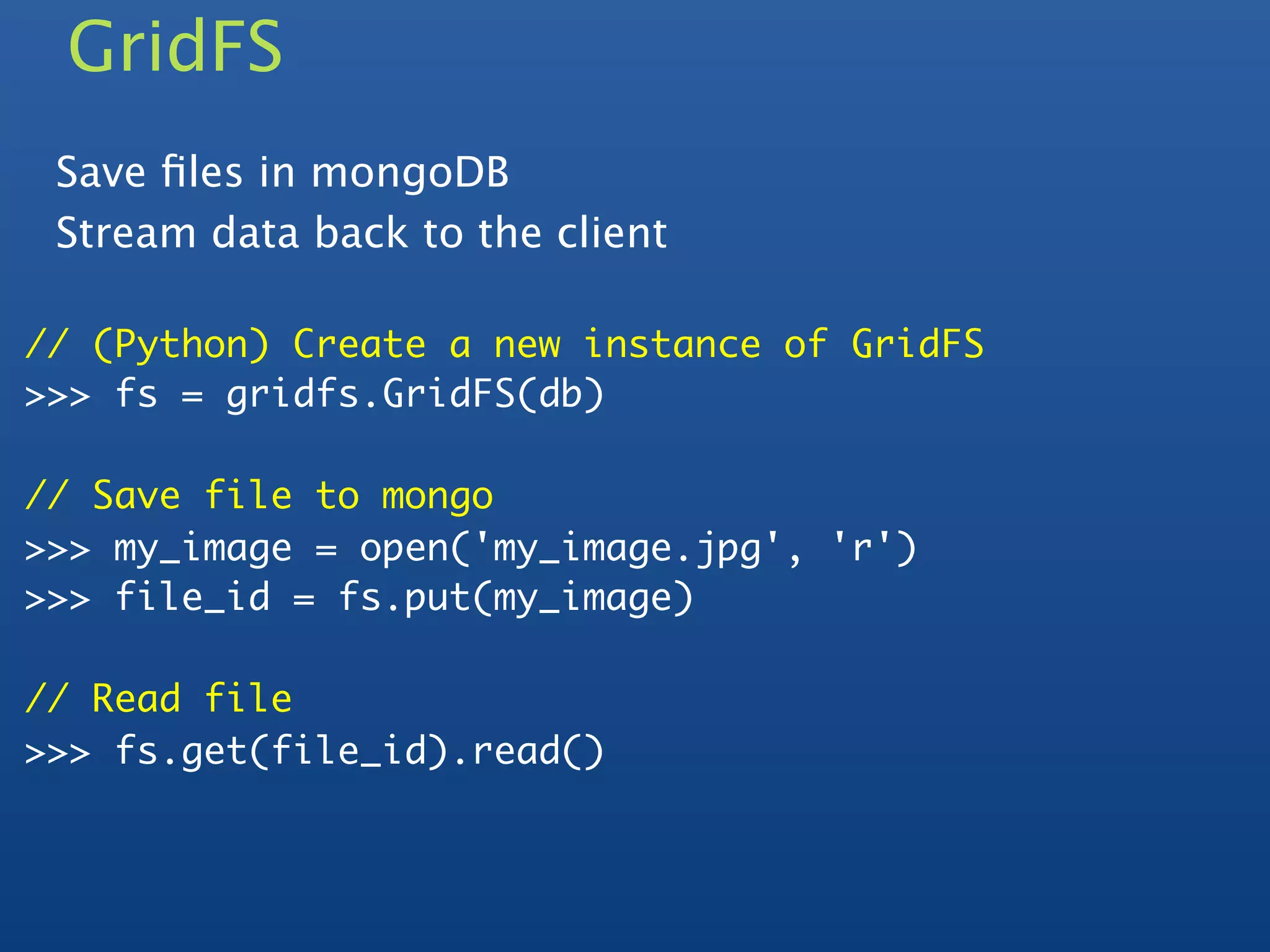

![Rich Documents
{ _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"),
line_items : [ { sku: 'tt-123',
name: 'Coltrane: Impressions' },
{ ski: 'tt-457',
name: 'Davis: Kind of Blue' } ],
address : { name: 'Banker',
street: '111 Main',
zip: 10010 },
payment: { cc: 4567,
exp: Date(2012, 7, 7) },
subtotal: 2355
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-intro-120413052917-phpapp02/75/Mongodb-intro-31-2048.jpg)