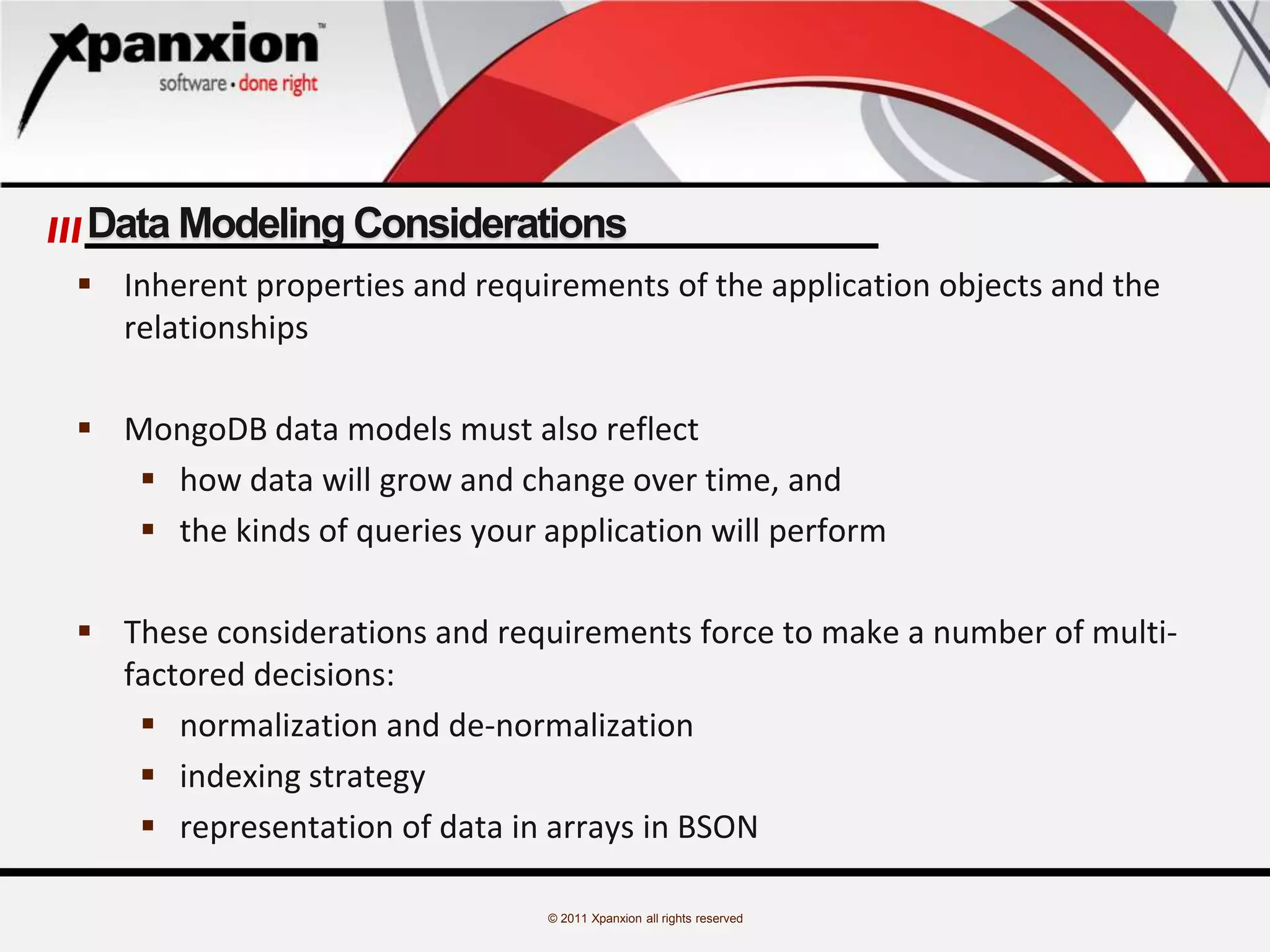
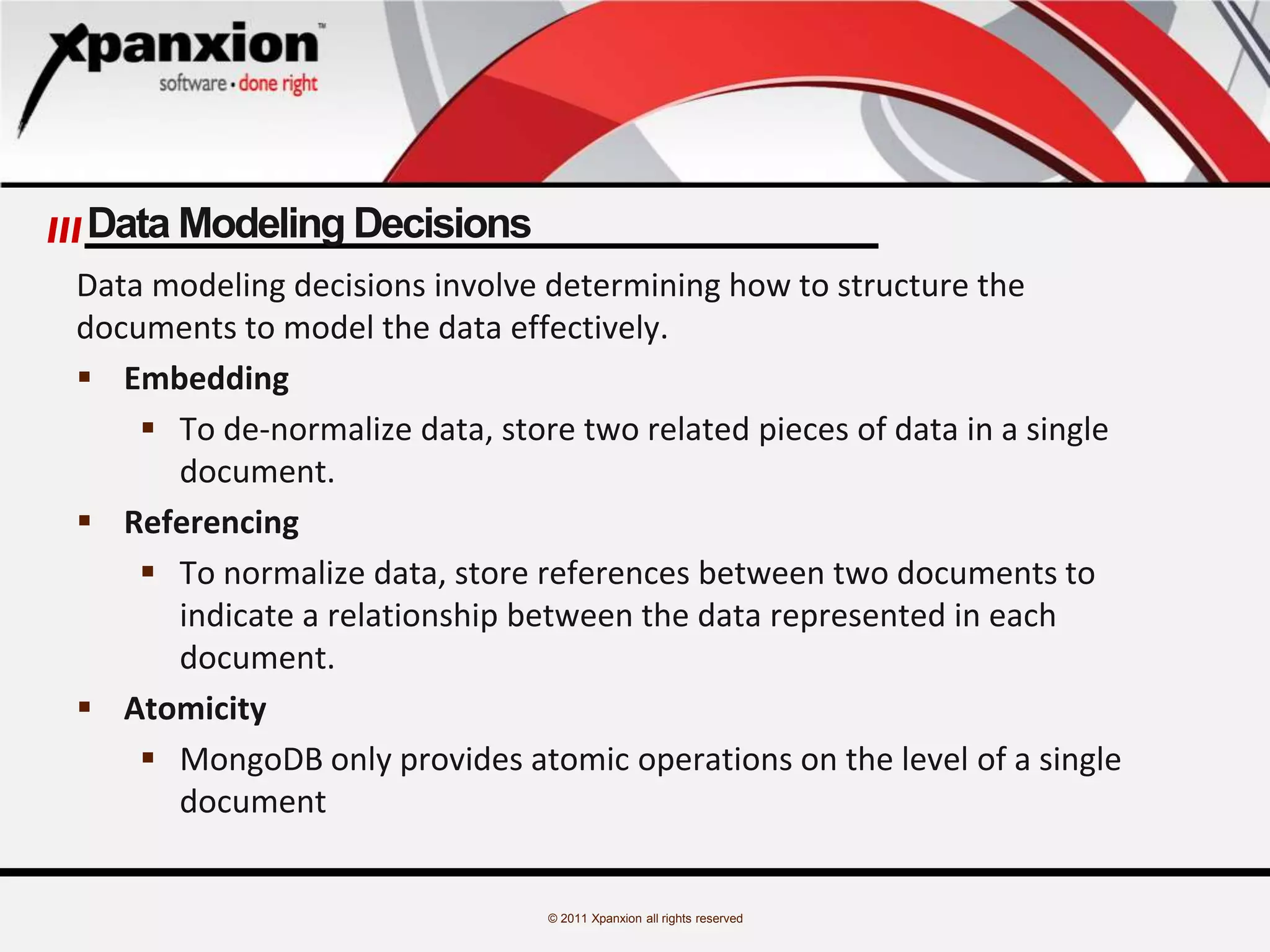
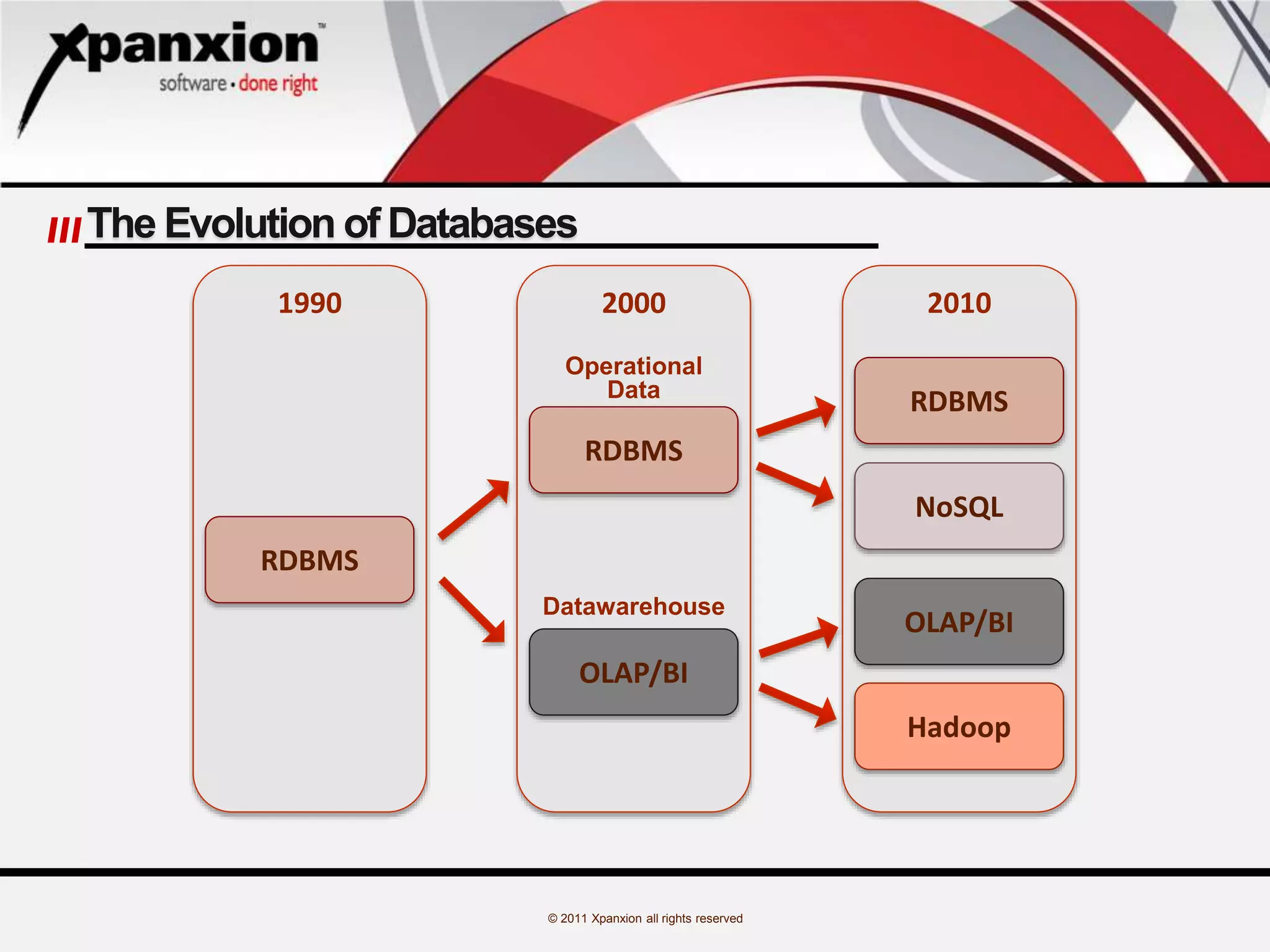
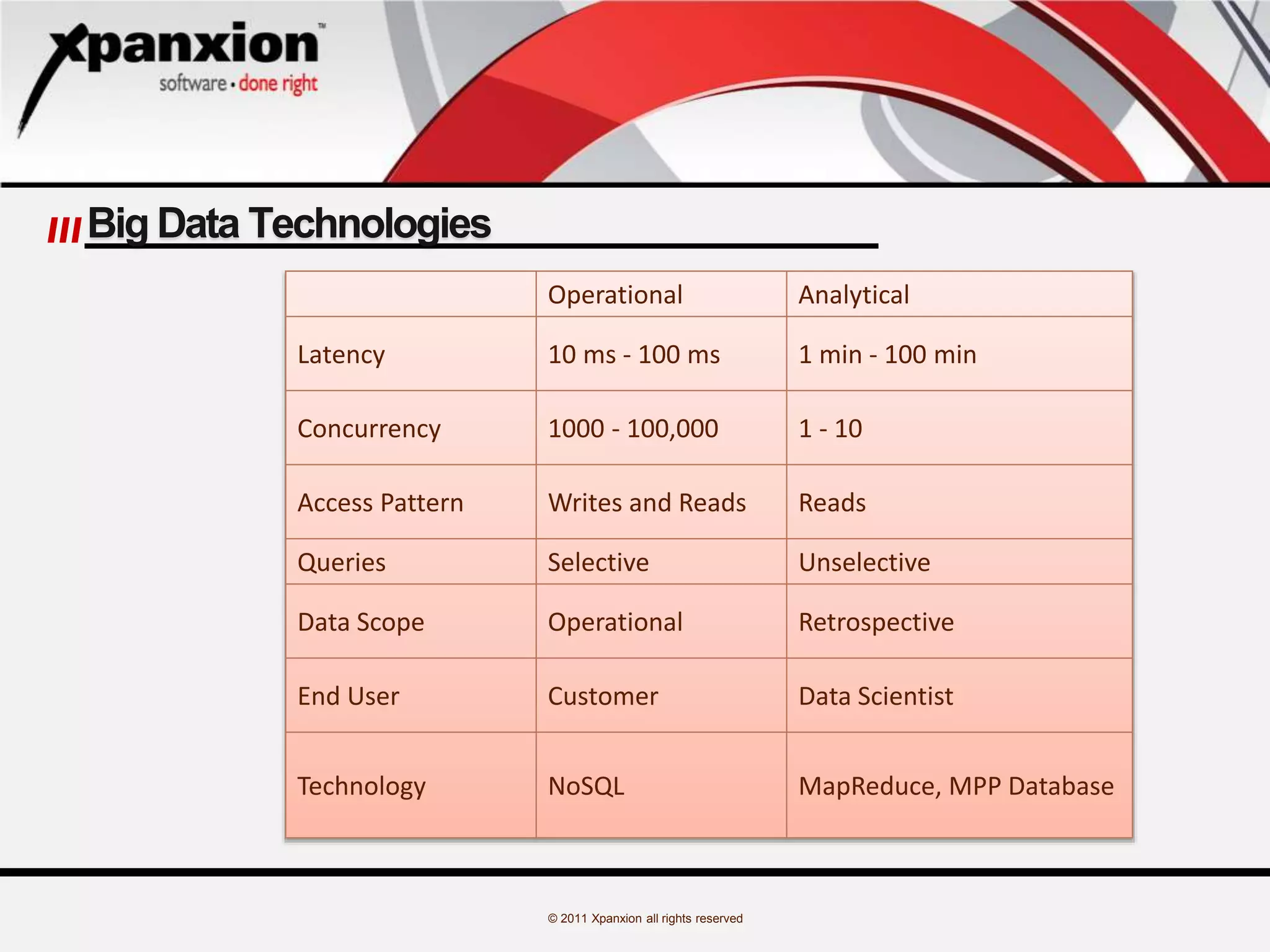
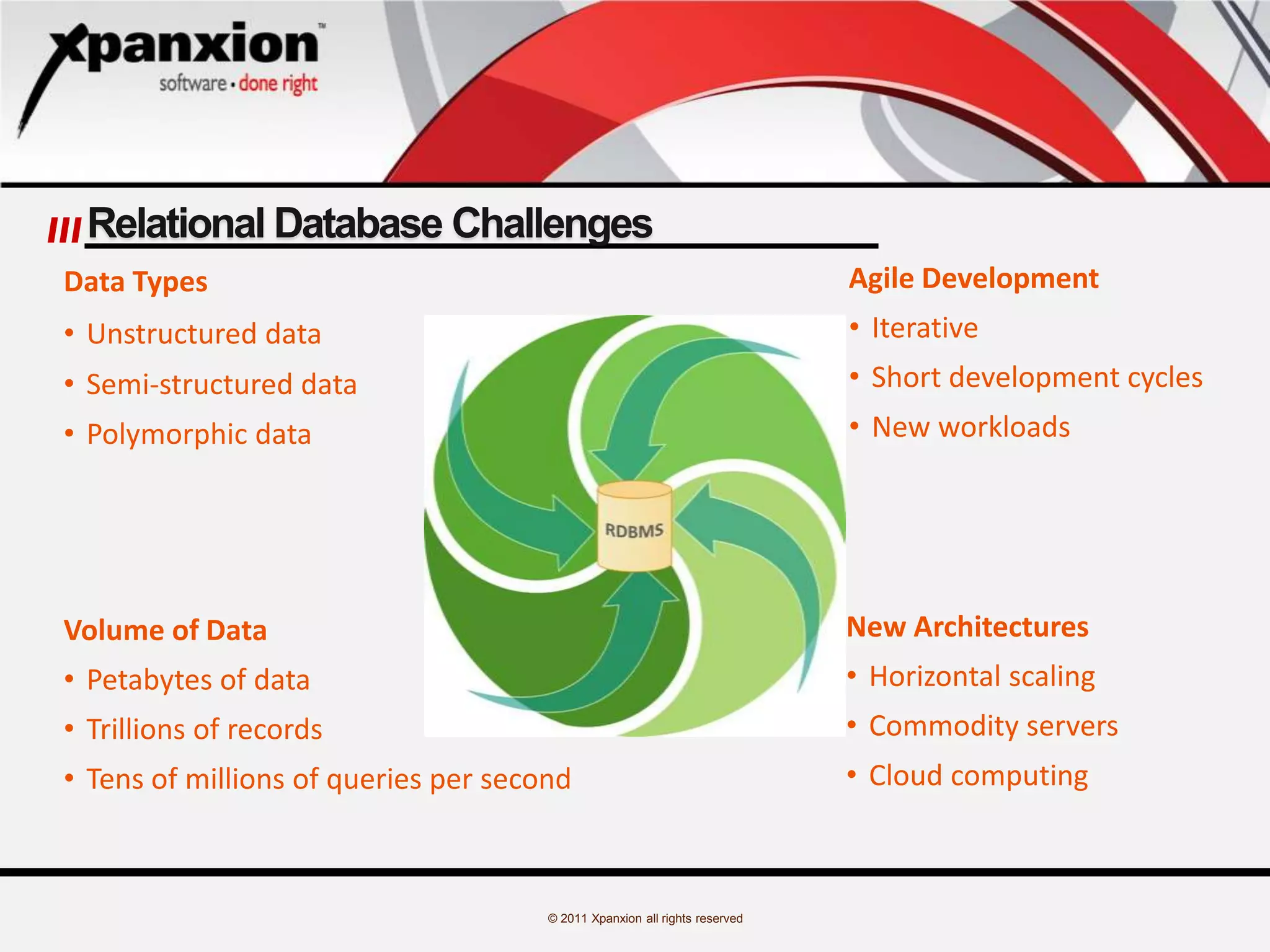
The document discusses the evolution of databases, emphasizing the challenges and advancements in handling 'big data', which refers to massive and complex datasets incompatible with traditional tools. It specifically focuses on MongoDB, highlighting its features as a high-performance, open-source, document-oriented database that allows flexible schema design and supports various programming languages. Additionally, it covers core operations, data modeling considerations, and use cases like a blogging project implementing MongoDB.



![© 2011 Xpanxion all rights reserved
Mongo Shell
vars / functions / data structs + types
Spidermonkey / V8
ObjectId("...")
new Date()
Object.bsonsize()
db["collection"].find/count/update
short-hand for collections
Doesn't require quoted keys
Don’t copy and paste too much
Embedded
Javascript
Interpreter
Global Functions
and Objects
MongoDB driver
Exposed
JSON-like stuff](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbysachinbhosale-151216121932/75/MongoDB-Introduction-and-Data-Modelling-17-2048.jpg)