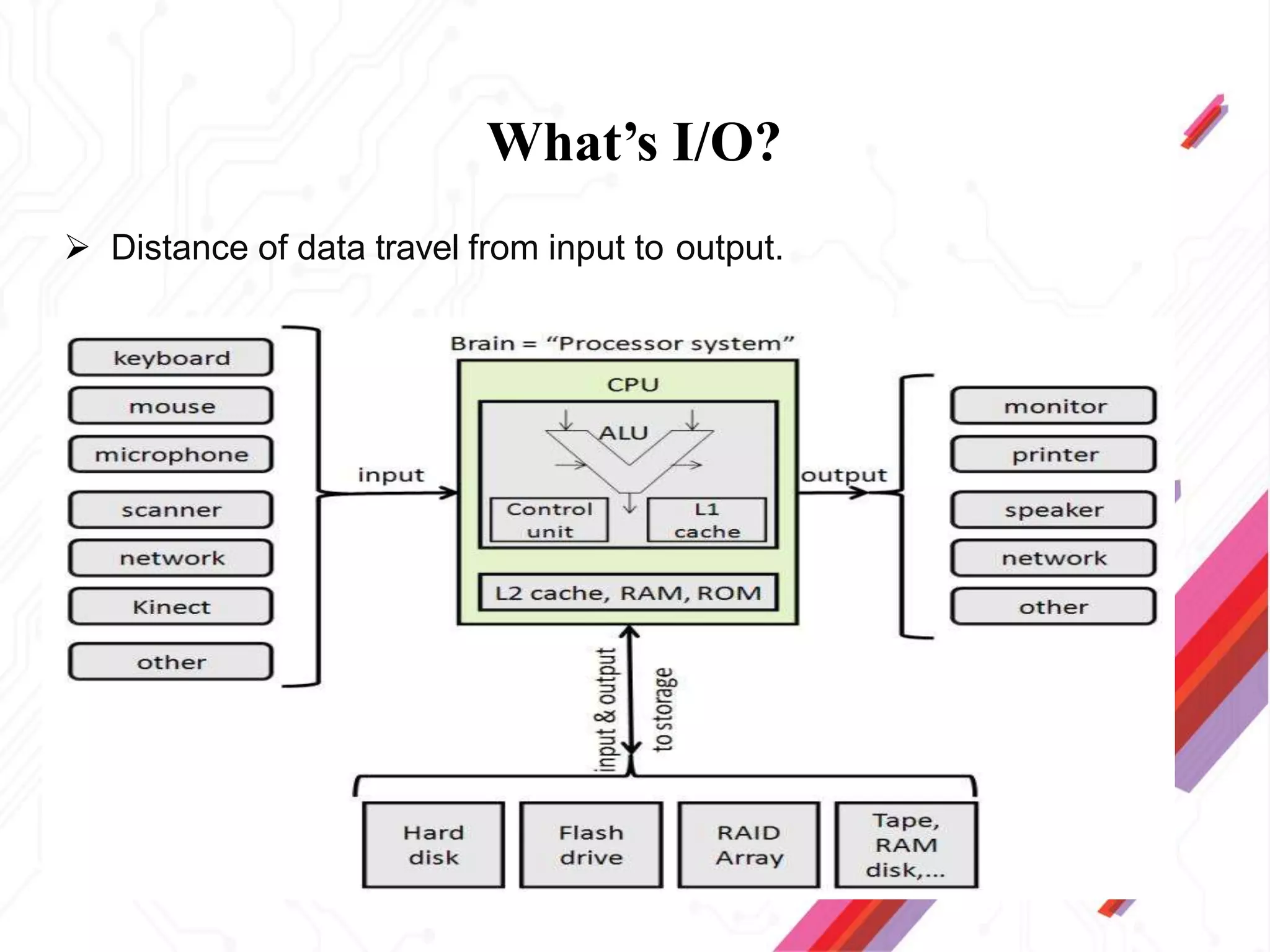
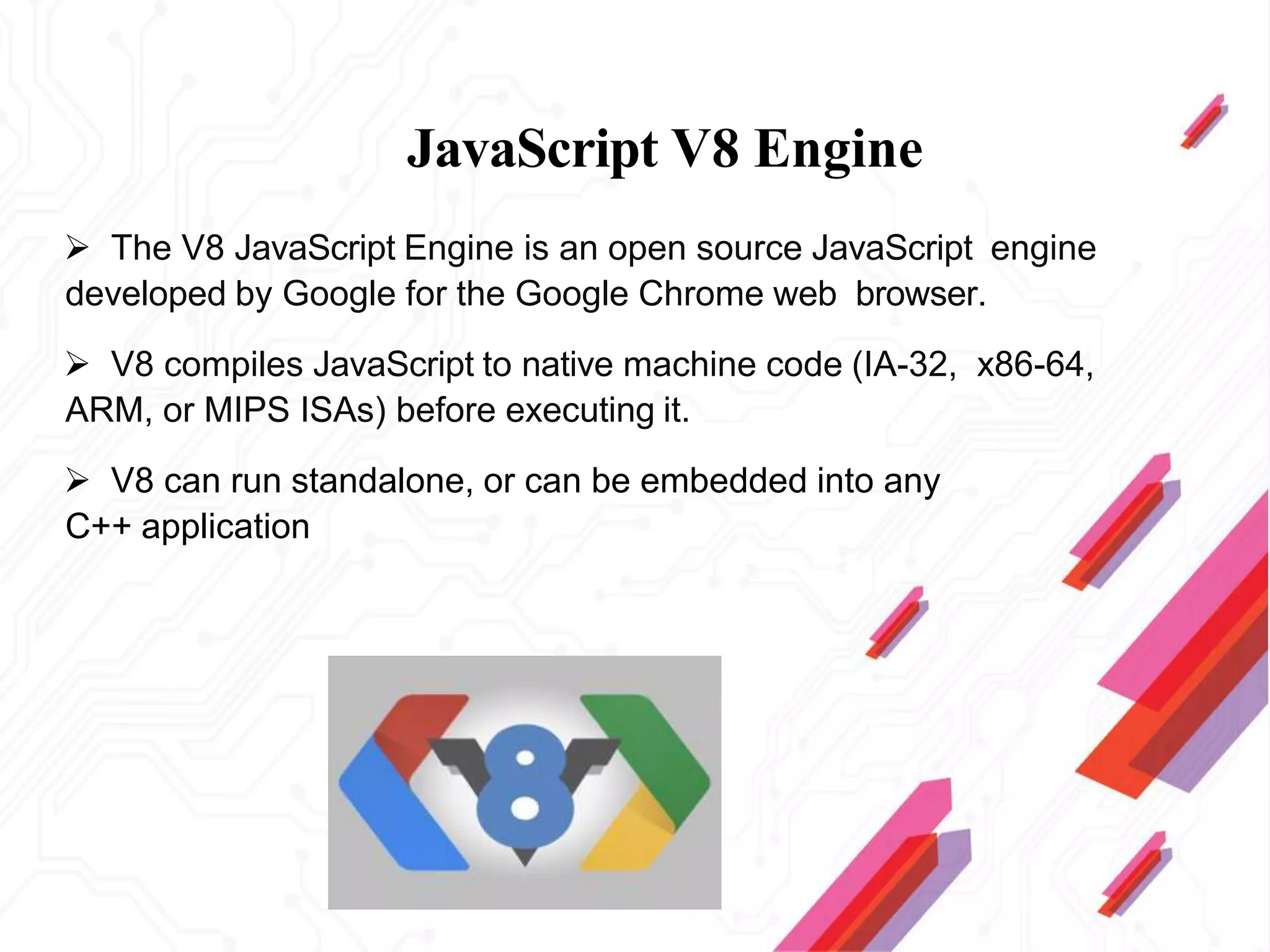
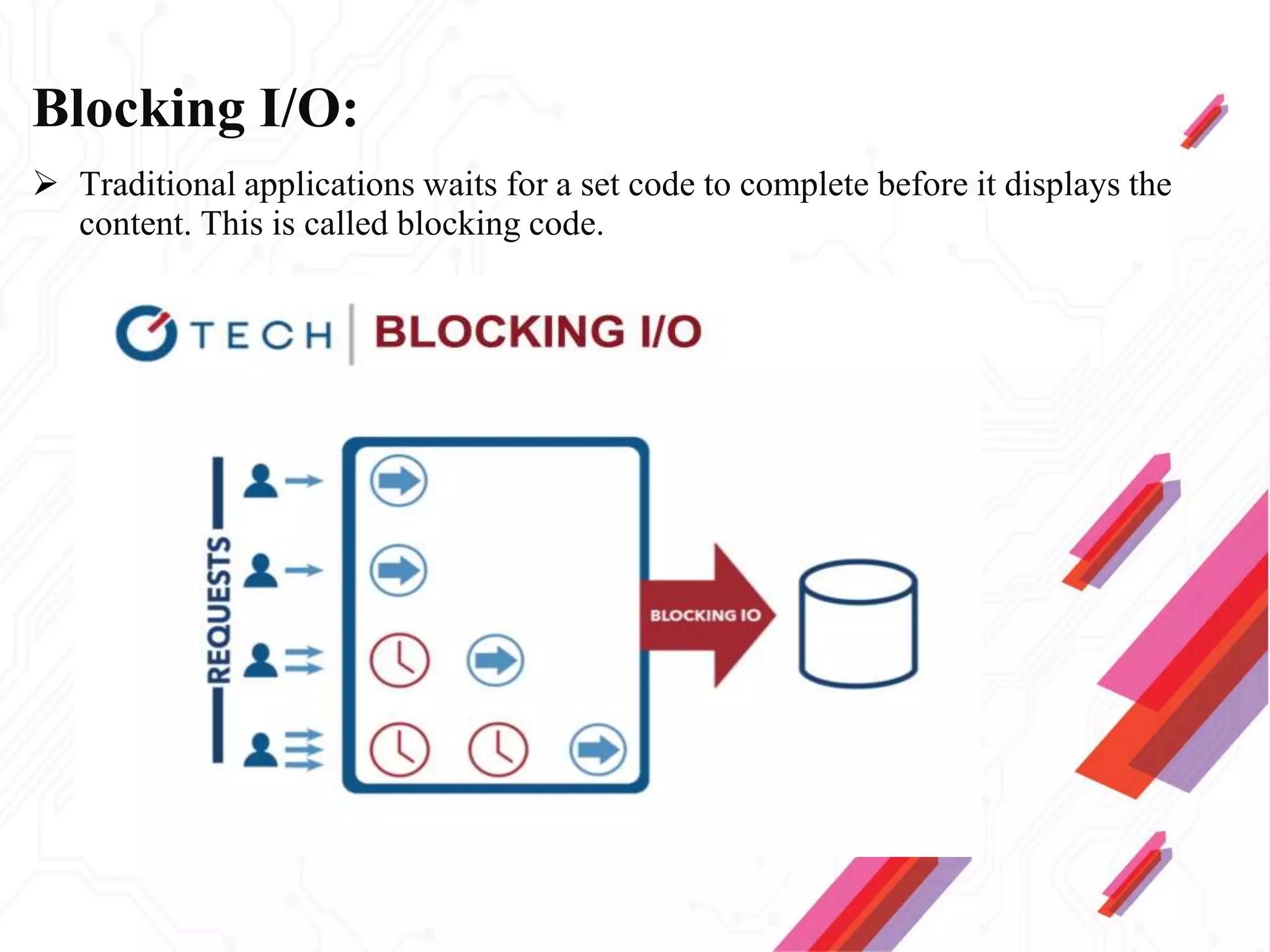
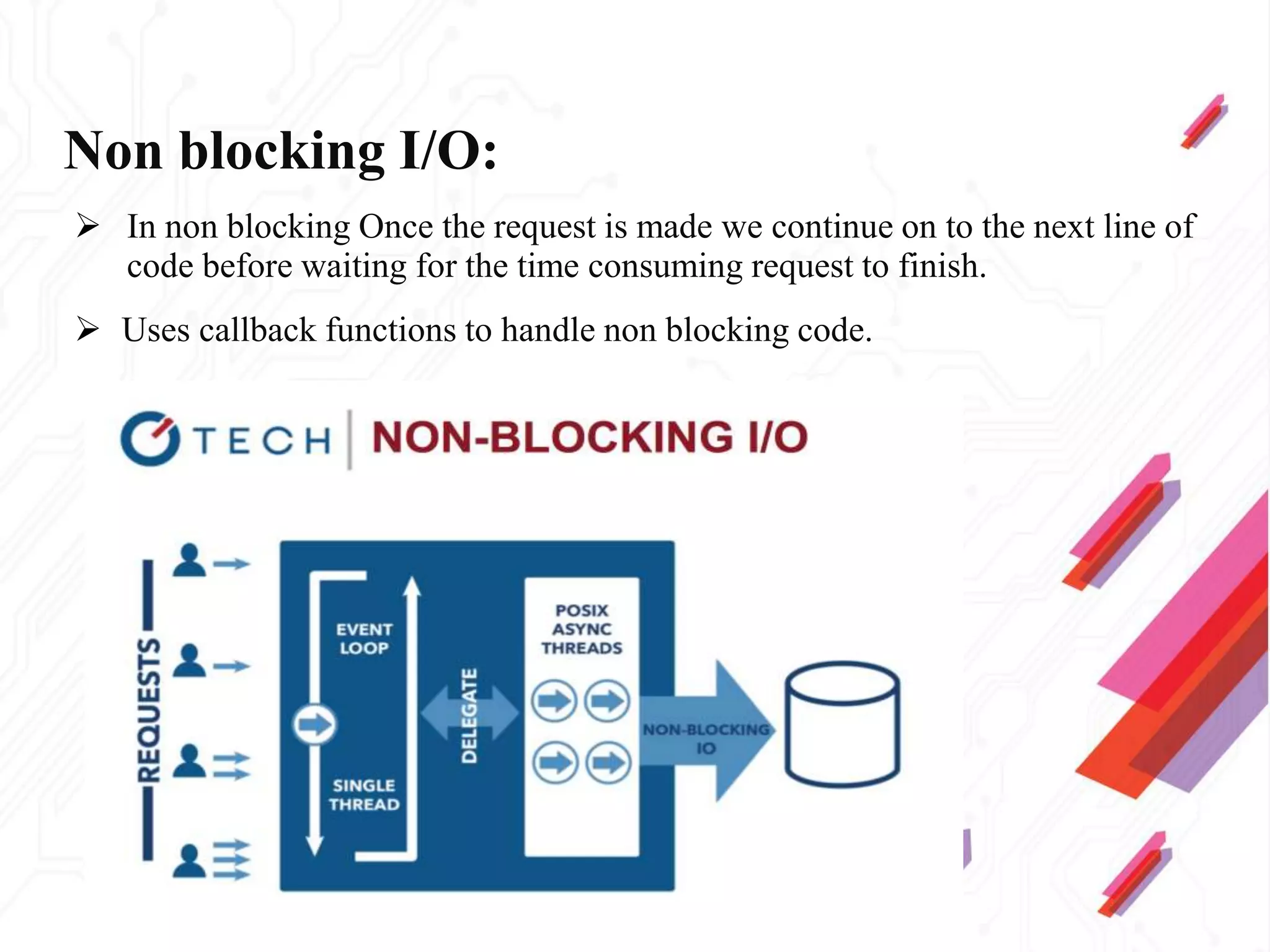
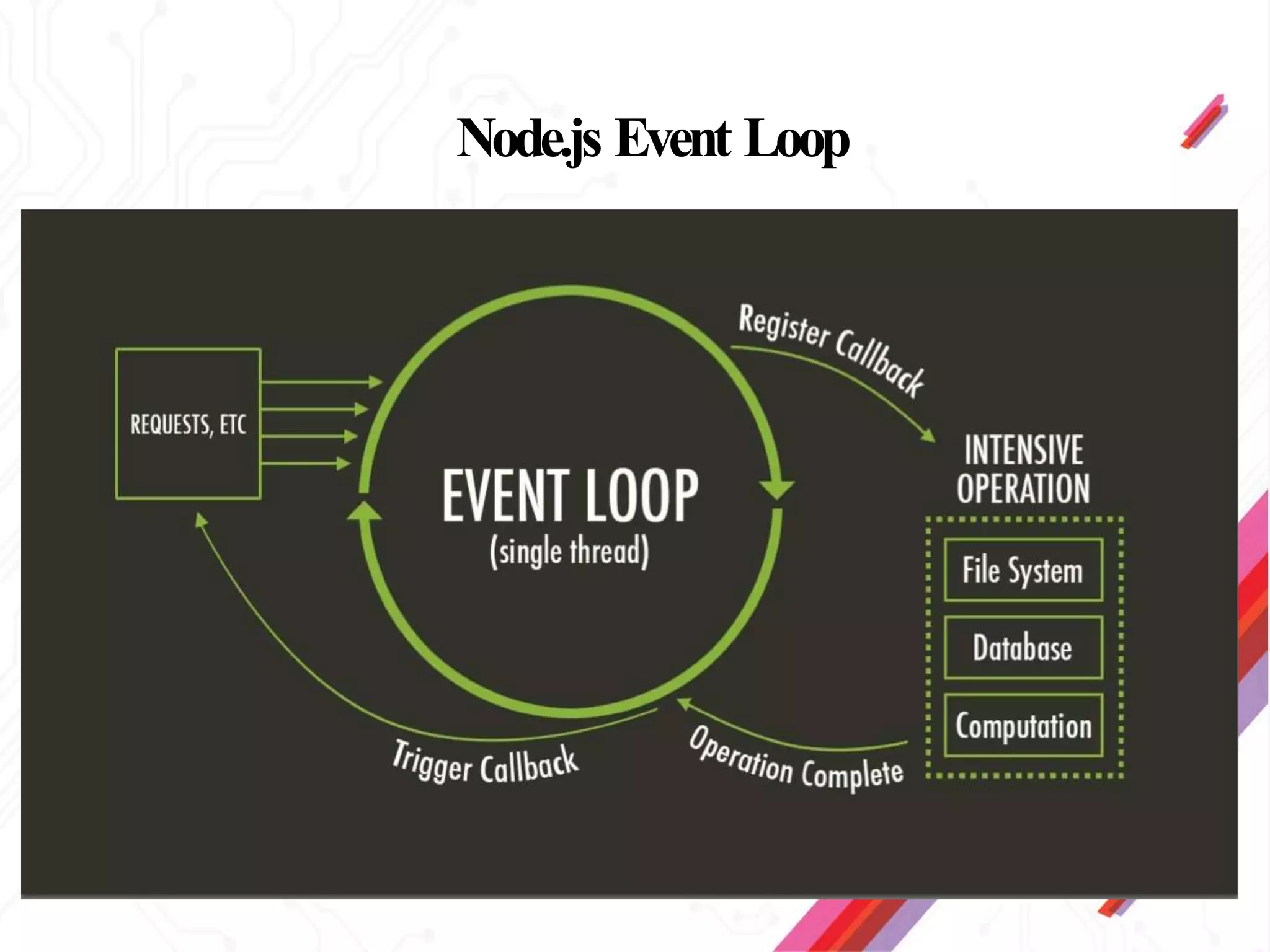
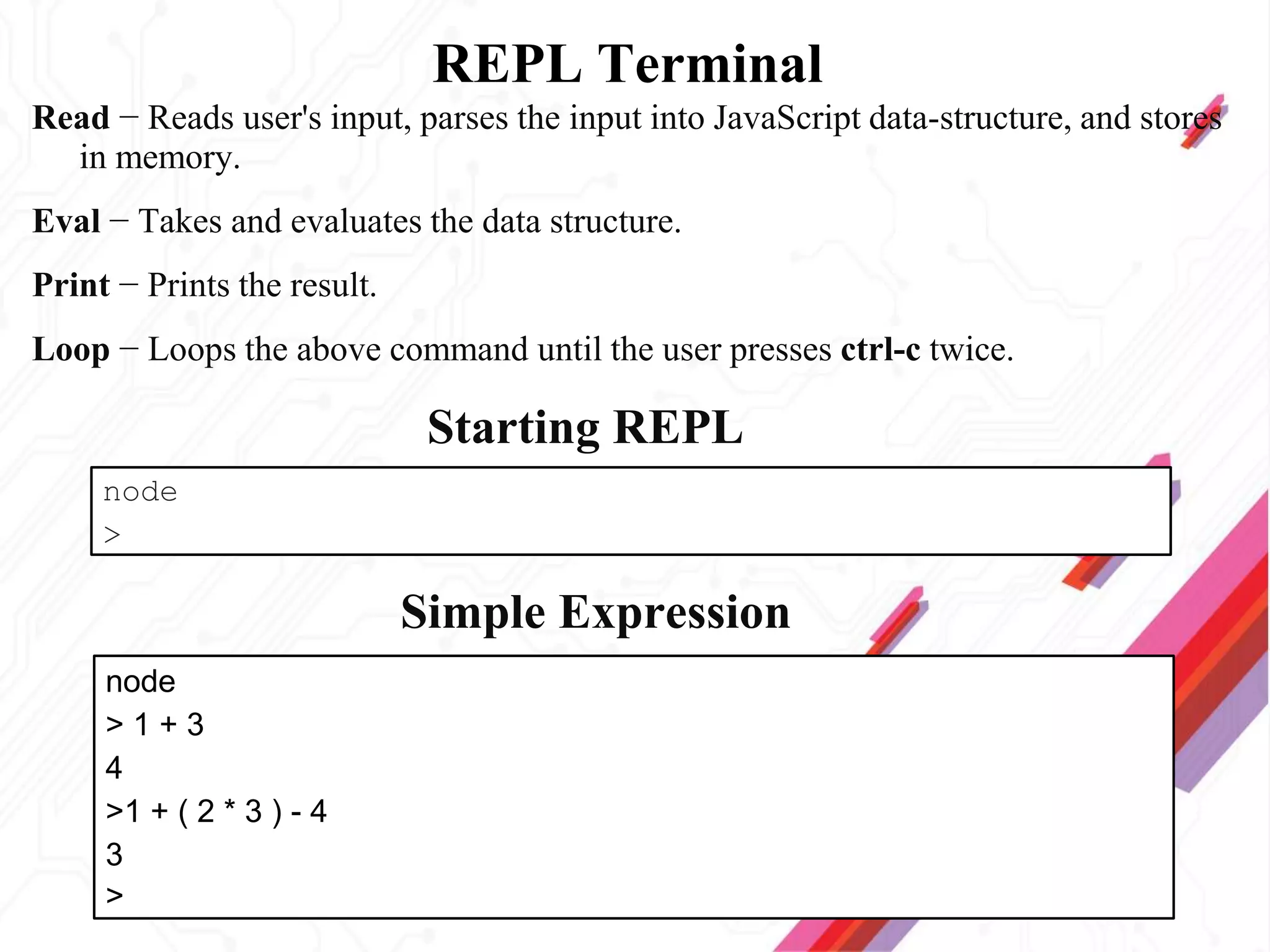
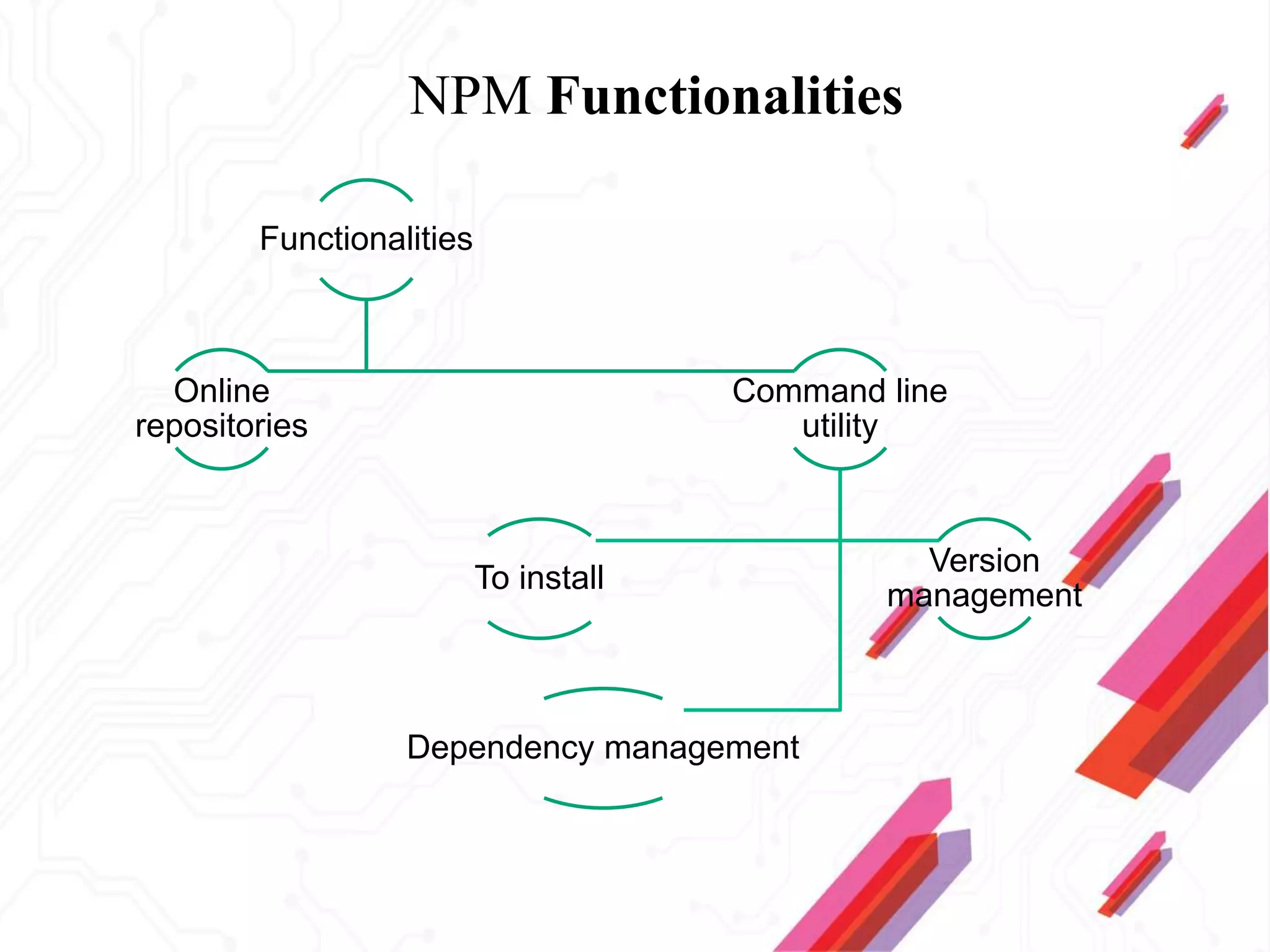
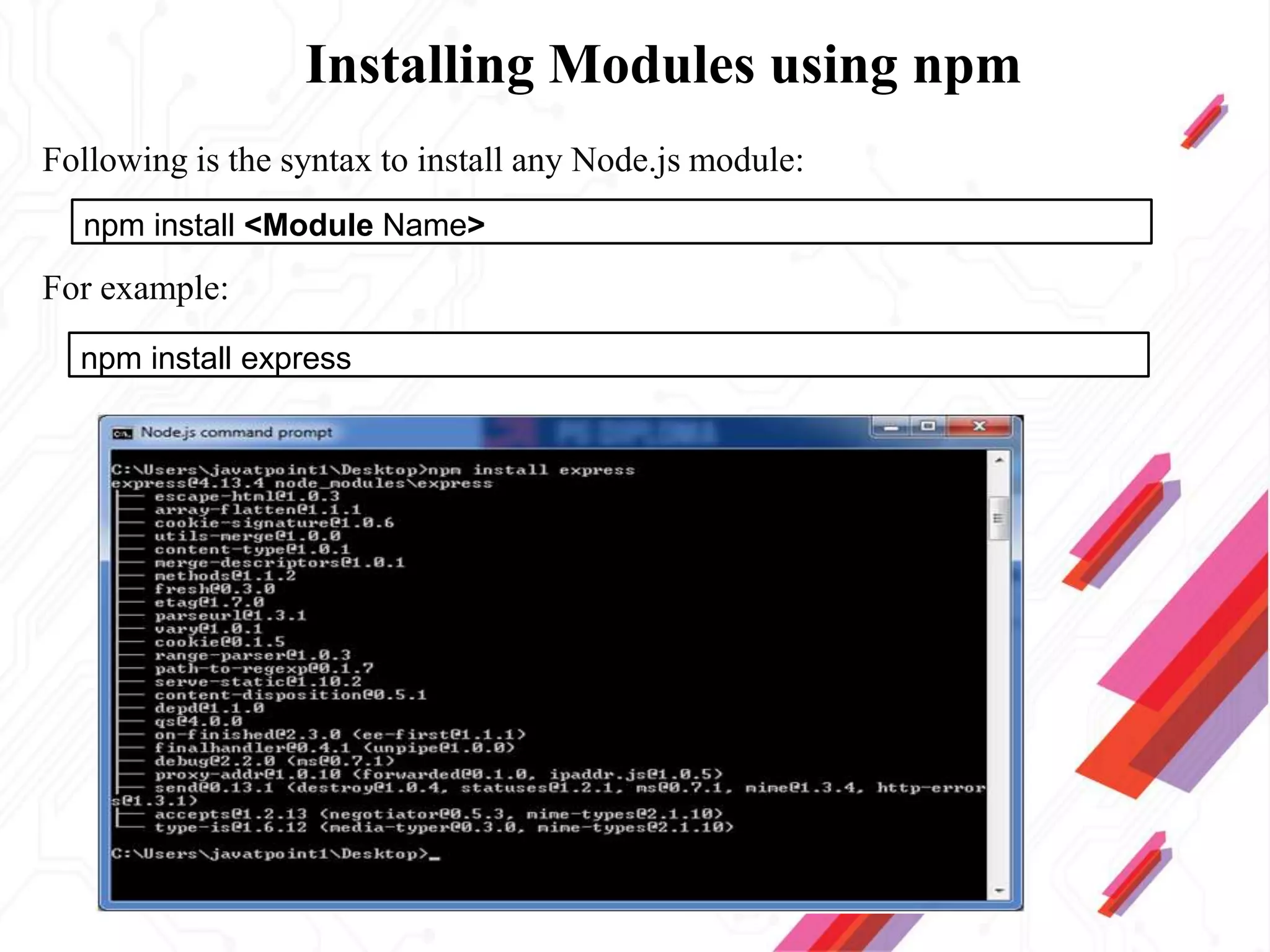
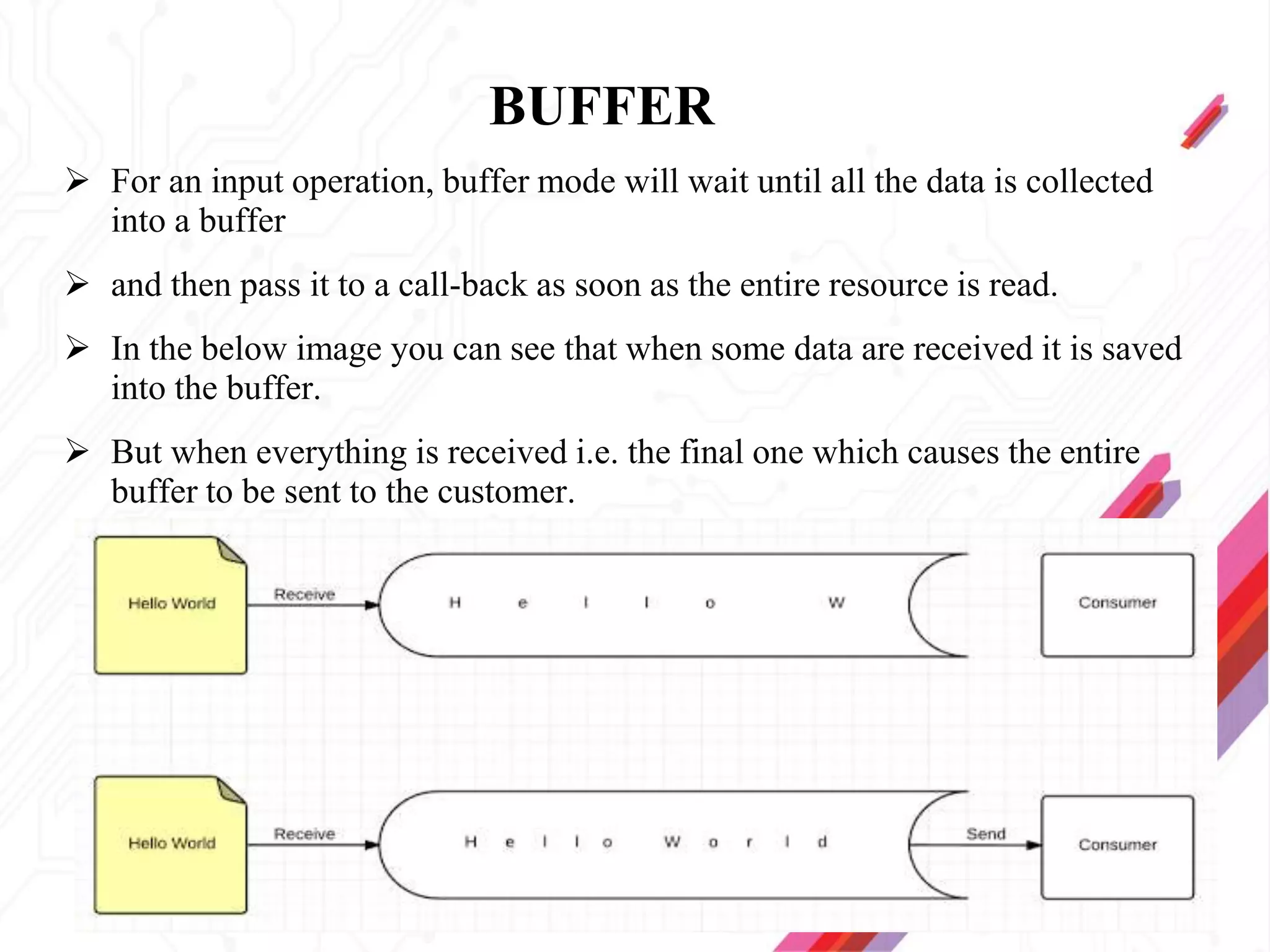
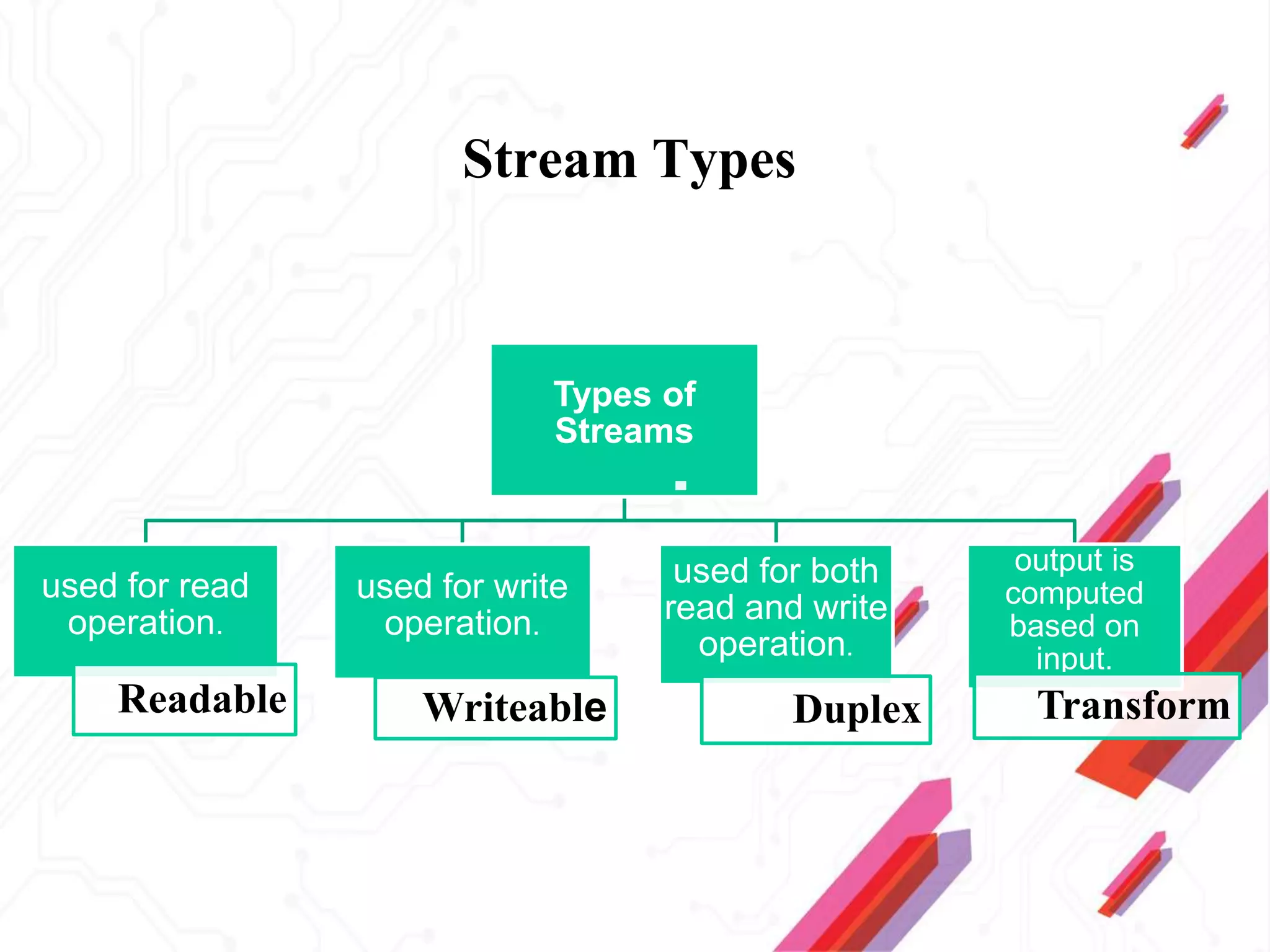
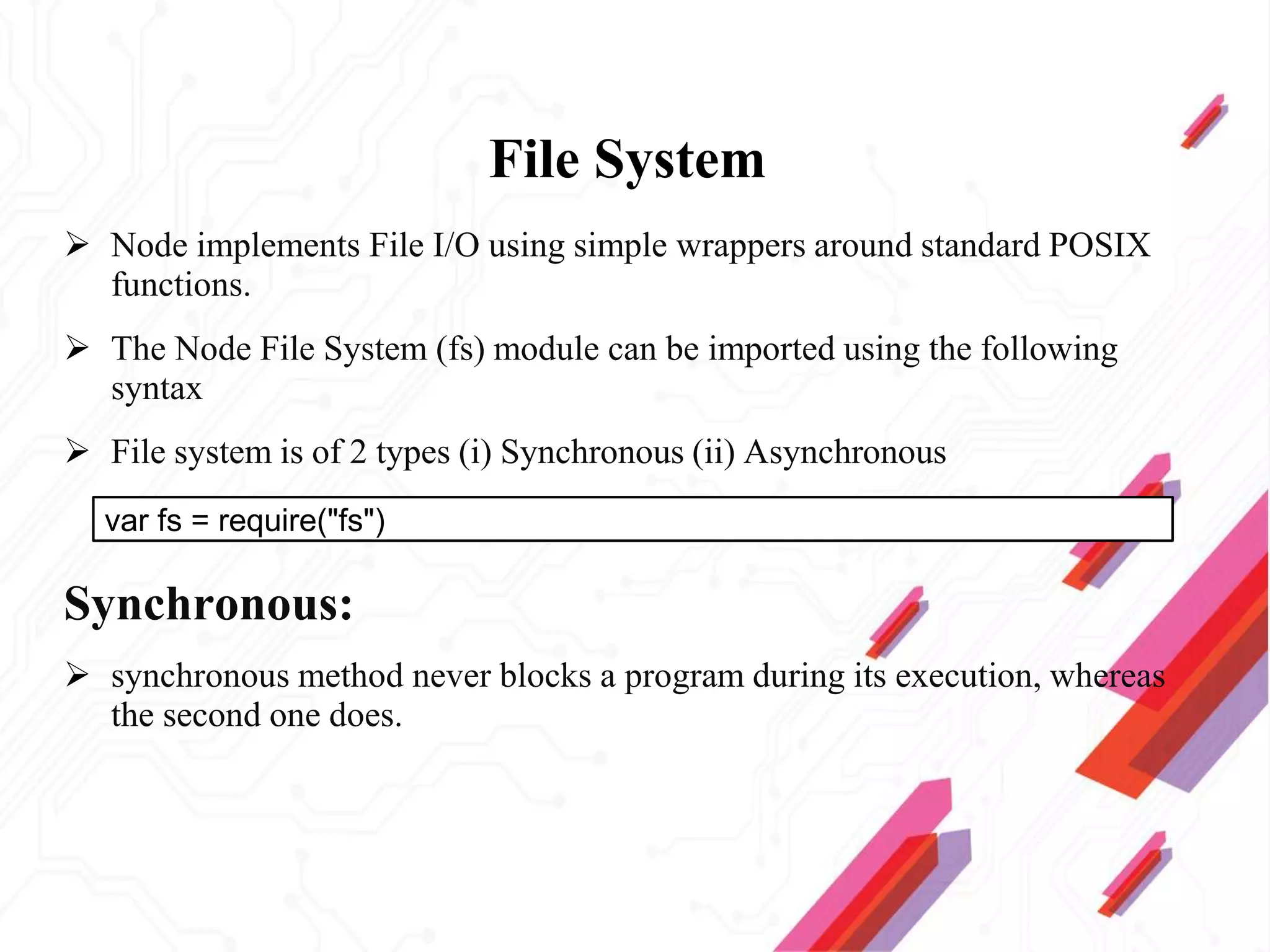
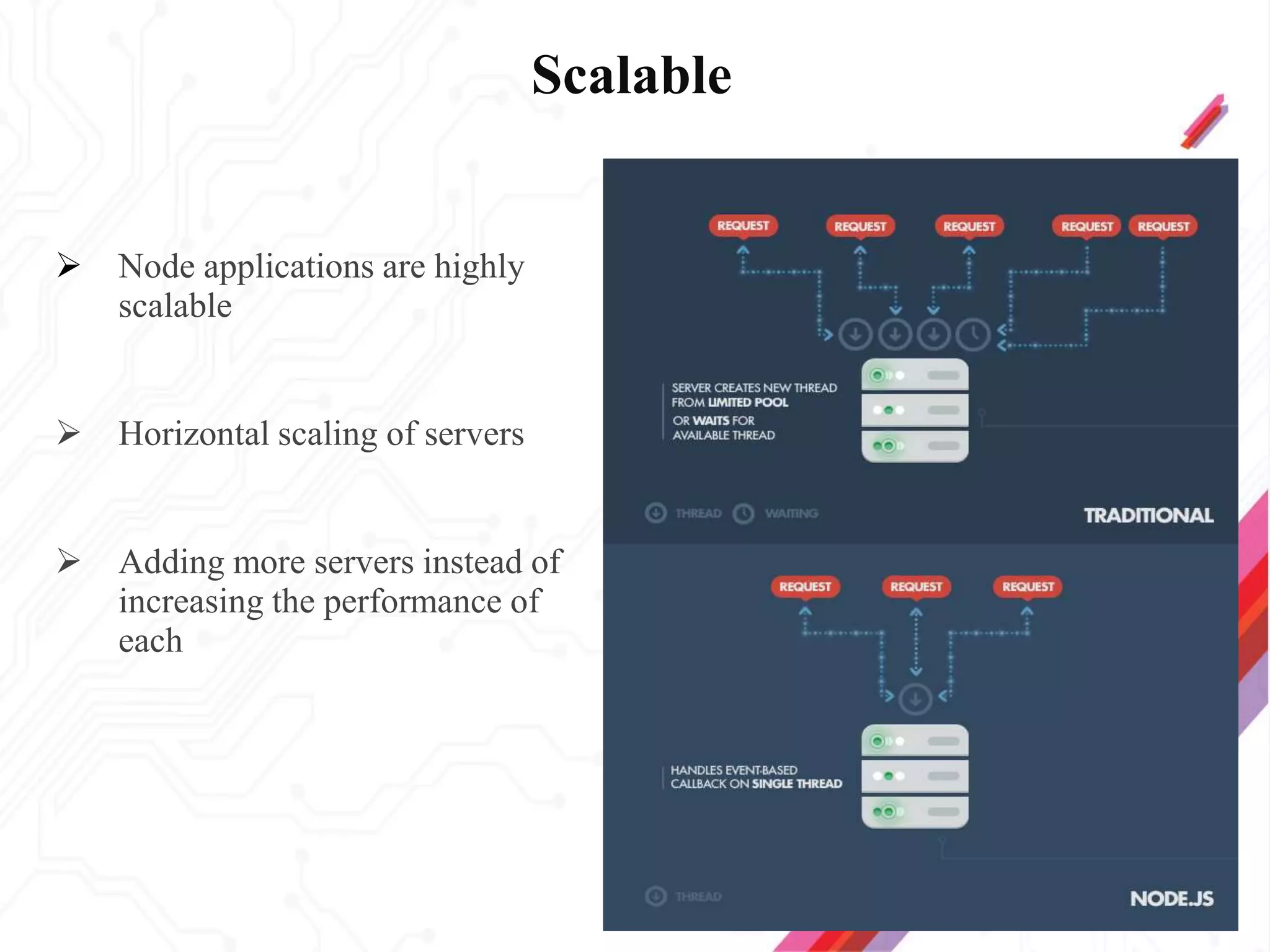
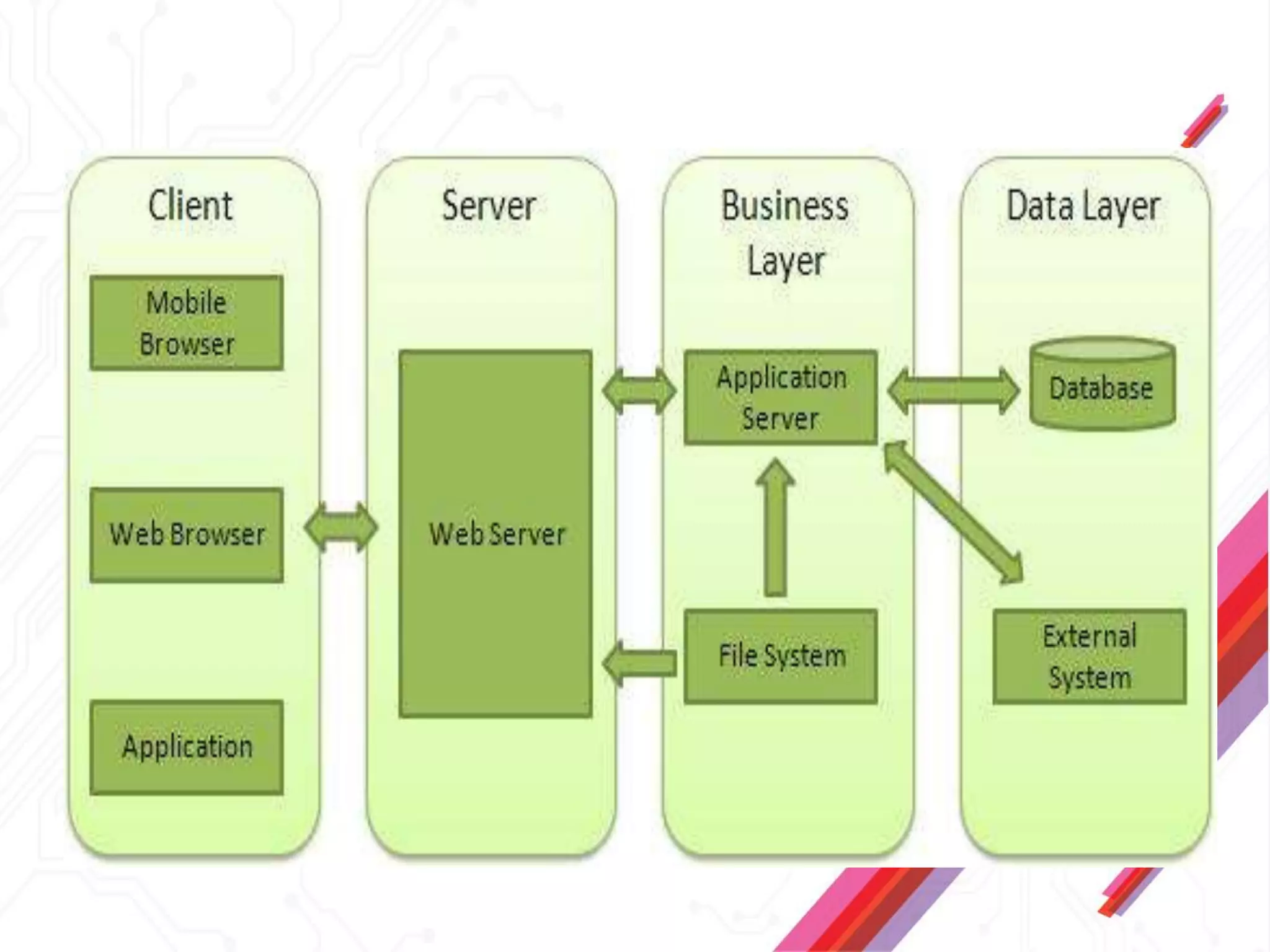
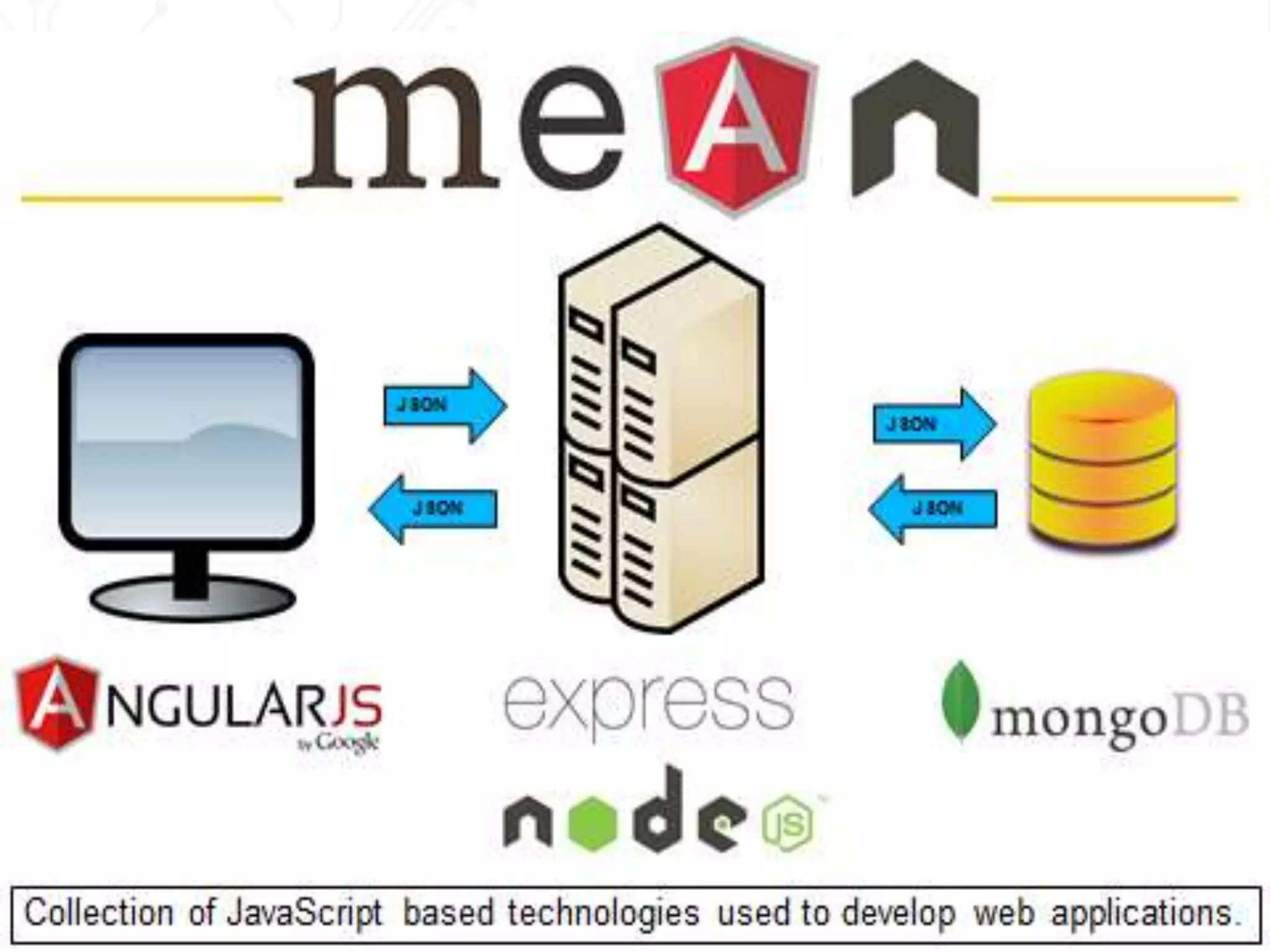
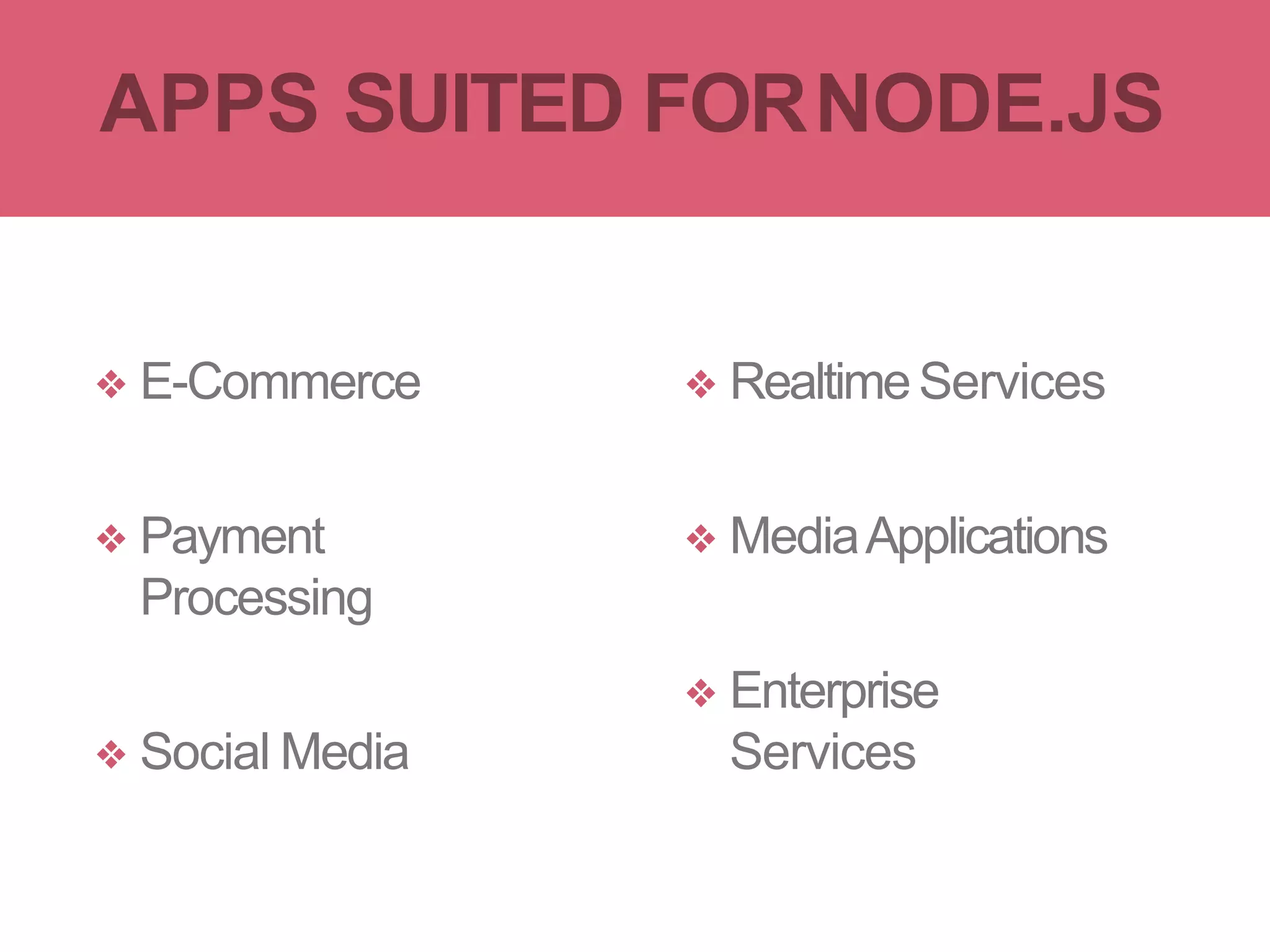
Node.js is an open-source JavaScript runtime environment that allows building scalable server-side and networking applications. It uses asynchronous, event-driven, non-blocking I/O which makes it lightweight and efficient for data-intensive real-time applications that run across distributed devices. Some key features of Node.js include excellent support for building RESTful web services, real-time web applications, IoT applications and scaling to many users. It uses Google's V8 JavaScript engine to execute code outside of a browser.