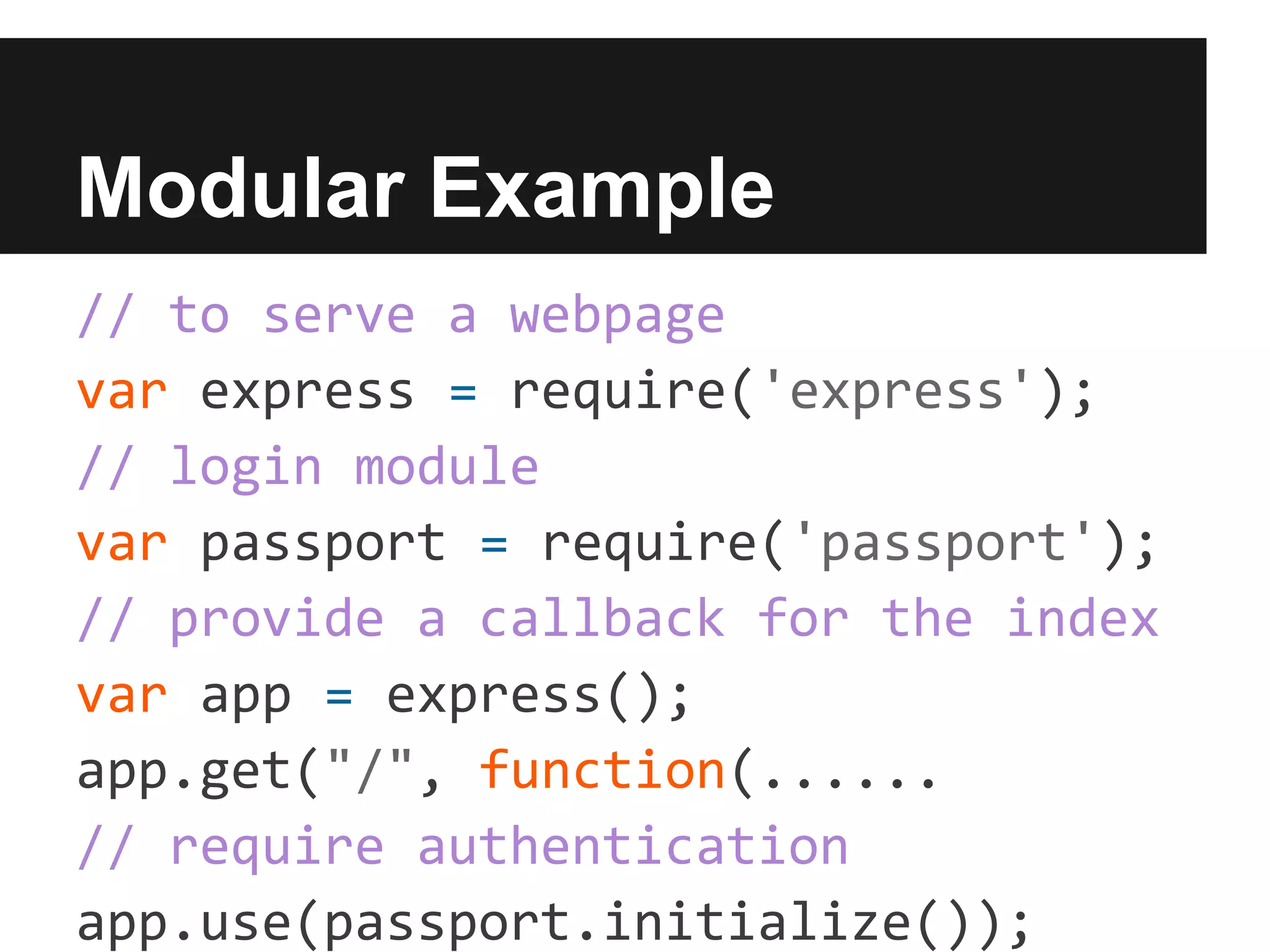
Node.js allows the use of JavaScript on the server side, enabling web server functionalities through the use of modules like Express for handling HTTP requests and Socket.io for real-time communication. It operates on a single-threaded model but can utilize clustering to handle multiple requests concurrently. There are numerous modules available for various purposes, which can be installed and managed using npm.