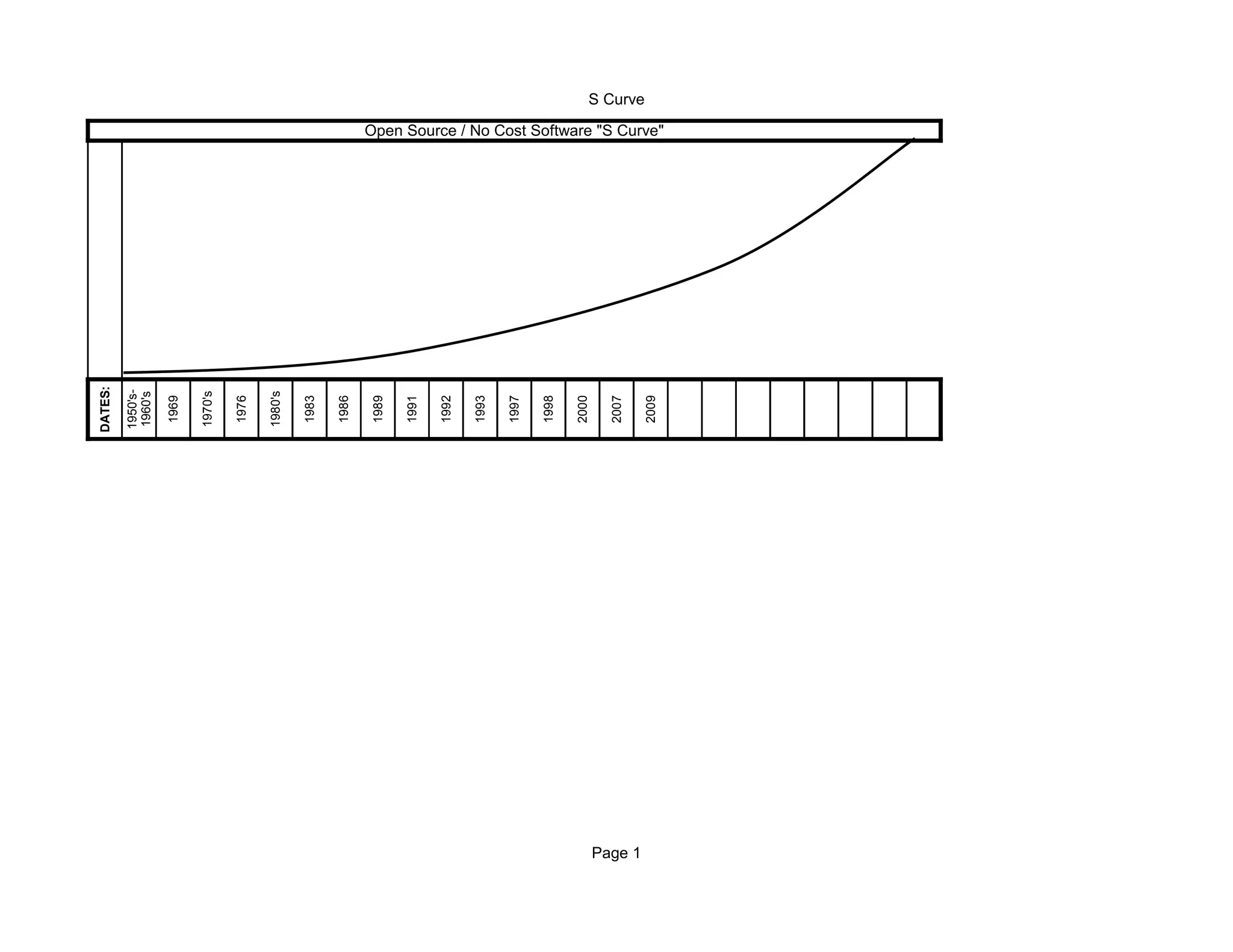
Open source software has seen widespread adoption in education. It allows for free collaboration and modification of software code. Over time, open source software has grown from isolated academic and research projects in the 1950s-60s to prominent free software projects like Linux and Firefox. Factors like cost savings, compatibility with older hardware, and educational benefits have contributed to its increasing use in education today.