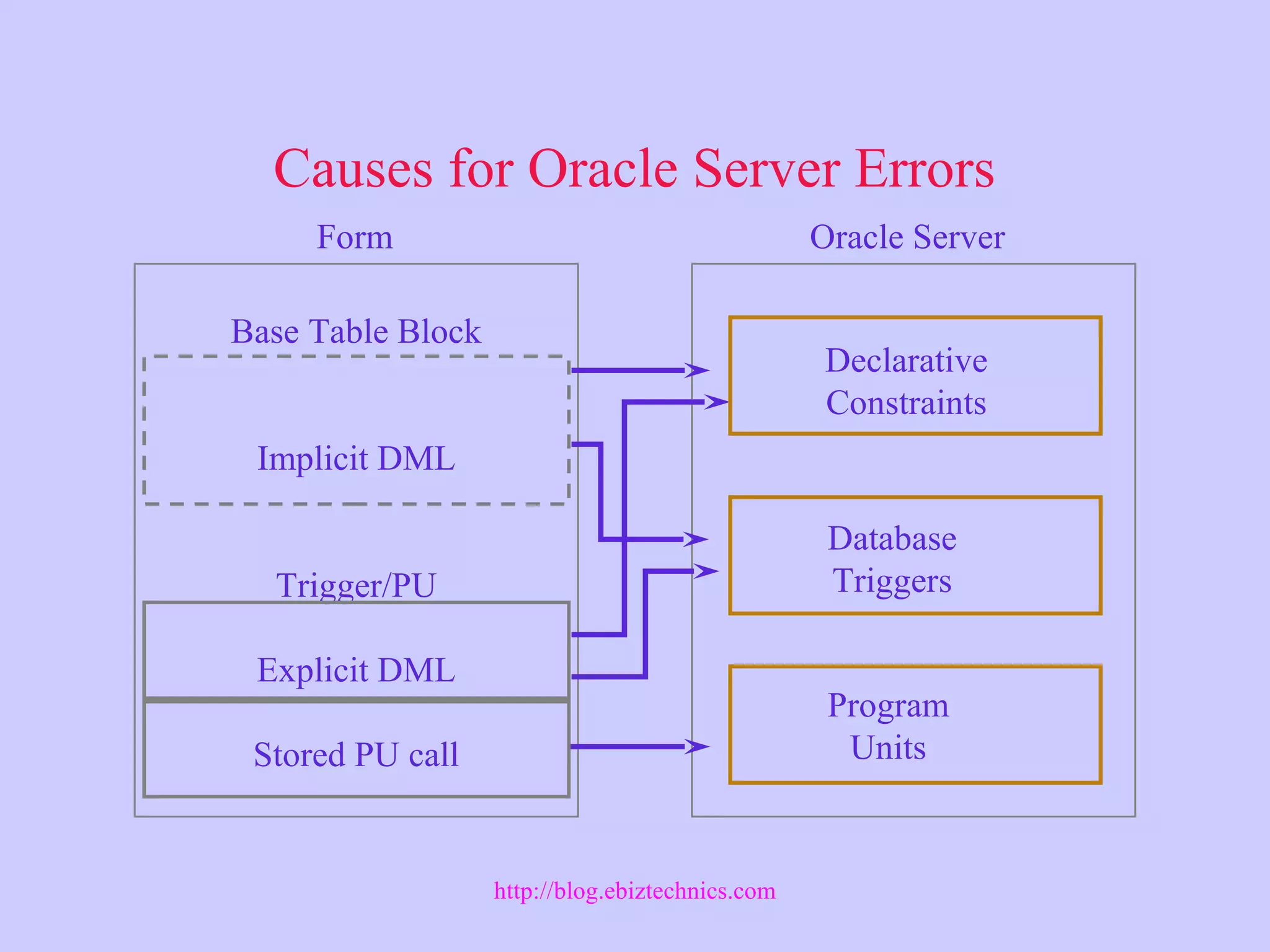
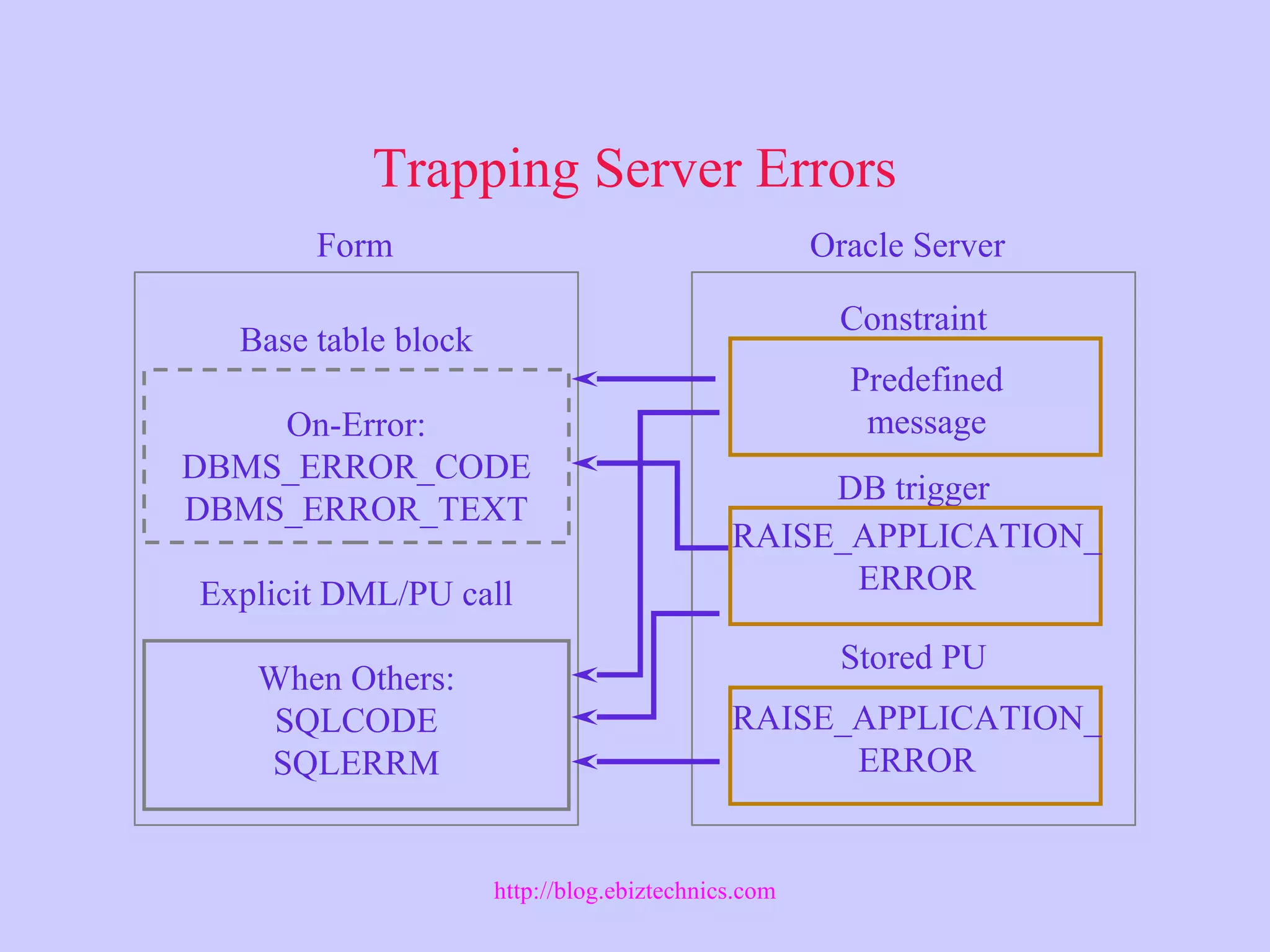
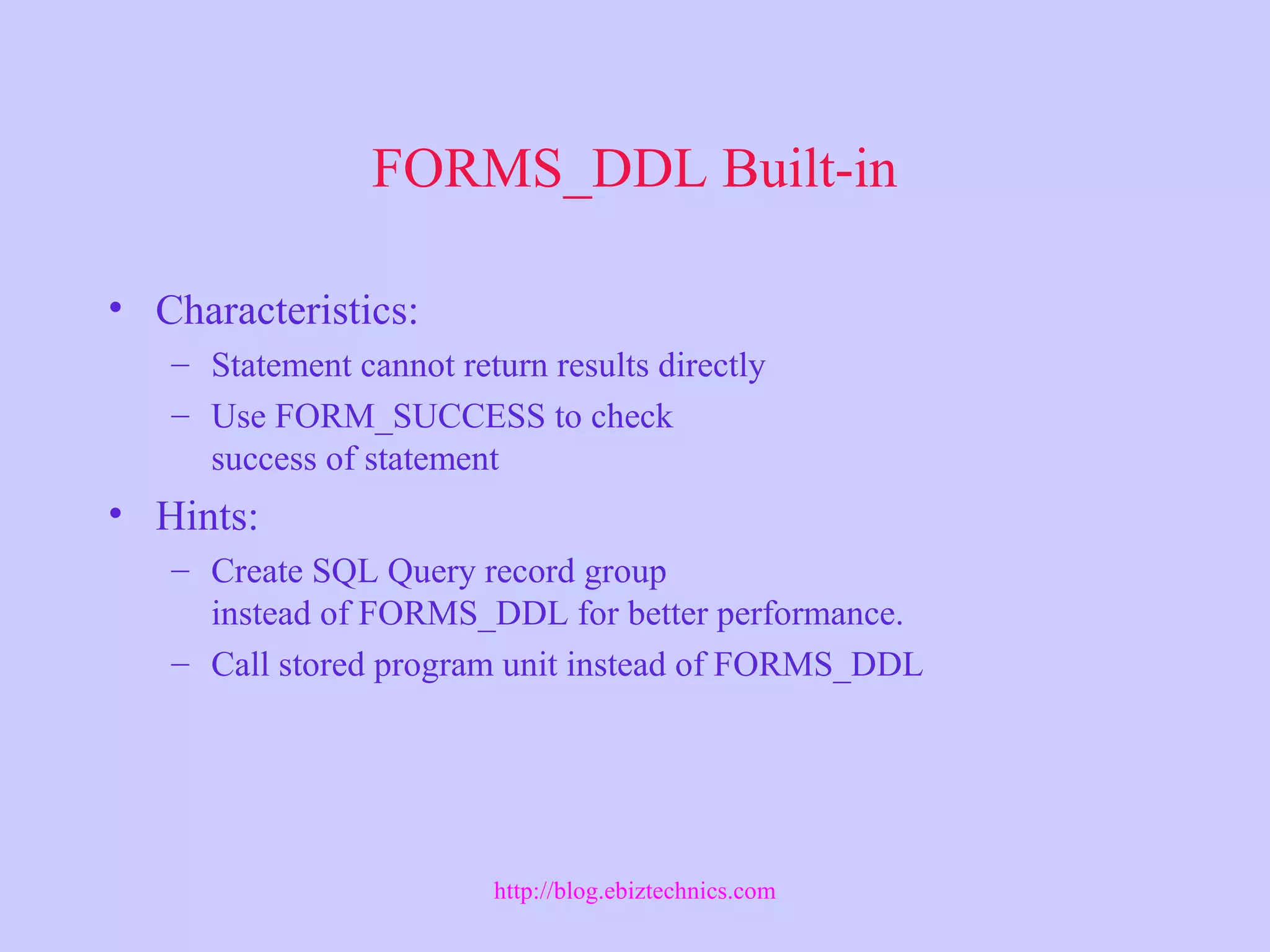
This document discusses using Oracle server features in Forms applications. It describes useful server features like constraints, triggers, and stored program units. It also covers handling PL/SQL code, trapping server errors, and performing DDL commands using the FORMS_DDL built-in subprograms. Supported PL/SQL8 features in Forms are also identified.