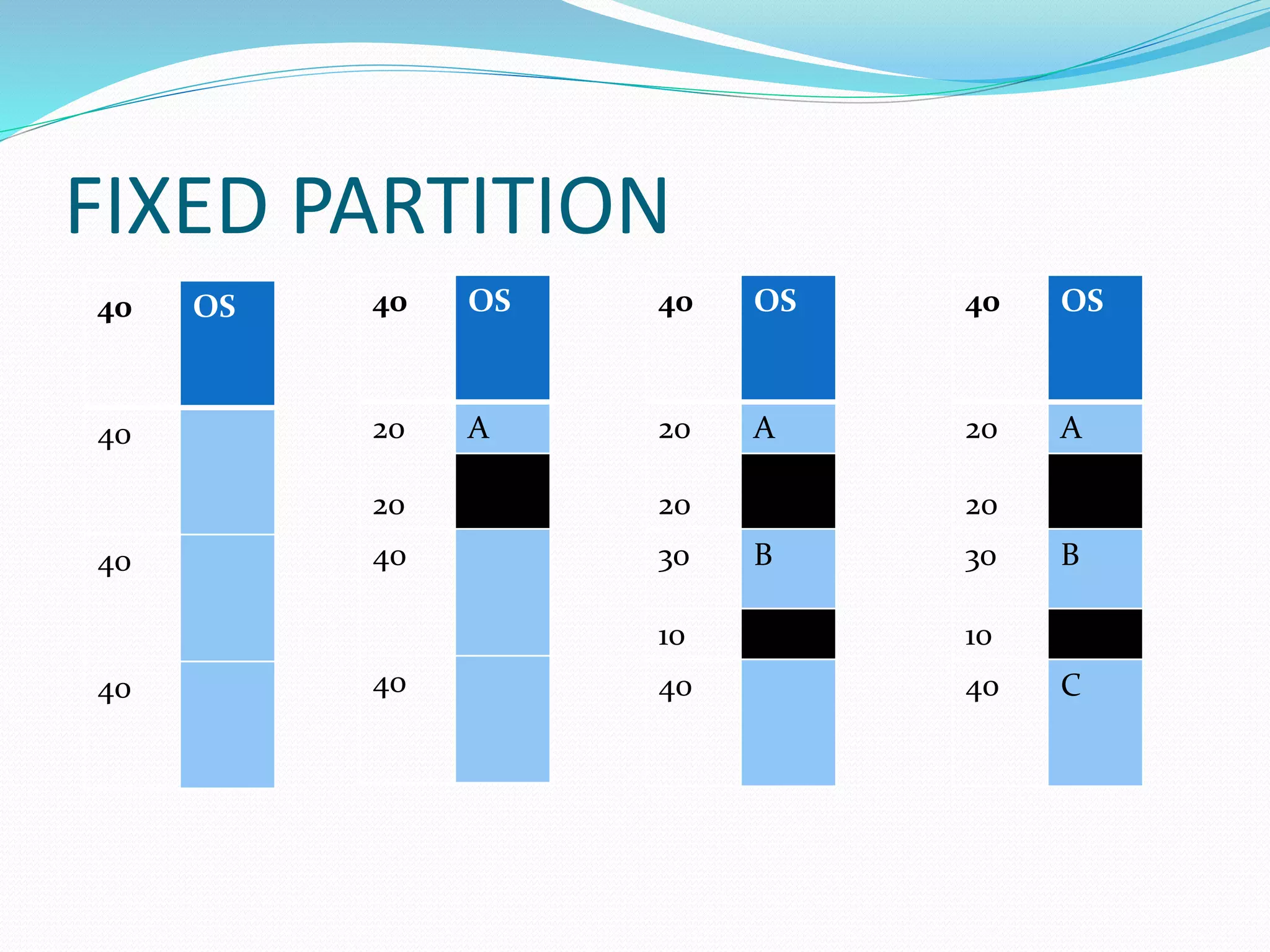
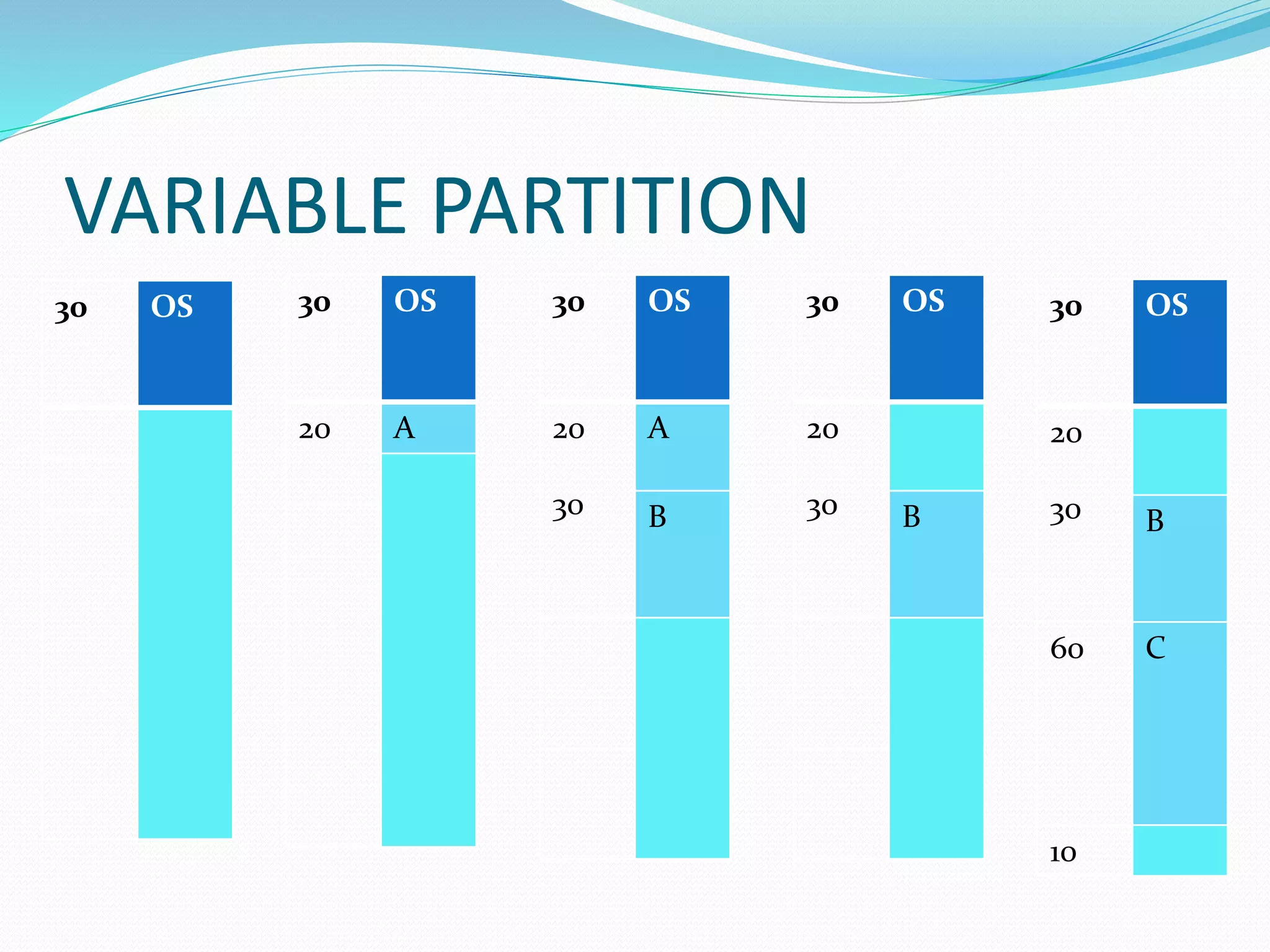
An operating system is system software that manages computer hardware resources and provides an interface between users and hardware. It performs key functions like process management, memory management, file management, device management, and security. Operating systems can be batch, multiprogramming, time-sharing, real-time, or network oriented depending on their design and purpose. Common examples include Windows, Linux, macOS, and UNIX variants.