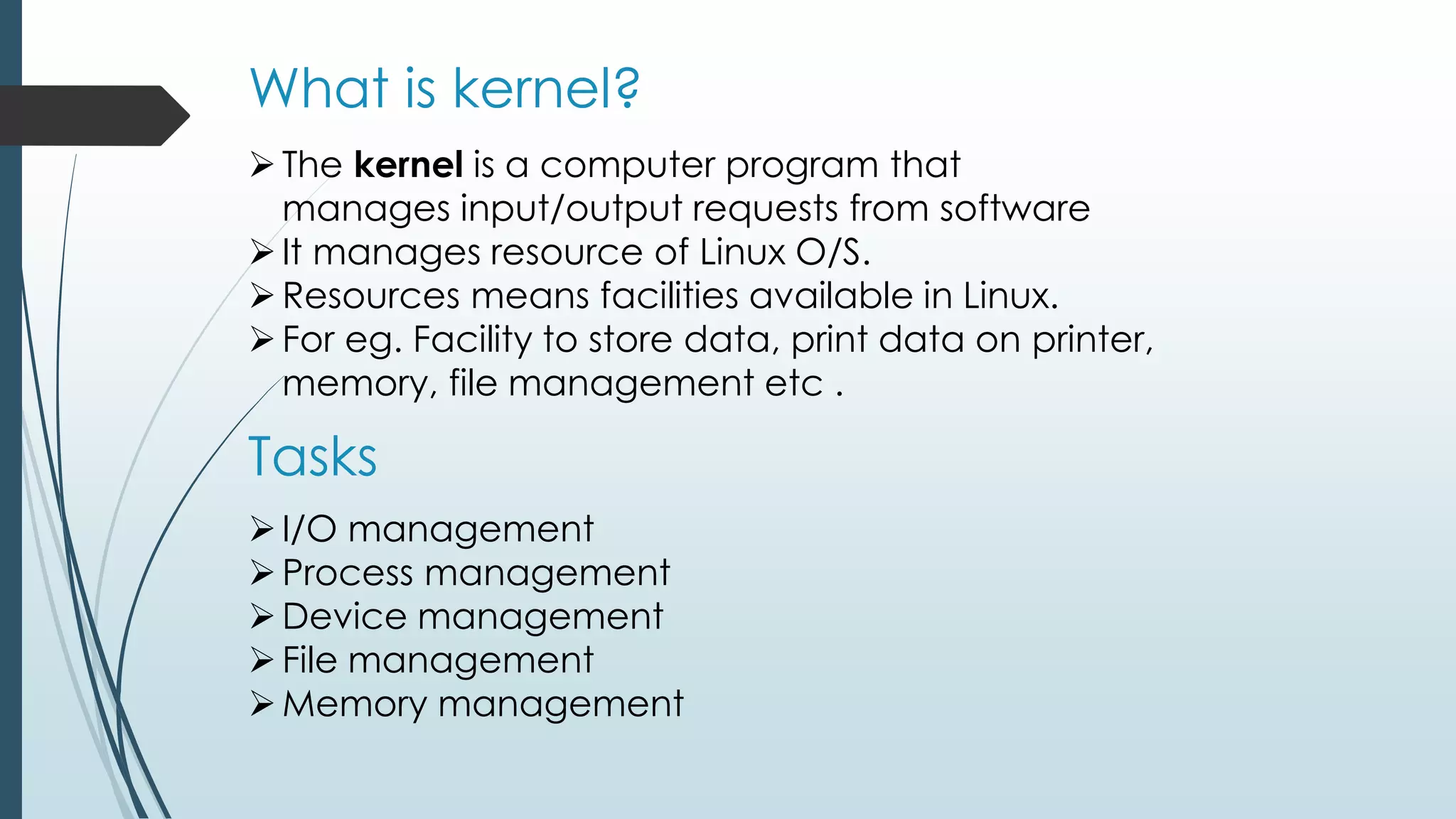
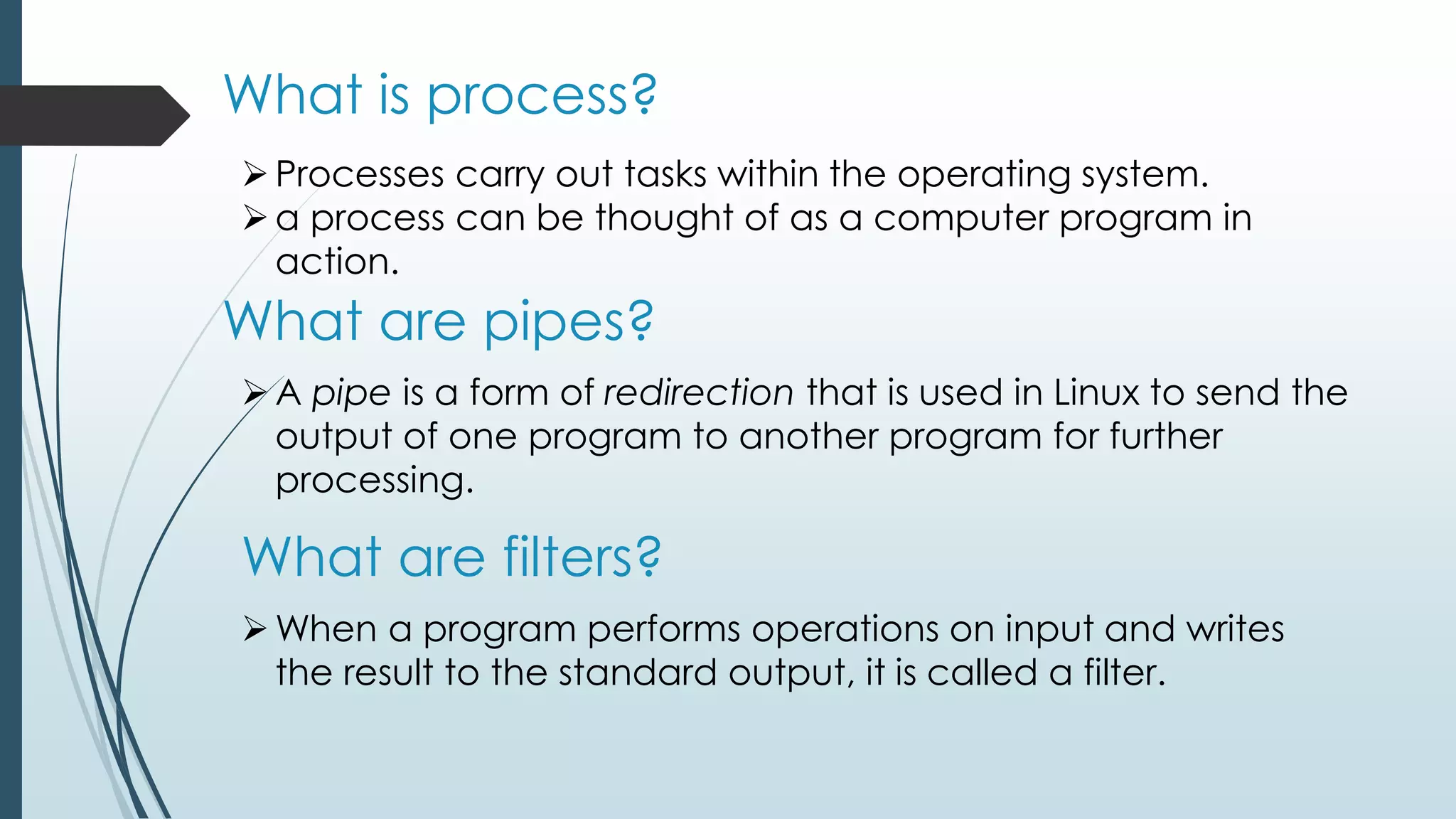
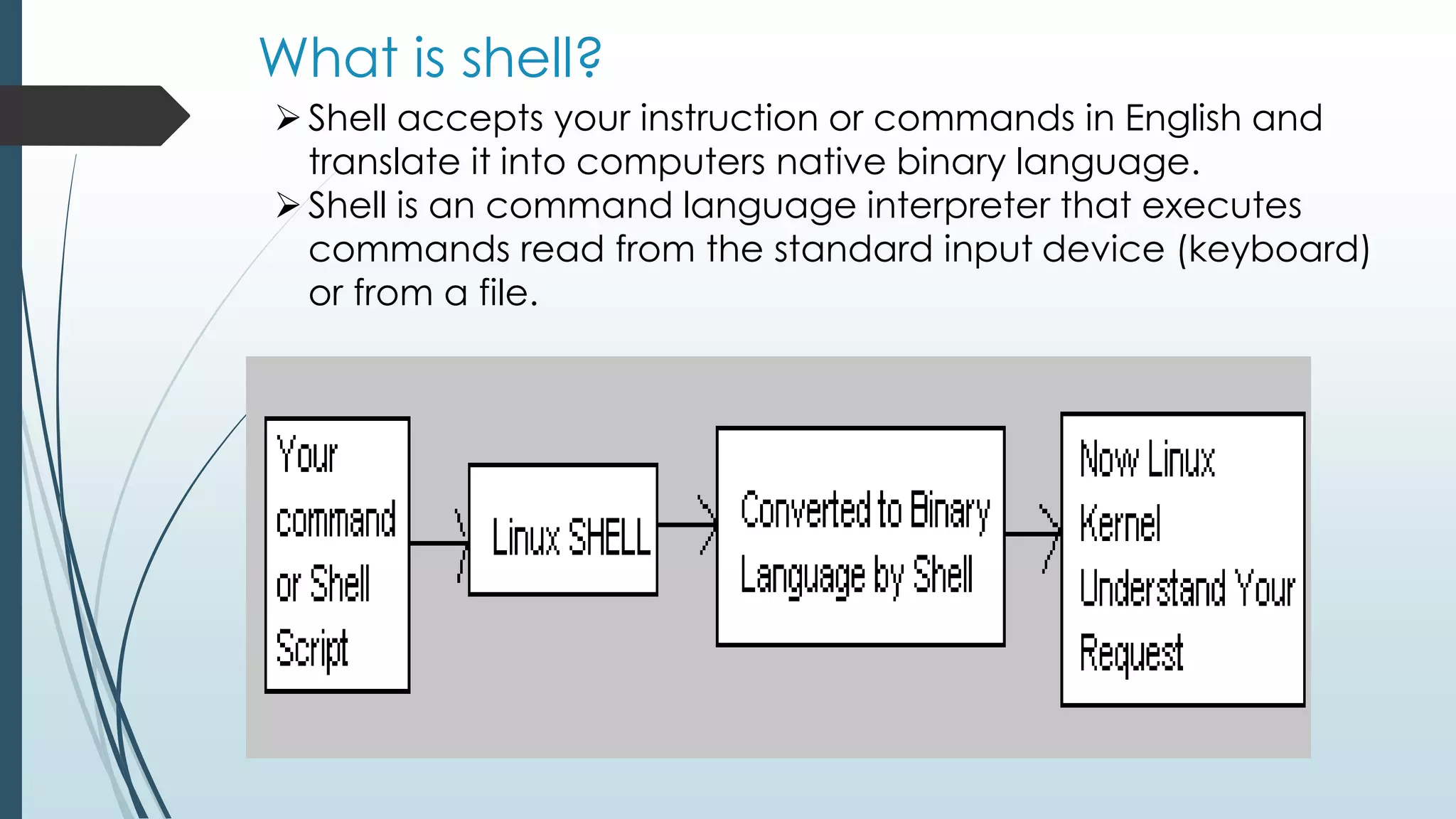
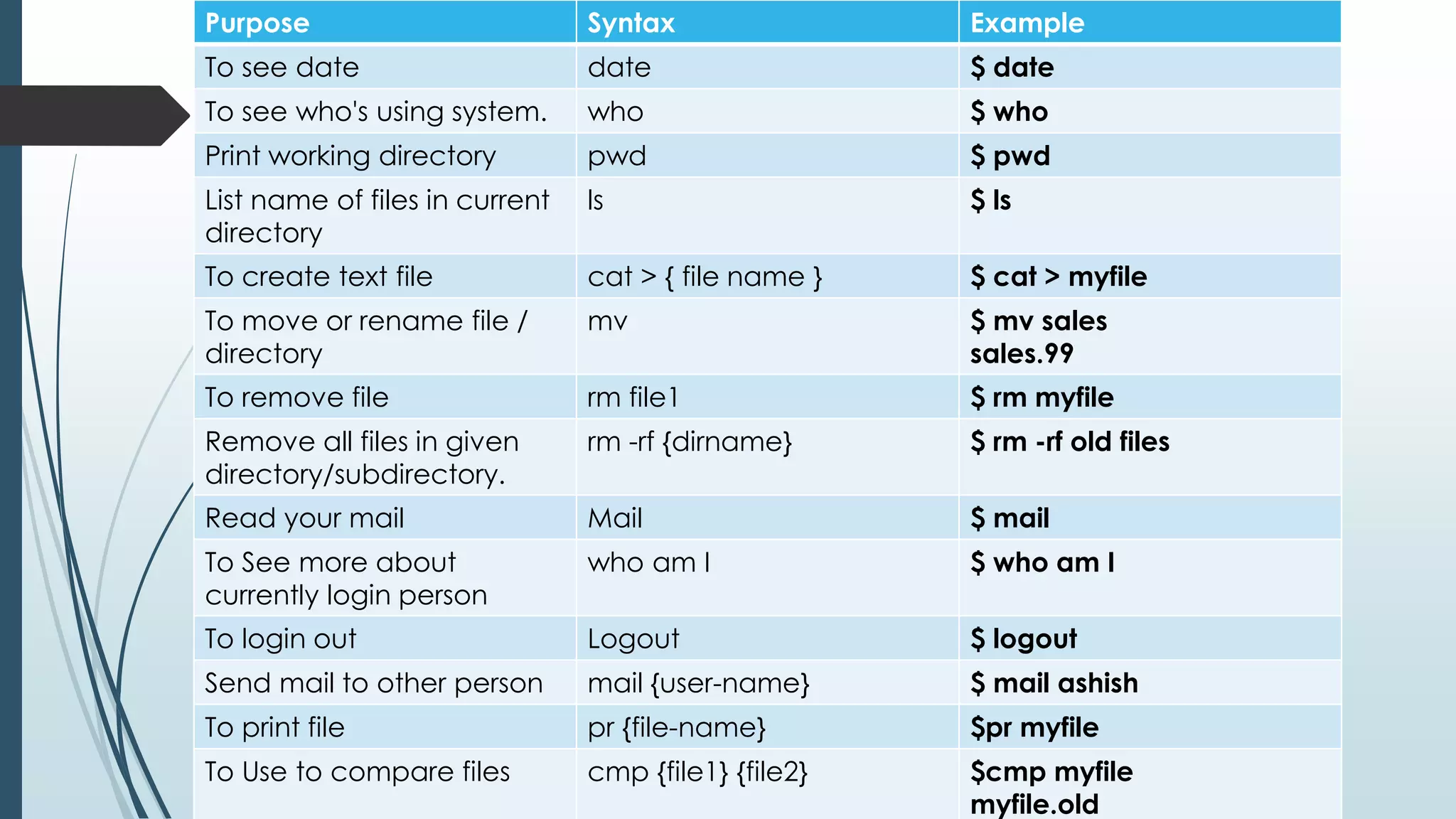
This document provides an introduction to shell programming in Linux. It defines key terms like the kernel, processes, pipes, and filters. It explains that the kernel manages resources and I/O, while processes carry out tasks. Pipes send output between programs and filters perform operations on input. Common shells like Bash, CSH, and KSH are outlined. Shells accept commands and translate them to binary for the OS. Basic Linux commands are listed along with examples. Variables, both system and user-defined, are explained as a way to store and process data in the shell. The document provides steps for writing, naming, running and debugging shell scripts using commands like echo, cat, chmod and expressions. Local and global variables









![Commands Related with Shell
Programming
1) echo [options] [string, variables...]
Displays text or variables value on screen.
The -e option is used to enable echo's interpretation
of additional instances of the newline character as
well as the interpretation of other special
characters, such as a horizontal tab, which is
represented by t
b backspace
n new line
t horizontal tab
backslash
For eg. $ echo -e "An apple a day keeps away tt
doctorn"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jinal-linux-140417094731-phpapp02/75/SHELL-PROGRAMMING-15-2048.jpg)




