The static keyword in Java is used for memory management and can be applied to variables, methods, blocks, and nested classes. Static variables and methods belong to the class rather than objects. A static variable is loaded when the class is loaded and there is only one copy per class, while instance variables are loaded each time an object is created. The main method must be static since it is called before any objects are created to start the program execution. Static blocks are used to initialize static variables and are executed when the class is loaded.





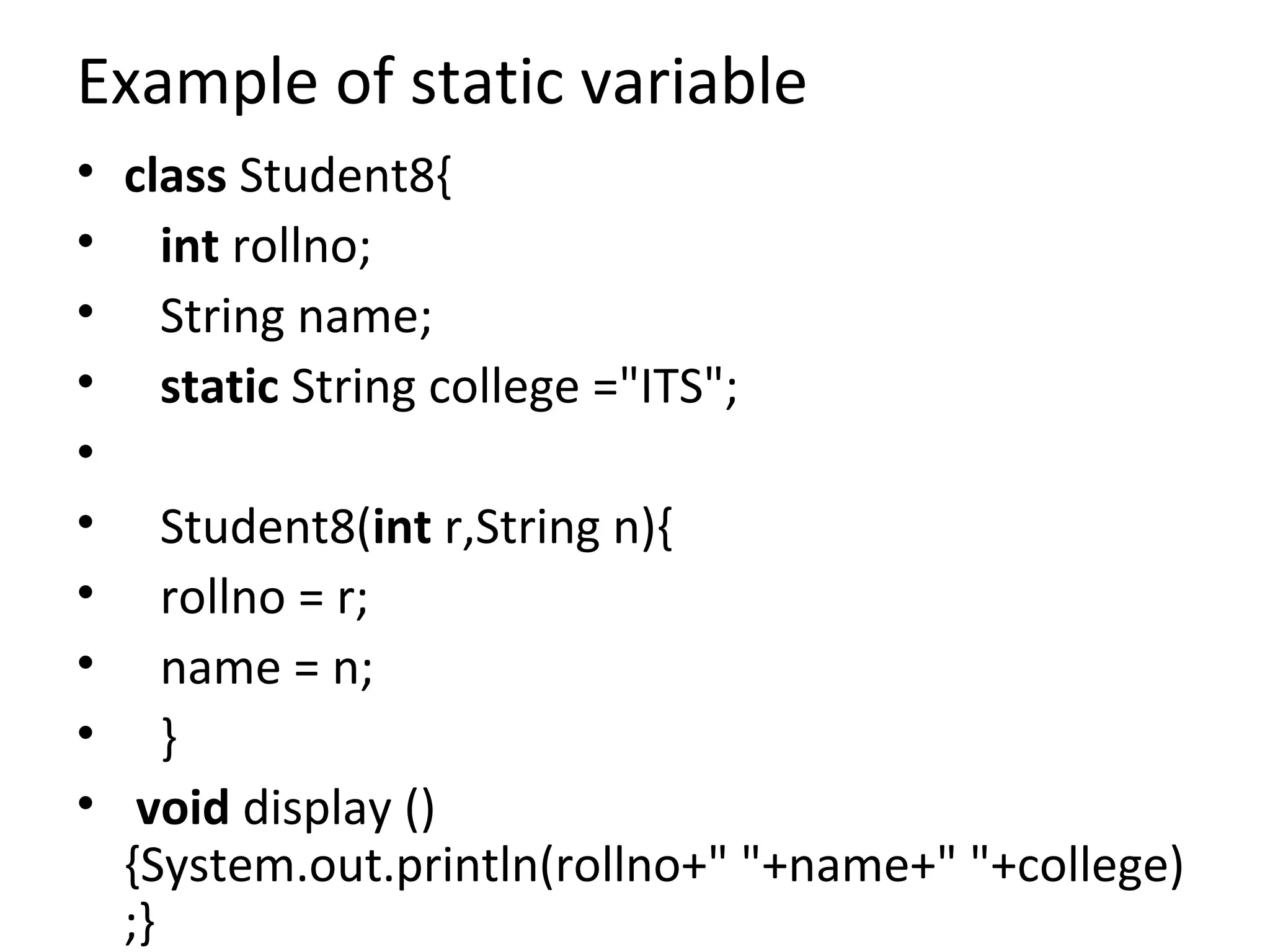
![• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• Student8 s1 = new Student8(111,"Karan");
• Student8 s2 = new Student8(222,"Aryan");
• s1.display();
• s2.display();
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-7-2048.jpg)

![• public static void main(String args[])
• {
•
• Counter c1=new Counter();
• Counter c2=new Counter();
• Counter c3=new Counter();
•
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-9-2048.jpg)

![• public static void main(String args[])
• {
•
• Counter2 c1=new Counter2();
• Counter2 c2=new Counter2();
• Counter2 c3=new Counter2();
•
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-11-2048.jpg)


![• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• int result=Calculate.cube(5);
• System.out.println(result);
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-14-2048.jpg)

![• class A
• {
• int a=40;//non static
•
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• System.out.println(a);
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-16-2048.jpg)


![• class A2
• {
• static
• {
• System.out.println("static block is invoked");
• }
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• System.out.println("Hello main");
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-19-2048.jpg)






![• class TestThis2
• {
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• Student s1=new Student(111,"ankit",5000f);
• Student s2=new Student(112,"sumit",6000f);
• s1.display();
• s2.display();
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-27-2048.jpg)
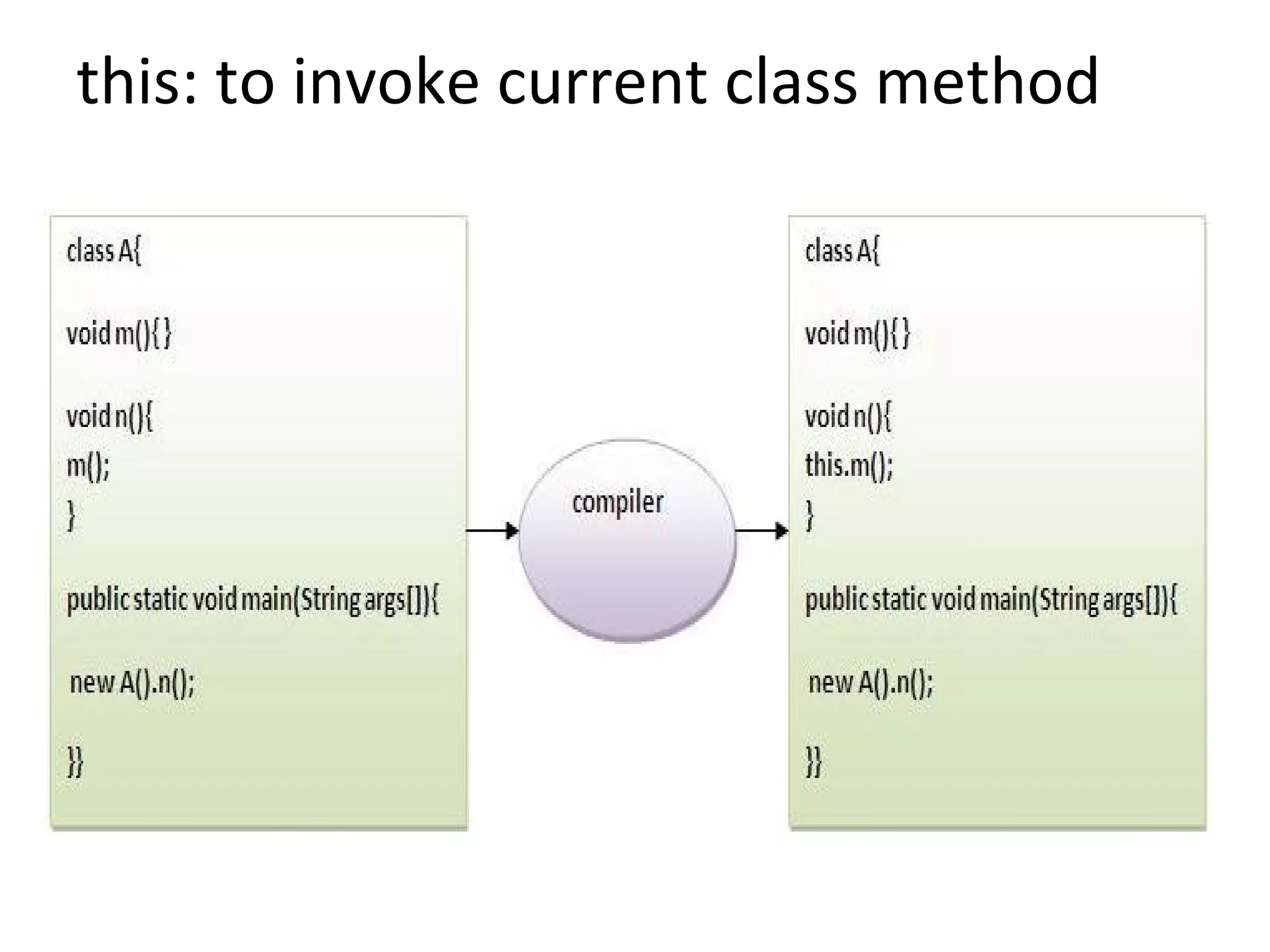

![• class TestThis4
• {
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• A a=new A();
• a.n();
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-30-2048.jpg)

![Calling default constructor from parameterized
constructor:
• class A{
• A(){System.out.println("hello a");}
• A(int x){
• this();
• System.out.println(x);
• }
• }
• class TestThis5{
• public static void main(String args[]){
• A a=new A(10);
• }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-32-2048.jpg)
![Calling parameterized constructor from default
constructor:
• class A{
• A(){
• this(5);
• System.out.println("hello a");
• }
• A(int x){
• System.out.println(x);
• }
• }
• class TestThis6{
• public static void main(String args[]){
• A a=new A();
• }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastatickeyword-170323175339/75/Java-static-keyword-33-2048.jpg)