The document summarizes key concepts from the Udacity CS259 Software Debugging course, including:
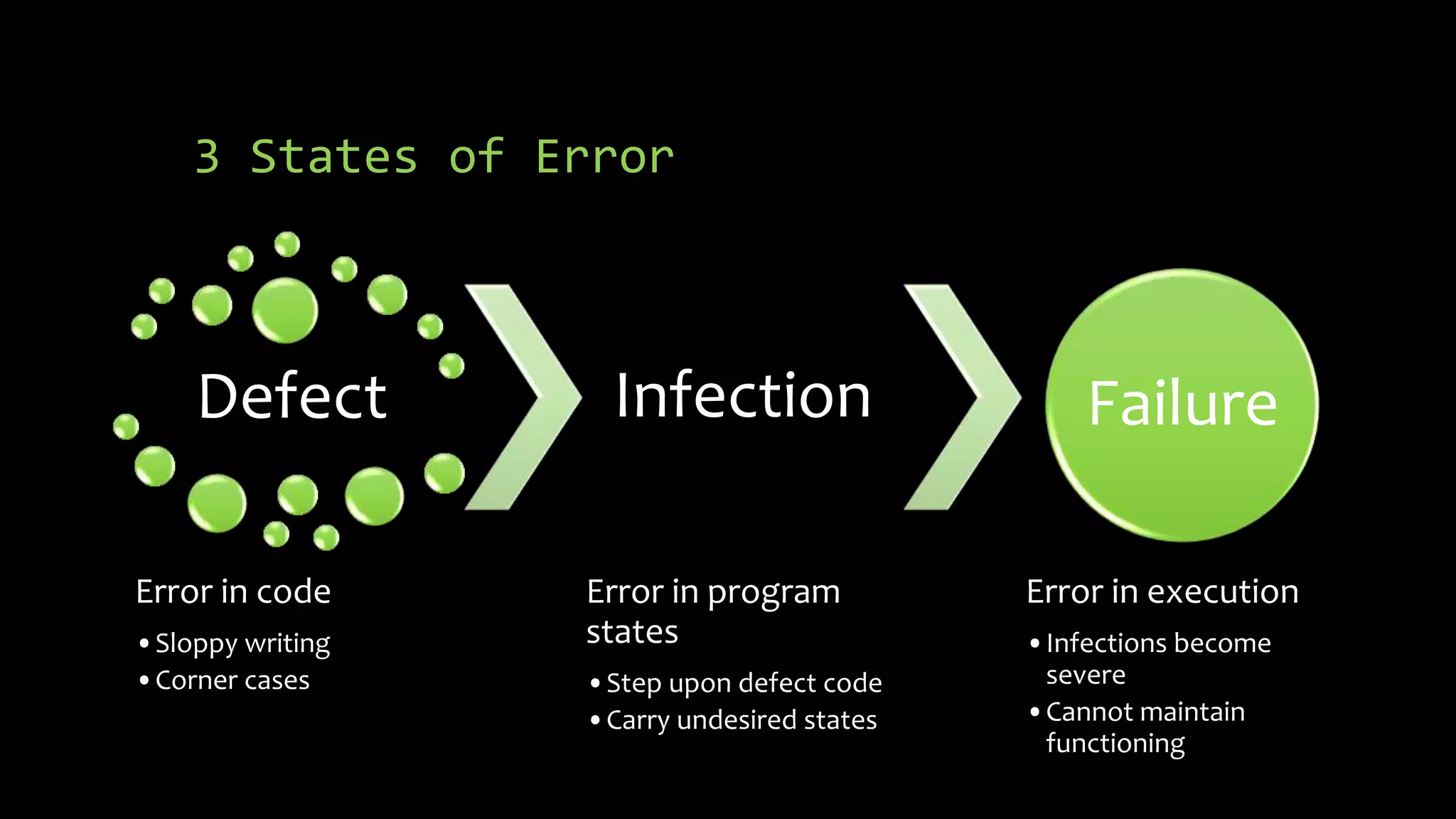
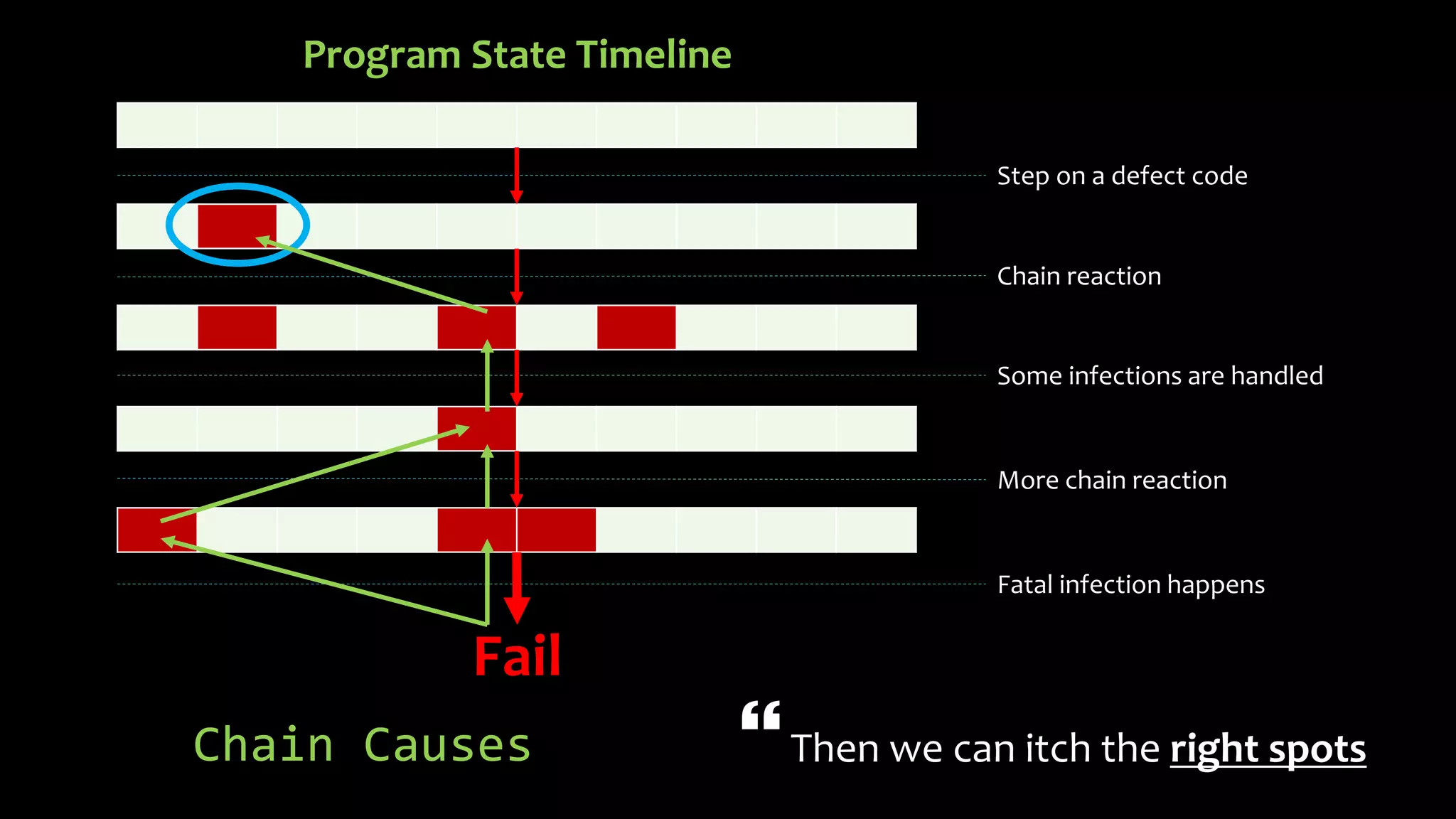
1) Three states of errors in programs - defects in code, infections spreading errors, and failures in execution. Understanding how errors propagate through a program is important to debugging.
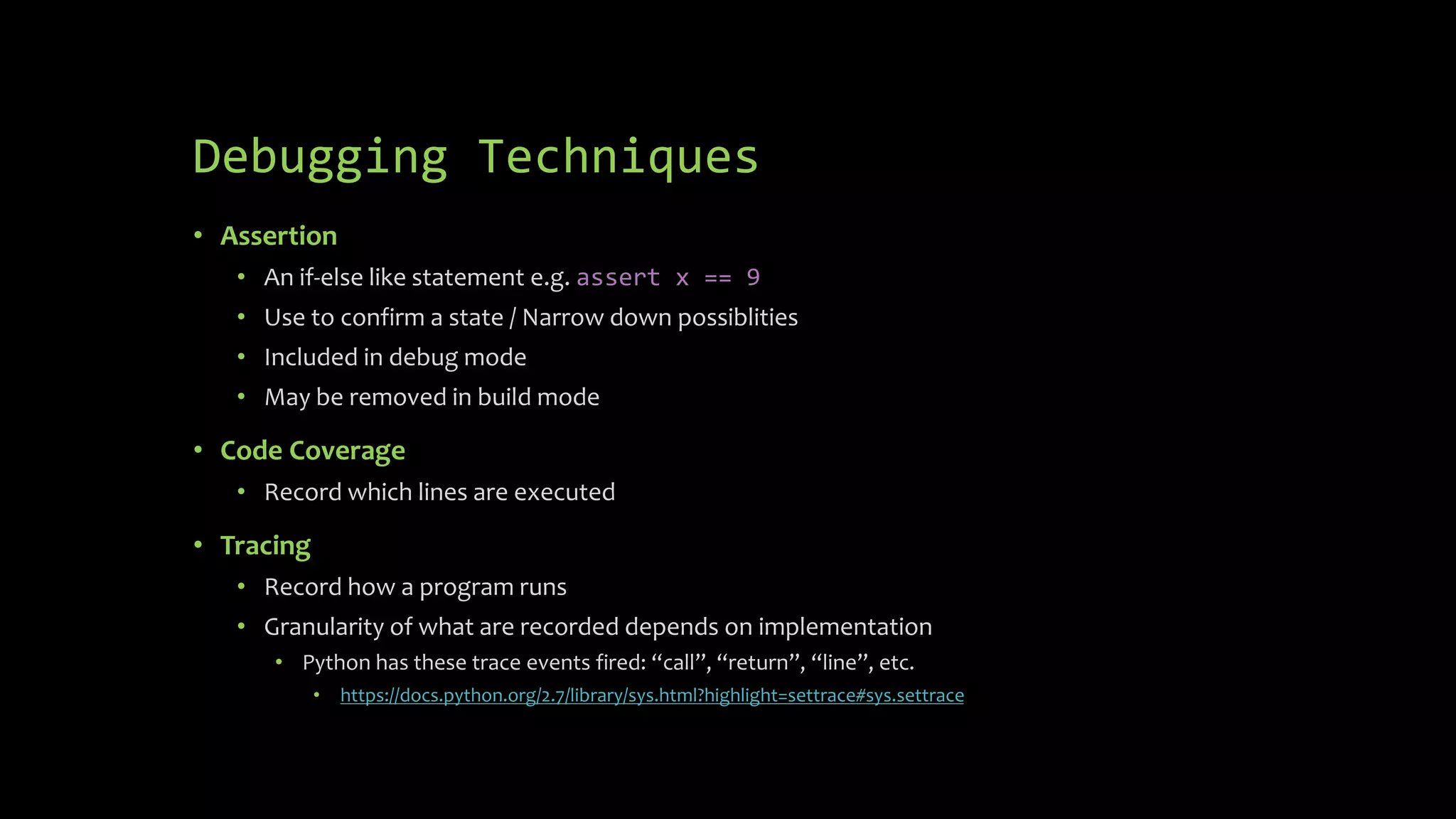
2) Techniques for debugging like assertions, code coverage, tracing, delta debugging and phi scoring to narrow relevant information and find root causes of failures.
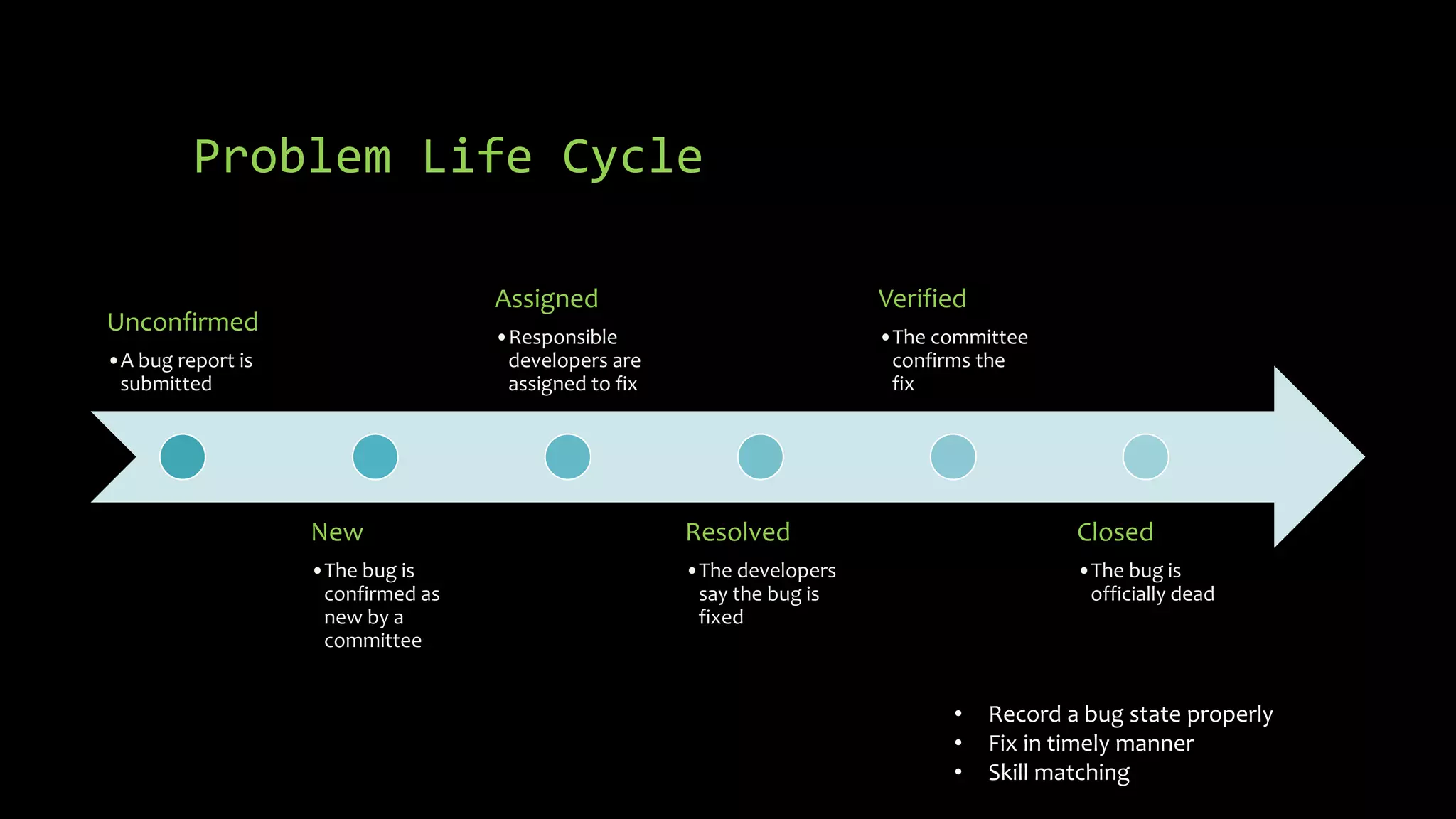
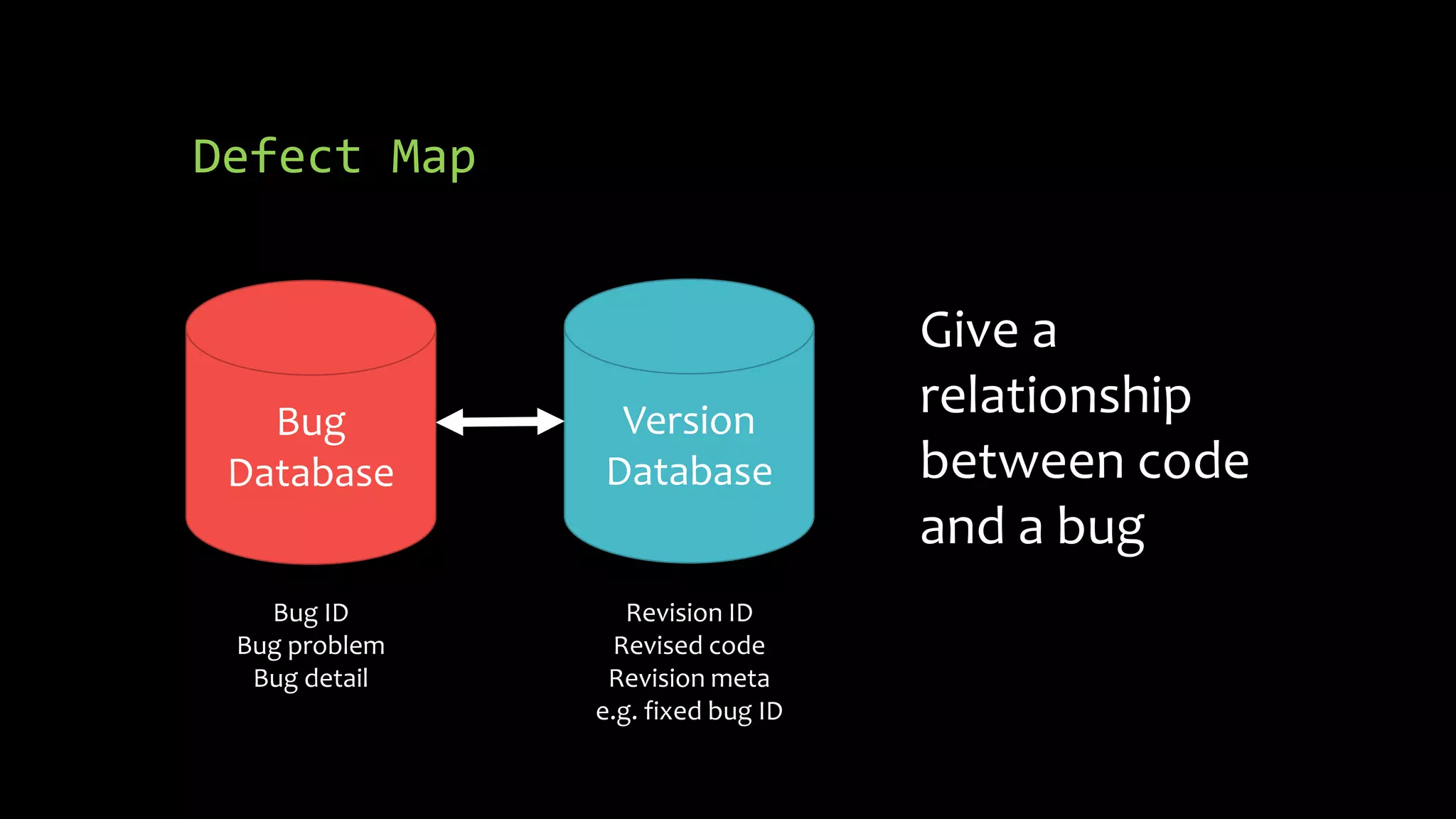
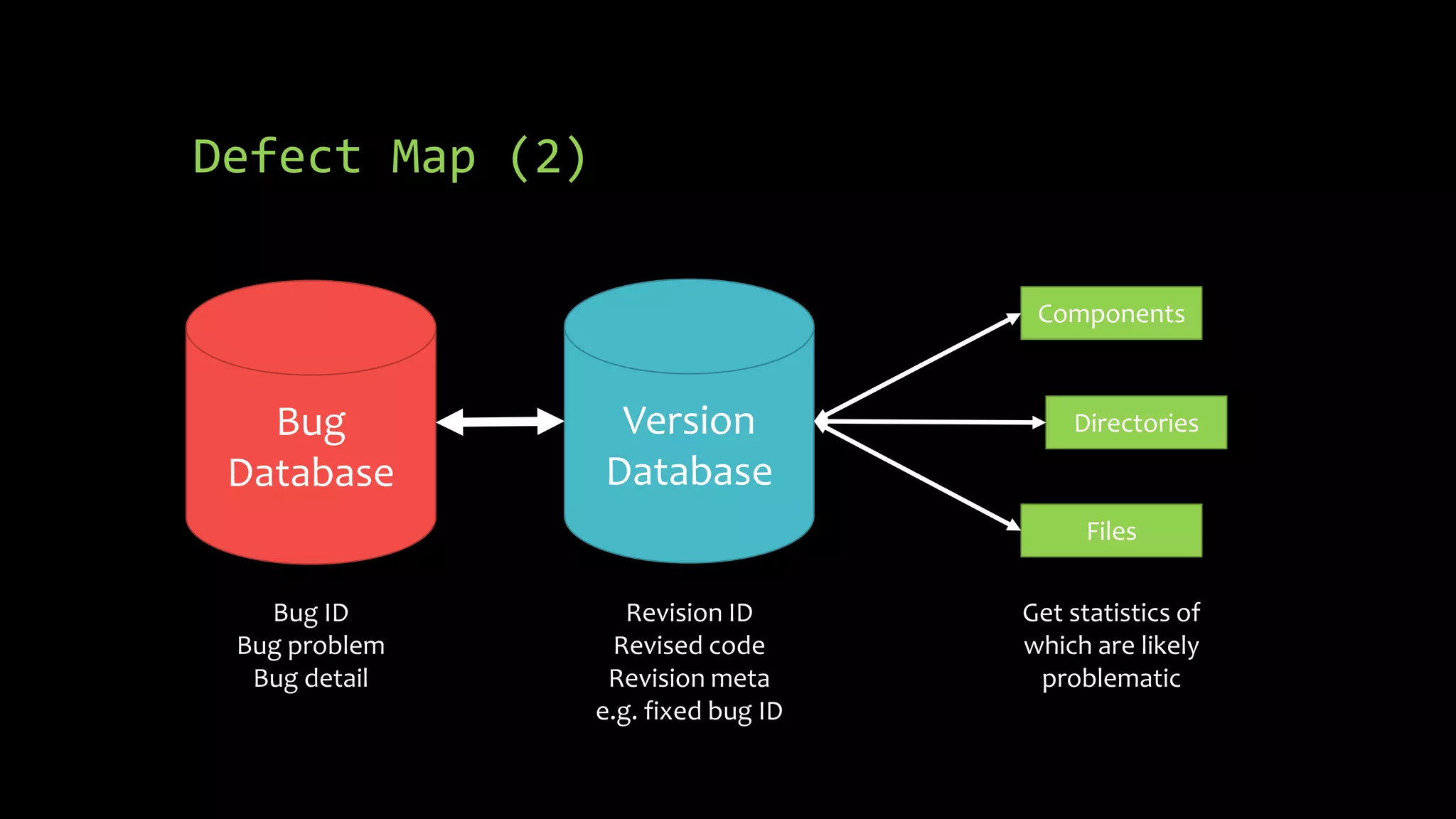
3) Managing bugs in a project through proper tracking of problem lifecycles from new to closed, and use of bug databases linked to version control to map defects to code revisions.