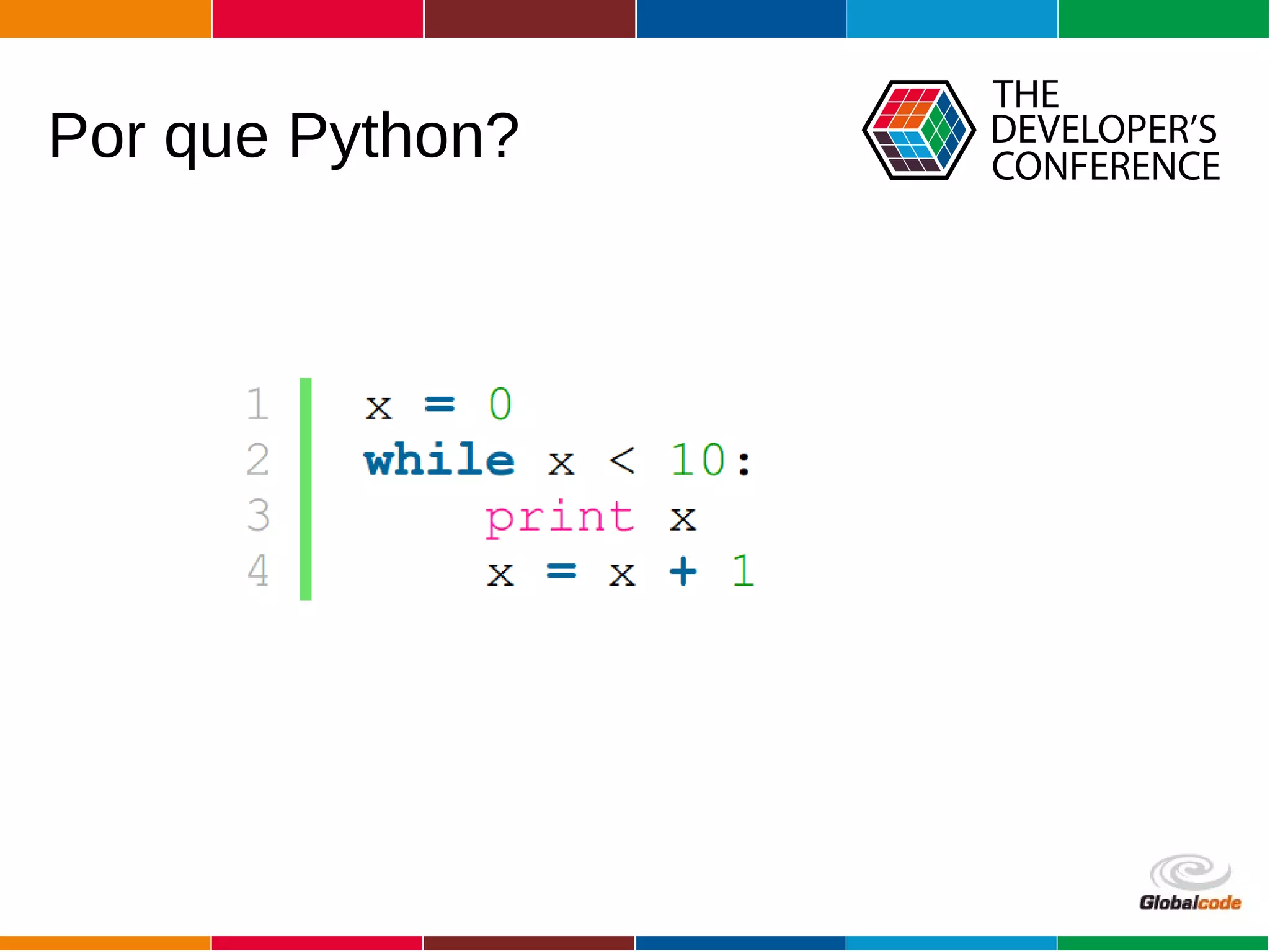
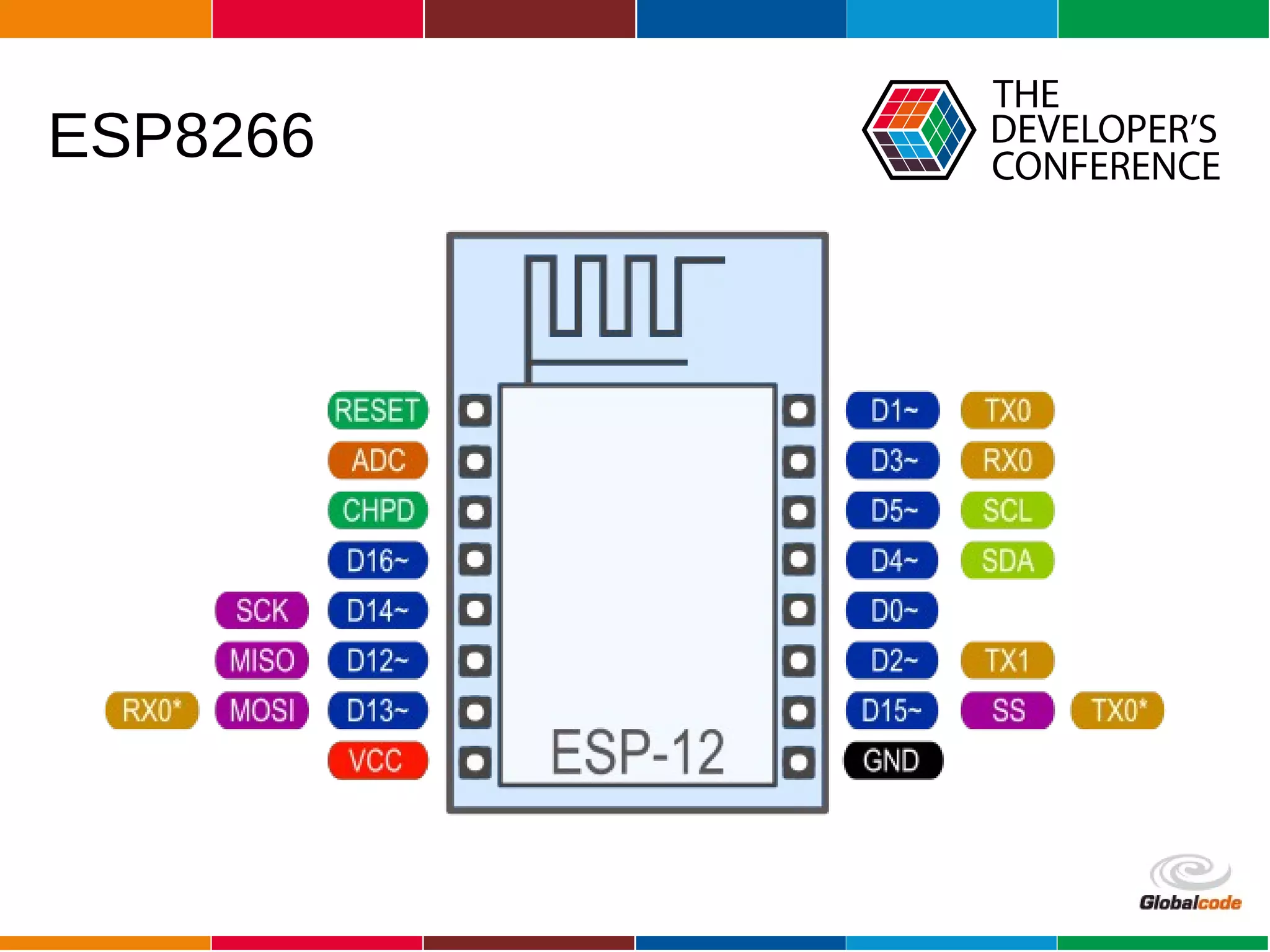
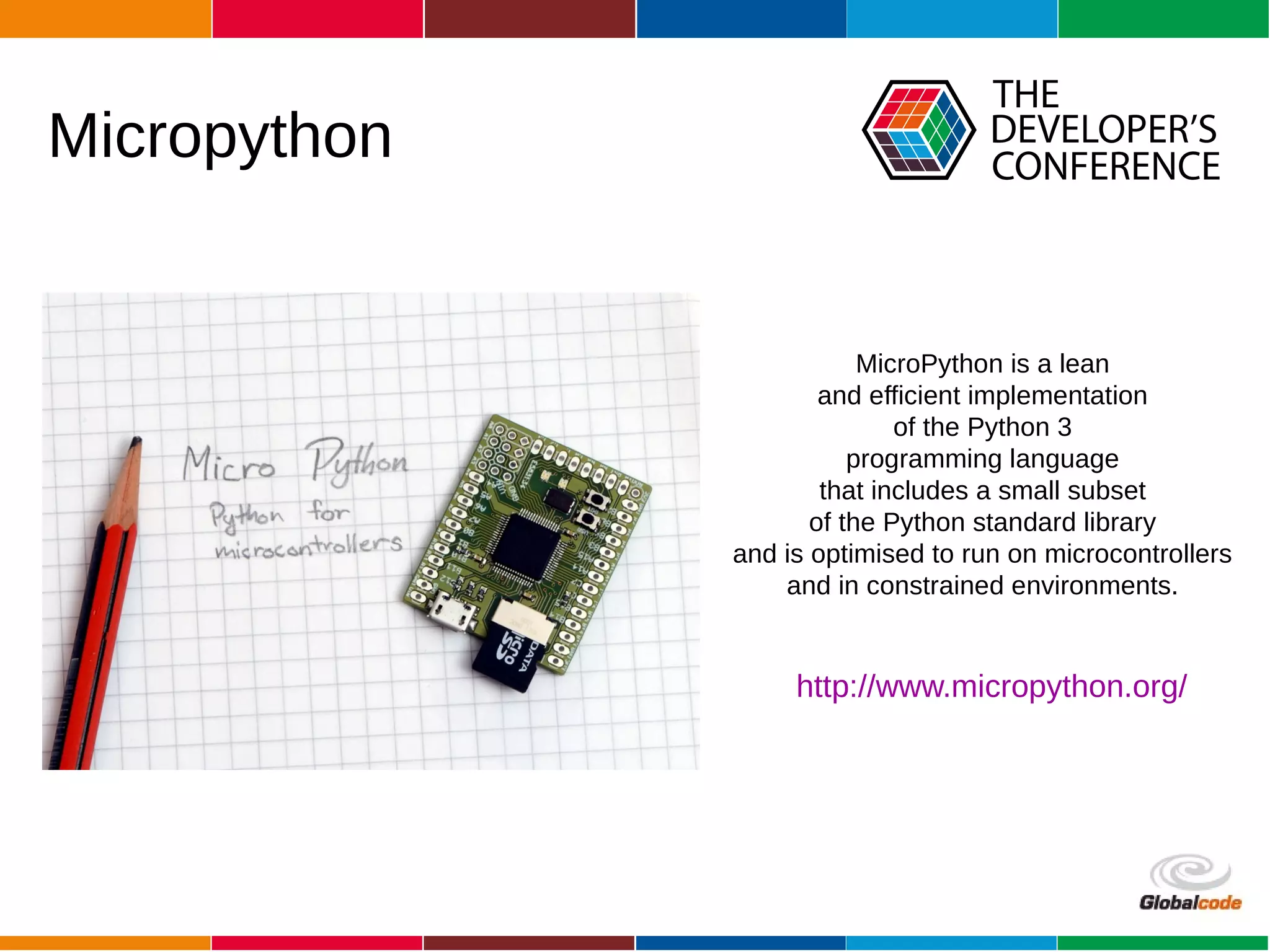
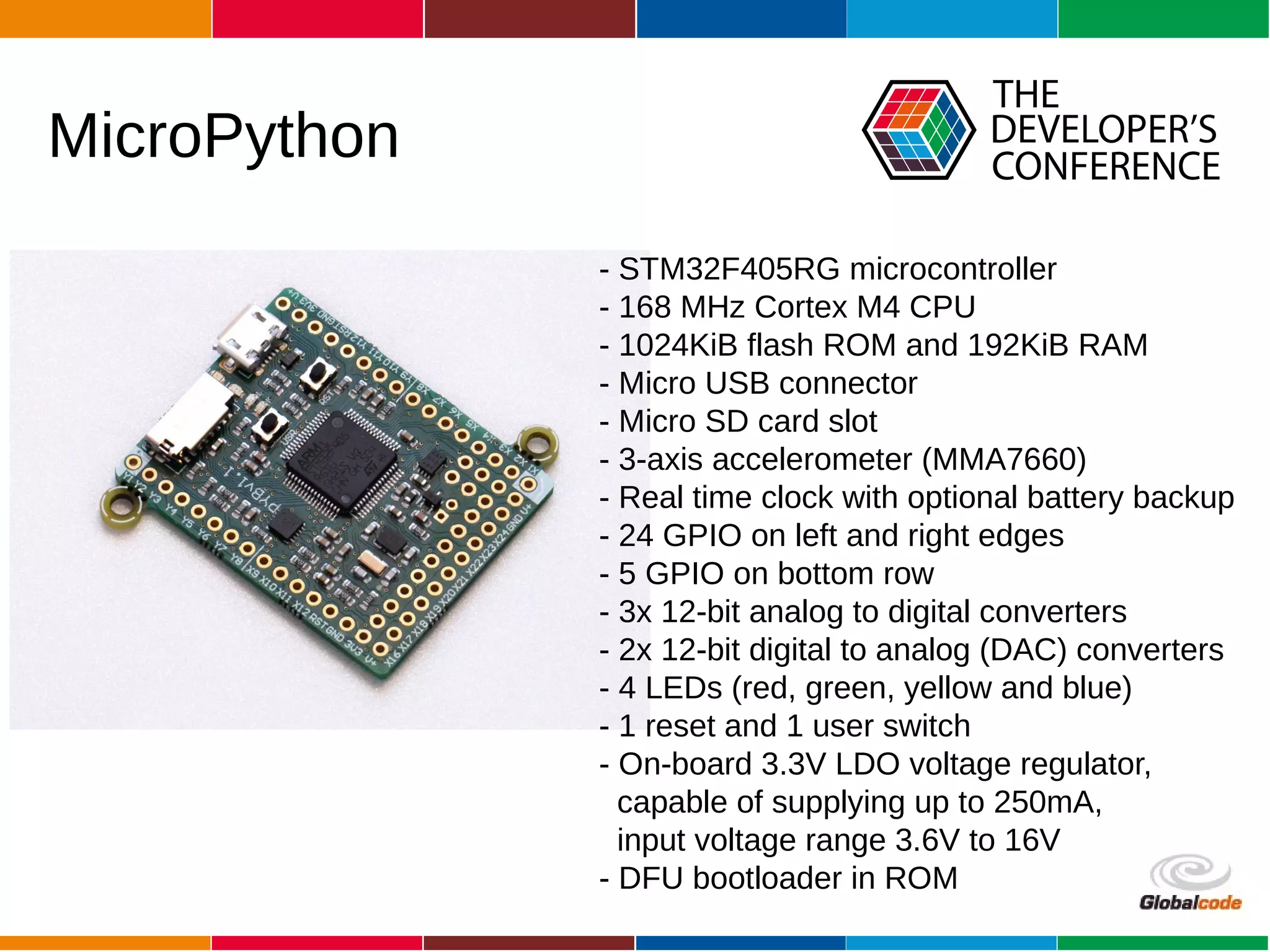
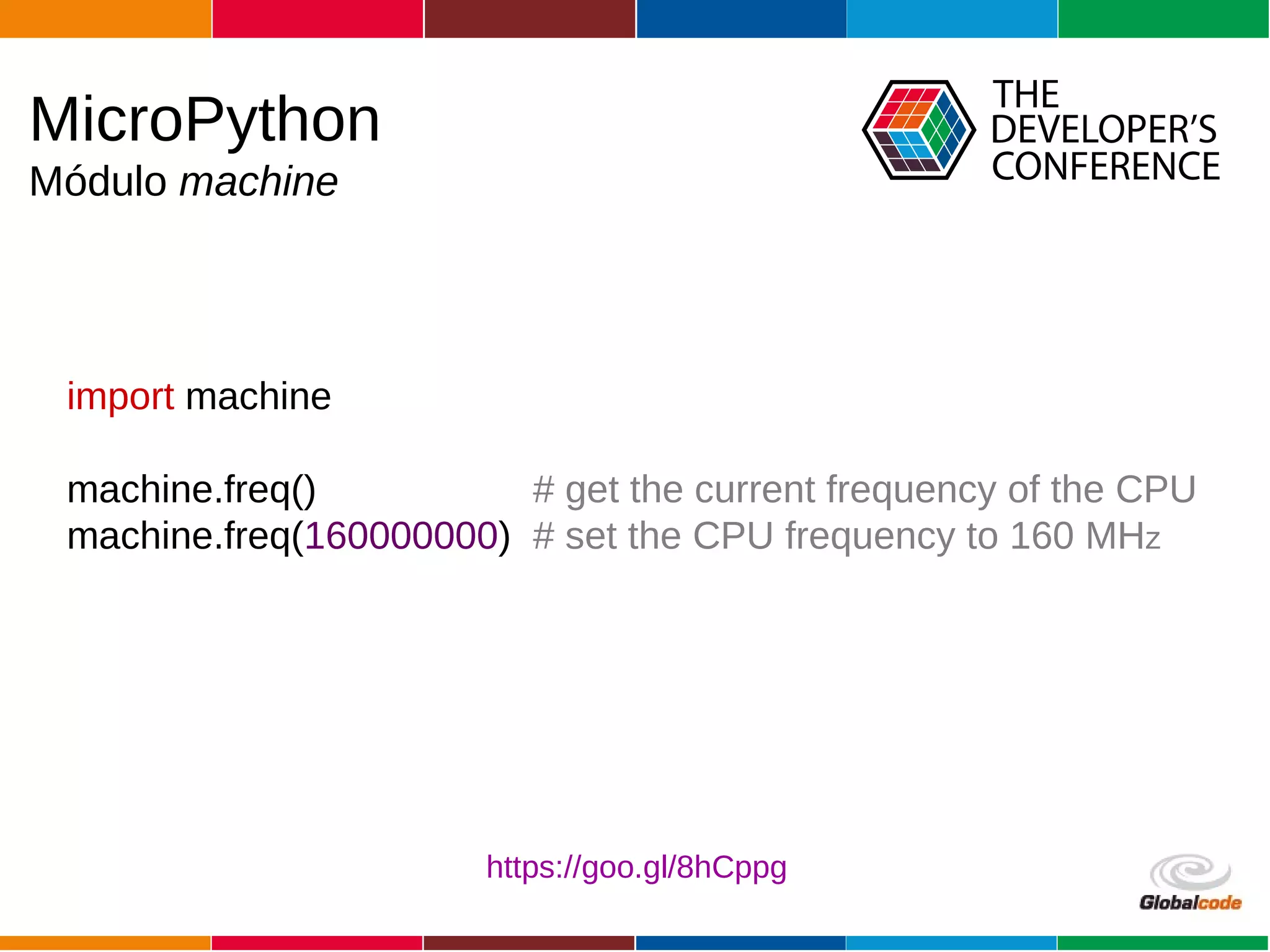
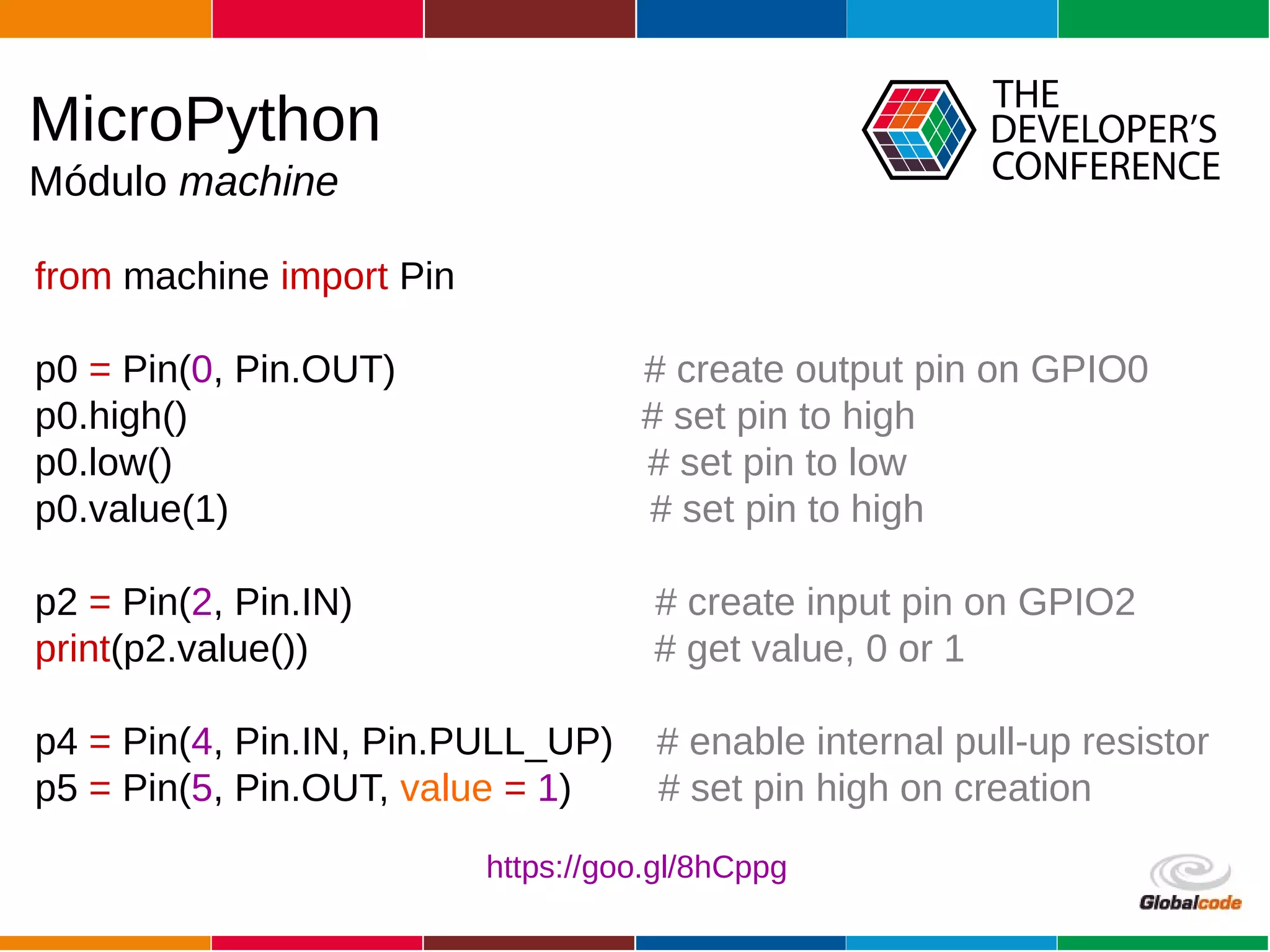
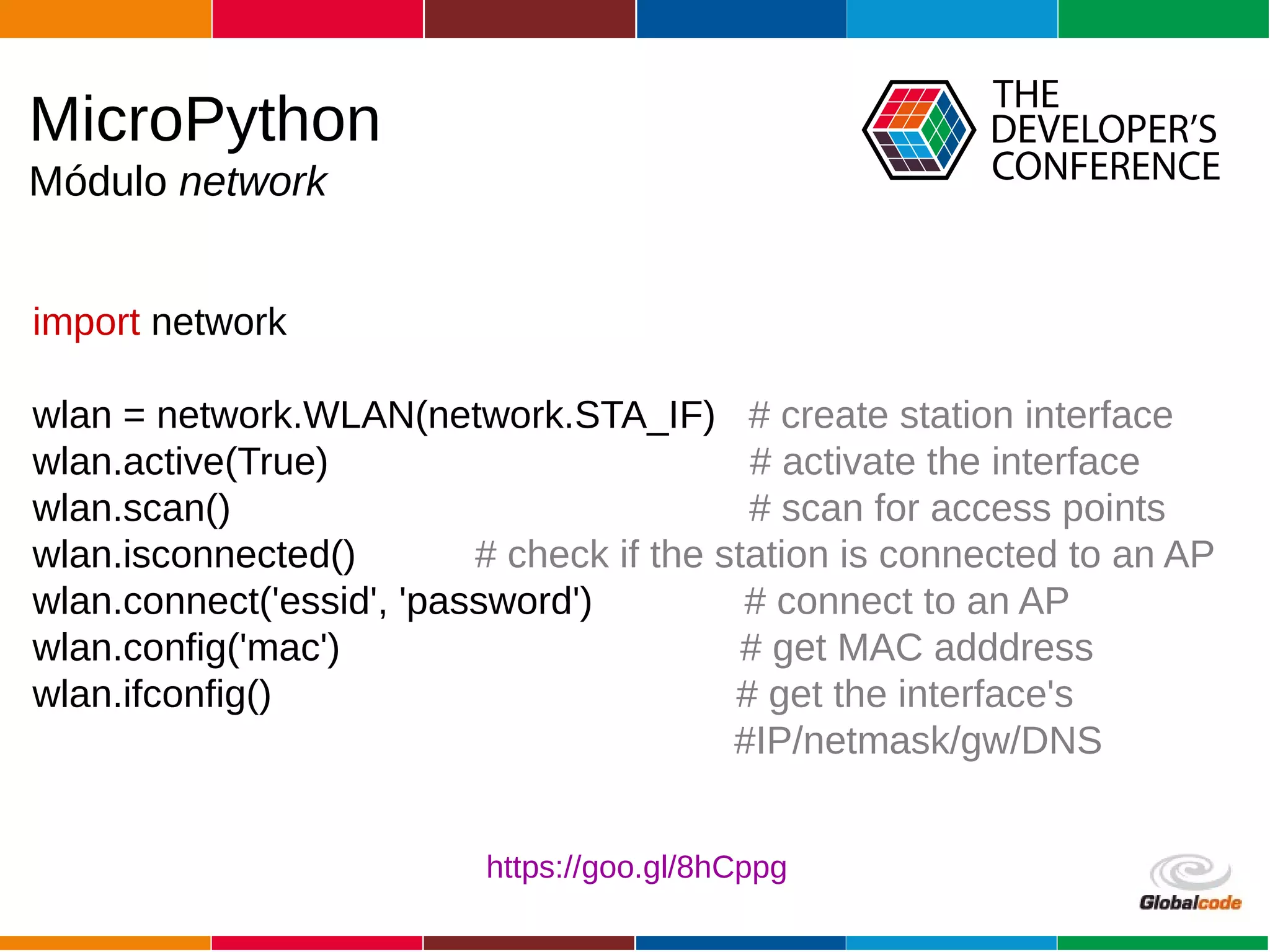
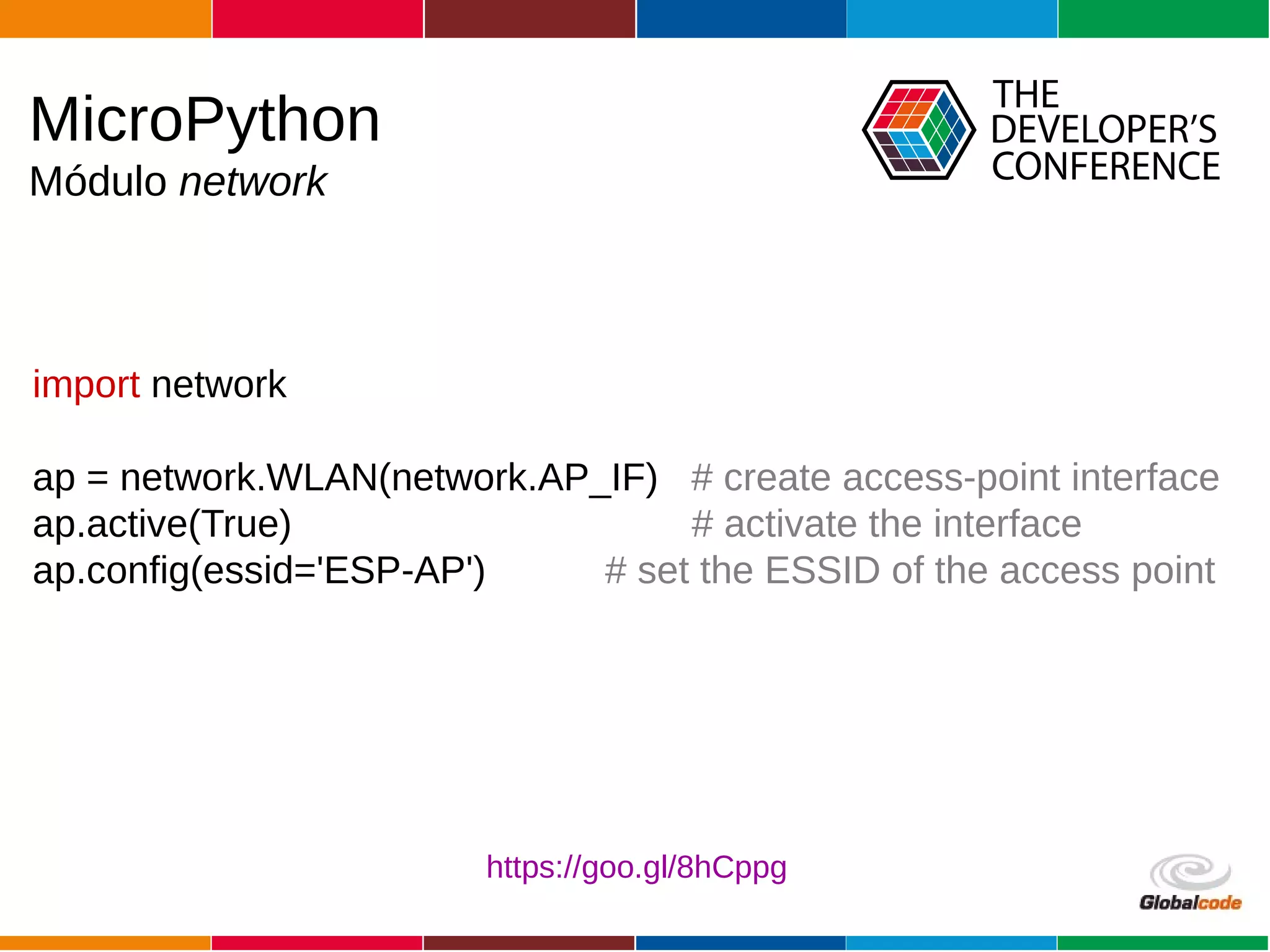
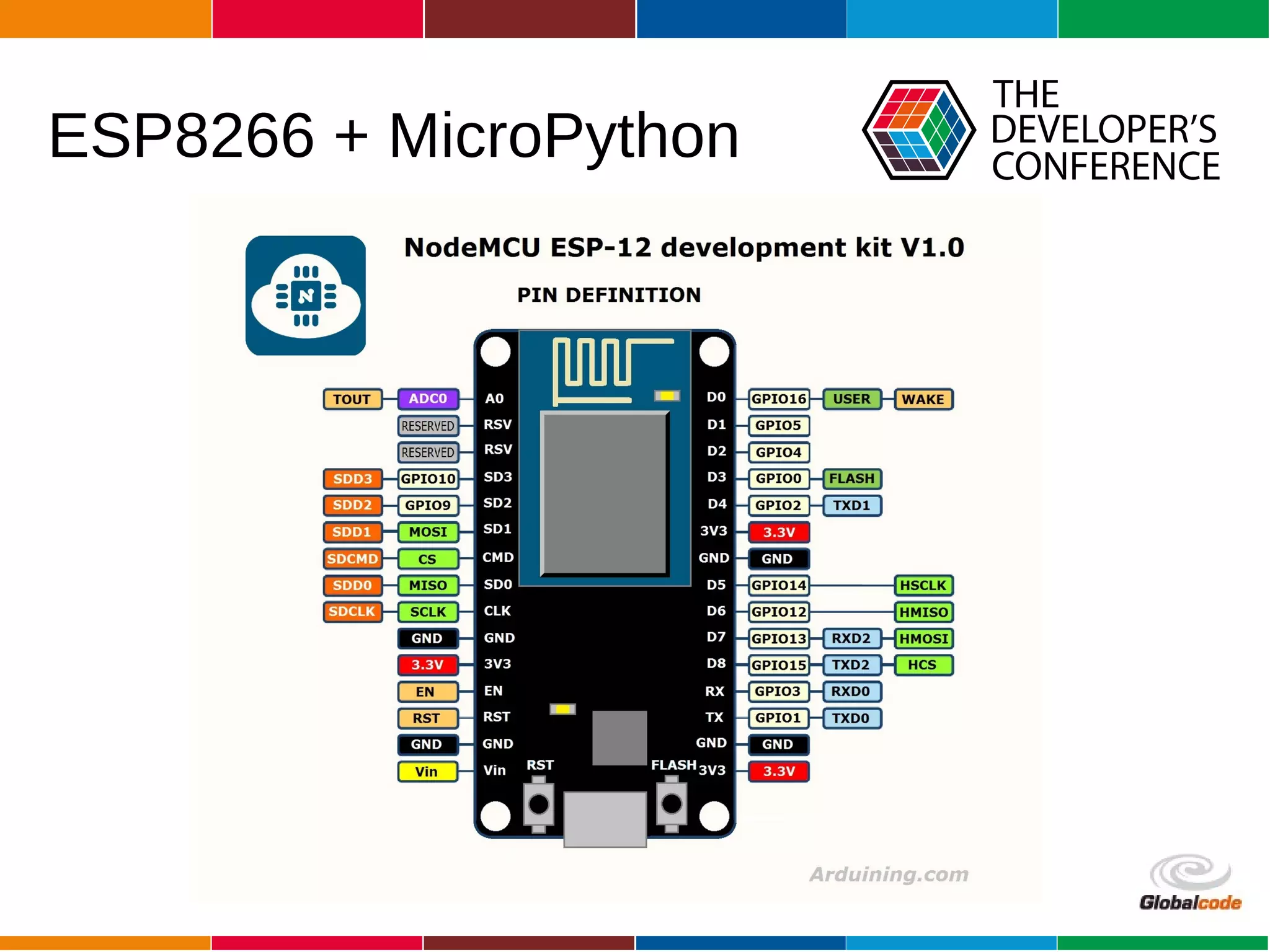
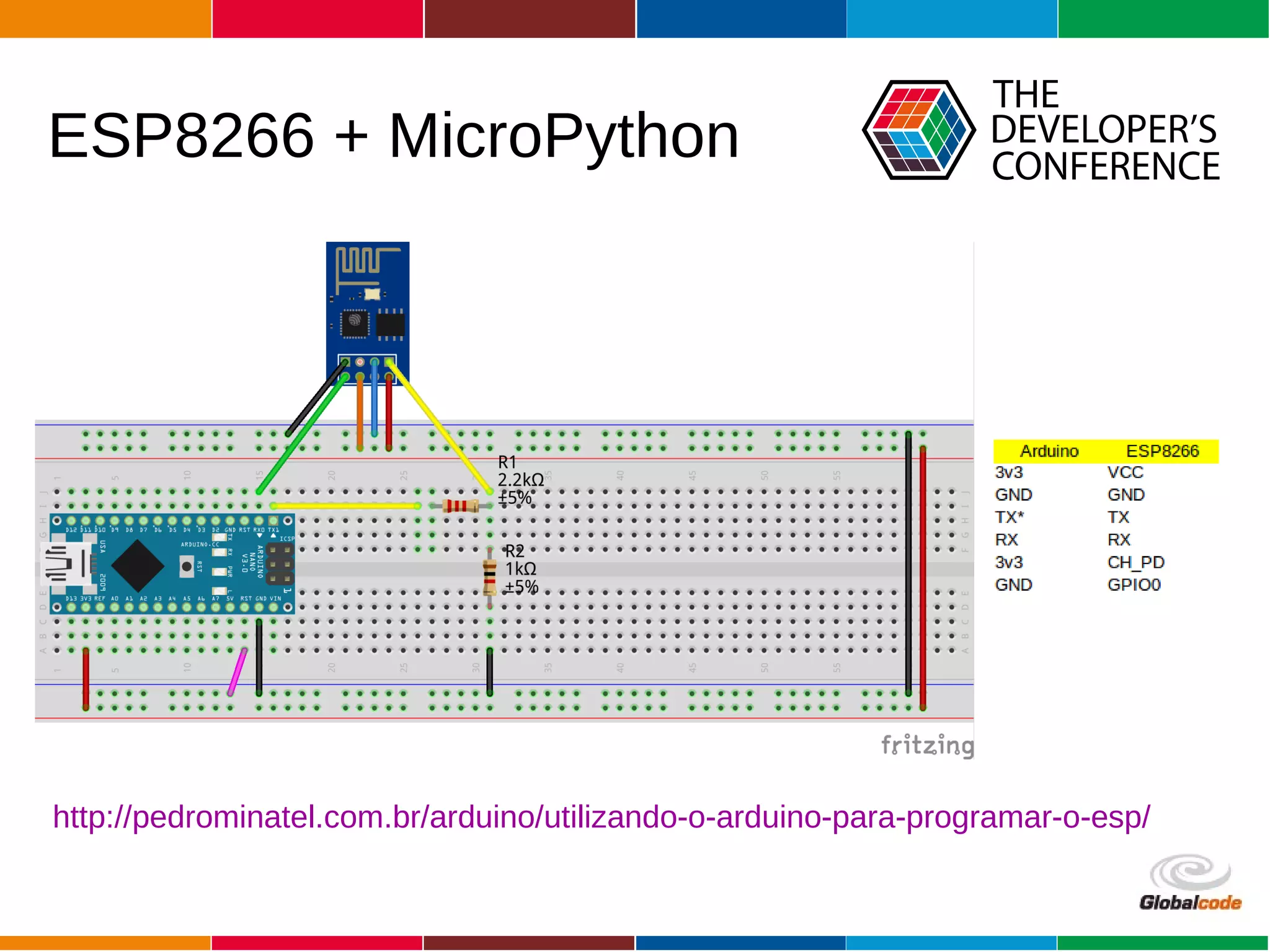
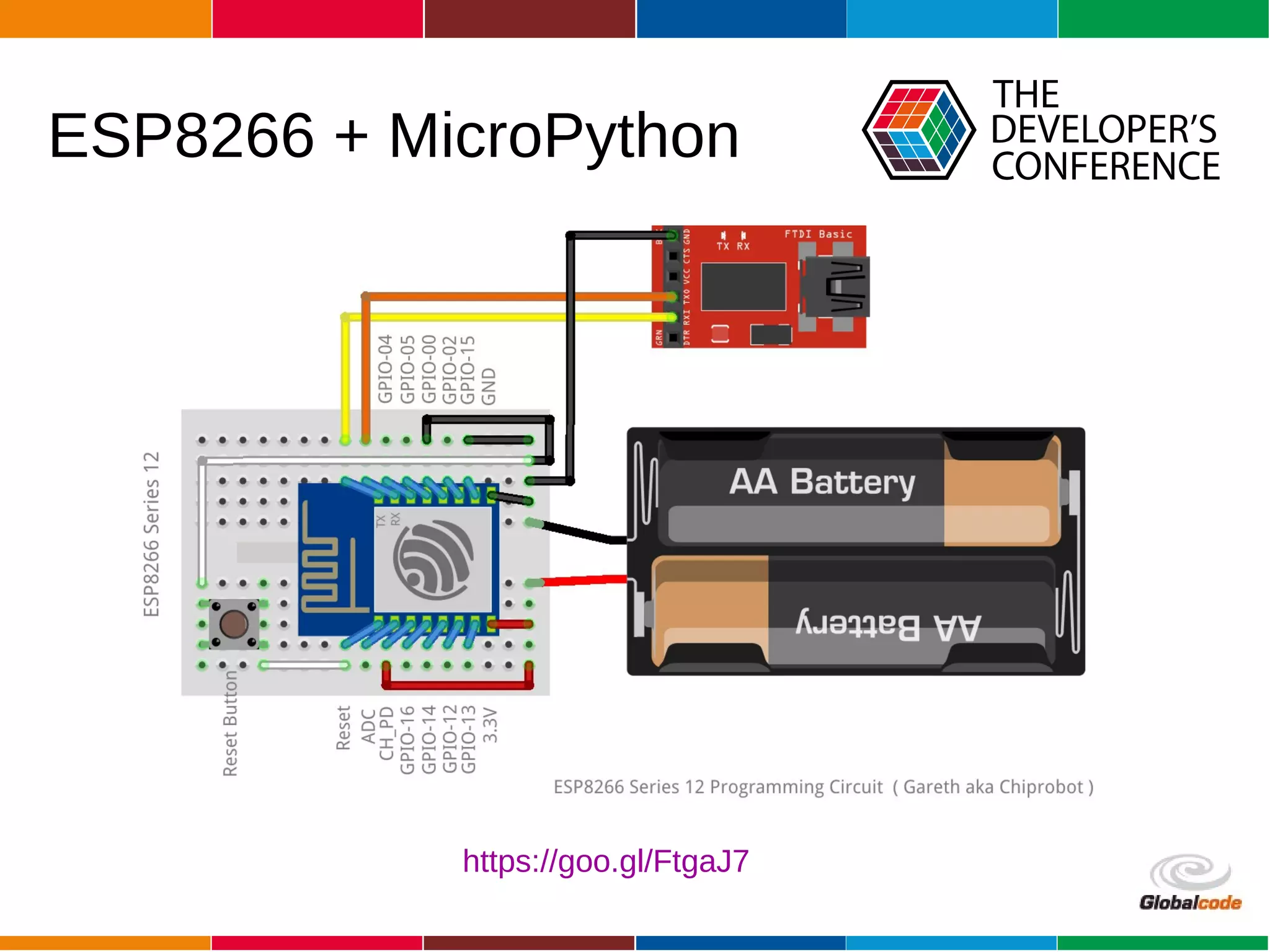
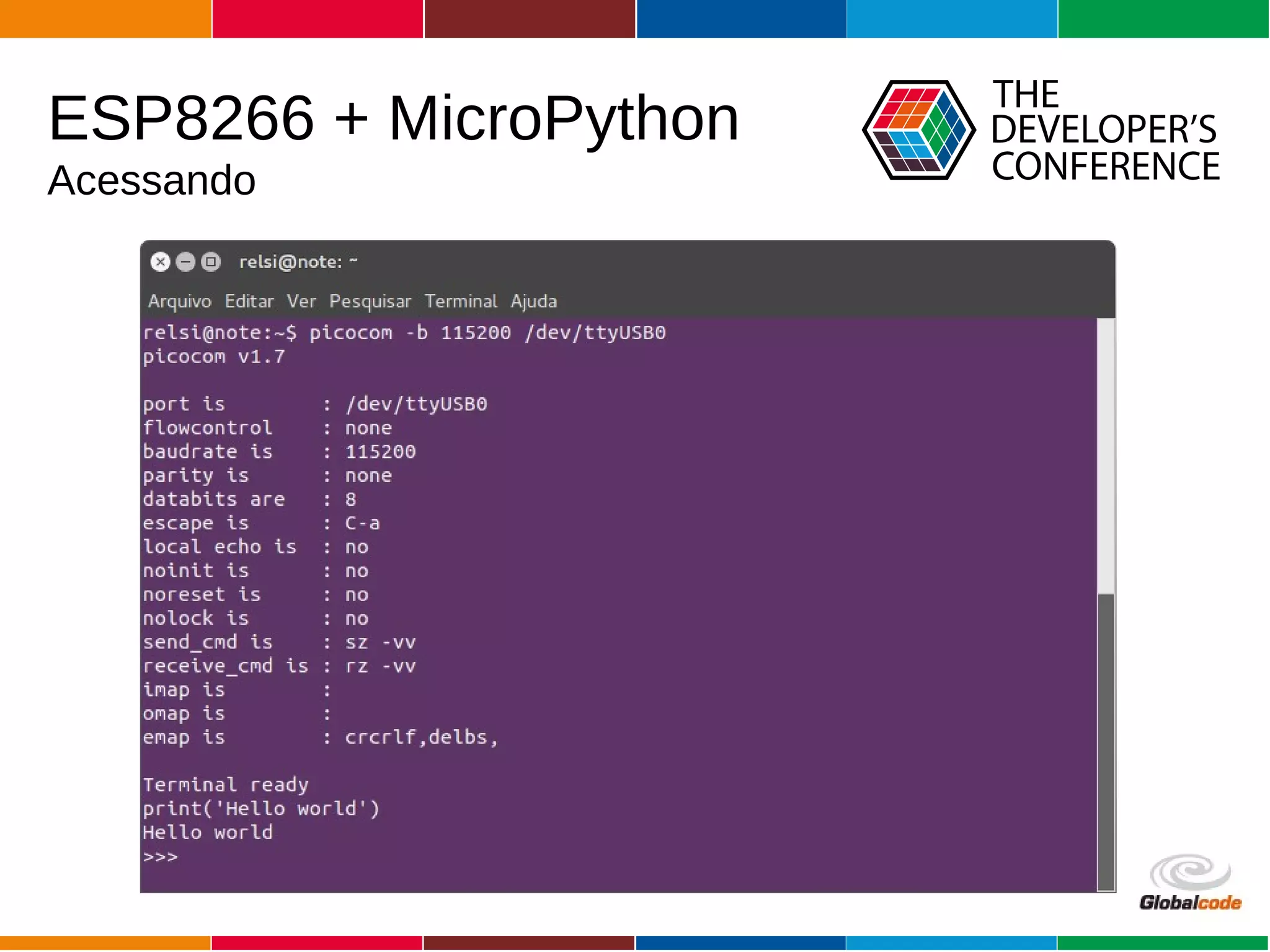
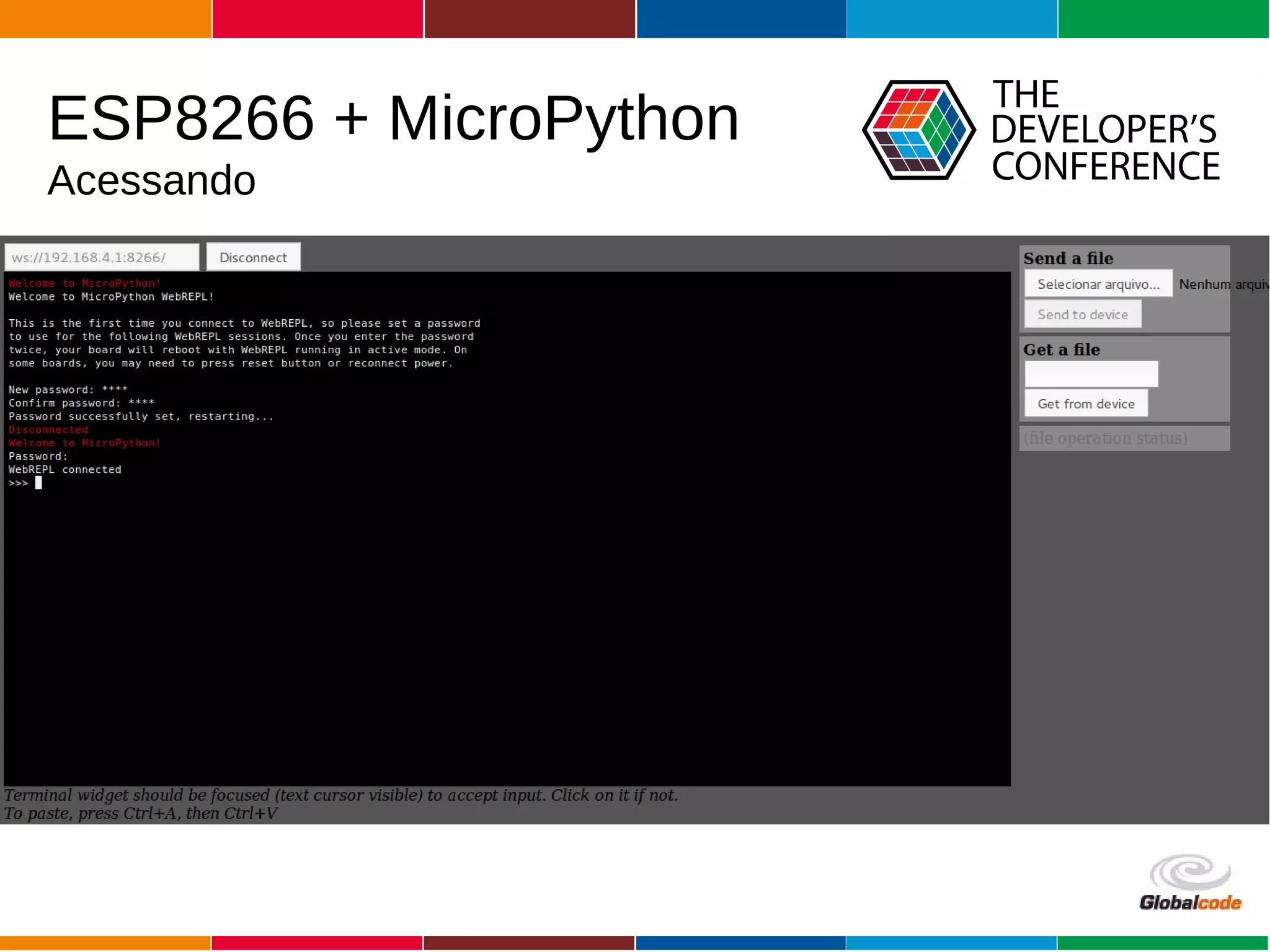
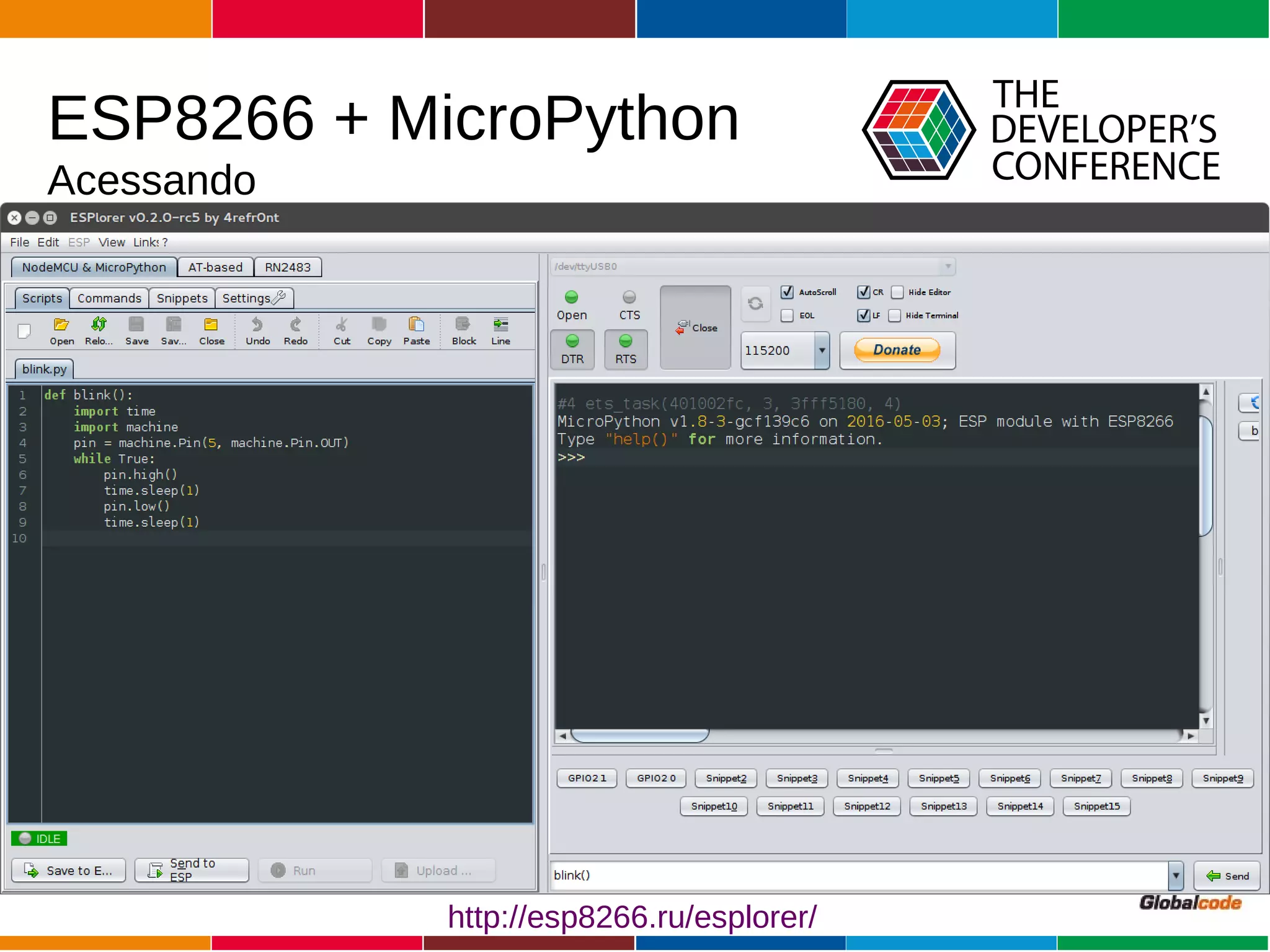
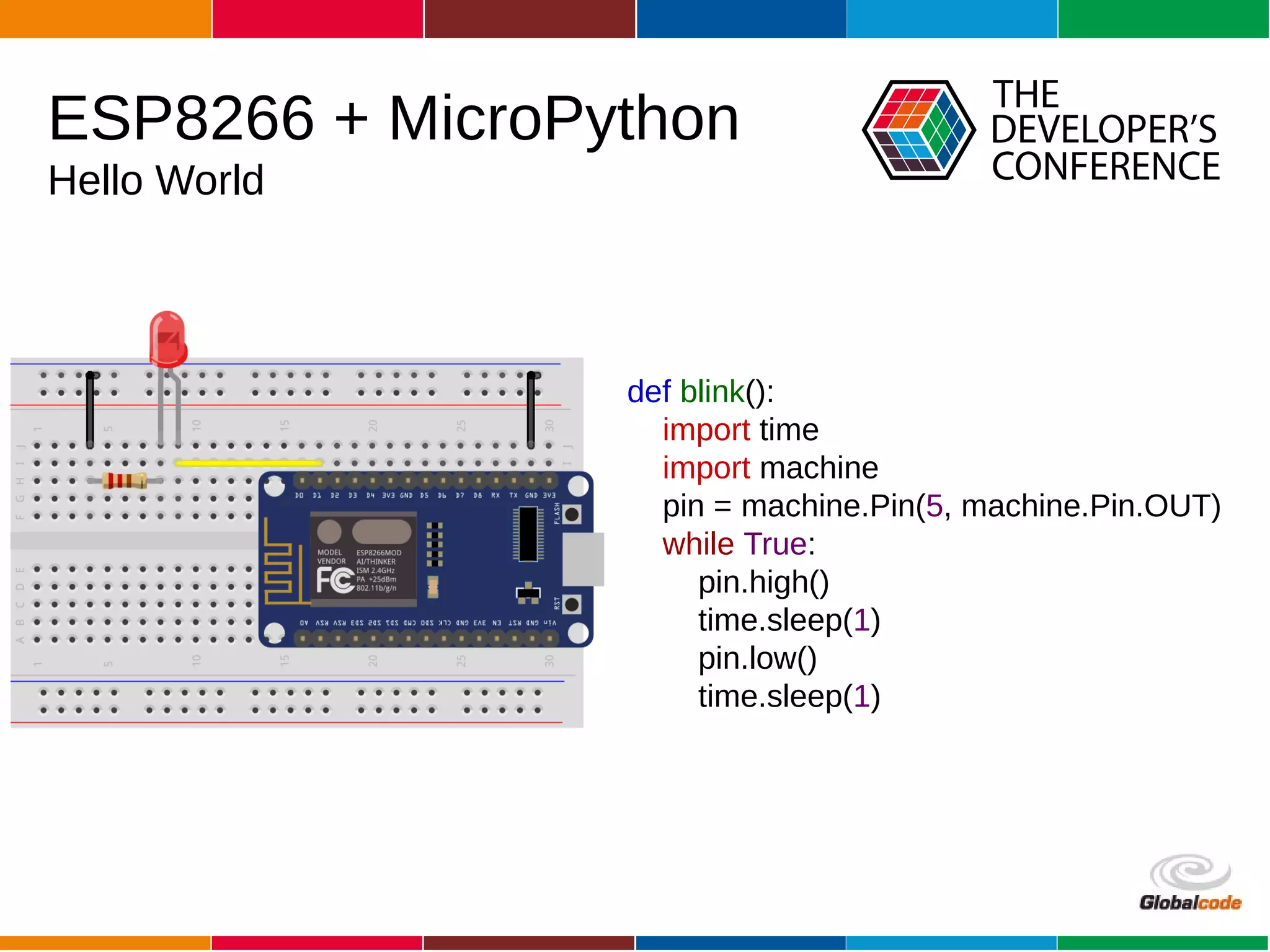
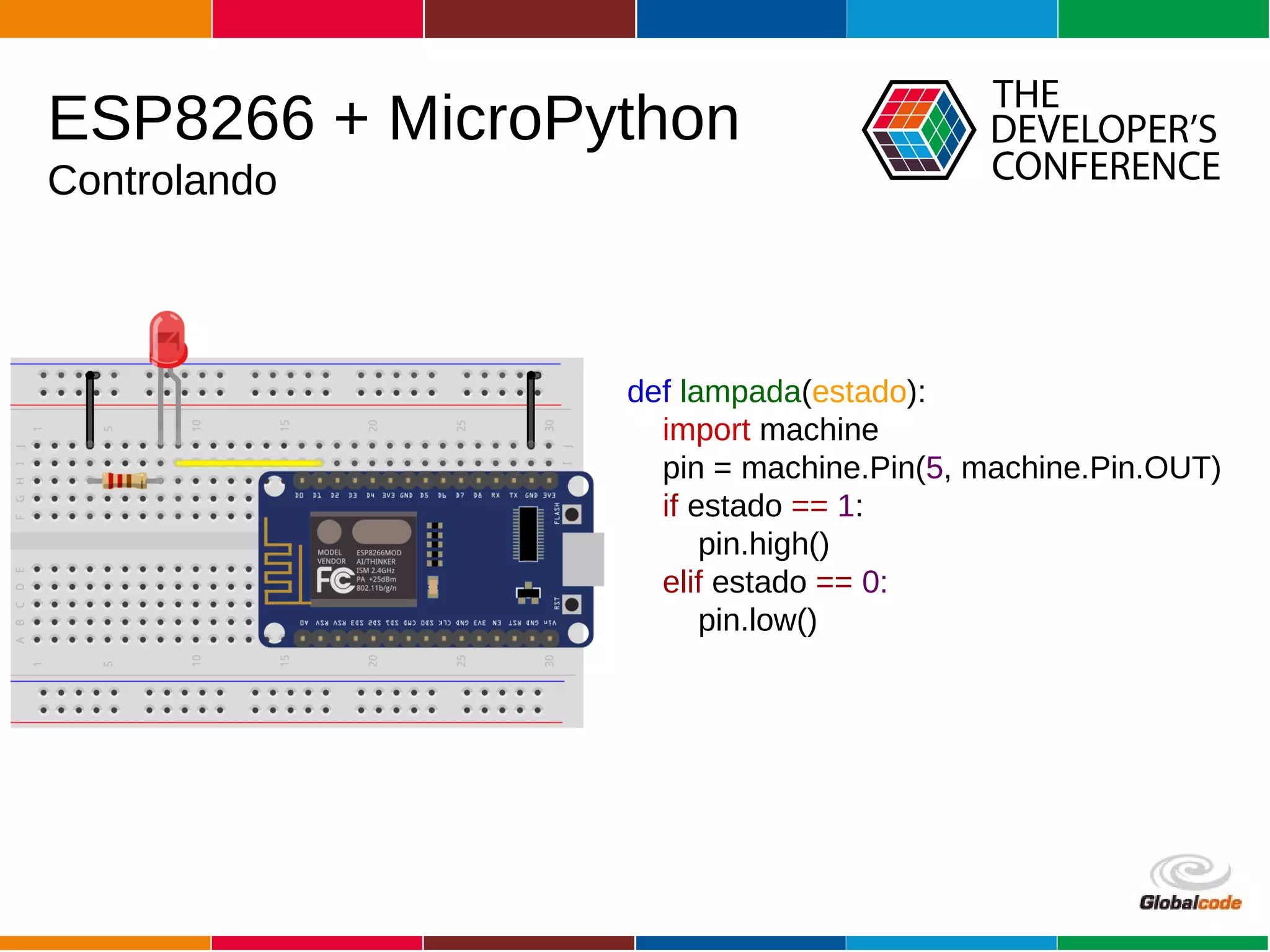
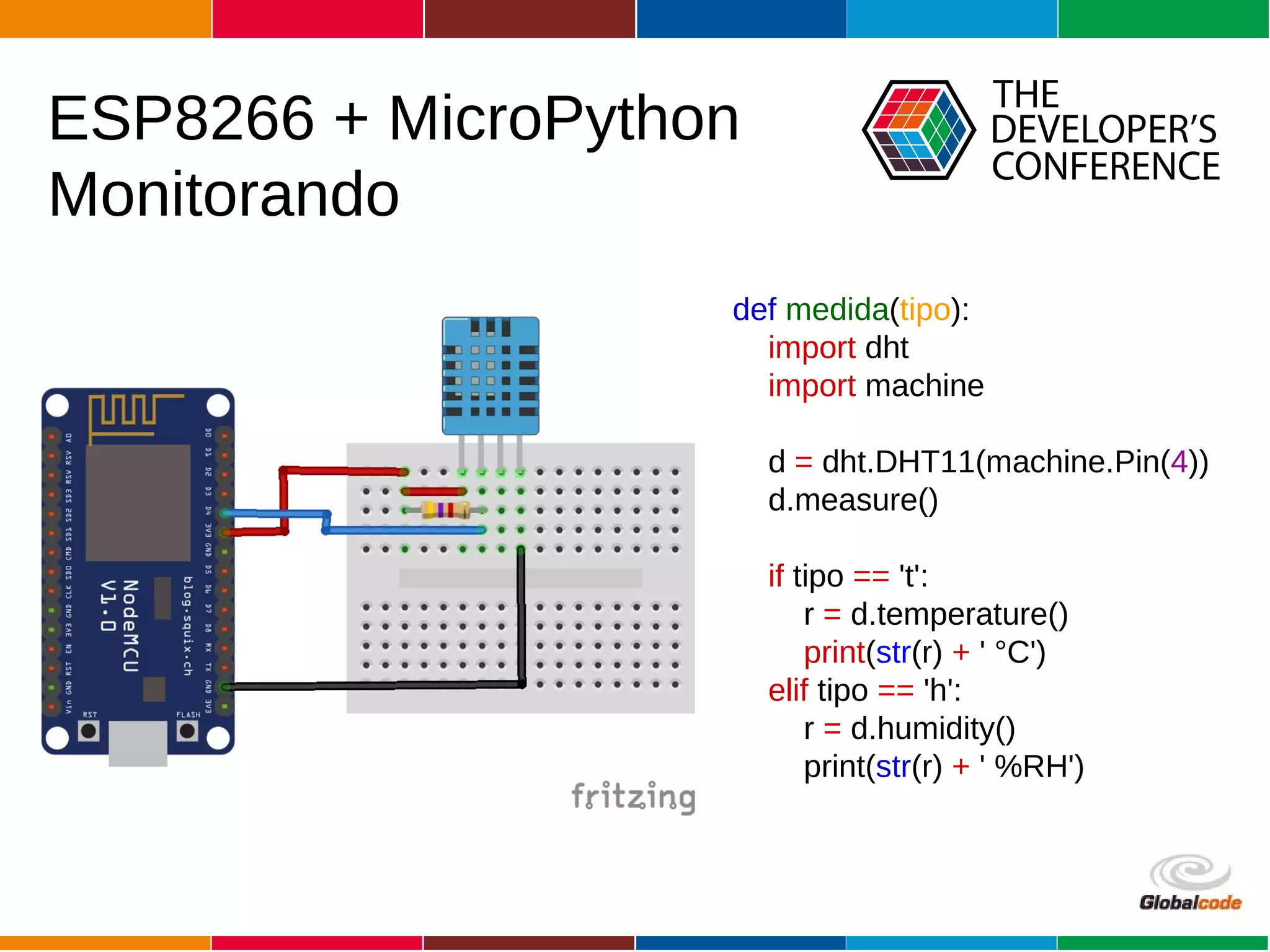
The document discusses programming the ESP8266 microcontroller using MicroPython, a lightweight implementation of Python 3 for constrained environments. It outlines the specifications of the ESP8266 and MicroPython, key libraries, and provides example code for functionalities like pin control and sensor monitoring. Additionally, it includes links to resources, tools for flashing firmware, and a call for questions and engagement.