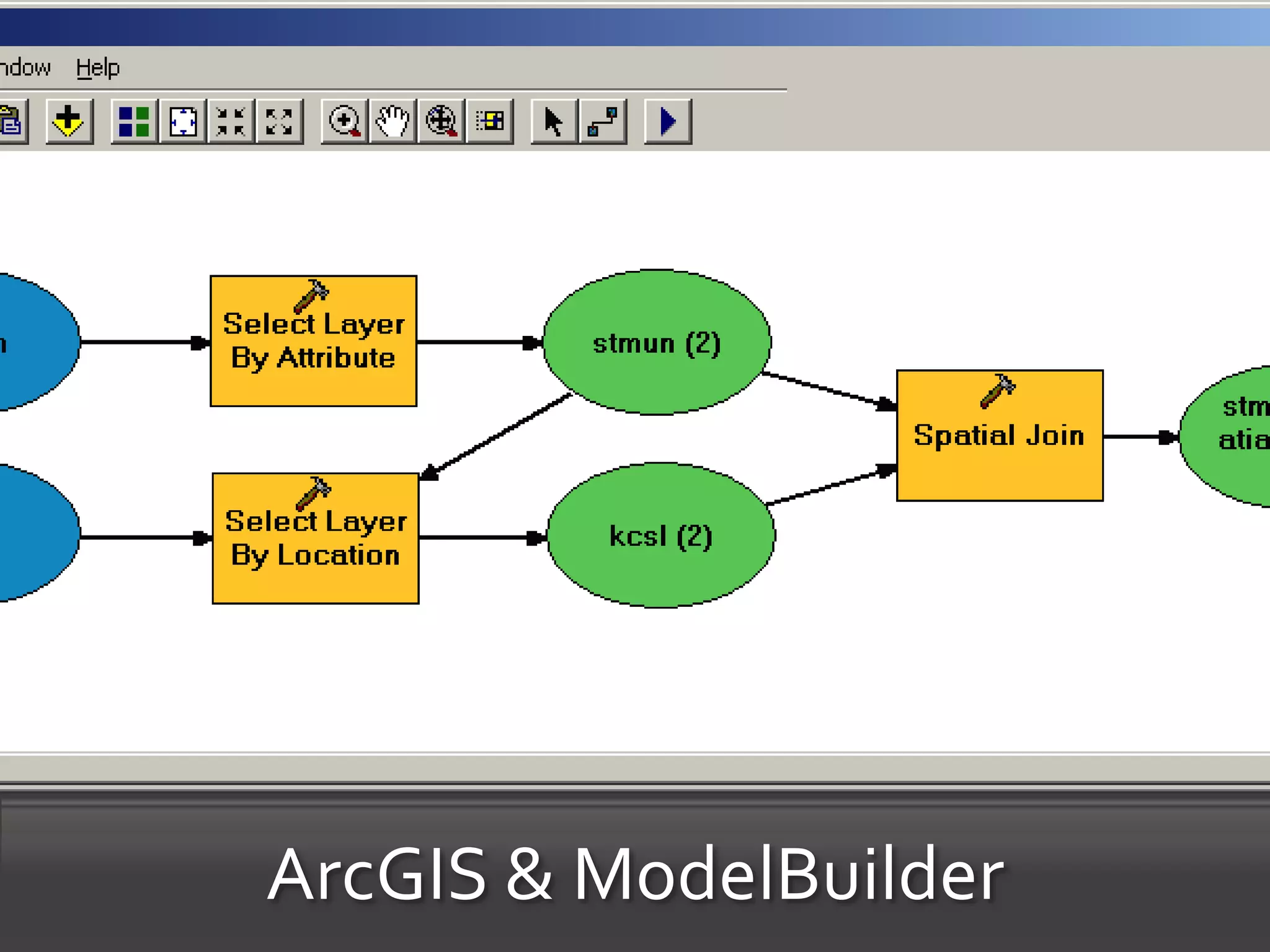
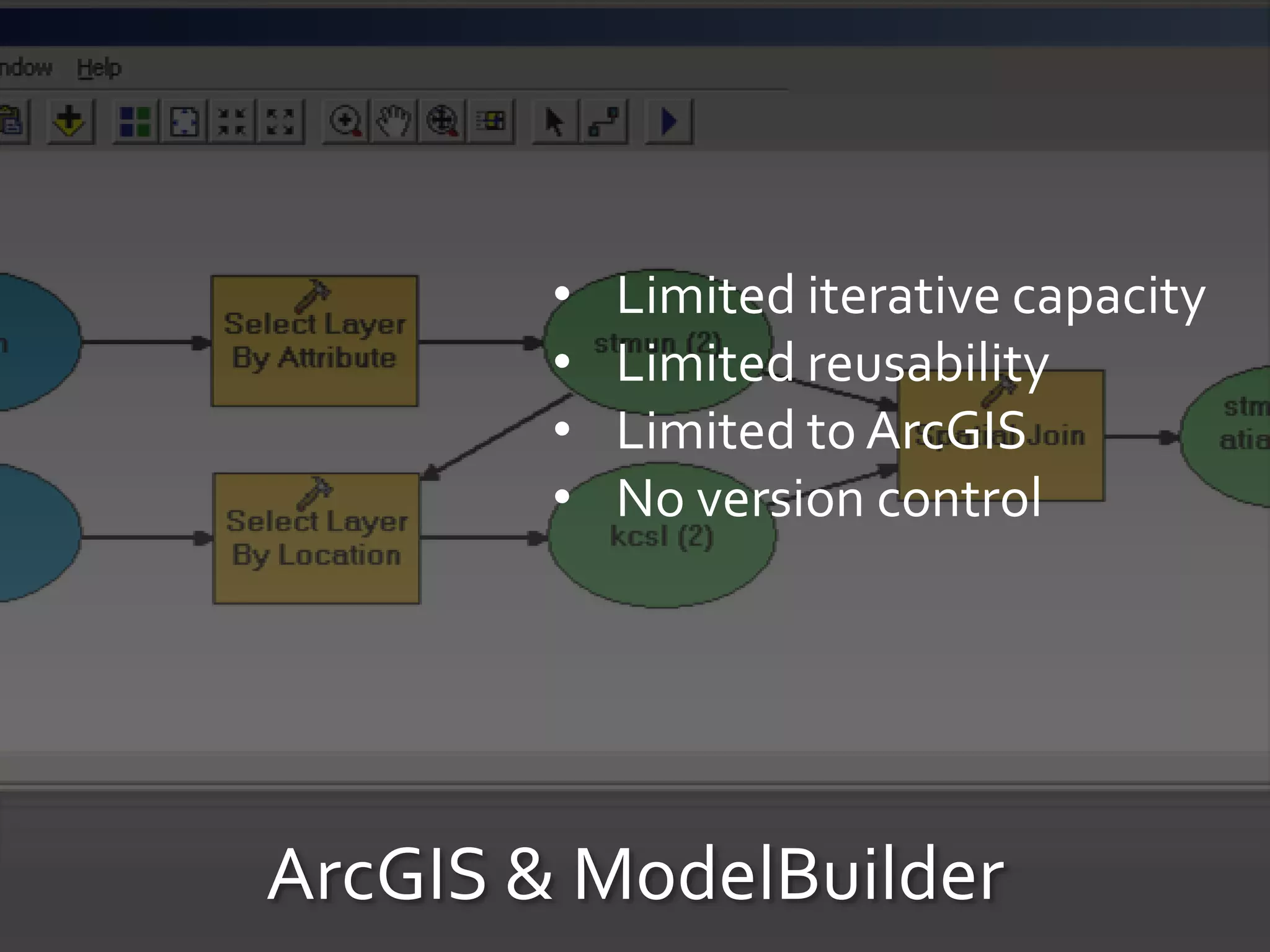
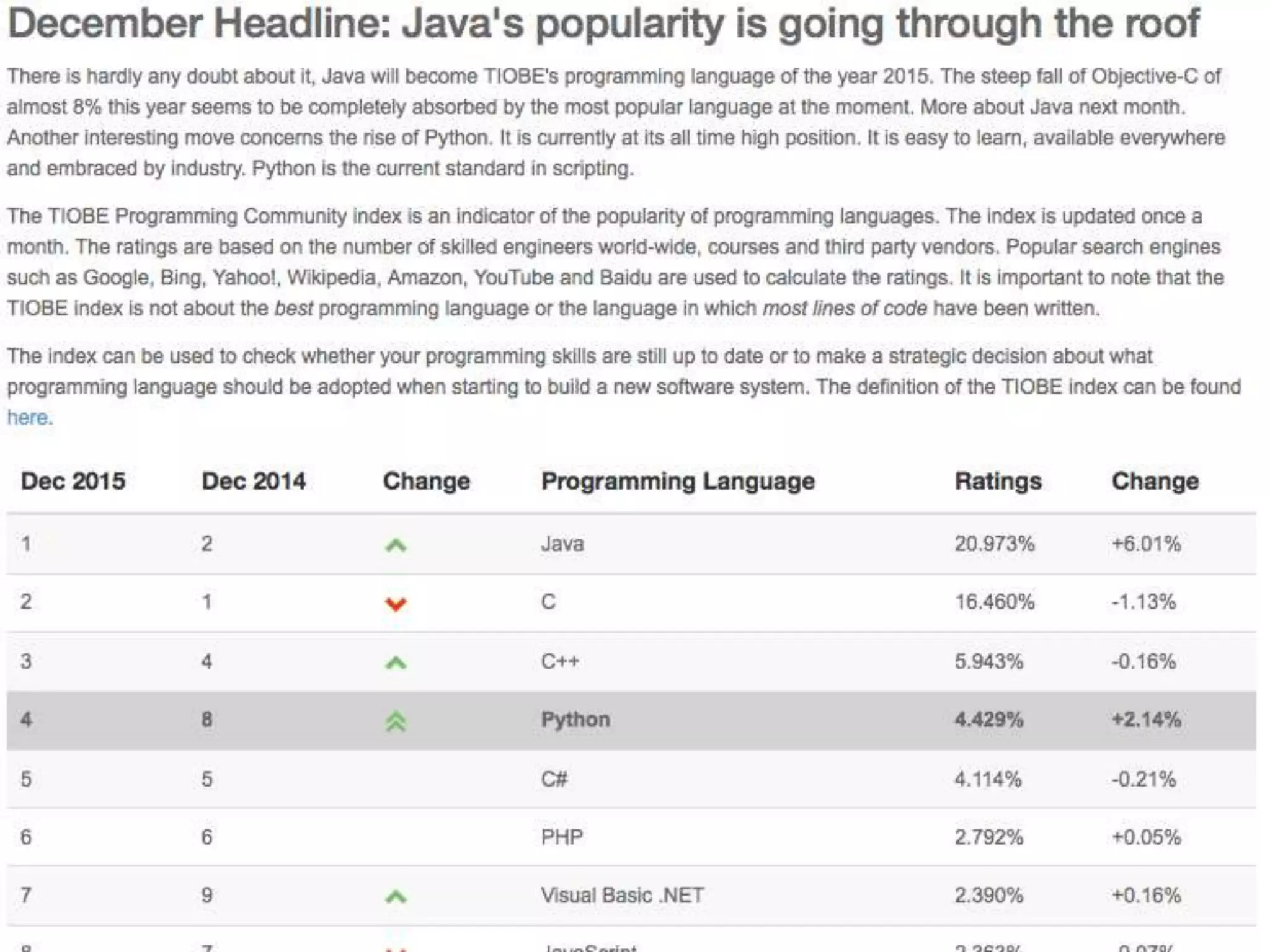
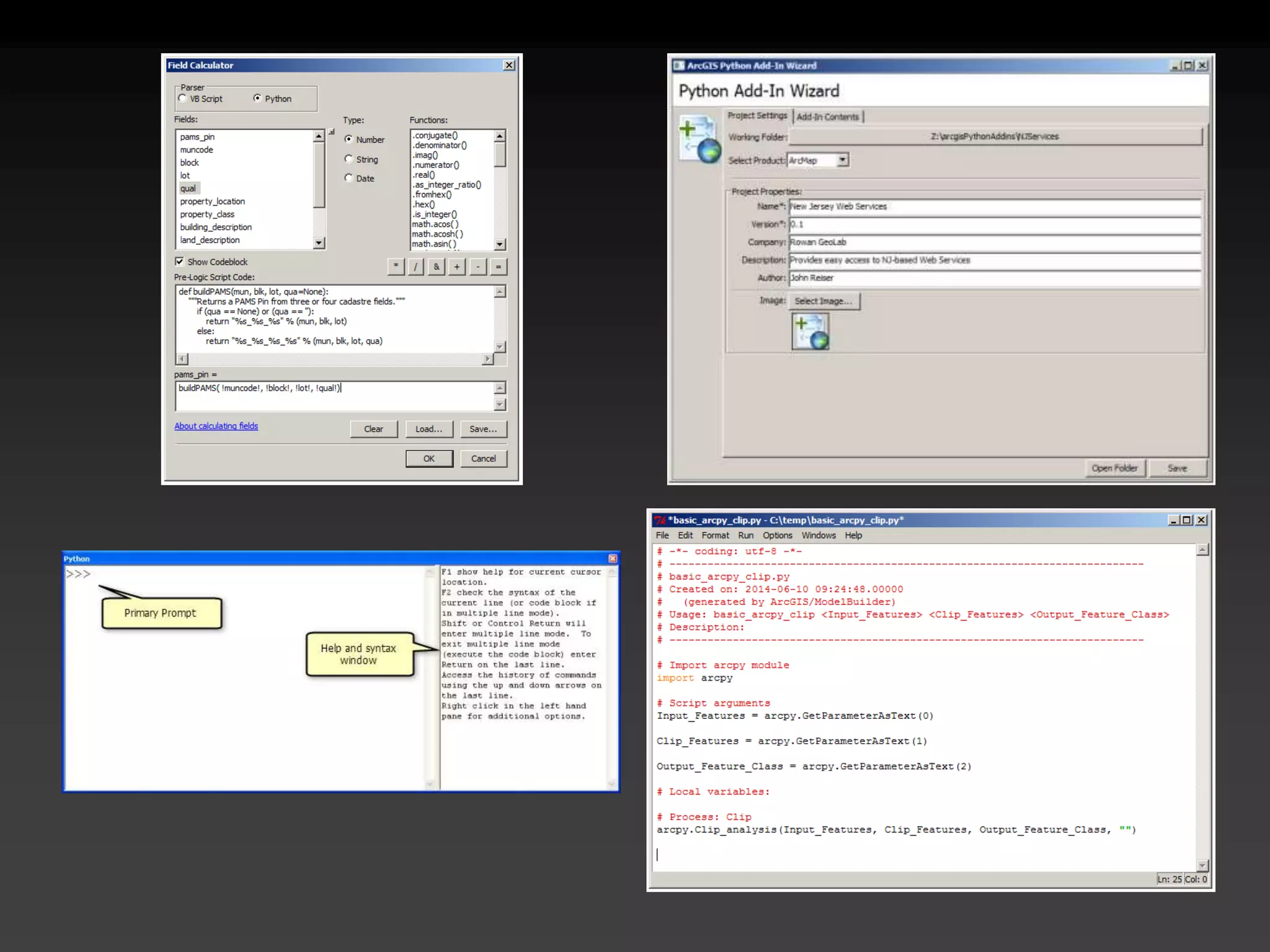
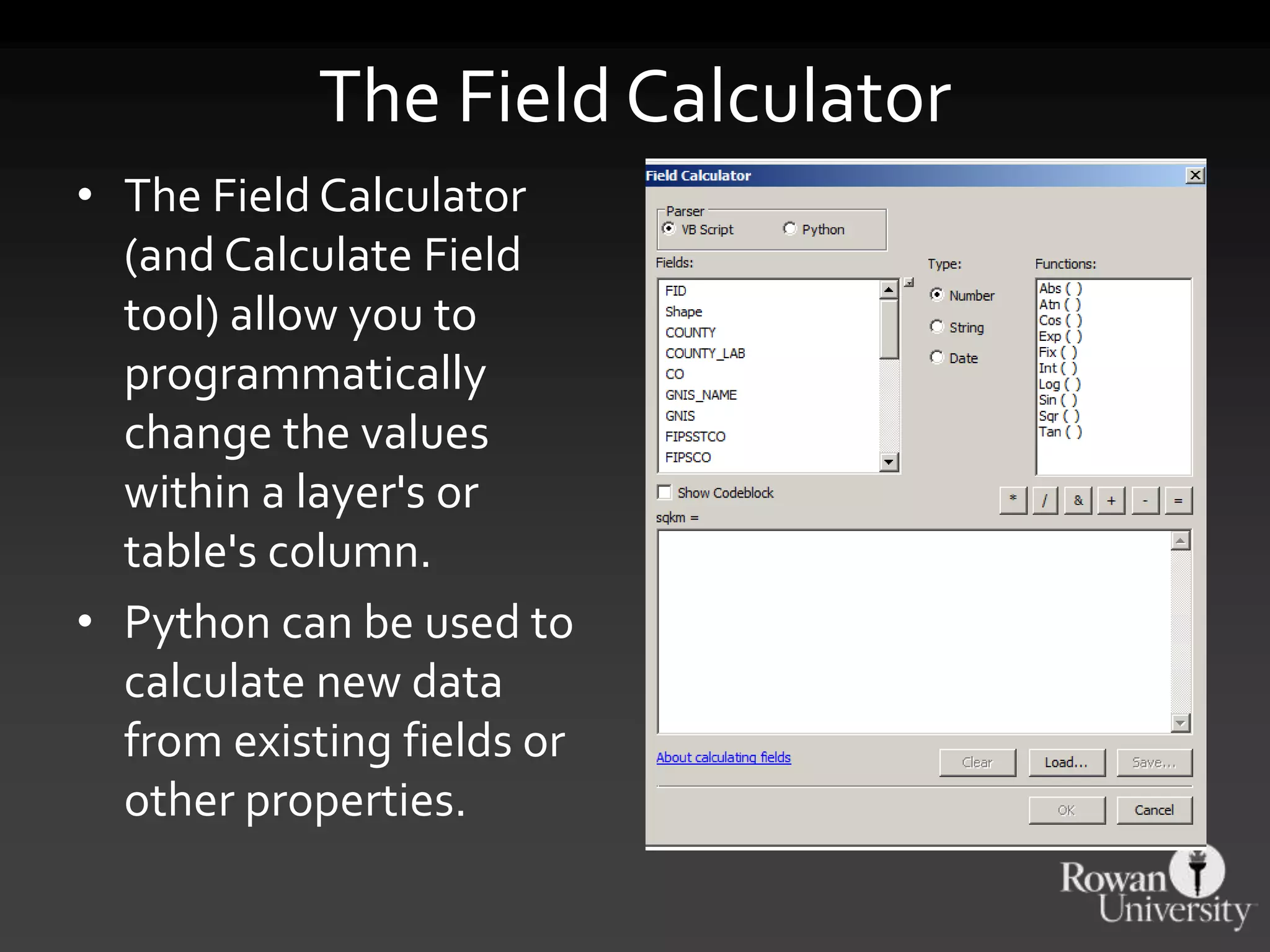
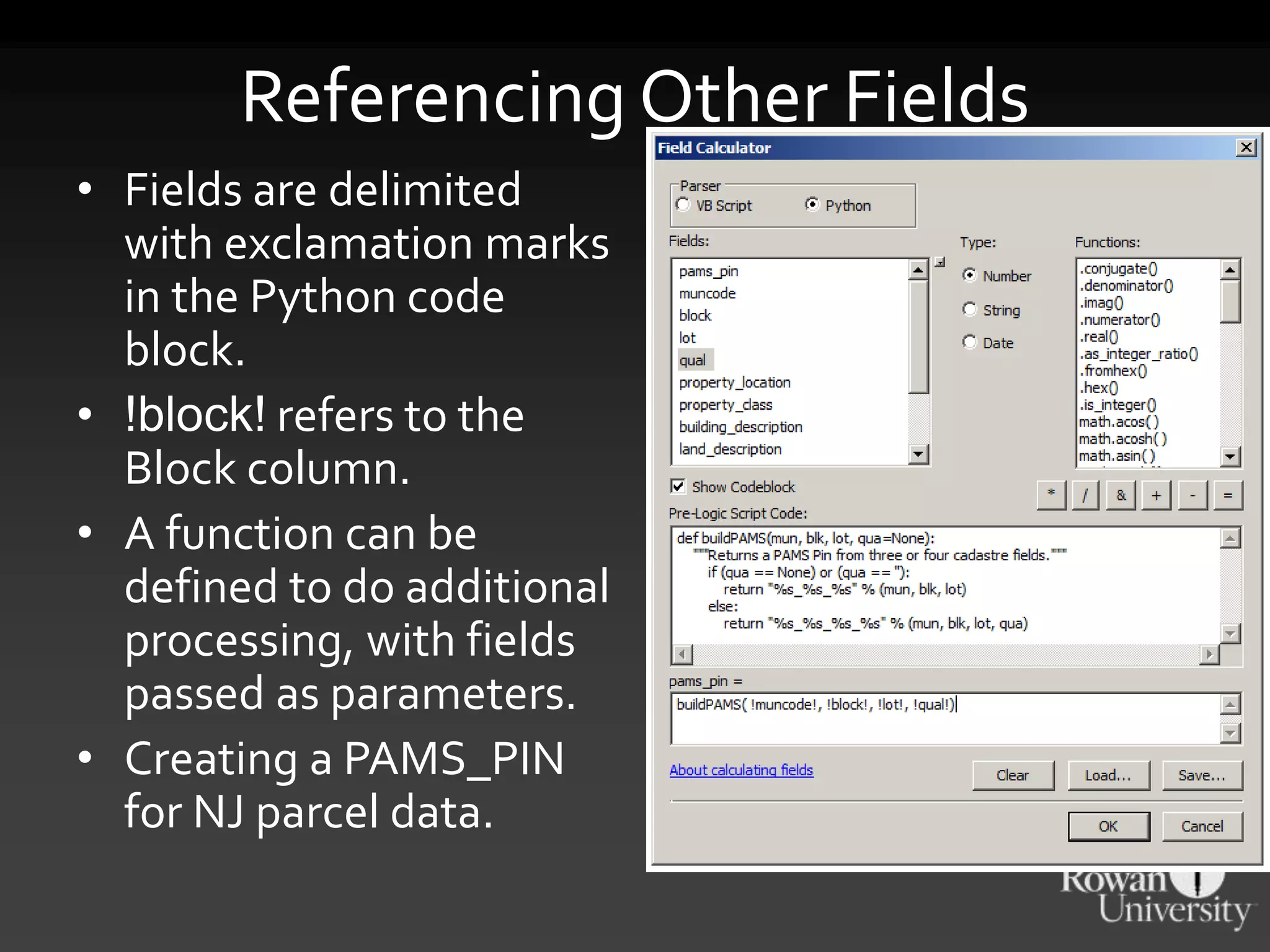
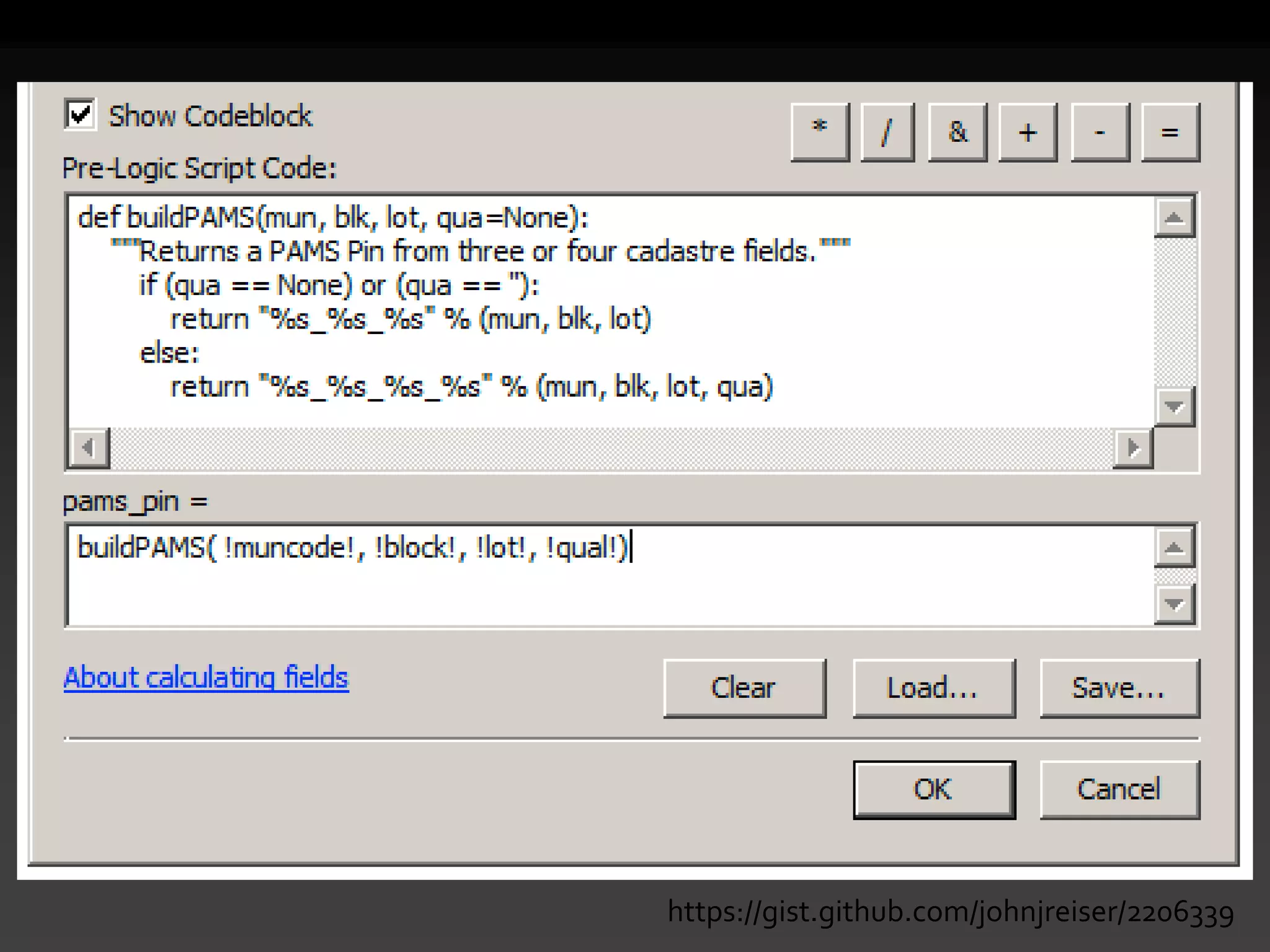
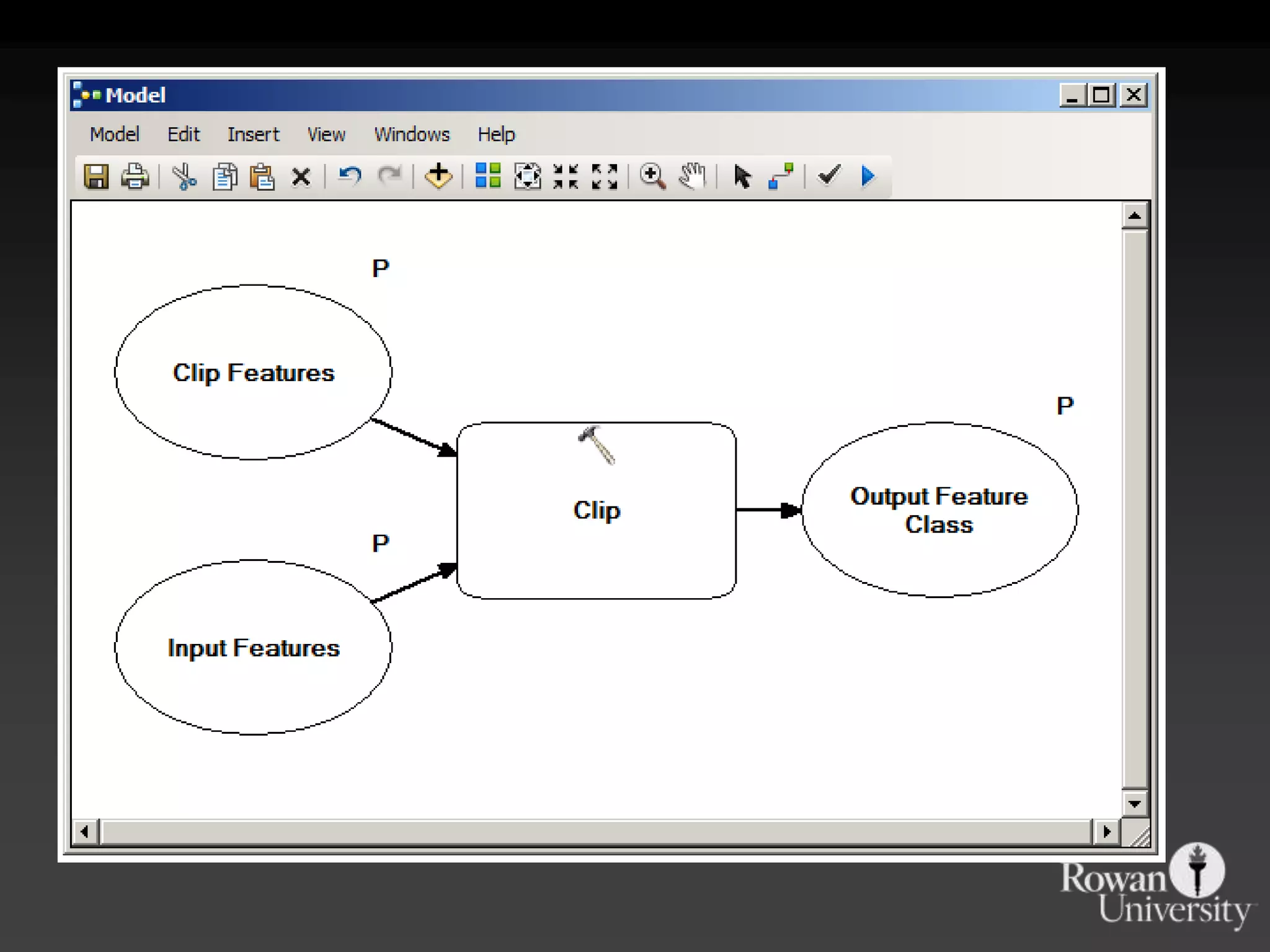
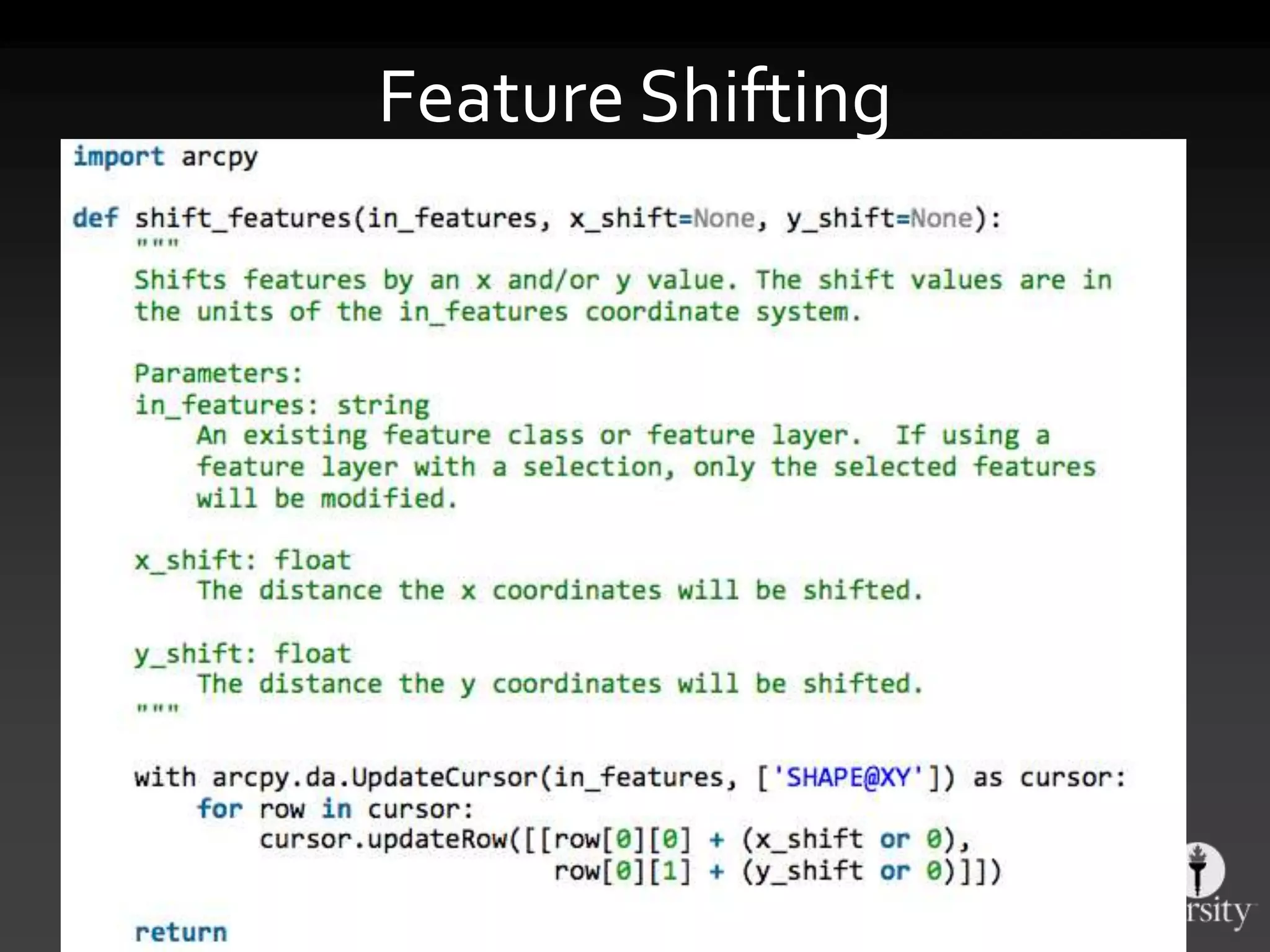
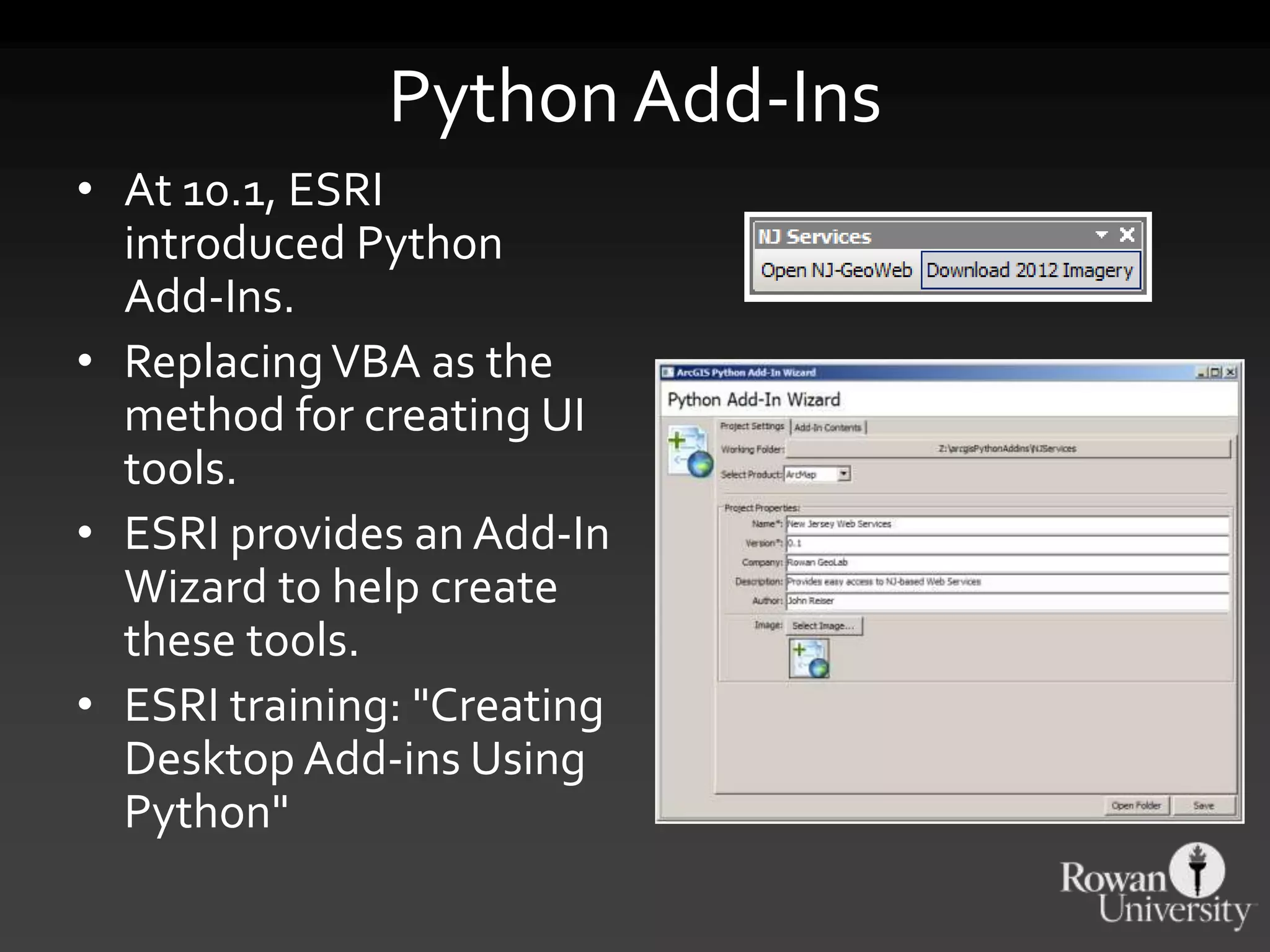
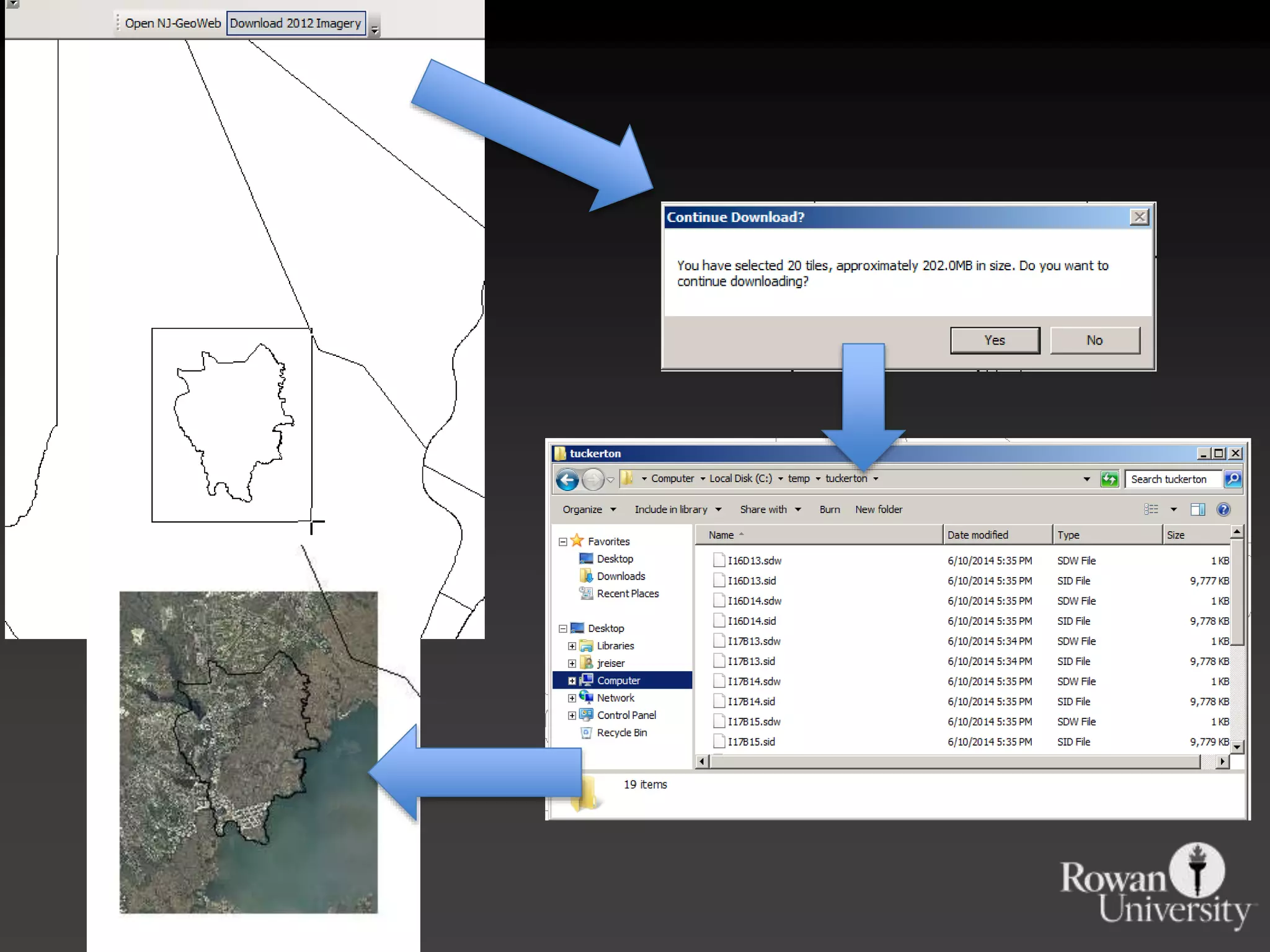
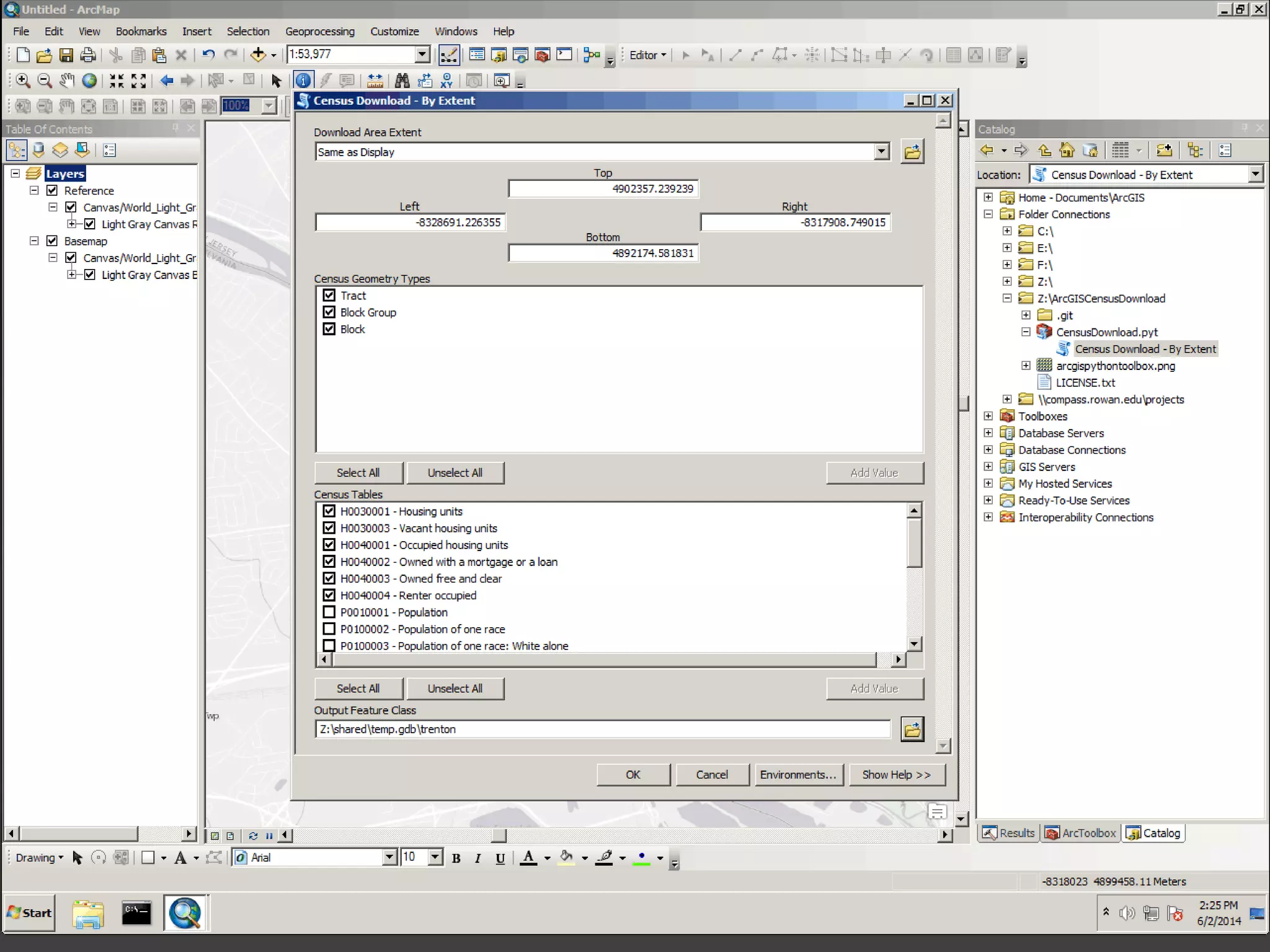
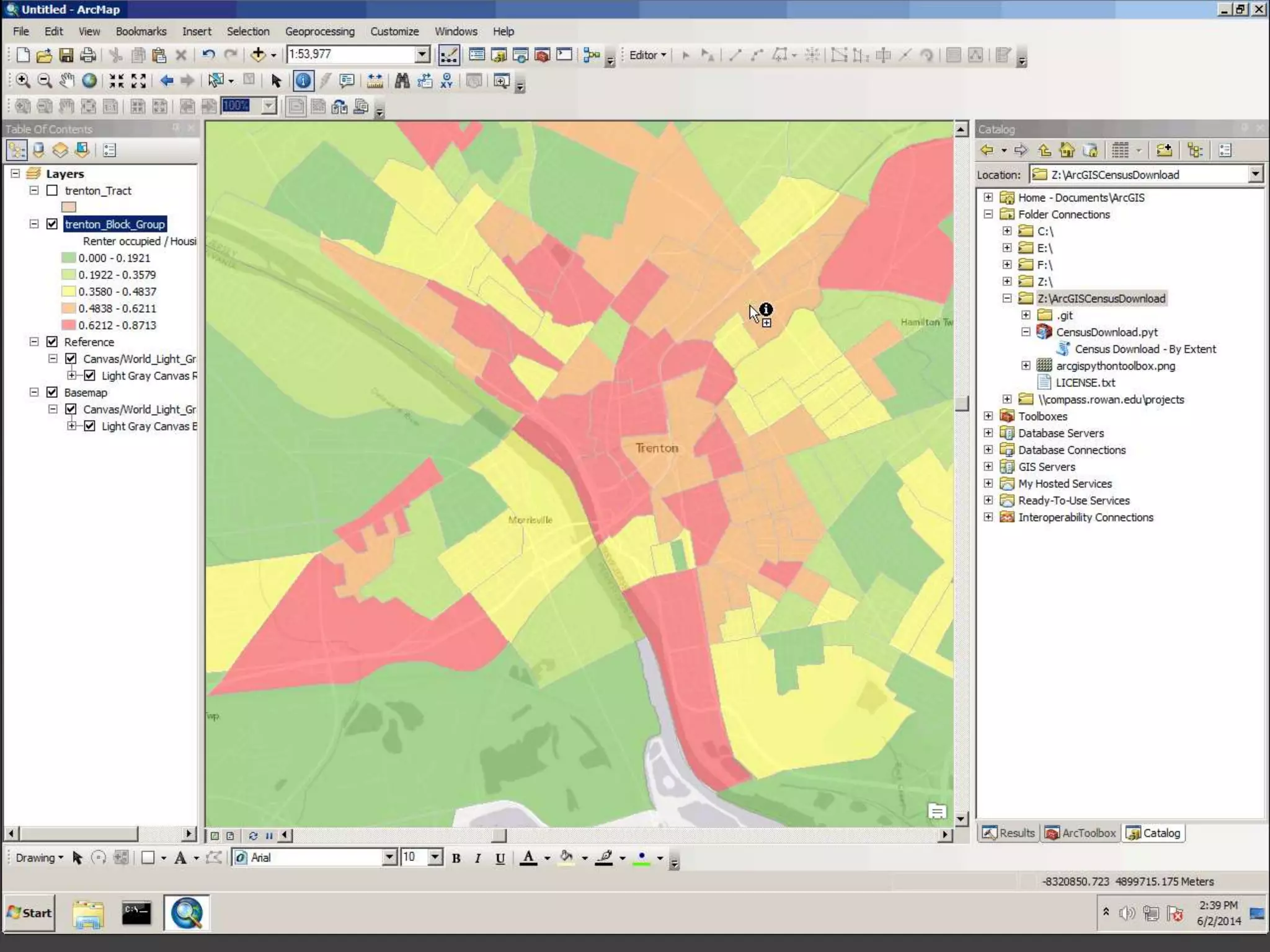
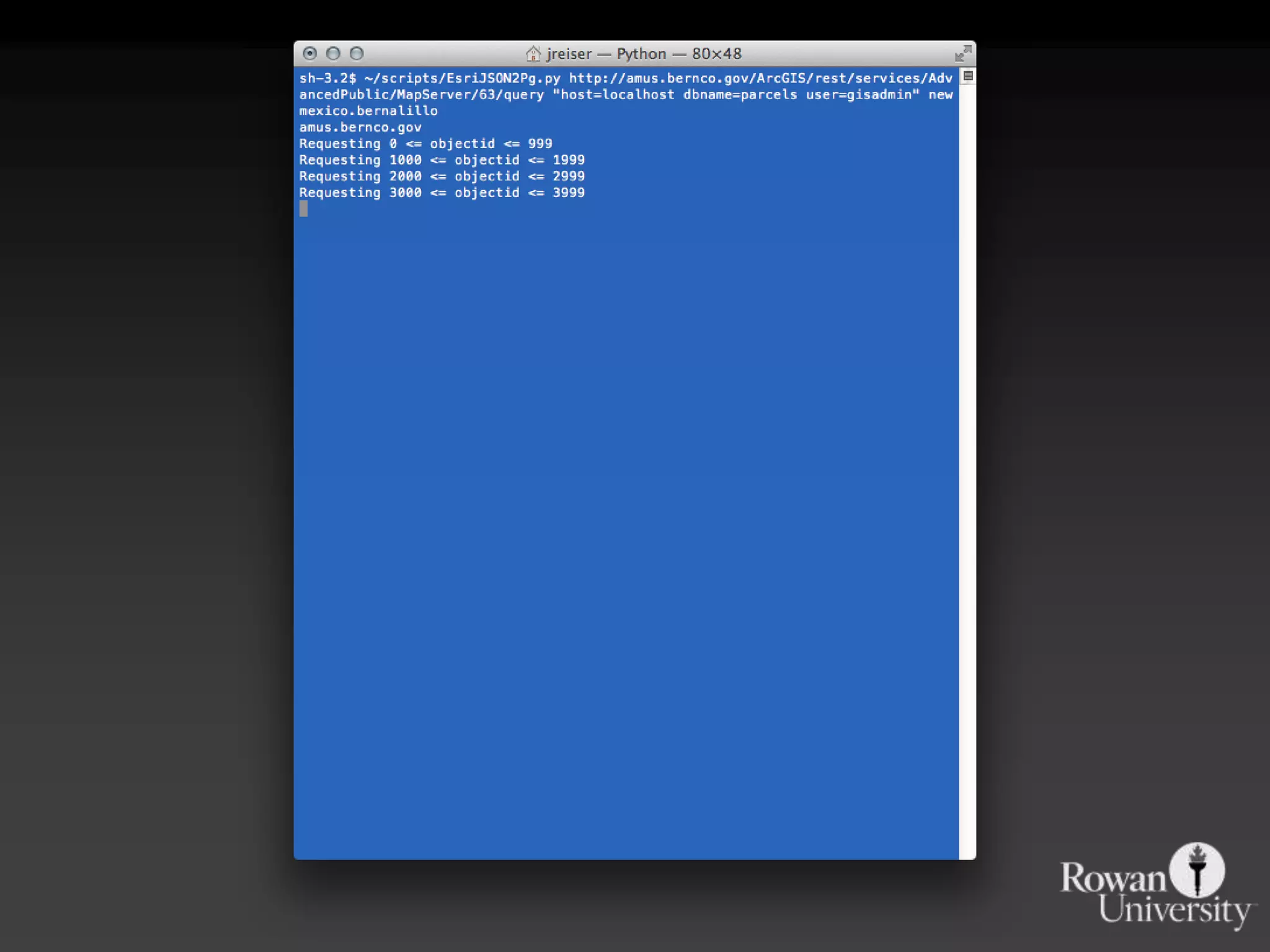
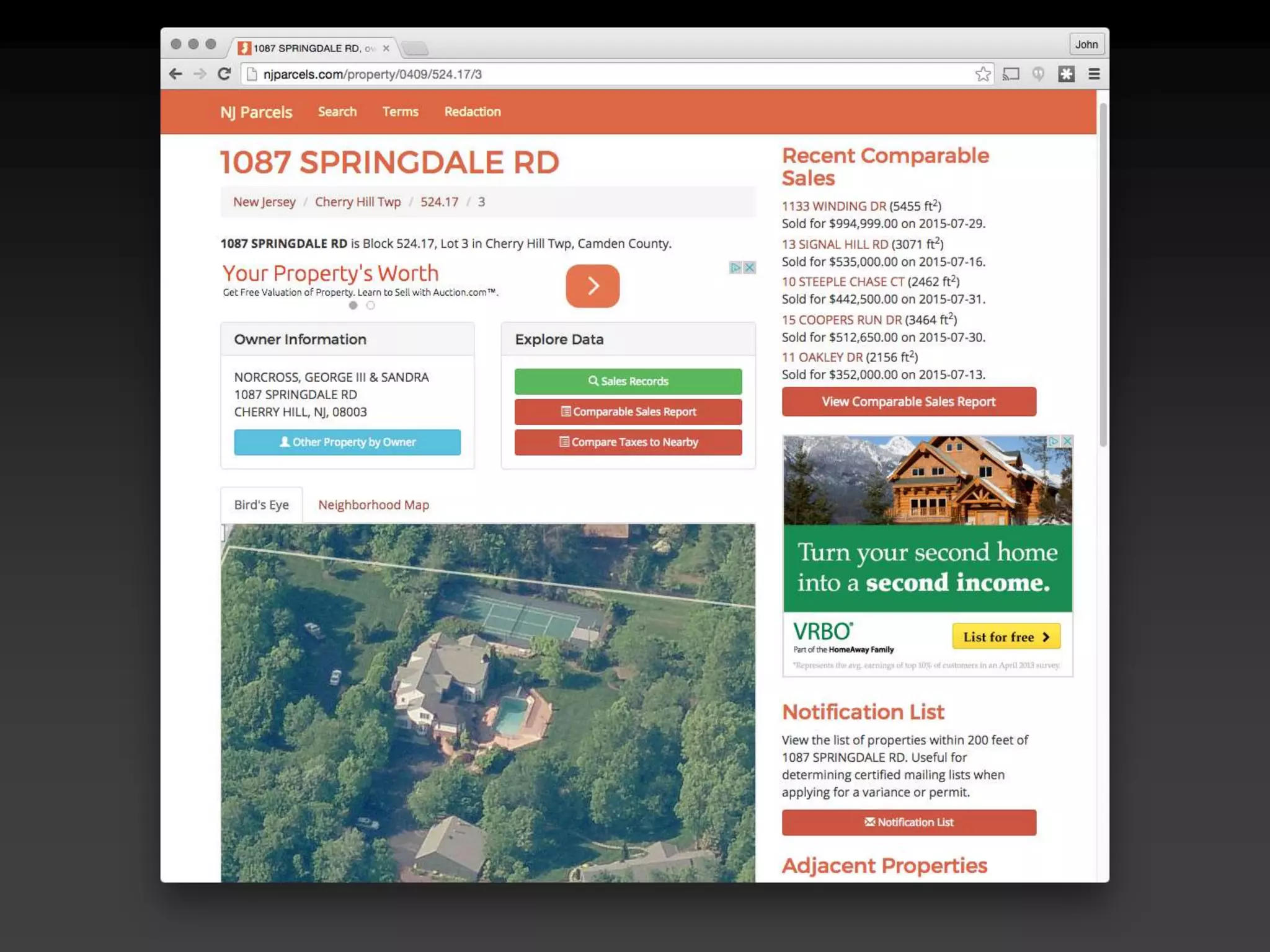
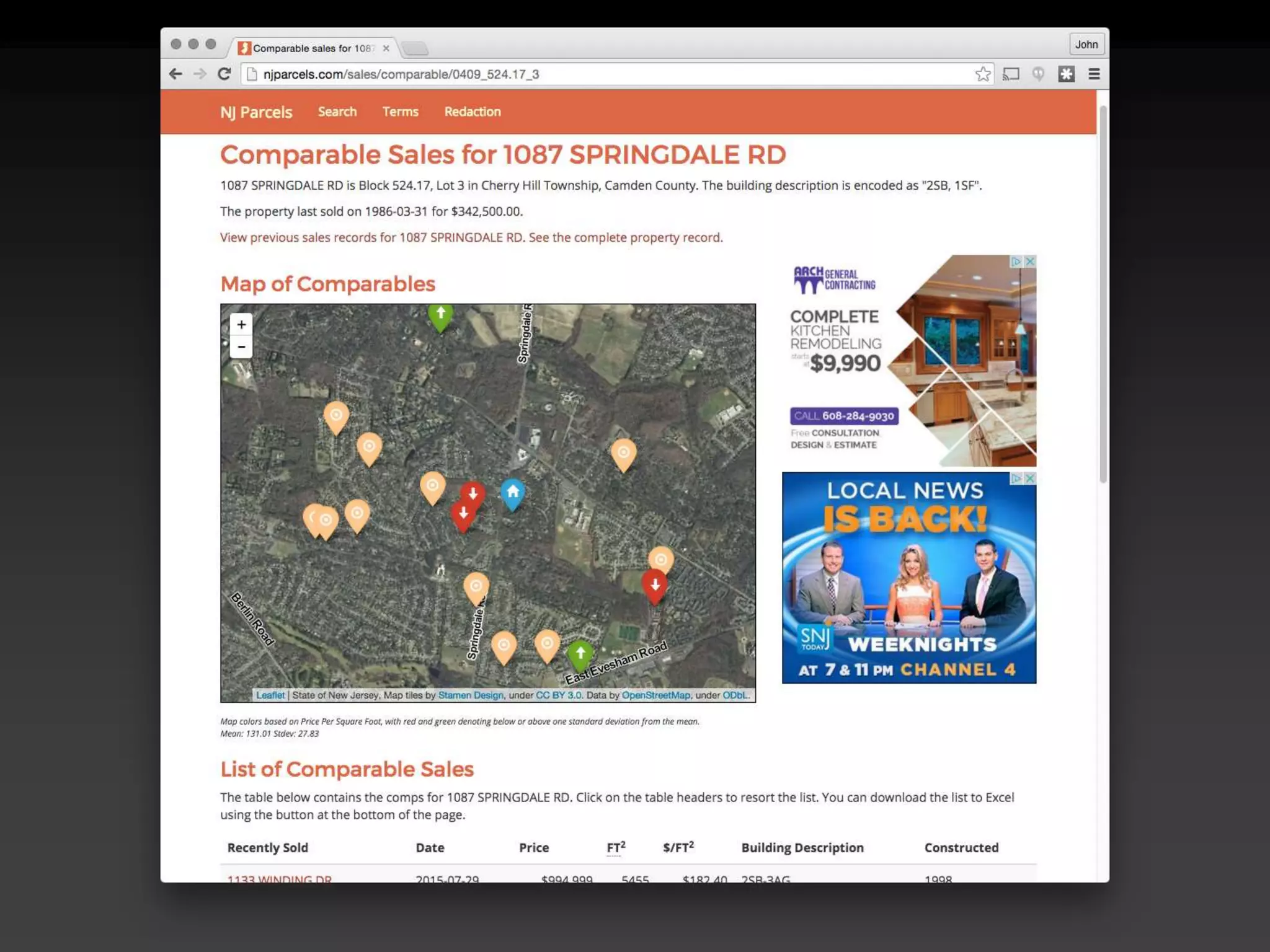
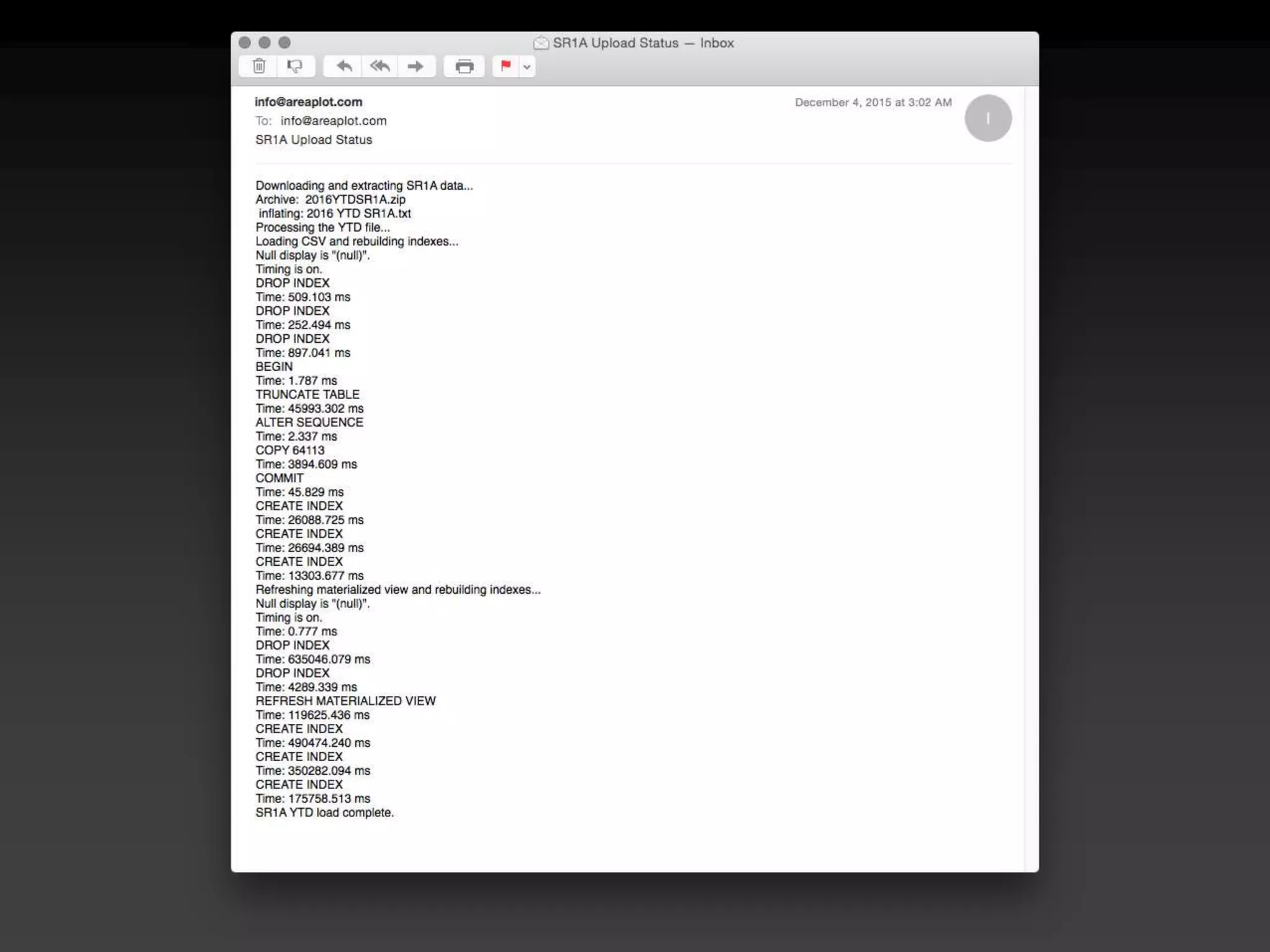
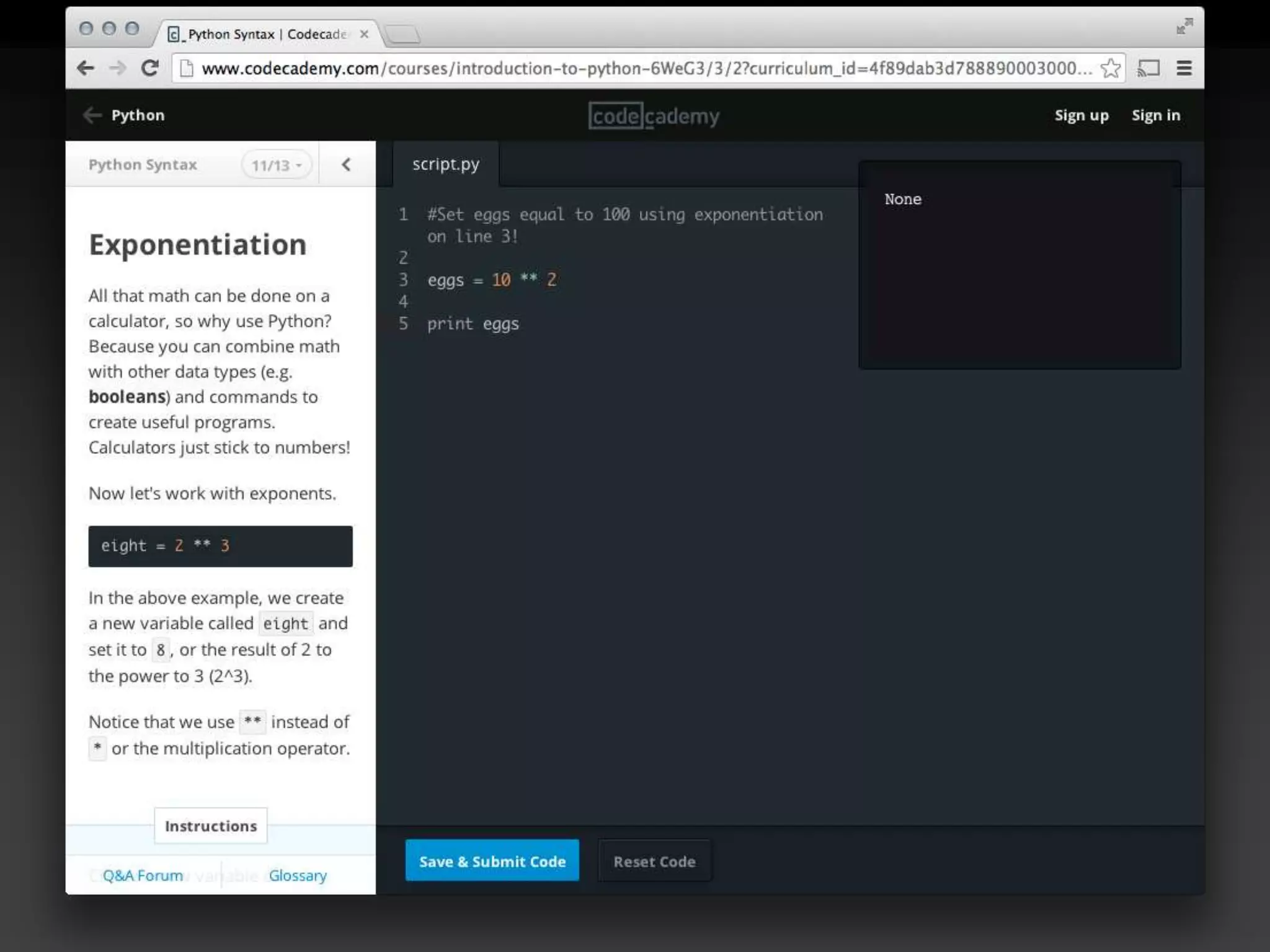
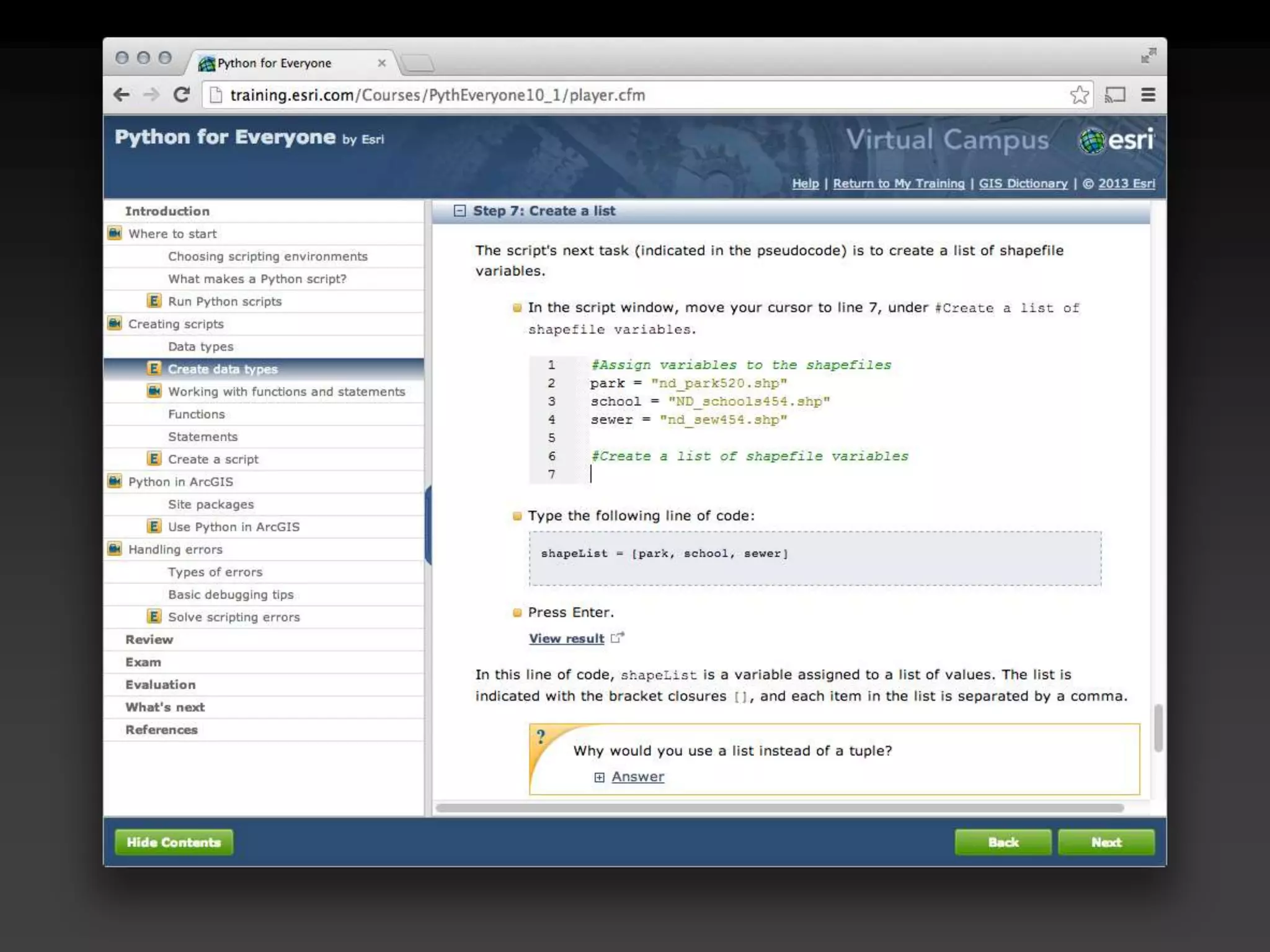
The document discusses the advantages of using Python with GIS, particularly ArcGIS, for automation and enhanced functionality. It highlights the integration of Python within ArcGIS, including field calculations, custom tools, and the ability to extend ArcGIS capabilities. Additionally, it covers topics like ETL processes, working with databases, and resources for learning Python in the context of GIS.