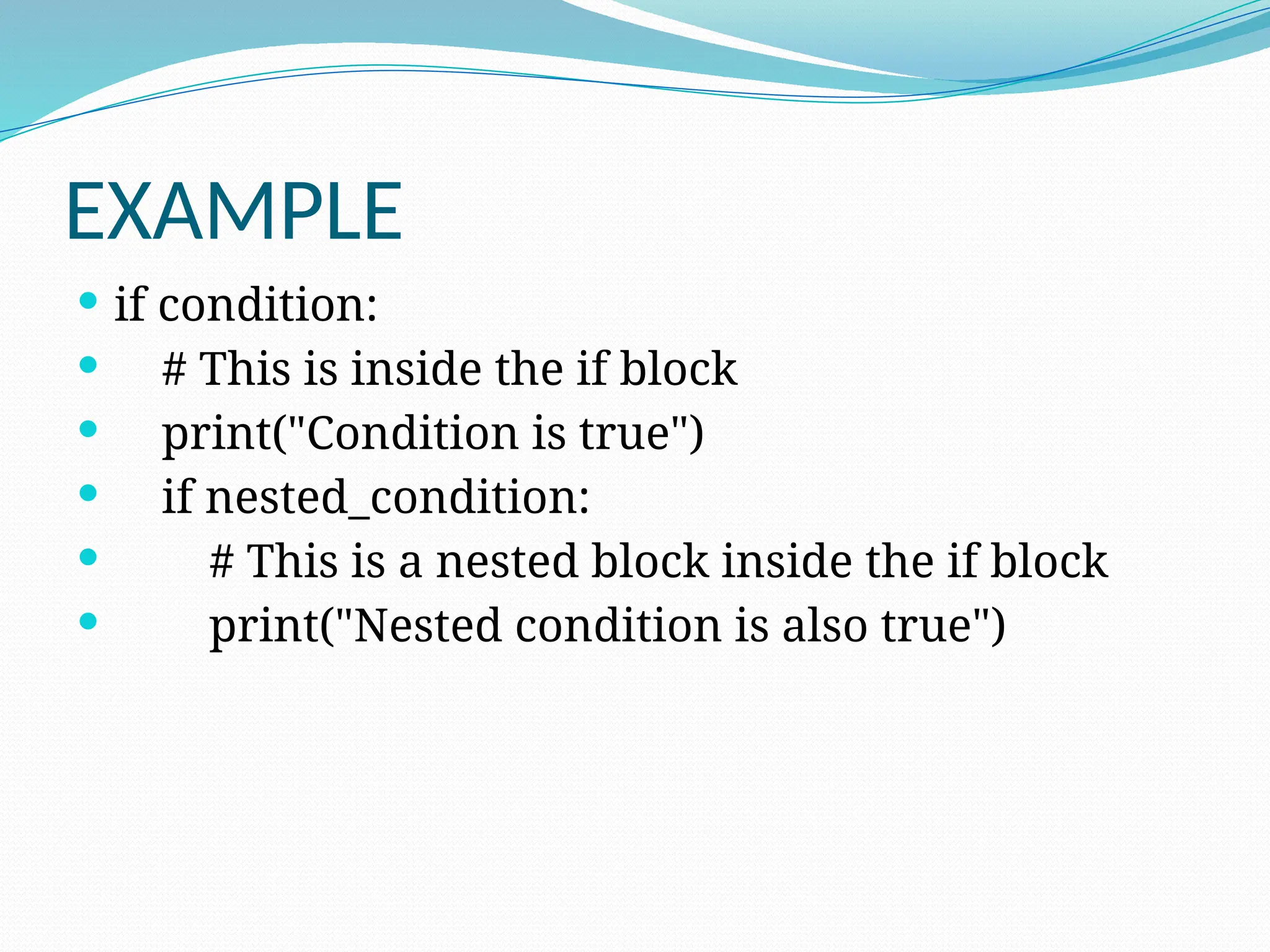
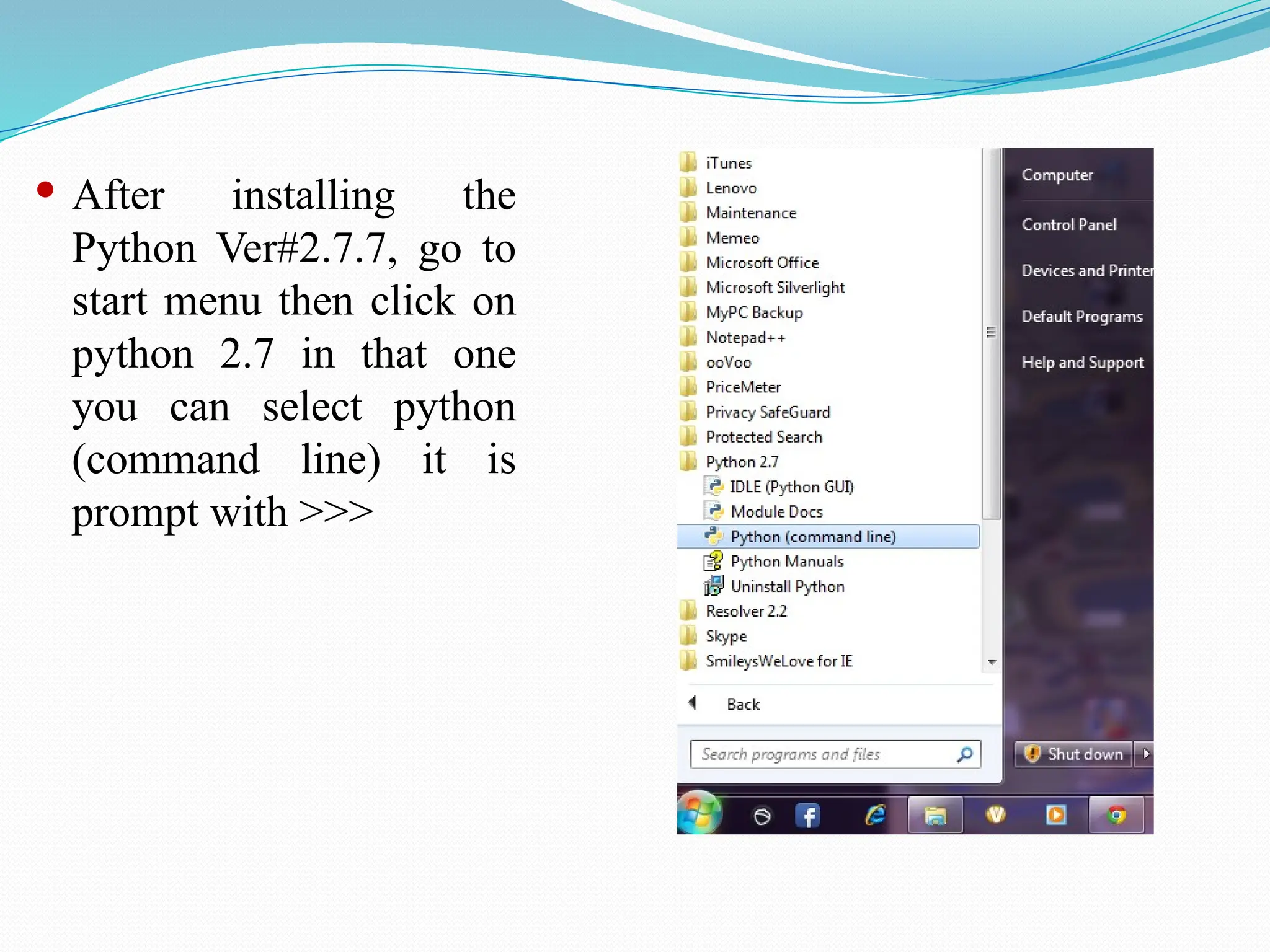
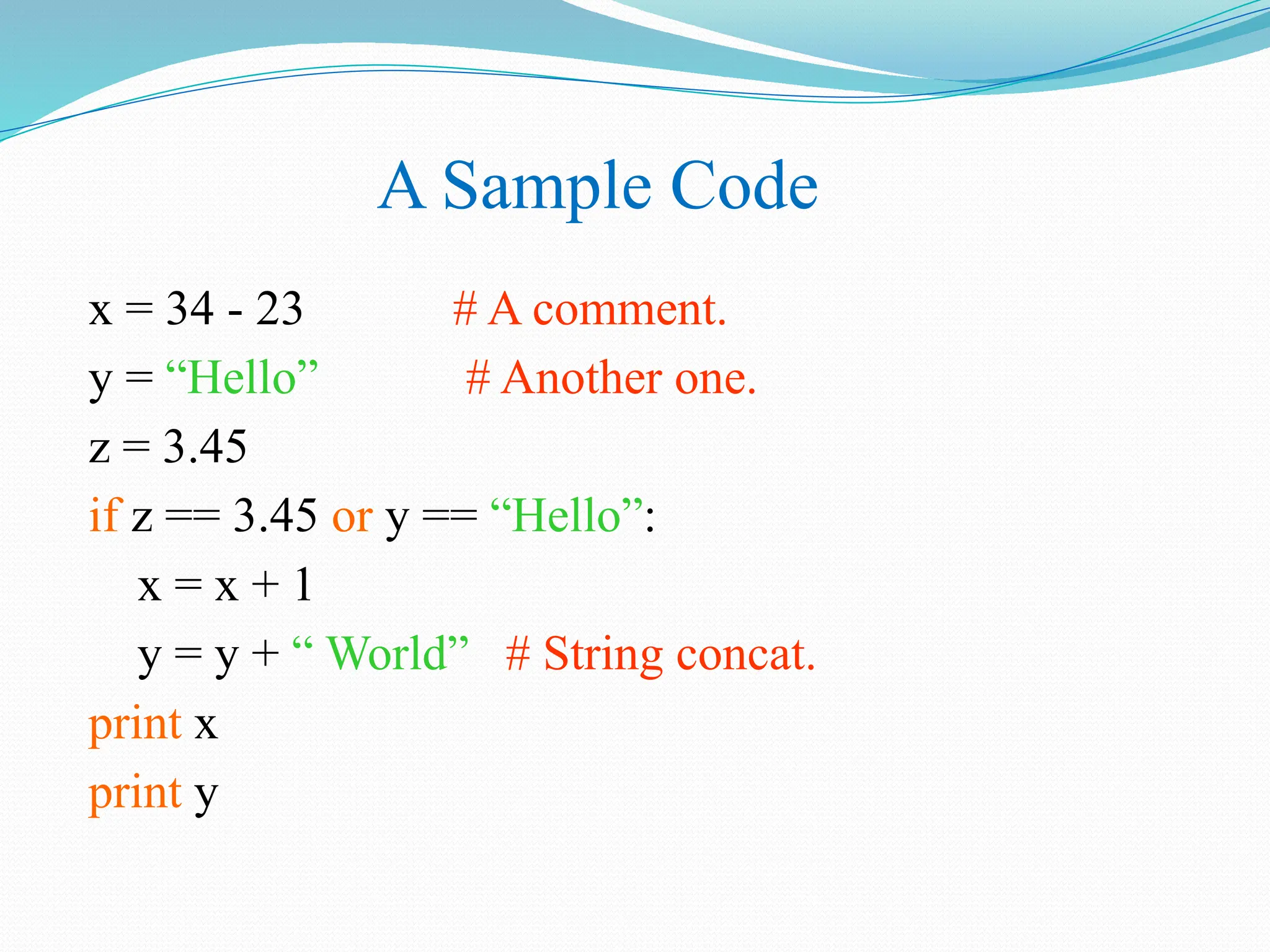
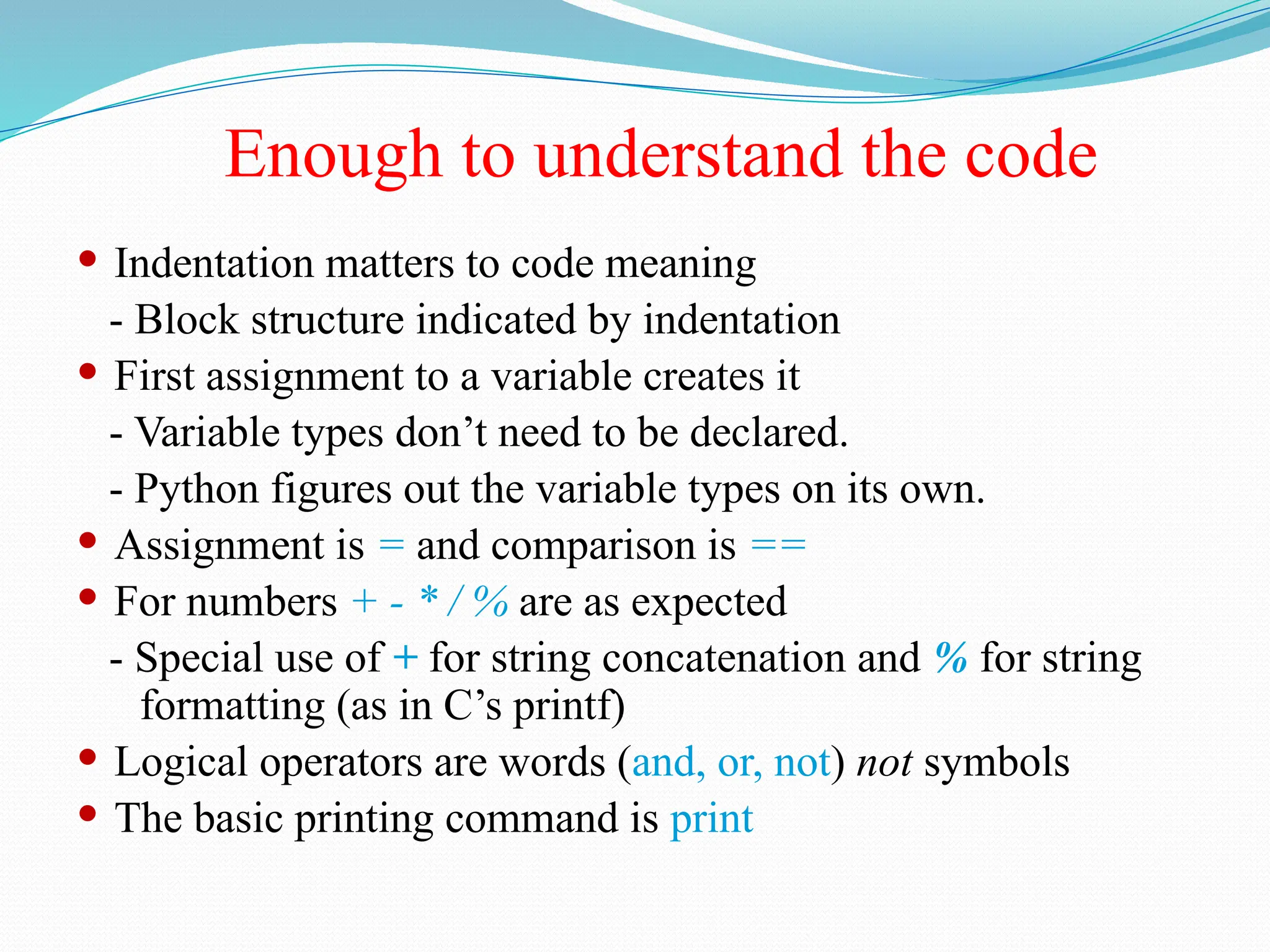
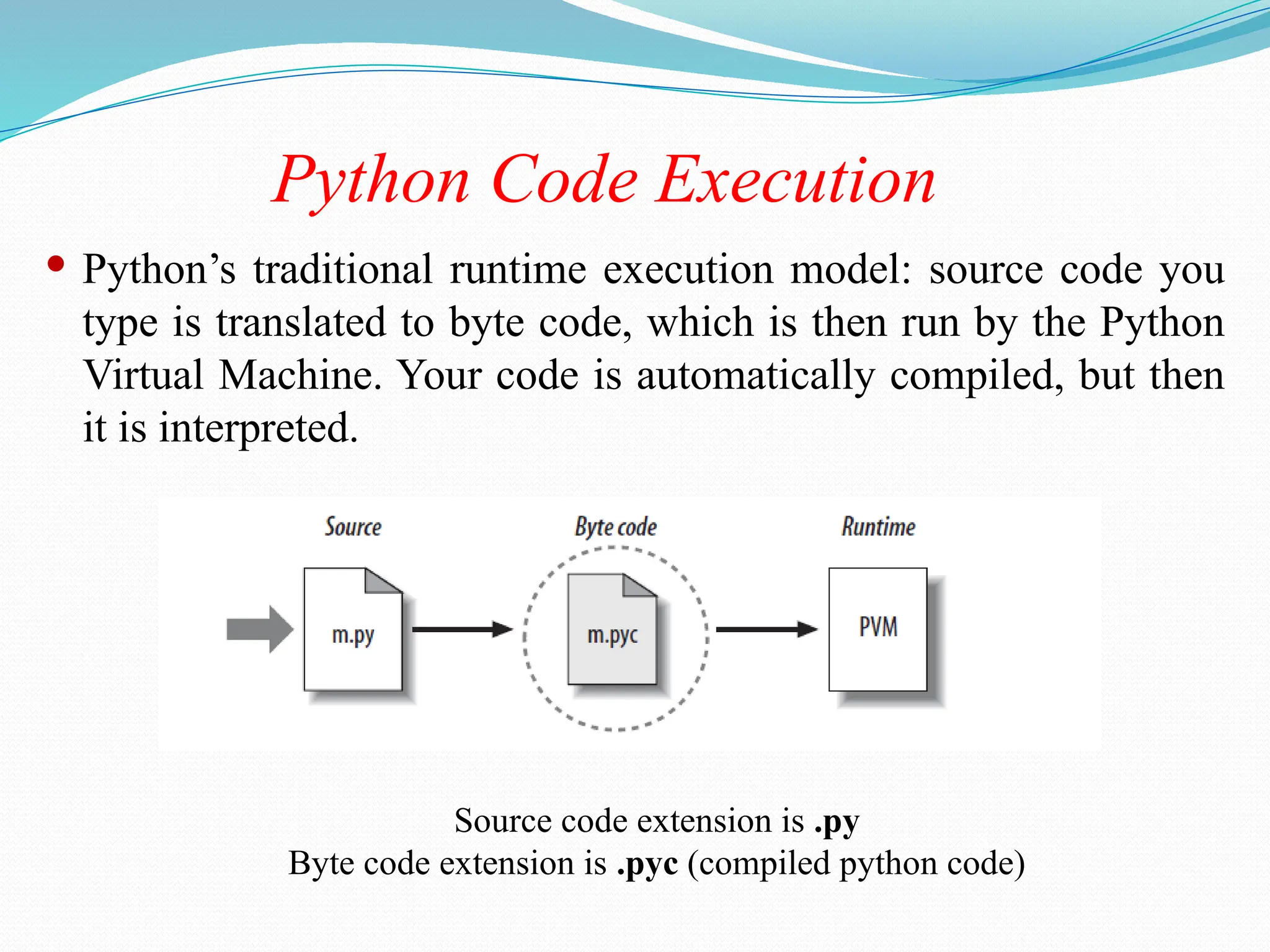
The document provides an overview of Python, discussing its definition as a general-purpose programming and scripting language, its history, and the reasons for its popularity. Key features include its simplicity, readability, versatility, and extensive libraries, making it suitable for various applications like web development, data science, and automation. The document also highlights how to install Python, its real-world usage by companies, and examples of Python code execution.




![Why was python created?
"My original motivation for creating Python was
the perceived need for a higher level language in
the Amoeba [Operating Systems] project.
I realized that the development of system
administration utilities in C was taking too long.
Moreover, doing these things in the Bourne shell
wouldn't work for a variety of reasons. ...
So, there was a need for a language that would
bridge the gap between C and the shell”
- Guido Van Rossum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-240916074849-57dd5510/75/python-programminig-and-introduction-pptx-5-2048.jpg)








![Running Python
Once you're inside the Python interpreter, type in commands at will.
• Examples:
>>> print 'Hello world'
Hello world
# Relevant output is displayed on subsequent lines without the >>>
symbol
>>> x = [0,1,2]
# Quantities stored in memory are not displayed by default
>>> x
# If a quantity is stored in memory, typing its name will display it
[0,1,2]
>>> 2+3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-240916074849-57dd5510/75/python-programminig-and-introduction-pptx-19-2048.jpg)