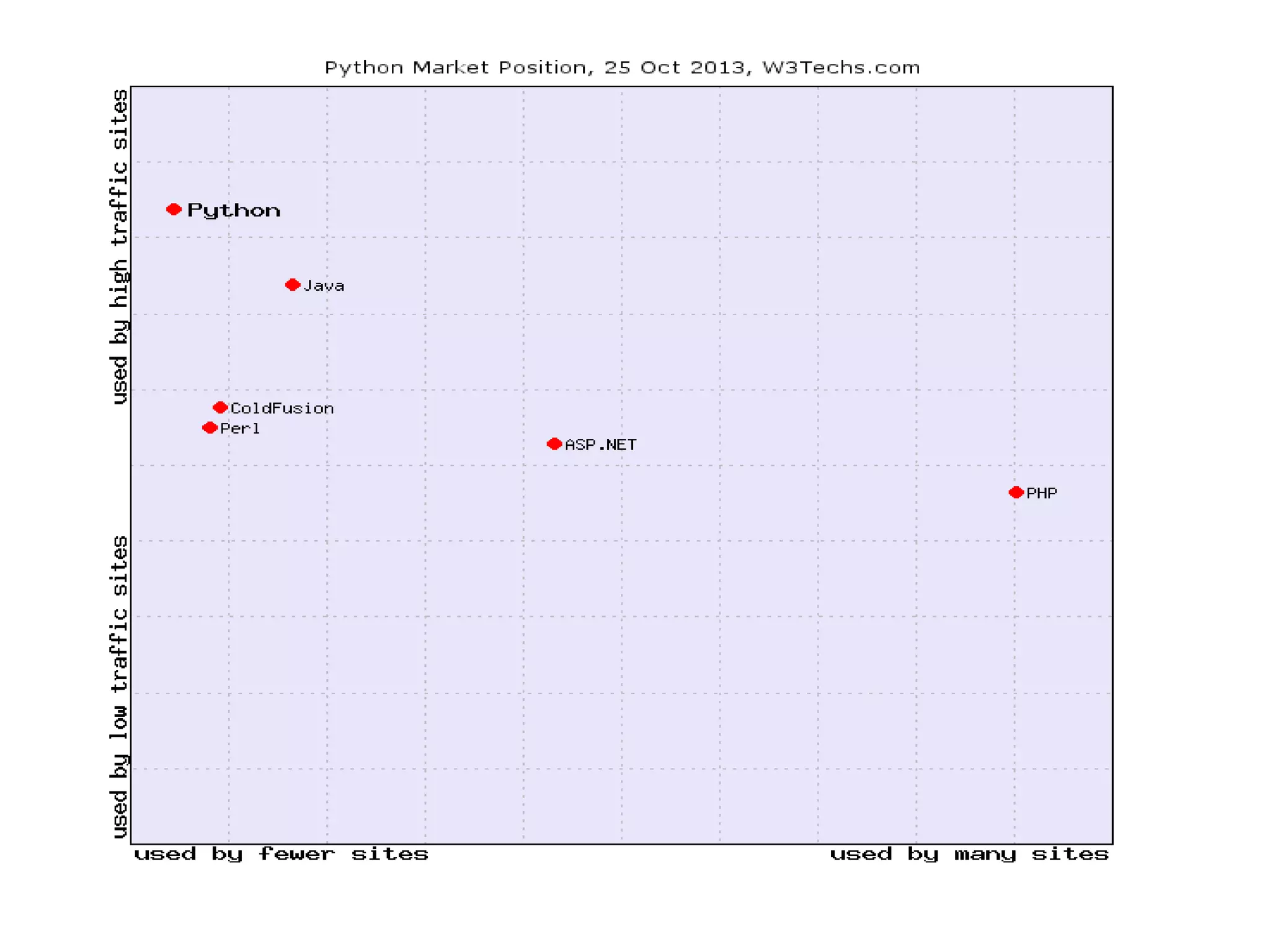
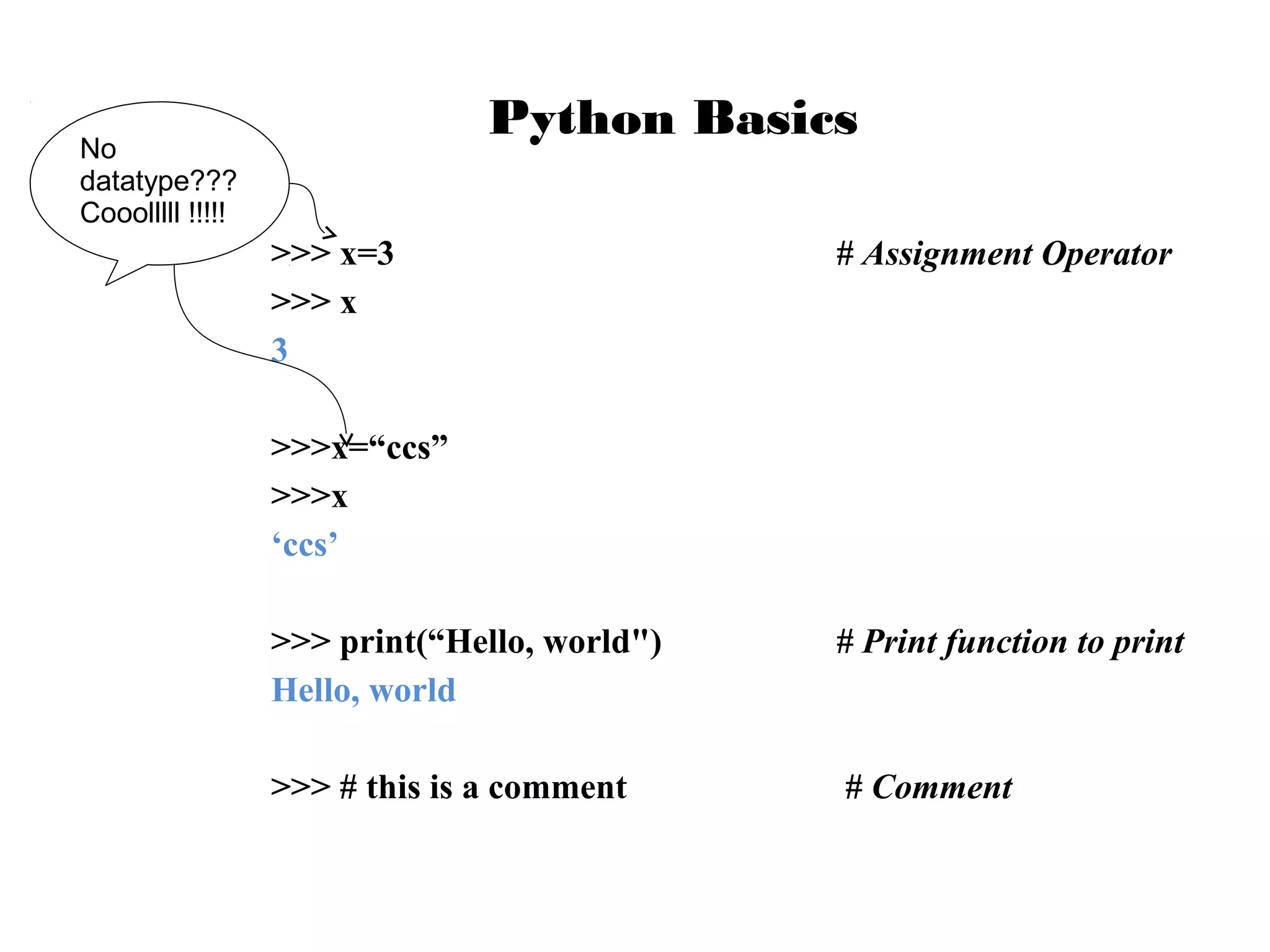
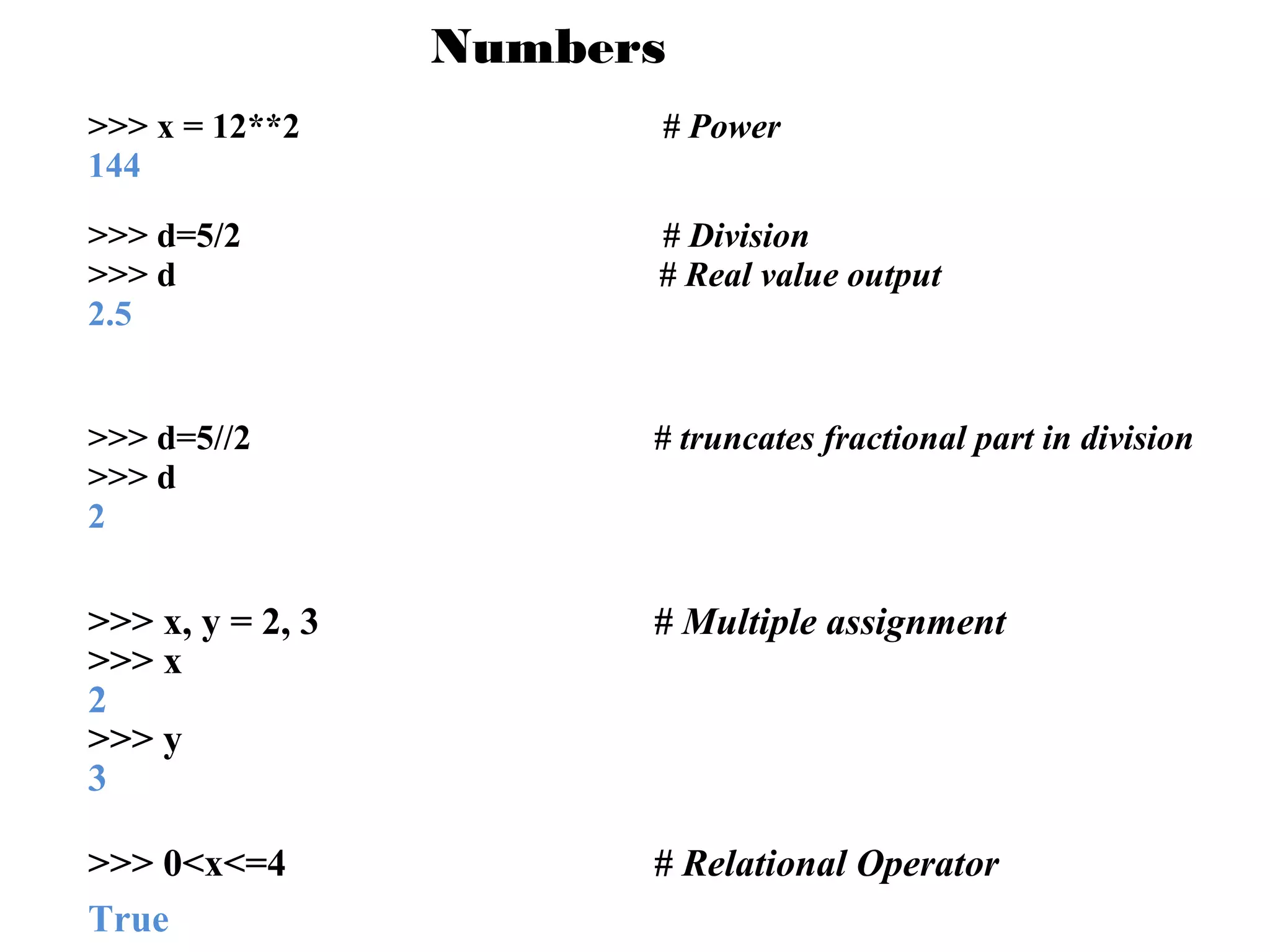
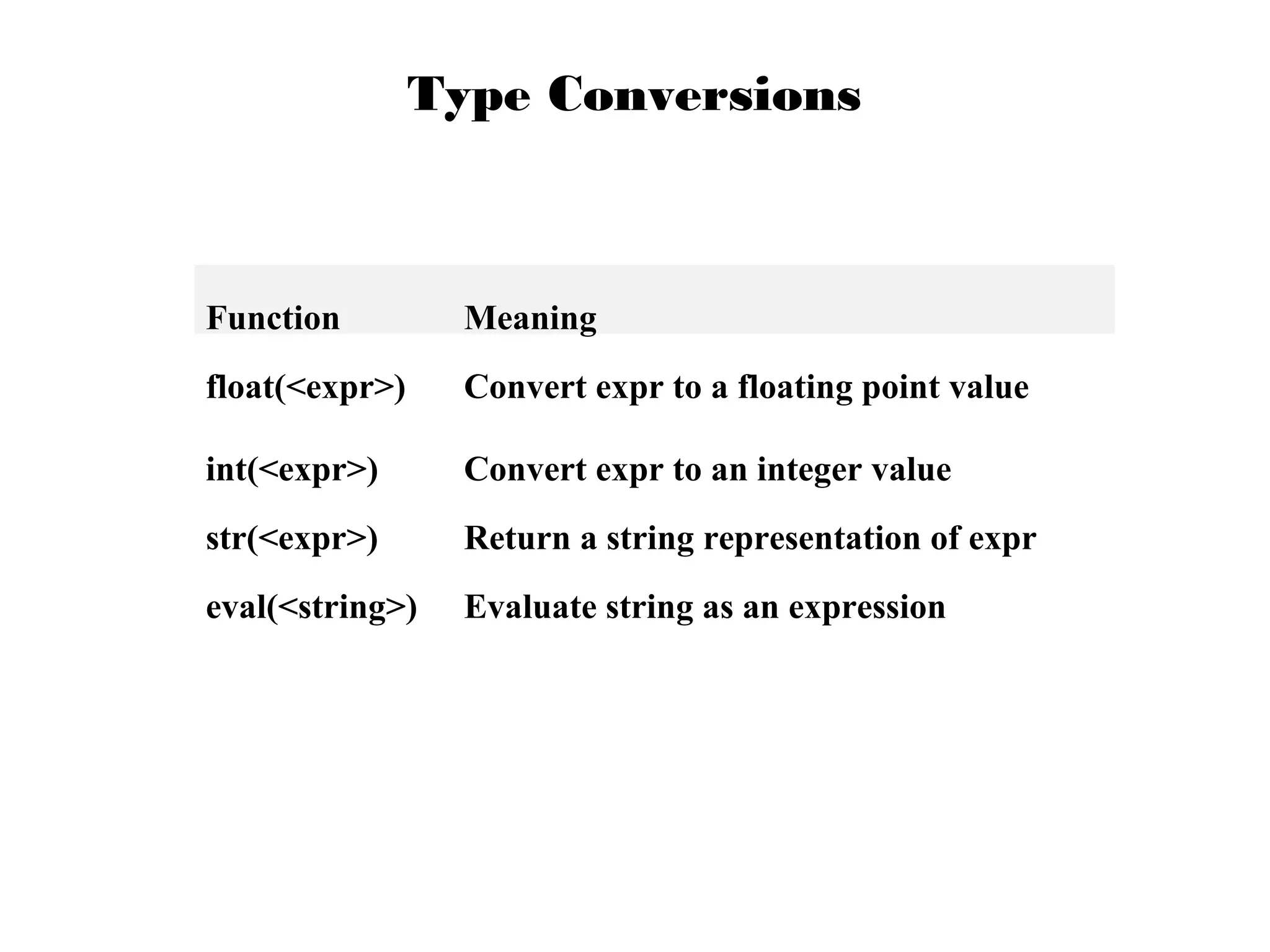
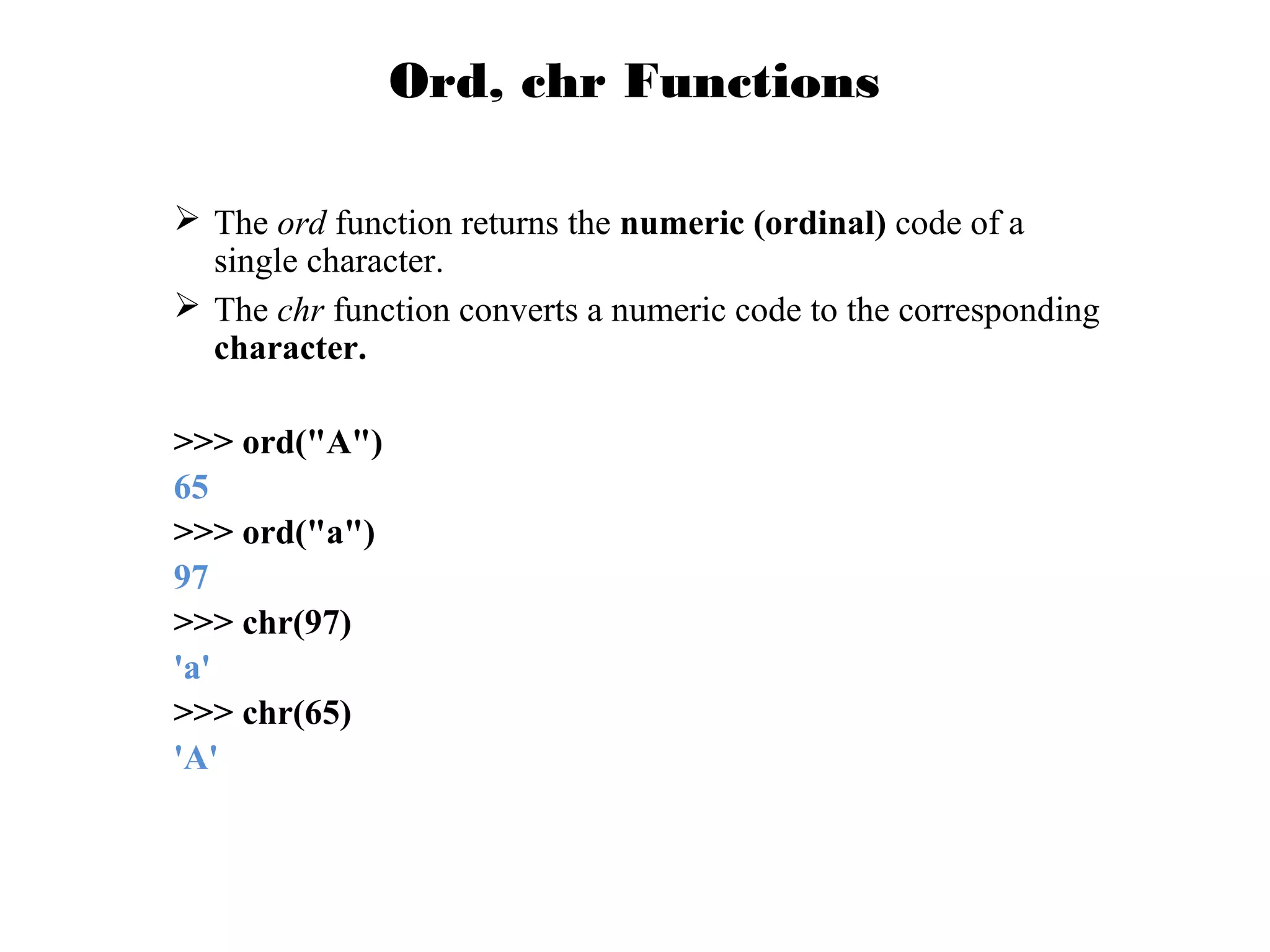
This document provides examples of popular Python usage and success stories, basics of the Python language like variables, data types, operators, control flow and functions. It lists companies that use Python like Google, YouTube, NASA, CIA. It also gives examples of basic Python concepts like variables, strings, numbers, operators, functions and control structures.





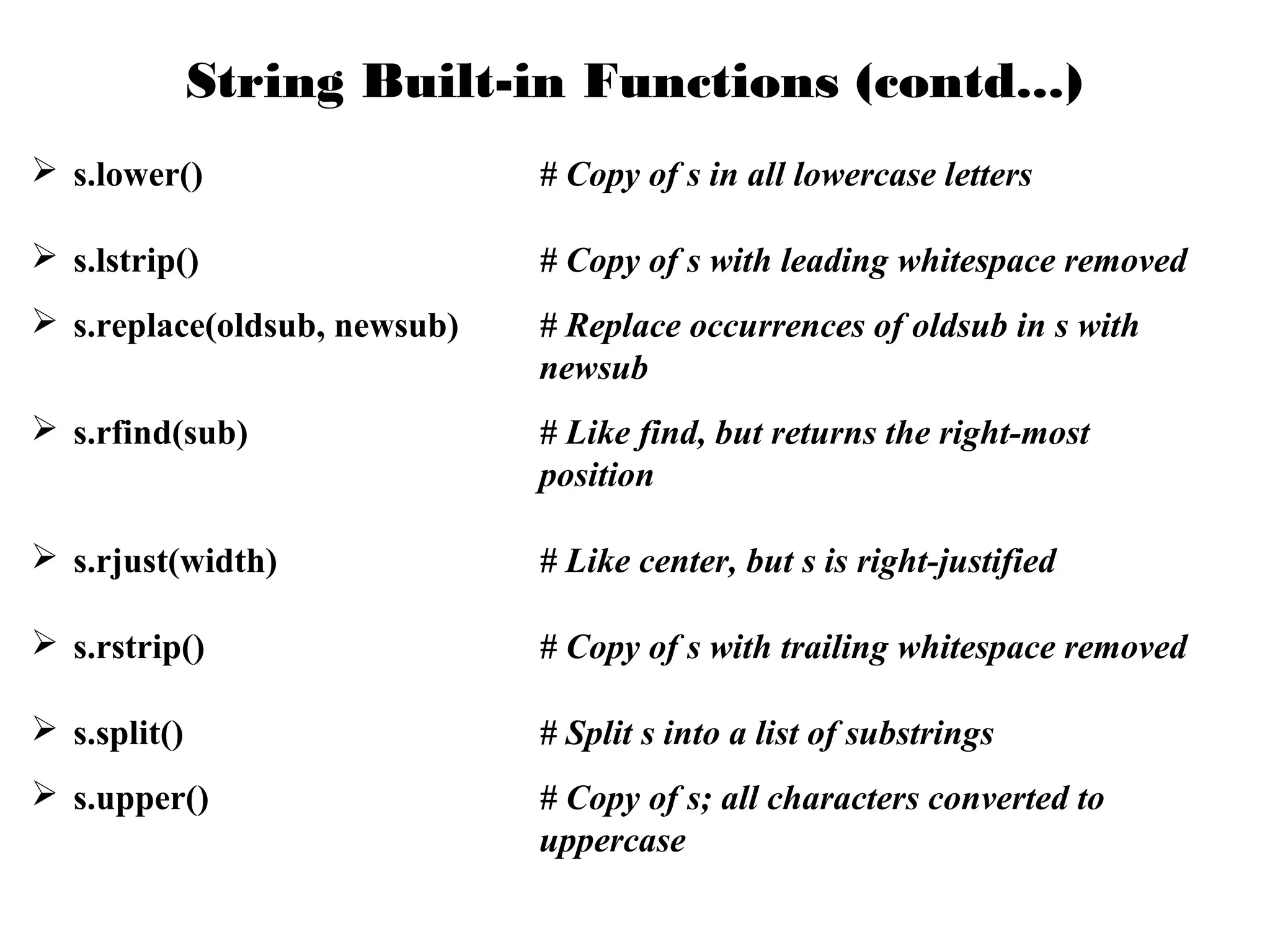
![String Operations
>>>"hello"+"world"
# concatenation
"helloworld"
>>>"hello"*3
# repetition
"hellohellohello“
>>>"hello"[0]
# indexing
"h"
>>>"hello"[-1]
# (from end)
"o”
>>>"hello"[1:4]
# slicing
"ell"
>>> len("hello")
# size
5
>>> "hello" < "jello"
True
# comparison](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopintrostring1-131026124003-phpapp02/75/Python-workshop-intro_string-1-9-2048.jpg)

![Example String Operations
>>> str=”string”
>>> str[0]
's'
>>> str[-1]
'g'
>>> str[0:]
'string'
>>> str[:-1]
'strin'
>>> len(str)
6
>>> str[:6]
'string'
>>> str[:]
'string'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopintrostring1-131026124003-phpapp02/75/Python-workshop-intro_string-1-11-2048.jpg)
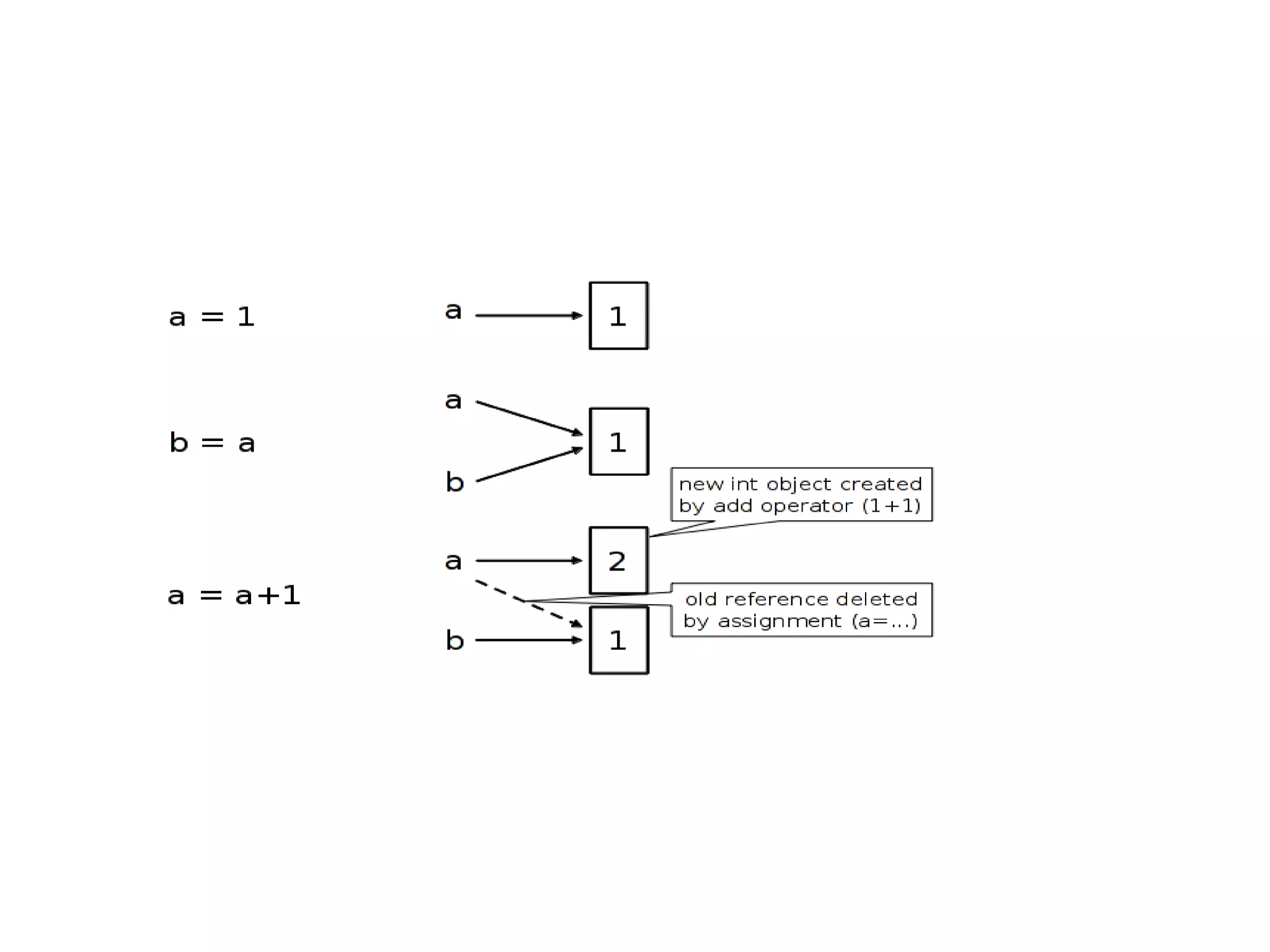
![String Immutability
>>> l1 = “Demo String”
>>> l2 = l1
# Both l1, l2 will refer to same reference,
l1
>>> l2 = l1[:]
# Independent copies, two references](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopintrostring1-131026124003-phpapp02/75/Python-workshop-intro_string-1-12-2048.jpg)


![Example
Given the month number, print the name of month. Names of all months are contained
in a string.
>>>months = "JanFebMarAprMayJunJulAugSepOctNovDec"
>>>n = eval(input("Enter a month number (1-12): "))
>>>pos = (n-1) * 3
>>>monthAbbrev = months[pos:pos+3]
>>>print ("The month abbreviation is", monthAbbrev + ".")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopintrostring1-131026124003-phpapp02/75/Python-workshop-intro_string-1-16-2048.jpg)




![Control Structures
if condition:
statements
while condition:
statements
[elif condition:
statements] ...
else:
for var in sequence:
statements
statements
break
continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopintrostring1-131026124003-phpapp02/75/Python-workshop-intro_string-1-24-2048.jpg)
