InfoQ is a news and community site that attracts 750,000 unique visitors monthly and offers content in multiple languages, including news, articles, videos, interviews, and books. The QCon conference aims to empower software development through knowledge sharing and has drawn over 12,000 delegates since its inception in 2007 across nine cities globally. The emphasis of the document is on software development, reactive programming, and cloud-scale solutions, with several technical references and programming examples included.






![
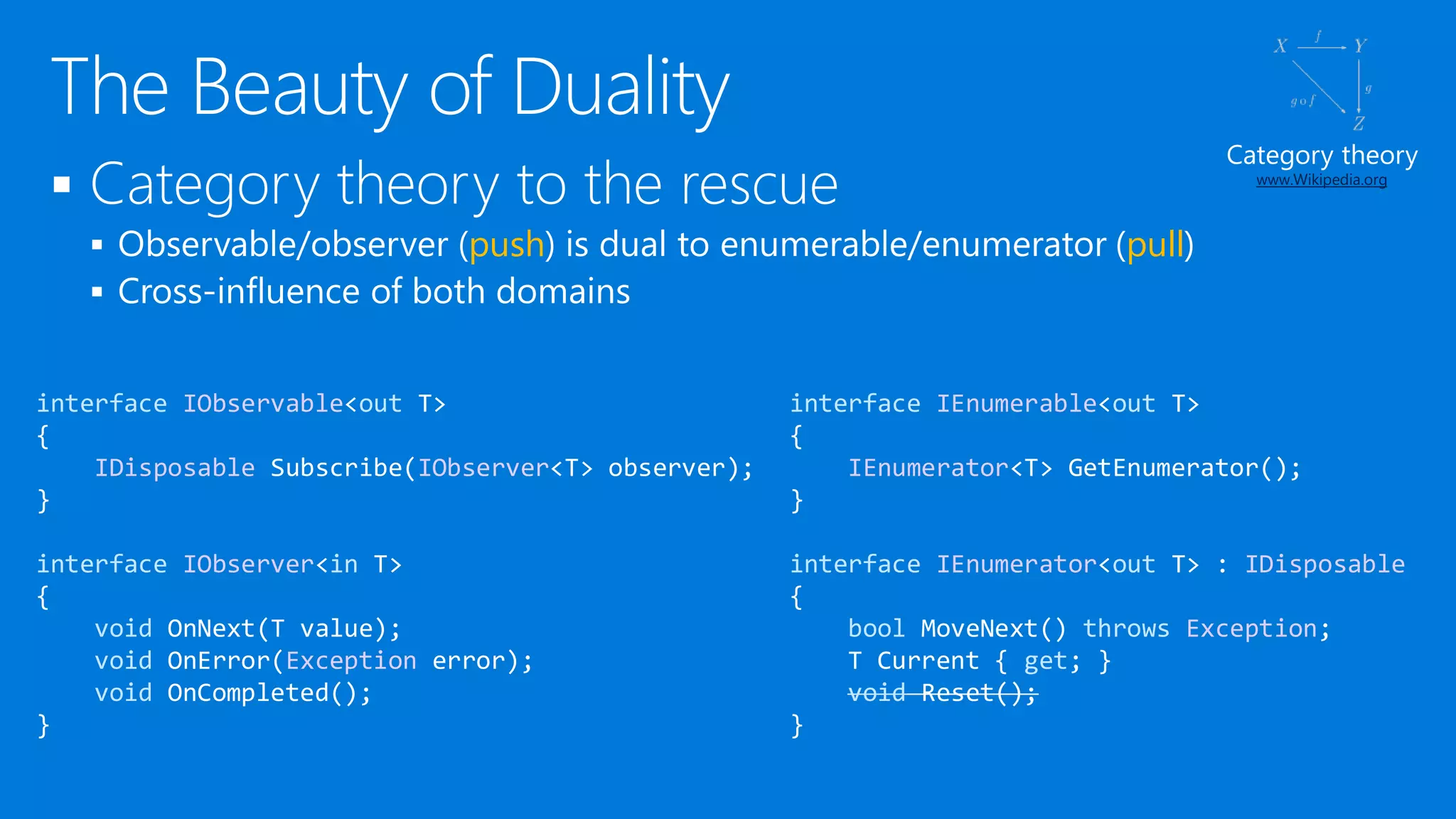
Events are not first-class objects
[RunOnClient]
public event EventHandler<MouseEventArgs> MouseMoved;
// Runs in cloud
public void CloudCanvas()
{
MouseMoved += (o, e) => { /* do stuff */ };
}
An electric eel…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/untitled-150915080116-lva1-app6891/75/Reactive-Programming-at-Cloud-Scale-and-Beyond-7-2048.jpg)

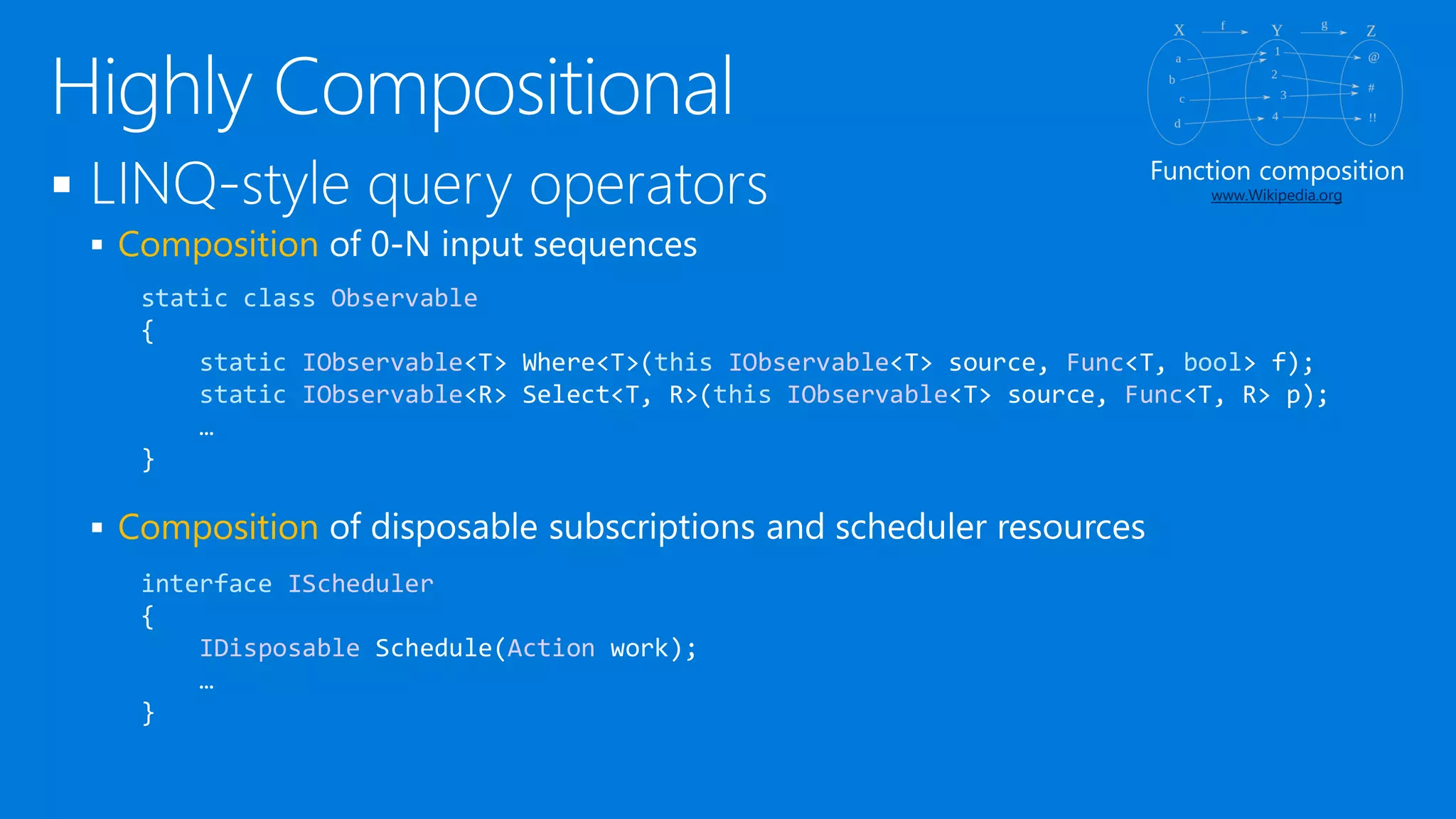
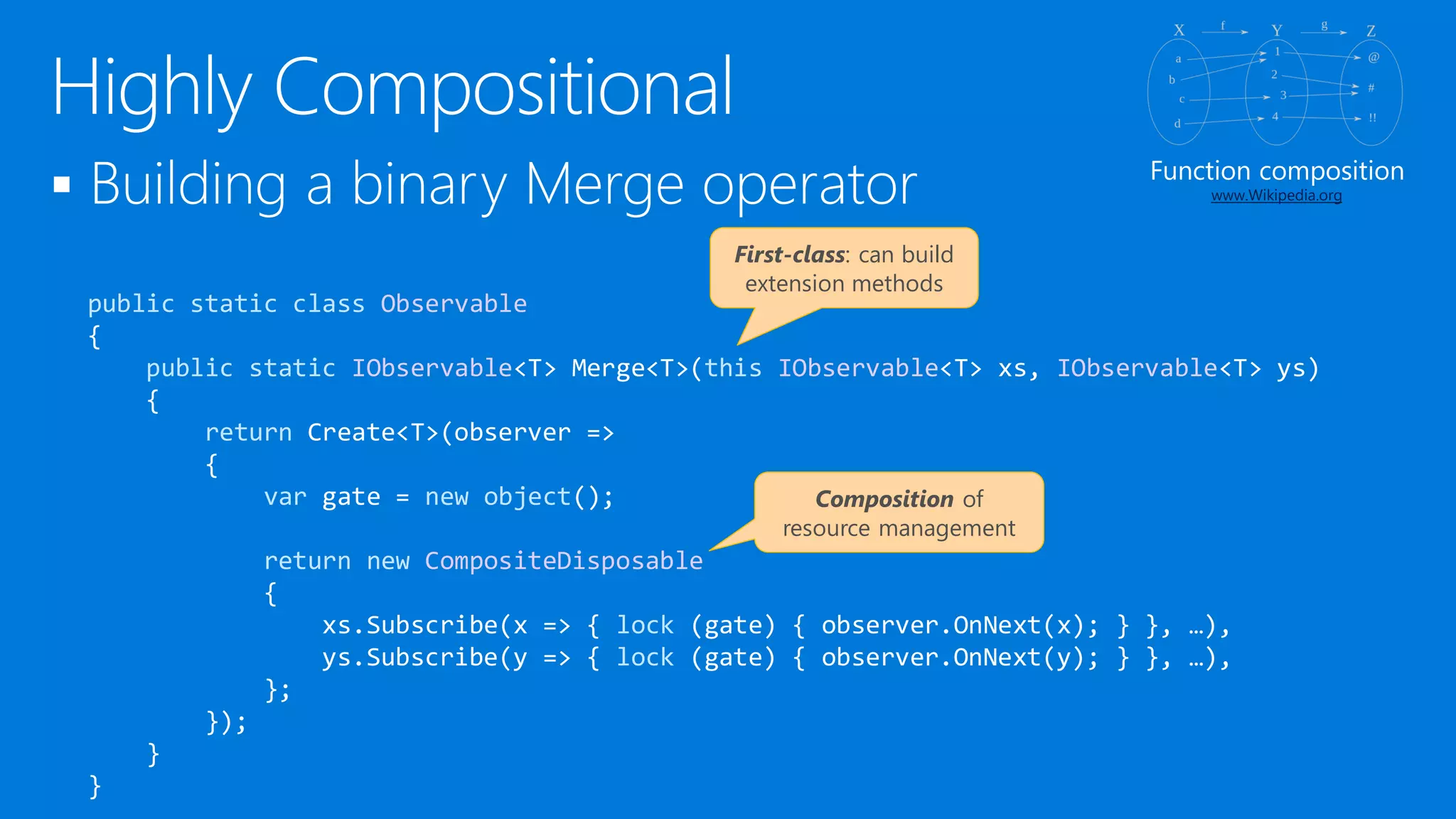
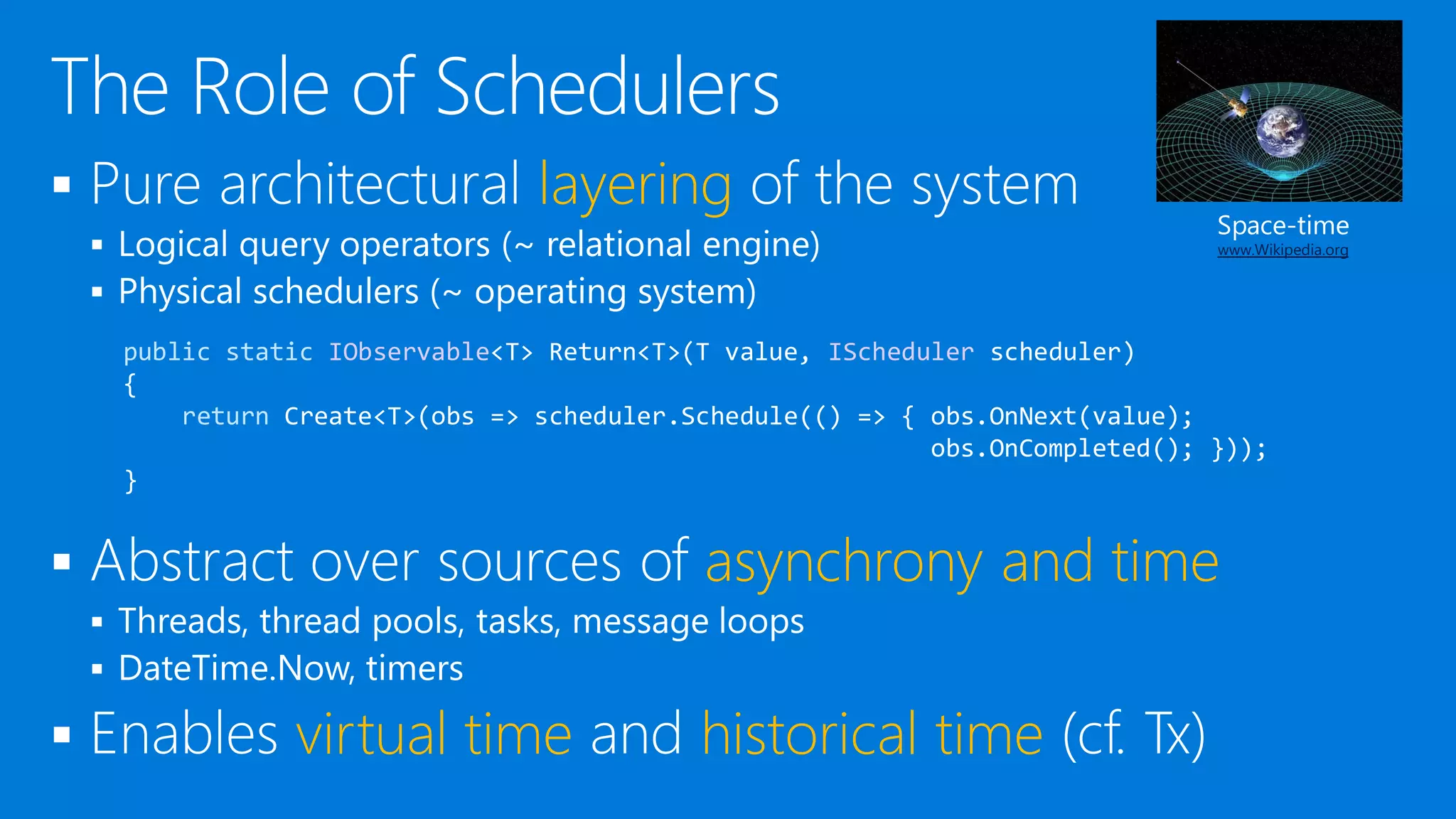









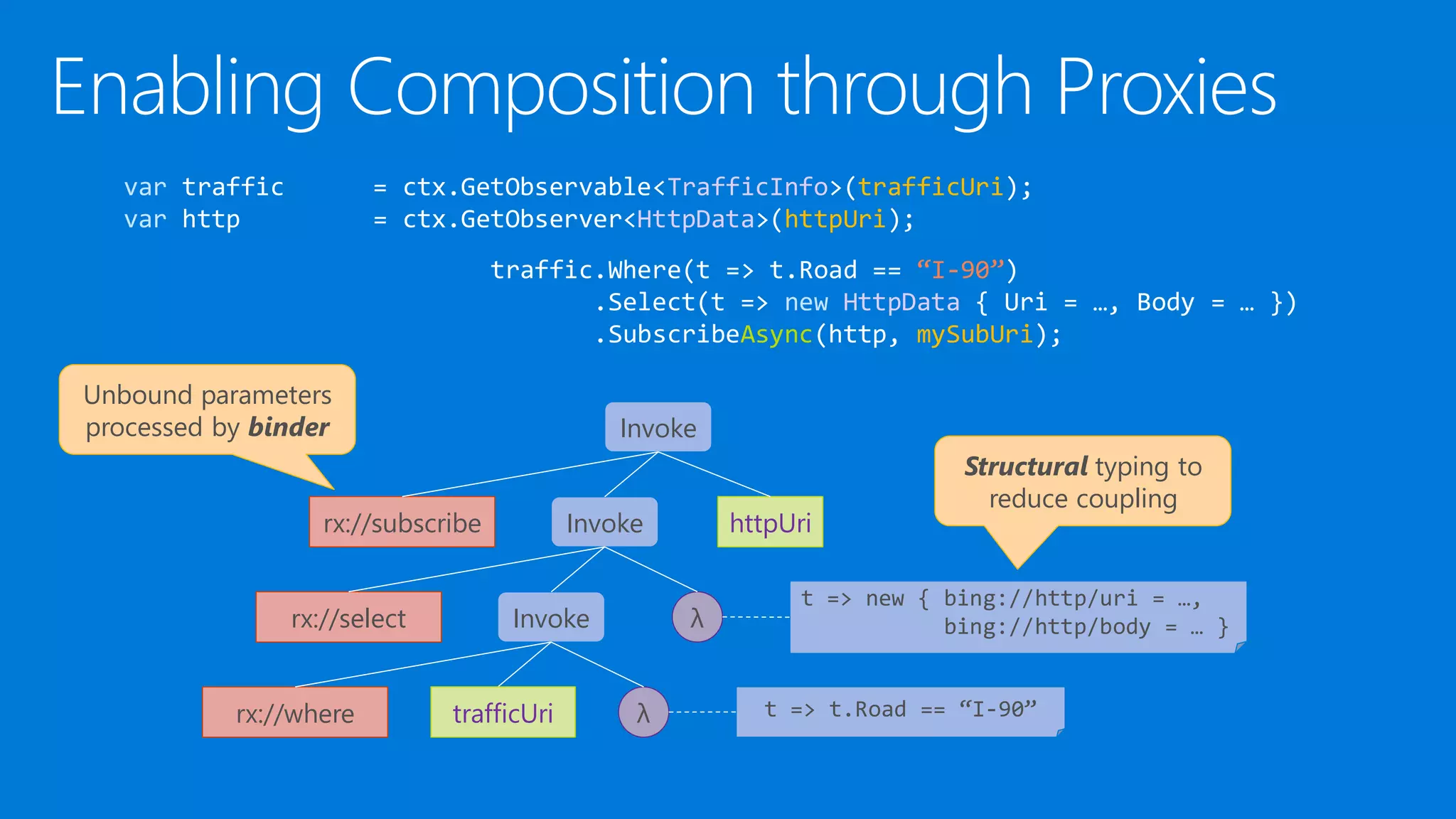


![ [KnownResource] attributes can be used everywhere
Provide shorthand syntax for Get* operations
Enable code generation using the Metadata facilities
What’s IAsyncReactiveQbservable<T>?
Async because it’s client-side (cf. SubscribeAsync)
Reactive because we had to disambiguate with Rx concepts
Qbservable because it’s expression tree based
static class AsyncReactiveQbservable
{
[KnownResource(whereUri)]
static IAsyncReactiveQbservable<T> Where<T>(this IAsyncReactiveQbservable<T> xs,
Expression<Func<T, bool>> filter) {…}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/untitled-150915080116-lva1-app6891/75/Reactive-Programming-at-Cloud-Scale-and-Beyond-33-2048.jpg)