Functional programming avoids changing-state and mutable data. Referential transparency means expressions can be replaced without affecting observable behavior. Pure functions only depend on argument values and have no other effects. Case classes provide functionality like equals, hashCode and pattern matching out of the box. Futures allow running blocking operations asynchronously and chaining results with map, flatMap and for comprehensions. Implicits allow type conversions and providing parameters implicitly. Sealed classes allow exhaustive pattern matching of a type hierarchy.




![Example of pure function:
def wrong(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a / b
def right(a: Int, b: Int): Try[Int] = Try(a / b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-5-2048.jpg)
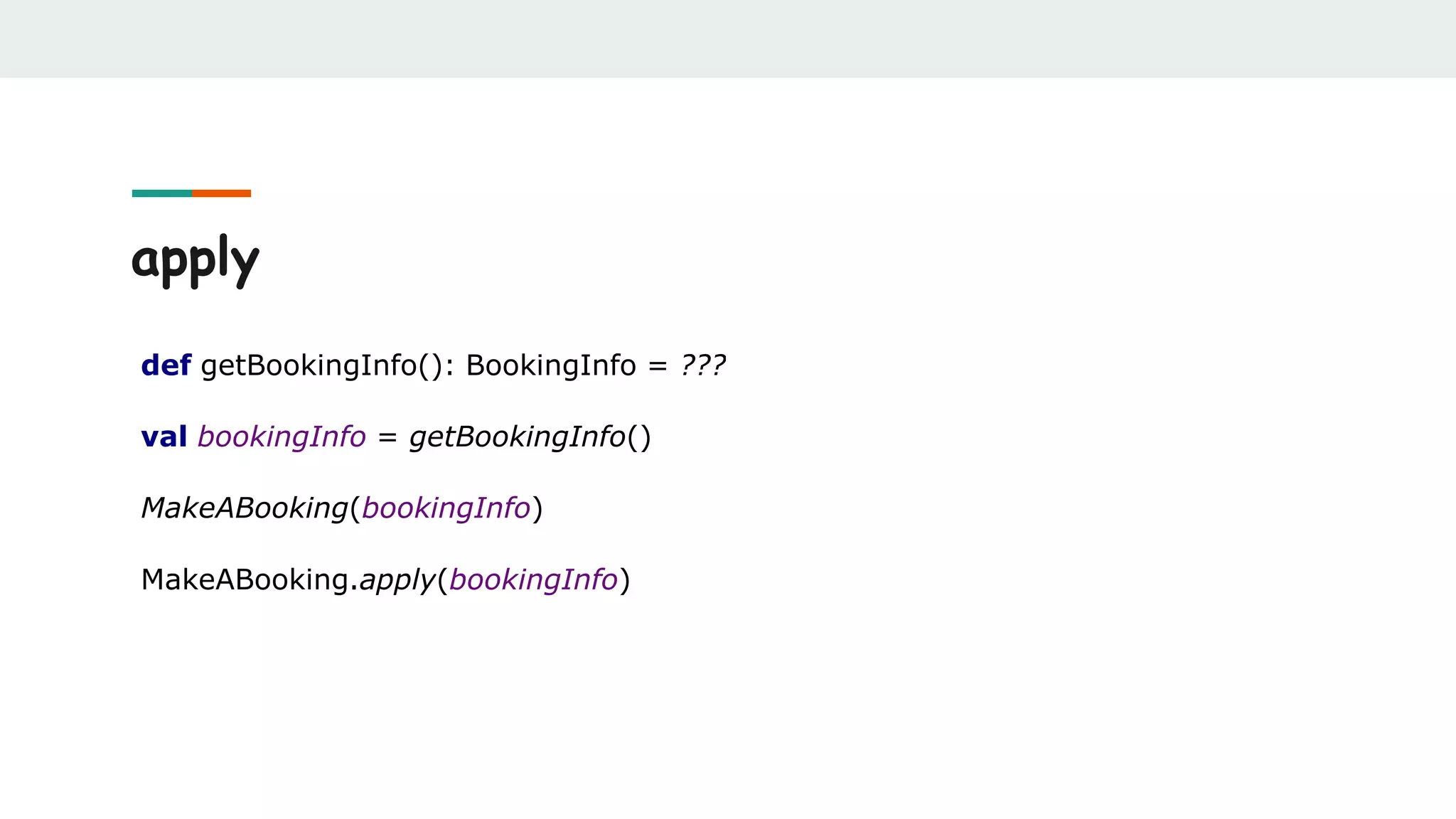


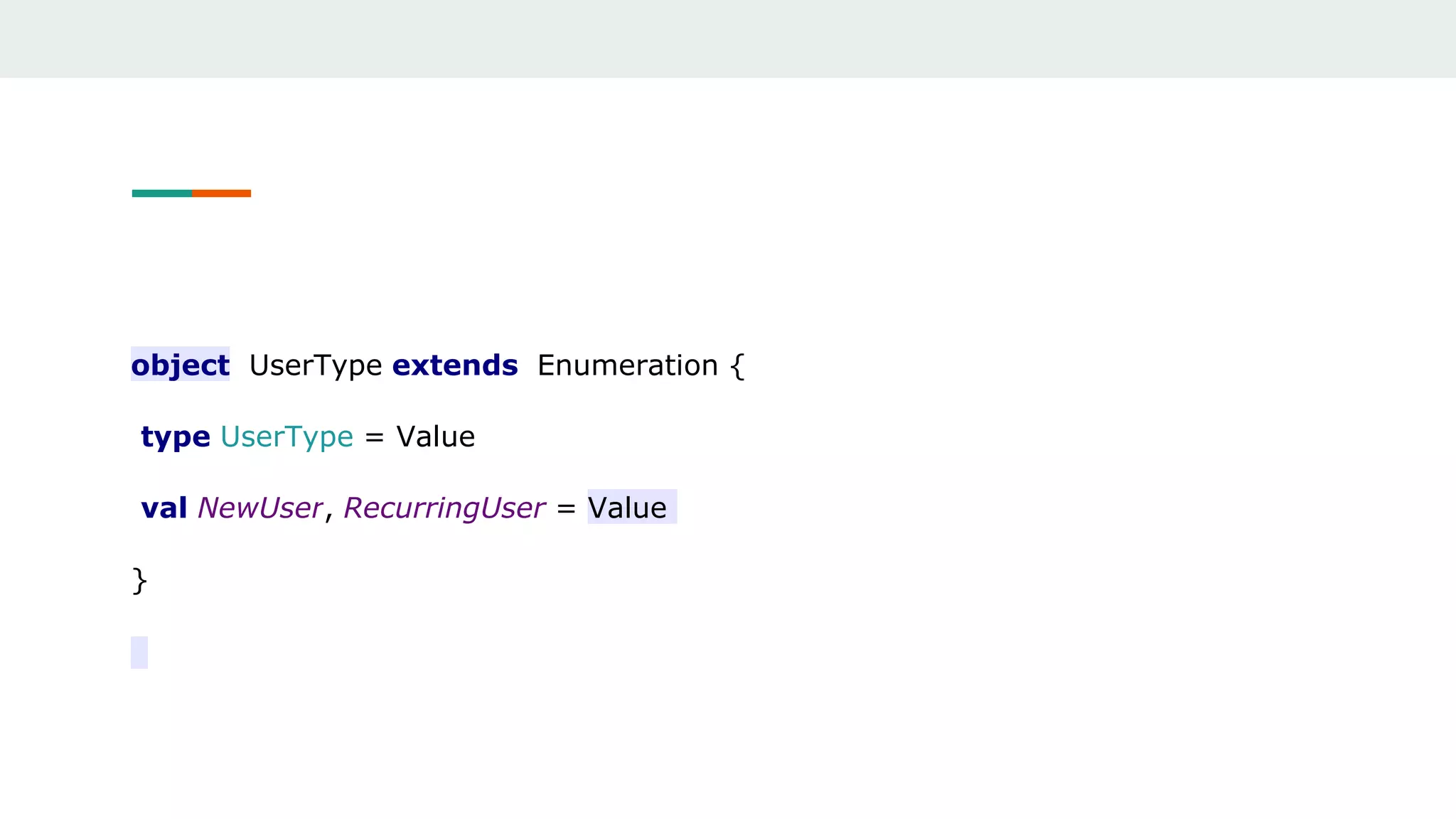

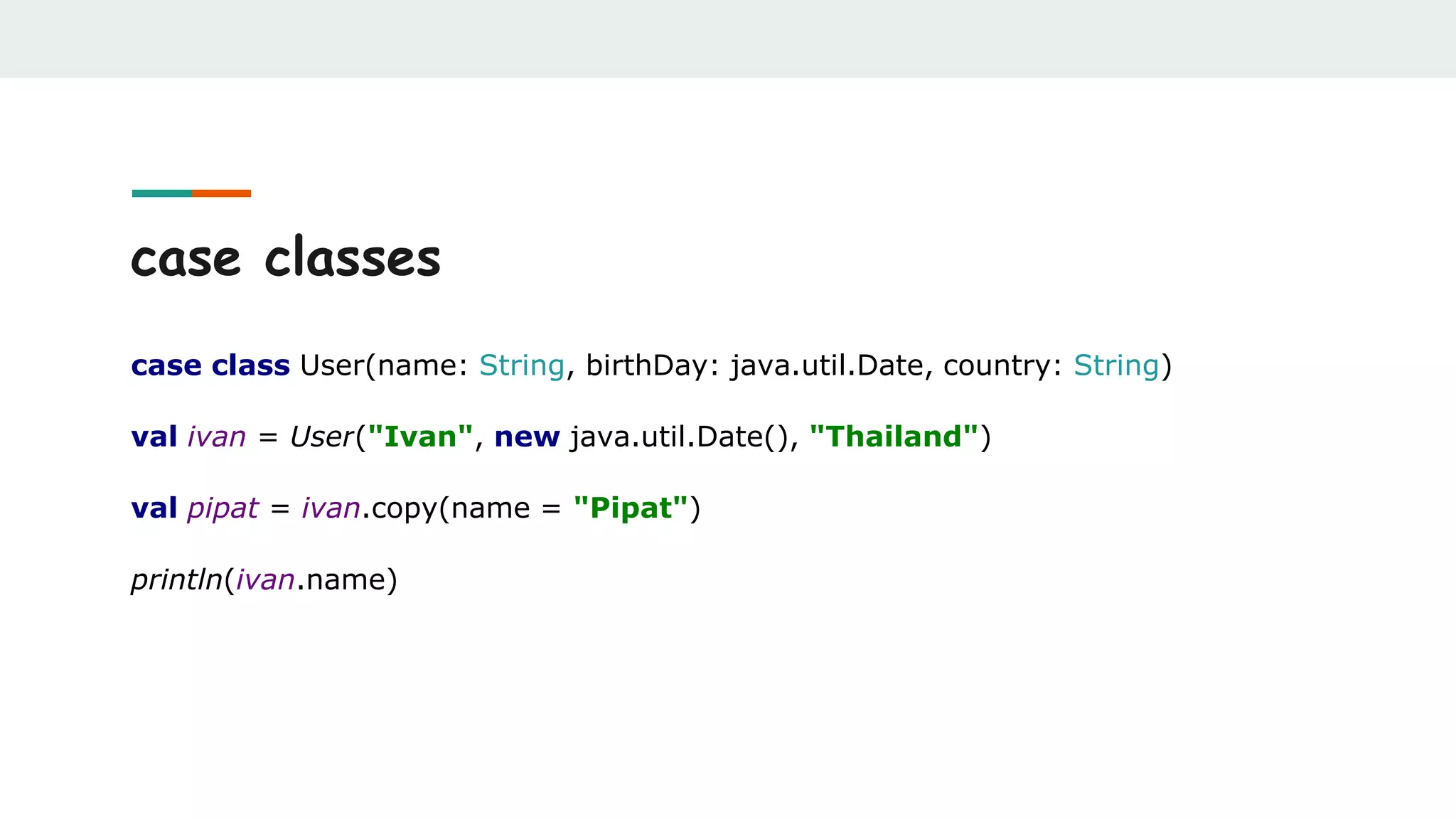


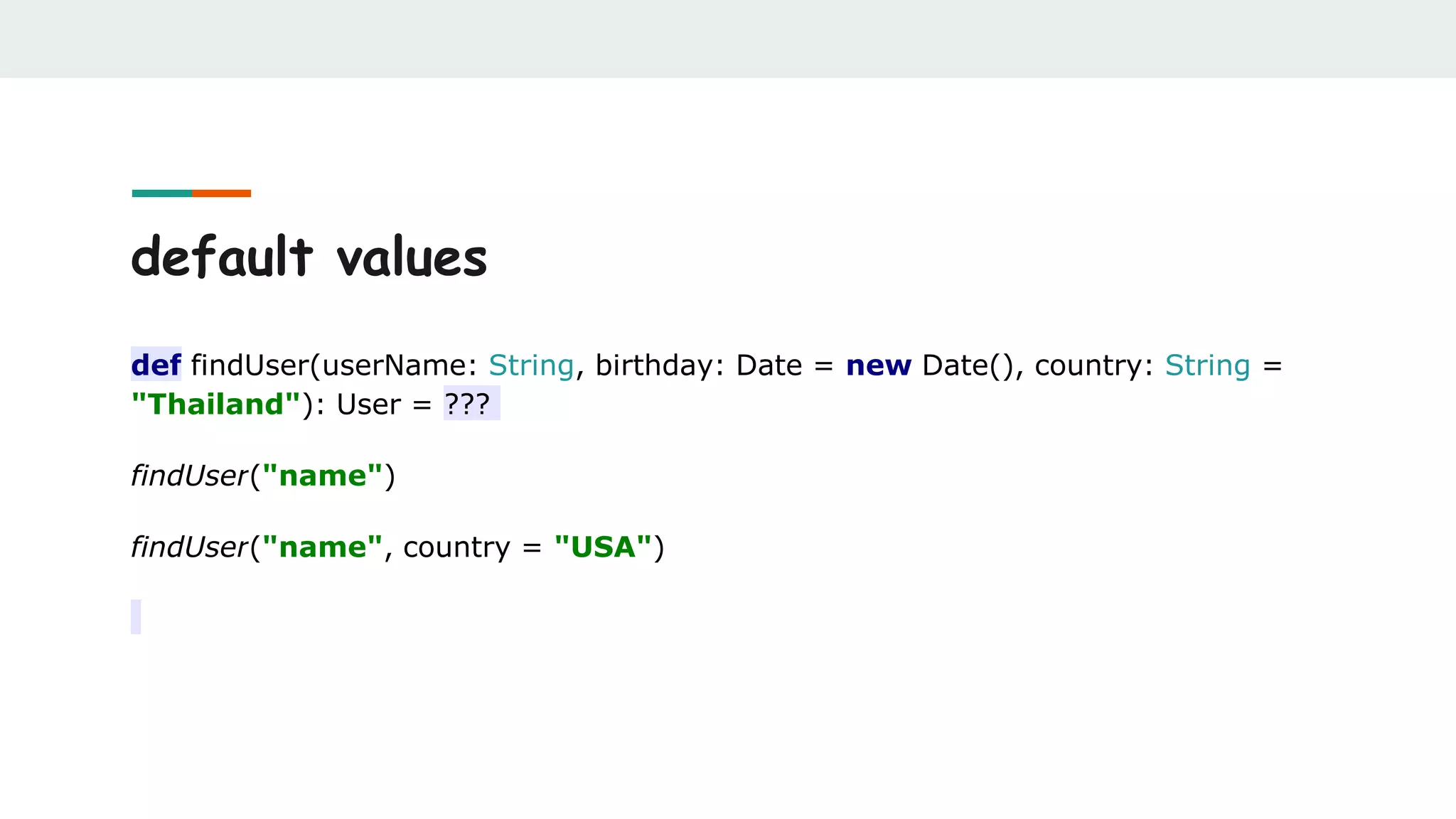
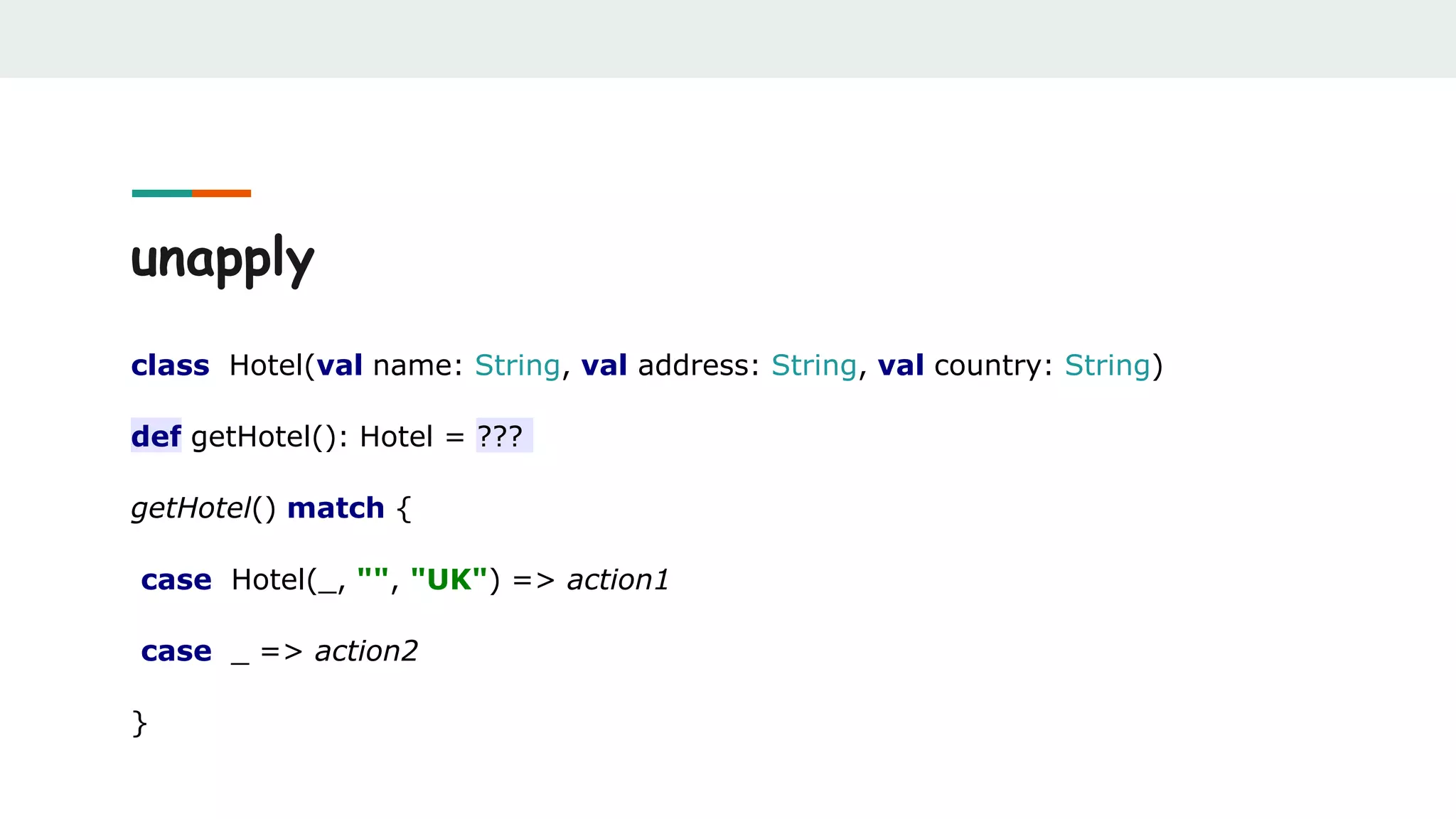
![unapply
object Hotel {
def unapply(hotel: Hotel): Option[(String, String, String)] = {
Option((hotel.name, hotel.address, hotel.country))
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-19-2048.jpg)


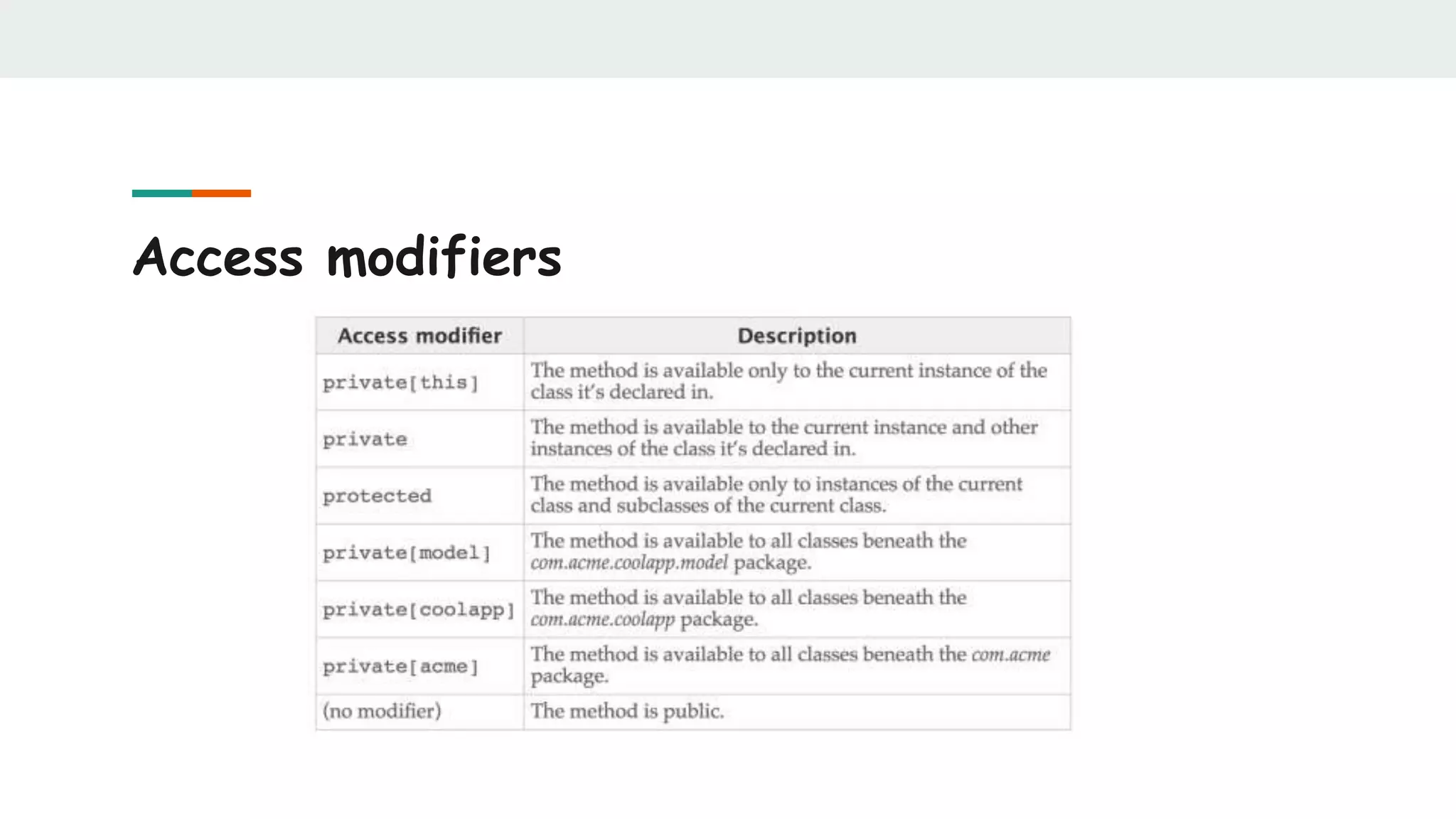



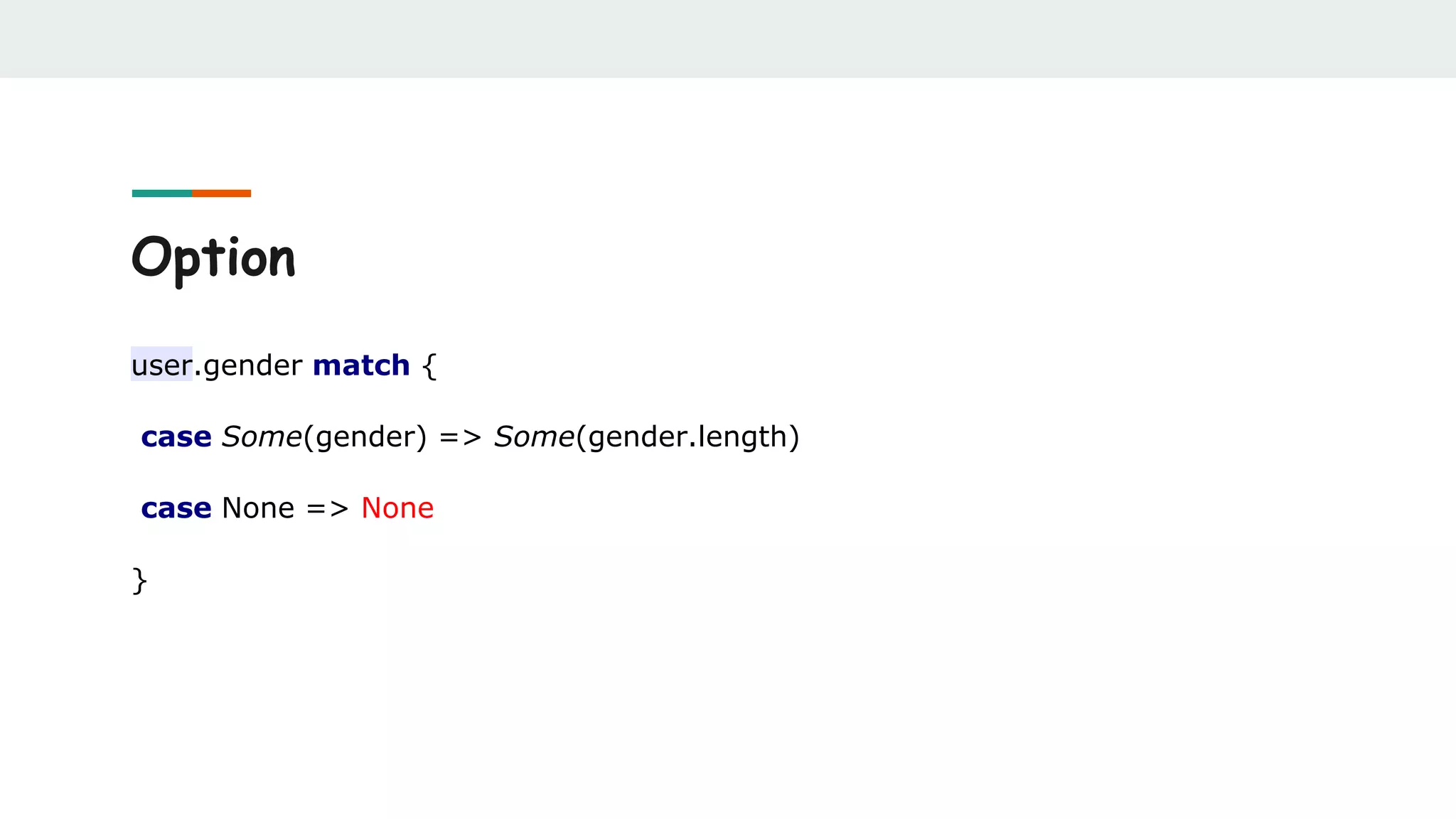
![Option
case class User(age: Int, name: String, gender: Option[String])
val user = User(25, "Ivan", Some("male"))
user.gender match {
case Some(gender) => println("Gender: " + gender)
case None => println("Gender: not specified")
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-30-2048.jpg)
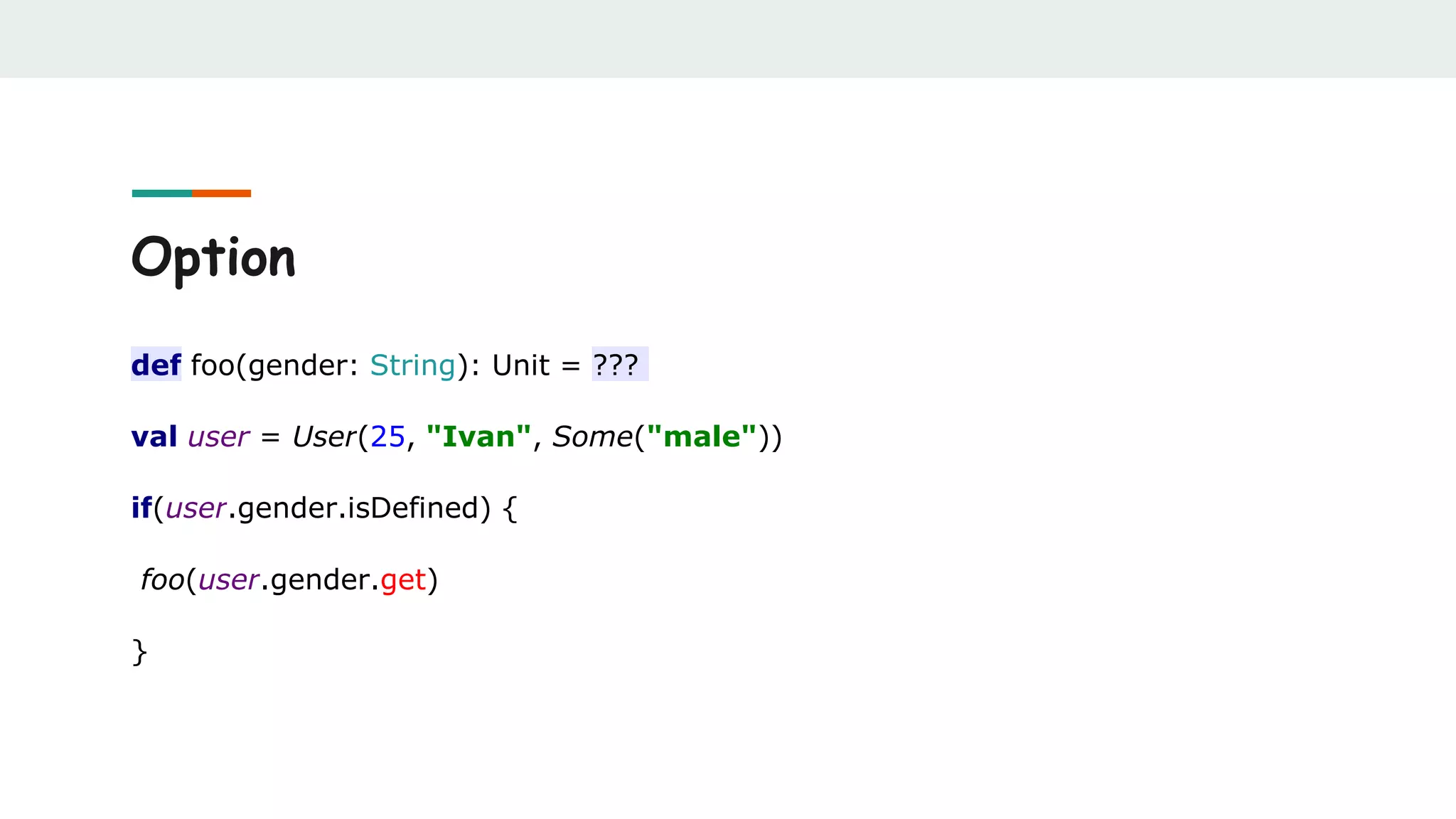
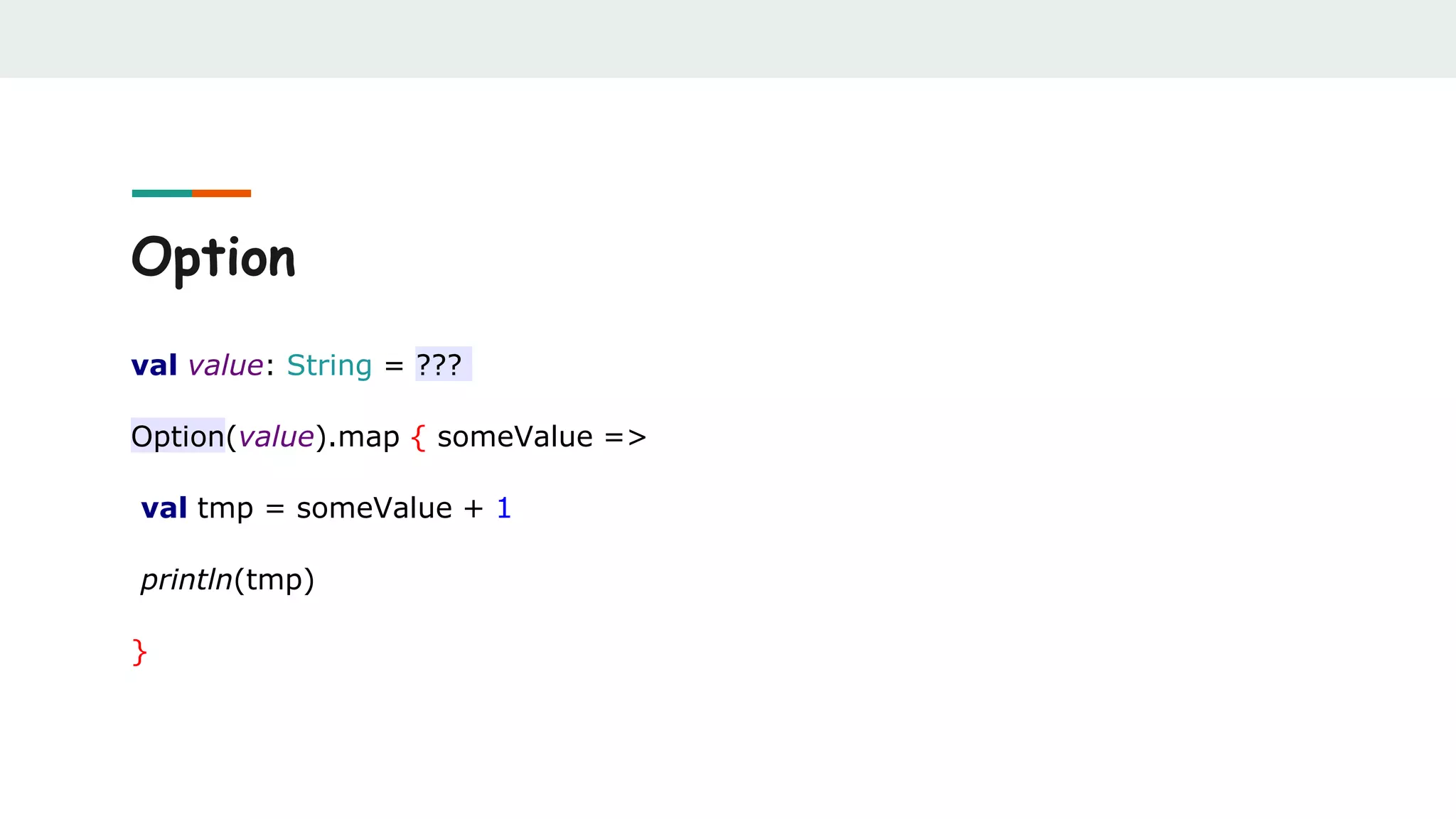
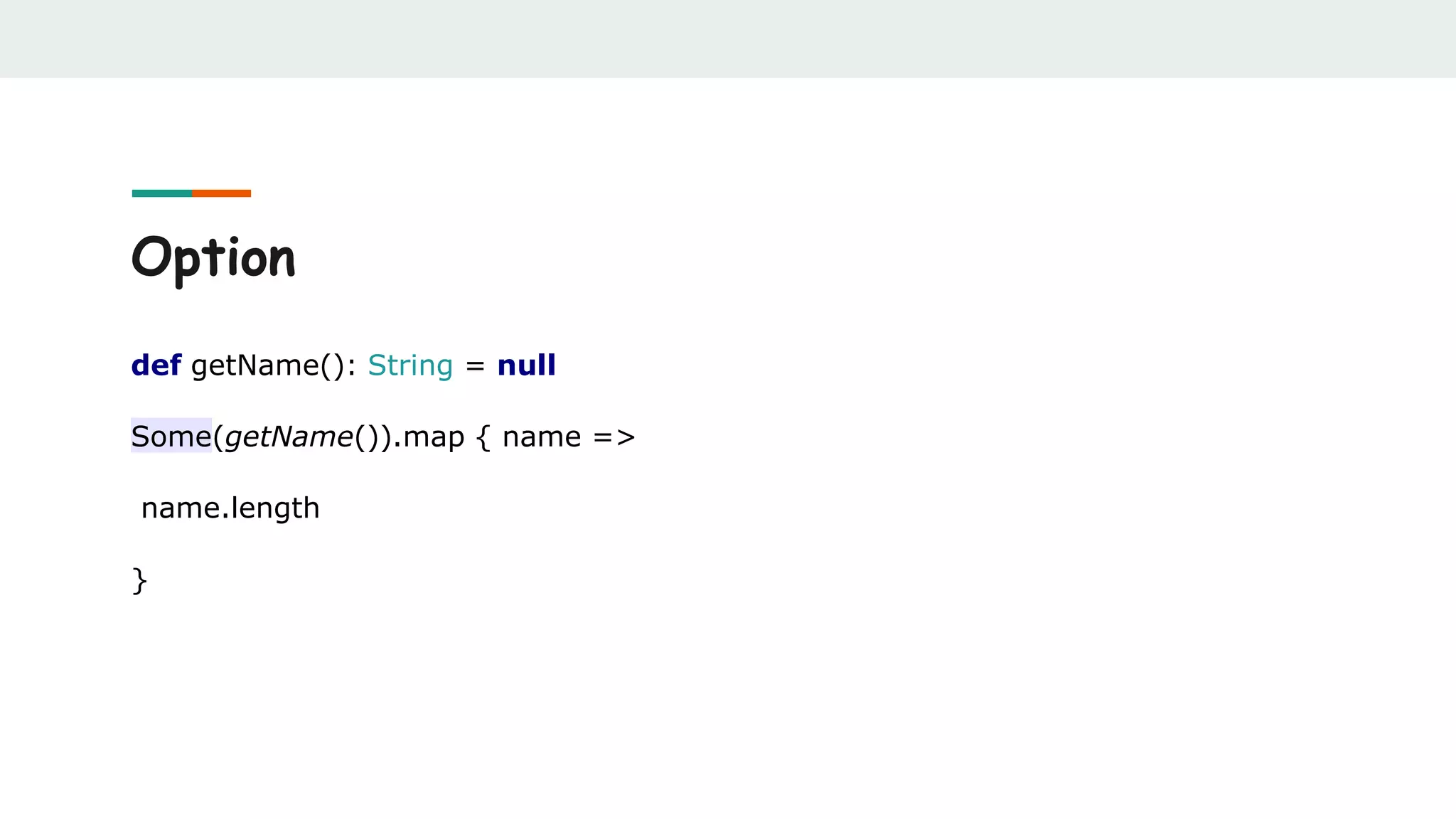
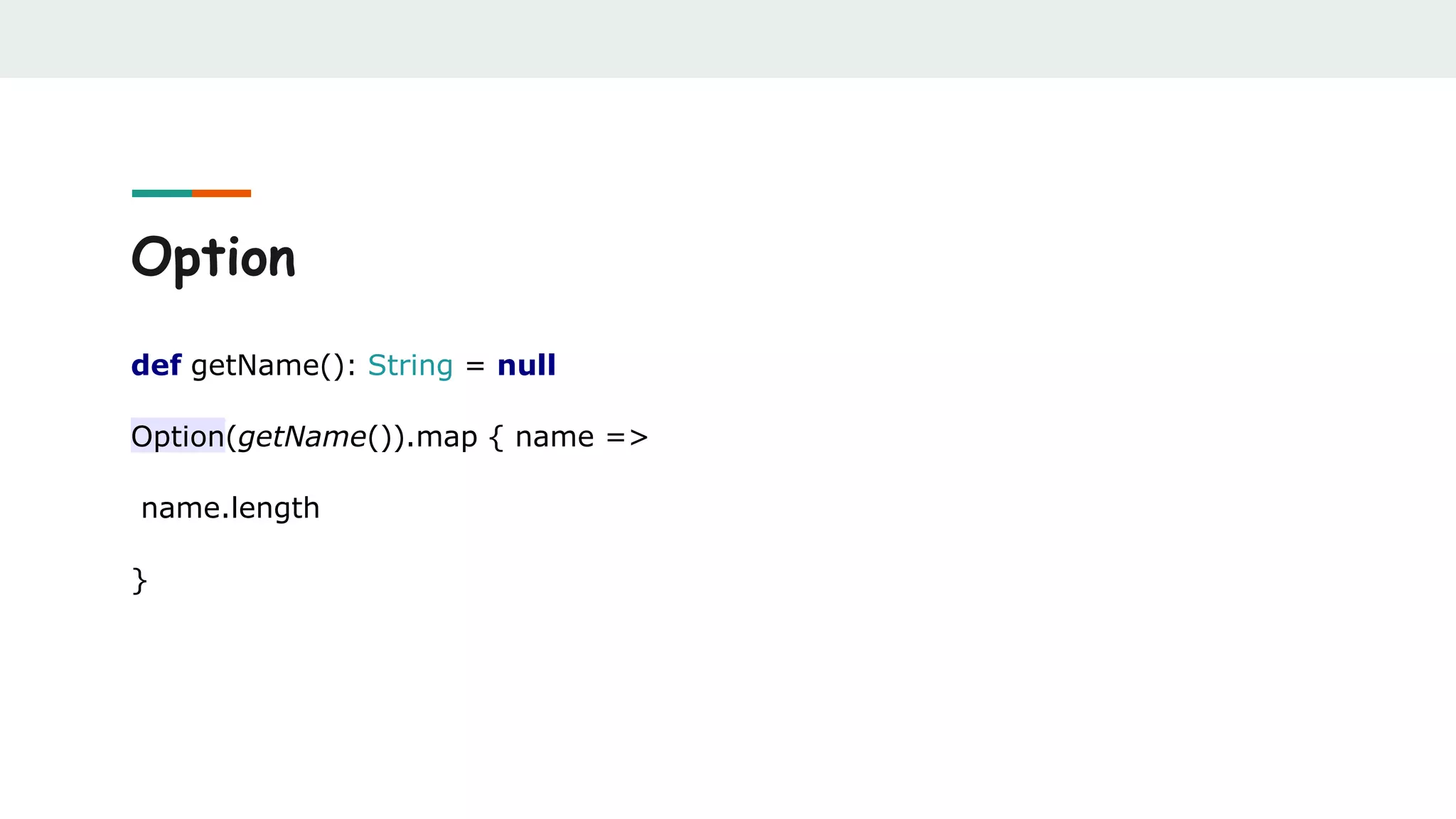
![Option
def findUserFromDb(userId: Int): Option[User] = ???
val currentUser = findUserFromDb(userId)
val defaultUser = findUserFromDb(defaultUserId)
currentUser orElse defaultUser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-33-2048.jpg)
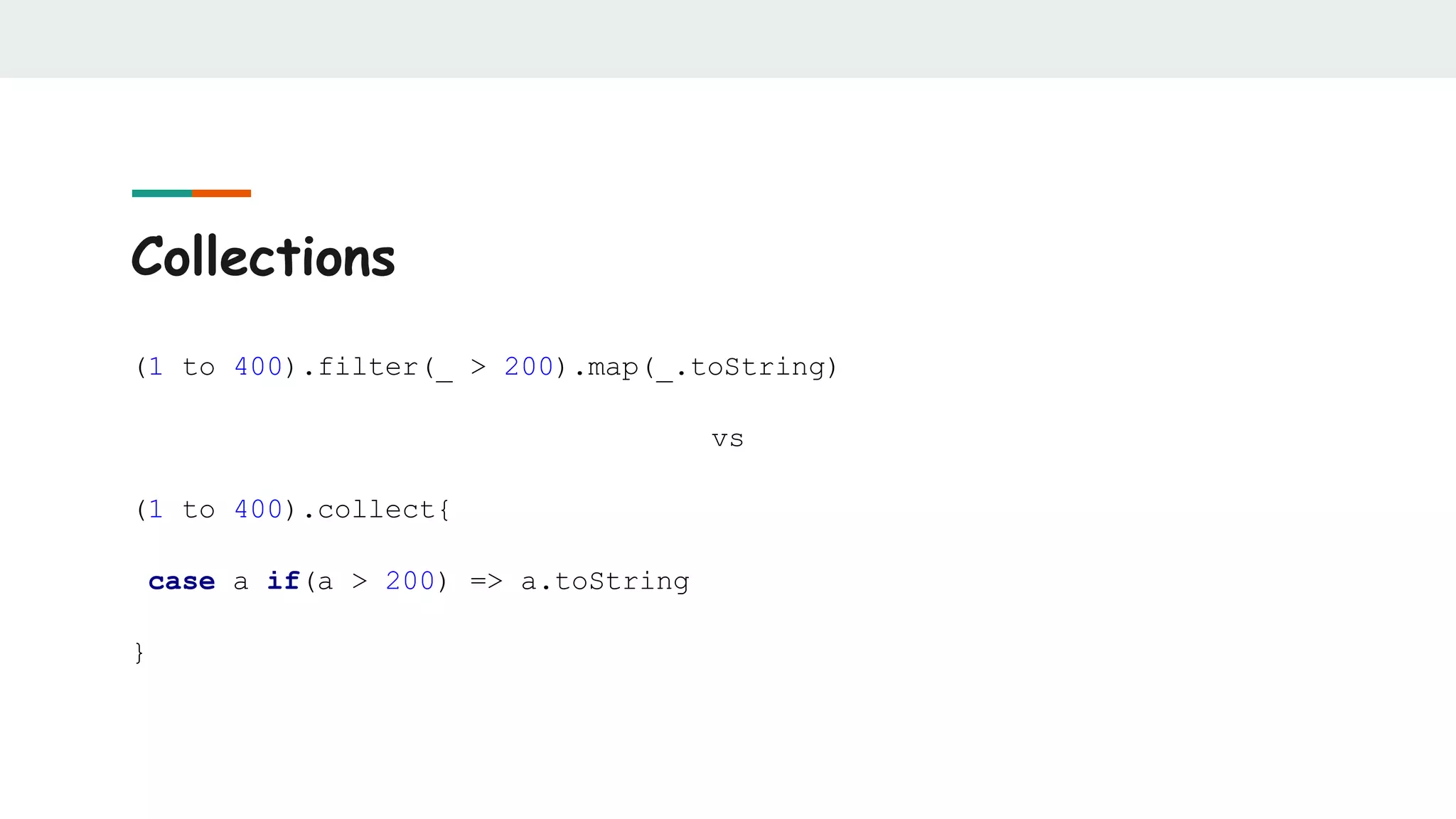
![Collections
def predicate: Boolean = ???
def foo(): List[Int] = ???
if(predicate) foo() else List()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-36-2048.jpg)
![List.empty, Map.empty, Array.empty
def predicate: Boolean = ???
def foo(): List[Int] = ???
if(predicate) foo() else List.empty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-37-2048.jpg)
![def foo(): List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
foo() match {
case b: List[String] => println("String")
case a: List[Int] => println("Int")
case c: List[AnyRef] => println("AnyRef")
case c: List[AnyVal] => println("AnyVal")
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-38-2048.jpg)






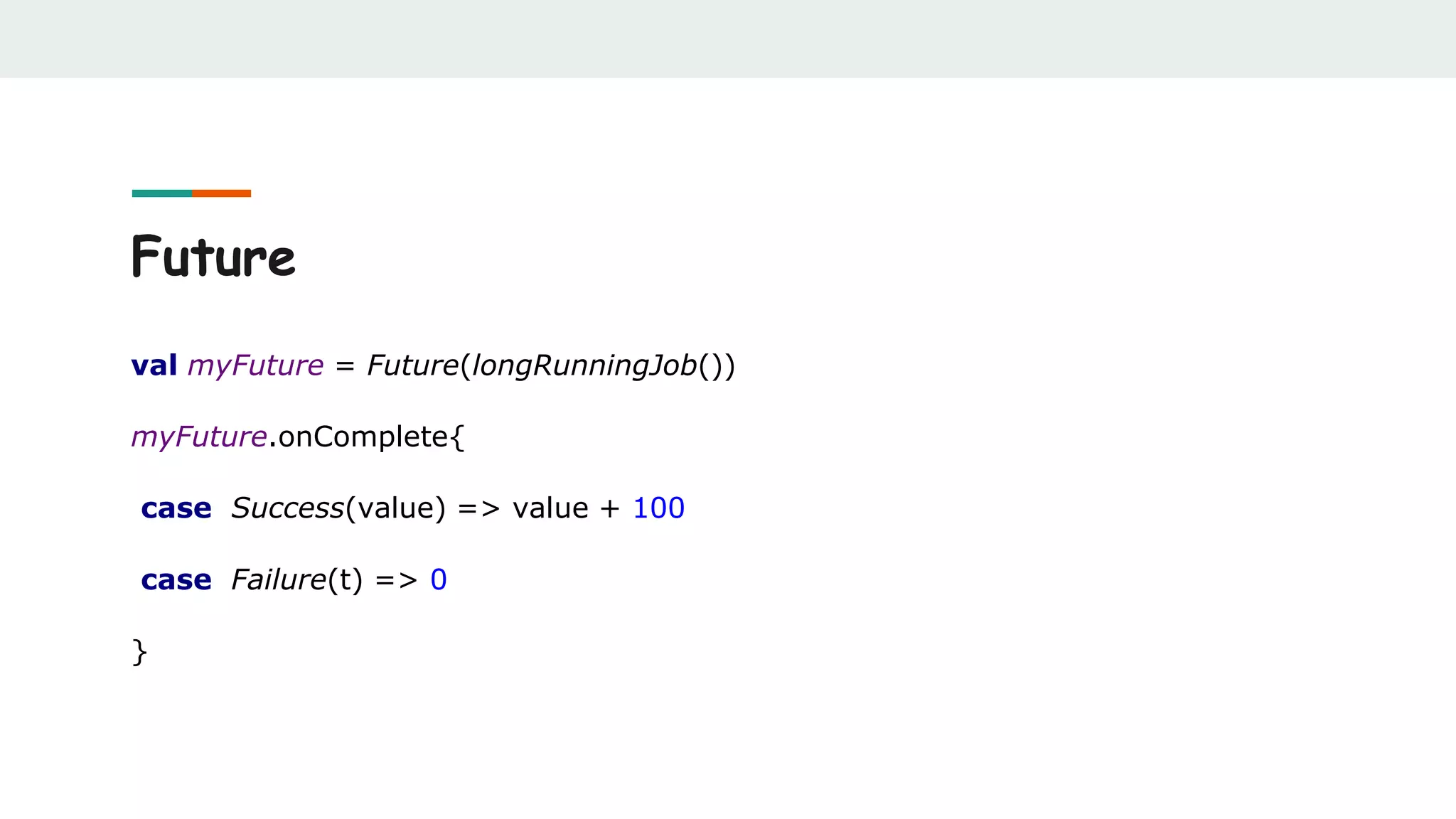
(implicit executor :ExecutionContext) : Future[T]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-49-2048.jpg)

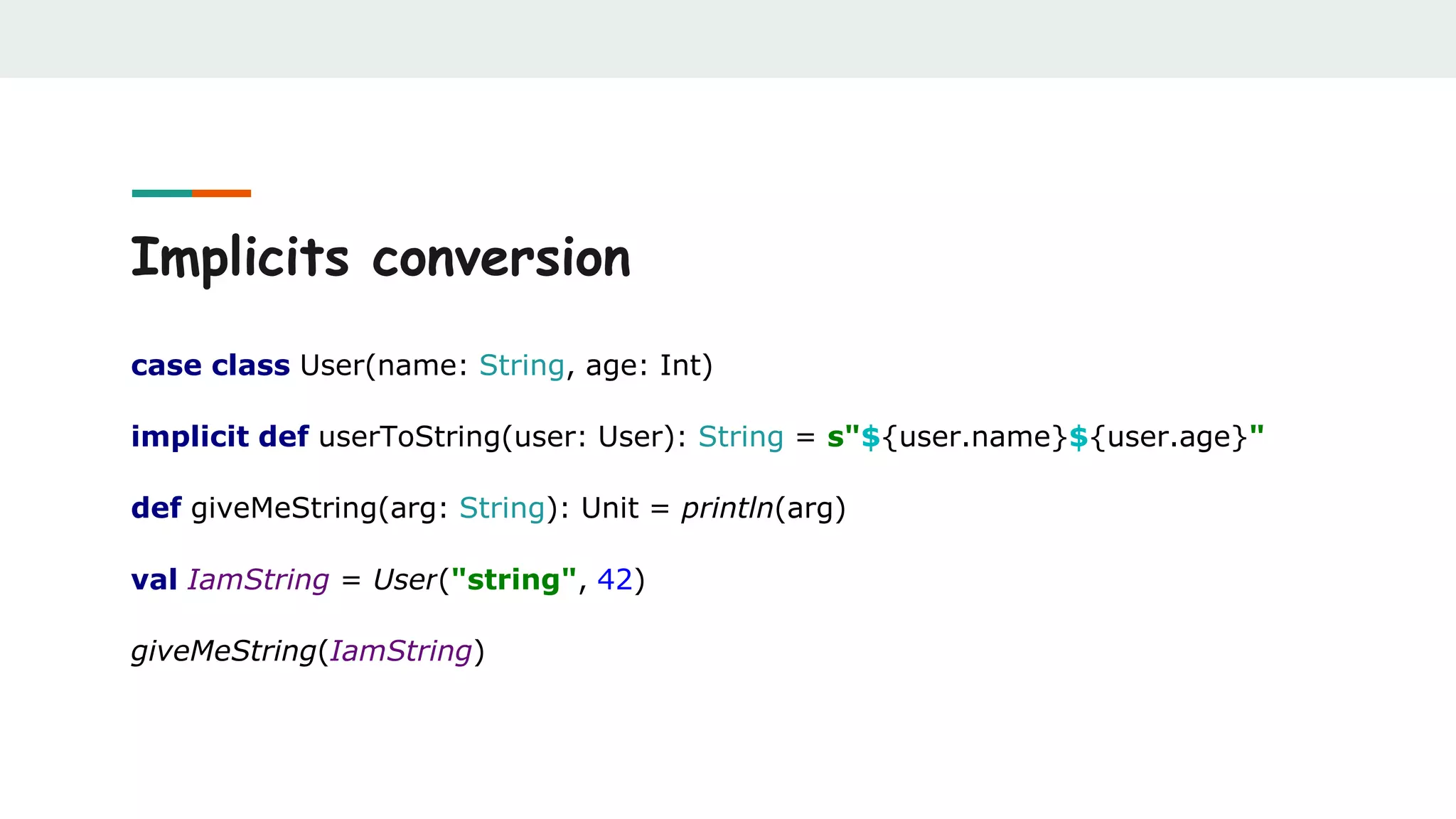
![Future
case class Hotel(id: Long)
val preCachedHotels: List[Hotel] = ???
def dbCall(id: Long): Future[Hotel] = ???
def findHotel(id: Long): Future[Hotel] = preCachedHotels.find(_.id == id).
map { user => Future(user) }.getOrElse(dbCall(id))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-52-2048.jpg)
![Future: successful
case class Hotel(id: Long)
val preCachedHotels: List[Hotel] = ???
def dbCall(id: Long): Future[Hotel] = ???
def findHotel(id: Long): Future[Hotel] = preCachedHotels.find(_.id == id).
map { user => Future.successful(user) }.getOrElse(dbCall(id))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-53-2048.jpg)
![Future
def callDB(id: Long): Future[User] = ???
def findUser(id: Long): Future[User] = {
if(id < 0) Future(new Exception("User can't contain negative id"))
else callDB(id)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-54-2048.jpg)
![Future: failed
def callDB(id: Long): Future[User] = ???
def findUser(id: Long): Future[User] = {
if(id < 0) Future.failed(new Exception("User can't contain negative id"))
else callDB(id)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-55-2048.jpg)
![Future.sequence
case class User(id: Long)
def getAllUserIds(): List[Long] = ???
def findUserById(id: Long): Future[User] = ???
val usersF: List[Future[User]] = getAllUserIds().map(findUserById)
val allUsersFetchedF: Future[List[User]] = Future.sequence(usersF)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-56-2048.jpg)






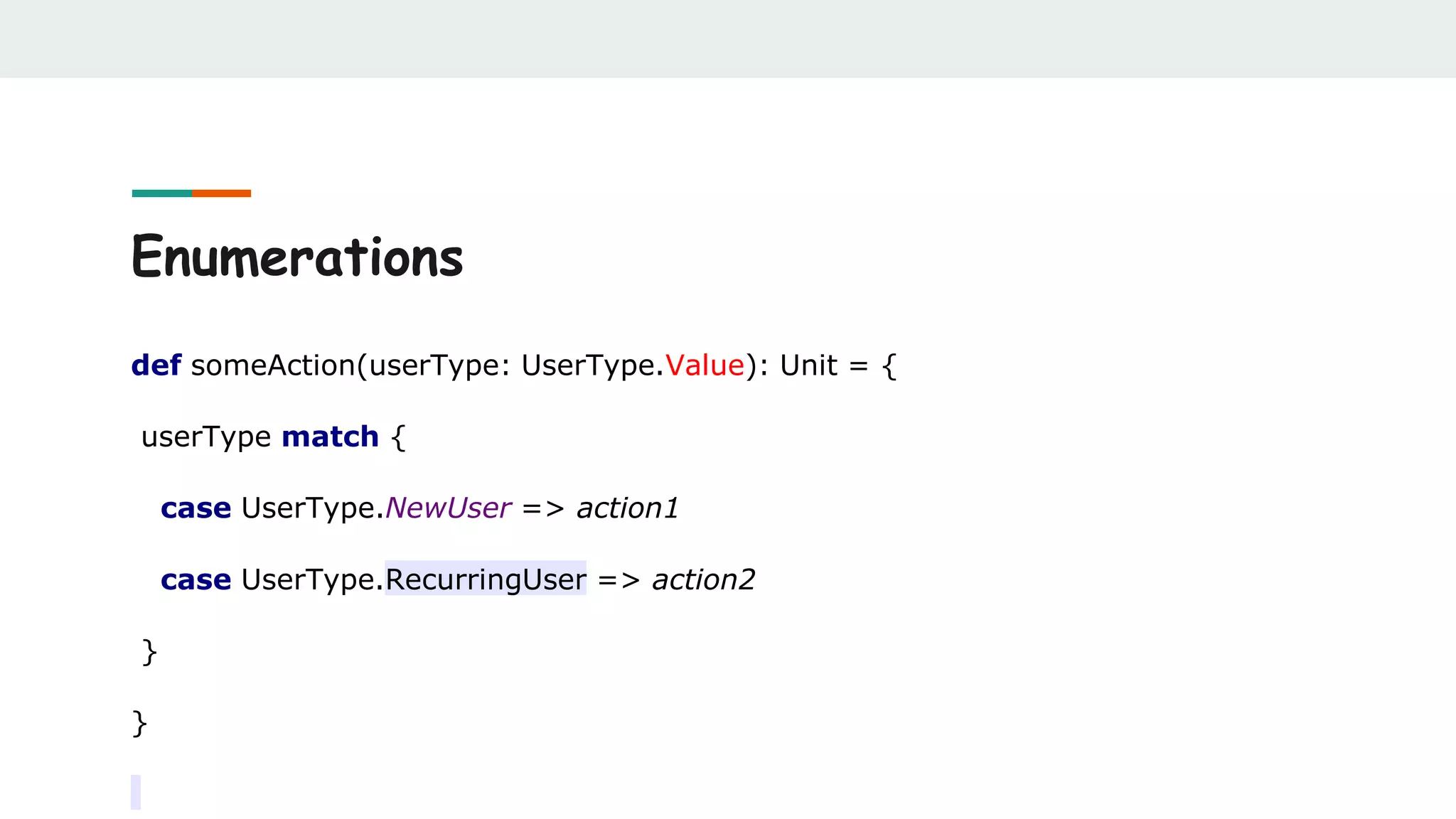
![Sealed classes
def getMyOption[T](): MyOption[T] =
???
getMyOption() match {
case MyEmpty => action1
case MySome(a) => action1
}
sealed abstract class
MyOption[T]
case object MyEmpty extends
MyOption[Nothing]
case class MySome[T](t: T)
extends MyOption[T]
case class MyAnotherState[T](t: T)
extends MyOption[T]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalabestpractices-170722121222/75/Scala-best-practices-64-2048.jpg)