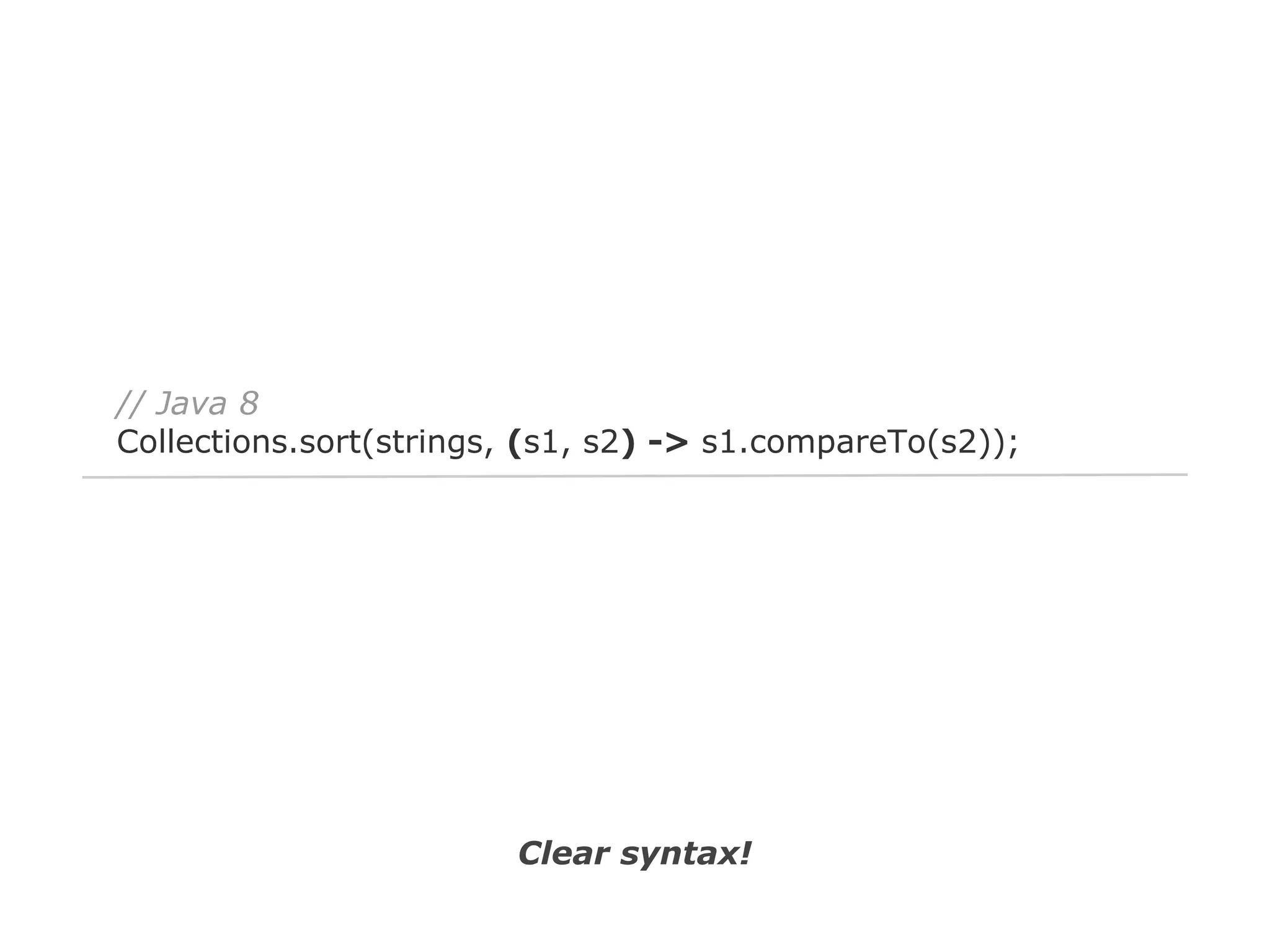
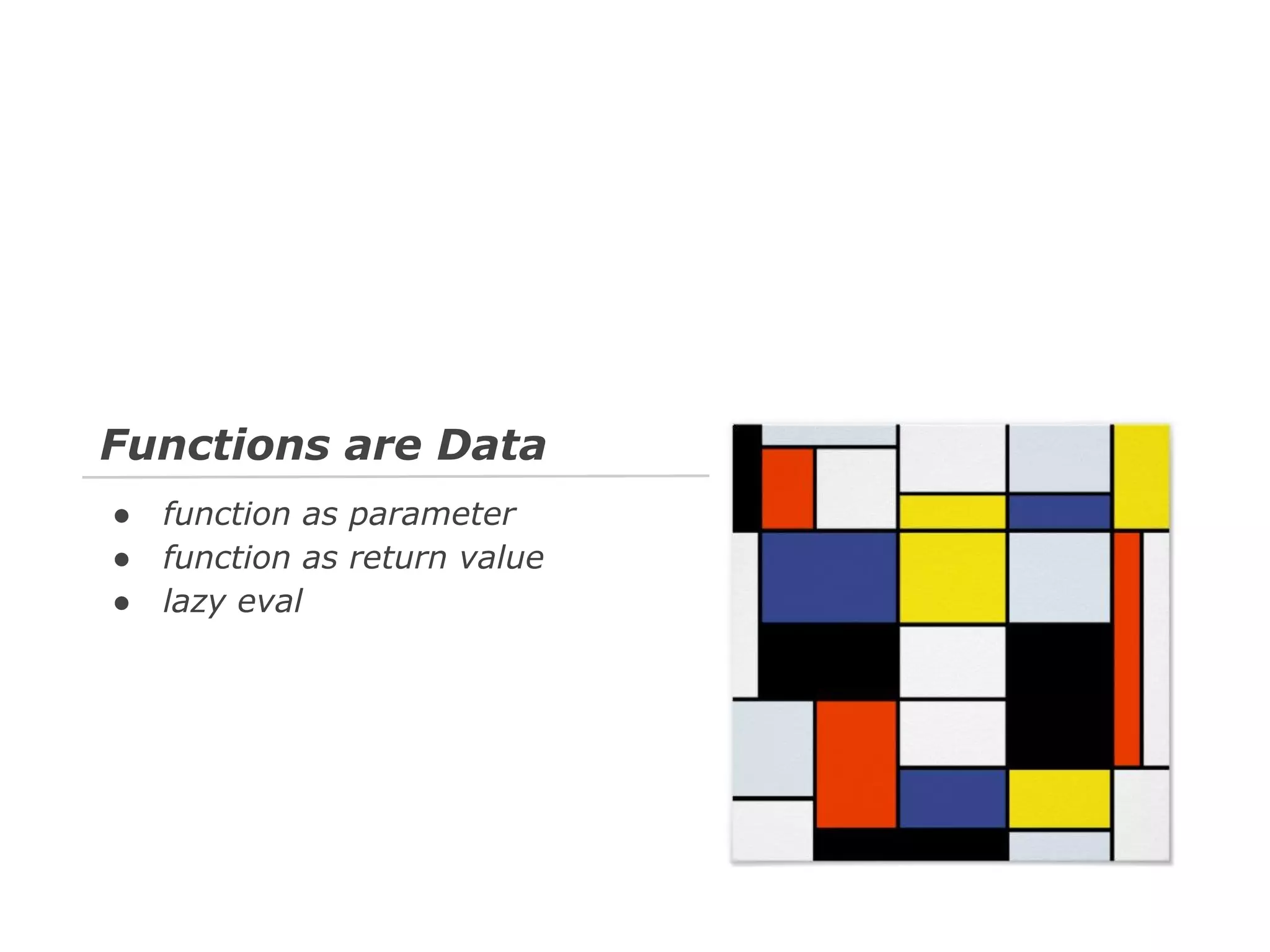
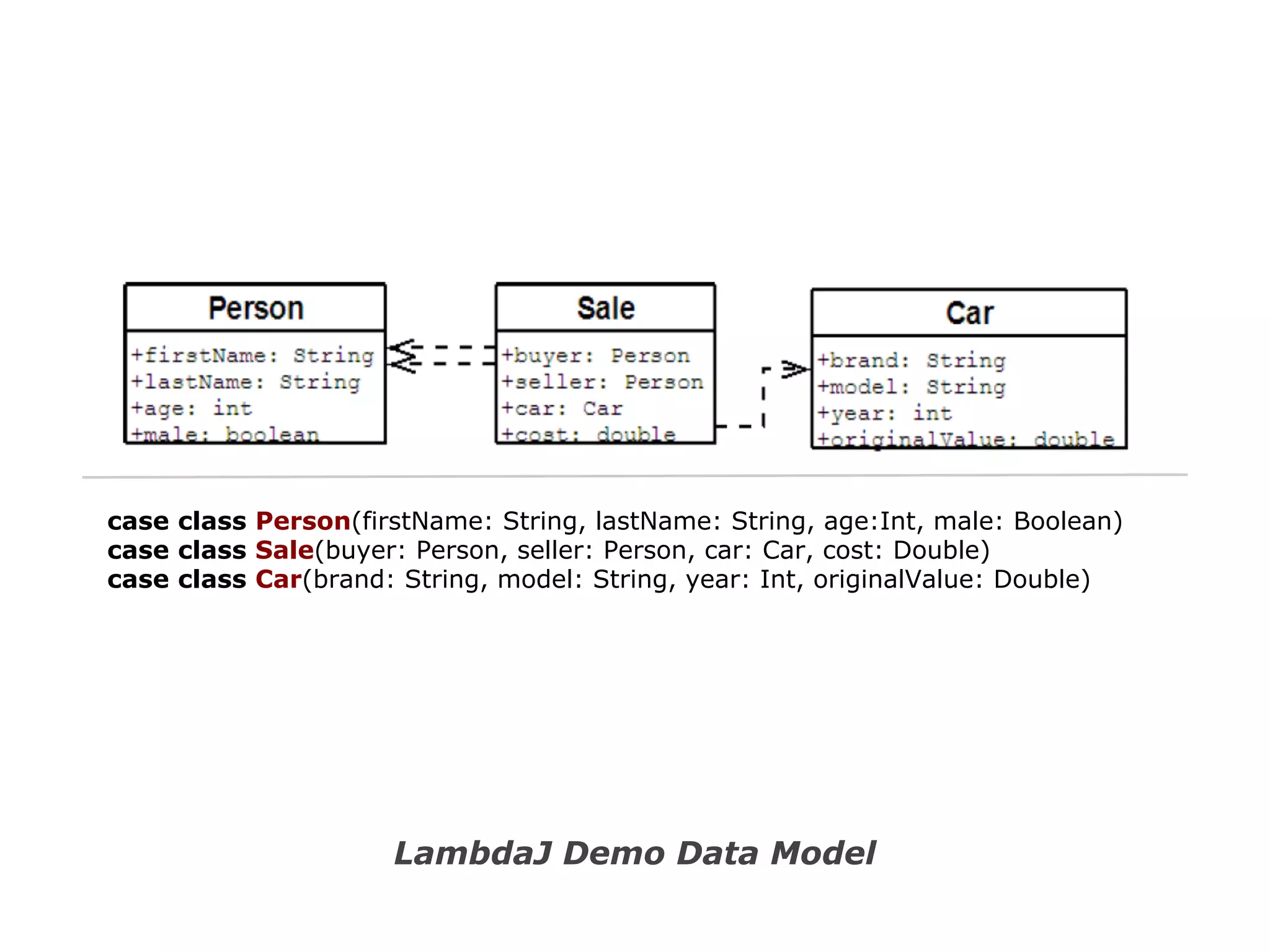
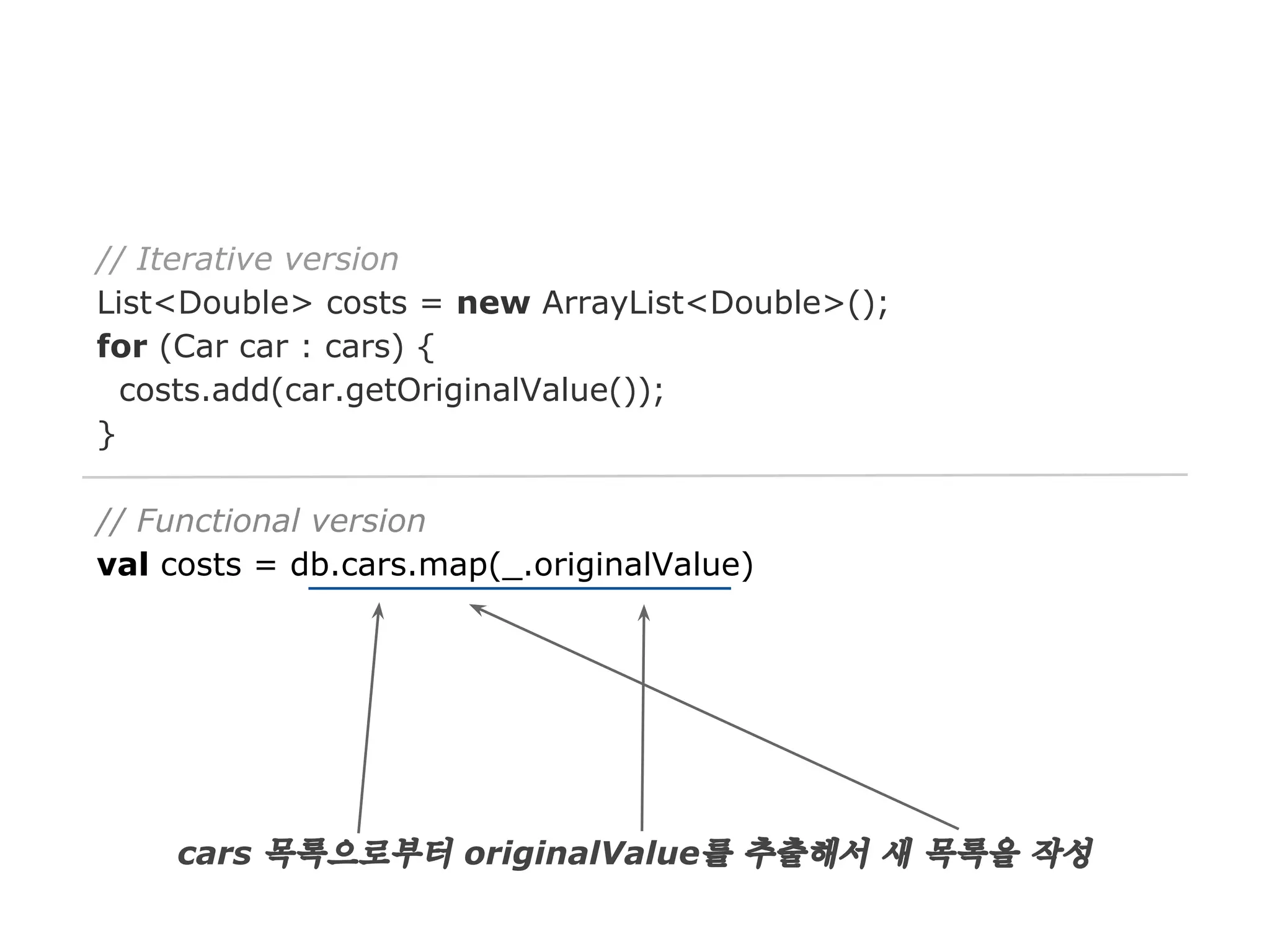
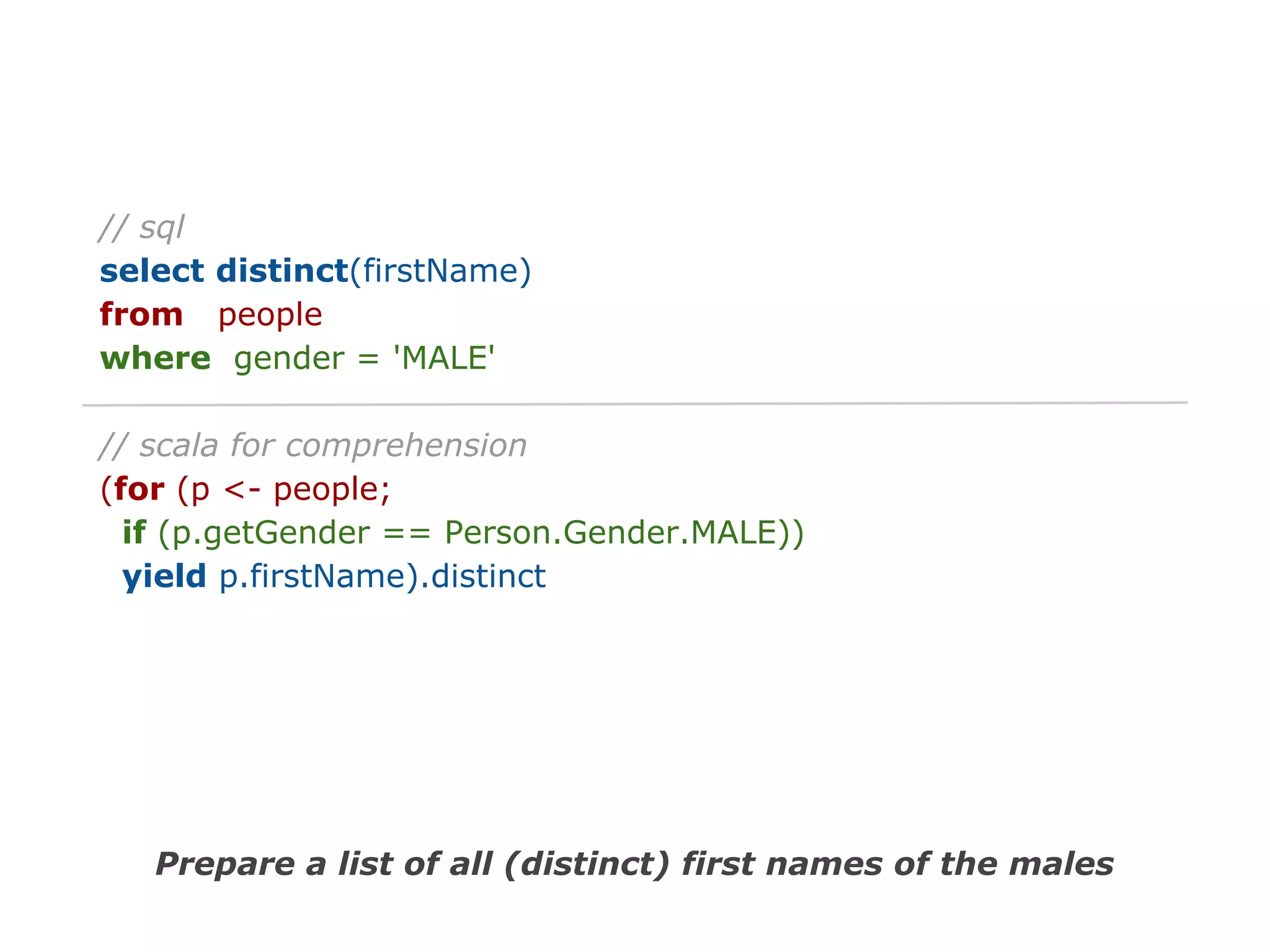
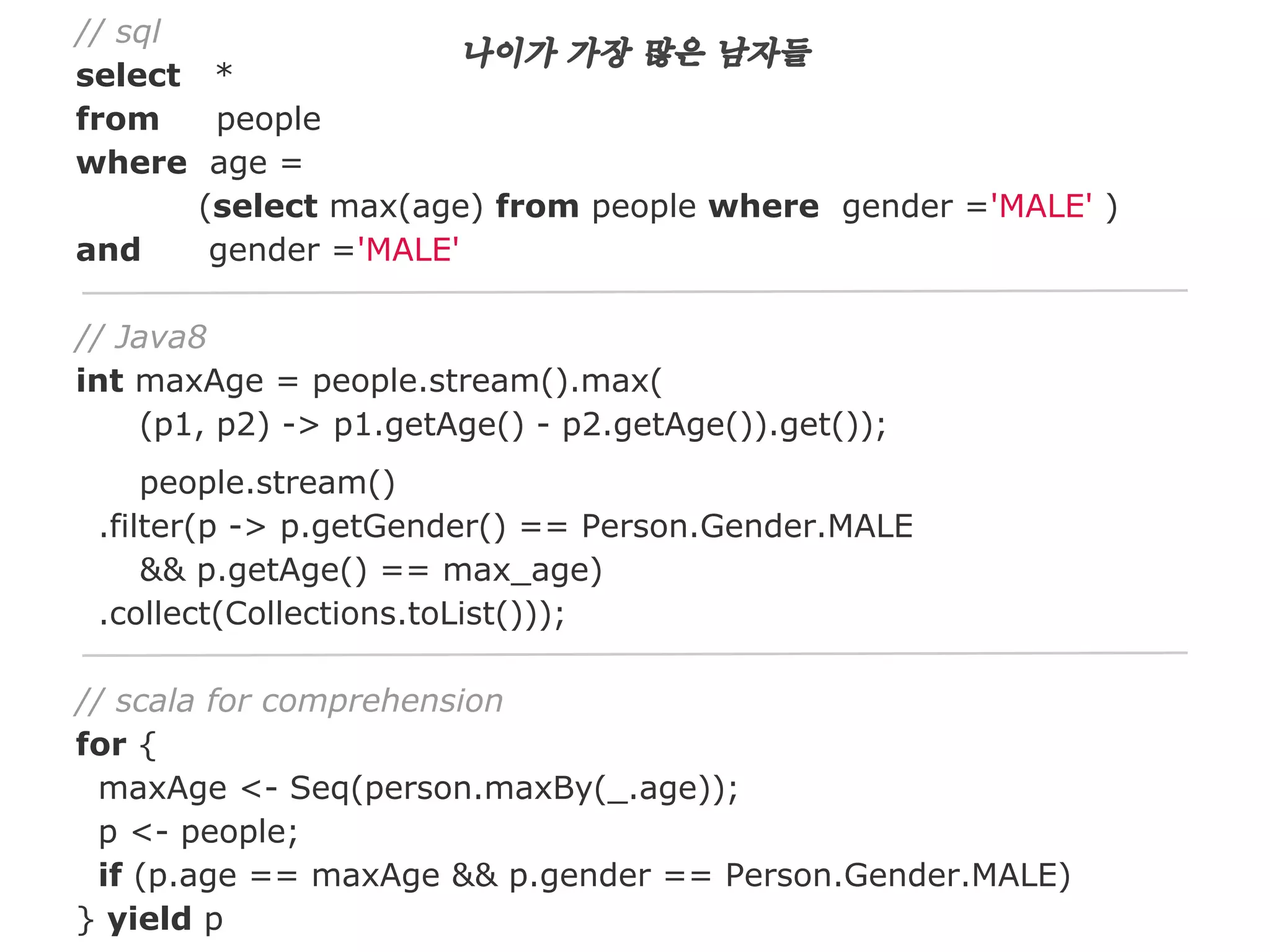
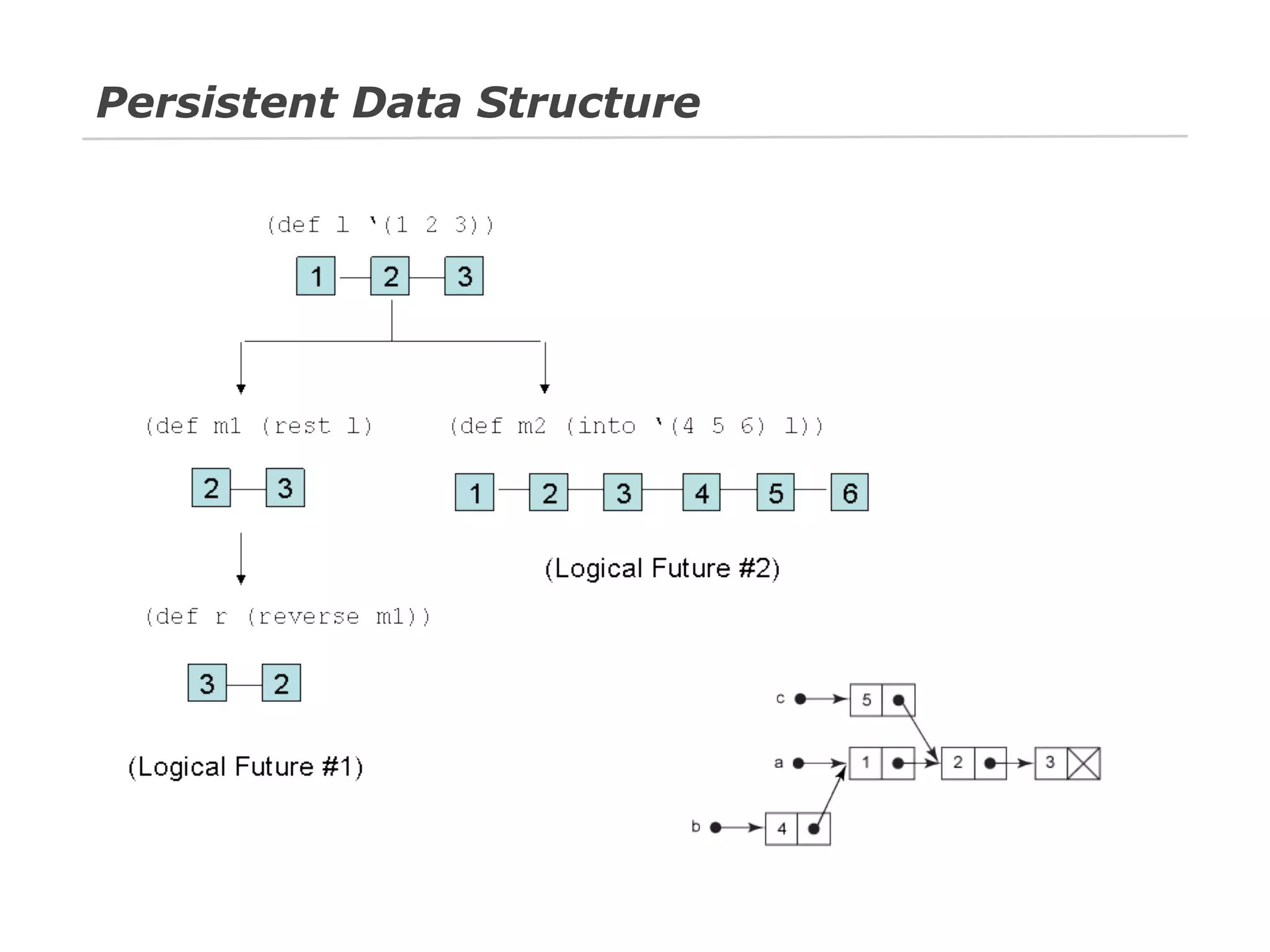
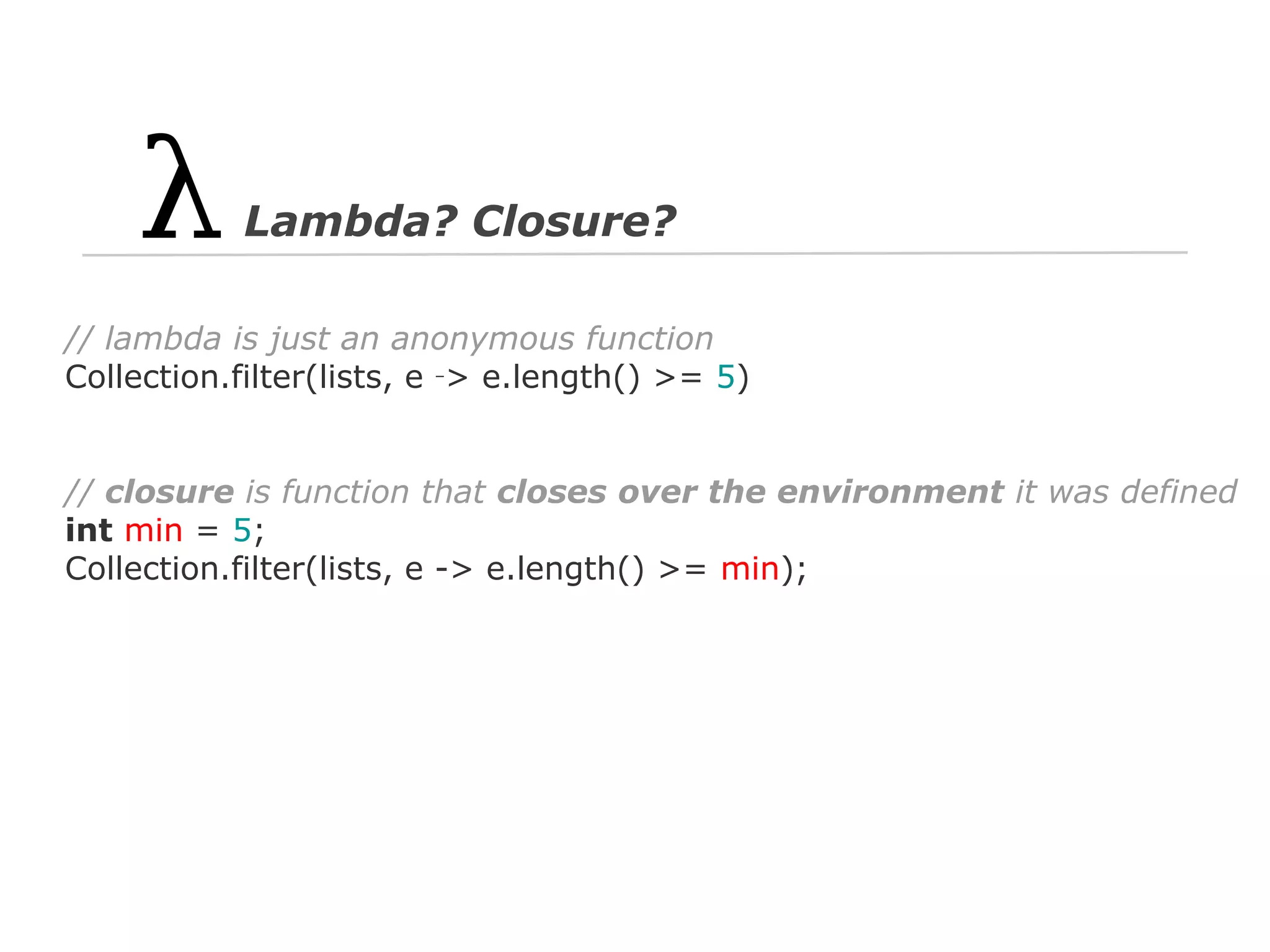
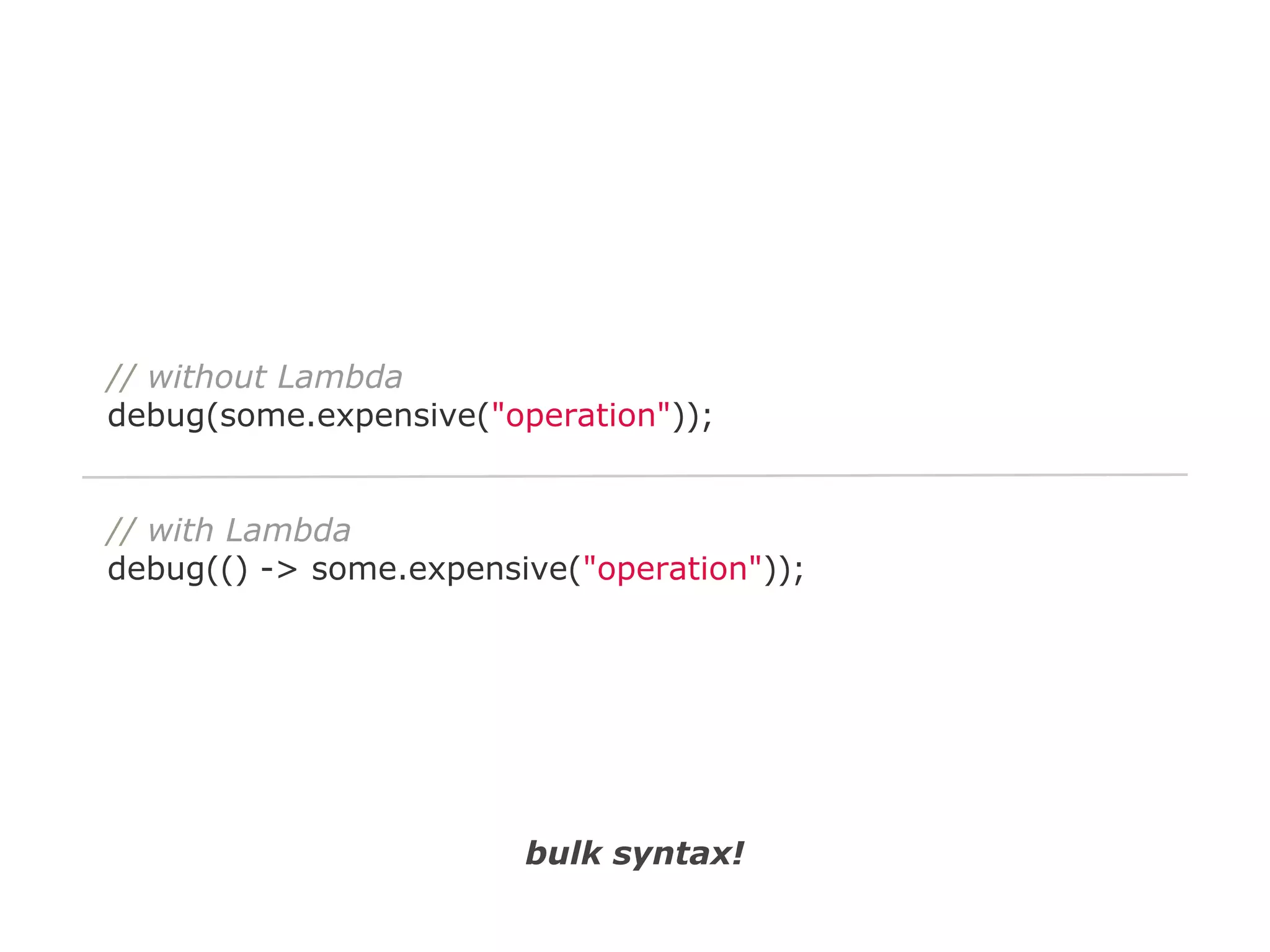
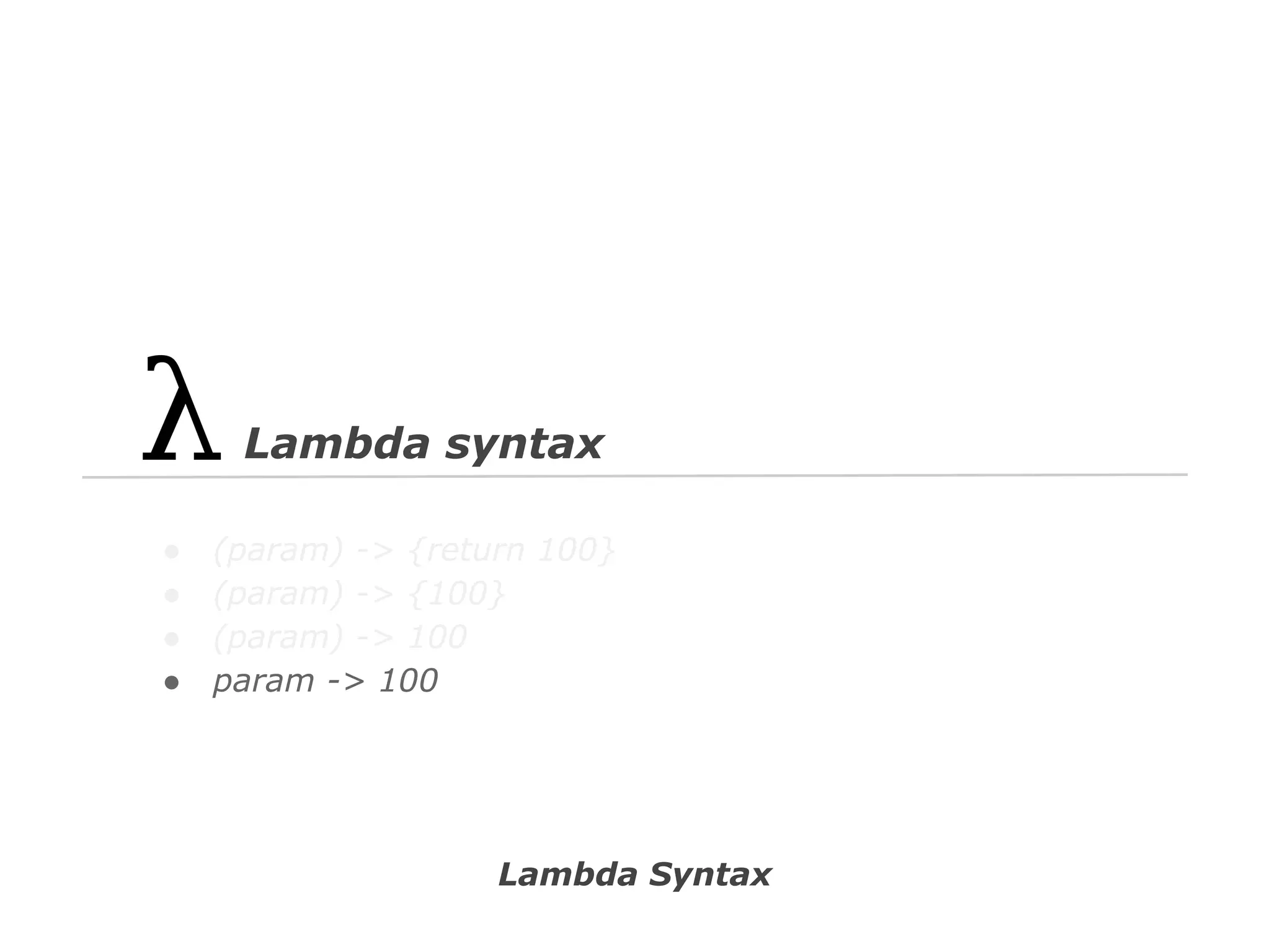
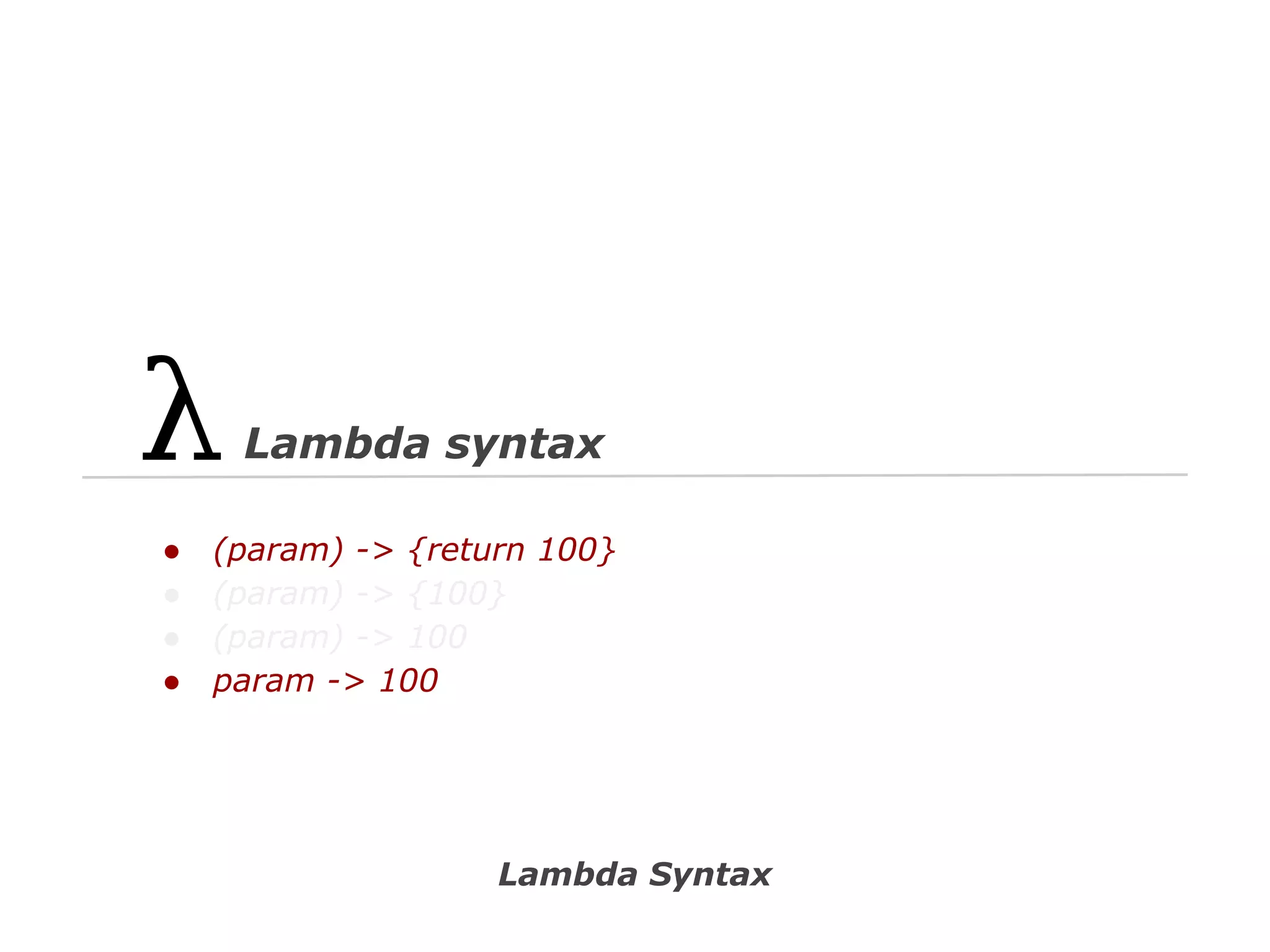
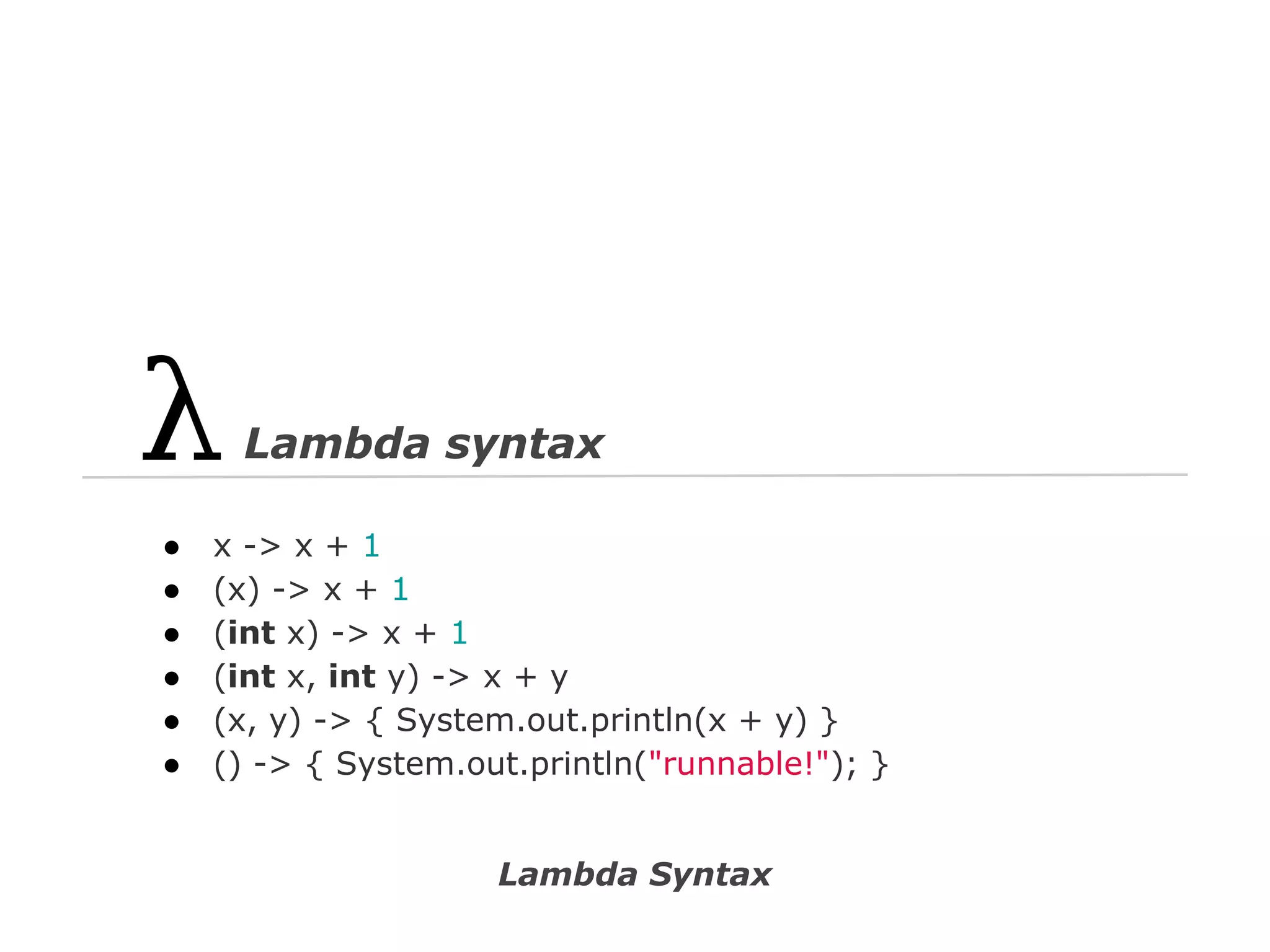
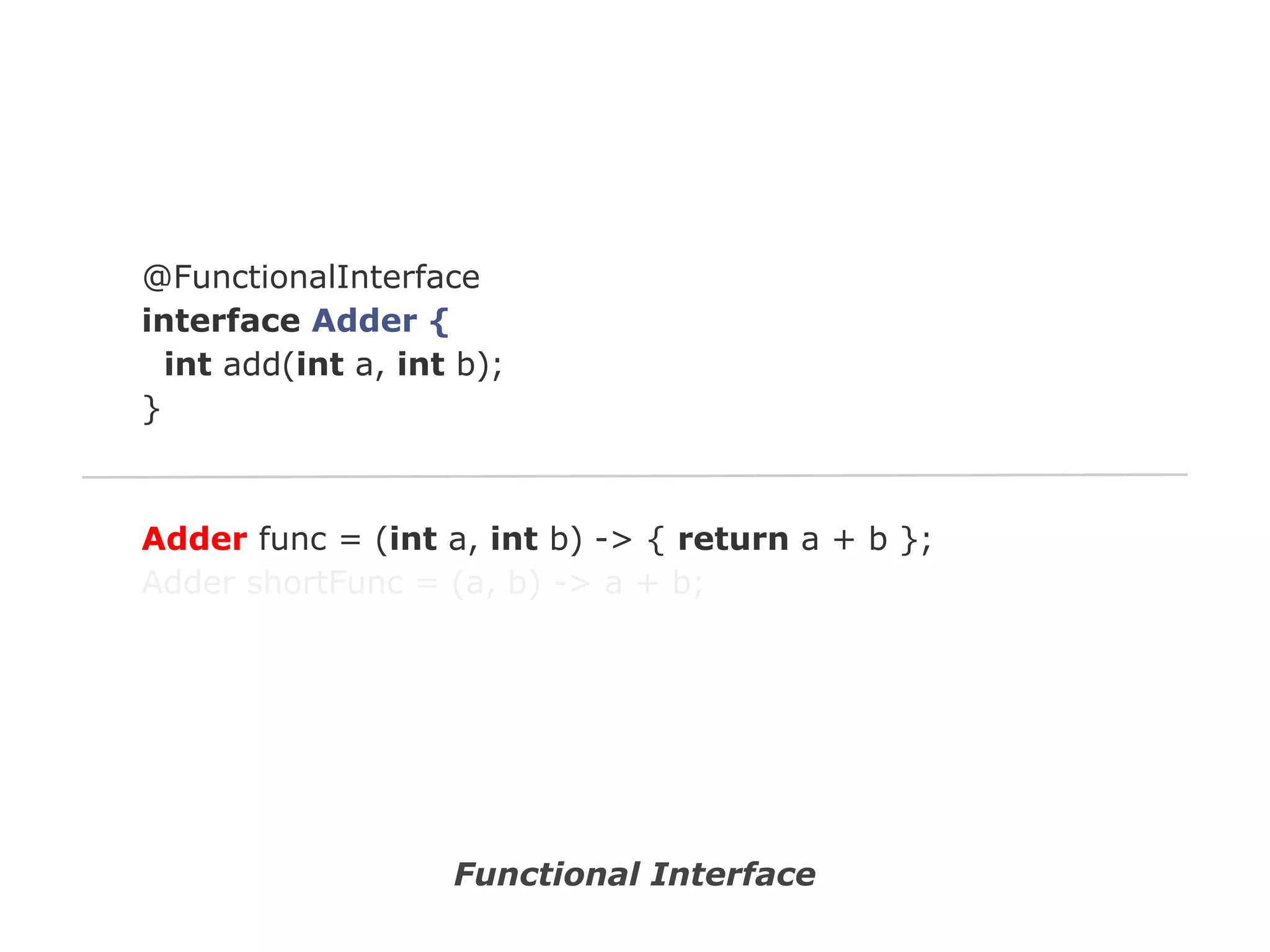
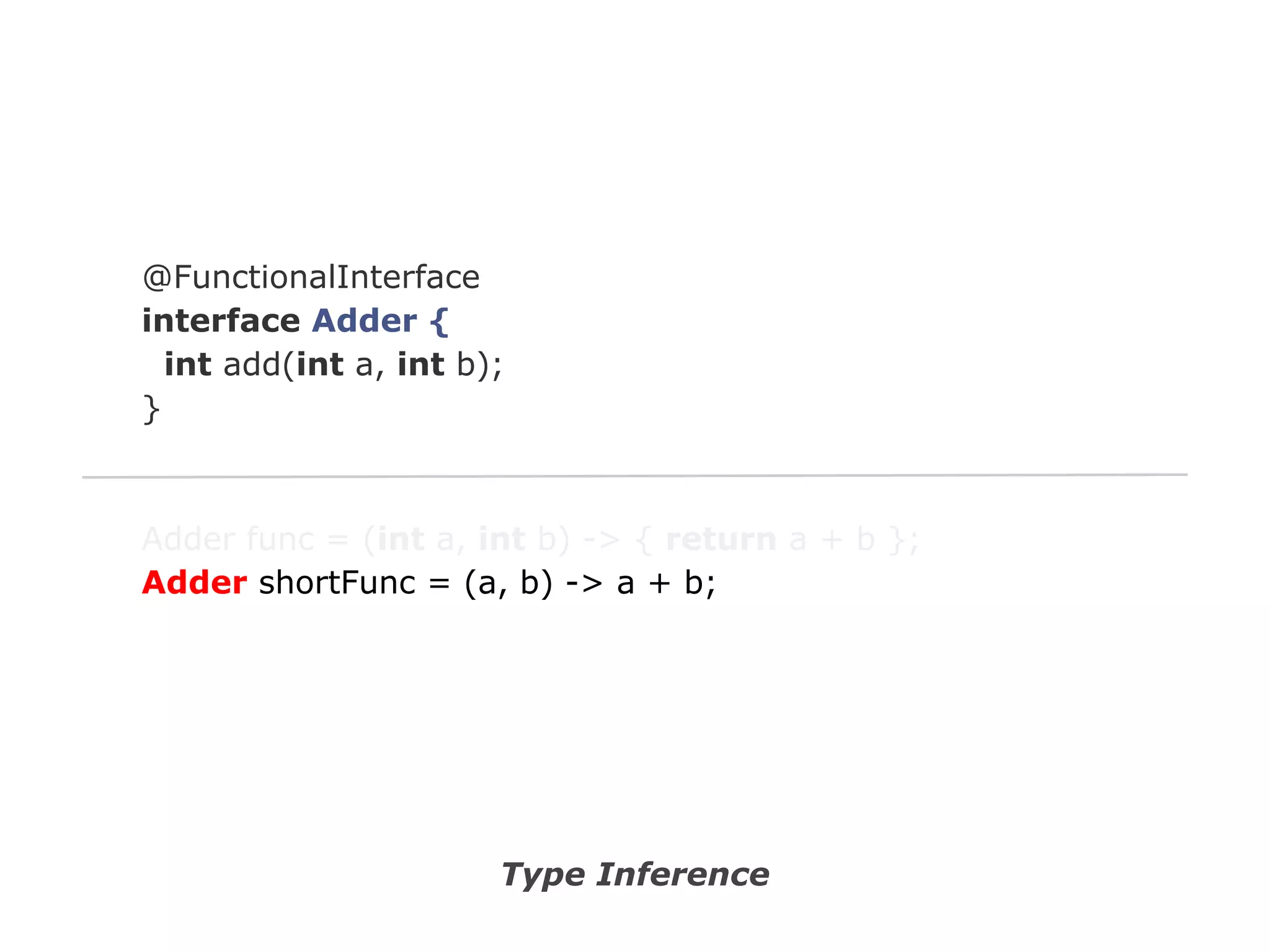
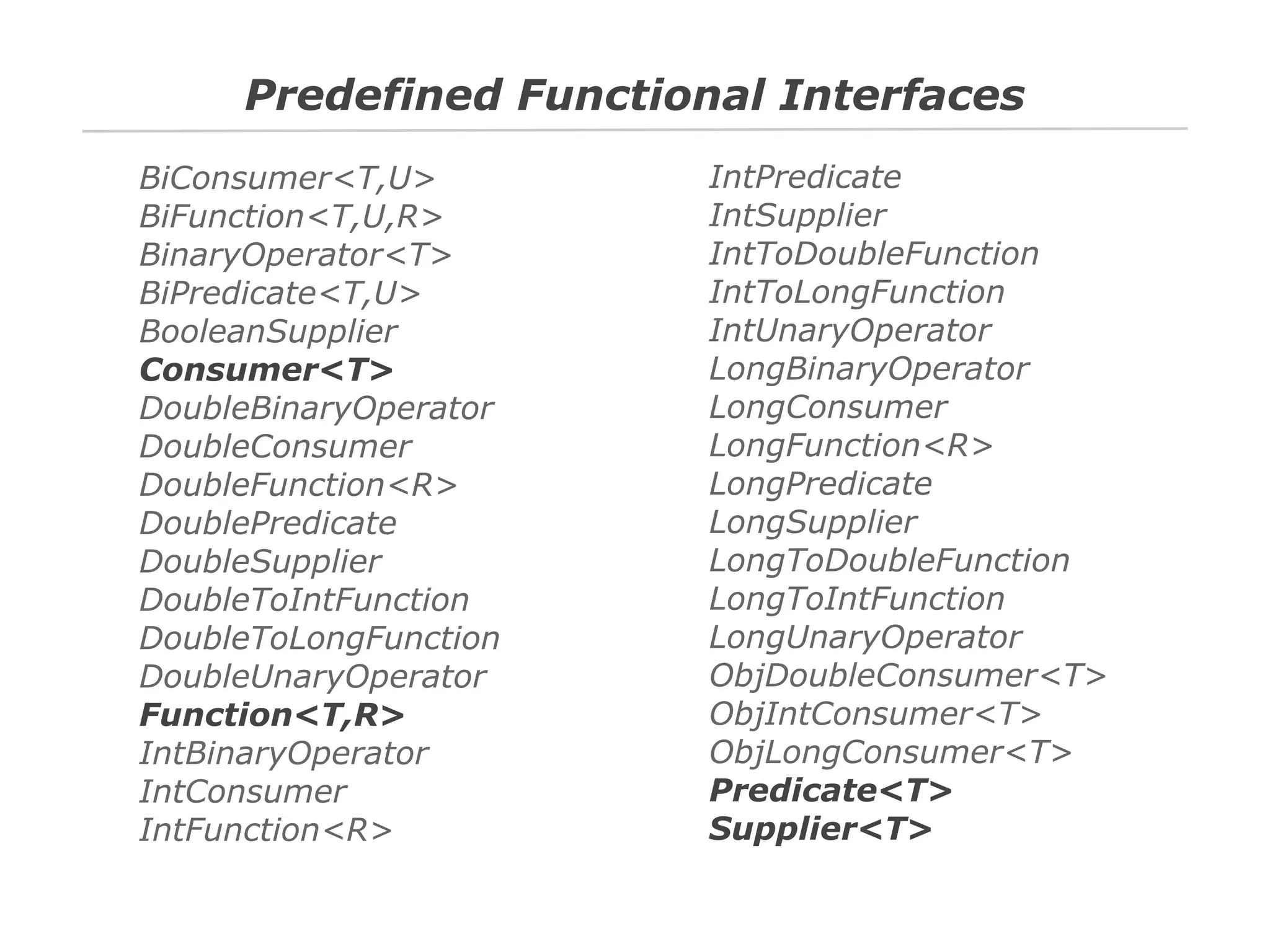
The document discusses Java 8 lambda expressions and how they improved Java by allowing for anonymous functions. It provides examples of code before and after Java 8 that demonstrate lambda expressions providing a clearer syntax compared to anonymous inner classes. Specifically, it shows how lambda expressions allowed sorting a list of strings in a more readable way. It also discusses how functions can be treated as data by being passed as parameters or returned from other functions.






















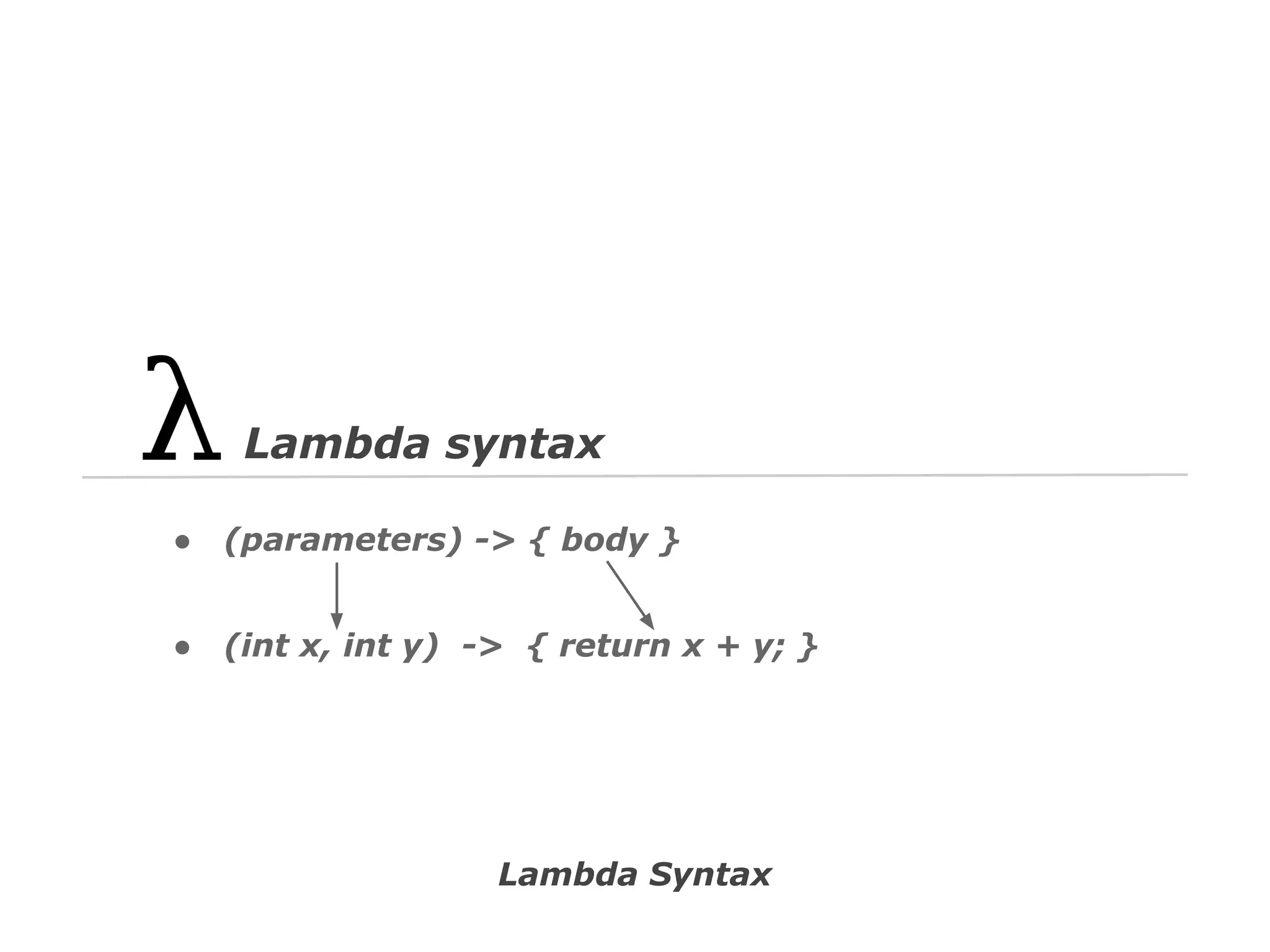
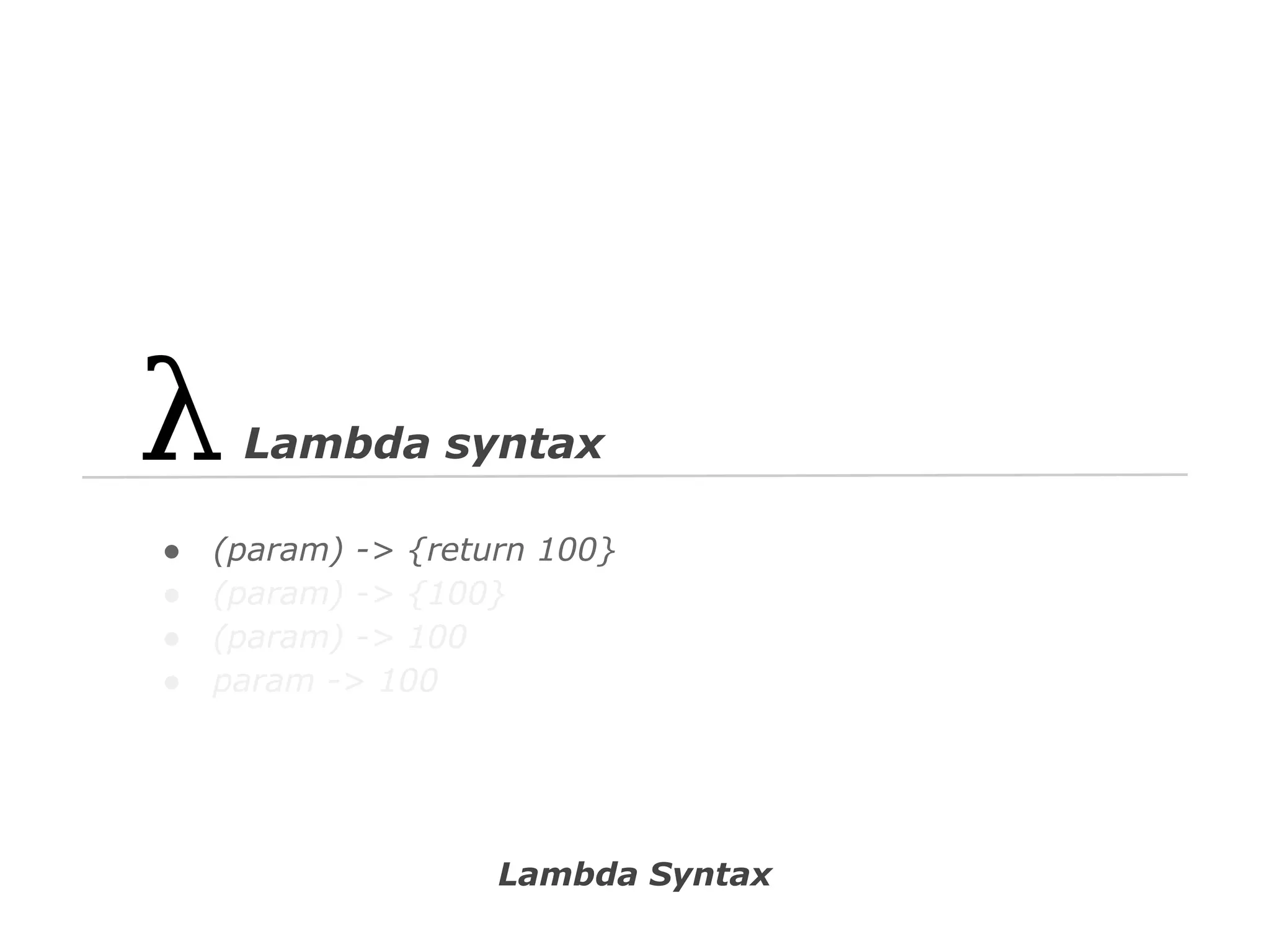
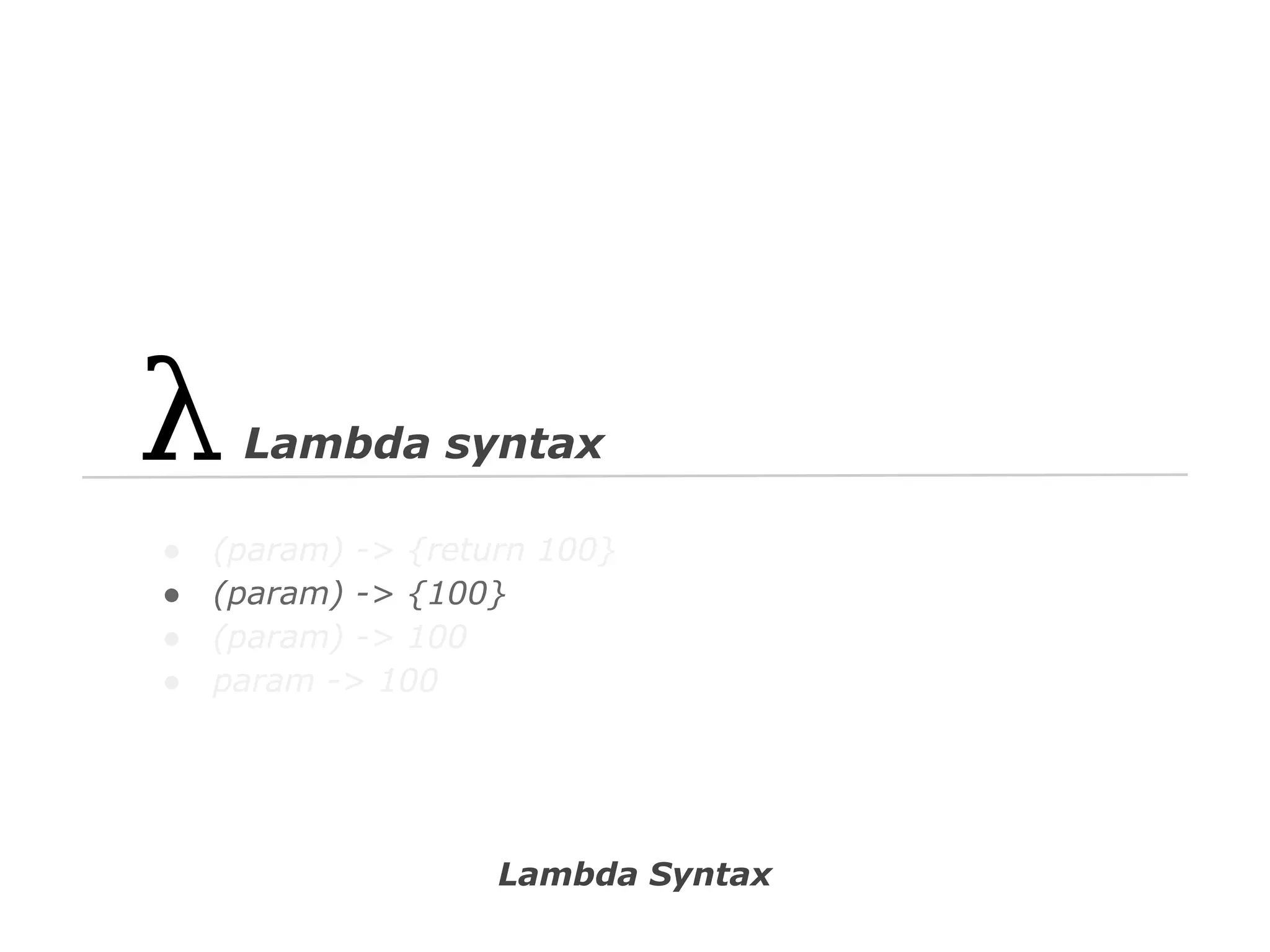
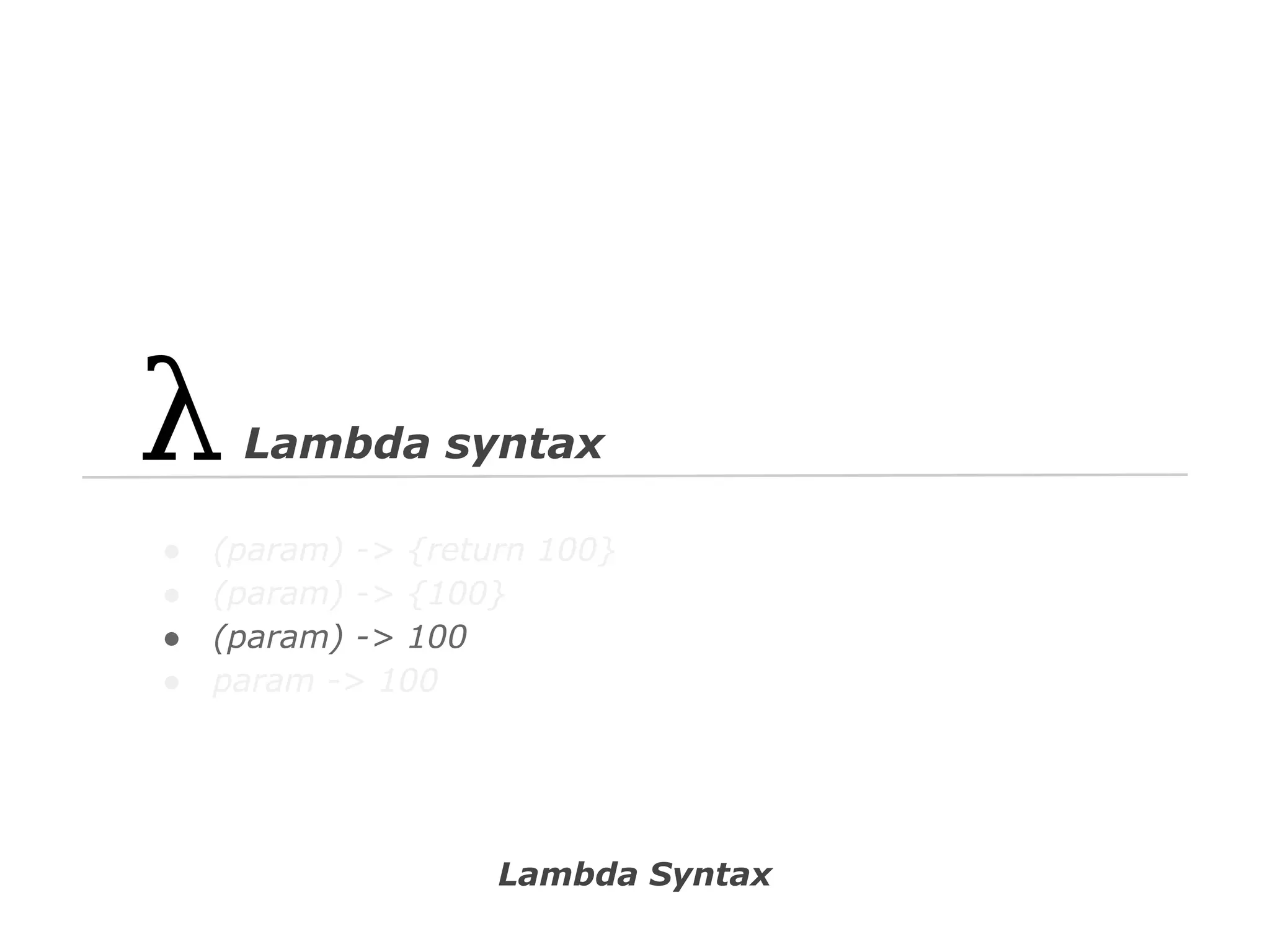






![// Spring
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from student where id = ?",
new Object[]{1212l},
new RowMapper() {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int n) throws SQLException {
return new Student(rs.getString("name"), rs.getInt("age"));
}
});
// Google Guava
Iterables.filter(persons, new Predicate<Person>() {
public boolean apply(Person p) {
return p.getAge() > 18;
}
});
Lambda in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalaisjava8-131014074003-phpapp02/75/Scala-is-java8-next-44-2048.jpg)
![// Spring
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from student where id = ?",
new Object[]{1212l},
new RowMapper() {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int n) throws SQLException {
return new Student(rs.getString("name"), rs.getInt("age"));
}
});
// Google Guava
Iterables.filter(persons, new Predicate<Person>() {
public boolean apply(Person p) {
return p.getAge() > 18;
}
});
Lambda in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalaisjava8-131014074003-phpapp02/75/Scala-is-java8-next-45-2048.jpg)