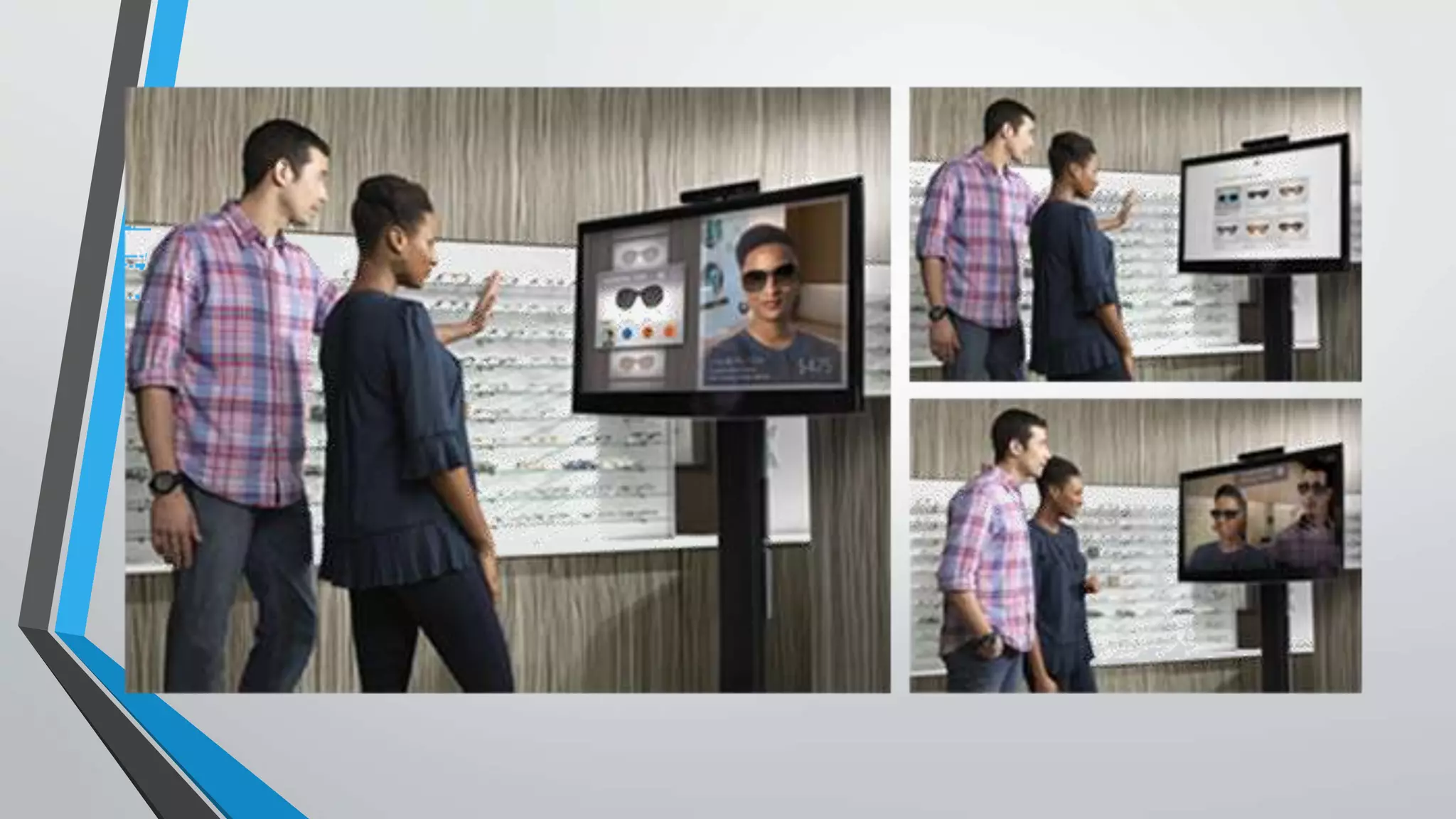
The document discusses gesture-based human-computer interaction (HCI) using Microsoft’s Kinect, emphasizing the limitations of traditional input devices like keyboards and mice. It outlines the functionalities of the Kinect sensor, including its RGB camera, infrared capabilities, and hardware/software requirements, while comparing glove-based and vision-based gesture recognition approaches. The summary highlights that Kinect enables intuitive control for various tasks but has limitations in tracking finger gestures and requires a specific distance for effective skeleton tracking.