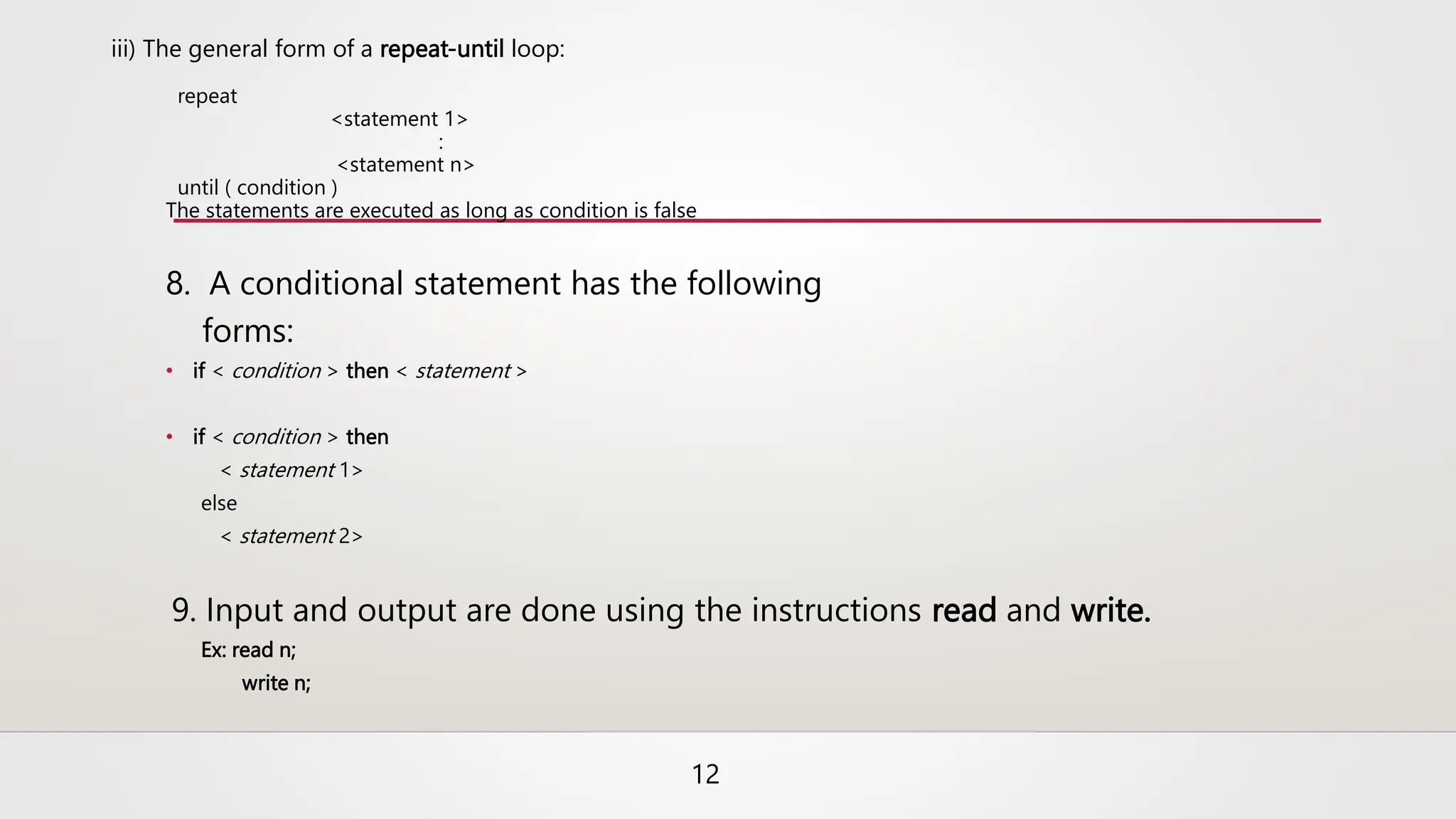
The document provides a comprehensive overview of algorithms, defining them as finite sets of instructions to accomplish tasks, with essential characteristics such as input, output, definiteness, finiteness, and effectiveness. It discusses areas for studying algorithms, including devising, validating, analyzing, and testing algorithms, as well as various representation methods like natural language, flow charts, and pseudo code. Additionally, it presents sample algorithms, programming concepts, and questions to test understanding of algorithms.









![4. Assignment of values to variables is done using the assignment
statement.
< variable > := < expression >
5. There are two boolean values true and false. To produce these values,
logical operators and, or and not and the relational operators <, ≤,=, ≠,
≥
and > are provided.
6. Elements of multidimensional arrays are accessed using [ and ]. For
example the (i,j)th element of the array A is denoted as A[i,j].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-1-240421055528-5ce00717/75/session-1_Design_Analysis_Algorithm-pptx-10-2048.jpg)


![WRITE AN ALGORITHM TO FIND SUM OF N NUMBERS IN THE
GIVEN LIST
Algorithm sum(a,n)
{
s:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
s:=s+a[i];
return s;
}
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-1-240421055528-5ce00717/75/session-1_Design_Analysis_Algorithm-pptx-14-2048.jpg)

