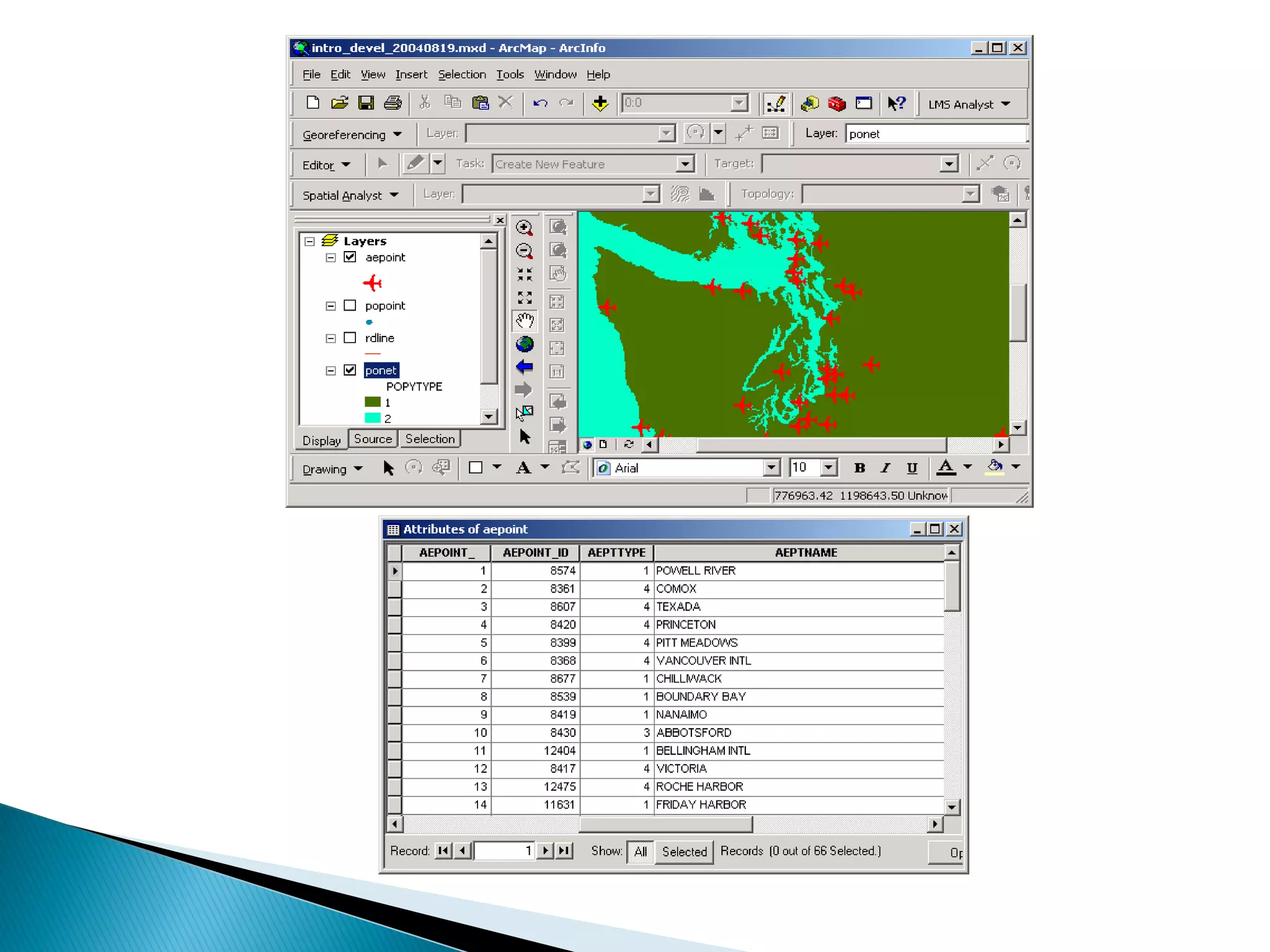
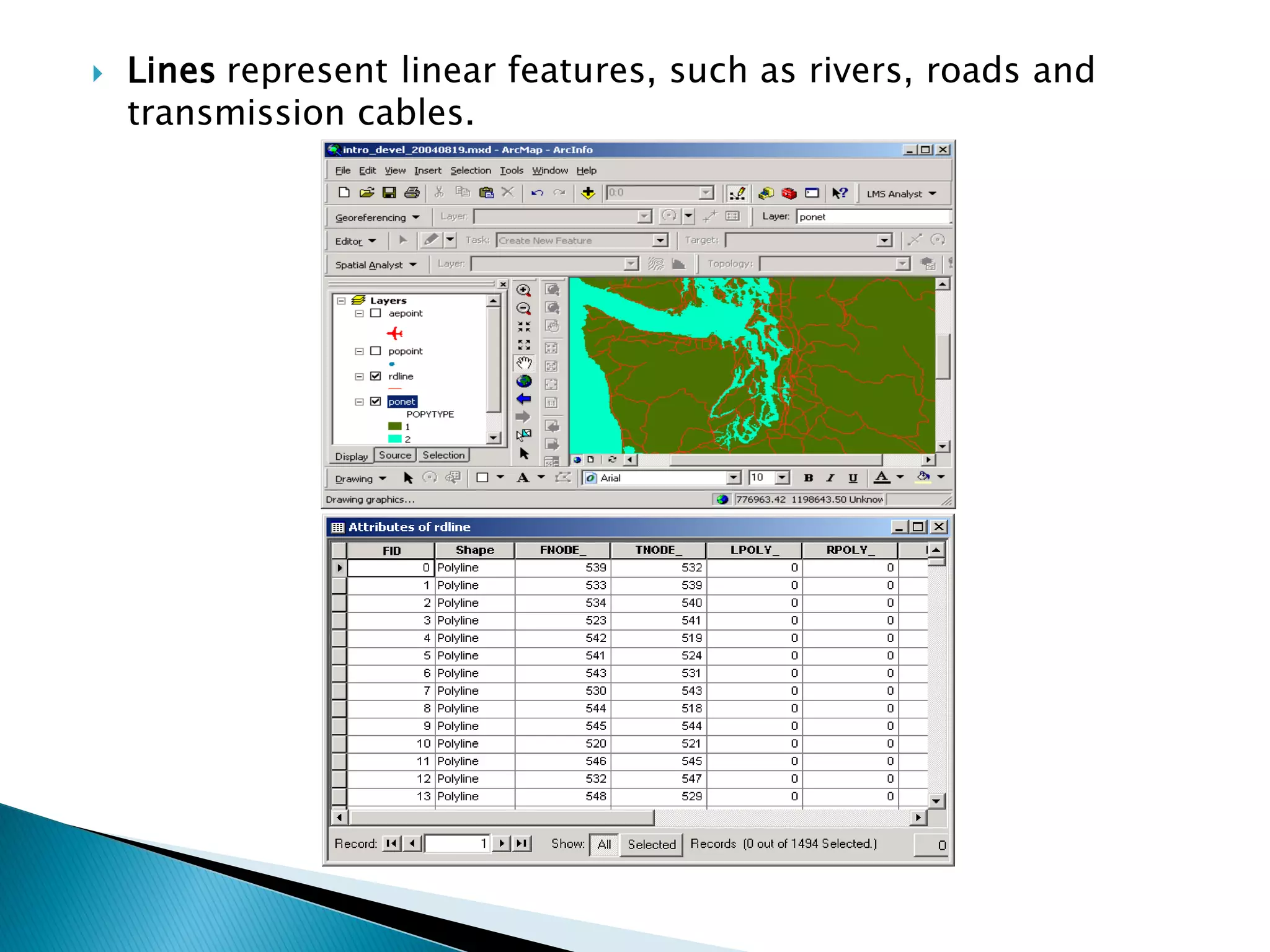
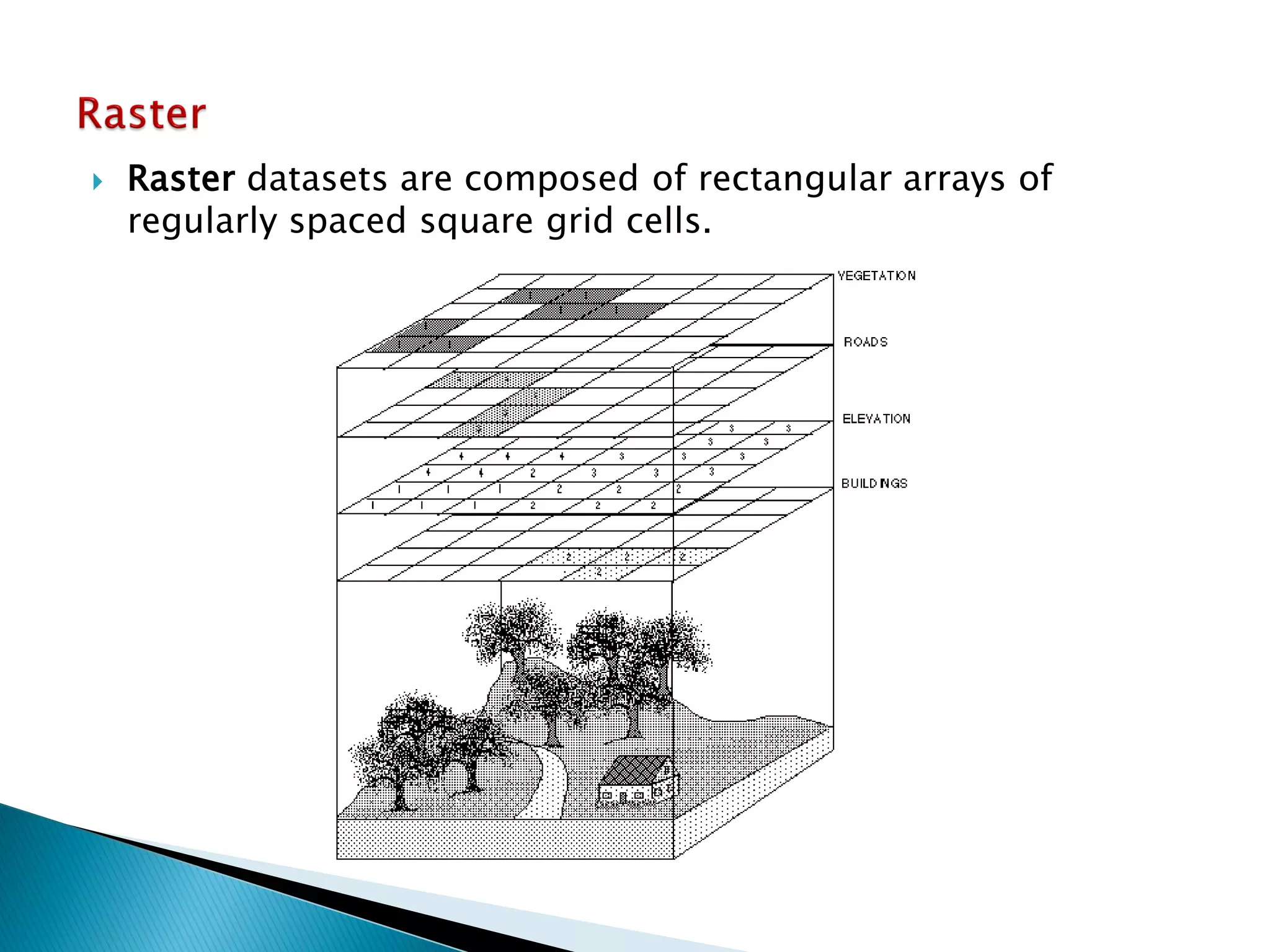
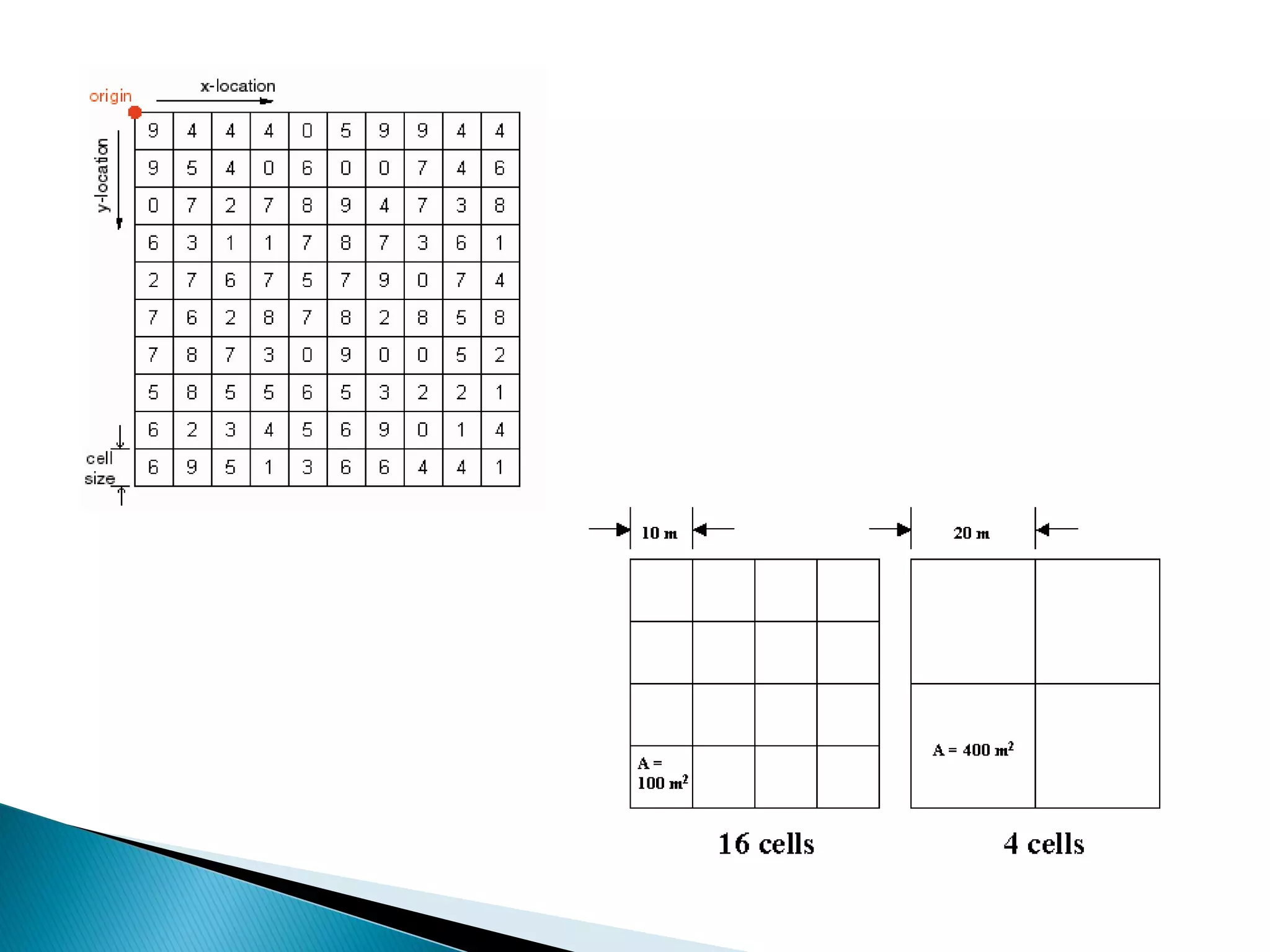
The document discusses different types of spatial data used in geographic information systems (GIS). It describes vector data, which represents geographic features as points, lines, and polygons, and raster data, which divides the landscape into a grid of cells. It outlines some common vector data formats like shapefiles, coverages, and geodatabases, and raster formats like grids and digital elevation models. It provides details on how vector data structures represent points, lines, polygons, and their topological relationships in ArcGIS.