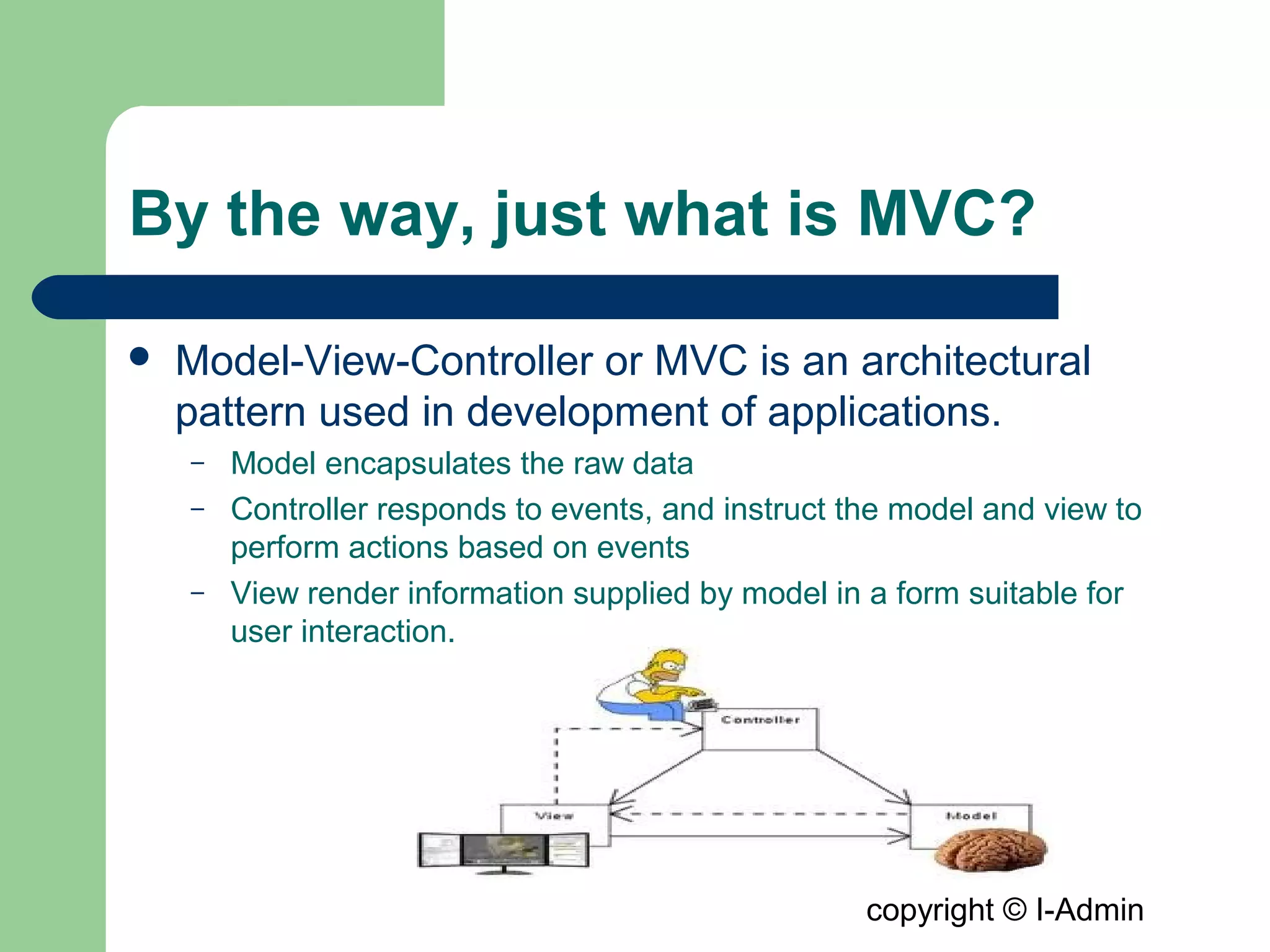
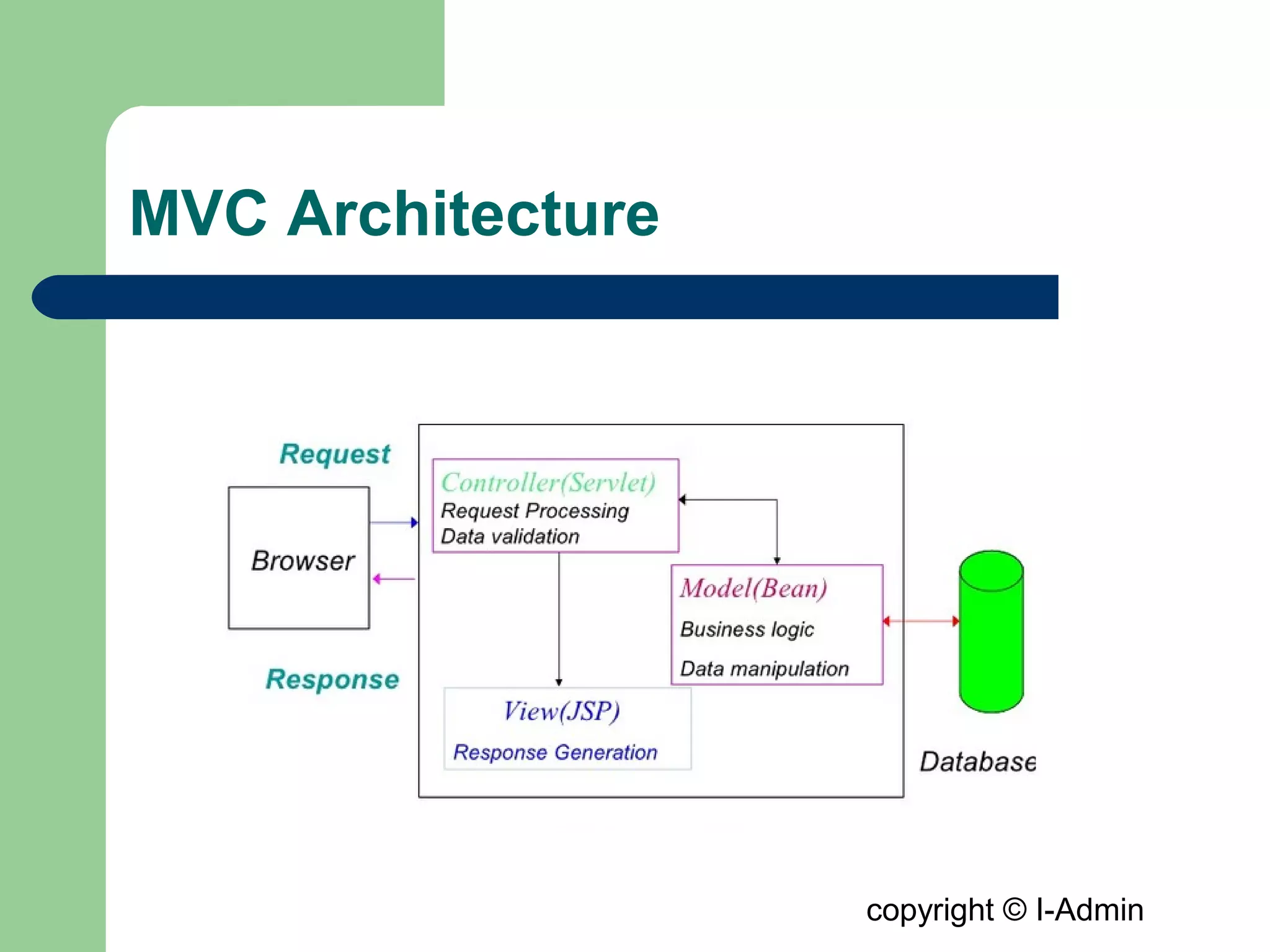
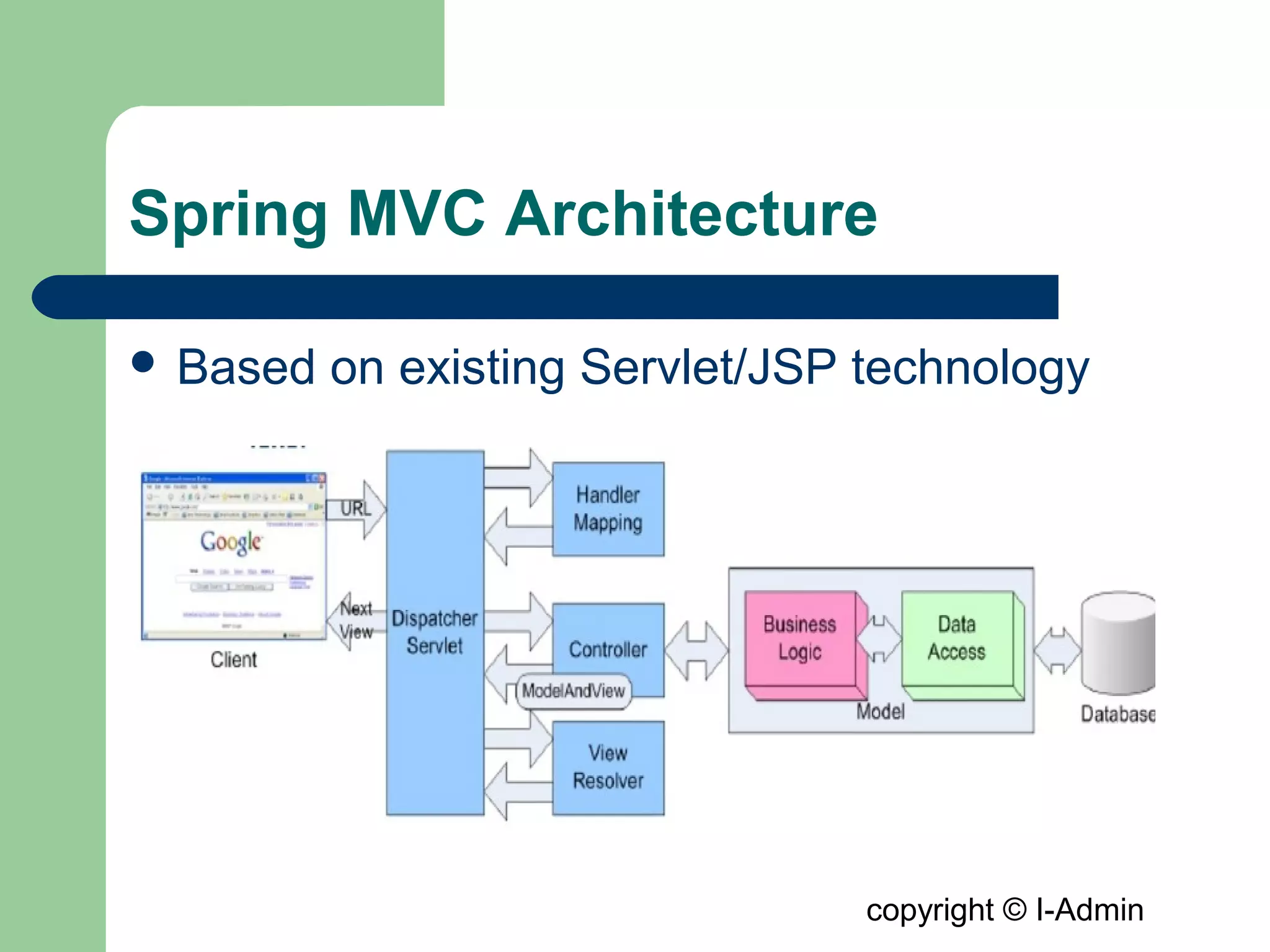
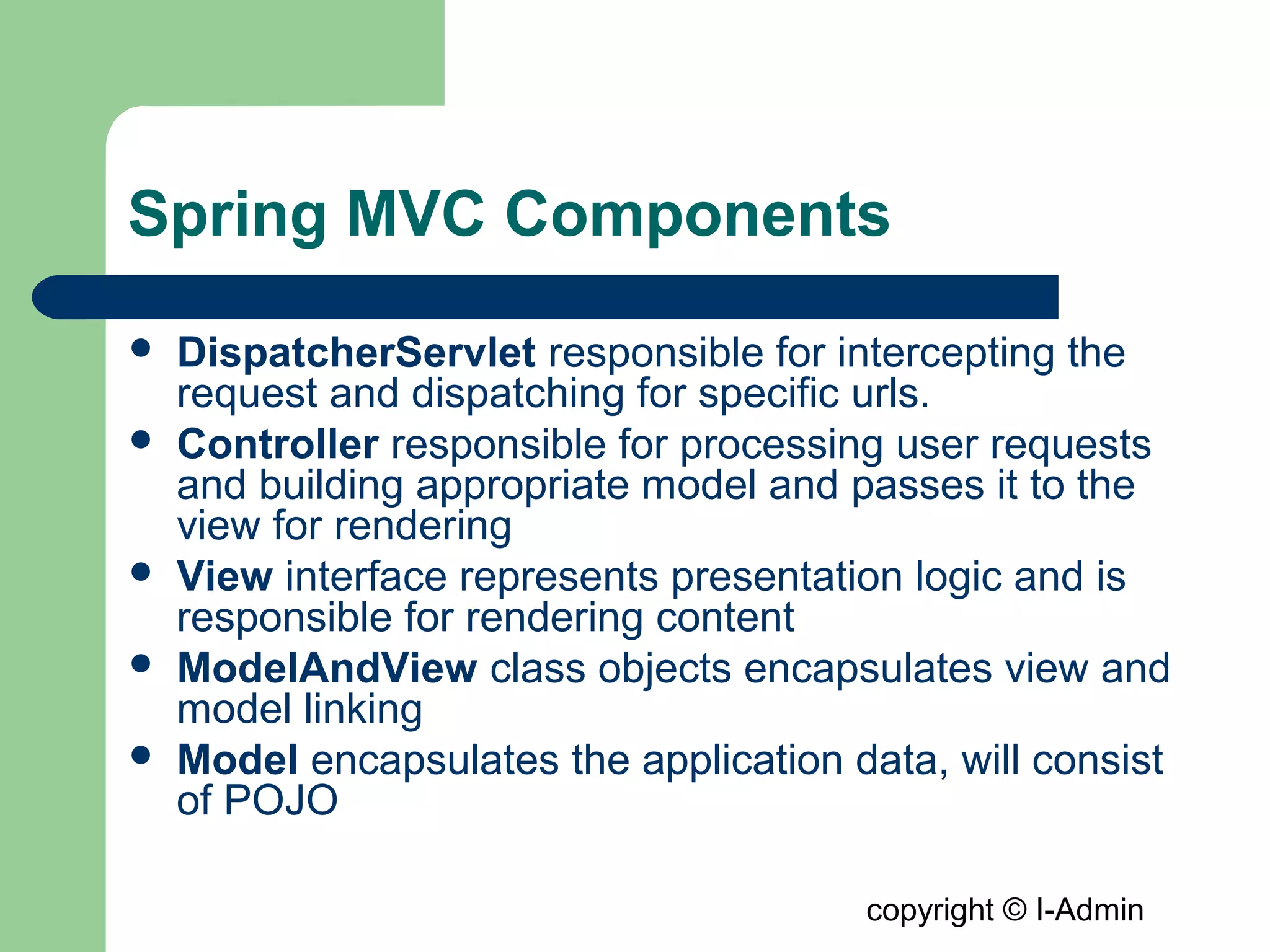
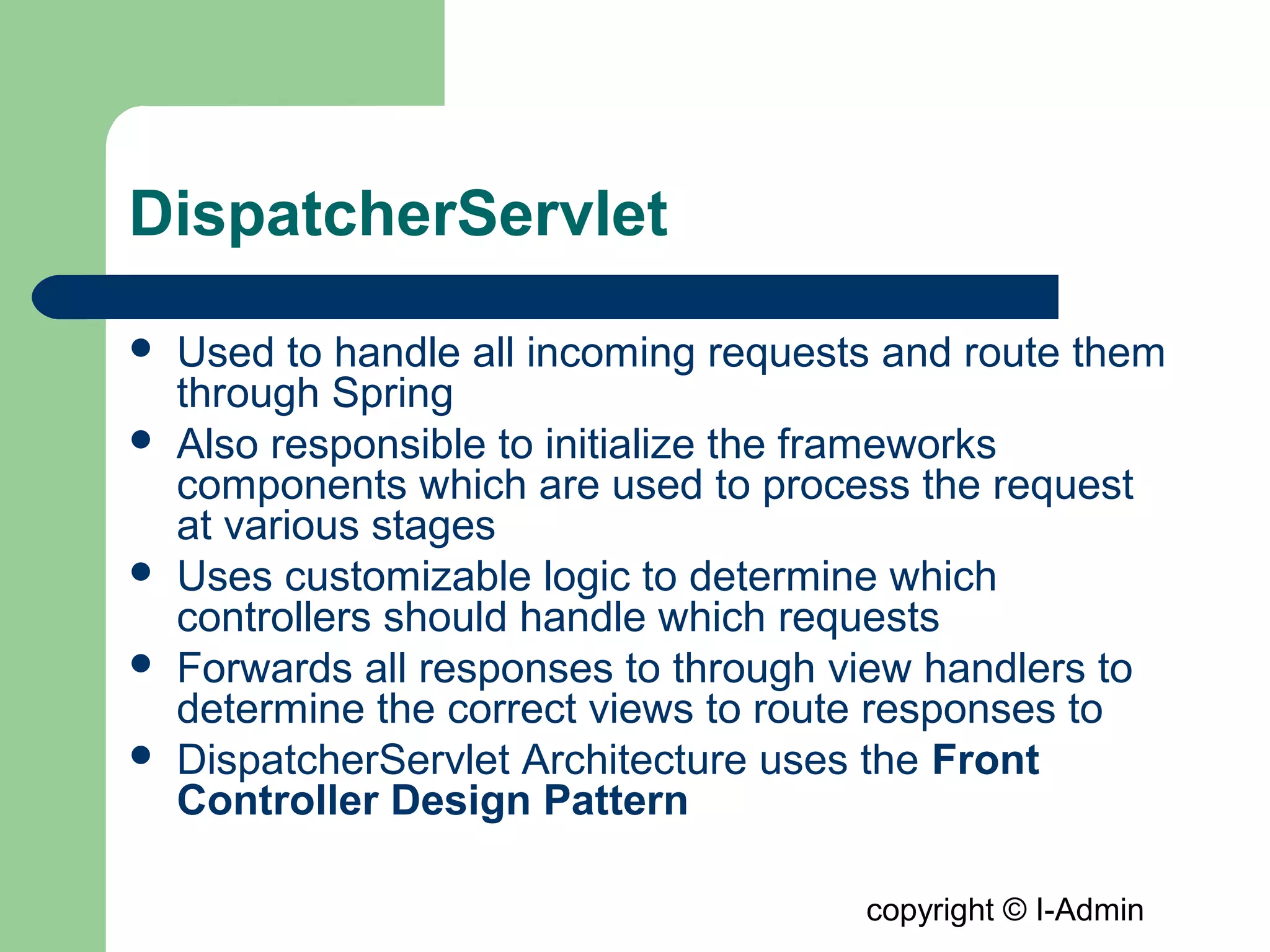
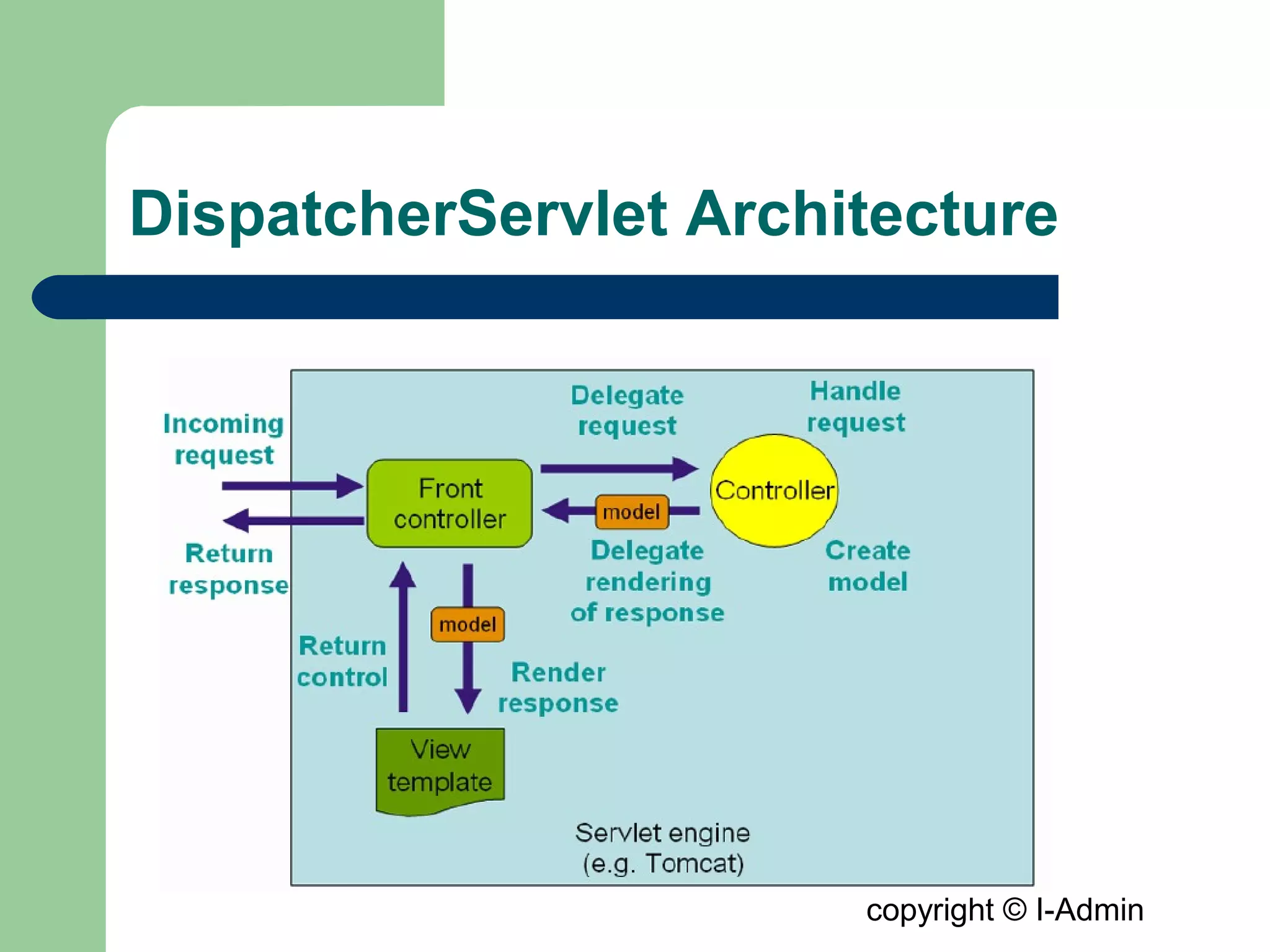
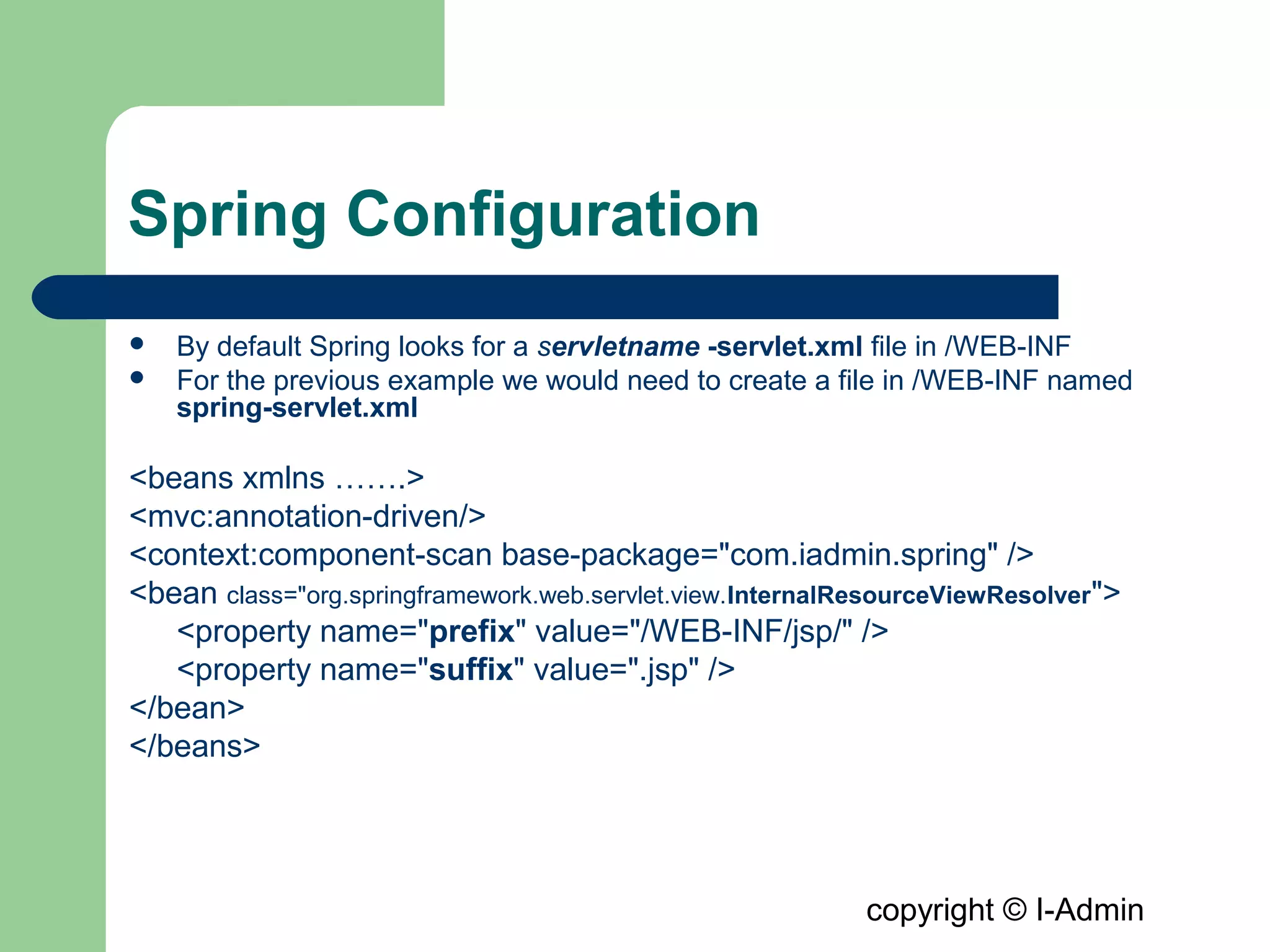
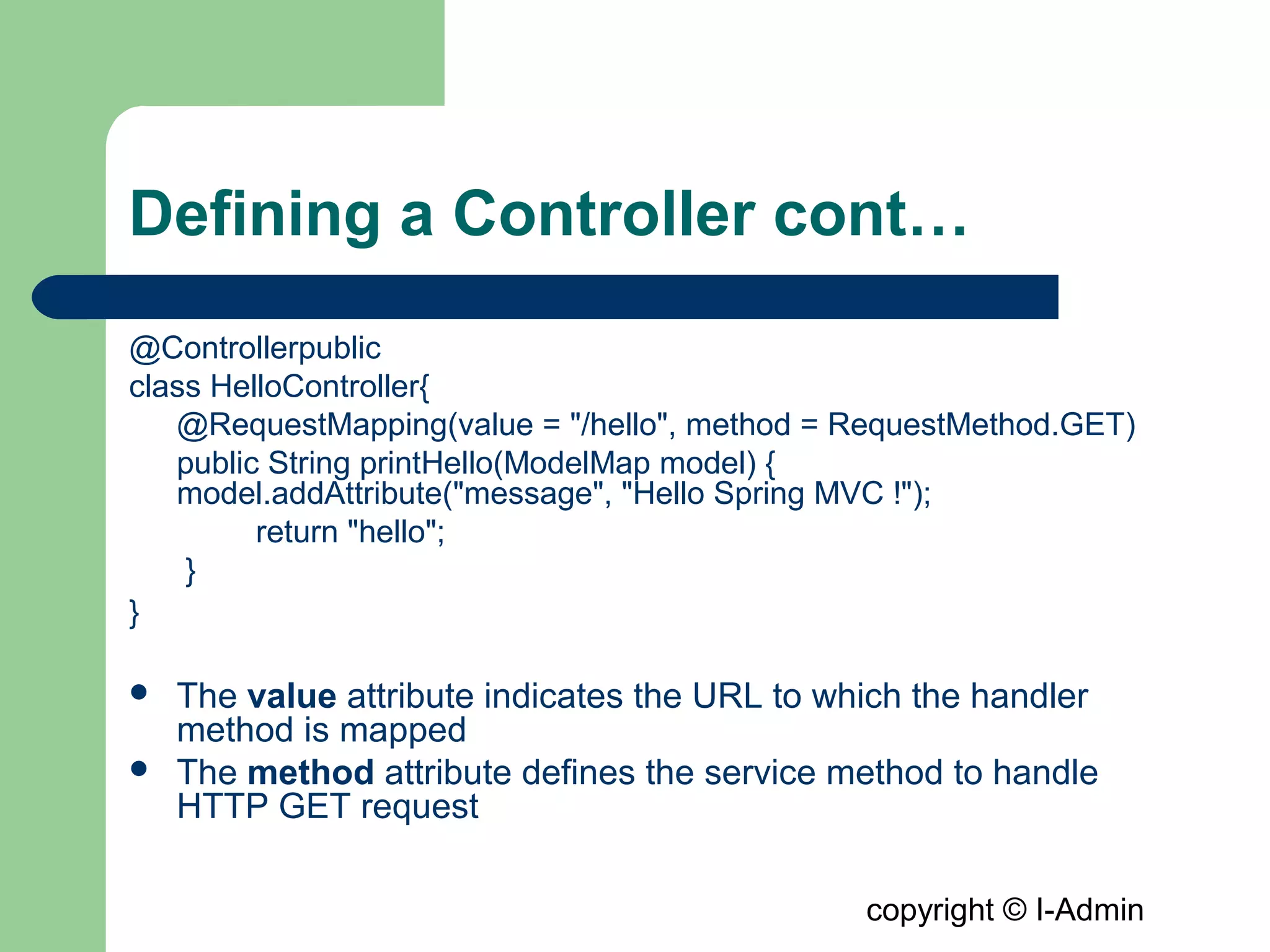
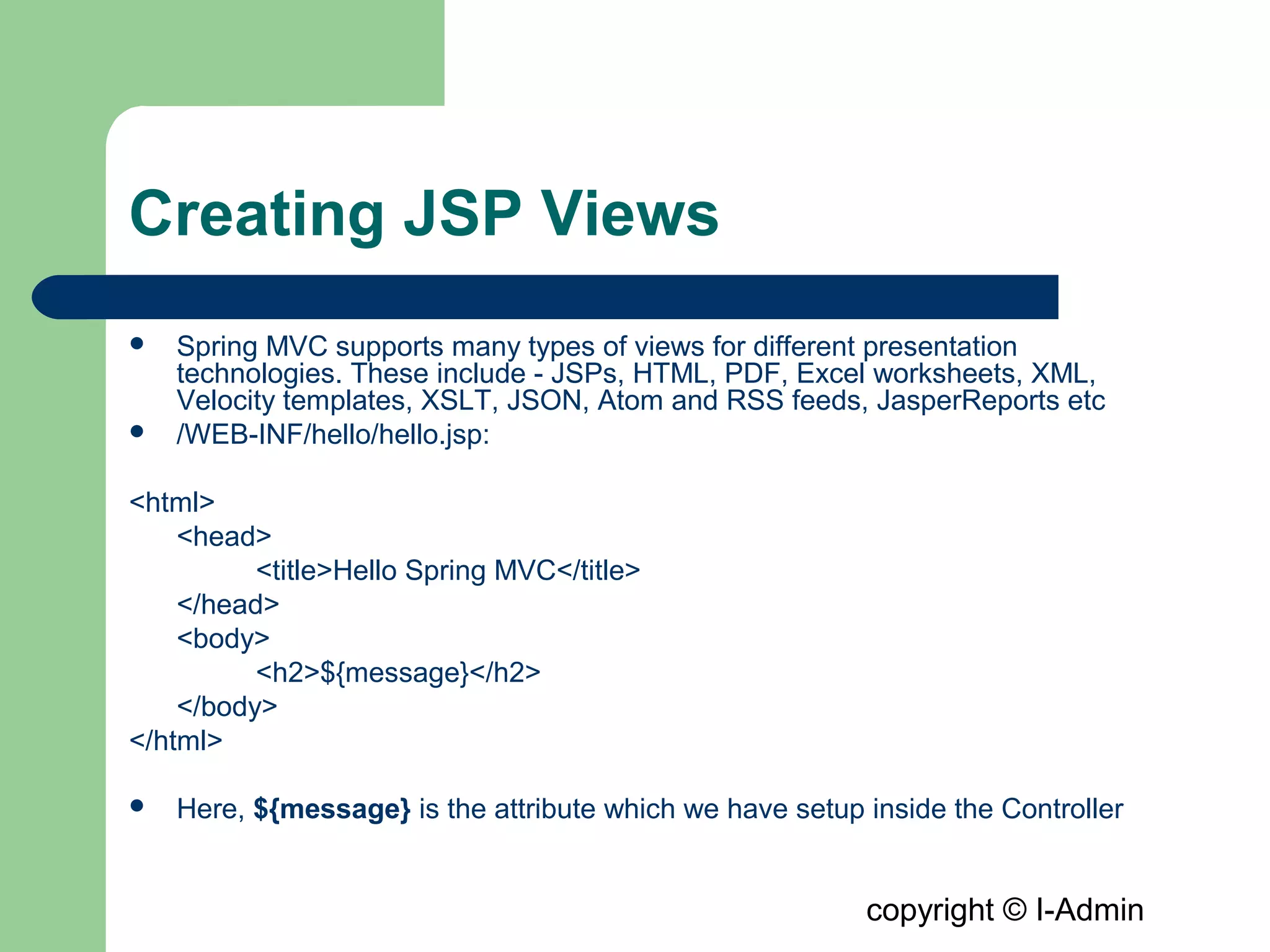
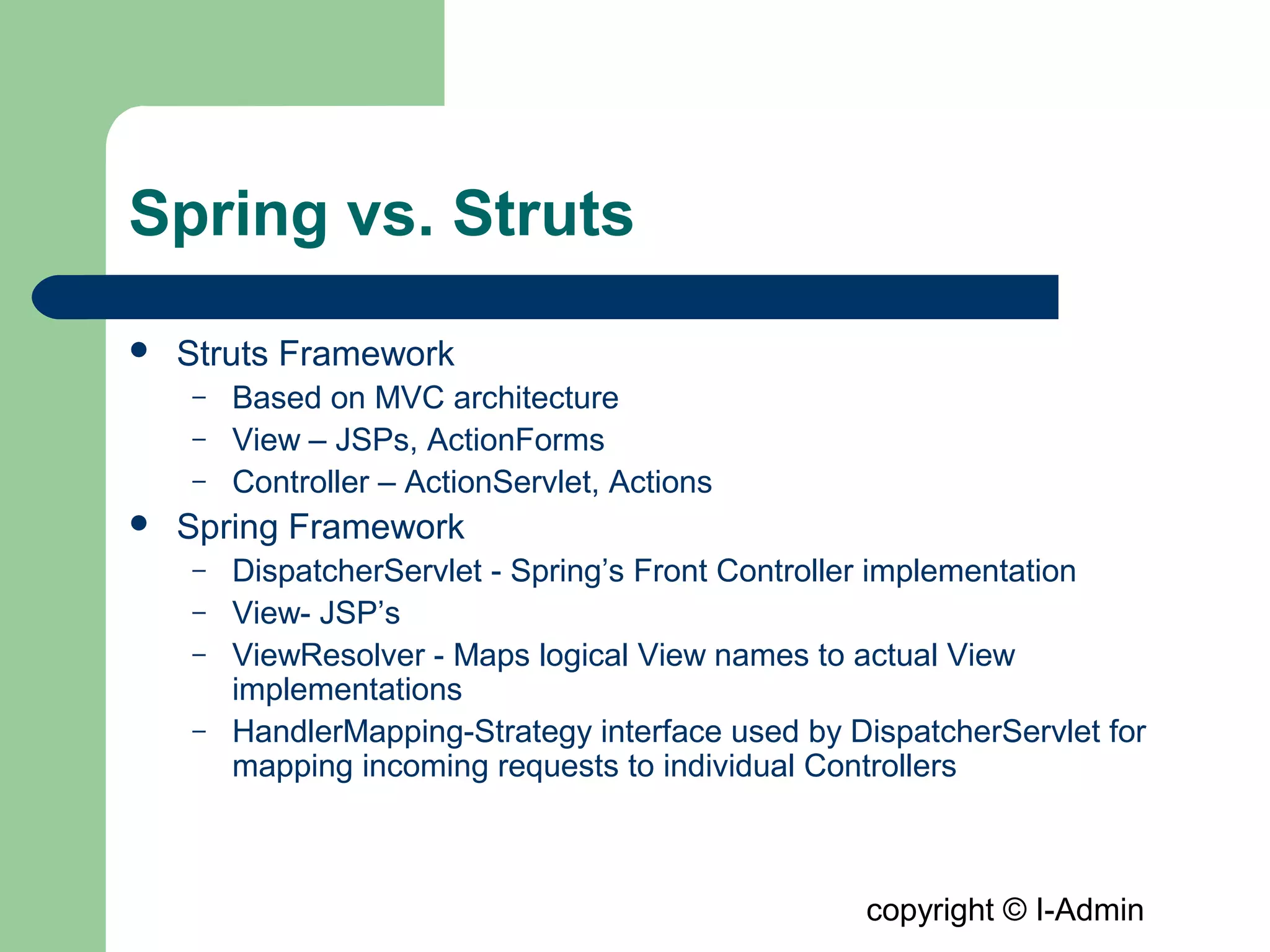
The document provides an overview of the Spring MVC framework, detailing its components such as DispatcherServlet, controllers, and views, while emphasizing its support for easier enterprise application development and testing. It explains the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern and how it functions within Spring to handle web requests and responses. Additionally, it contrasts Spring MVC with the Struts framework, outlining their respective roles and architectures.