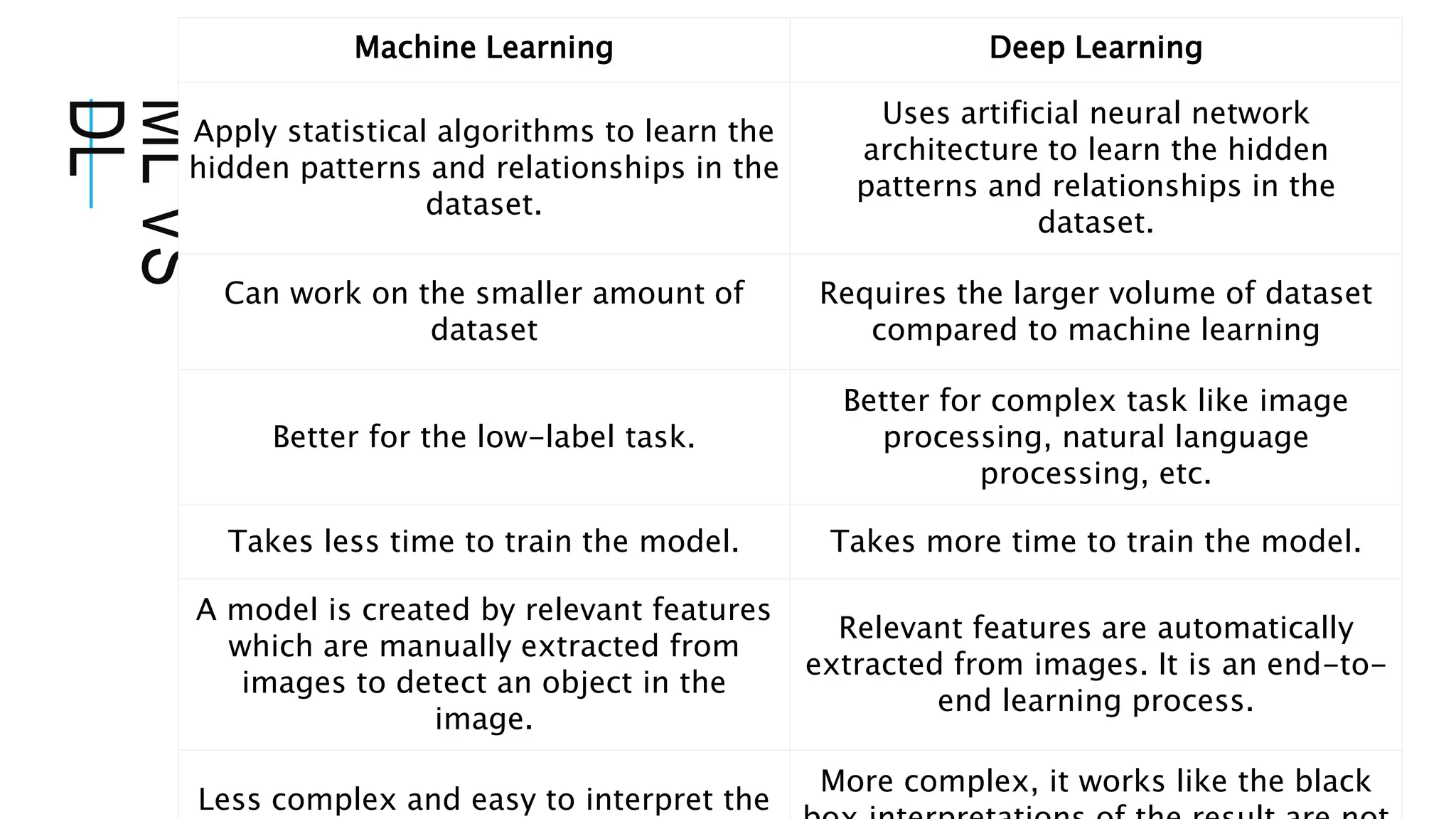
The document provides an overview of deep learning (DL) as a subfield of machine learning (ML) that utilizes artificial neural networks for data processing. It outlines the differences between ML and DL, emphasizing the need for larger datasets in DL and its applications in areas like image recognition, natural language processing, and finance. Additionally, it details various algorithms used in DL, including feedforward neural networks, convolutional neural networks, and recurrent neural networks.