This document provides an overview of key concepts related to programming languages. It discusses the definition of a programming language and the history and evolution of popular languages from 1951 to present. It covers programming language paradigms like procedural, object-oriented, functional, and logic-based languages. It also discusses factors that influence language design like efficiency, regularity, and issues in language translation. Finally, it summarizes the structure and operation of computers and how different programming models map to underlying computer architectures.





































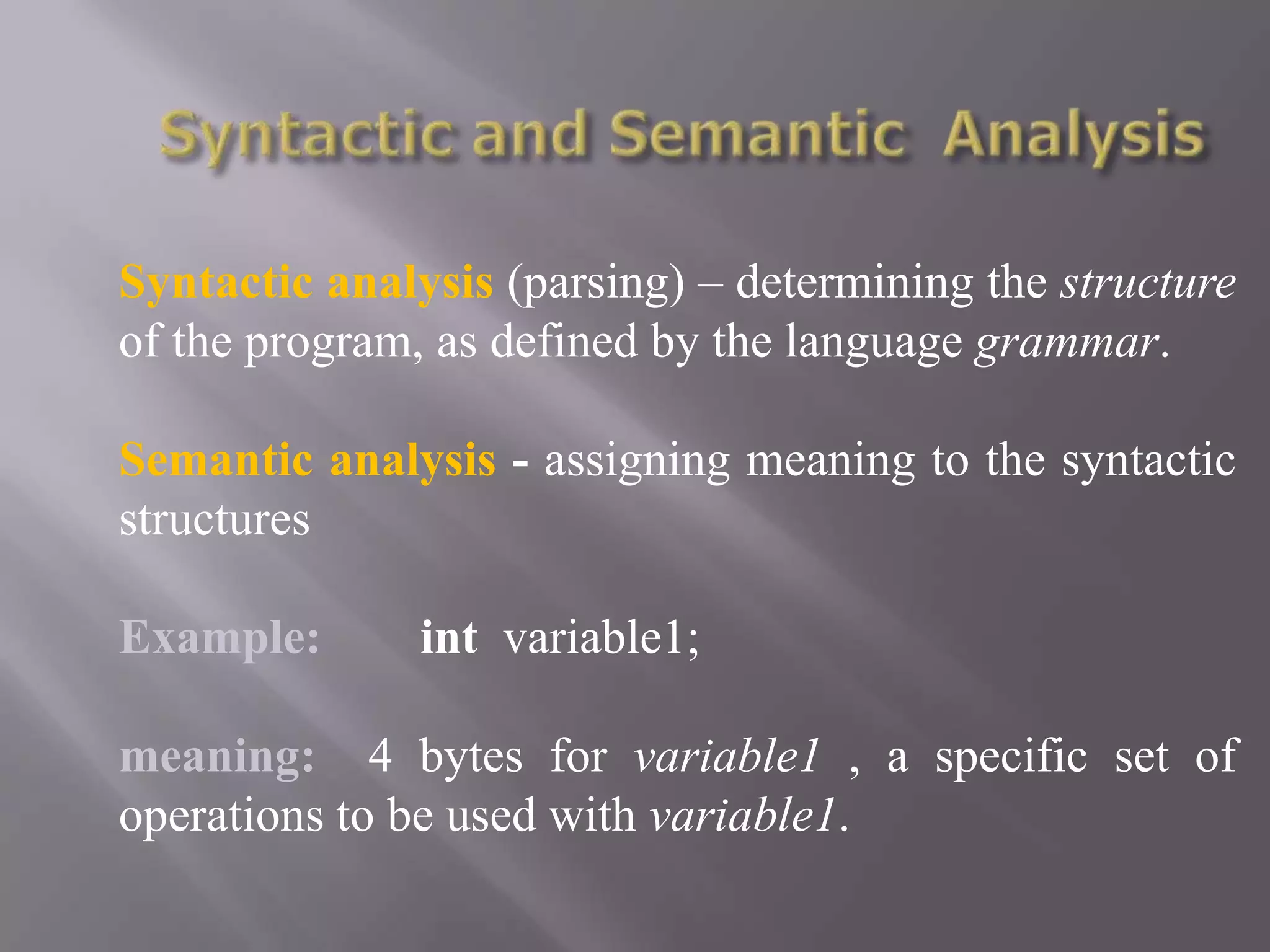




![ Syntax: what the program looks like.
Semantics: the meaning given to the various
syntactic constructs.
Example:
V: array [0..9] of integer;
int V[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-130131031436-phpapp01/75/Unit1-principle-of-programming-language-46-2048.jpg)
