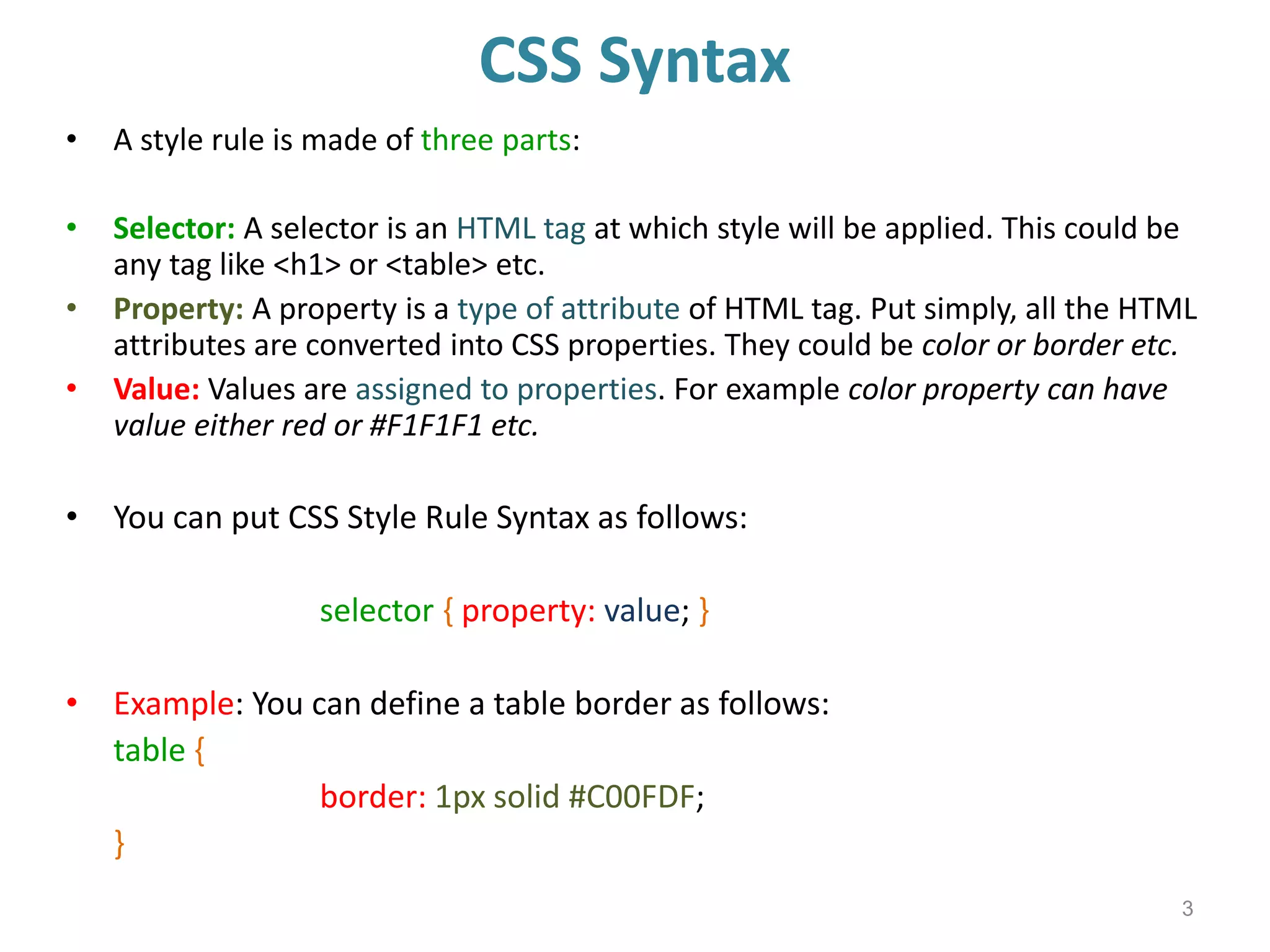
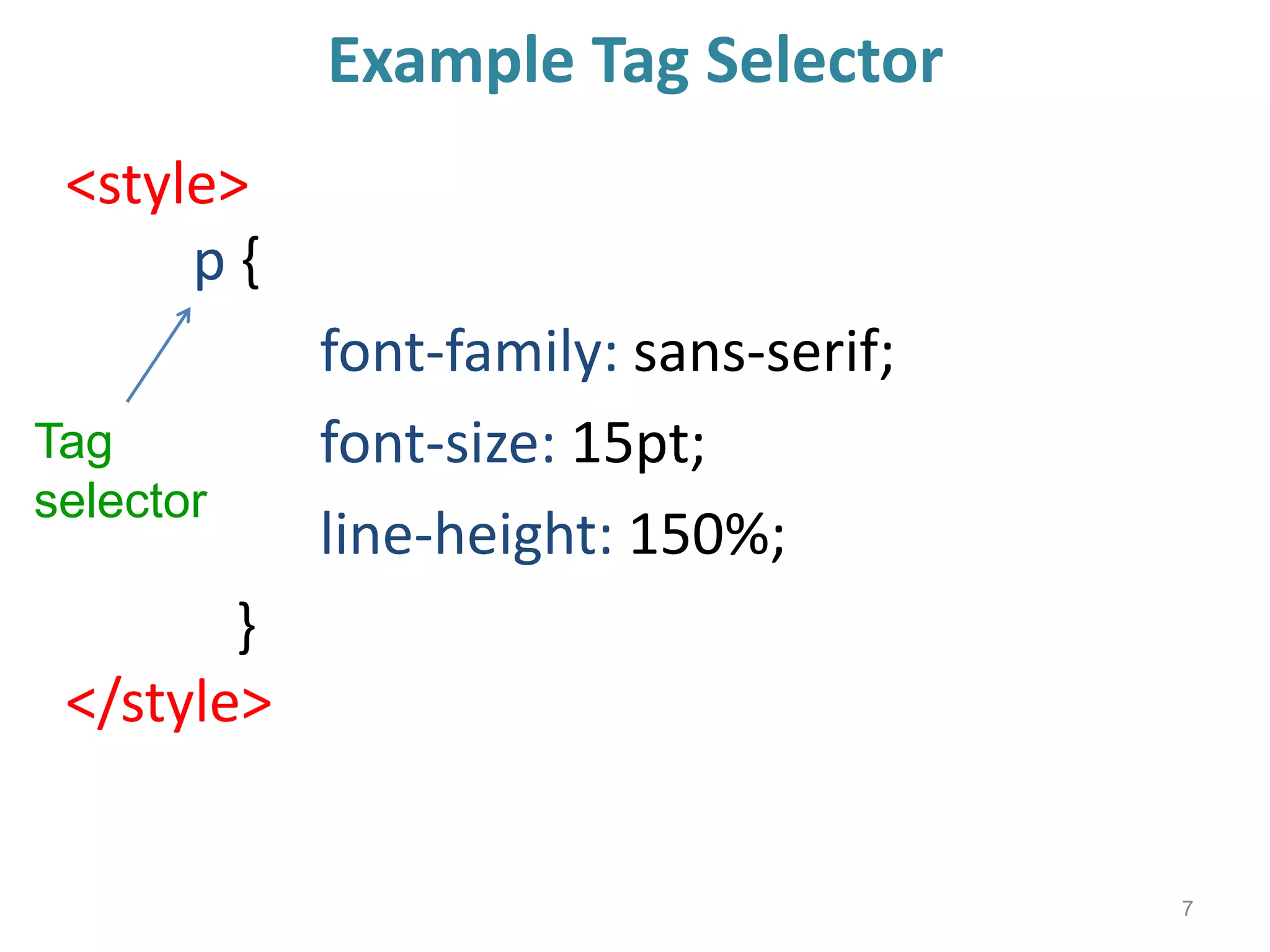
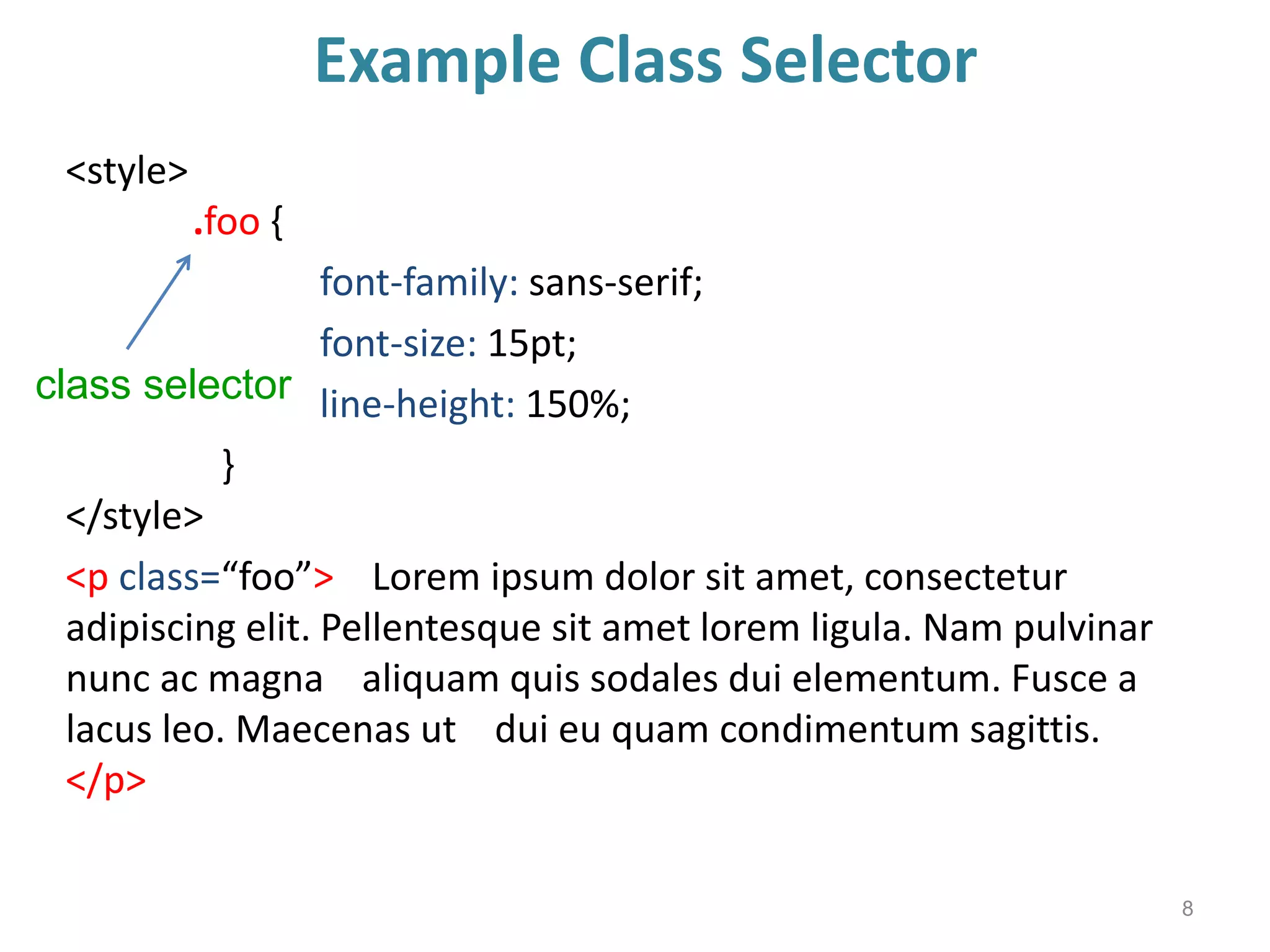
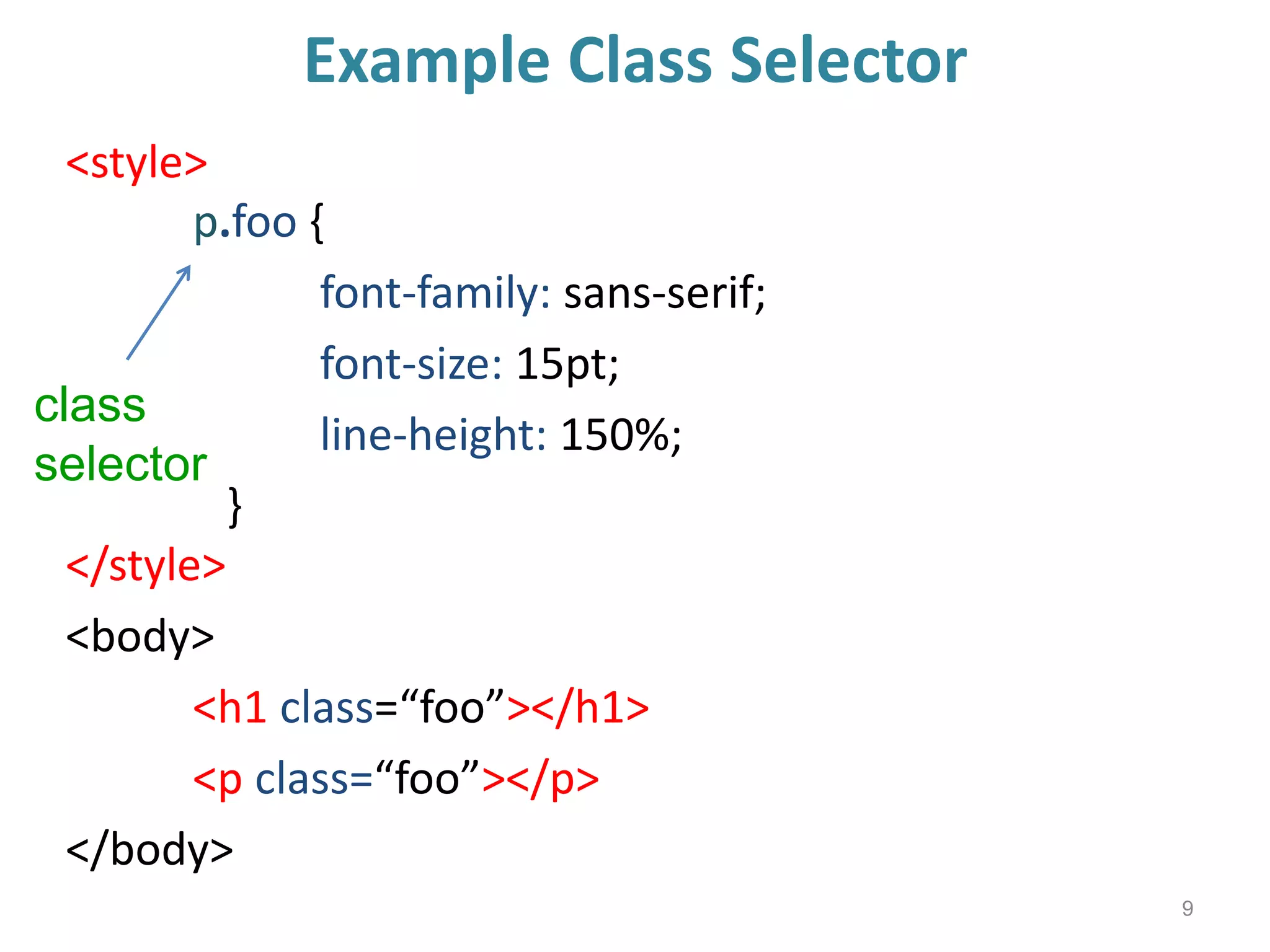
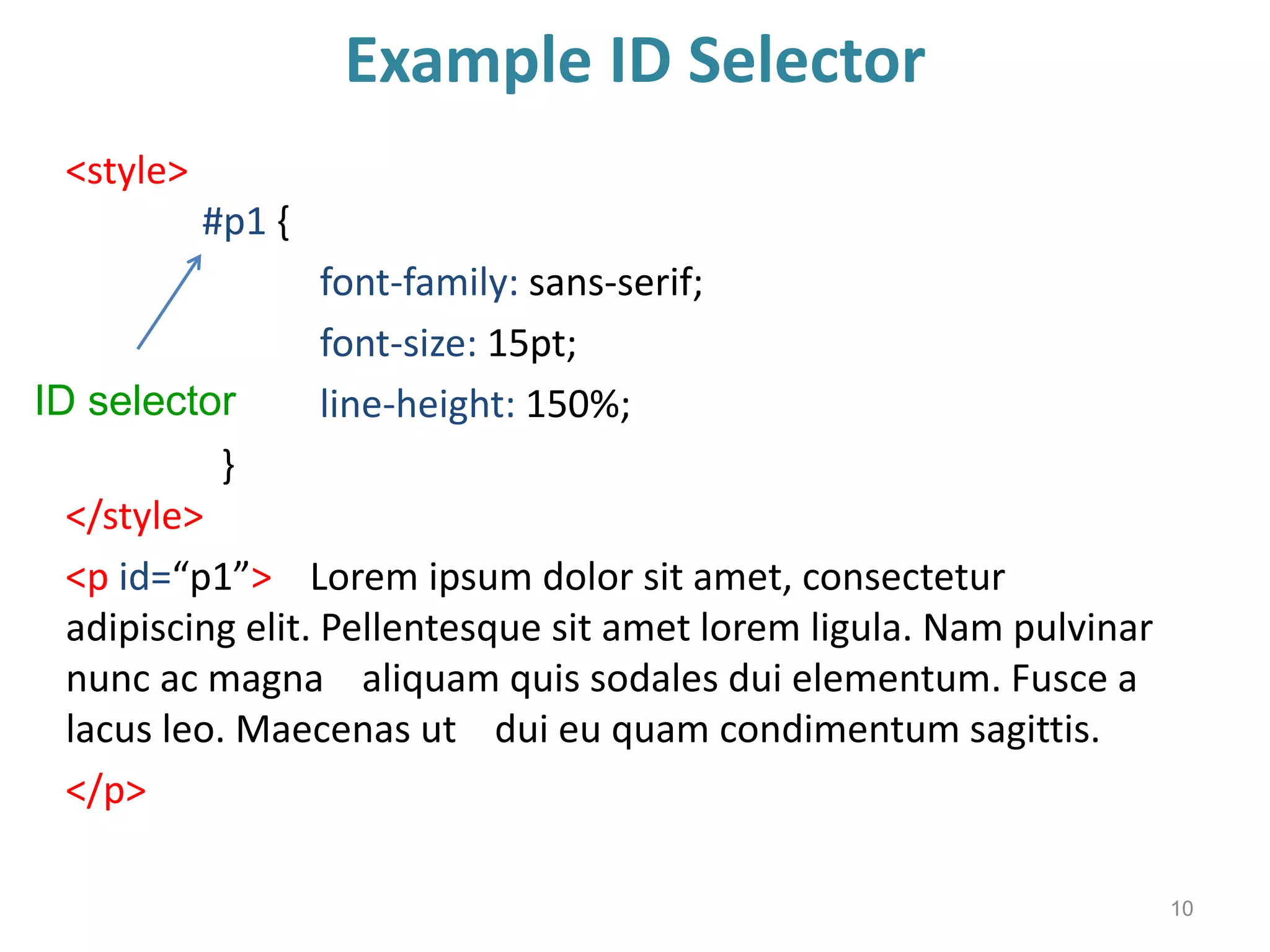
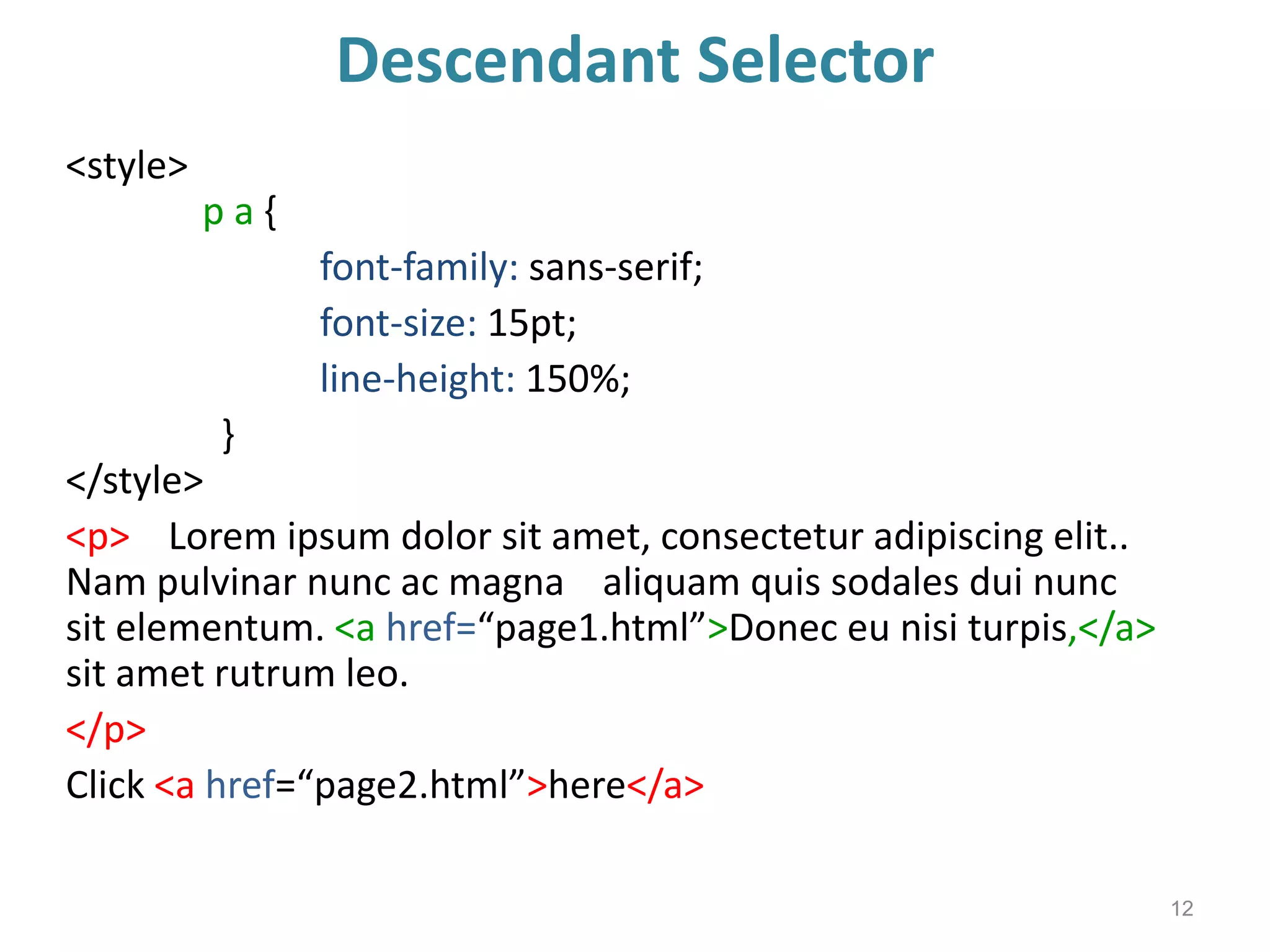
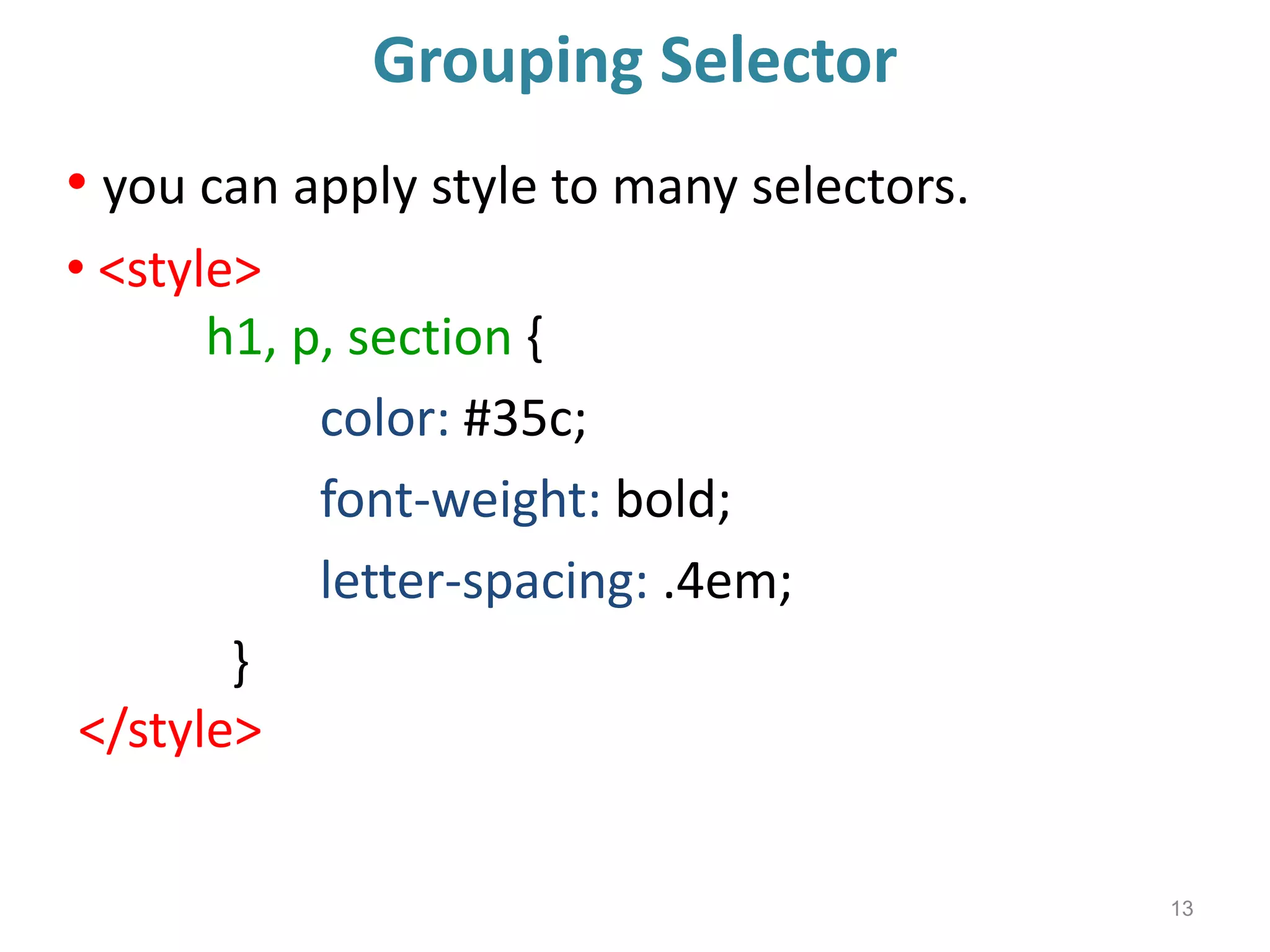
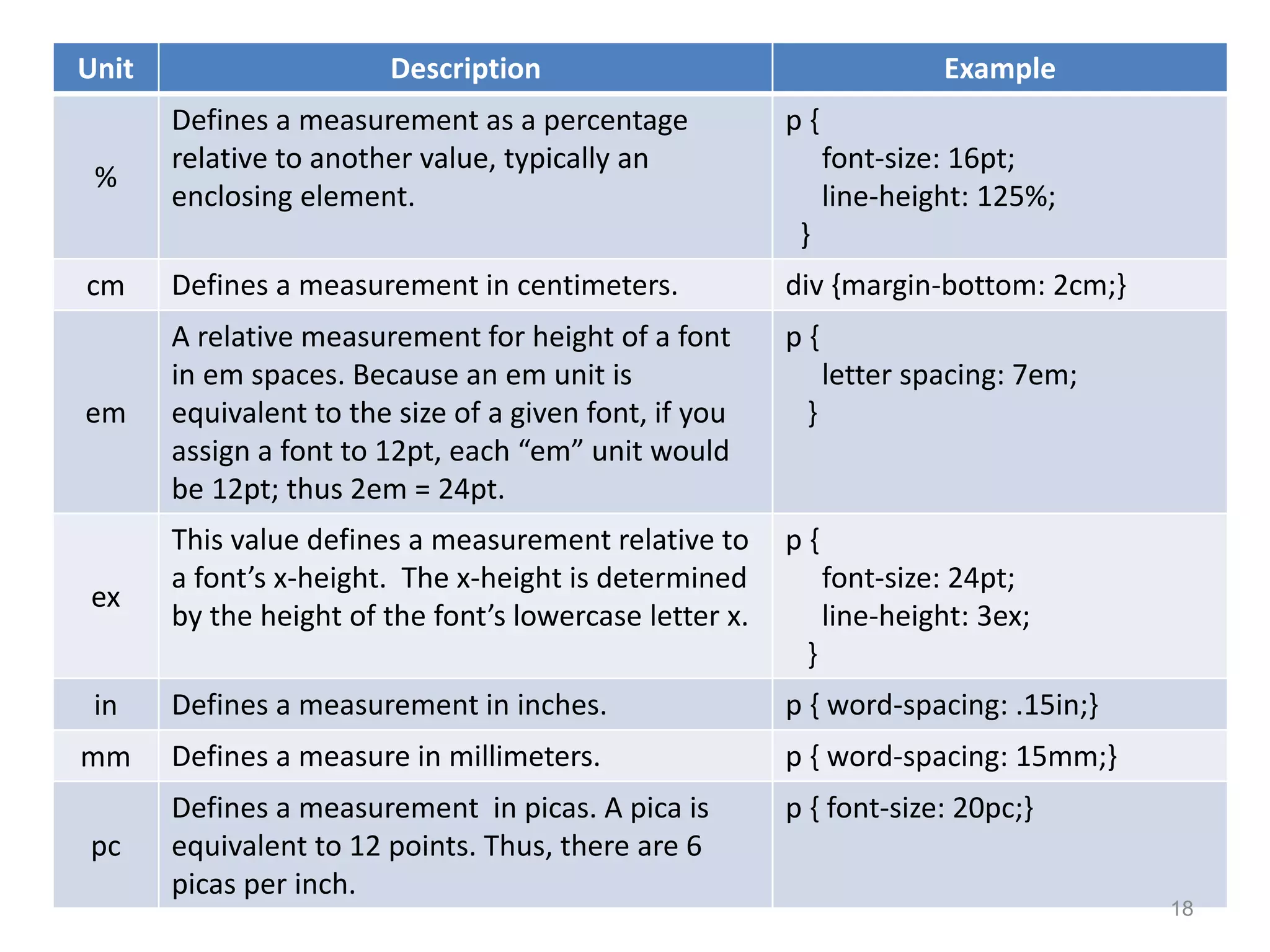
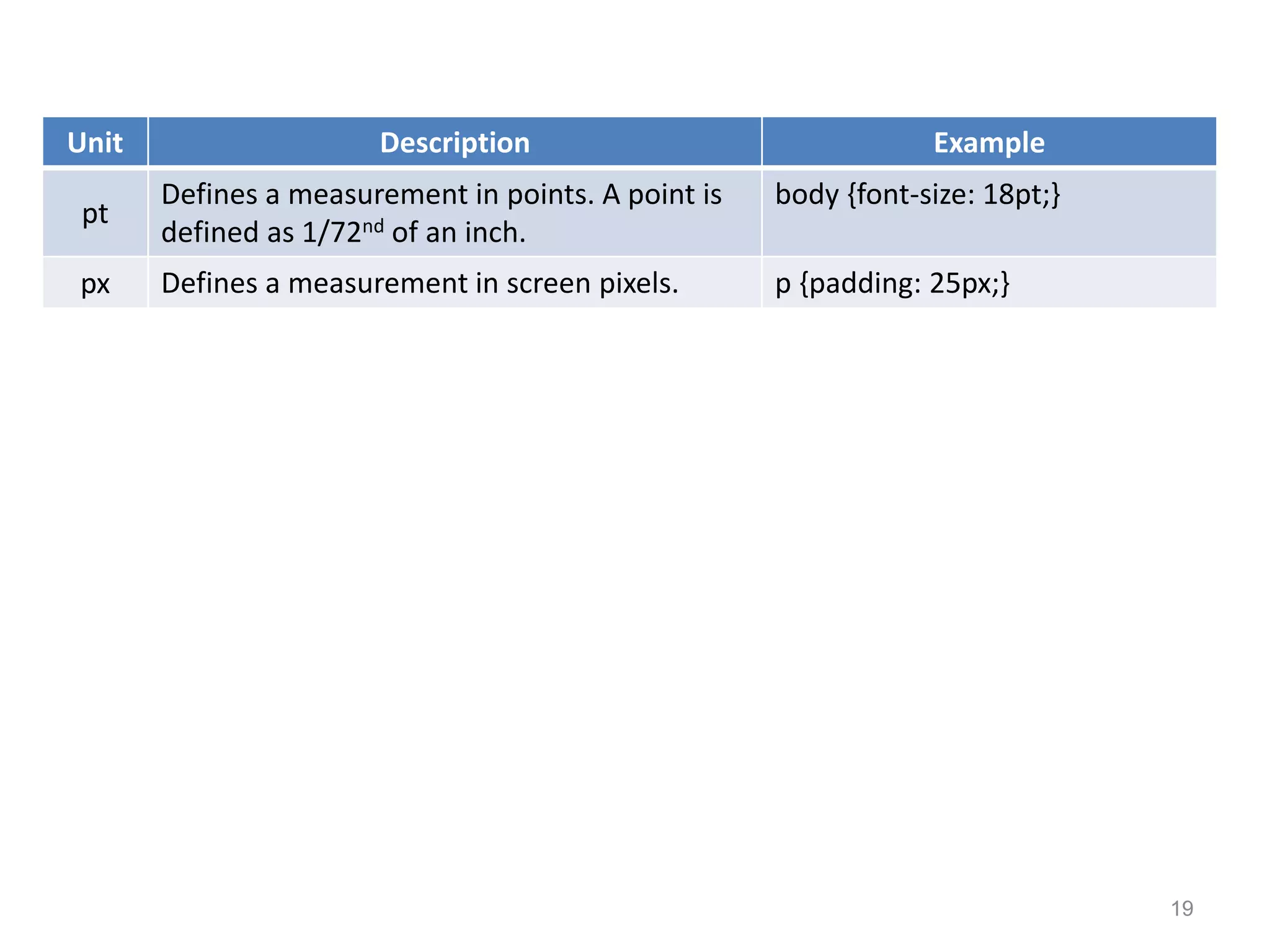
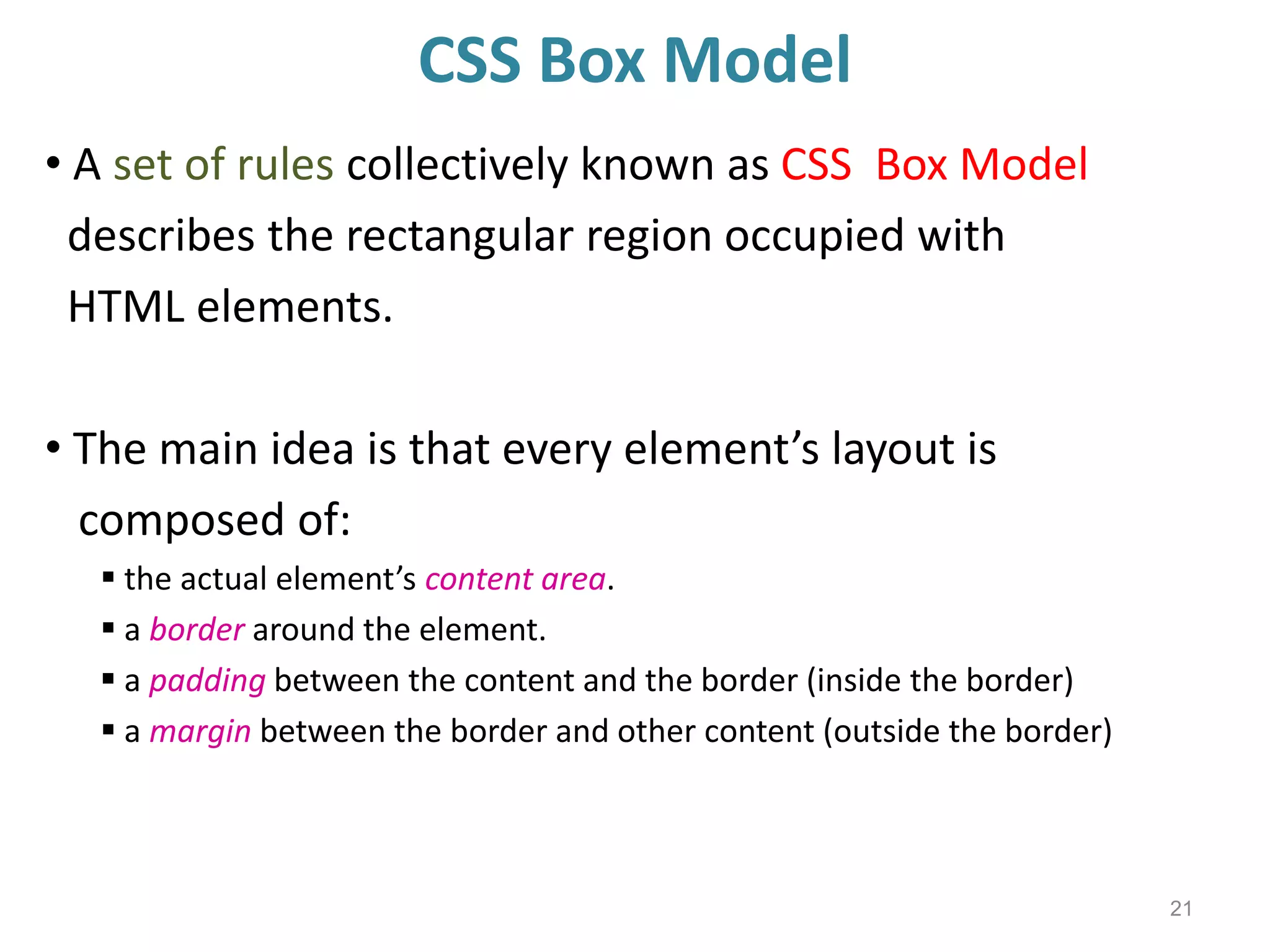
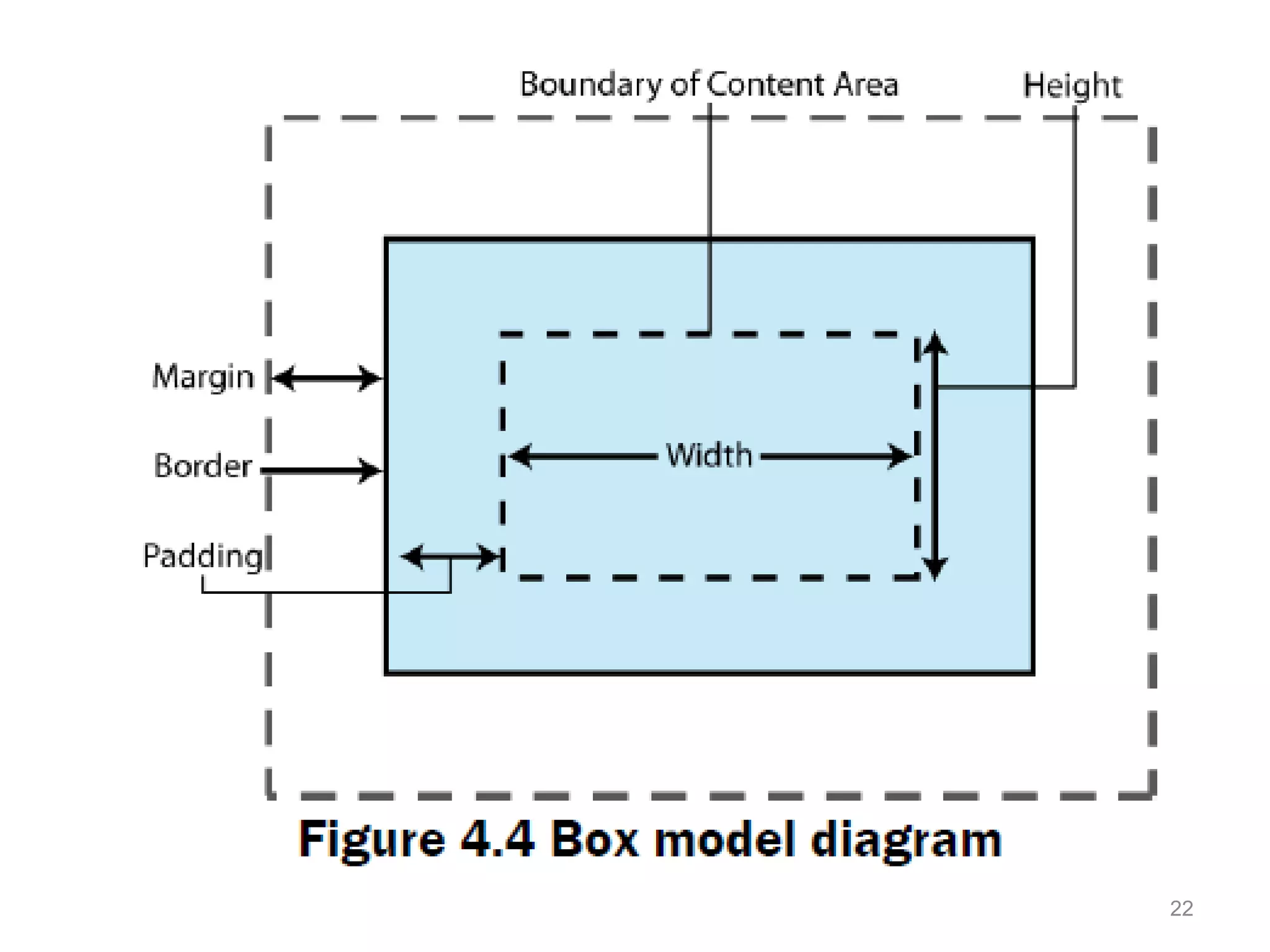
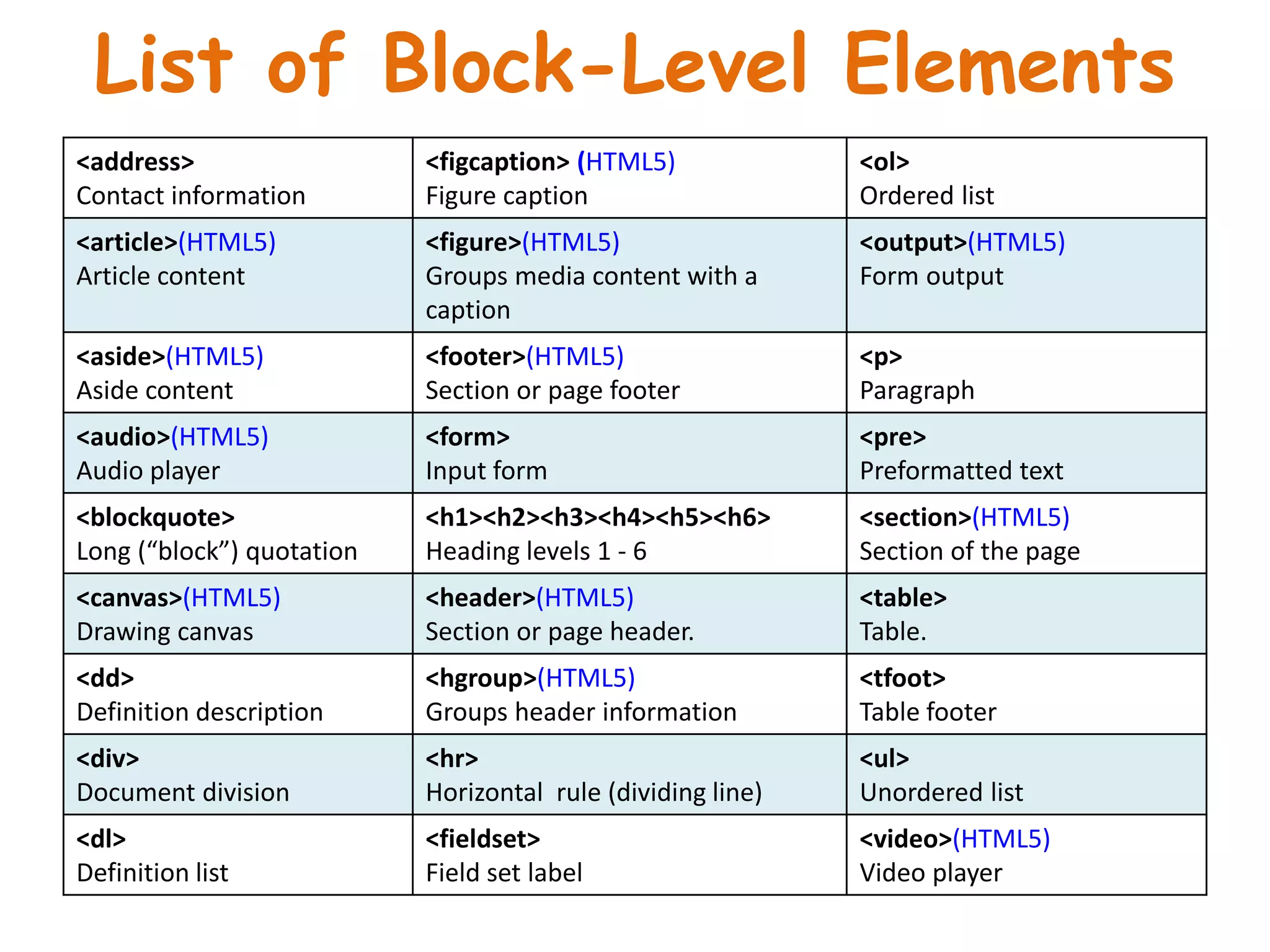
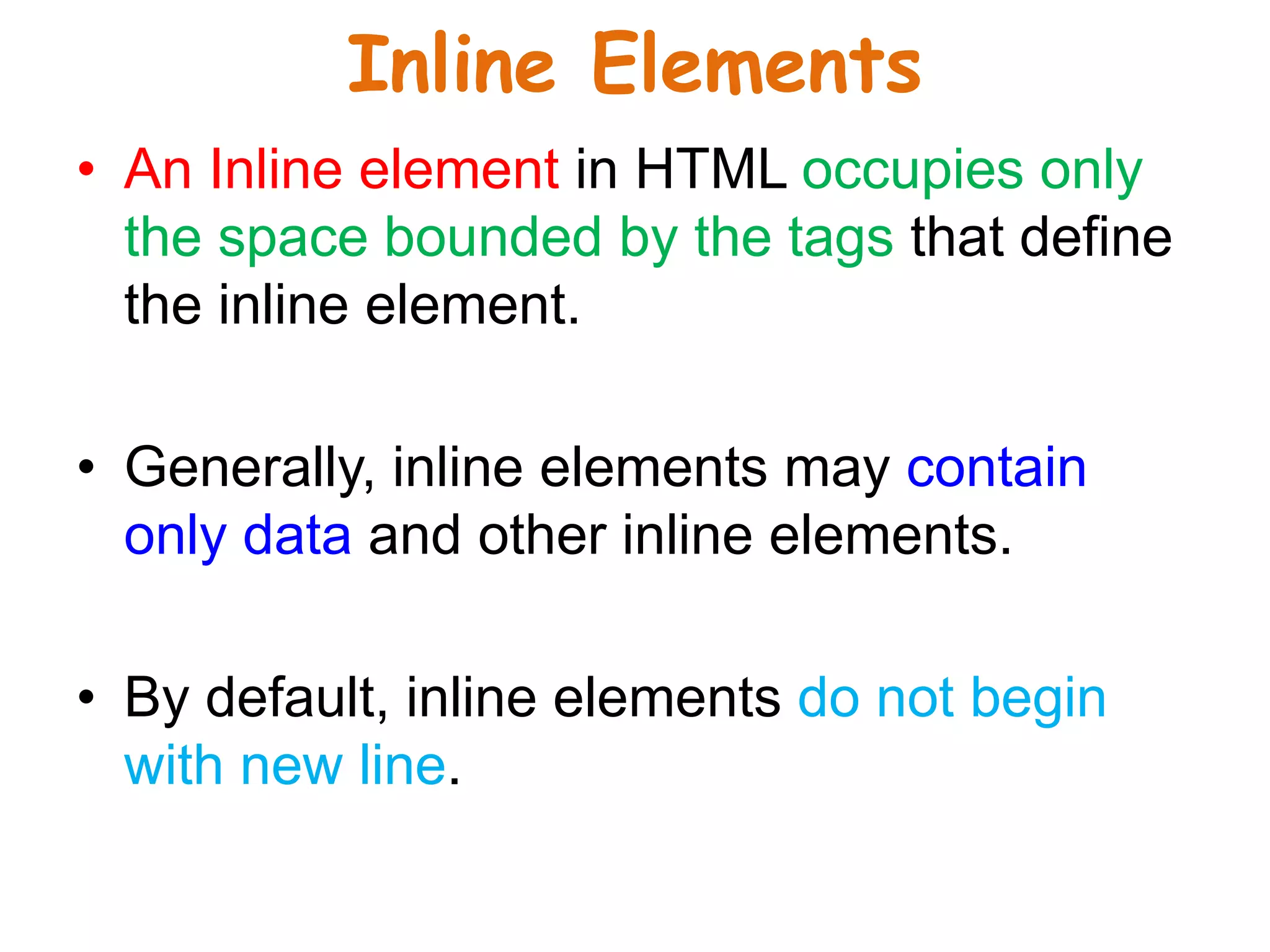
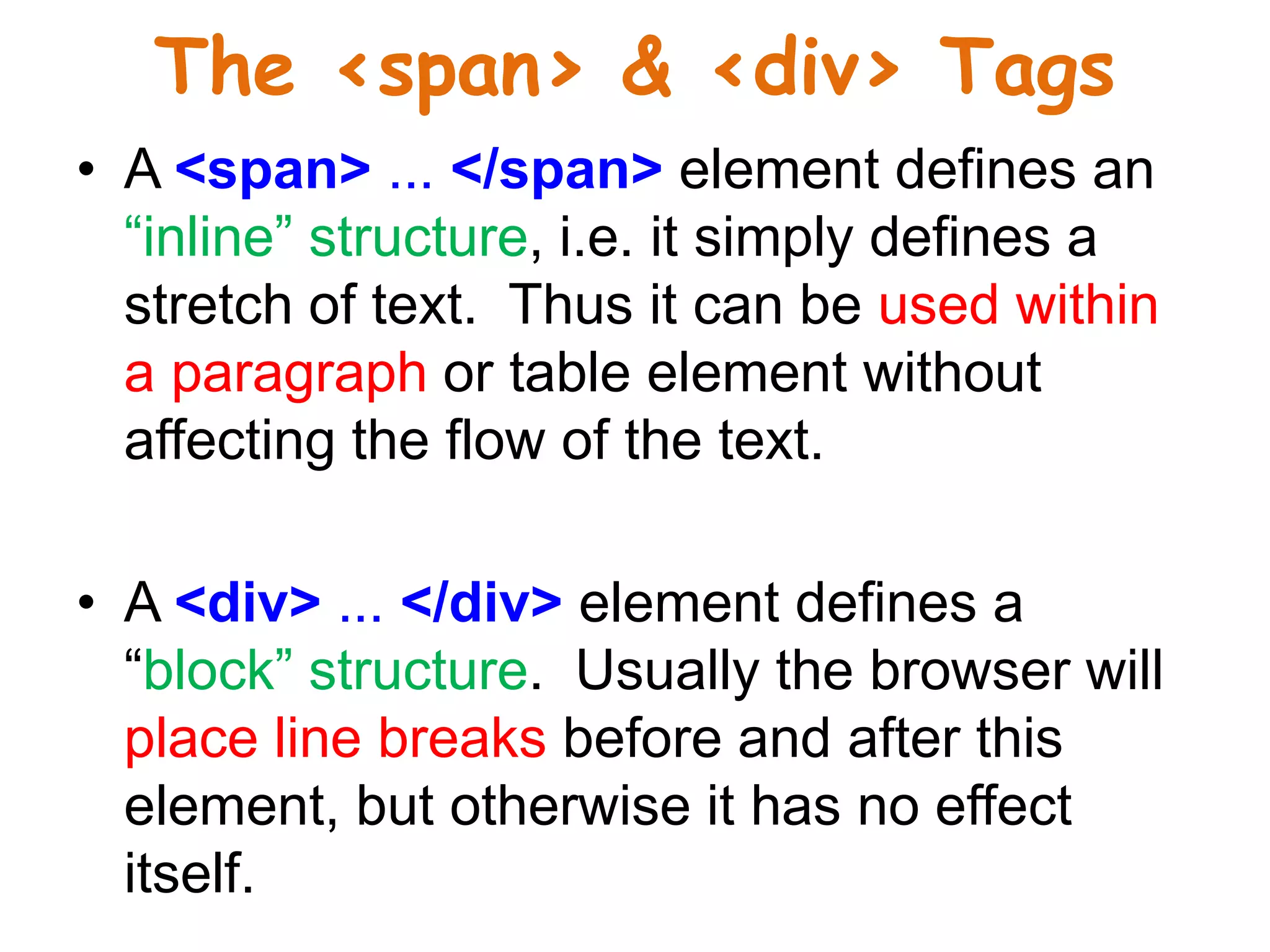
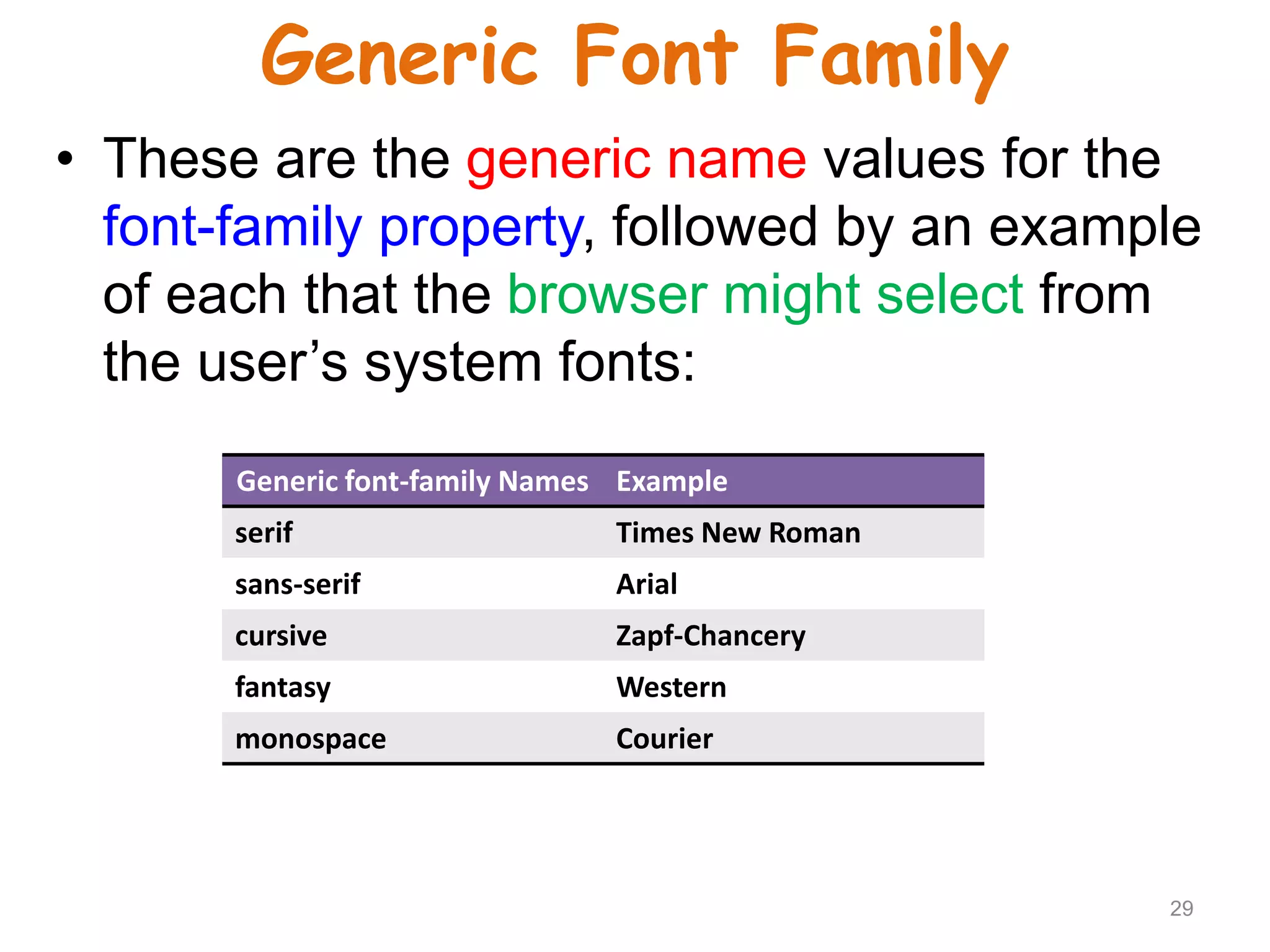
This document provides an introduction to CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). It discusses key CSS concepts like selectors, properties, values and syntax. It also covers different ways to apply CSS like inline, internal and external stylesheets. Common CSS properties for formatting text like font, color, text-decoration are described. The document also discusses CSS box model and different units of measurement in CSS.