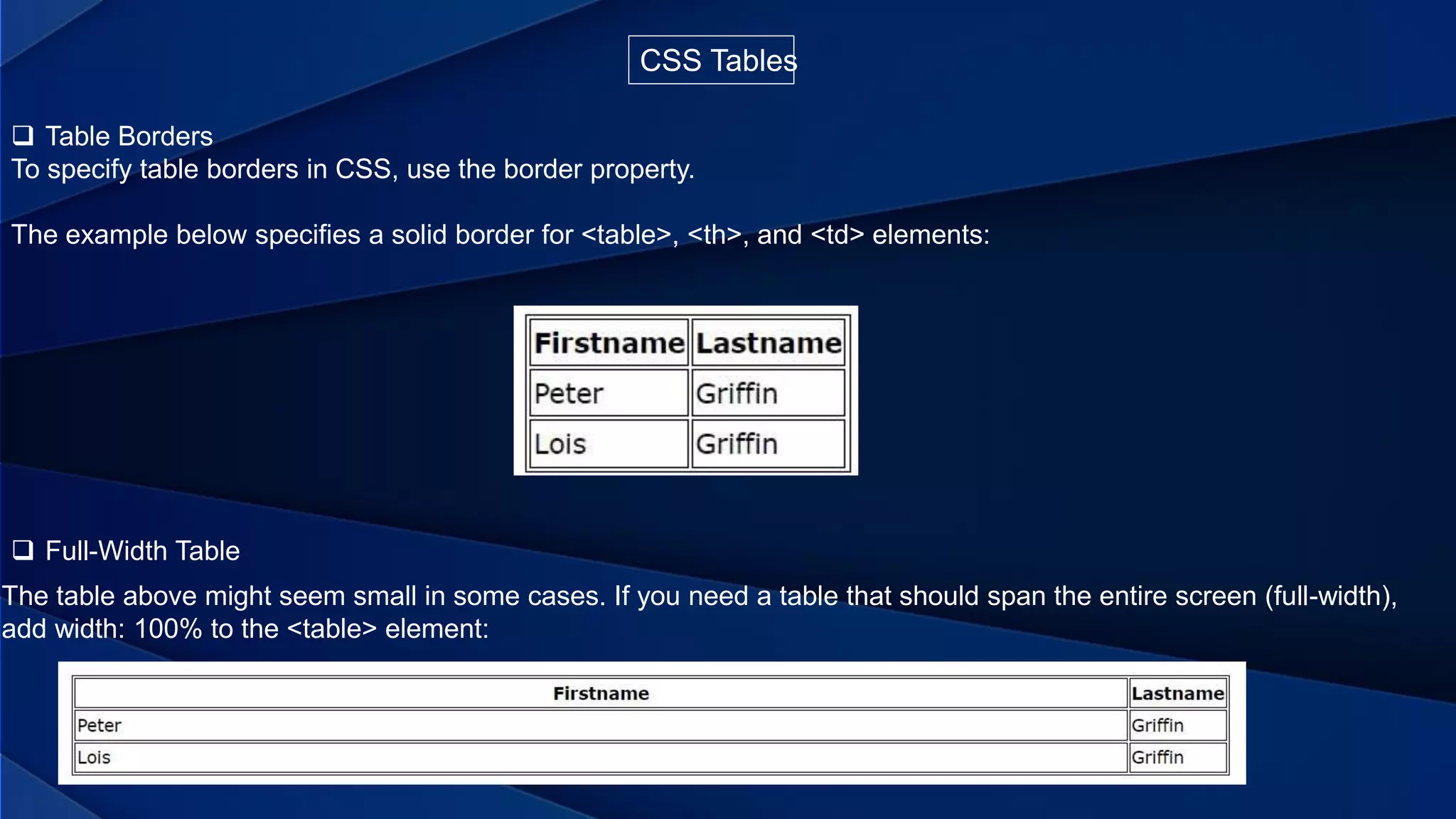
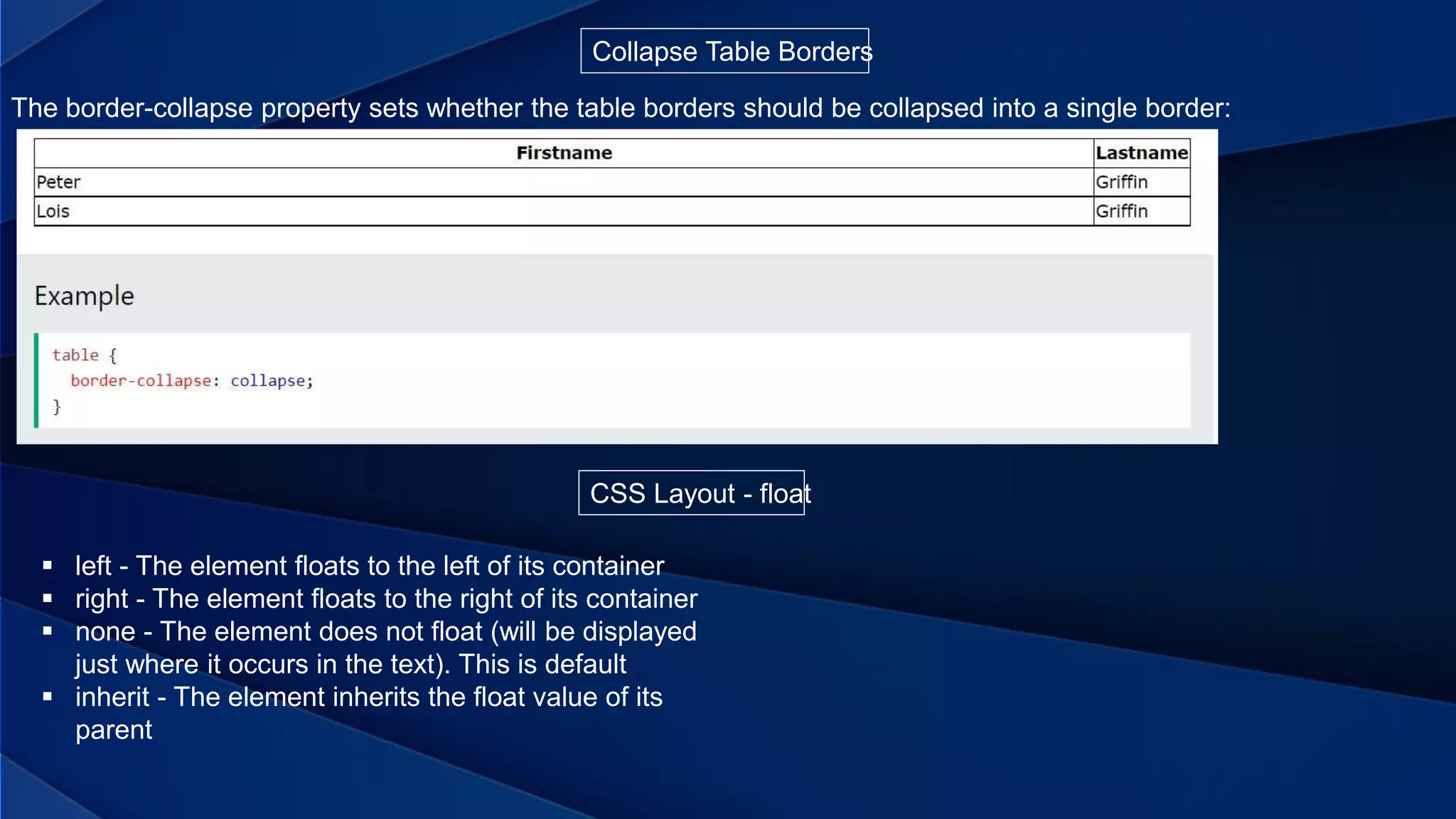
This document provides information about different web programming languages and concepts. It discusses Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and the different types of CSS like inline, internal, and external CSS. It also describes CSS tables, layouts using float, and positioning elements using static, relative, absolute, fixed, and sticky positioning. The document then discusses JavaScript, how it adds interactivity to web pages, and the benefits of client-side programming compared to server-side programming. It also explains how to embed JavaScript in HTML directly or link to an external JavaScript file.