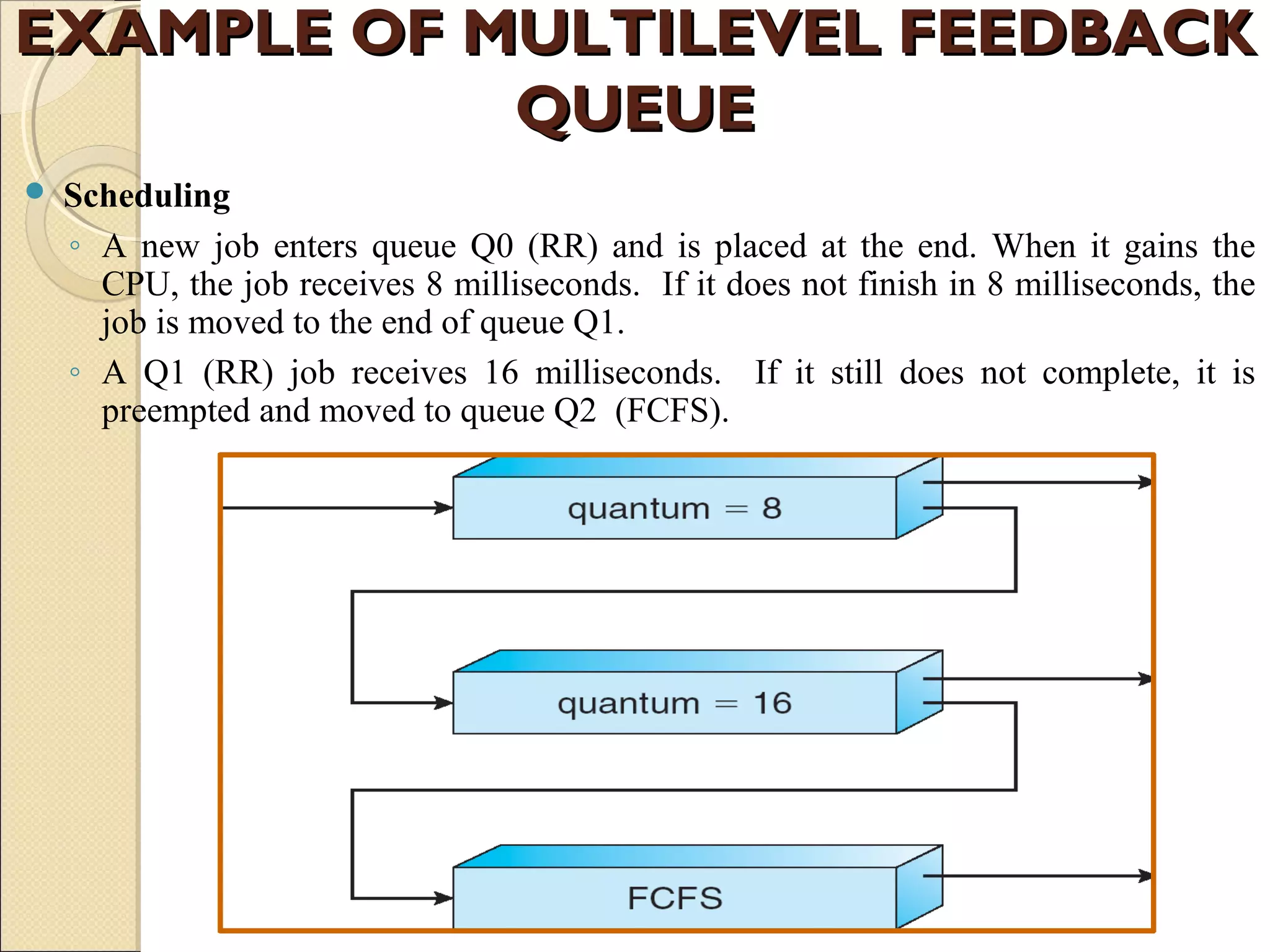
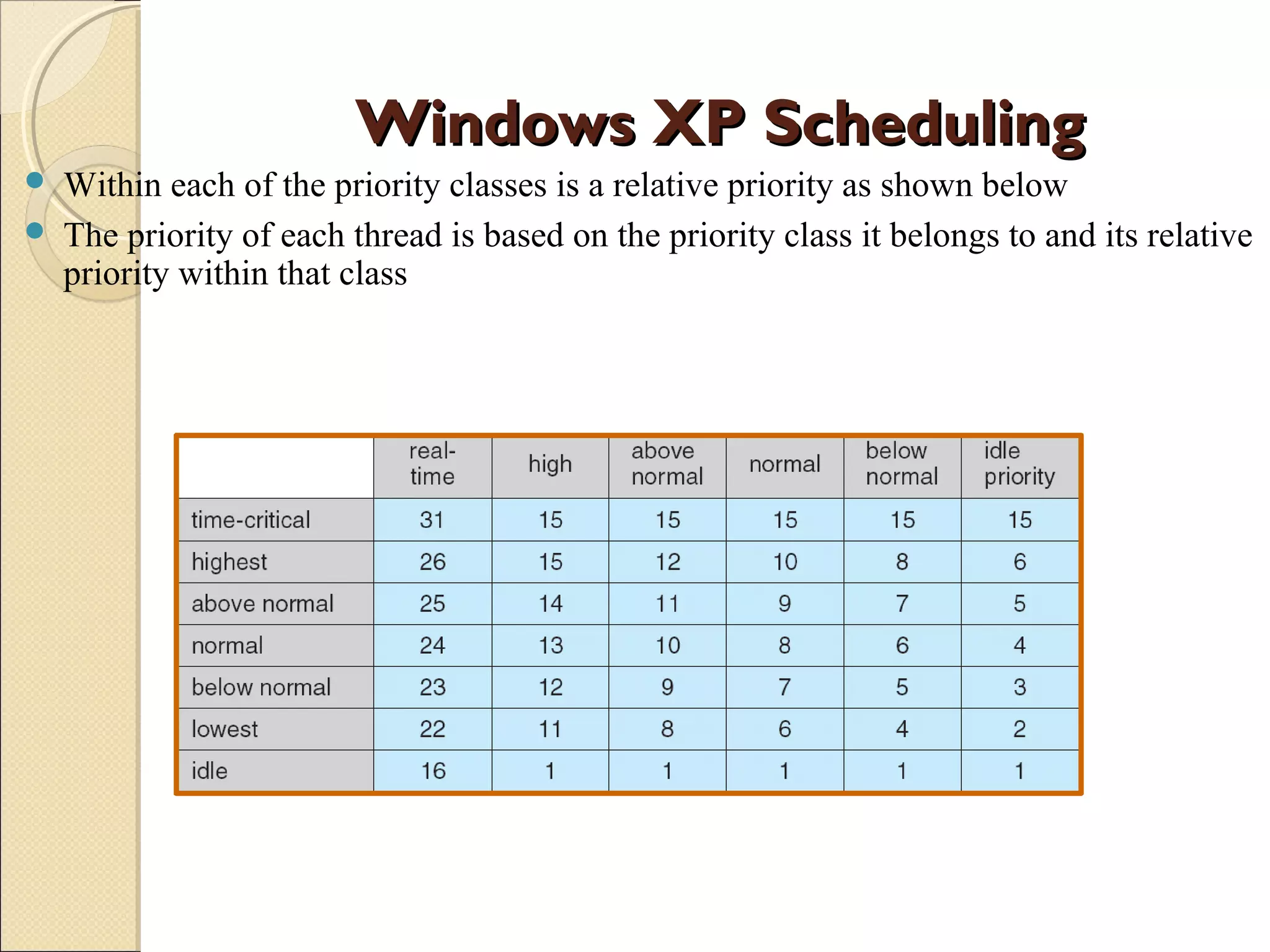
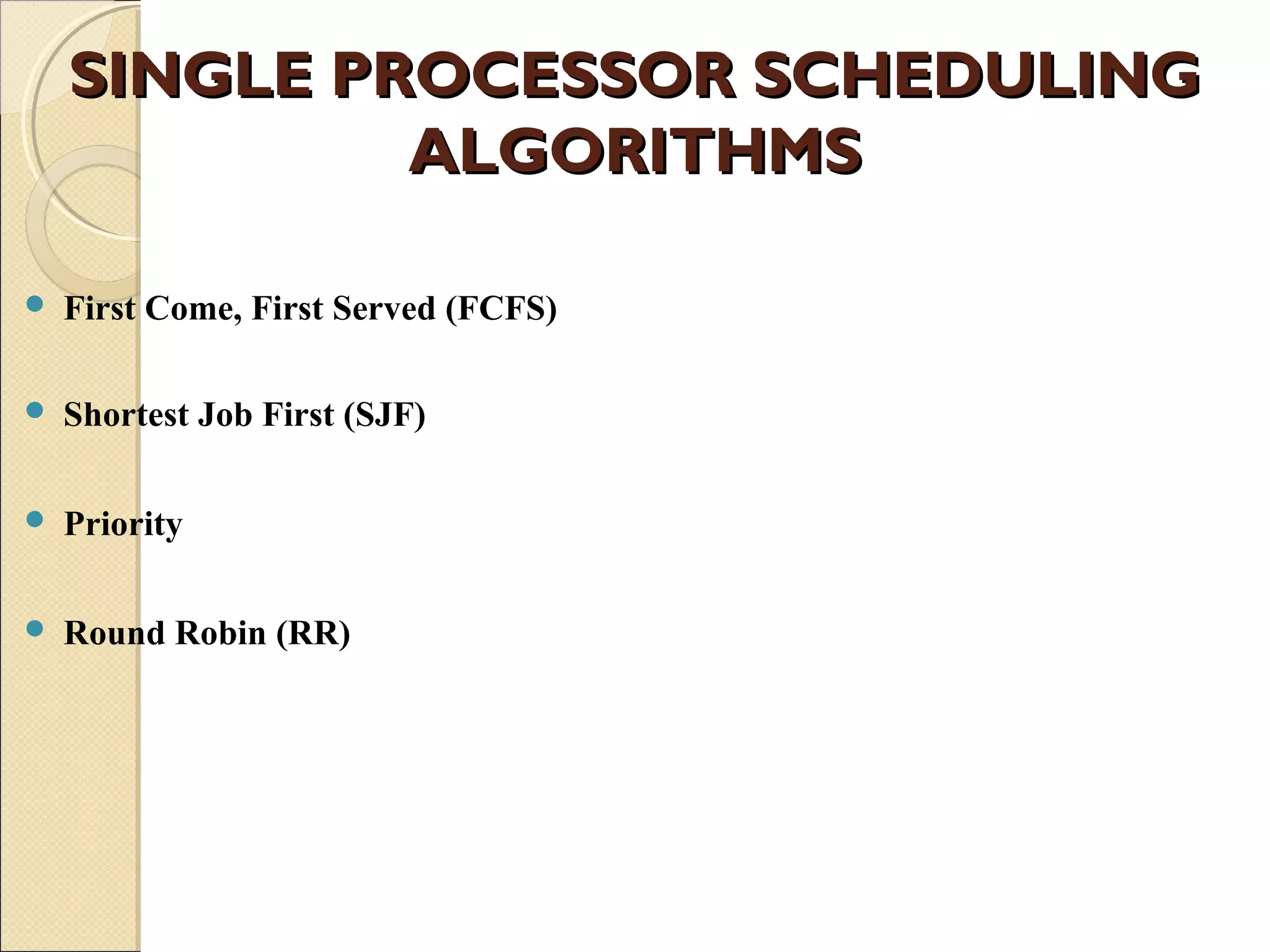
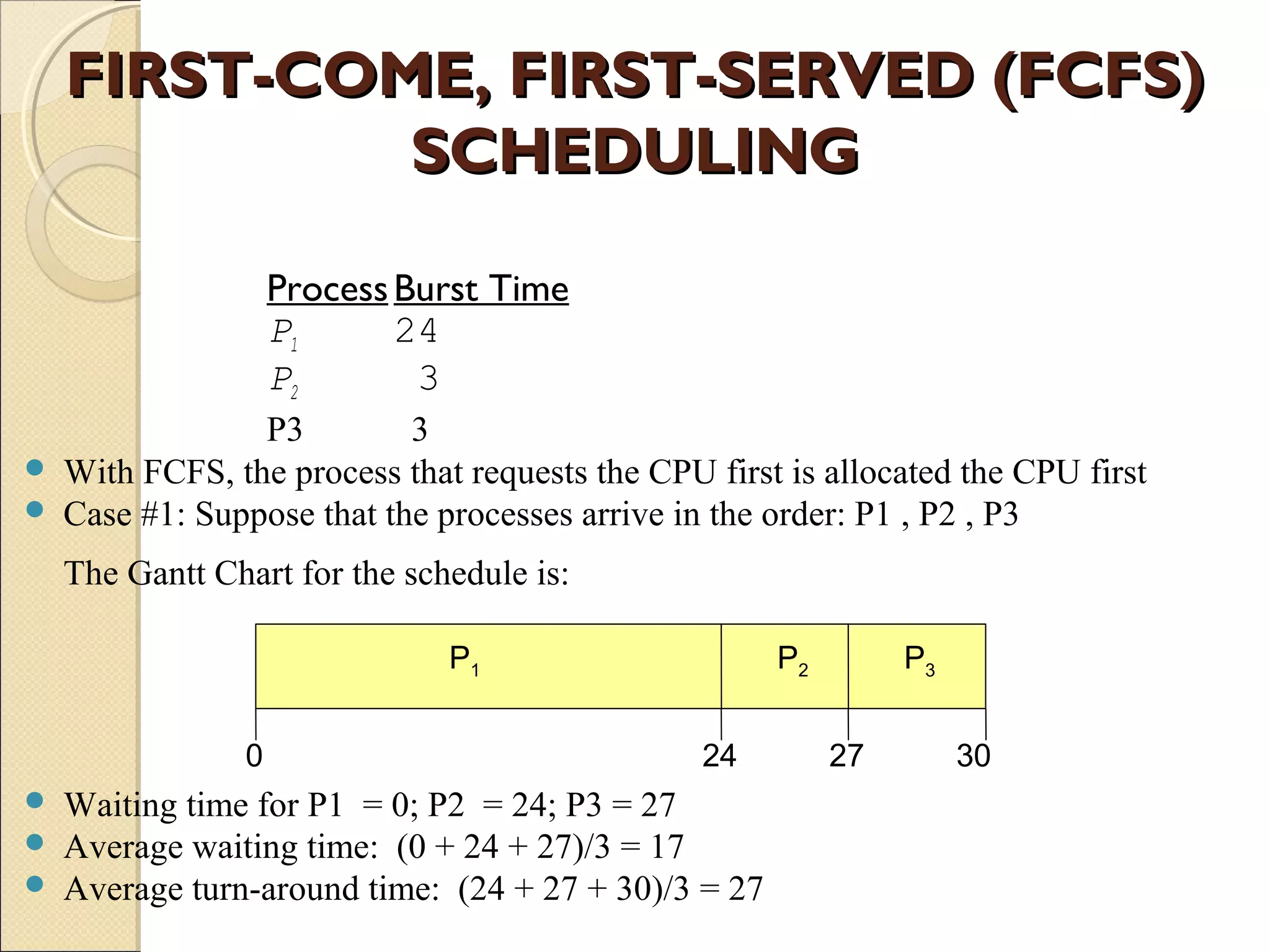
The document discusses Windows XP's scheduling algorithm. It uses a priority-based, preemptive approach with 32 priority levels divided into variable and real-time classes. The scheduler ensures the highest priority thread runs by maintaining queues for each priority level and traversing from highest to lowest. Threads start at the process' base priority and may have their priority lowered after time quantums expire to limit CPU consumption of compute-intensive threads.

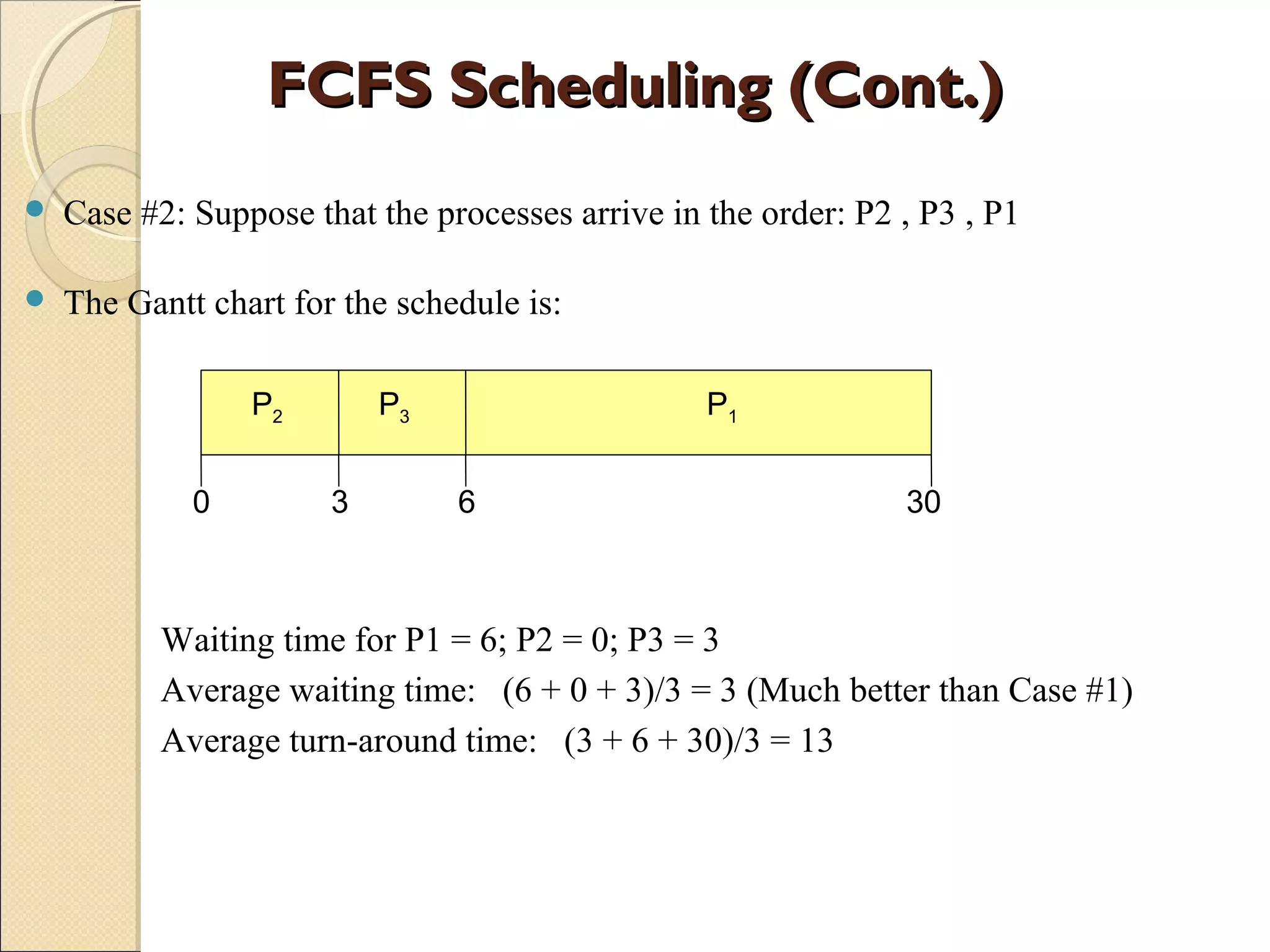

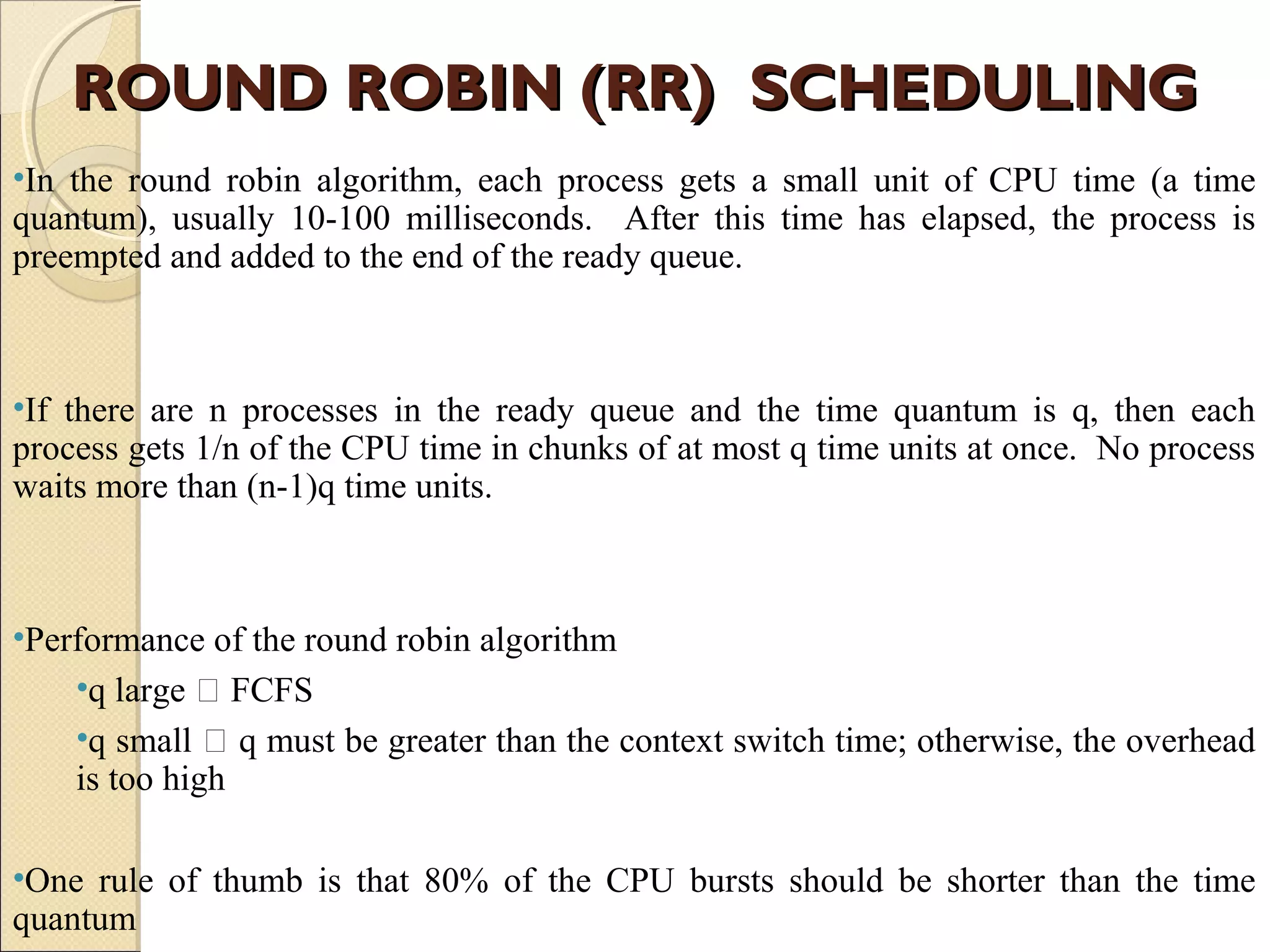

![Example of RR with TimeExample of RR with Time
Quantum = 20Quantum = 20
Typically, higher average turnaround than SJF, but better response time
Average waiting time
= ( [(0 – 0) + (77 - 20) + (121 – 97)] + (20 – 0) + [(37 – 0) + (97 - 57) +
(134 – 117)] + [(57 – 0) + (117 – 77)] ) / 4
= (0 + 57 + 24) + 20 + (37 + 40 + 17) + (57 + 40) ) / 4
= (81 + 20 + 94 + 97)/4
= 292 / 4 = 73
Average turn-around time = 134 + 37 + 162 + 121) / 4 = 113.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowschedulingalgorithm-150504063254-conversion-gate02/75/Window-scheduling-algorithm-14-2048.jpg)