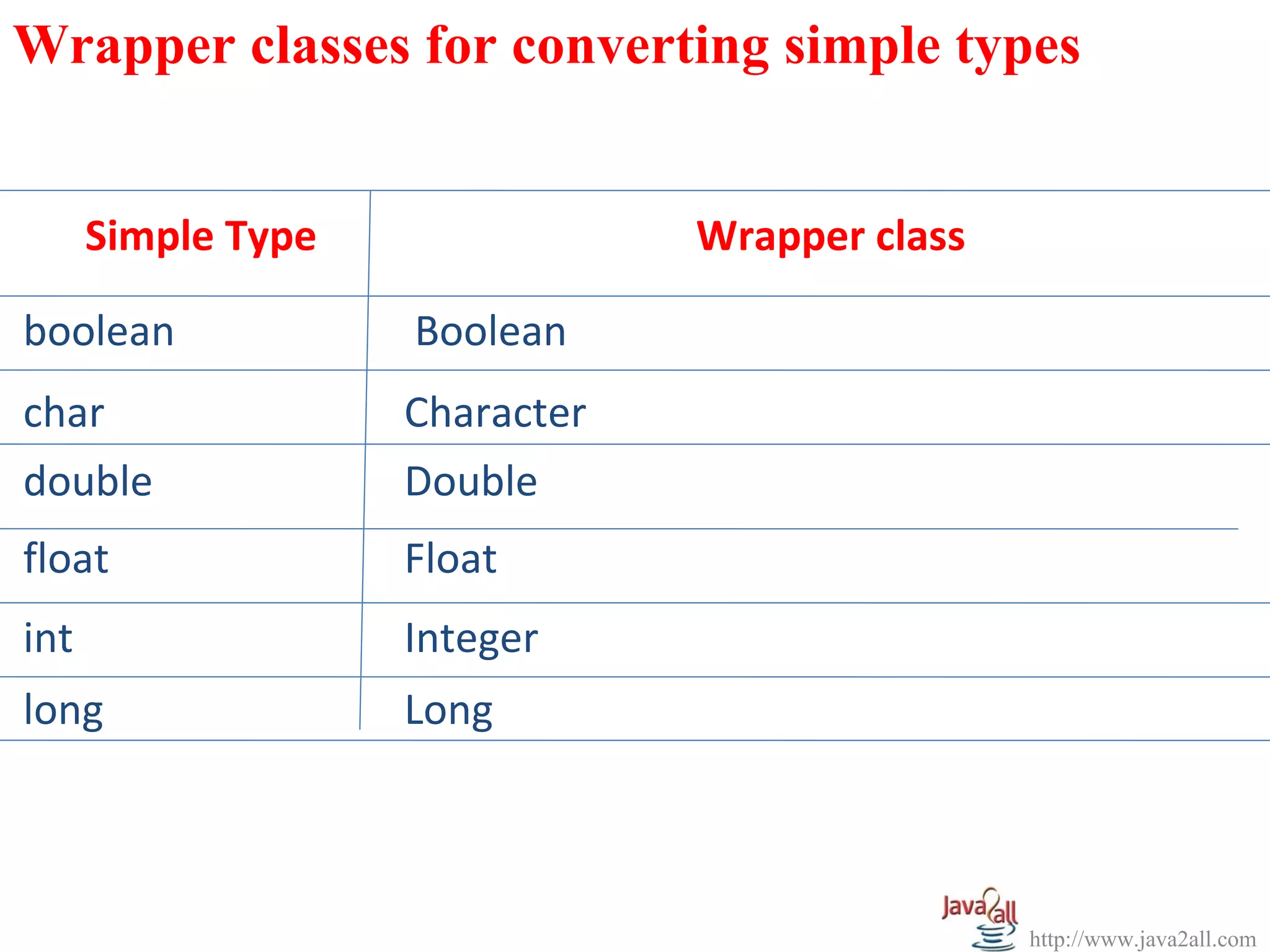
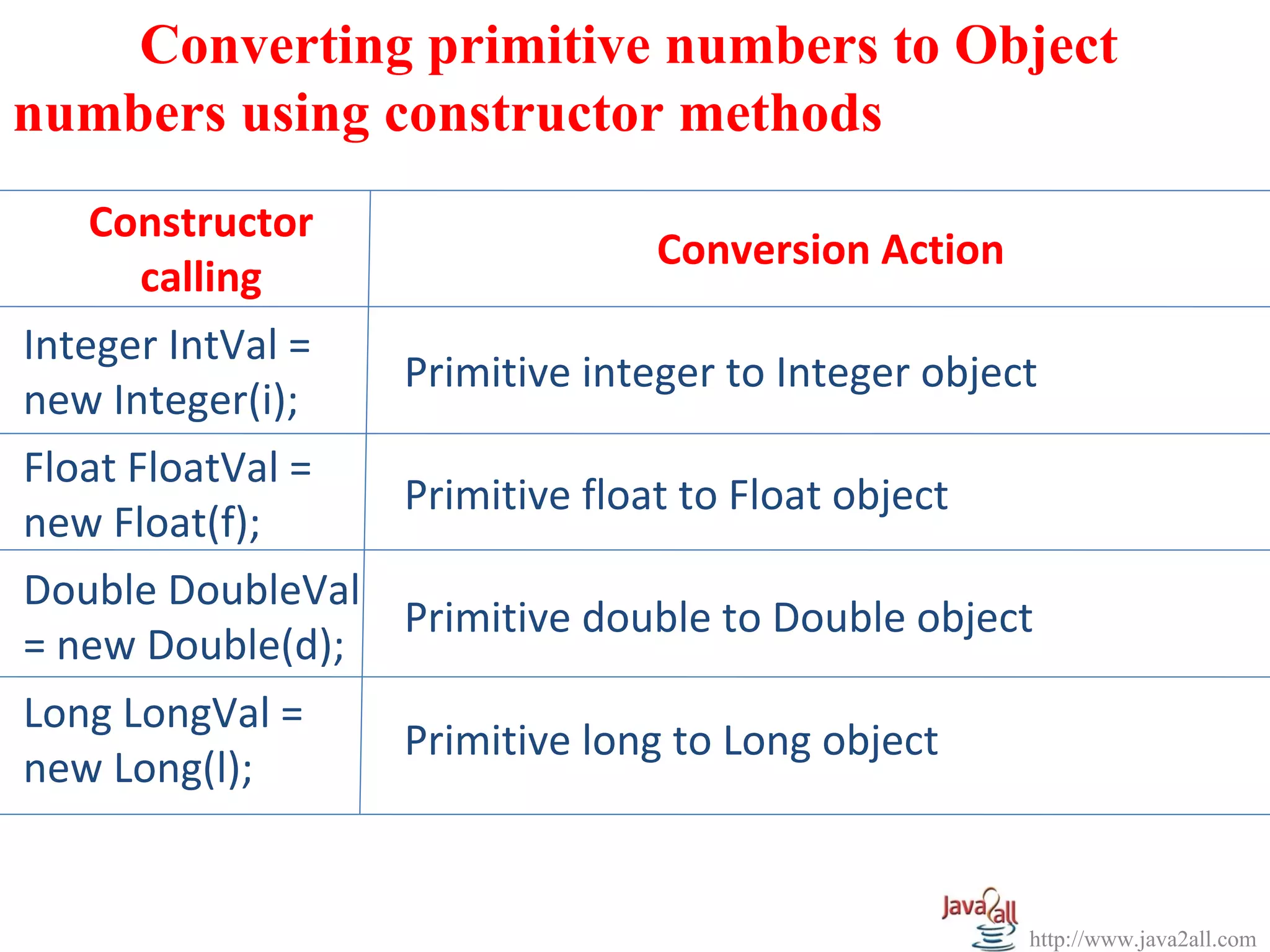
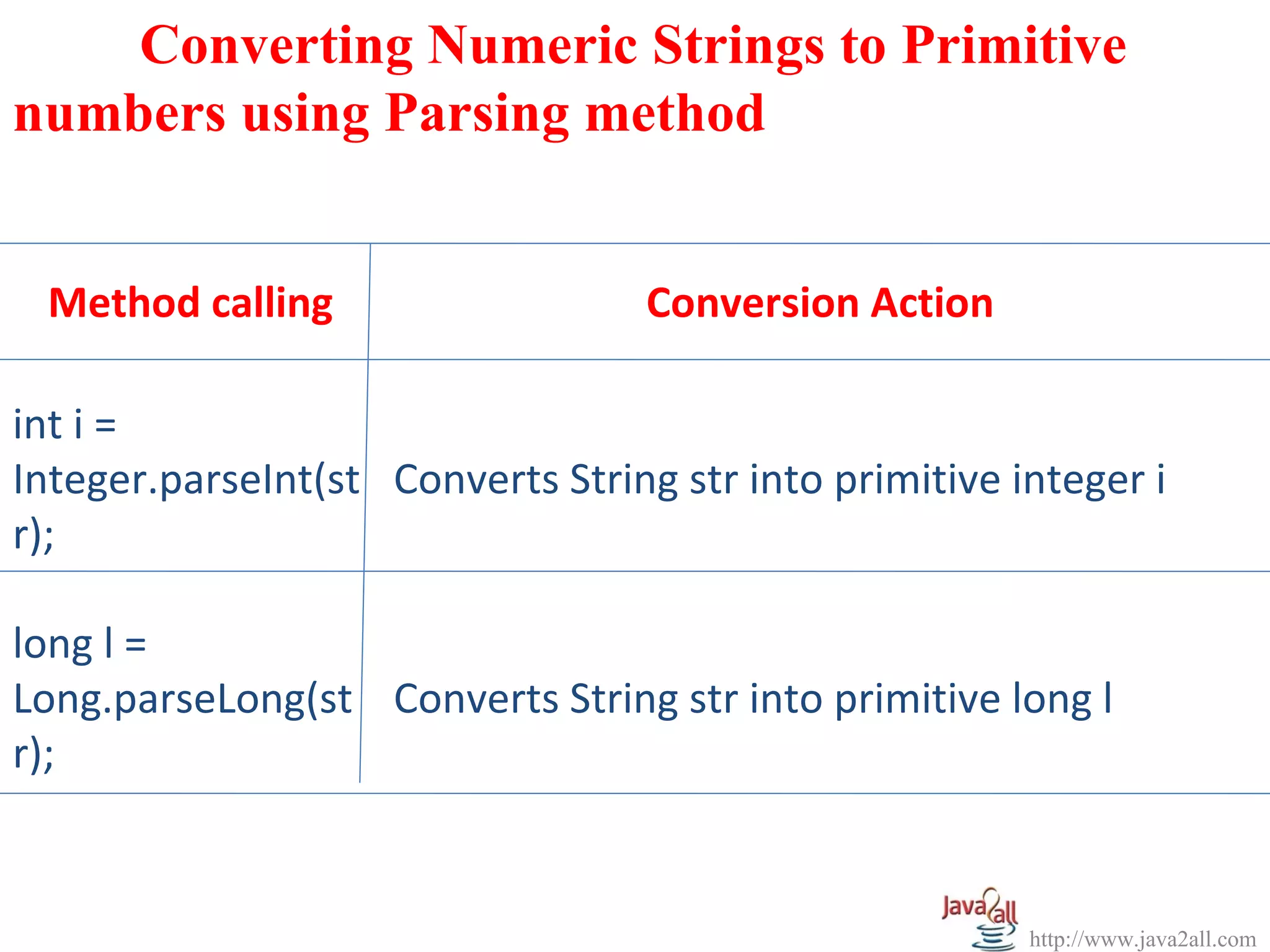
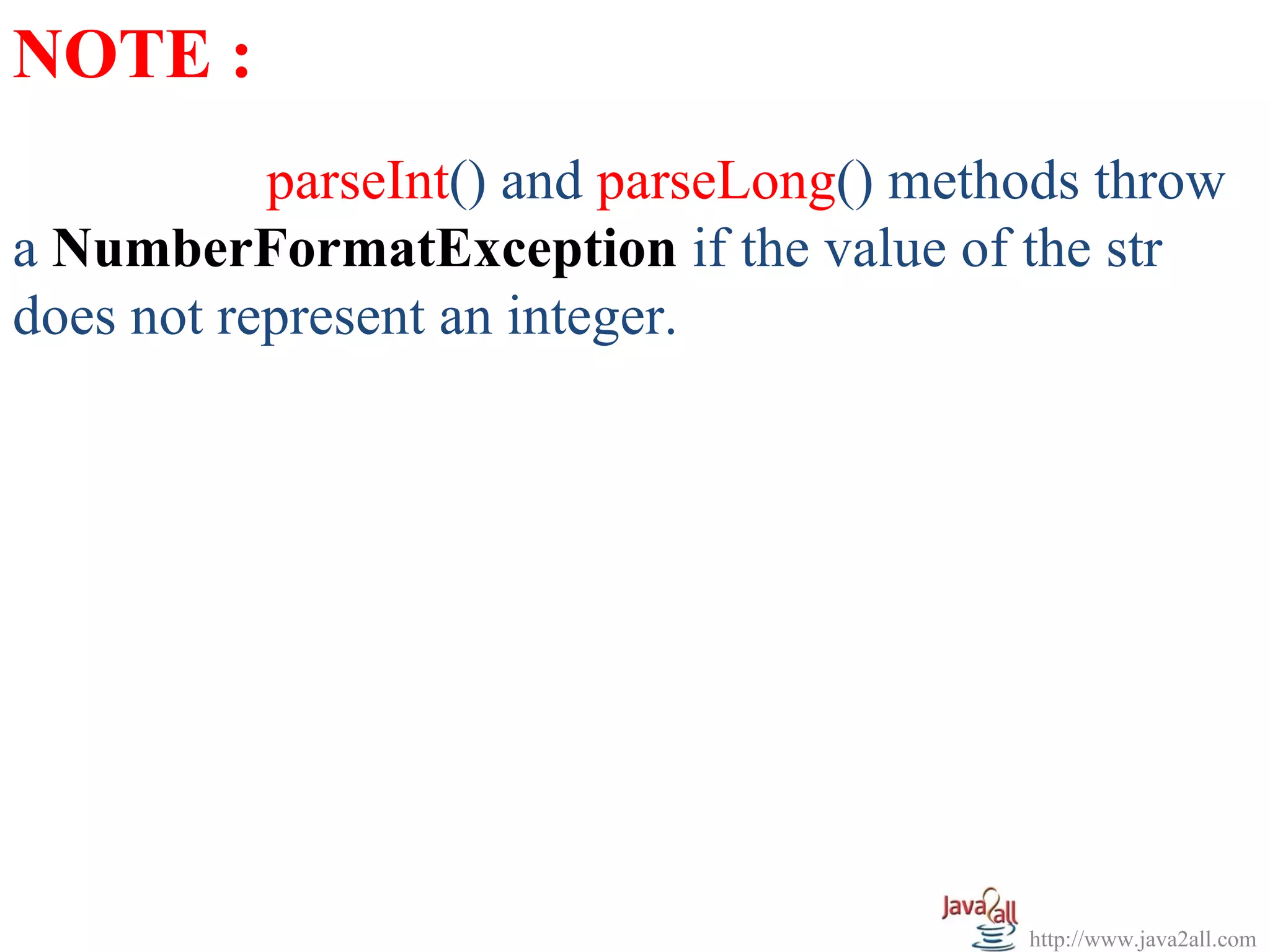
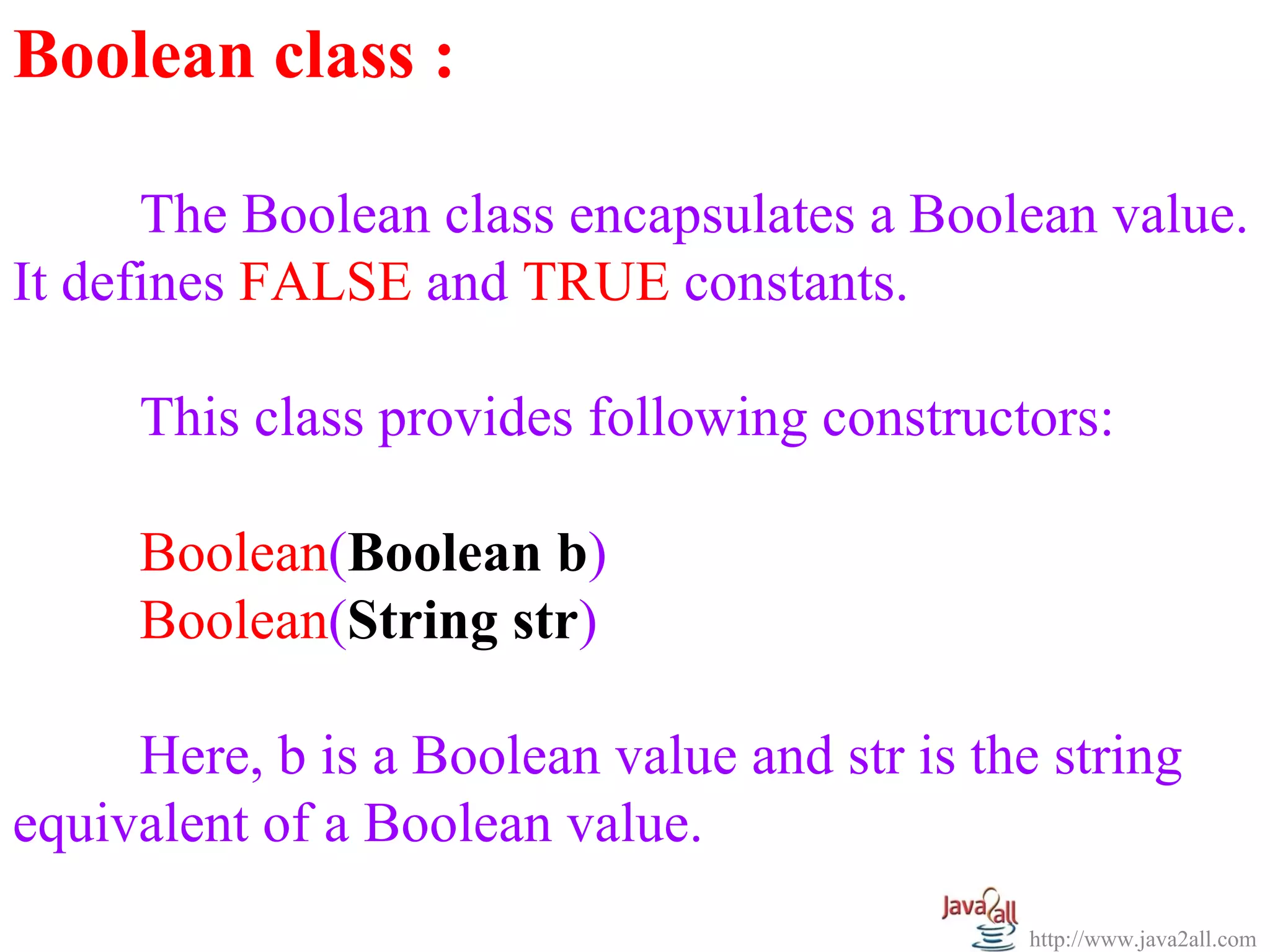
The document discusses Java wrapper classes. Wrapper classes wrap primitive data types like int, double, boolean in objects. This allows primitive types to be used like objects. The main wrapper classes are Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Character, Boolean, Double, Float. They provide methods to convert between primitive types and their wrapper objects. Constructors take primitive values or strings to create wrapper objects. Methods like parseInt() convert strings to primitive types.





![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Byte_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
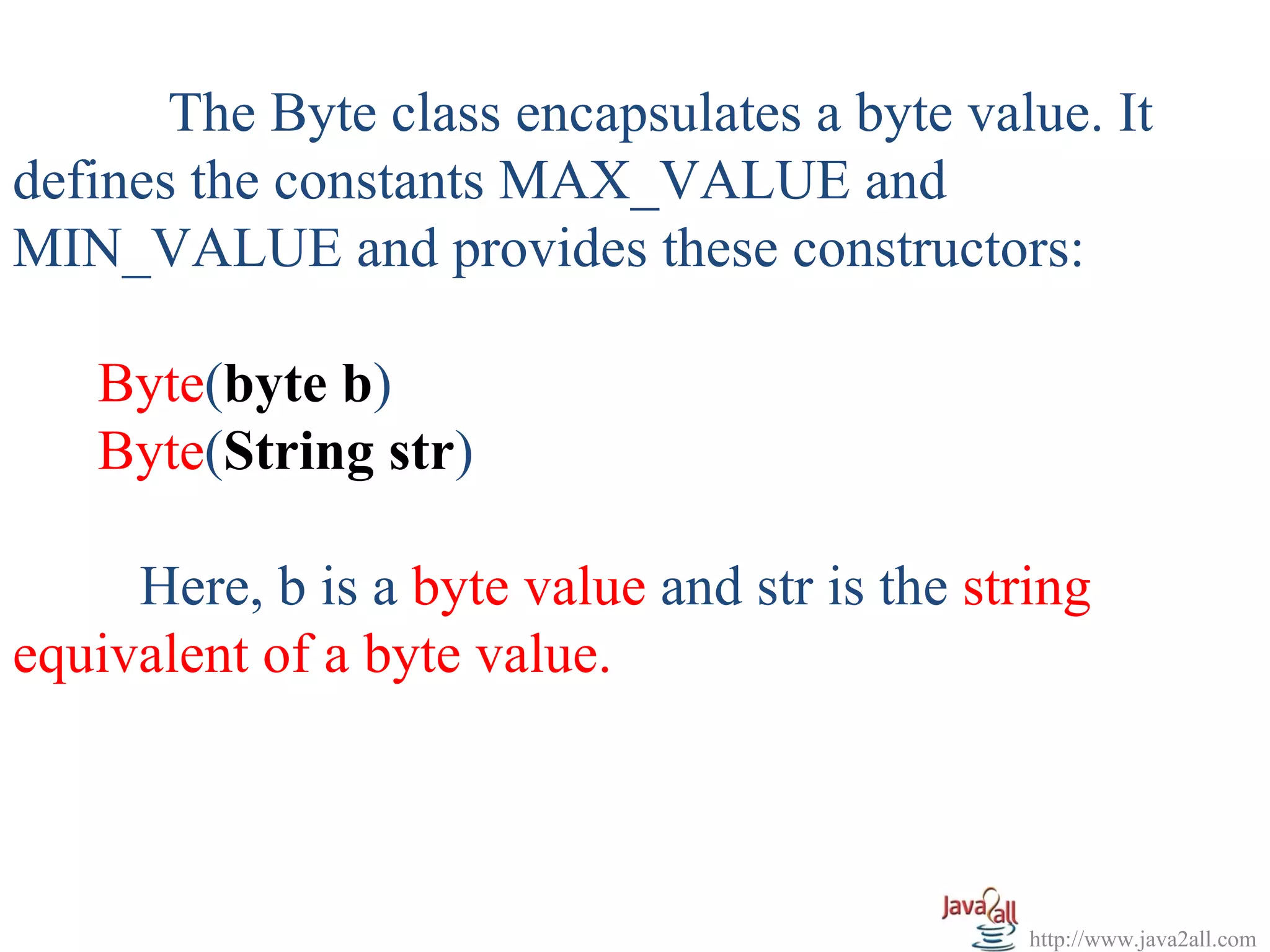
Byte b1 = new Byte((byte)120);
for(int i = 125; i<=135; i++)
{
Byte b2 = new Byte((byte)i);
System.out.println("b2 = " + b2);
}
System.out.println("b1 Object = " + b1);
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Byte = " + Byte.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Byte = " + Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("b1* 2 = " + b1*2);
System.out.println("b1* 2 = " + b1.byteValue()*2);
Byte b3 = new Byte("120");
System.out.println("b3 Object = " + b3);
System.out.println("(b1==b3)? " + b1.equals(b3));
System.out.println("(b1.compareTo(b3)? " + b1.compareTo(b3));
/*Returns 0 if equal. Returns -1 if b1 is less than b3 and 1 if b1 is
greater than 1*/
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-11-2048.jpg)


![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Short_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
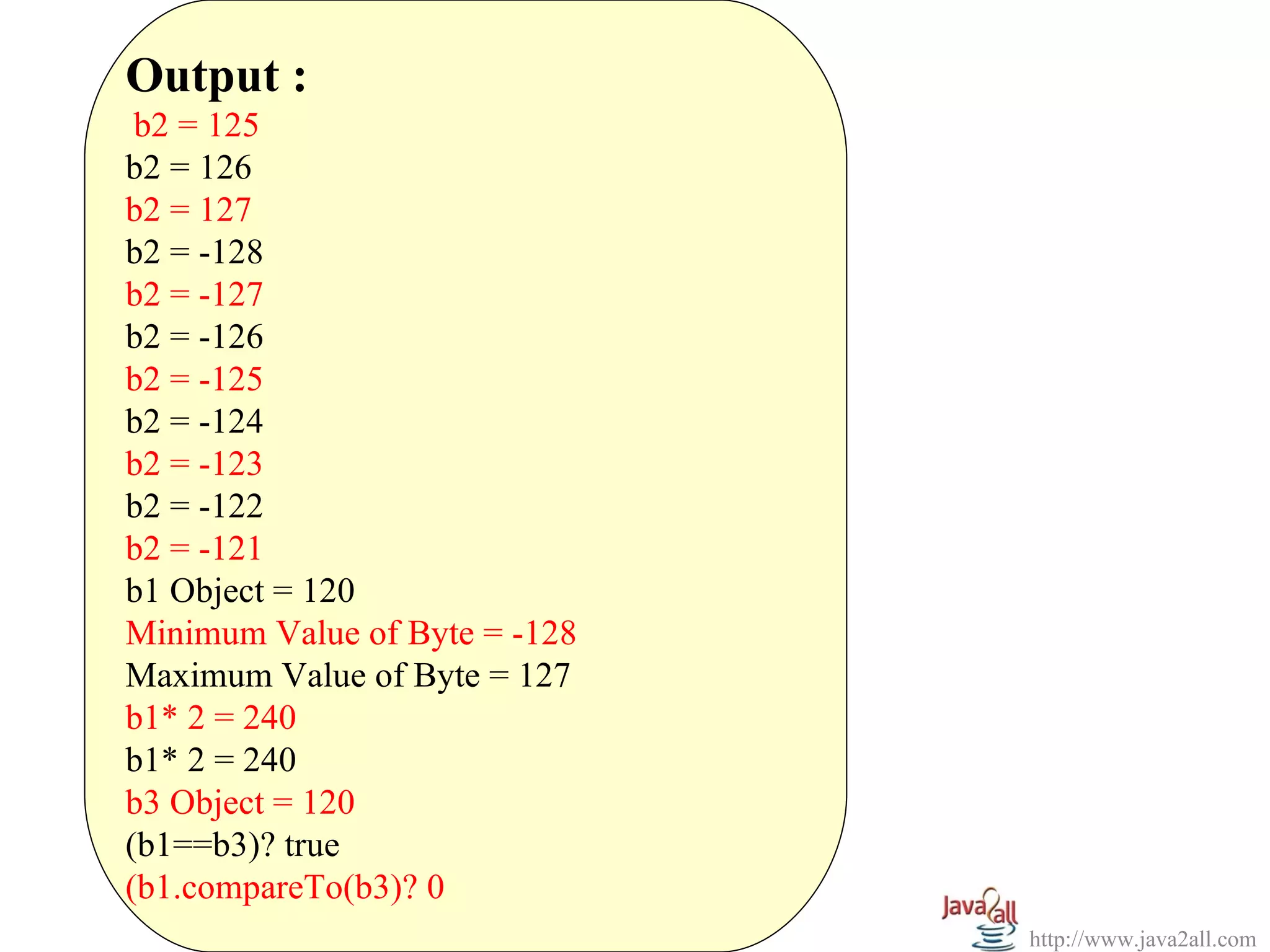
Short s1 = new Short((short)2345);
for(int i = 32765; i<=32775; i++)
{
Short s2 = new Short((short)i);
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2);
}
System.out.println("s1 Object = " + s1);
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Short = " + Short.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Short = " + Short.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("s1* 2 = " + s1.shortValue()*2);
Short s3 = new Short("2345");
System.out.println("s3 Object = " + s3);
System.out.println("(s1==s3)? " + s1.equals(s3));
Short s4 = Short.valueOf("10", 16);
System.out.println("s4 Object = " + s4);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-15-2048.jpg)


![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Int_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
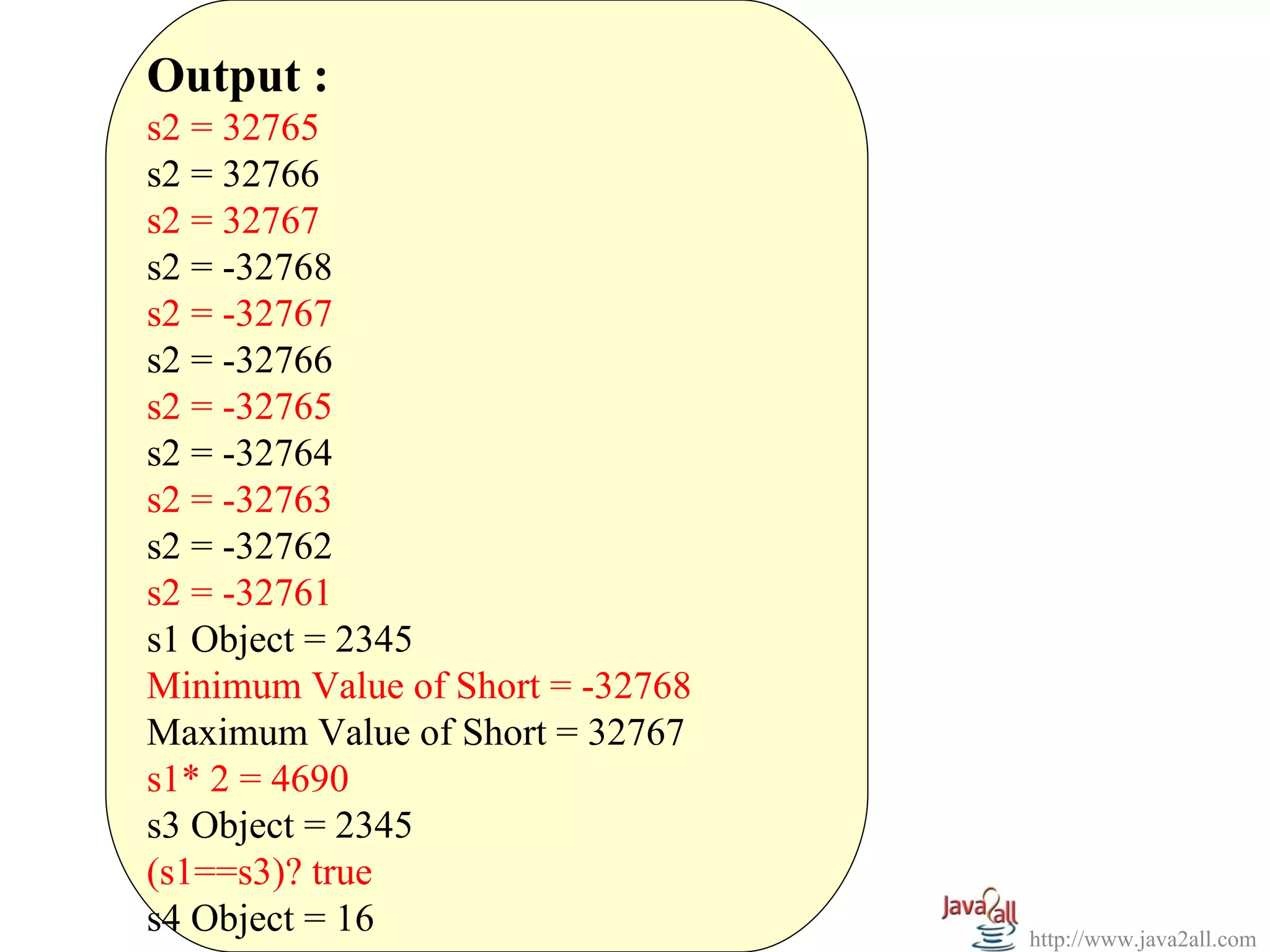
Integer i1 = new Integer(12);
System.out.println("I1 = " + i1);
System.out.println("Binary Equivalent = " + Integer.toBinaryString(i1));
System.out.println("Hexadecimal Equivalent = " + Integer.toHexString(i1));
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Integer = " + Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Integer = " + Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("Byte Value of Integer = " + i1.byteValue());
System.out.println("Double Value of Integer = " + i1.doubleValue());
Integer i2 = new Integer(12);
System.out.println("i1==i2 " + i1.equals(i2));
System.out.println("i1.compareTo(i2) = " + i2.compareTo(i1));
// Compareto - if it is less than it returns -1 else 1, if equal it return 0.
Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf("11", 16);
System.out.println("i3 = " + i3);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-19-2048.jpg)


![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Long_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Long L1 = new Long(68764);
Long L2 = new Long("686748");
System.out.println("Object L1 = " + L1);
System.out.println("Object L2 = " + L2);
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Long = " + Long.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Long = " + Long.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("L1 * 2 = " + L1 * 2);
System.out.println("L1.longValue() * 2 = " + L1.longValue() * 2);
System.out.println("L1.compareTo(l2) = " + L1.compareTo(L2));
System.out.println("L1==L2 ? = " + L1.equals(L2));
Long L3 = Long.valueOf("10", 16);
System.out.println("Object L3 = " + L3);
System.out.println("Byte value of Long = " + L1.byteValue());
System.out.println("int value of Long = " + L1.intValue());
System.out.println("Double value of Long = " + L1.doubleValue());
int i = 12;
System.out.println("Binary equivalent of decimal " + i + "=" + Long.toBinaryString(i));
System.out.println("Hexadecimal equivalent of decimal " + i + "=" + Long.toHexString(i));
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-23-2048.jpg)



![EX :
import java.util.*;
class Double_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Double d1 = new Double(687642365.4563);
Double d2 = new Double("686748");
System.out.println("Object d1 = " + d1);
System.out.println("Object d2 = " + d2);
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Double = " + Double.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Double = " + Double.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("Byte value of Double = " + d1.byteValue());
System.out.println("int value of Double = " + d1.intValue());
System.out.println("Float value of Double = " + d1.floatValue());
Double d3 = Double.parseDouble("765.89");
System.out.println("Double value from the string "765.89"="+d3);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-28-2048.jpg)



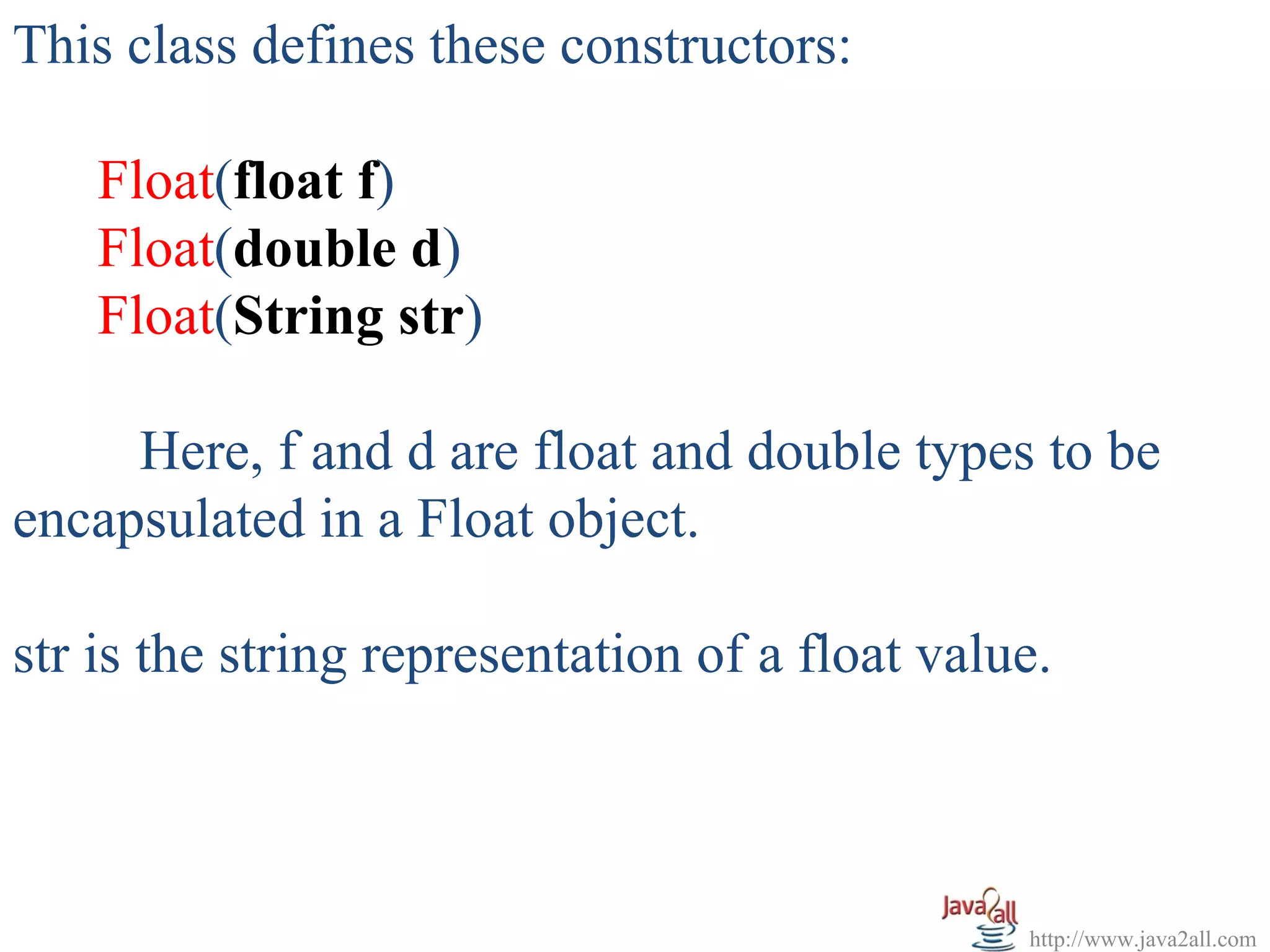
![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Float_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
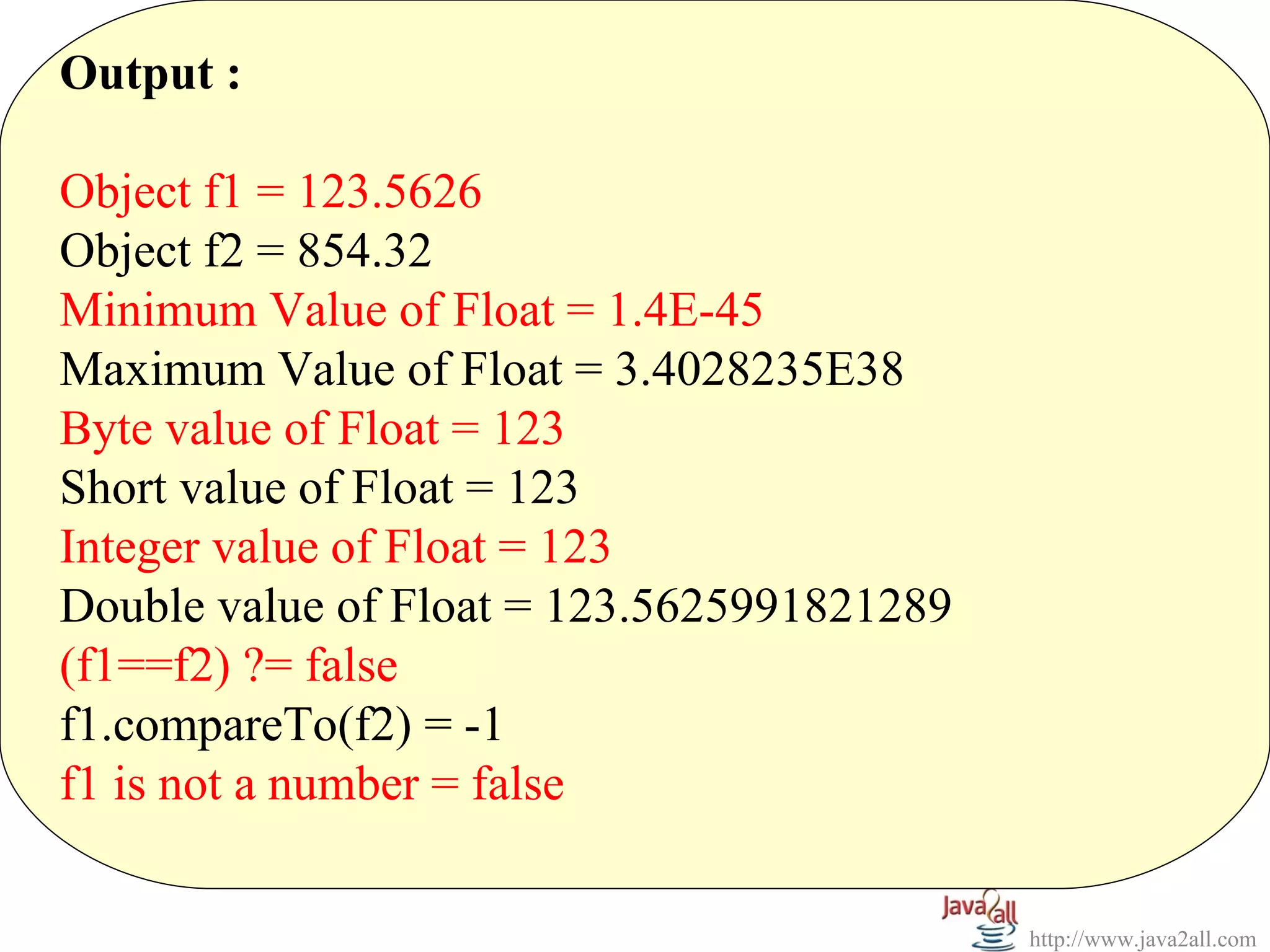
Float f1 = new Float(123.5626);
Float f2 = new Float(854.32f);
Float i = new Float(10);
System.out.println("Object f1 = " + f1);
System.out.println("Object f2 = " + f2);
System.out.println("Minimum Value of Float = " + Float.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("Maximum Value of Float = " + Float.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("Byte value of Float = " + f1.byteValue());
System.out.println("Short value of Float = " + f1.shortValue());
System.out.println("Integer value of Float = " + f1.intValue());
System.out.println("Double value of Float = " + f1.doubleValue());
System.out.println("(f1==f2) ?= " + f1.equals(f2));
System.out.println("f1.compareTo(f2) = " + f1.compareTo(f2));
System.out.println("f1 is not a number = " + i.isNaN());
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-33-2048.jpg)

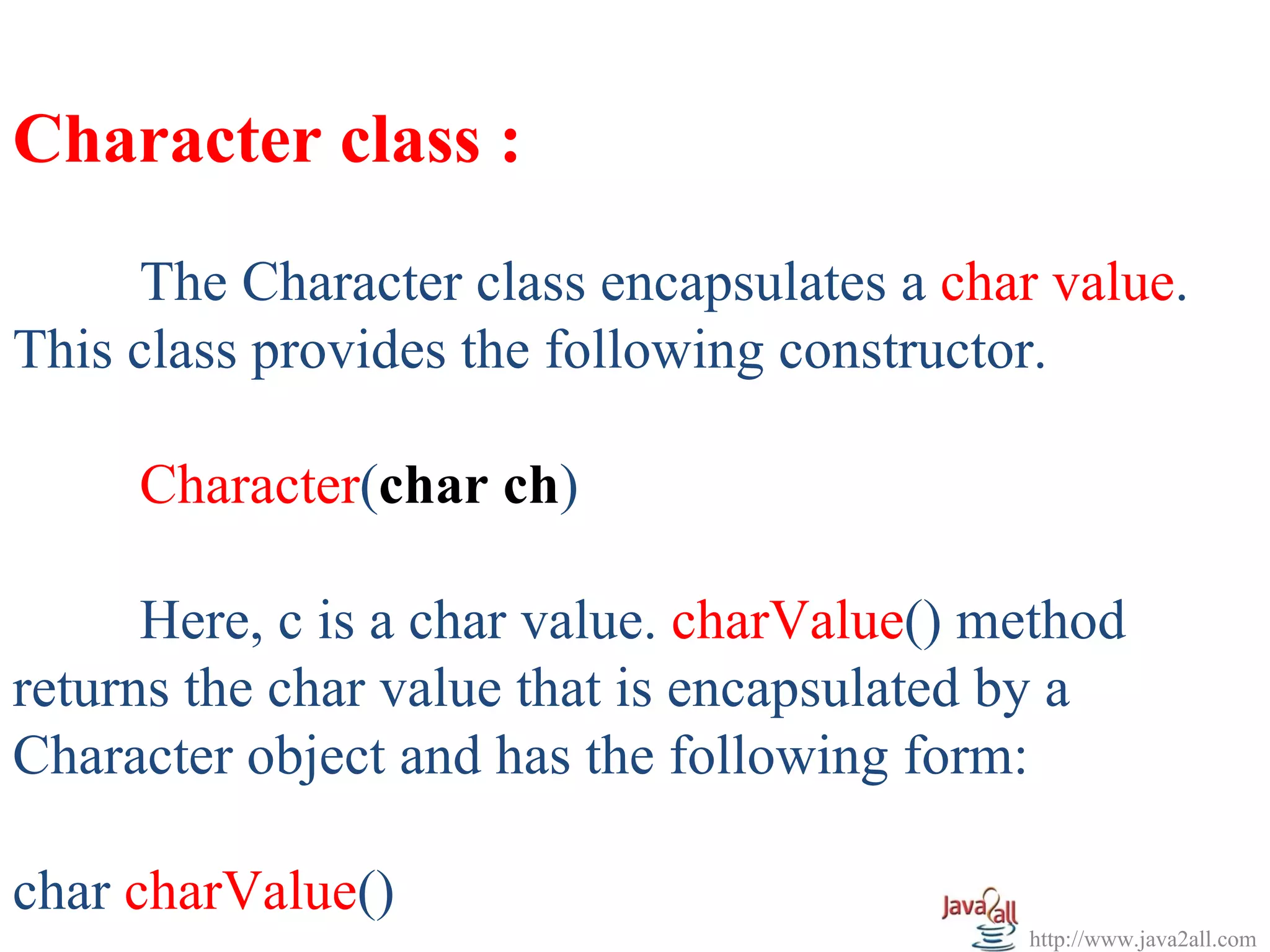
![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Char_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Character c1 = new Character('m');
char c2 = 'O';
System.out.println("Object C1 = " + c1);
System.out.println("char value of Character Object = " + c1.charValue());
System.out.println(c2 + " is defined character set ? " + Character.isDefined(c2));
System.out.println("c2 is digit = " + Character.isDigit(c2));
System.out.println("c2 is lowercase character = " + Character.isLowerCase(c2));
System.out.println("c2 is uppercase character = " + Character.isUpperCase(c2));
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-37-2048.jpg)


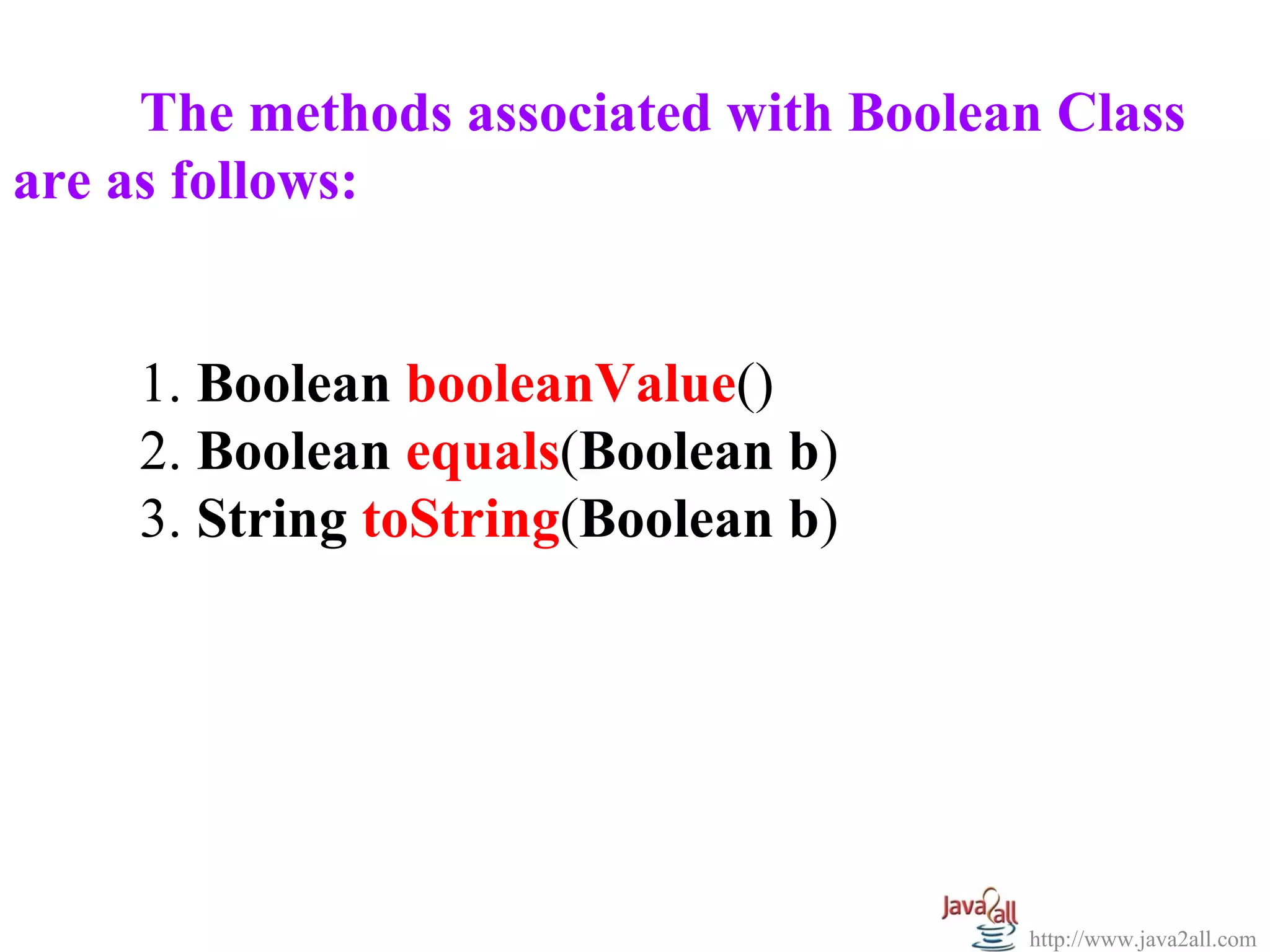
![EX :
import java.util.*;
public class Boolean_Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean b2 = new Boolean(false);
System.out.println("Object B1 = " + b1);
System.out.println("Object B2 = " + b2);
Boolean b3 = new Boolean("true");
Boolean b4 = new Boolean("false");
System.out.println("Object B3 = " + b3);
System.out.println("Object B4 = " + b4);
System.out.println("Boolean Value = " + b1.booleanValue());
System.out.println("(b1==b2)? " + b1.equals(b2));
String S1 = b1.toString();
System.out.println("String S1 " + S1);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wrapperclasschepter10-120701053417-phpapp02/75/Wrapper-class-42-2048.jpg)
