0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views16 pagesDecision Condition Loop
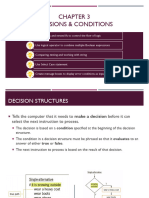
The document discusses various types of decision, condition, and loop statements in programming languages including:
- IF statements with logical and relational operators to evaluate conditions
- Nested IF/ELSEIF statements
- DO loops with pre-test and post-test conditions to repeat blocks of code
- FOR/NEXT loops using a counter variable to repeat code a specified number of times
Examples are provided of using these statements to calculate areas and discounts, evaluate roots of quadratic equations, and calculate future values in loops.
Uploaded by
Aasrith KandulaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views16 pagesDecision Condition Loop
The document discusses various types of decision, condition, and loop statements in programming languages including:
- IF statements with logical and relational operators to evaluate conditions
- Nested IF/ELSEIF statements
- DO loops with pre-test and post-test conditions to repeat blocks of code
- FOR/NEXT loops using a counter variable to repeat code a specified number of times
Examples are provided of using these statements to calculate areas and discounts, evaluate roots of quadratic equations, and calculate future values in loops.
Uploaded by
Aasrith KandulaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16